A First Look at the Inhibitory Potential of Urospatha sagittifolia (Araceae) Ethanolic Extract for Bothrops atrox Snakebite Envenomation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Biochemical Profile of B. atrox Venom
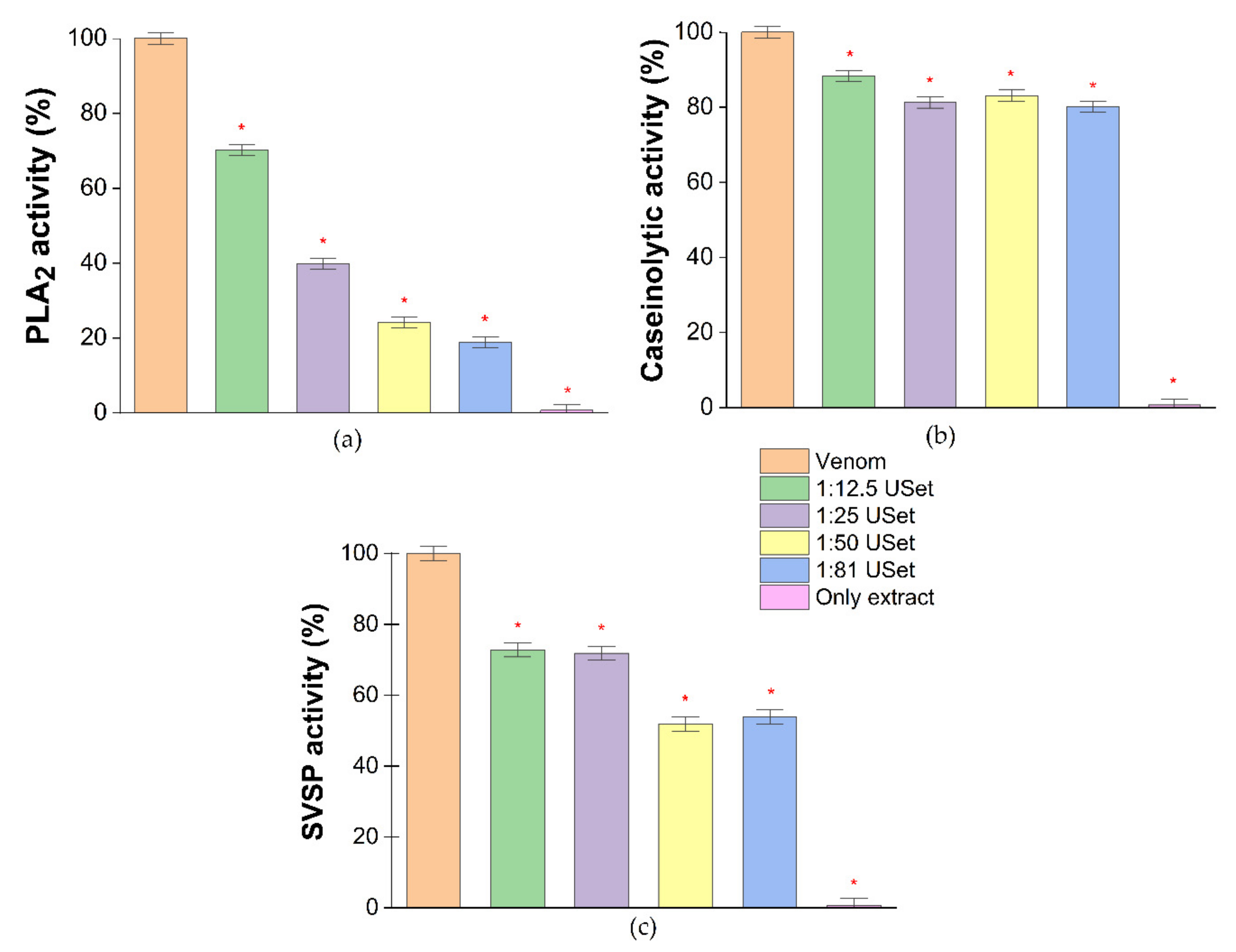
2.2. Enzyme Inhibition Assays
2.3. In Vivo Assays
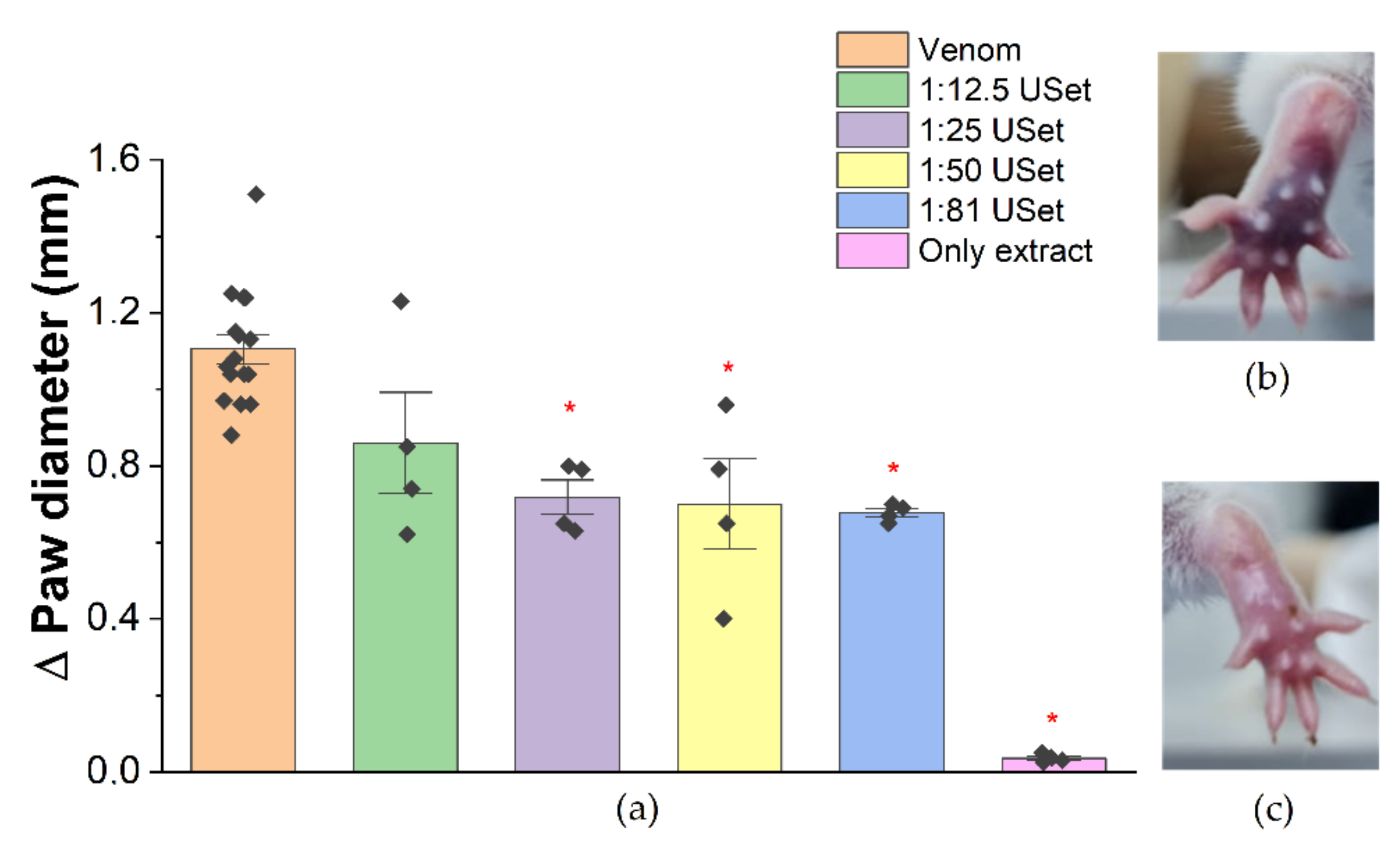
2.3.1. Edema
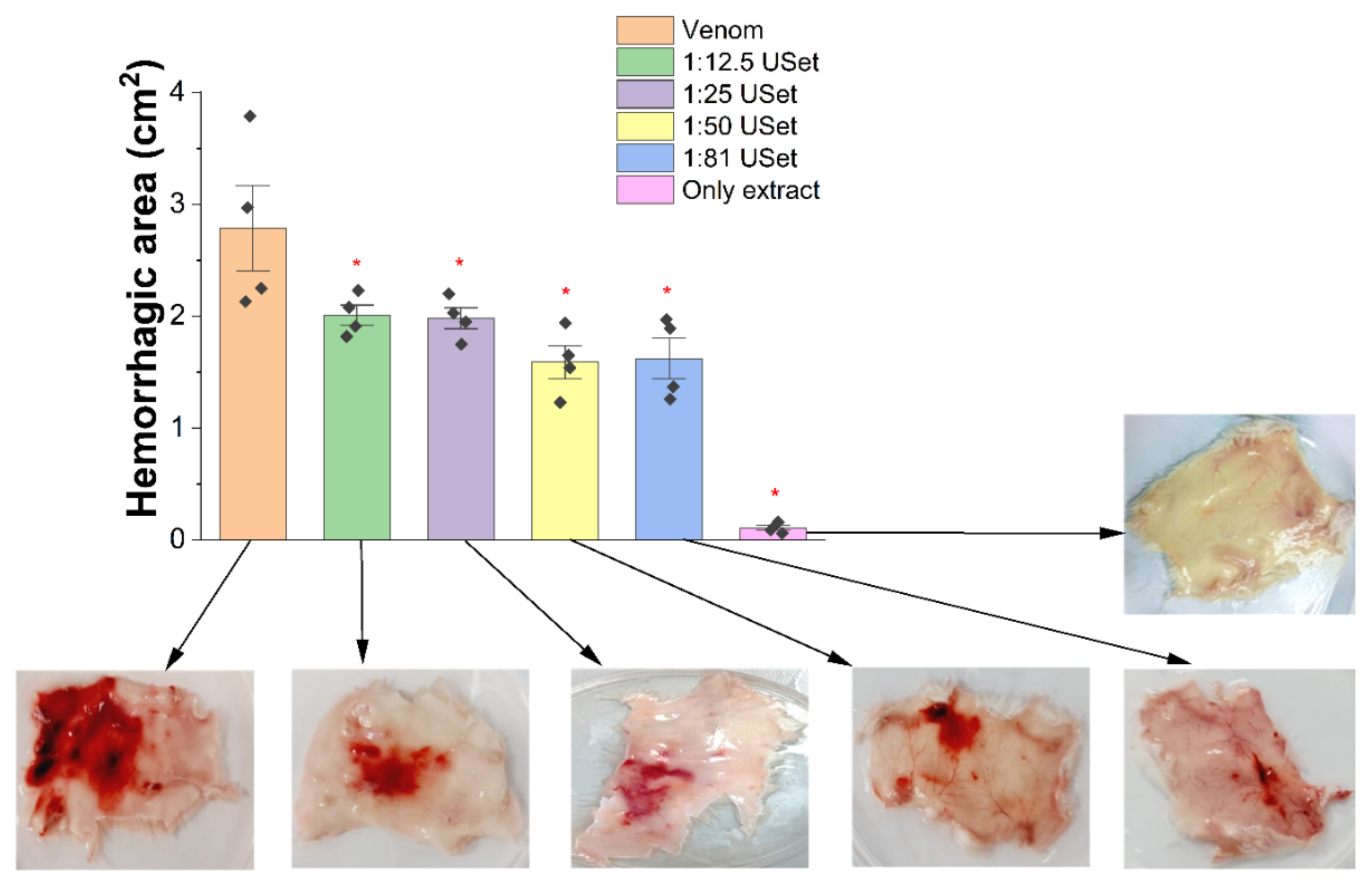
2.3.2. Hemorrhage
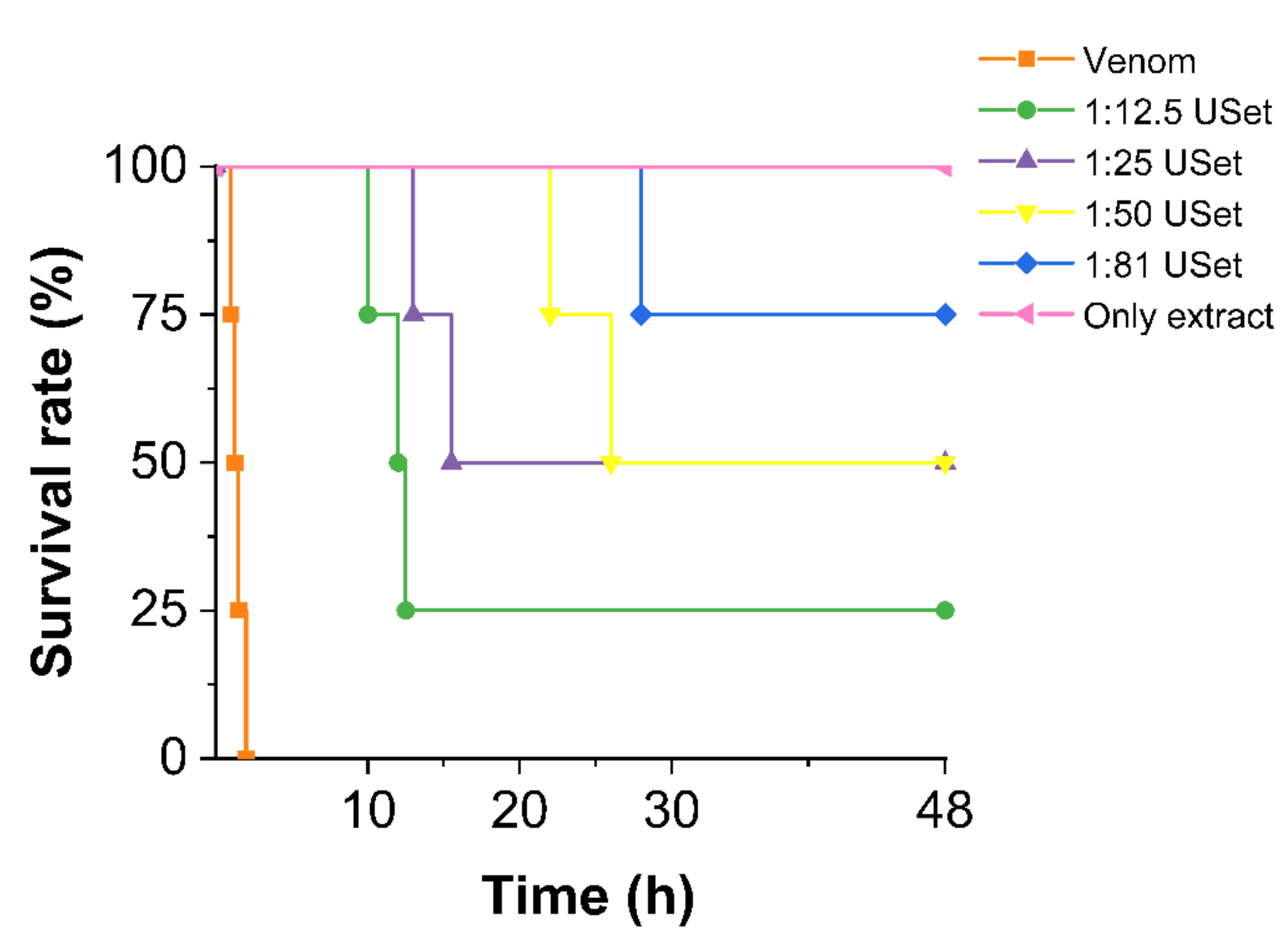
2.3.3. Lethality
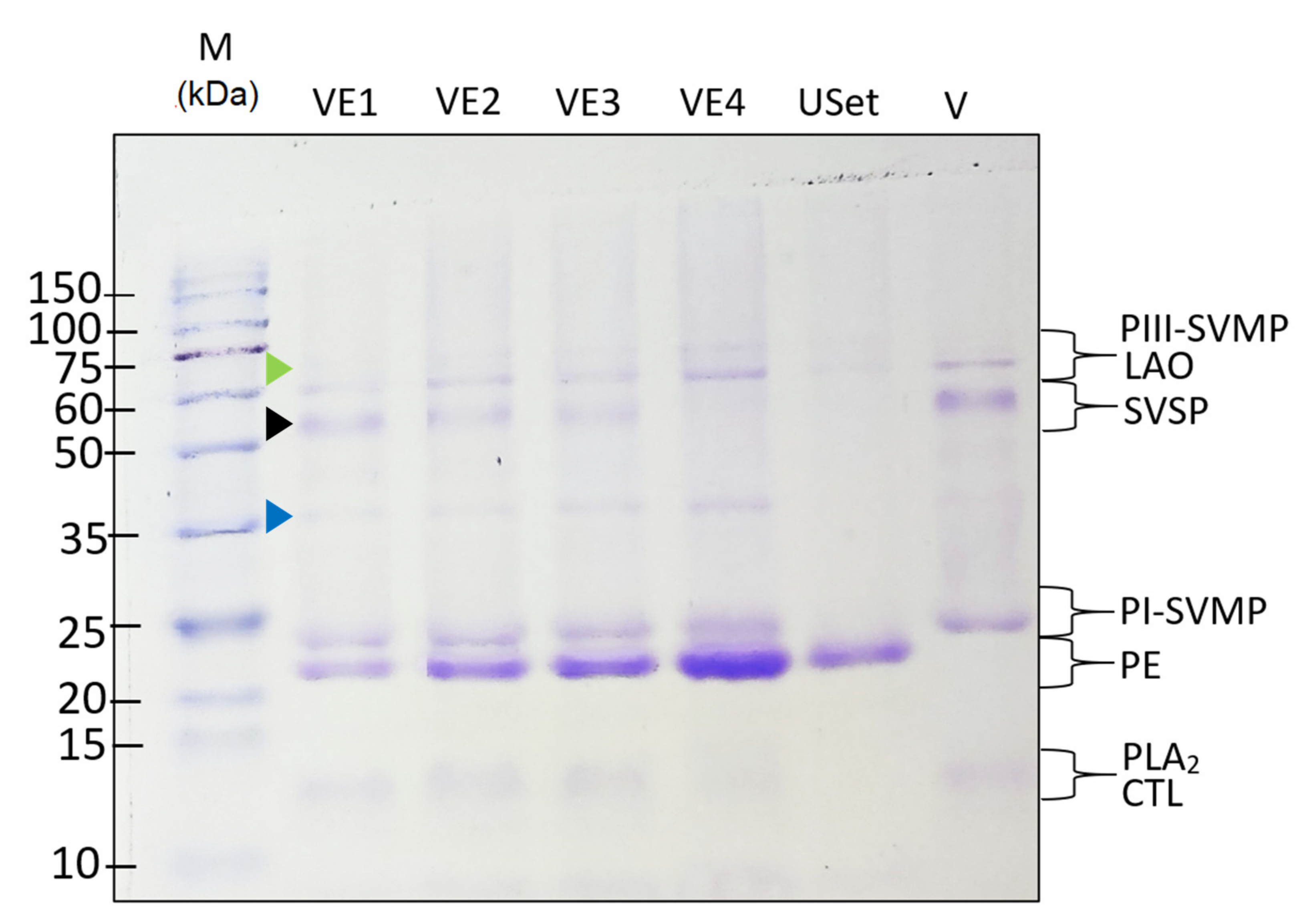
2.4. Venom–Extract Interaction
2.5. A View on Phytochemical Profile of Ethanolic Extract from U. sagittifolia
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Venom Extraction
5.2. Plant Collection, Identification and Preparation of Ethanolic Extract
5.3. Biochemical Composition of B. atrox Venom
5.4. Enzyme Inhibition Assays
5.4.1. Inhibition of Phospholipase A2
5.4.2. Inhibition of Serine Proteinases
5.4.3. Inhibition of Caseinolytic Activity
5.5. In Vivo Experimentation
5.5.1. Survival Curve
5.5.2. Edema
5.5.3. Hemorrhage
5.6. Venom–Extract Interaction by SDS-PAGE
5.7. Insights into Phytochemical Content of U. sagittifolia Extract
5.8. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Williams, D.; Fan, H.W.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite Envenoming from a Global Perspective: Towards an Integrated Approach. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resiere, D.; Monteiro, W.; Houcke, S.; Pujo, J.M.; Mathien, C.; Mayence, C.; Neviere, R.; Hommel, D.; de Almeida Gonçalves Sachett, J.; Mehdaoui, H.; et al. Bothrops Snakebite Envenomings in the Amazon Region. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2020, 72, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, W.M.; Contreras-Bernal, J.C.; Bisneto, P.F.; Sachett, J.; Mendonça da Silva, I.; Lacerda, M.; Guimarães da Costa, A.; Val, F.; Brasileiro, L.; Sartim, M.A.; et al. Bothrops Atrox, the Most Important Snake Involved in Human Envenomings in the Amazon: How Venomics Contributes to the Knowledge of Snake Biology and Clinical Toxinology. Toxicon X 2020, 6, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretto Del-Rei, T.H.; Sousa, L.F.; Rocha, M.M.T.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Travaglia-Cardoso, S.R.; Grego, K.; Sant’Anna, S.S.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Functional Variability of Bothrops Atrox Venoms from Three Distinct Areas across the Brazilian Amazon and Consequences for Human Envenomings. Toxicon 2019, 164, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento da Costa, T.; Mota-da-Silva, A.; Colombini, M.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Medeiros de Souza, R.; Monteiro, W.M.; Bernarde, P.S. Relationship between Snake Size and Clinical, Epidemiological and Laboratory Aspects of Bothrops atrox Snakebites in the Western Brazilian Amazon. Toxicon 2020, 186, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.R.; Mendes, B.; Patiño, R.S.; Pico, J.; Laines, J.; Terán, M.; Mogollón, N.G.S.; Zaruma-Torres, F.; Caldeira, C.A.S.; da Silva, S.L. Assessing the Stability of Historical and Desiccated Snake Venoms from a Medically Important Ecuadorian Collection. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 230, 108702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alangode, A.; Rajan, K.; Nair, B.G. Snake Antivenom: Challenges and Alternate Approaches. