Genotoxicity of Natural Water during the Mass Development of Cyanobacteria Evaluated by the Allium Test Method: A Model Experiment with Microcosms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Number and Biomass of Cyanobacteria
2.2. Microcystin Concentrations
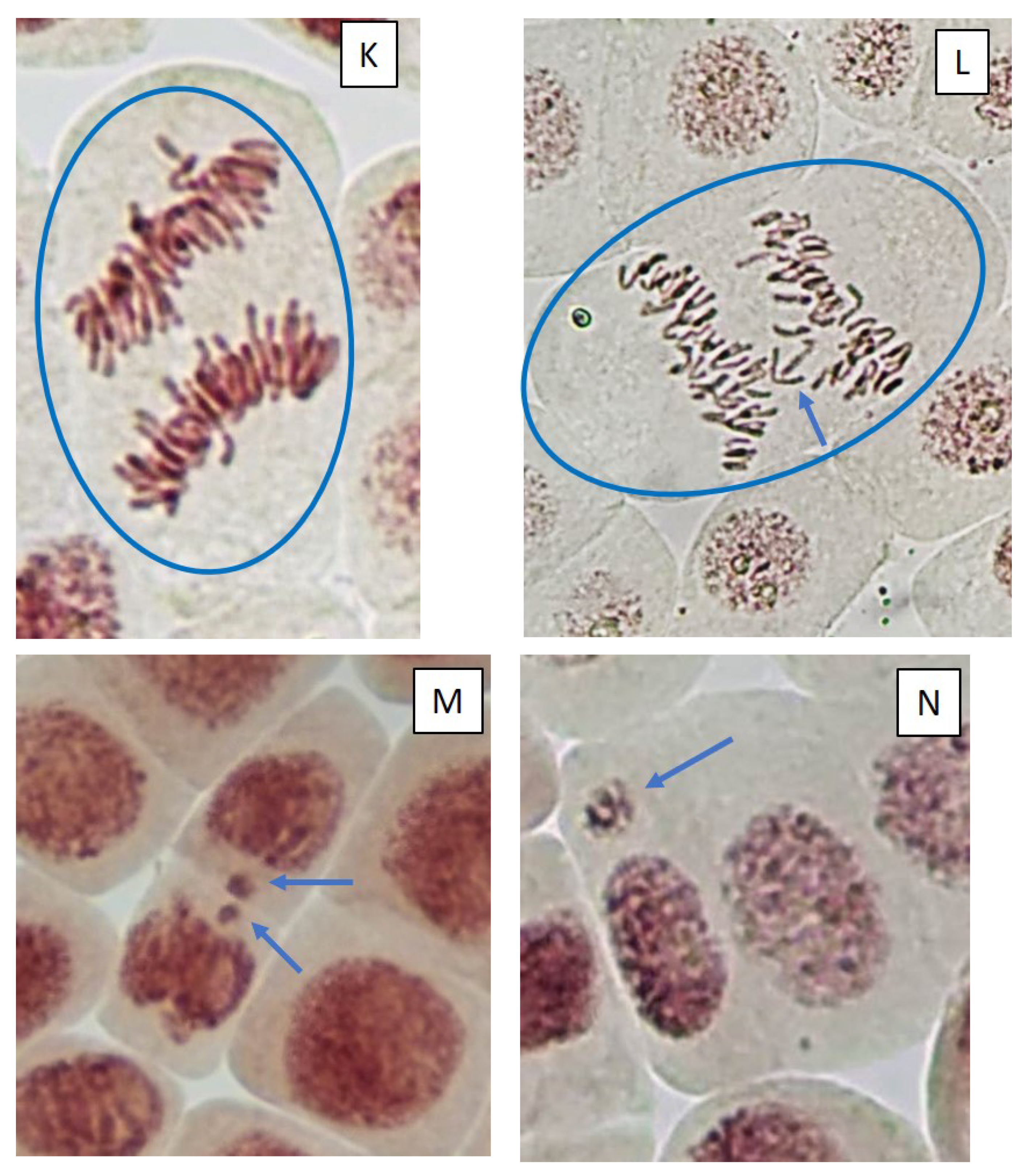
2.3. Mitotic and Phase Indexes, and Genotoxic Effects
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Microcosms Organization
5.2. Phytoplankton
5.3. Cyanotoxin Analysis
5.4. Genotoxicity Testing
5.5. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, E.D.; Beasley, V.R. One health and cyanobacteria in freshwater systems: Animal illnesses and deaths are sentinel events for human health risks. Toxins 2015, 7, 1374–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onodera, H.; Oshims, Y.; Henriksen, P.; Yasumoto, T. Confirmation of anatoxin-a(s), in the cyanobacterium Anabaena lemmermanii, as the cause of bird kills in Danish lakes. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puschner, B.; Pratt, C.; Tor, E.R. Treatment and diagnosis of dog with fulminant neurological deterioration due to anatoxin-a intoxication. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2010, 20, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Apeldoorn, M.E.; van Egmond, H.P.; Speijers, G.J.A.; Bakker, G.J.I. Toxins of cyanobacteria. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 7–60. [Google Scholar]
- Buratti, F.M.; Manganelli, M.; Vichi, S.; Stefanelli, M.; Scardala, S.; Testai, E.; Funan, E. Cyanotoxins: Producing organisms, occurrence, toxicity, mechanism of action and human health toxicological risk evaluation. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1049–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorus, I. Current Approaches to Cyanotoxin Risk Assessment, Risk Management and Regulations in Different Countries. Fed. Environ. Agency 2012, 63, 1–147. Available online: http://www.uba.de/uba-info-medien-e/4390.html (accessed on 24 November 2021).
- Chen, L.; Giesy, J.P.; Adamovsky, O.; Svirčev, Z.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G.A.; Mijovic, B.; Shi, T.; Tuo, X.; Li, S.-C.; et al. Challenges of using blooms of Microcystis spp. in animal feeds: A comprehensive review of nutritional, toxicological and microbial health evaluation. Sci. Total Environment. 2021, 764, 142319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Pinto, E.; Torres, M.A.; Dörr, F.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Szubert, K.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; et al. CyanoMetDB, a comprehensive public database of secondary metabolites from cyanobacteria. Water Research. 2021, 196, 117017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughinghouse, H.D., IV; Prá, D.; Silva-Stenico, M.E.; Rieger, A.; Frescura, V.D.-S.; Fiore, M.F.; Tedesco, S.B. Biomonitoring genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of Microcistis aeruginosa (Chroococcales, Cyanobacteria) using the Allium cepa test. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamplona-Silva, M.T.; Gonçalves, L.C.; Marin-Morales, M.A. Genetic toxicity of water contaminated by microcystins collected during a cyanobacteria bloom. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsche, L.; Vicari, T.; Calado, S.L.M.; Wojciechowski, J.; Magalhães, V.F.; Assis, H.C.S.; Leme, D.M.; Cestari, M.M. Genotoxicity detected during cyanobacteria bloom in a water supply reservoir. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Contam. 