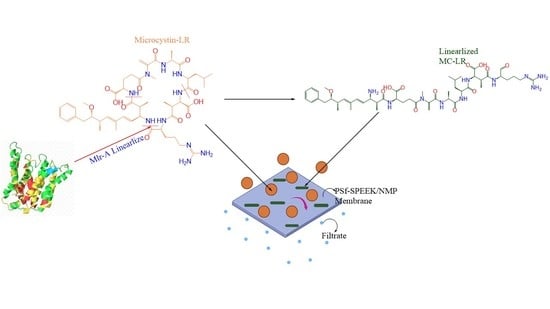
Microcystin-LR Removal from Water via Enzymatic Linearization and Ultrafiltration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. MlrA Expression and Experiments
2.1.1. Protein Expression and MlrA Purification
2.1.2. Microcystin-LR Linearization Activity of MlrA
2.2. Membrane Fabrication and Experiments
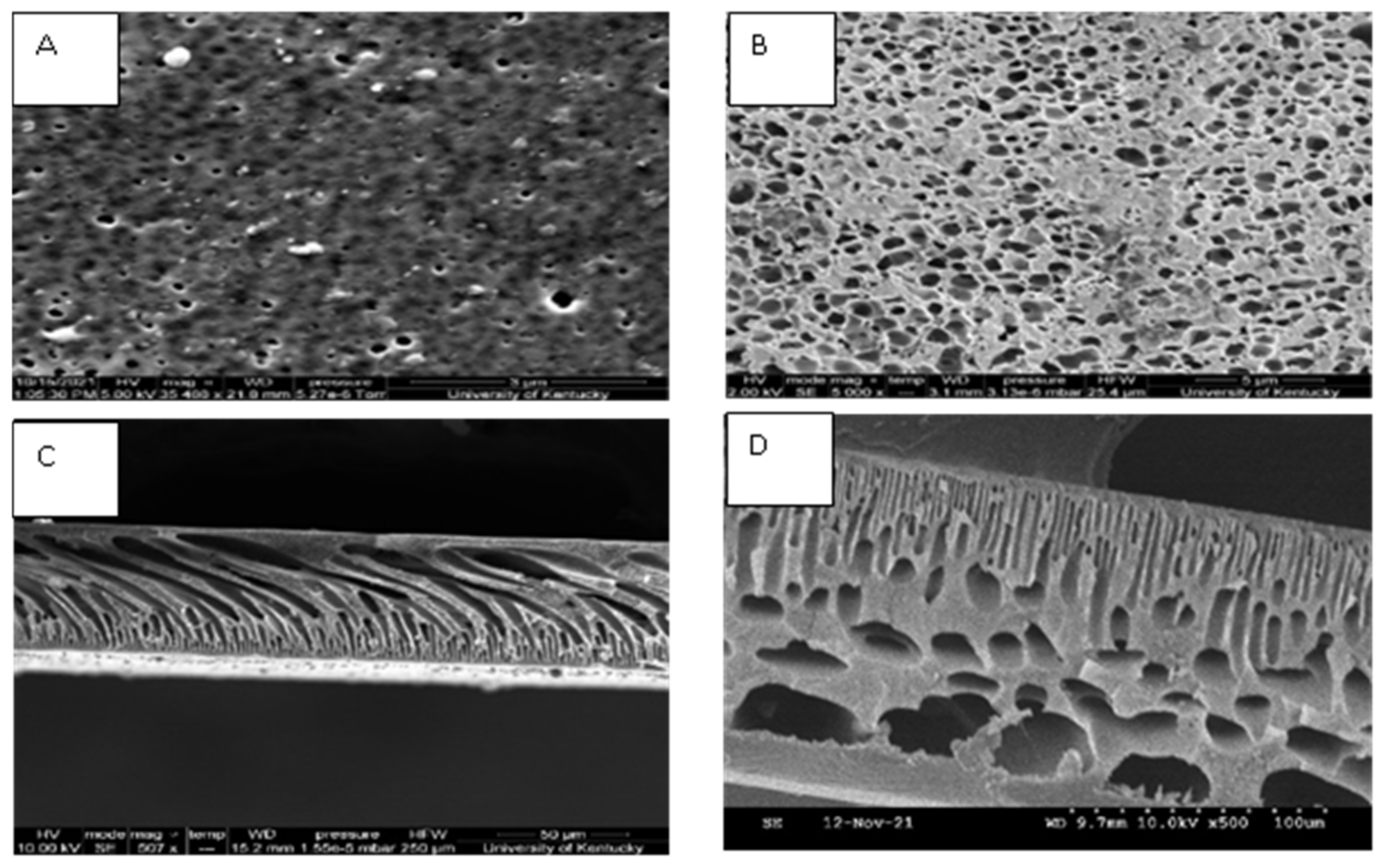
2.2.1. Morphological Characterization
2.2.2. Structural Characterization
2.2.3. Contact Angle and Zeta Potential
2.2.4. Adsorption and Desorption of Microcystin-LR on Membranes
2.2.5. Filtration of MC-LR and Linearization Byproducts through Membrane
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. MlrA Expression and Experiments
4.2.1. Strain and Plasmid Construction
4.2.2. Media, Growth, and Expression of Recombinant MlrA Enzyme
4.2.3. Cell Lysate Preparation and Hisx6-tag MlrA Purification
4.2.4. Microcystin-LR Linearization Activity of MlrA
4.2.5. LC-MS Methods for Detecting MC-LR
4.3. Membrane Fabrication and Experiments
4.3.1. Sulfonation of SPEEK
4.3.2. Membrane Formation
4.3.3. Membrane Characterization
4.3.4. Adsorption and Desorption of Microcystin-LR on Membrane
4.3.5. Membrane Filtration
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dziga, D.; Tokodi, N.; Drobac, D.; Kokociński, M.; Antosiak, A.; Puchalski, J.; Strzałka, W.; Madej, M.; Svirčev, Z.; Meriluoto, J. The Effect of a Combined Hydrogen Peroxide-MlrA Treatment on the Phytoplankton Community and Microcystin Concentrations in a Mesocosm Experiment in Lake Ludoš. Toxins 2019, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, S.K.; Trainer, V.L.; Mantua, N.J.; Parker, M.S.; Laws, E.A.; Backer, L.C.; Fleming, L.E. Impacts of climate variability and future climate change on harmful algal blooms and human health. Environ. Health 2008, 7, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourne, D.G.; Jones, G.J.; Blakeley, R.L.; Jones, A.; Negri, A.P.; Riddles, P. Enzymatic pathway for the bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin LR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4086–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dziga, D.; Wladyka, B.; Zielińska, G.; Meriluoto, J.; Wasylewski, M. Heterologous expression and characterisation of microcystinase. Toxicon 2012, 59, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dexter, J.; Dziga, D.; Lv, J.; Zhu, J.; Strzalka, W.; Maksylewicz, A.; Maroszek, M.; Marek, S.; Fu, P. Heterologous expression of mlrA in a photoautotrophic host—Engineering cyanobacteria to degrade microcystins. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, F.; Feng, H.; Wei, J.; Massey, I.Y.; Liang, G.; Zhang, F.; Yin, L.; Kacew, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. A complete route for biodegradation of potentially carcinogenic cyanotoxin microcystin-LR in a novel indigenous bacterium. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, L.; Yan, M.; Li, J.; Hou, S.; Wan, J.; Feng, L. Simultaneous Microcystin Degradation and Microcystis Aeruginosa Inhibition with Single Enzyme Microcystinase A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8811–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Riddles, P.; Jones, G.J.; Smith, W.; Blakeley, R.L. Characterisation of a gene cluster involved in bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin LR. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormas, K.A.; Lymperopoulou, D.S. Cyanobacterial Toxin Degrading Bacteria: Who Are They? BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dexter, J.; Mccormick, A.J.; Fu, P.; Dziga, D. Microcystinase—A review of the natural occurrence, heterologous expression, and biotechnological application of MlrA. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Shao, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, R. Active and silent members in the mlr gene cluster of a microcystin-degrading bacterium isolated from Lake Taihu, China. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 322, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Wu, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, R.; Sheng, Q.; Ye, J. Effect of the immobilized microcystin-LR-degrading enzyme MlrA on nodularin degradation and its immunotoxicity study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raran-Kurussi, S.; Waugh, D.S. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins in Escherichia coli with a His6 or Dual His6-MBP Tag. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Waugh, D.S. Making the most of affinity tags. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eke, J.; Wagh, P.; Escobar, I.C. Ozonation, biofiltration and the role of membrane surface charge and hydrophobicity in removal and destruction of algal toxins at basic pH values. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Peng, G.; Wang, S.; Fan, Z. A Novel Photocatalytic Material for Removing Microcystin-LR under Visible Light Irradiation: Degradation Characteristics and Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Martínez, G.; Gómez, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly (ether ether ketone) Derivatives Obtained by Carbonyl Reduction. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 6885–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, R.S.L.; Zhang, K.; Ladewig, B.P. The Effects of Sulfonated Poly (ether ether ketone) Ion Exchange Preparation Conditions on Membrane Properties. Membranes 2013, 3, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.M.; Shao, P.; Burns, C.M.; Feng, X. Sulfonation of poly (ether ether ketone) (PEEK): Kinetic study and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleva, G.; Galabov, B.; Kong, J.; Schaefer, H.F.; Schleyer, P.V.R. Electrophilic Aromatic Sulfonation with SO3: Concerted or Classic SEAr Mechanism? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19094–19101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.V.; Ngo, T.H.A.; Do, K.D.; Nguyen, M.N.; Dang, N.T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Vien, V.; Vu, T.A. Preparation and Characterization of a Hydrophilic Polysulfone Membrane Using Graphene Oxide. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 3164373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, W.; Xu, H.; Yang, W.; Kong, Q.; Wang, A.; Ding, M.; Shang, J. Fabrication of a Novel Antifouling Polysulfone Membrane with in Situ Embedment of Mxene Nanosheets. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eke, J.; Elder, K.; Escobar, I.C. Self-Cleaning Nanocomposite Membranes with Phosphorene-Based Pore Fillers for Water Treatment. Membranes 2018, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giakoumis, T.; Vaghela, C.; Voulvoulis, N. Chapter Six—The Role of Water Reuse in the Circular Economy. In Advances in Chemical Pollution, Environmental Management and Protection; Verlicchi, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 5, pp. 227–252. [Google Scholar]
- Teli, S.B.; Molina, S.; Sotto, A.; Calvo, E.G.; Abajob, J.D. Fouling Resistant Polysulfone–PANI/TiO2 Ultrafiltration Nanocomposite Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 9470–9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.; Leslie, G. 22-Degradation of Polymeric Membranes in Water and Wastewater Treatment. In Advanced Membrane Science and Technology for Sustainable Energy and Environmental Applications; Basile, A., Nunes, S.P., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 718–745. [Google Scholar]
- Altaner, S.; Puddick, J.; Wood, S.A.; Dietrich, D.R. Adsorption of Ten Microcystin Congeners to Common Laboratory-Ware Is Solvent and Surface Dependent. Toxins 2017, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szweda, P.; Kotłowski, R.; Kur, J. New effective sources of the Staphylococcus simulans lysostaphin. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 117, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziga, D.; Zielinska, G.; Wladyka, B.; Bochenska, O.; Maksylewicz, A.; Strzalka, W.; Meriluoto, J. Characterization of Enzymatic Activity of MlrB and MlrC Proteins Involved in Bacterial Degradation of Cyanotoxins Microcystins. Toxins 2016, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Lu, D.; Harris, T.A.L.; Escobar, I.C. Polymers and Solvents Used in Membrane Fabrication: A Review Focusing on Sustainable Membrane Development. Membranes 2021, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.T.; Kim, J.F.; Wang, H.H.; Di Nicolo, E.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Understanding the non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) effect during the fabrication of microporous PVDF membranes via thermally induced phase separation (TIPS). J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Name | Peak BE | FWHM eV | Area (p) CP | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1s | 530.75 | 3.14 | 981,557.4 | 20.25 |