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, E.G.; Oliveira, S.S.; Noronha, M.d.D.N.; Saraiva, M.d.G.G.; Sano-Martins, I.S. Use of Freeze-Dried Trivalent Antivenom to Neutralize the Toxic Activities of Bothrops Atrox Snake Venoms from the Amazon. Toxicon 2021, 200, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, R.; Nuñez, V.; Osorio, R.G.; Gutiérrez, J.; Giraldo, C.A.; Posada, L.E. Ability of Six Latin American Antivenoms to Neutralize the Venom of Mapaná Equis (Bothrops atrox) from Antioquia and Chocó (Colombia). Toxicon 1995, 33, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix-Silva, J.; Gomes, J.A.S.; Xavier-Santos, J.B.; Passos, J.G.R.; Silva-Junior, A.A.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F. Inhibition of Local Effects Induced by Bothrops erythromelas Snake Venom: Assessment of the Effectiveness of Brazilian Polyvalent Bothropic Antivenom and Aqueous Leaf Extract of Jatropha gossypiifolia. Toxicon 2017, 125, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picolo, G.; Chacur, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Teixeira, C.F.P.; Cury, Y. Evaluation of Antivenoms in the Neutralization of Hyperalgesia and Edema Induced by Bothrops jararaca and Bothrops asper Snake Venoms. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2002, 35, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda, I.C.H.; Pereañez, J.A.; Preciado, L.M. Synthetic Inhibitors of Snake Venom Enzymes: Thioesters Derived from 2-Sulfenyl Ethylacetate. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, B.M.A.A.; Santos, J.D.L.L.; Xavier, B.M.; Almeida, J.R.; Resende, L.M.; Martins, W.; Marcussi, S.; Marangoni, S.; Stábeli, R.G.; Calderon, L.A.; et al. Snake Venom PLA2s Inhibitors Isolated from Brazilian Plants: Synthetic and Natural Molecules. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 153045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix-Silva, J.; Silva-Junior, A.A.; Zucolotto, S.M.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.D.F. Medicinal Plants for the Treatment of Local Tissue Damage Induced by Snake Venoms: An Overview from Traditional Use to Pharmacological Evidence. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 5748256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastin Santhosh, M.; Hemshekhar, M.; Sunitha, K.; Thushara, R.M.; Jnaneshwari, S.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Snake Venom Induced Local Toxicities: Plant Secondary Metabolites as an Auxiliary Therapy. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, M.A.; Tomaz, M.A.; Monteiro-Machado, M.; Ricardo, H.D.; Cons, B.L.; Fernandes, F.F.A.A.; El-Kik, C.Z.; Azevedo, M.S.; Melo, P.A. Antiophidic Activity of the Extract of the Amazon Plant Humirianthera Ampla and Constituents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moura, V.M.; de Souza, L.Y.A.; da Costa Guimarães, N.; dos Santos, I.G.C.; de Almeida, P.D.O.; de Oliveira, R.B.; Mourão, R.H.V.; Dos-Santos, M.C. The Potential of Aqueous Extracts of Bellucia dichotoma Cogn. (Melastomataceae) to Inhibit the Biological Activities of Bothrops atrox Venom: A Comparison of Specimens Collected in the States of Pará and Amazonas, Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 196, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, V.M.; Freitas De Sousa, L.A.; Cristina Dos-Santos, M.; Almeida Raposo, J.D.; Evangelista Lima, A.; De Oliveira, R.B.; Da Silva, M.N.; Veras Mourão, R.H. Plants Used to Treat Snakebites in Santarém, Western Pará, Brazil: An Assessment of Their Effectiveness in Inhibiting Hemorrhagic Activity Induced by Bothrops jararaca Venom. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 161, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Guimarães, N.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Scheffer de Souza, M.C.; Oliveira de Almeida, P.D.; Dos-Santos, M.C.; Nunez, C.V.; Bezerra de Oliveira, R.; Veras Mourão, R.H.; Mourão de Moura, V. Evaluation of the Anti-Snakebite, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Potential of Philodendron megalophyllum Schott (Araceae), Traditionally Used in Accidents Caused by Snakes in the Western Region of Pará, Brazil. Toxicon 2020, 184, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, D.; Ocampo, Y.; Castro, J.; Barrios, L.; Salas, R.; Franco, L.A. Protective Effect of Dracontium dubium against Bothrops asper Venom. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovera, A.; Bonilla, C.; Hidalgo, J. Efecto Neutralizador Del Extracto Acuoso de Dracontium loretense (JERGÓN SACHA) Sobre La Actividad Letal Del Veneno de Bothrops atrox. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Pública 2006, 23, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Winterton, S.; Scher, J.; Burnett, J.; Redford, A. Urospatha Sagittifolia. Available online: http://idtools.org/id/appw/factsheet.php?name=16106 (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- DeFilipps, R.R.; Maina, S.; Crepin, J. Medicinal Plants of the Guianas (Guyana, Surinam, French Guiana); Department of Botany National Museum of Natural History Smithsonian Institution: Washington, WA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nina-Cueva, O.; Olazábal-Chambilla, D.; Quispe-Arpasi, J.; Alzamora-Sánchez, A.; Gomes-Heleno, M.; Huancahuire-Vega, S. Biochemical Characterization of Bothrops roedingeri Mertens, 1942 Snake Venom and Its Edematogenic, Hemorrhagic, and Myotoxic Activities. Biomedica 2020, 40, 682–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásquez, J.; Jiménez, S.L.; Gómez, I.C.; Rey, J.P.; Henao, A.M.; Marín, D.M.; Romero, J.O.; Alarcón, J.C. Snakebites and Ethnobotany in the Eastern Region of Antioquia, Colombia—The Traditional Use of Plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, P. Medicinal Plants of the Achuar (Jivaro) of Amazonian Ecuador: Ethnobotanical Survey and Comparison with Other Amazonian Pharmacopoeias. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltos, R.V.A.; Vásquez, T.E.R.; Alonso Lazo, J.; Banguera, D.V.; Guayasamín, P.D.R.; Vargas, J.K.A.; Peñas, I.V. The Use of Medicinal Plants by Rural Populations of the Pastaza Province in the Ecuadorian Amazon. Acta Amaz. 2016, 46, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odonne, G.; Valadeau, C.; Alban-Castillo, J.; Stien, D.; Sauvain, M.; Bourdy, G. Medical Ethnobotany of the Chayahuita of the Paranapura Basin (Peruvian Amazon). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwin, M.M.; Samy, R.P.; Satyanarayanajois, S.D.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Venom Neutralization by Purified Bioactive Molecules: Synthetic Peptide Derivatives of the Endogenous PLA2 Inhibitory Protein PIP (a Mini-Review). Toxicon 2010, 56, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, T.; Franceschi, A.; Rucavado, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Effectiveness of Batimastat, a Synthetic Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinases, in Neutralizing Local Tissue Damage Induced by BaP1, a Hemorrhagic Metalloproteinase from the Venom of the Snake Bothrops asper. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, P.; Bhattacharyya, D. Characterization of the Aqueous Extract of the Root of Aristolochia indica: Evaluation of Its Traditional Use as an Antidote for Snake Bites. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.K.; Doley, R.; Saikia, D. Isolation of a Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) Inhibitor (AIPLAI) from Leaves of Azadirachta indica (Neem): Mechanism of PLA2 Inhibition by AIPLAI in Vitro Condition. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mors, W.B.; Célia Do Nascimento, M.; Ruppelt Pereira, B.M.; Alvares Pereira, N. Plant Natural Products Active against Snake Bite--the Molecular Approach. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, R.P.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Chow, V.T.K. Therapeutic Application of Natural Inhibitors against Snake Venom Phospholipase A(2). Bioinformation 2012, 8, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.M.; Ticli, F.K.F.K.; Marcussi, S.; Lourenco, M.V.; Januario, A.H.; Sampaio, S.V.; Giglio, J.R.J.R.; Lomonte, B.; Pereira, P.S.; Lourenço, M.V.; et al. Medicinal Plants with Inhibitory Properties Against Snake Venoms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2625–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopi, K.; Renu, K.; Sannanaik Vishwanath, B.; Jayaraman, G. Protective Effect of Euphorbia hirta and Its Components against Snake Venom Induced Lethality. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 165, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal Botanic Gardens Urospatha sagittifolia (Rudge) Schott Plants of the World Online. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:89296-1 (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- Bhattacharjee, P.; Bhattacharyya, D. Medicinal Plants as Snake Venom Antidotes. J. Exp. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2014, 1, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Ana Malaque, C.M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; María Gutiérrez, J.; Maria Sant, C.; Malaque, A. Snakebite Envenomation in Central and South America. Snakebite Envenomation Cent. S. Am. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite Envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, L.F.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Nicolau, C.A.; Bernardoni, J.L.; Nishiyama-Jr, M.Y.; Amazonas, D.R.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Mourão, R.H.V.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Valente, R.H.; et al. Functional Proteomic Analyses of Bothrops atrox Venom Reveals Phenotypes Associated with Habitat Variation in the Amazon. J. Proteomics 2017, 159, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, R.S.P.P.; Salazar-Valenzuela, D.; Medina-Villamizar, E.; Mendes, B.; Proaño-Bolaños, C.; da Silva, S.L.; Almeida, J.R. Bothrops atrox from Ecuadorian Amazon: Initial Analyses of Venoms from Individuals. Toxicon 2021, 193, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, V.; Cid, P.; Sanz, L.; De La Torre, P.