Altered RNome expression in Murine Gastrocnemius Muscle following Exposure to Jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca Venom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
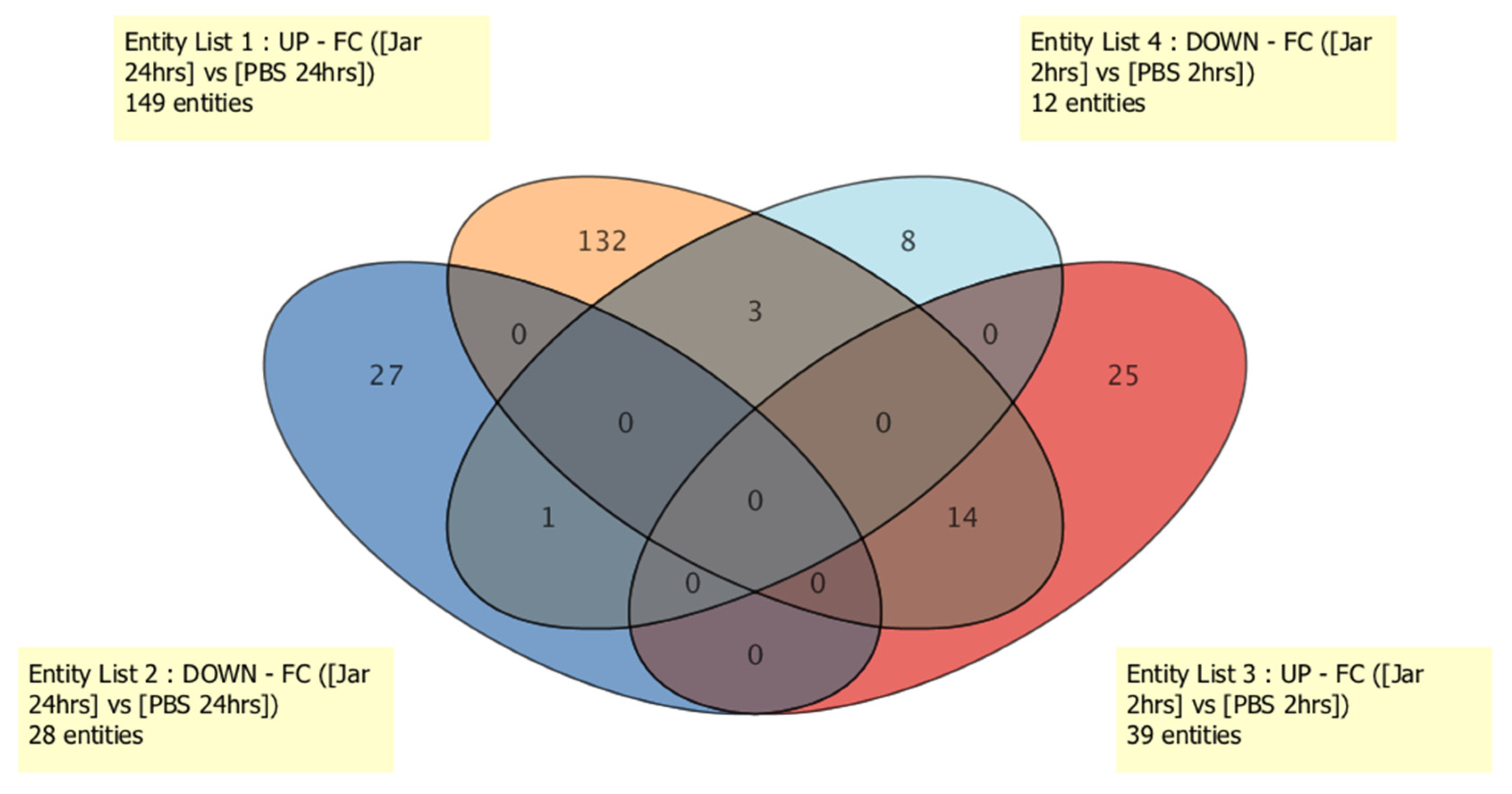
2. Results
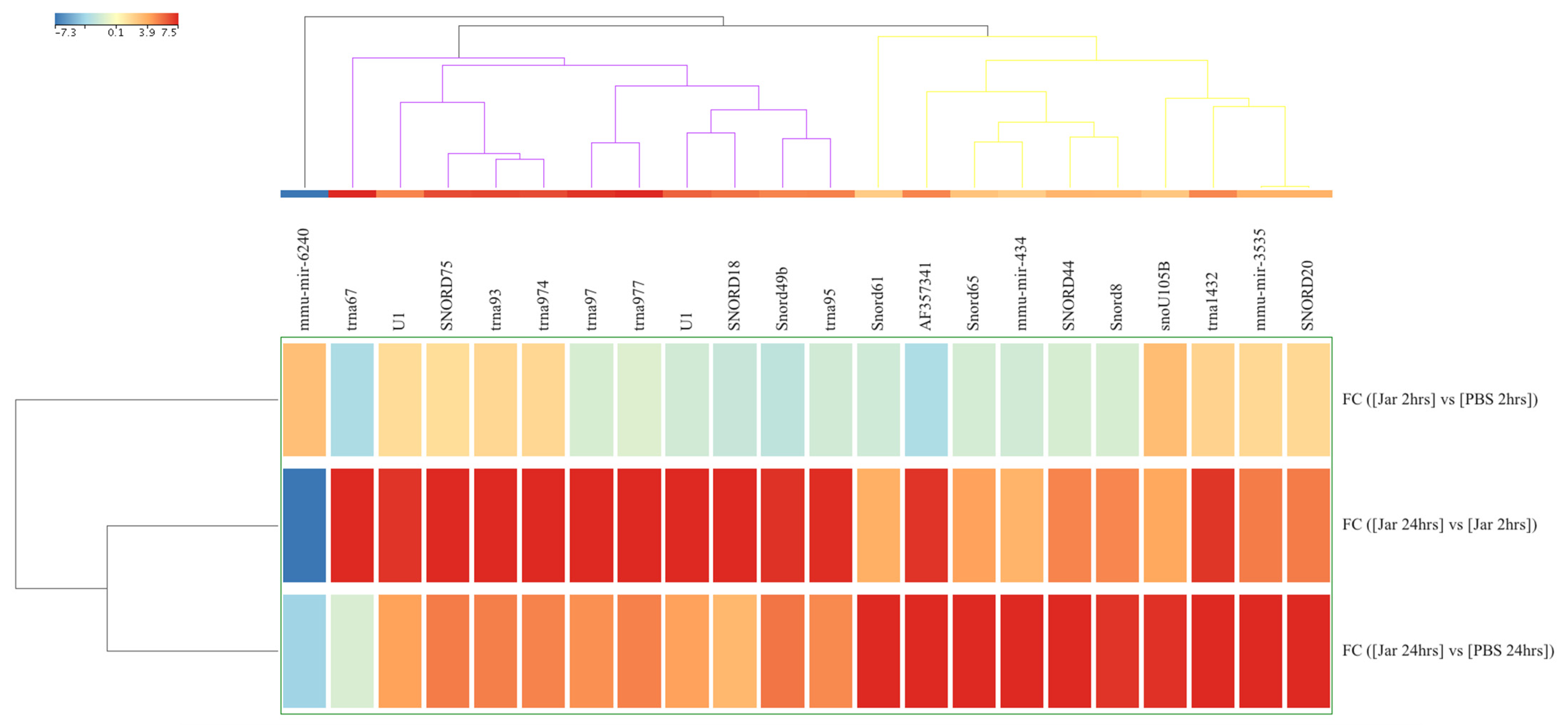
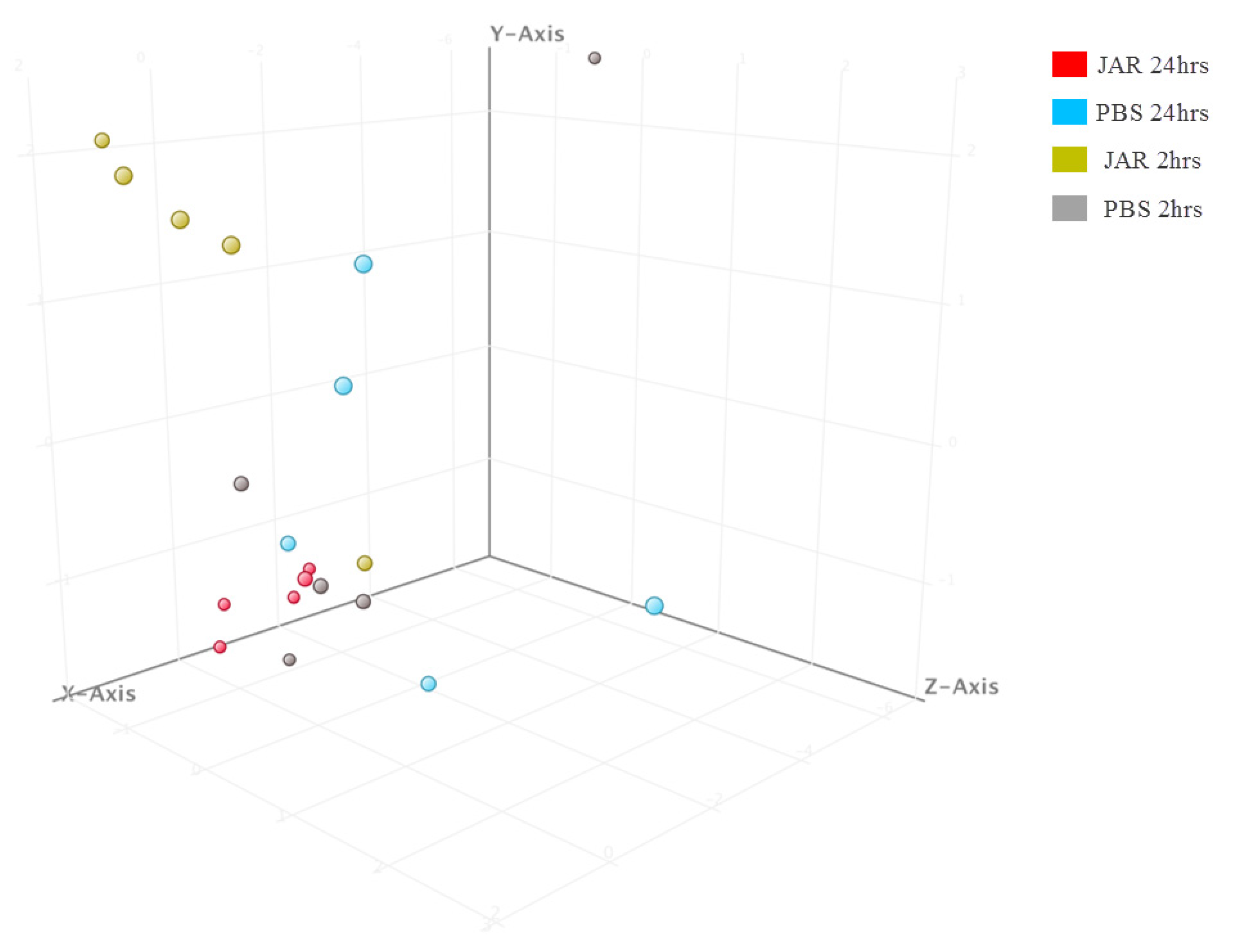
2.1. Known sRNA Expression Profile Following Jararhagin and PBS Challenge
