Determination of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins in Seed of Milk Thistle [Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn.] Using Immunoaffinity Column by UPLC-MS/MS
Abstract
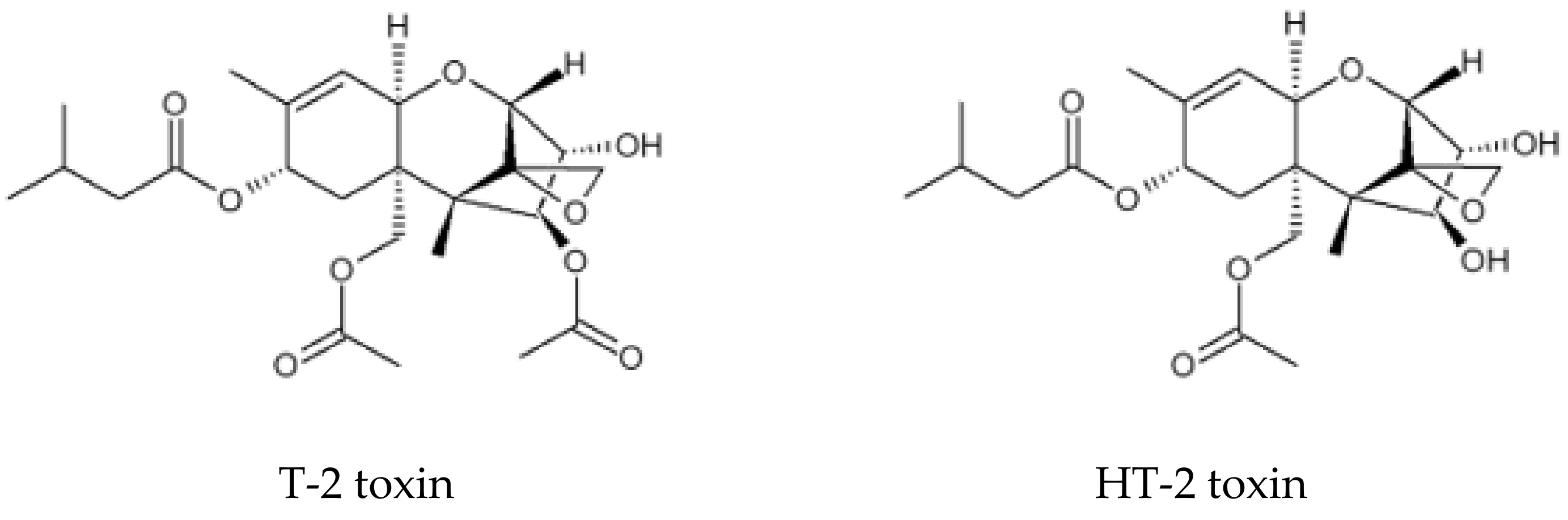
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Method Validation
2.2. Determination of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins in Milk Thistle by UPLC-MS/MS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Standards and Chemicals
4.2. Samples Collection
4.3. Sample Preparation and Clean-Up by Immunoaffinity Columns
4.4. UPLC-MS/MS Mycotoxin Analysis
4.5. Development, Optimization and Validation of Method
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Habán, M.; Habánová, M.; Otepka, P.; Kobida, Ľ. Milk thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaertn.) cultivated in polyfunctional crop rotation and its evaluation. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 42, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Habán, M.; Luščáková, D.; Macak, M.; Ražná, K. The Impact of Multifunctional Crop Rotation on the Yield of Milk Thistle Fruits in the Years 2012–2015. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2016, 17, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Pharmacopoeia. European Pharmacopoeia, 6th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 2425–2427. [Google Scholar]
- Morazzoni, P.; Bombardelli, E. Silybum marianum (Carduus marianus). Fitoterapia 1995, 66, 6–42. [Google Scholar]
- Saller, R.; Meier, R.; Brignoli, R. The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs 2001, 61, 2035–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habán, M.; Otepka, P.; Habánová, M. Production and quality of milk thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaertn.) cultivated in cultural conditions of warm agri-climatic macroregion. Hort. Sci. 2009, 36, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Škottová, N.; Krečman, V. Silymarin as a potential hypocholesterolaemic drug. Physiol. Res. 1998, 47, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wellington, K.; Jarvis, B. Silymarin: A review of its clinical properties in the management of liver disorders. BioDrugs 2001, 15, 465–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickova, D.; Ostry, V.; Toman, J.; Malir, F. Presence of Mycotoxins in Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Food Supplements: A Review. Toxins 2020, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Deep, G.; Chittezhath, M.; Kaur, M.; Dwyer-Nield, L.D.; Malkinson, A.M.; Agarwal, R. Effect of silibinin on the growth and progression of primary lung tumors in mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valková, V.; Ďúranová, H.; Bilčíková, J.; Habán, M. Milk thistle (Silybum marianum): A valuable medicinal plant with several therapeutic purposes. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournas, V.H.; Sapp, C.; Trucksess, M.W. Occurrence of aflatoxins in milk thistle herbal supplements. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2012, 29, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosalec, I.; Cvek, J.; Tomic, S. Contaminants of medicinal herbs and herbal products. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2009, 60, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veprikova, Z.; Zachariasova, M.; Dzuman, Z.; Zachariasova, A.; Fenclova, M.; Slavikova, P.; Vaclavikova, M.; Mastovska, K.; Hengst, D.; Hajslova, J. Mycotoxins in plant-based dietary supplements: Hidden health risk for consumers. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6633–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassaneeyakul, W.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E.; Porasuphatana, S.; Bohm, J. Contamination of aflatoxins in herbal medicinal products in Thailand. Mycopathologia 2004, 158, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, D.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Li, L. Fecal metabolome profiling of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma patients by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 691, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadzki, P.; Watson, L.; Ernst, E. Contamination and adulteration of herbal medicinal products (HMPs): An overview of systematic reviews. Eur. J. Clin. Pharm. 2013, 69, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.I.; Hocking, A.D. Fungi and Food Spoilage, 3rd ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 89–122. [Google Scholar]