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake Venomics and Antivenomics of Bothrops atrox Venoms from Colombia and the Amazon Regions of Brazil, Perú and Ecuador Suggest the Occurrence of Geographic Variation of Venom Phenotype by a Trend towards Paedomorphism. J. Proteomics 2009, 73, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander dos Santos, R.; Villalta-Romero, F.; Stanisic, D.; Borro, L.; Neshich, G.; Tasic, L. Citrus Bioflavonoid, Hesperetin, as Inhibitor of Two Thrombin-like Snake Venom Serine Proteases Isolated from Crotalus Simus. Toxicon 2018, 143, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.O.; Fernandes, R.S.; Ticli, F.K.; Oliveira, C.Z.; Mazzi, M.V.; Franco, J.J.; Giuliatti, S.; Pereira, P.S.; Soares, A.M.; Sampaio, S.V. Triterpenoid Saponins, New Metalloprotease Snake Venom Inhibitors Isolated from Pentaclethra macroloba. Toxicon 2007, 50, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, P.A.; Nipate, S.S.; Sonpetkar, J.M.; Salvi, N.C.; Waghmare, A.B.; Chaudhari, P.D. Anti-Snake Venom Activities of Ethanolic Extract of Fruits of Piper longum L. (Piperaceae) against Russell’s Viper Venom: Characterization of Piperine as Active Principle. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ticli, F.K.; Hage, L.I.S.; Cambraia, R.S.; Pereira, P.S.; Magro, Â.J.; Fontes, M.R.M.; Stábeli, R.G.; Giglio, J.R.; França, S.C.; Soares, A.M.; et al. Rosmarinic Acid, a New Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 Inhibitor from Cordia verbenacea (Boraginaceae): Antiserum Action Potentiation and Molecular Interaction. Toxicon 2005, 46, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badilla, B.; Chaves, F.; Mora, G.; Poveda, L. Edema Induced by Bothrops asper (Squamata: Viperidae) Snake Venom and Its Inhibition by Costa Rican Plant Extracts. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2006, 54, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, C.M.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Silva, M.A.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Vilegas, W.; Hiruma-Lima, C.A. Anti-Hemorrhagic Activity of Four Brazilian Vegetable Species against Bothrops jararaca Venom. Molecules 2009, 14, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.P.D.; De Moura, V.M.; De Souza, M.C.S.; Santos, V.N.C.; Da Silva, K.A.M.M.; Mendes, M.G.G.; Nunez, C.V.; De Almeida, P.D.O.; Lima, E.S.; Mourão, R.H.V.; et al. Connarus Favosus Planch.: An Inhibitor of the Hemorrhagic Activity of Bothrops atrox Venom and a Potential Antioxidant and Antibacterial Agent. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 183, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, O.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Barrios, M.; Castro, I.; Romero, M.; Umaña, E. Neutralización Del Efecto Hemorrágico Inducido Por Veneno de Bothrops asper (Serpentes: Viperidae) Por Extractos de Plantas Tropicales. Rev. Biol. Trop. 1999, 47, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azocasein, S.L.S. Protease Substrate. Available online: https://www.scientificlabs.co.uk/product/A2765-5G#overview (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A. Experimental Pathophysiology of Systemic Alterations Induced by Bothrops asper Snake Venom. Toxicon 2009, 54, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Betancur, I.; Gogineni, V.; Salazar-Ospina, A.; León, F. Perspective on the Therapeutics of Anti-Snake Venom. Molecules 2019, 24, 3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.Z.; Maiorano, V.A.; Marcussi, S.; Sant’Ana, C.D.; Januário, A.H.; Lourenço, M.V.; Sampaio, S.V.; França, S.C.; Pereira, P.S.; Soares, A.M. Anticoagulant and Antifibrinogenolytic Properties of the Aqueous Extract from Bauhinia forficata against Snake Venoms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 98, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, L.H.F.; Mendes, M.M.; Hamaguchi, A.; Soares, A.M.