2020, 15, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehringer, M.M. Microcystin-LR and okadaic acid-induced cellular effects: A dualistic response. FEBS Lett. 2004, 557, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, J.C.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Microcystin dynamics in aquatic organisms. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2009, 12, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, H.; Suganuma, M. Tumor promoters—Microcystin-LR, Nodularin and TNF-α and human cancer development. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Quijada, L.; Prieto, A.I.; Puerto, M.; Jos, Á.; Cameán, A.M. In Vitro Mutagenic and Genotoxic Assessment of a Mixture of the Cyanotoxins Microcystin-LR and Cylindrospermopsin. Toxins 2019, 11, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lankoff, A.; Wojcik, A.; Fessard, V.; Meriluoto, J. Nodularin-induced genotoxicity following oxidative DNA damage and aneuploidy in HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 164, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melegari, S.P.; de Carvalho, P.C.R.; Moukha, S.; Creppy, E.E.; Matias, W.G. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Cell Death In-duced In Vitro by Saxitoxin in Mammalian Cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2015, 78, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieroslawska, A. Assessment of the mutagenic potential of cyanobacterial extracts and pure cyanotoxins. Toxicon 2013, 74, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriens, A.; Nawrot, T.S.; Janssen, B.G.; Baeyens, W.; Bruckers, L.; Covaci, A.; De Craemer, S.; Henauw, S.; Hond, E.D.; Loots, I.; et al. Exposure to Environmental Pollutants and Their Association with Biomarkers of Aging: A Multipollutant Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5966–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y. Evaluation of in vivo mutagenesis for assessing the health risk of air pollutants. Genes Environ. 2017, 39, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Mejiba, S.E.; Zhai, Z.; Akram, H.; Pye, Q.N.; Hensley, K.; Kurien, B.T.; Scofield, R.H.; Ramirez, D.C. Inhalation of environmental stressors & chronic inflammation: Autoimmunity and neurodegeneration. Mutat. Res. 2009, 674, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hercog, K.; Štern, A.; Maisanaba, S.; Filipič, M.; Žegura, B. Plastics in Cyanobacterial Blooms—Genotoxic Effects of Binary Mixtures of Cylindrospermopsin and Bisphenols in HepG2 Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díez-Quijada, L.; Medrano-Padial, C.; Llana-Ruiz-Cabello, M.; Cătunescu, G.M.; Moyano, R.; Risalde, M.A.; Cameán, A.M.; Jos, Á. Cylindrospermopsin-Microcystin-LR Combinations May Induce Genotoxic and Histopathological Damage in Rats. Toxins 2020, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, M.; Štern, A.; Smutná, M.; Hilscherová, K.; Žegura, B. Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Cyanobacterial and Algal Extracts—Microcystin and Retinoic Acid Content. Toxins 2021, 13, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Bruning, K.; de Jonge, J.; Wolfstein, K.; Dionosio Pires, L.M.; Postma, J.; Burger, T. Distribution of microcystins in a lake foodweb: No evidence for biomagnification. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A.; Bernasińska, J.; Jurczak, T.; Gwoździński, K.; Frankiewicz, P.; Wielanek, M. Microcystin assimilation and detoxification by Daphnia spp. In two ecosystems of different cyanotoxin concentrations. J. Limnol. 2013, 72, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, T.