- Běláková, S.; Benešová, K.; Čáslavský, J.; Svoboda, Z.; Mikulíková, R. The occurrence of the selected Fusarium mycotoxins in Czech malting barley. Food Contr. 2014, 37, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Wu, W.; Zhang, H. Comparison of anorectic potencies of type a trichothecenes T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, diacetoxyscirpenol, and neosolaniol. Toxins 2018, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beccari, G.; Caproni, L.; Tini, F.; Uhlig, S.; Covarelli, L. Presence of Fusarium species and other toxigenic fungi in malting barley and multi-mycotoxin analysis by liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4390–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.G.; Imathiu, S.M.; Ray, R.V.; Back, M.; Hare, M.C. Molecular studies to identify the Fusarium species responsible for HT-2 and T-2 mycotoxins in UK oats. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 156, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernica, M.; Kyralová, B.; Svoboda, Z.; Boško, R.; Brožková, I.; Česlová, L.; Benešová, K.; Červenka, L.; Běláková, S. Levels of T-2 toxin and its metabolites, and the occurrence of Fusarium fungi in spring barley in the Czech Republic. Food Microbiol. 2022, 102, 103875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malachova, A.; Cerkal, R.; Ehrenbergerova, J.; Dzuman, Z.; Vaculova, K.; Hajslova, J. Fusarium mycotoxins in various barley cultivars and their transfer into malt. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.; Marín, S.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.J. Screening of mycotoxin multicontamination in medicinal and aromatic herbs sampled in Spain. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenclova, M.; Novakova, A.; Viktorova, J.; Jonatova, P.; Dzuman, Z.; Ruml, T.; Kren, V.; Hajslova, J.; Vitek, L.; Stranska-Zachariasova, M. Poor chemical and microbiological quality of the commercial milk thistle-based dietary supplements may account for their reported unsatisfactory and non-reproducible clinical outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Gámiz-Gracia, L. Multiclass mycotoxin analysis in Silybum marianum by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry using a procedure based on QuEChERS and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1282, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernica, M.; Piacentini, K.C.; Benešová, K.; Čáslavský, J.; Běláková, S. Analytical techniques for determination of mycotoxins in barley, malt and beer: A review. Kvas. Prum. 2019, 65, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Beier, R.C.; Shen, J.; Smet, D.D.; De Saeger, S.; Zhang, S. T-2 toxin, a trichothecene mycotoxin: Review of toxicity, metabolism, and analytical methods. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2011, 59, 3441–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karron, E.; Runno-Paurson, E.; Lõiveke, H.; Islamov, B.; Kütt, M.L.; Talve, T.; Lauringson, E.; Horak, H.; Edesi, L.; Niinemets, Ü. Application of widely used fungicides does not necessarily affect grain yield, and incidence of Fusarium spp. and mycotoxins DON, HT-2 and T-2 in spring barley in northern climates. Kvas. Prum. 2020, 66, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateo, J.J.; Mateo, R.; Jimenez, M. Accumulation of type A trichothecenes in maize, wheat and rice by Fusarium sporotrichioides isolates under diverse culture conditions. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2002, 72, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesenska, Z.; Sajbidorova, I. T-2 toxin degradation by micromycetes. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 1991, 35, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Liu, P.; Cui, Y.; Xiao, B.; Liu, M.; Song, M.; Huang, W.; Li, Y. Review of the reproductive toxicity of T-2 toxin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čonková, E.; Laciaková, A.; Kováč, G.; Seidel, H. Fusarial toxins and their role in animal diseases. Vet. J. 2003, 165, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Ishigami, N.; Sehata, S. T-2 toxin-induced toxicity in pregnant mice and rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2146–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rafai, P.; Bata, A.; Vanyi, A.; Papp, Z.; Brydl, E.; Jakab, L.; Tuboly, S.; Tury, E. Effect of various levels of T-2 toxin on the clinical status, performance and metabolism of growing pigs. Vet. Rec. 1995, 136, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Xiao, X.