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Homsi-Brandeburgo, M.I. Neutralization of Pharmacological and Toxic Activities of Bothrops Snake Venoms by Schizolobium parahyba (Fabaceae) Aqueous Extract and Its Fractions. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 103, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourão De Moura, V.; Serra Bezerra, A.N.; Veras Mourão, R.H.; Varjão Lameiras, J.L.; Almeida Raposo, J.D.; Luckwu De Sousa, R.; Boechat, A.L.; Bezerra De Oliveira, R.; De Menezes Chalkidis, H.; Dos-Santos, M.C. A Comparison of the Ability of Bellucia dichotoma Cogn. (Melastomataceae) Extract to Inhibit the Local Effects of Bothrops atrox Venom When Pre-Incubated and When Used According to Traditional Methods. Toxicon 2014, 85, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuani Floriano, R. Effect of Mikania Glomerata (Asteraceae) Leaf Extract Combined with Anti-Venom Serum on Experimental Crotalus Durissus (Squamata: Viperidae) Envenomation in Rats. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2009, 57, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reyes-Chilpa, R.; Gómez-Garibay, F.; Quijano, L.; Magos-Guerrero, G.A.; Ríos, T. Preliminary Results on the Protective Effect of (-)-Edunol, a Pterocarpan from Brongniartia podalyrioides (Leguminosae), against Bothrops atrox Venom in Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 42, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrique, F.; Vale, L.; Mendes, M.; Fernandes, R.S.; Costa, T.R.; Hage-Melim, L.I.S.; Sousa, M.A.; Hamaguchi, A.; Homsi-Brandeburgo, M.I.; Franca, S.C.; et al. Protective Effect of Schizolobium parahyba Flavonoids against Snake Venoms and Isolated Toxins. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 2566–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pithayanukul, P.; Leanpolchareanchai, J.; Saparpakorn, P. Molecular Docking Studies and Anti-Snake Venom Metalloproteinase Activity of Thai Mango Seed Kernel Extract. Molecules 2009, 14, 3198–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorano, V.A.; Marcussi, S.; Daher, M.A.F.; Oliveira, C.Z.; Couto, L.B.; Gomes, O.A.; França, S.C.; Soares, A.M.; Pereira, P.S. Antiophidian Properties of the Aqueous Extract of Mikania Glomerata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 102, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilo Patiño, A.; María Benjumea, D.; Andrés Pereañez, J. Inhibition of Venom Serine Proteinase and Metalloproteinase Activities by Renealmia Alpinia (Zingiberaceae) Extracts: Comparison of Wild and in Vitro Propagated Plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, K.; Renu, K.; Jayaraman, G. Inhibition of Naja Naja Venom Enzymes by the Methanolic Extract of Leucas Aspera and Its Chemical Profile by GC-MS. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, J.F.; de Oliveira, E.C.; da Silva, A.C.R.; da Silva, V.P.; Coelho Kaplan, M.A.; Figueiredo, M.R.; Flores Sanchez, E.; Lopes Fuly, A. Potential Use of Extract of the Plant Schwartiza Brasiliensis (Choisy) Bedell Ex Gir.-Cañas against the Toxic Effects of the Venom of Bothrops jararaca or B. jararacussu. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barani Kumar, R.; Xavier Suresh, M. Computational Analysis of Bioactive Phytochemicals as Potential Inhibitors for Calcium Activated Potassium Channel Blocker, Tamulotoxin from Mesobuthus tamulus. Pharmacogn. J. 2013, 5, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, K.S.; Kemparaju, K. Inhibition of Naja Naja Venom Hyaluronidase by Plant-Derived Bioactive Components and Polysaccharides. Biochemistry 2005, 70, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, C.; Moreira-Dill, L.; Fernandes, R.; Costa, T.; Hage-Melim, L.; Marcussi, S.; Carvalho, B.; Silva, S.; Zuliani, J.; Fernandes, C.; et al. Biodiversity as a Source of Bioactive Compounds against Snakebites. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 2952–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekiyo, S.M.; Mackessy, S.P. Effects of Temperature and Storage Conditions on the Electrophoretic, Toxic and Enzymatic Stability of Venom Components. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 119, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mori, B. Animal Testing: The Ethical Principle of the 3Rs from laboratories to “fielf” research with wild animals. Ethics Politics 2019, 21, 553–570. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, L.S.; Nogueira-Souza, P.D.; Rocha-Junior, J.R.S.; Monteiro-Machado, M.; Strauch, M.A.; Prado, S.A.L.; Melo, P.A.; Veiga-Junior, V.F. Phytochemical Composition, Antisnake Venom and Antibacterial Activities of Ethanolic Extract of Aegiphila Integrifolia (Jacq) Moldenke Leaves. Toxicon 2021, 198, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, P.; Bodakhe, S.H. Antivenom Potential of Ethanolic Extract of Cordia Macleodii Bark against Naja Venom. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, S449–S454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas Fajardo, C.J. Determinación y Cuantificación de Compuestos Fenólicos En Flores de Taraxacum Officinale, Mediante HPLC-DAD-MS y Ensayos Colorimétricos UV-VIS; Universidad de los Andes: Bogota, Colombia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Bautista-Bautista, N.; Blasco-Cabal, J.L.; Gonzalez-Ávila, M.; Gutiérrez-Lomelí, M.; Arriaga-Alba, M. Antimutagenicity of Methanolic Extracts from Anemopsis californica in Relation to Their Antioxidant Activity. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 273878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.Q.C.; Binh, T.D.; Kusunoki, R.; Pham, T.L.A.; Nguyen, Y.D.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kanaori, K.; Kamei, K. Effects of Launaea sarmentosa Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of NF-ΚB/MAPK Signaling and Nrf2 Activation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengifo-Rios, A.M.; Muñoz-Gómez, L.M.; Cabezas-Fajardo, F.A.; Guerrero-Vargas, J.A. Edematic and Coagulant Effects Caused by the Venom of Bothrops rhombeatus Neutralized by the Ethanolic Extract of Piper auritum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 242, 112046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Specialized Metabolite | Ethanolic Extract |
|---|---|
| Alkaloids | +++ |
| Saponins | ++ |
| Terpenoids | + |
| Tannins | ++ |
| Quinones | - |
| Coumarins | +++ |
| Phenolic compounds | +++ |
| Flavonoids | +++ |
| Anthocyanins | - |
| Plant | Extraction/Metabolite | Inhibitory Effects on | Snake Venom | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aristolochia indica | Aqueous extract of the roots | L-amino acid oxidase and protease | Daboia russelii | [32] |
| Azadirachta indica | Purified molecule (AIPLAI) from the methanolic leaf extract | PLA2 activity | Naja naja, Naja kaouthia and Daboia russelli | [33] |
| Philodendron megalophyllum | Aqueous extract using the stem | Hemorrhagic and fibrinolytic activities | B. atrox | [19] |