-H.; Cabrera, G.L.; Owens, E. Genotoxic Agents Detected by Plant Bioassays. Rev. Environ. Health 2005, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, M.J.; Andrade-Vieira, L.F.; Trento, M.V.C.; de Faria Eleuterio, M.W.; Luber, J.; Davide, L.C.; Marcussi, S. Cytogenotoxic Effects of Spent Pot Liner (SPL) and Its Main Components on Human Leukocytes and Meristematic Cells of Allium cepa. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonciu, E.; Firbas, P.; Fontanetti, C.S.; Wusheng, J.; Karaismailoğlu, M.C.; Liu, D.; Menicucci, F.; Popescu, A.; Pesnya, D.S.; Romanovsky, A.V.; et al. An evaluation for the standardization of the Allium cepa test as cytotoxicity and genotoxicity assay. Caryologia 2018, 71, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiskesjö, G. The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas 1985, 102, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernova, E.; Sidelev, S.; Russkikh, I.; Korneva, L.; Solovyova, V.; Mineeva, N.; Stepanova, I.; Zhakovskaya, Z. Spatial distribution of cyanotoxins and ratios of microcystin to biomass indicators in the reservoirs of the Volga, Kama and Don Rivers, the European part of Russia. Limnologica 2020, 84, 125819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.I.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Potapov, S.A.; Fedorova, G.A. Microcystin-Producing Cyanobacteria in Water Reservoirs of Russia, Belarus and Ukraine. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 21, 347–361. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Stumpf, R.P.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Werdell, P.J.; Loftin, K.A.; Meredith, A. Measurement of Cyanobacterial Bloom Magnitude using Satellite Remote Sensing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyanobacterial Toxins: Microcystins. Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality and Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Was, H.; Borkowska, A.; Olszewska, A.; Klemba, A.; Marciniak, M.; Synowiec, A.; Kieda, C. Polyploidy formation in cancer cells: How a Trojan horse is born. Semin. Cancer Bio. 2022, 81, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankoff, A.; Banasik, A.; Obe, G.; Deperas, M.; Kuzminski, K.; Tarczynska, M.; Jurczak, T.; Wojcik, A. Effect of microcystin-LR and cyanobacterial extract from Polish reservoir of drinking water on cell cycle progression, mitotic spindle, and apoptosis in CHO-K1 cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 189, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunduri, N.K.; Barthel, K.; Storchova, Z. Consequences of Chromosome Loss: Why Do Cells Need Each Chromosome Twice? Cells 2022, 11, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Frost, P.C.; Hansson, L.-A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E.; Lürling, M. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Z. Rising temperature more strongly promotes low-abundance Paramecium to remove Microcystis and degrade microcystins. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, A.S.; Sidelev, S.I.; Dmitrieva, O.A. Experimental investigation of natural populations of Daphnia galeata G.O. Sars from the Curonian lagoon feeding on potentially toxigenic cyanobacteria. Biol. Bull. 2017, 44, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tõnno, I.; Agasild, H.; Kõiv, T.; Freiberg, R.; Nõges, P.; Nõges, T. Algal diet of small-bodied crustacean zooplankton in a cyanobacteria-dominated eutrophic lake. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozak, A.; Celewicz-Gołdyn, S.