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hoyer, D.; Shen, J.; Tang, S.; Velkov, T. T-2 toxin neurotoxicity: Role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3041–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozuka, J.; Suzuki, M.; Noguchi, N.; Sugimoto, T.; Uetsuka, K.; Nakayama, H.; Doi, K. T-2 toxin-induced apoptosis in hematopoietic tissues of mice. Toxicol. Pathol. 1998, 26, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Han, J.; Guo, X.; Qu, C.; Yu, F.; Wu, X. The effects of T-2 toxin on the prevalence and development of Kashin–Beck disease in China: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 731–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visconti, A. Problems associated with Fusarium mycotoxins in cereals. Bull. Inst. Compr. Agric. Sci. Kinki. Univ. 2001, 9, 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Stratakou, I. T-2 toxin and HT-2 toxin in grain and grain-based commodities in Europe: Occurrence, factors affecting occurrence, co-occurrence and toxicological effects. World Mycotoxin J. 2010, 3, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canady, R.A.; Coker, R.D.; Egan, S.; Krska, R.; Olsen, M.; Resnik, S.; Schlatter, J. T-2 and HT-2 toxins. Saf. Eval. Certain Mycotoxins Food. WHO Food Addit. Ser. 2001, 47, 557–597. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Dohnal, V.; Huang, L.; Kuča, K.; Yuan, Z. Metabolic pathways of trichothecenes. Drug Metab Rev. 2010, 42, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, N.; Currie, V.; Duncan, G.; Busman, M.; Gratz, S.W. Intestinal hydrolysis and microbial biotransformation of diacetoxyscirpenol-α-glucoside, HT-2-β-glucoside and N-(1-deoxy-D-fructos-1-yl) fumonisin B1 by human gut microbiota in vitro. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific Opinion on the risks for animal and public health related to the presence of T-2 and HT-2 toxin in food and feed. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, H.R.; Pan, X.; Pestka, J.J. Comparison of anorectic potencies of the trichothecenes T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin and satratoxin G to the ipecac alkaloid emetine. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Appropriateness to set a group health based guidance value for T-2 and HT-2 toxin and its modified forms. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04655. [Google Scholar]
- Ałtyn, I.; Twarużek, M. Mycotoxin Contamination Concerns of Herbs and Medicinal Plants. Toxins 2020, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steiner, D.; Malachová, A.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R. Challenges and future directions in LC-MS-based multiclass method development for the quantification of food contaminants. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, D.J.; Crowe, T.; Sokhansanj, S.; Wahab, J.; Barl, B. Milk thistle, Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn., flower head development and associated marker compound profile. J. Herbs. Spices Med. Plants 2003, 10, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewska, J.; Sadowska, K.; Mielcarek, S. Effect of sowing date and rate on the yield and flavonolignan content of the fruits of milk thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaertn.) grown on light soil in a moderate climate. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champeil, A.; Doré, T.; Fourbet, J.F. Fusarium head blight: Epidemiological origin of the effects of cultural practices on head blight attacks and the production of mycotoxins by Fusarium in wheat grains. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1389–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiš, M.; Vulić, A.; Kudumija, N.; Šarkanj, B.; Jaki Tkalec, V.; Aladić, K.; Škrivanko, M.; Furmeg, S.; Pleadin, J. A Two-Year Occurrence of Fusarium T-2 and HT-2 Toxin in Croatian Cereals Relative of the Regional Weather. Toxins 2021, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. 2013/165/EU Commission Recommendation of 27 March 2013 on the presence of T-2 and HT-2 toxin in cereals and cereal product. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, L91, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S. Milk thistle seeds in health. In Nuts and Seeds in Health and Disease Prevention; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 429–438. [Google Scholar]