| C1s | 284.11 | 3.57 | 1,041,084 | 51.95 |
| N1s | 398.37 | 1.69 | 295,204.8 | 9.49 |
| Na1s | 1070.11 | 2.75 | 101,255.2 | 1.03 |
| Cl2p | 196.83 | 3.43 | 34,208.35 | 0.59 |
| S2p | 166.82 | 2.96 | 33,040.04 | 0.82 |
| P2p | 132.07 | 3.01 | 19,959.85 | 0.67 |
| Ca2p | 346.13 | 2.43 | 28,255.31 | 0.25 |
| Si2p | 100.88 | 3.68 | 13,253.4 | 0.66 |
| Name | Peak BE | FWHM eV | Area (p) CP | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1s | 284.92 | 3.11 | 1,420,861 | 71.25 |
| O1s | 532.15 | 3.06 | 1,064,064 | 22.08 |
| S2p | 167.91 | 2.69 | 77,509.07 | 1.92 |
| N1s | 399.44 | 1.71 | 109,829.3 | 3.55 |
| Na1s | 1071.35 | 2.82 | 82,496.91 | 0.85 |
| Cl2p | 198.08 | 5.38 | 20,673.64 | 0.36 |
| Solution | TOC Measurements (mg/L) | Components |
|---|---|---|
| MC-LR stock solution before linearization | 252 | MC-LR, water, ethanol, phosphate buffer, and acetic acid |
| After linearization before filtration | 396 | MC-LR, water, ethanol, acetone, MlrA enzyme, and acetic acid |
| After linearization after filtration | 366 | MC-LR, water, ethanol, acetone, MlrA enzyme, and acetic acid |
| Chemicals | Concentration (mg/L) | Volume Added to Stock Solution (µL) | Mass That Should Be Present (mg) | Volume Present in Solution after Linearization | Mass That Should Be Present (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC-LR in phosphate buffer | 1 | 720 | 0.72 | 720 | 0.72 |
| Phosphate buffer 5 mM | 2.06 | 1800 | 3.69 | 6480 | 13.32 |
| MlrA solution | 2.4 | 0 | 0 | 800 | 1.92 |
| Acetic acid | 50 | 200 | 10 | 200 | 10 |
| Potassium phosphate monobasic | 25.4 | 1.28 | 0.03 | 1.28 | 0.03 |
| Potassium phosphate dibasic | 34.1 | 0.95 | 0.03 | 0.95 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fionah, A.; Hackett, C.; Aljewari, H.; Brady, L.; Alqhtani, F.; Escobar, I.C.; Thompson, A.K. Microcystin-LR Removal from Water via Enzymatic Linearization and Ultrafiltration. Toxins 2022, 14, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040231
Fionah A, Hackett C, Aljewari H, Brady L, Alqhtani F, Escobar IC, Thompson AK. Microcystin-LR Removal from Water via Enzymatic Linearization and Ultrafiltration. Toxins. 2022; 14(4):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040231
Chicago/Turabian StyleFionah, Abelline, Cannon Hackett, Hazim Aljewari, Laura Brady, Faisal Alqhtani, Isabel C. Escobar, and Audie K. Thompson. 2022. "Microcystin-LR Removal from Water via Enzymatic Linearization and Ultrafiltration" Toxins 14, no. 4: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040231
APA StyleFionah, A., Hackett, C., Aljewari, H., Brady, L., Alqhtani, F., Escobar, I. C., & Thompson, A. K. (2022). Microcystin-LR Removal from Water via Enzymatic Linearization and Ultrafiltration. Toxins, 14(4), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040231