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N. Cyanobacteria in small water bodies: The effect of habitat and catchment area conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbatova, S.A.; Berezina, N.A.; Mavrin, A.S.; Otyukova, N.G. Metabolic rate in hydrobionts of different ecological groups in the experiment. Inland Water Biol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Omidi, A.; Pflugmacher, S.; Kaplan, A.; Kim, Y.J.; Esterhuizen, M. Reviewing Interspecies Interactions as a Driving Force Affecting the Community Structure in Lakes via Cyanotoxins. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Hansson, L.-A.; Lürling, M. Understanding cyanobacteria-zooplankton interaction in a more eutrophic world. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1783–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarvainen, M.; Ventela, A.-M.; Helminen, H.; Sarvala, J. Nutrient release and resuspension generated by ruffe (Gymnocephaluscernuus) and chironomids. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmakov, V.I. Role of Microcystis aeruginosa passing through the digestive tracts of filter-feeding animals in eutrophic water reservoirs (review). Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2014, 7, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Mou, X. A Brief Review of the Structure, Cytotoxicity, Synthesis, and Biodegradation of Microcystins. Water 2021, 13, 2147. [Google Scholar]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.-D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenina, I.; Hajdu, S.; Edler, L.; Andersson, A.; Wasmund, N.; Busch, S.; Göbel, J.; Gromisz, S.; Huseby, S.; Huttunen, M.; et al. Biovolumes and Size-Classes of Phytoplankton in the Baltic Sea; HELCOM Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings No.106; Helsinki Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/BSEP106.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Chernova, E.; Russkikh, I.; Voyakina, E.; Zhakovskaya, Z. Occurrence of microcystins and anatoxin-a in eutrophic lakes of Saint Petersburg, northwestern Russia. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2016, 45, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pesnya, D.S.; Kurbatova, S.A.; Sharov, A.N.; Chernova, E.N.; Yershov, I.Y.; Shurganova, G.V.; Vodeneeva, E.L. Genotoxicity of Natural Water during the Mass Development of Cyanobacteria Evaluated by the Allium Test Method: A Model Experiment with Microcosms. Toxins 2022, 14, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14050359
Pesnya DS, Kurbatova SA, Sharov AN, Chernova EN, Yershov IY, Shurganova GV, Vodeneeva EL. Genotoxicity of Natural Water during the Mass Development of Cyanobacteria Evaluated by the Allium Test Method: A Model Experiment with Microcosms. Toxins. 2022; 14(5):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14050359
Chicago/Turabian StylePesnya, Dmitry S., Svetlana A. Kurbatova, Andrey N. Sharov, Ekaterina N. Chernova, Igor Y. Yershov, Galina V. Shurganova, and Ekaterina L. Vodeneeva. 2022. "Genotoxicity of Natural Water during the Mass Development of Cyanobacteria Evaluated by the Allium Test Method: A Model Experiment with Microcosms" Toxins 14, no. 5: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14050359
APA StylePesnya, D. S., Kurbatova, S. A., Sharov, A. N., Chernova, E. N., Yershov, I. Y., Shurganova, G. V., & Vodeneeva, E. L. (2022). Genotoxicity of Natural Water during the Mass Development of Cyanobacteria Evaluated by the Allium Test Method: A Model Experiment with Microcosms. Toxins, 14(5), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14050359