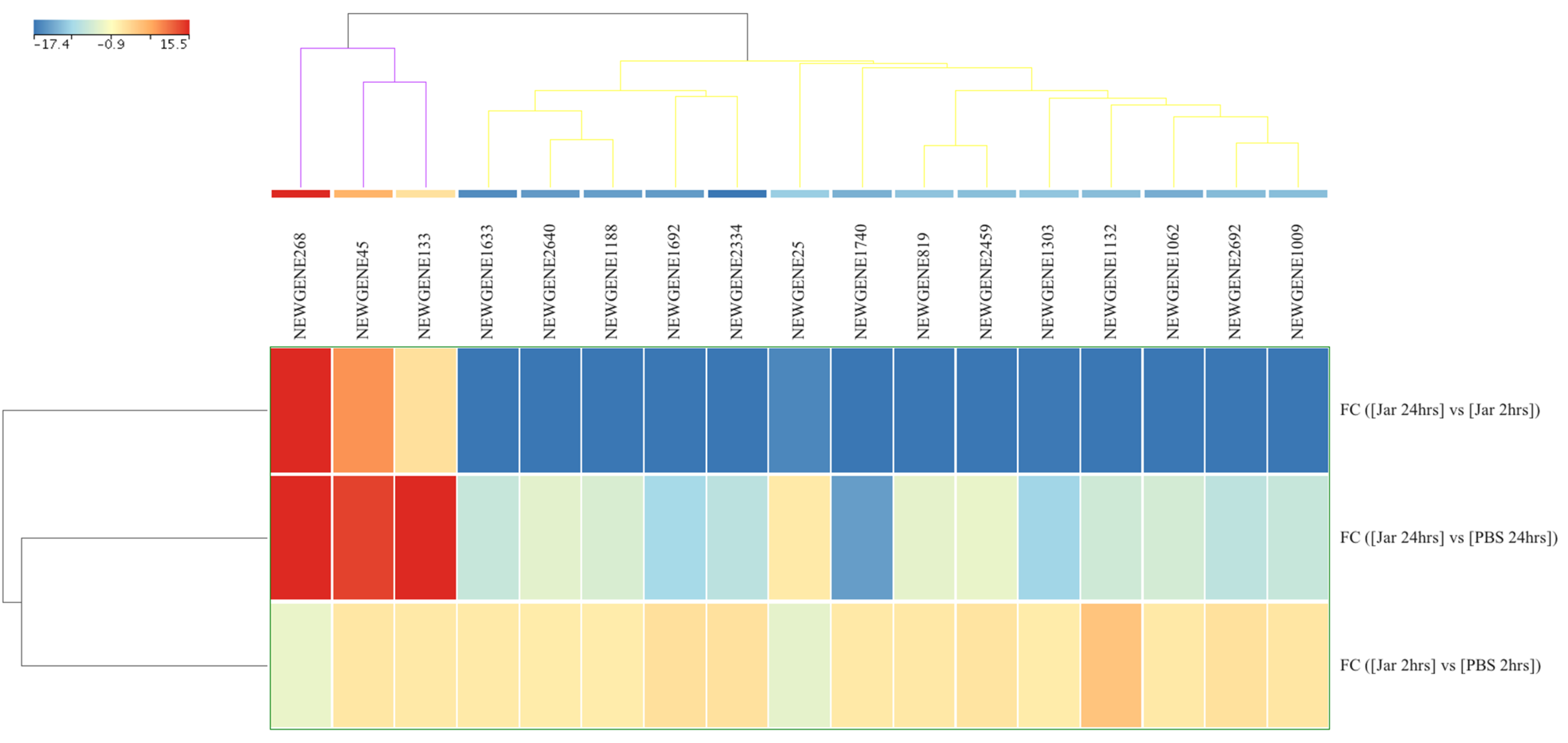
2.2. Novel sRNA Expression Profile Following Jararhagin and PBS Challenge
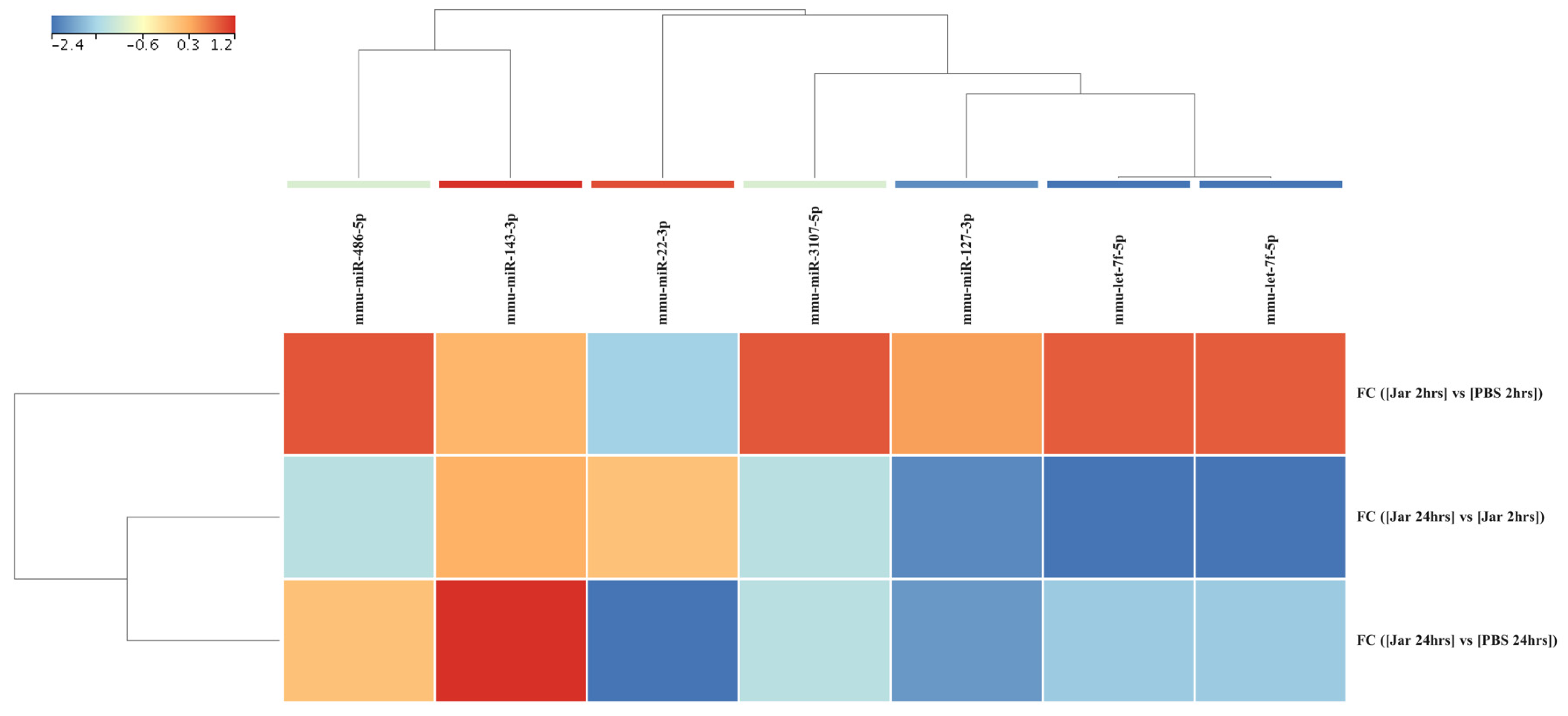
2.3. Mature miRNA Expression Profile Following Jararhagin and PBS Challenge
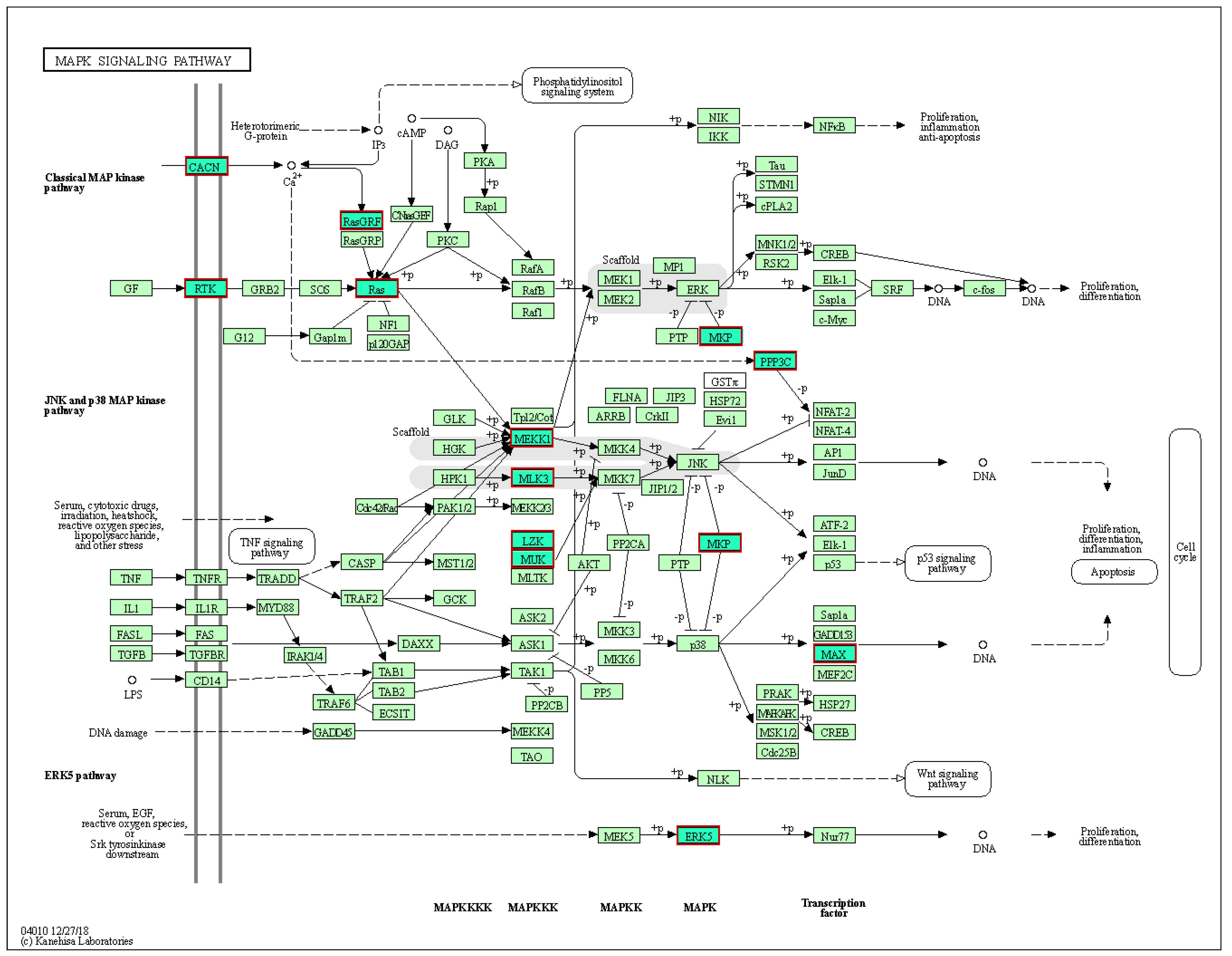
2.4. Target Genes, KEGG Pathway, and GO Enrichment Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Experimental Design
5.2. Jararhagin Purification and Depyrogenation
5.3. RNA Extraction
5.4. Library Construction
5.5. Functional Annotation and Pathway Analysis of miRNA Target Genes
5.6. Constructing Regulatory Network between miRNAs and Their Targets
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knudsen, C.; Jürgensen, J.A.; Føns, S.; Haack, A.M.; Friis, R.U.W.; Dam, S.H.; Bush, S.P.; White, J.; Laustsen, A.H. Snakebite Envenoming Diagnosis and Diagnostics. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 661457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, C.; Jamora, C.; Yamanouye, N.; Zorn, T.M.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Mechanisms of vascular damage by hemorrhagic snake venom metalloproteinases: Tissue distribution and in situ hydrolysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministério-da-Saúde. Acidente por Animais Peçonhentos—Descrição da Doença. Available online: https://www.saude.gov.br/saude-de-a-z/acidentes-por-animais-peconhentos/13713-descricao-da-doenca (accessed on 28 March 2020).
