Effectiveness and Safety of Intracavernosal IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) 100 U as an Add-on Therapy to Standard Pharmacological Treatment for Difficult-to-Treat Erectile Dysfunction: A Case Series
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Response to the First IncobotulinumtoxinA ICI
2.2. Second IncobotulinumtoxinA ICI
2.3. Further IncobotulinumtoxinA ICI
2.4. Men Who Did Not Request Further IncobotulinumtoxinA ICI
2.5. Reported Side Effects of IncobotulinumtoxinA ICI
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Methods
5.1. Design
5.2. Participants
5.3. Procedure
5.4. Outcomes
- (i)
- the achievement of a clinically relevant improvement in erectile function at the 1st post-injection follow-up visit. The change was considered clinically relevant if it was ≥the minimally clinical important difference (MCID) for EF score corrected for baseline severity of the ED. The MCID for each level of ED severity was mild: 2 points, moderate: 5 points, and severe: 7 points [19].
- (ii)
- the factors associated with the response to the 1st incobotulinumtoxinA ICI at the 1st follow-up visit and with the request for a 2nd injection.
- (iii)
- patient-reported side effects.
5.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poulain, B.; Lemichez, E.; Popoff, M.R. Neuronal Selectivity of Botulinum Neurotoxins. Toxicon 2020, 178, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F. Targets for Botulinum Toxin in the Lower Urinary Tract. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2014, 33, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.-F.; Chiu, H.-C.; Chen, K.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Chou, E.C.-L. Botulinum Toxin A for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder. Toxins 2016, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humeau, Y.; Doussau, F.; Grant, N.J.; Poulain, B. How Botulinum and Tetanus Neurotoxins Block Neurotransmitter Release. Biochimie 2000, 82, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtois, F.J.; Macdougall, J.C.; Sachs, B.D. Erectile Mechanism in Paraplegia. Physiol. Behav. 1993, 53, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, M.E.; Spitzer, N.C. Action of Botulinum Toxin on Transmission from Sympathetic Nerves to the Vas Deferens. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1973, 47, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, A.; Cruz, F.; Cruz, C.D.; Avelino, A. Spread of OnabotulinumtoxinA after Bladder Injection. Experimental Study Using the Distribution of Cleaved SNAP-25 as the Marker of the Toxin Action. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, F.; Brock, G. Botox for Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2017, 14, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.L.; Jobling, P.; Gibbins, I.L. Differential Inhibition by Botulinum Neurotoxin A of Cotransmitters Released from Autonomic Vasodilator Neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 281, H2124–H2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albersen, M.; Mwamukonda, K.B.; Shindel, A.W.; Lue, T.F. Evaluation and Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 95, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonia, A.; Bettocchi, C.; Boeri, L.; Capogrosso, P.; Carvalho, J.; Cilesiz, N.C.; Cocci, A.; Corona, G.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Gül, M.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Sexual and Reproductive Health—2021 Update: Male Sexual Dysfunction. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 333–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbani, K.J.; Tauqeer, F.; Rabbani, R. Prostaglandin E1 for the medical management of erectile dysfunction. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2010, 4, 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanem, H.; Raheem, A.A.; AbdelRahman, I.F.S.; Johnson, M.; Abdel-Raheem, T. Botulinum Neurotoxin and Its Potential Role in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction. Sex. Med. Rev. 2018, 6, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shaer, W.; Ghanem, H.; Diab, T.; Abo-Taleb, A.; Kandeel, W. Intra-Cavernous Injection of BOTOX® (50 and 100 Units) for Treatment of Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction: Randomized Controlled Trial. Andrology 2021, 9, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, F.; Joussain, C.; Denys, P. Safety and Efficacy of Intracavernosal Injections of AbobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®) as Add on Therapy to Phosphosdiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors or Prostaglandin E1 for Erectile Dysfunction-Case Studies. Toxins 2019, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giuliano, F.; Joussain, C.; Denys, P. Long Term Effectiveness and Safety of Intracavernosal Botulinum Toxin A as an Add-on Therapy to Phosphosdiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors or Prostaglandin E1 Injections for Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2022, 19, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, I.F.S.; Raheem, A.A.; Elkhiat, Y.; Aburahma, A.A.; Abdel-Raheem, T.; Ghanem, H. Safety and Efficacy of Botulinum Neurotoxin in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction Refractory to Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Andrology 2022, 10, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, W.H.; Benecke, R.; Hauschke, D.; Jankovic, J.; Kaňovský, P.; Roggenkämper, P.; Simpson, D.M.; Comella, C.L. Clinical and Pharmacological Properties of IncobotulinumtoxinA and Its Use in Neurological Disorders. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, R.C.; Allen, K.R.; Ni, X.; Araujo, A.B. Minimal Clinically Important Differences in the Erectile Function Domain of the International Index of Erectile Function Scale. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglione, F. Conversion Ratio between Botox®, Dysport®, and Xeomin® in Clinical Practice. Toxins 2016, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dressler, D.; Mander, G.; Fink, K. Measuring the Potency Labelling of OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox(®)) and IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin (®)) in an LD50 Assay. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.R.; Ranoux, D.; Wissel, J. Using Translational Medicine to Understand Clinical Differences between Botulinum Toxin Formulations. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13 (Suppl. S4), 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, F.; Joussain, C.; Denys, P.; Laurin, M.; Behr-Roussel, D.; Assaly, R. Intracavernosal onabotulinumtoxinA exerts a synergistic pro-erectile effect when combined with sildenafil in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Sex. Med. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.L.; Jobling, P.; Gibbins, I.L. Botulinum Neurotoxin A Attenuates Release of Norepinephrine but Not NPY from Vasoconstrictor Neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 283, H2627–H2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.P.; Franks, M.E.; McNeil, B.K.; Ghosh, R.; de Groat, W.C.; Chancellor, M.B.; Somogyi, G.T. Effect of Botulinum Toxin A on the Autonomic Nervous System of the Rat Lower Urinary Tract. J. Urol. 2003, 169, 1896–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senbel, A.M.; Hashad, A.M.; Sharabi, F.M.; Daabees, T.T. Combined Effect of Sildenafil and Guanethidine, Propranolol or Verapamil on Erectile Function in Rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.A.; Lie, J.D. Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) Inhibitors in the Management of Erectile Dysfunction. P & T. 2013, 38, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Salamanca, J.I.; La Fuente, J.M.; Martínez-Salamanca, E.; Fernández, A.; Pepe-Cardoso, A.J.; Louro, N.; Carballido, J.; Angulo, J. A1A-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonism Improves Erectile and Cavernosal Responses in Rats with Cavernous Nerve Injury and Enhances Neurogenic Responses in Human Corpus Cavernosum from Patients with Erectile Dysfunction Secondary to Radical Prostatectomy. J. Sex. Med. 2016, 13, 1844–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Oh, M.M. Norepinephrine Involvement in Response to Intracorporeal Injection of Papaverine in Psychogenic Impotence. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 1530–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpas, S.C. Sympathetic Nervous System Overactivity and Its Role in the Development of Cardiovascular Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 513–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, S.A.; Downie, J.W. Sympathetic Dyssynergia in the Region of the External Sphincter: A Possible Source of Lower Urinary Tract Obstruction. J. Urol. 1977, 118, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Zabbarova, I.V.; Birder, L.A.; de Groat, W.C.; McCarthy, C.J.; Hanna-Mitchell, A.T.; Kanai, A.J. Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A Suppresses Neurotransmitter Release from Afferent as Well as Efferent Nerves in the Urinary Bladder. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kennelly, M.; Dmochowski, R.; Schulte-Baukloh, H.; Ethans, K.; Del Popolo, G.; Moore, C.; Jenkins, B.; Guard, S.; Zheng, Y.; Karsenty, G.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of OnabotulinumtoxinA Therapy Are Sustained over 4 Years of Treatment in Patients with Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity: Final Results of a Long-Term Extension Study. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


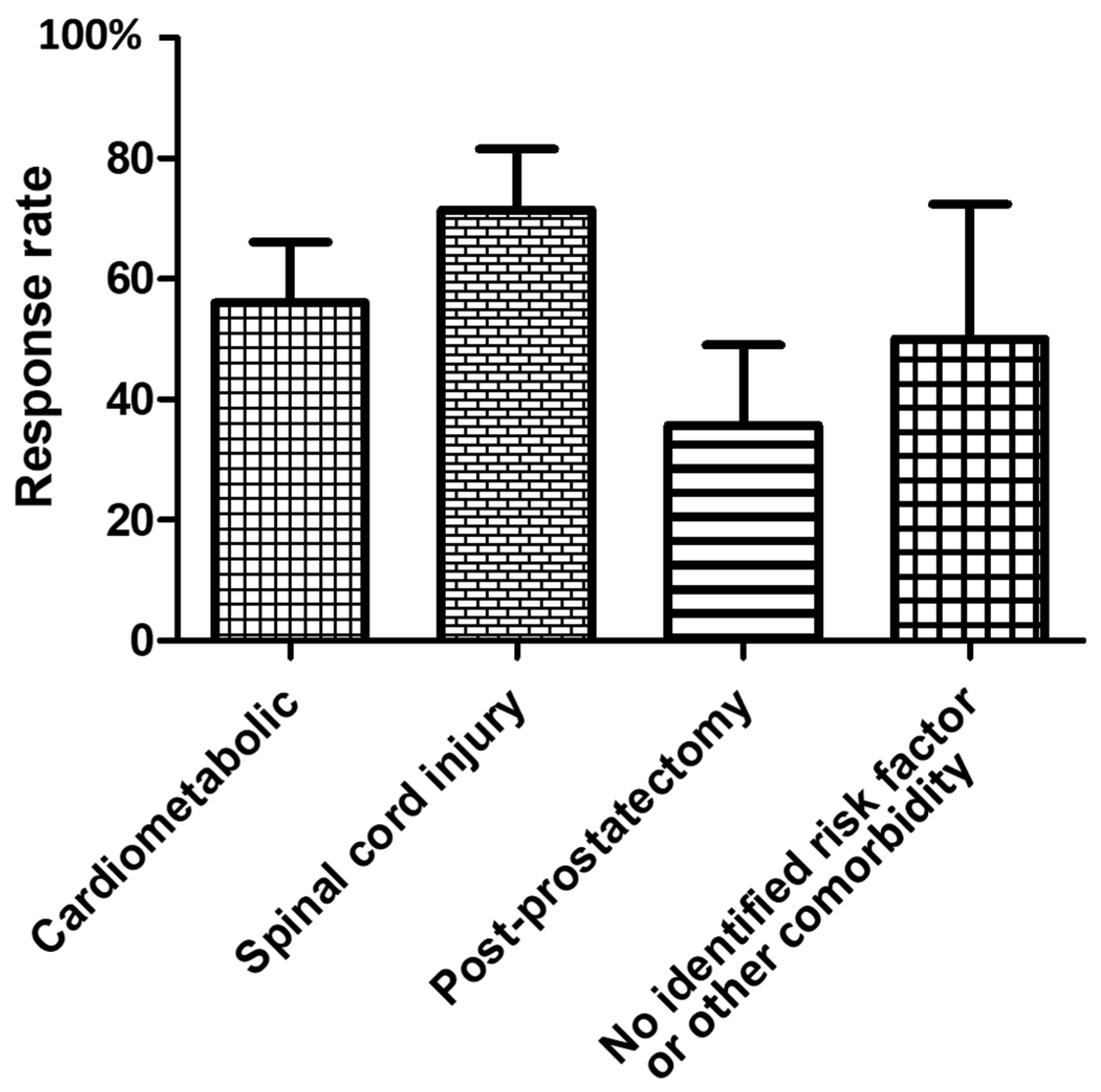
| Men Who Did Not Request a 2nd Injection (n = 29) | Men Who Requested a 2nd Injection (n = 22) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 59.3 (13.3) | 53 (14.1) |
| ED duration (years), median (1st quartile–3rd quartile) | 5 (2–6) | 3 (2–12.7) |
| ED severity according to ED domain score [19] | ||
| Severe n (%) | 10 (35) | 8 (36) |
| Moderate n (%) | 7 (24) | 4 (18) |
| Mild n (%) | 12 (41) | 10 (45) |
| ED risk factors and etiologies | ||
| No identified organic risk factor/etiology or other comorbidity n (%) | 4 (14) | 2 (9) |
| Cardiometabolic n (%) | 13 (45) | 10 (45) |
| Spinal cord injury n (%) | 8 (28) | 11(50) |
| Post-prostatectomy n (%) | 9 (31) | 5 (23) |
| ED treatment prior to incobotulinumtoxinA ICI | ||
| PDE5-Is n (%) | 23 (79) | 17 (77) |
| PGE1 ICIs n (%) | 6 (21) | 5 (23) |
| dose PGE1 ICI (µg), mean (SD) | 43 (20) | 44 (22) |
| 1st incobotulinumtoxinA ICI outcome | ||
| EF domain score at baseline on treatment, median (1st quartile–3rd quartile) | 13 (7–18) | 15 (8–20) |
| EF domain score post 1st injection, median (1st quartile–3rd quartile) | 13 (7–23) | 25 (18–29) |
| Responders n (%) [19] | 11 (38) | 17 (77) |
| Time between 1st injection and 1st assessment (days), median (1st quartile–3rd quartile) | 43 (30–57) | 46.5 (32–70) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giuliano, F.; Denys, P.; Joussain, C. Effectiveness and Safety of Intracavernosal IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) 100 U as an Add-on Therapy to Standard Pharmacological Treatment for Difficult-to-Treat Erectile Dysfunction: A Case Series. Toxins 2022, 14, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040286
Giuliano F, Denys P, Joussain C. Effectiveness and Safety of Intracavernosal IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) 100 U as an Add-on Therapy to Standard Pharmacological Treatment for Difficult-to-Treat Erectile Dysfunction: A Case Series. Toxins. 2022; 14(4):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040286
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiuliano, Francois, Pierre Denys, and Charles Joussain. 2022. "Effectiveness and Safety of Intracavernosal IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) 100 U as an Add-on Therapy to Standard Pharmacological Treatment for Difficult-to-Treat Erectile Dysfunction: A Case Series" Toxins 14, no. 4: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040286
APA StyleGiuliano, F., Denys, P., & Joussain, C. (2022). Effectiveness and Safety of Intracavernosal IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) 100 U as an Add-on Therapy to Standard Pharmacological Treatment for Difficult-to-Treat Erectile Dysfunction: A Case Series. Toxins, 14(4), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040286