| Citrus limon, Citrus sinensis, Citrus aurantium | Hesperetinb obtained from hesperidin in citrus peels | Serine proteinase activity | Crotalus simus | [45] |
| Pentaclethra macroloba | Purified molecules of the aqueous extract of the bark. (macrolobin-A and B) | Hemorrhagic, proteolytic, and fibrinolytic activities | B. neuwiedi and B. jararacussu | [46] |
| Dracontium dubium | Ethanolic extract from tubers | Lethality, inflammatory, and hemolytic effects | B. asper | [20] |
| Piper longum | Ethanolic extract of the fruits | Lethality, hemorrhage, necrosis, defibrinogenation, and inflammatory paw edema | Daboia russelli | [47] |
| Cordia verbenacea | Methanolic extracts of leaves | Paw edema | B. jararacussu | [48] |
| Urera bacífera, Loasa speciosa Chaptalia nutans Satureja viminea | Aqueous extracts of leaves | Edema | B. asper | [49] |
| Uncaria tomentosa | Aqueous extracts of roots | Edema | B. asper | [49] |
| Mouriri pusa, Davilla elliptica, Byrsonima crassa | Methanolic extracts from leaves | Hemorrhage | B. jararaca | [50] |
| Bursera Simaruba, Phoebe Brenesii, Virola koschnyi | Extraction water:ethanol (85:15) of barks | Hemorrhage | B. asper | [52] |
| Clusia palmana, Croton Draco | Extraction water:ethanol (85:15) of leaves | Hemorrhage | B. asper | [52] |
| Persea americana | Extraction water:ethanol (85:15) of seed | Hemorrhage | B. asper | [52] |
| Harpalyce brasiliana | Purified edunol extracted from roots | PLA2 activity | B. jararacucu | [13] |
| Brongniartia podalyrioides | Purified edunol isolated from roots | Lethality | B. atrox | [60] |
| Schizolobium parahyba | Purificated molecules from aqueous extract of leaves (isoquercitrin, myricetin-3-O-glucoside, catechin, and gallocatechin) | Hemorrhagic and fibrinogenolytic activities | B. alternatus | [61] |
| Mangifera indica | Ethanolic extract from seeds | Caseinolytic and fibrinogenolytic activities | Calloselasma rhodostoma Naja siamensis | [62] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vera-Palacios, A.L.; Sacoto-Torres, J.D.; Hernández-Altamirano, J.A.; Moreno, A.; Peñuela-Mora, M.C.; Salazar-Valenzuela, D.; Mogollón, N.G.S.; Almeida, J.R. A First Look at the Inhibitory Potential of Urospatha sagittifolia (Araceae) Ethanolic Extract for Bothrops atrox Snakebite Envenomation. Toxins 2022, 14, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070496
Vera-Palacios AL, Sacoto-Torres JD, Hernández-Altamirano JA, Moreno A, Peñuela-Mora MC, Salazar-Valenzuela D, Mogollón NGS, Almeida JR. A First Look at the Inhibitory Potential of Urospatha sagittifolia (Araceae) Ethanolic Extract for Bothrops atrox Snakebite Envenomation. Toxins. 2022; 14(7):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070496
Chicago/Turabian StyleVera-Palacios, Antonio L., Juan D. Sacoto-Torres, Josselin A. Hernández-Altamirano, Andres Moreno, Maria C. Peñuela-Mora, David Salazar-Valenzuela, Noroska G. S. Mogollón, and José R. Almeida. 2022. "A First Look at the Inhibitory Potential of Urospatha sagittifolia (Araceae) Ethanolic Extract for Bothrops atrox Snakebite Envenomation" Toxins 14, no. 7: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070496
APA StyleVera-Palacios, A. L., Sacoto-Torres, J. D., Hernández-Altamirano, J. A., Moreno, A., Peñuela-Mora, M. C., Salazar-Valenzuela, D., Mogollón, N. G. S., & Almeida, J. R. (2022). A First Look at the Inhibitory Potential of Urospatha sagittifolia (Araceae) Ethanolic Extract for Bothrops atrox Snakebite Envenomation. Toxins, 14(7), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070496