- Imathiu, S.M.; Edwards, S.G.; Ray, R.V.; Back, M.A. Fusarium langsethiae—A HT-2 and T-2 toxins producer that needs more attention. J. Phytopathol. 2013, 161, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleadin, J.; Vahčić, N.; Perši, N.; Ševelj, D.; Markov, K.; Frece, J. Fusarium mycotoxins’ occurrence in cereals harvested from Croatian fields. Food Control 2013, 32, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochiieru, Y.; Mankevičienė, A.; Cesevičienė, J.; Semaškienė, R.; Dabkevičius, Z.; Janavičienė, S. The influence of harvesting time and meteorological conditions on the occurrence of Fusarium species and mycotoxin contamination of spring cereals. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochiieru, Y.; Mankevičienė, A.; Cesevičienė, J.; Semaškienė, R.; Ramanauskienė, J.; Gorash, A.; Janavičienė, S.; Venslovas, E. The Impact of Harvesting Time on Fusarium Mycotoxins in Spring Wheat Grain and Their Interaction with Grain Quality. Agronomy 2021, 11, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Source of Variability | DF | T-2 Toxin [µg/kg] MS | HT-2 Toxin [µg/kg] MS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 1 | 194,669.8 *** | 317,040.4 *** |
| Variant | 11 | 2938.6 *** | 2303.2 *** |
| Year*variant | 11 | 1972.0 *** | 2540.0 *** |
| Error | 24 | 5.8 | 18.3 |
| Year | Variant | T-2 Toxin [µg/kg] | HT-2 Toxin [µg/kg] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1. (12.5 cm) | A | 180.3 ± 2.9 | j | 238.9 ± 3.4 | o |
| B | 284.8 ± 7.7 | n | 277.6 ± 8.4 | p | ||
| C | 136.5 ± 4.1 | h | 172.9 ± 1.2 | k | ||
| D | 200.2 ± 1.5 | l | 204.8 ± 6.5 | n | ||
| 2. (25 cm) | A | 125.4 ± 1.3 | g | 187.8 ± 5.8 | lm | |
| B | 136.5 ± 0.2 | h | 188.9 ± 4.6 | lm | ||
| C | 124.3 ± 2.2 | g | 157.8 ± 1.2 | j | ||
| D | 160.2 ± 5.3 | i | 186.6 ± 6.0 | l | ||
| 3. (37 cm) | A | 176.1 ± 0.3 | j | 239.2 ± 9.8 | o | |
| B | 187.1 ± 0.7 | k | 201.4 ± 5.1 | n | ||
| C | 158.9 ± 3.2 | i | 196.6 ± 1.7 | mn | ||
| D | 236.1 ± 1.8 | m | 313.9 ± 7.3 | q | ||
| 2021 | 1. (12.5 cm) | A | 33.8 ± 0.0 | a | 38.4 ± 1.1 | bc |
| B | 69.5 ± 0.6 | f | 73.2 ± 3.1 | h | ||
| C | 42.0 ± 0.2 | bc | 48.7 ± 1.3 | de | ||
| D | 57.4 ± 0.5 | e | 62.9 ± 1.1 | fg | ||
| 2. (25 cm) | A | 29.2 ± 0.4 | a | 25.0 ± 1.2 | a | |
| B | 58.2 ± 0.4 | e | 54.7 ± 2.6 | ef | ||
| C | 56.9 ± 0.2 | e | 53.7 ± 1.6 | de | ||
| D | 33.3 ± 0.3 | a | 87.7 ± 2.5 | i | ||
| 3. (37 cm) | A | 44.9 ± 1.5 | cd | 28.1 ± 1.8 | a | |
| B | 39.0 ± 0.3 | b | 33.5 ± 1.5 | ab | ||
| C | 65.8 ± 0.7 | f | 64.7 ± 2.6 | gh | ||
| D | 47.9 ± 0.2 | d | 45.3 ± 0.4 | cd | ||
| Mycotoxin | Retention Time [min] | Precursor Ion [m/z] | Product Ion [m/z] | Collision Energy [V] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-2 toxin | 10.66 | [M + NH4]+ | 185.00 * | 22 |
| 484.25 | 215.15 ** | 22 | ||
| HT-2 toxin | 10.03 | [M + NH4]+ | 215.13 * | 12 |
| 442.17 | 263.15 ** | 12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boško, R.; Pernica, M.; Běláková, S.; Bjelková, M.; Pluháčková, H. Determination of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins in Seed of Milk Thistle [Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn.] Using Immunoaffinity Column by UPLC-MS/MS. Toxins 2022, 14, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040258
Boško R, Pernica M, Běláková S, Bjelková M, Pluháčková H. Determination of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins in Seed of Milk Thistle [Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn.] Using Immunoaffinity Column by UPLC-MS/MS. Toxins. 2022; 14(4):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040258
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoško, Rastislav, Marek Pernica, Sylvie Běláková, Marie Bjelková, and Helena Pluháčková. 2022. "Determination of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins in Seed of Milk Thistle [Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn.] Using Immunoaffinity Column by UPLC-MS/MS" Toxins 14, no. 4: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040258
APA StyleBoško, R., Pernica, M., Běláková, S., Bjelková, M., & Pluháčková, H. (2022). Determination of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins in Seed of Milk Thistle [Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn.] Using Immunoaffinity Column by UPLC-MS/MS. Toxins, 14(4), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040258