- Cardoso, J.L.; Fan, H.W.; Franca, F.O.; Jorge, M.T.; Leite, R.P.; Nishioka, S.A.; Avila, A.; Sano-Martins, I.S.; Tomy, S.C.; Santoro, M.L.; et al. Randomized comparative trial of three antivenoms in the treatment of envenoming by lance-headed vipers (Bothrops jararaca) in Sao Paulo, Brazil. QJM Int. J. Med. 1993, 86, 315–325. [Google Scholar]
- Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Baldo, C. Jararhagin, a hemorrhagic snake venom metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca. Toxicon 2012, 60, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, S.D.; de Souza, A.; Nunes, F.P.; Goncalves, L.R. Effect of dexamethasone associated with serum therapy on treatment of Bothrops jararaca venom-induced paw edema in mice. Inflamm. Res. 2007, 56, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zychar, B.C.; Dale, C.S.; Demarchi, D.S.; Goncalves, L.R. Contribution of metalloproteases, serine proteases and phospholipases A2 to the inflammatory reaction induced by Bothrops jararaca crude venom in mice. Toxicon 2010, 55, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cidade, D.A.; Simao, T.A.; Davila, A.M.; Wagner, G.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.; Ho, P.L.; Bon, C.; Zingali, R.B.; Albano, R.M. Bothrops jararaca venom gland transcriptome: Analysis of the gene expression pattern. Toxicon 2006, 48, 437–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.M.; Messias, E.A.; Sorroche, B.P.; Oliveira, A.D.N.; Arantes, L.; de Carvalho, A.C.; Tanaka-Azevedo, A.M.; Grego, K.F.; Carvalho, A.L.; Melendez, M.E. In-depth transcriptome reveals the potential biotechnological application of Bothrops jararaca venom gland. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 26, e20190058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assakura, M.T.; Reichl, A.P.; Mandelbaum, F.R. Comparison of immunological, biochemical and biophysical properties of three hemorrhagic factors isolated from the venom of Bothrops jararaca (jararaca). Toxicon 1986, 24, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, M.; Sugiki, M.; Yoshida, E.; Mihara, H.; Nakajima, N. Purification and characterization of two fibrinolytic enzymes from Bothrops jararaca (jararaca) venom. Toxicon 1992, 30, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, M.J.; Desmond, H.P.; Theakston, R.D.; Crampton, J.M. Purification, cloning, and molecular characterization of a high molecular weight hemorrhagic metalloprotease, jararhagin, from Bothrops jararaca venom. Insights into the disintegrin gene family. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 22869–22876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.W.; Serrano, S.M. Insights into and speculations about snake venom metalloproteinase (SVMP) synthesis, folding and disulfide bond formation and their contribution to venom complexity. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 3016–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, T.; Shannon, J.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Fox, J.W. Novel insights into capillary vessel basement membrane damage by snake venom hemorrhagic metalloproteinases: A biochemical and immunohistochemical study. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 455, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zychar, B.C.; Clissa, P.B.; Carvalho, E.; Alves, A.S.; Baldo, C.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L.; Goncalves, L.R.C. Modulation of Adhesion Molecules Expression by Different Metalloproteases Isolated from Bothrops Snakes. Toxins 2021, 13, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.P.; Clissa, P.B.; Teixeira, C.F.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Importance of metalloproteinases and macrophages in viper snake envenomation-induced local inflammation. Inflammation 2002, 26, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clissa, P.B.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Della-Casa, M.S.; Farsky, S.H.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Importance of jararhagin disintegrin-like and cysteine-rich domains in the early events of local inflammatory response. Toxicon 2006, 47, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Calixto-Campos, C.; Manchope, M.F.; Casagrande, R.; Clissa, P.B.; Baldo, C.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Jararhagin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia depends on TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and NFkappaB in mice. Toxicon 2015, 103, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.A.; Deconte, S.R.; de Moura, F.B.R.; Tomiosso, T.C.; Clissa, P.B.; Andrade, S.P.; Araujo, F.A. Inflammation, angiogenesis and fibrogenesis are differentially modulated by distinct domains of the snake venom metalloproteinase jararhagin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Sanchez, M.A.; Liu, J.; Hannon, G.J.; Parker, R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brennecke, J.; Hipfner, D.R.; Stark, A.; Russell, R.B.; Cohen, S.M. bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 2003, 113, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wienholds, E.; Koudijs, M.J.; van Eeden, F.J.; Cuppen, E.; Plasterk, R.H. The microRNA-producing enzyme Dicer1 is essential for zebrafish development. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Vernooy, S.Y.; Guo, M.; Hay, B.A. The Drosophila microRNA Mir-14 suppresses cell death and is required for normal fat metabolism. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ardekani, A.M.; Naeini, M.M. The Role of MicroRNAs in Human Diseases. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2010, 2, 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, S.; Magee, P.; Garofalo, M. MiRNA-based therapeutic intervention of cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, P.; Benito, E.; Fischer, A. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for CNS disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafi, G.; Aliya, N.; Munshi, A. MicroRNA signatures in neurological disorders. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 37, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garo, L.P.; Ajay, A.K.; Fujiwara, M.; Gabriely, G.; Raheja, R.; Kuhn, C.; Kenyon, B.; Skillin, N.; Kadowaki-Saga, R.; Saxena, S.; et al. MicroRNA-146a limits tumorigenic inflammation in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hu, L.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhou, Y.; An, Q.; Zhu, W. Changes in the Small RNA Expression in Endothelial Cells in Response to Inflammatory Stimulation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8845520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clissa, P.B.; Laing, G.D.; Theakston, R.D.; Mota, I.; Taylor, M.J.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. The effect of jararhagin, a metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca venom, on pro-inflammatory cytokines released by murine peritoneal adherent cells. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.; Bao, Y.; Serrano, S.M.; Laing, G.D.; Theakston, R.D.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Escalante, T.; Zigrino, P.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Nischt, R.; et al. Role of the snake venom toxin jararhagin in proinflammatory pathogenesis: In vitro and in vivo gene expression analysis of the effects of the toxin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 441, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Henkel, C.V.; Heimberg, A.M.; Jansen, H.J.; McCleary, R.J.; Kerkkamp, H.M.; Vos, R.A.; Guerreiro, I.; Calvete, J.J.; et al. The king cobra genome reveals dynamic gene evolution and adaptation in the snake venom system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20651–20656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durban, J.; Perez, A.; Sanz, L.; Gomez, A.; Bonilla, F.; Rodriguez, S.; Chacon, D.; Sasa, M.; Angulo, Y.; Gutierrez, J.M.; et al. Integrated “omics” profiling indicates that miRNAs are modulators of the ontogenetic venom composition shift in the Central American rattlesnake, Crotalus simus simus. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guercio, R.A.; Shevchenko, A.; Shevchenko, A.; Lopez-Lozano, J.L.; Paba, J.; Sousa, M.V.; Ricart, C.A. Ontogenetic variations in the venom proteome of the Amazonian snake Bothrops atrox. Proteome Sci. 2006, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Cid, P.; de la Torre, P.; Flores-Diaz, M.; Dos Santos, M.C.; Borges, A.; Bremo, A.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; et al. Snake venomics of the Central American rattlesnake Crotalus simus and the South American Crotalus durissus complex points to neurotoxicity as an adaptive paedomorphic trend along Crotalus dispersal in South America. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.B.; Zou, Q.; Lv, X.; Zhou, R.L.; Niu, X.; Weng, C.; Chen, F.; Fan, Y.W.; Deng, Z.Y.; Li, J. 9t18:1 and 11t18:1 activate the MAPK pathway to regulate the expression of PLA2 and cause inflammation in HUVECs. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, L.; Bostrom, P.; Ericson, J.; Rutberg, M.; Magnusson, B.; Marchesan, D.; Ruiz, M.; Asp, L.; Huang, P.; Frohman, M.A.; et al. PLD1 and ERK2 regulate cytosolic lipid droplet formation. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2246–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.N.; Ye, Y.X.; Niu, J.W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; You, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, L.D.; Zeng, X.F.; Zhang, F.C.; et al. Defective PTEN regulation contributes to B cell hyperresponsiveness in systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 246ra299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.F.; Cao, L.L.; Huang, F.; Qiao, X.; Yu, J.; Ye, H.; Xi, C.L.; Zhou, Q.C.; Zhang, G.F.; Gong, Z.L. Role of miR-22 in intestinal mucosa tissues and peripheral blood CD4+ T cells of inflammatory bowel disease. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Mateos, E.M.; Arribas-Blazquez, M.; Sanz-Rodriguez, A.; Concannon, C.; Olivos-Ore, L.A.; Reschke, C.R.; Mooney, C.M.; Mooney, C.; Lugara, E.; Morgan, J.; et al. microRNA targeting of the P2X7 purinoceptor opposes a contralateral epileptogenic focus in the hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovicic, A.; Zaldivar Jolissaint, J.F.; Moser, R.; Silva Santos Mde, F.; Luthi-Carter, R. MicroRNA-22 (miR-22) overexpression is neuroprotective via general anti-apoptotic effects and may also target specific Huntington’s disease-related mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auler, M.; Bergmeier, V.; Georgieva, V.S.; Pitzler, L.; Frie, C.; Nuchel, J.; Eckes, B.; Hinz, B.; Brachvogel, B. miR-127-3p Is an Epigenetic Activator of Myofibroblast Senescence Situated within the MicroRNA-Enriched Dlk1-Dio3Imprinted Domain on Mouse Chromosome 12. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1076–1086 e1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ju, S.; Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Jing, R.; Yang, C.; Chu, H.; Cong, H. Combined detection of plasma miR-127-3p and HE4 improves the diagnostic efficacy of breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 18, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.H.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Yu, J.; He, J.S. The Tumor Suppressor Roles of miR-433 and miR-127 in Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14171–14184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Reviews. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.Y.; Huang, X.X.; Li, N.M.; Lv, C.Y.; Lv, C.H.; Wei, M.L.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.P. MiR-127-3p inhibits proliferation of ovarian cancer in rats through down-regulating MAPK4. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 10383–10390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clissa, P.B.; Pessoa, R.; Ferraz, K.F.; de Souza, D.R.; Sanabani, S.S. Data on global expression of non-coding RNome in mice gastrocnemius muscle exposed to jararhagin, snake venom metalloproteinase. Data Brief 2016, 9, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadao de Souza, D.R.; Pessoa, R.; Nascimento, A.; Nukui, Y.; Pereira, J.; Casseb, J.; Penalva de Oliveira, A.C.; da Silva Duarte, A.J.; Clissa, P.B.; Sanabani, S.S. Small RNA profiles of HTLV-1 asymptomatic carriers with monoclonal and polyclonal rearrangement of the T-cell antigen receptor gamma-chain using massively parallel sequencing: A pilot study. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2311–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, A.; Valadao de Souza, D.R.; Pessoa, R.; Pietrobon, A.J.; Nukui, Y.; Pereira, J.; Casseb, J.; Penalva de Oliveira, A.C.; Loureiro, P.; da Silva Duarte, A.J.; et al. Global expression of noncoding RNome reveals dysregulation of small RNAs in patients with HTLV-1-associated adult T-cell leukemia: A pilot study. Infect. Agents Cancer 2021, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticht, C.; De La Torre, C.; Parveen, A.; Gretz, N. miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nascimento, A.; Zychar, B.C.; Pessôa, R.; Duarte, A.J.d.S.; Clissa, P.B.; Sanabani, S.S. Altered RNome expression in Murine Gastrocnemius Muscle following Exposure to Jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca Venom. Toxins 2022, 14, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070472
Nascimento A, Zychar BC, Pessôa R, Duarte AJdS, Clissa PB, Sanabani SS. Altered RNome expression in Murine Gastrocnemius Muscle following Exposure to Jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca Venom. Toxins. 2022; 14(7):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070472
Chicago/Turabian StyleNascimento, Andrezza, Bianca Cestari Zychar, Rodrigo Pessôa, Alberto José da Silva Duarte, Patricia Bianca Clissa, and Sabri Saeed Sanabani. 2022. "Altered RNome expression in Murine Gastrocnemius Muscle following Exposure to Jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca Venom" Toxins 14, no. 7: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070472
APA StyleNascimento, A., Zychar, B. C., Pessôa, R., Duarte, A. J. d. S., Clissa, P. B., & Sanabani, S. S. (2022). Altered RNome expression in Murine Gastrocnemius Muscle following Exposure to Jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca Venom. Toxins, 14(7), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070472




