Structure and Biological Properties of Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins and Lectins from Elder (Sambucus nigra L.) Leaves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
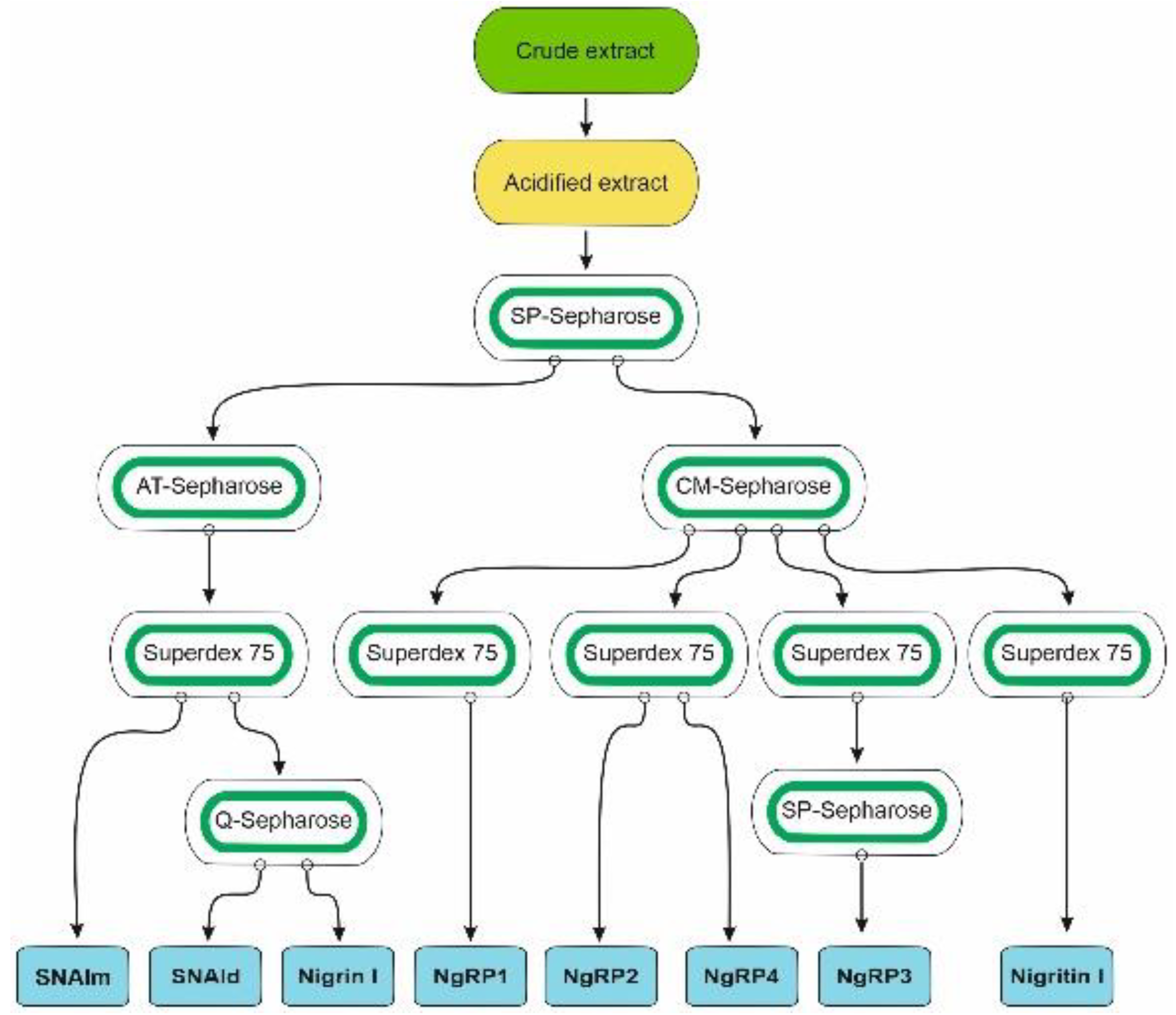
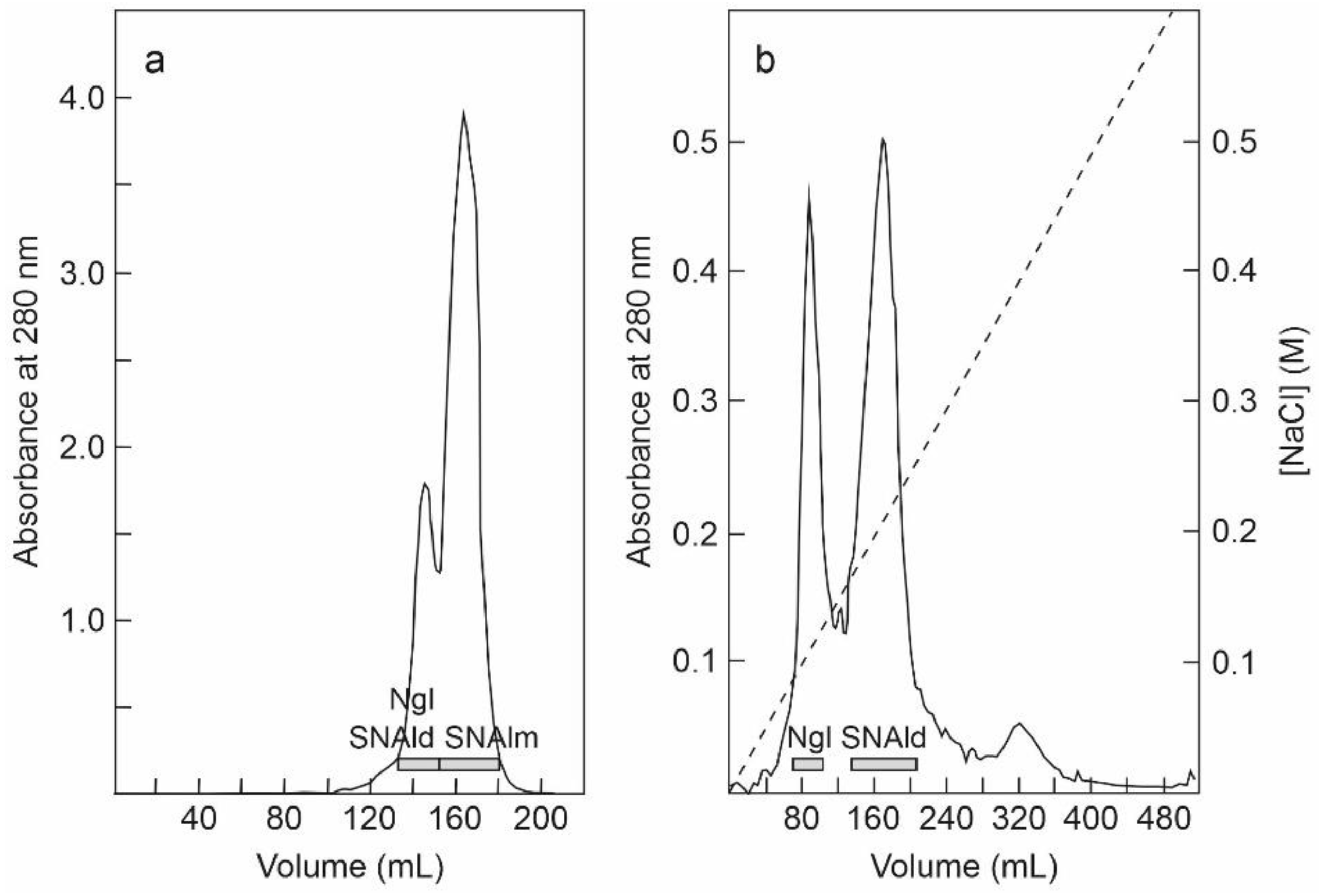
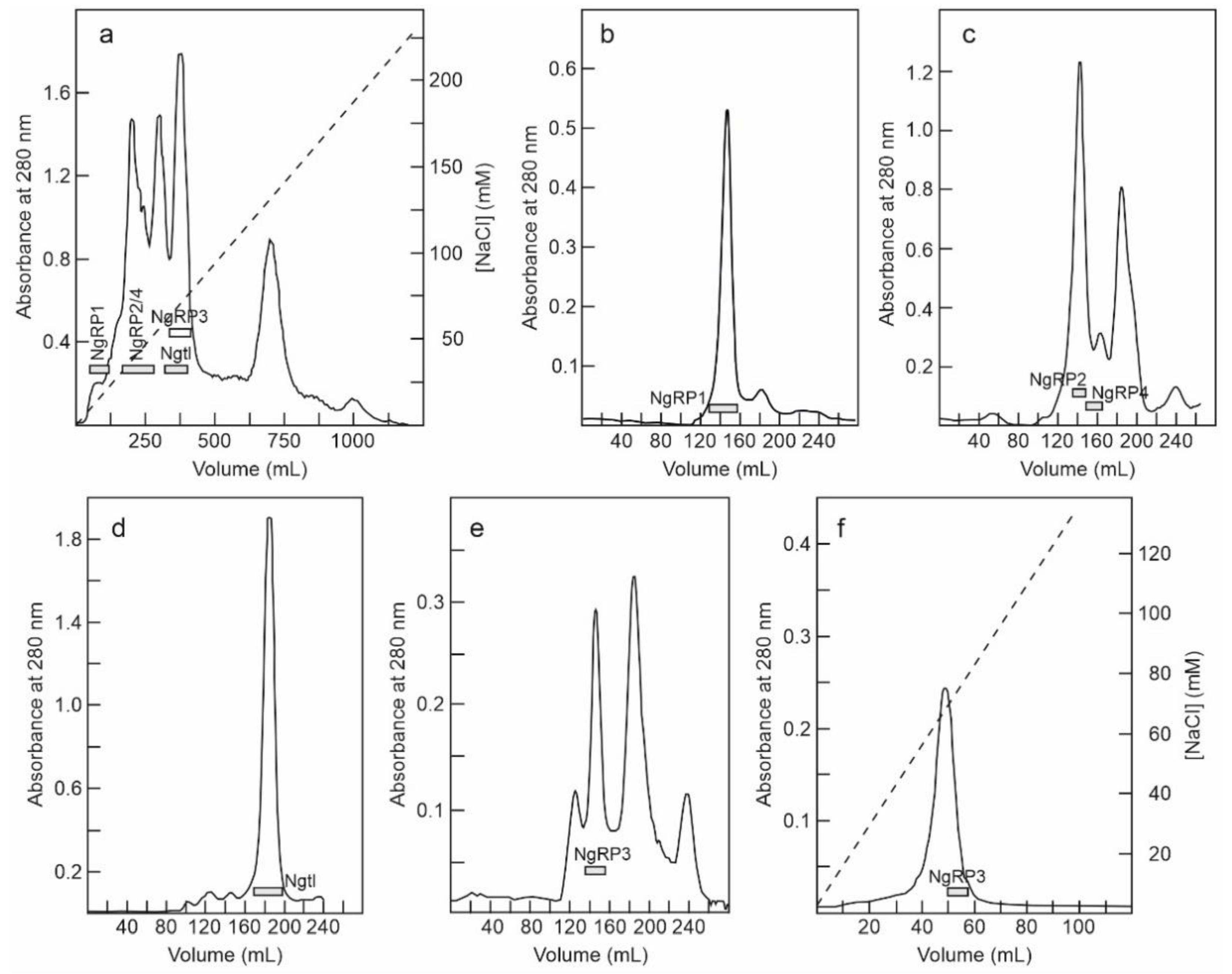
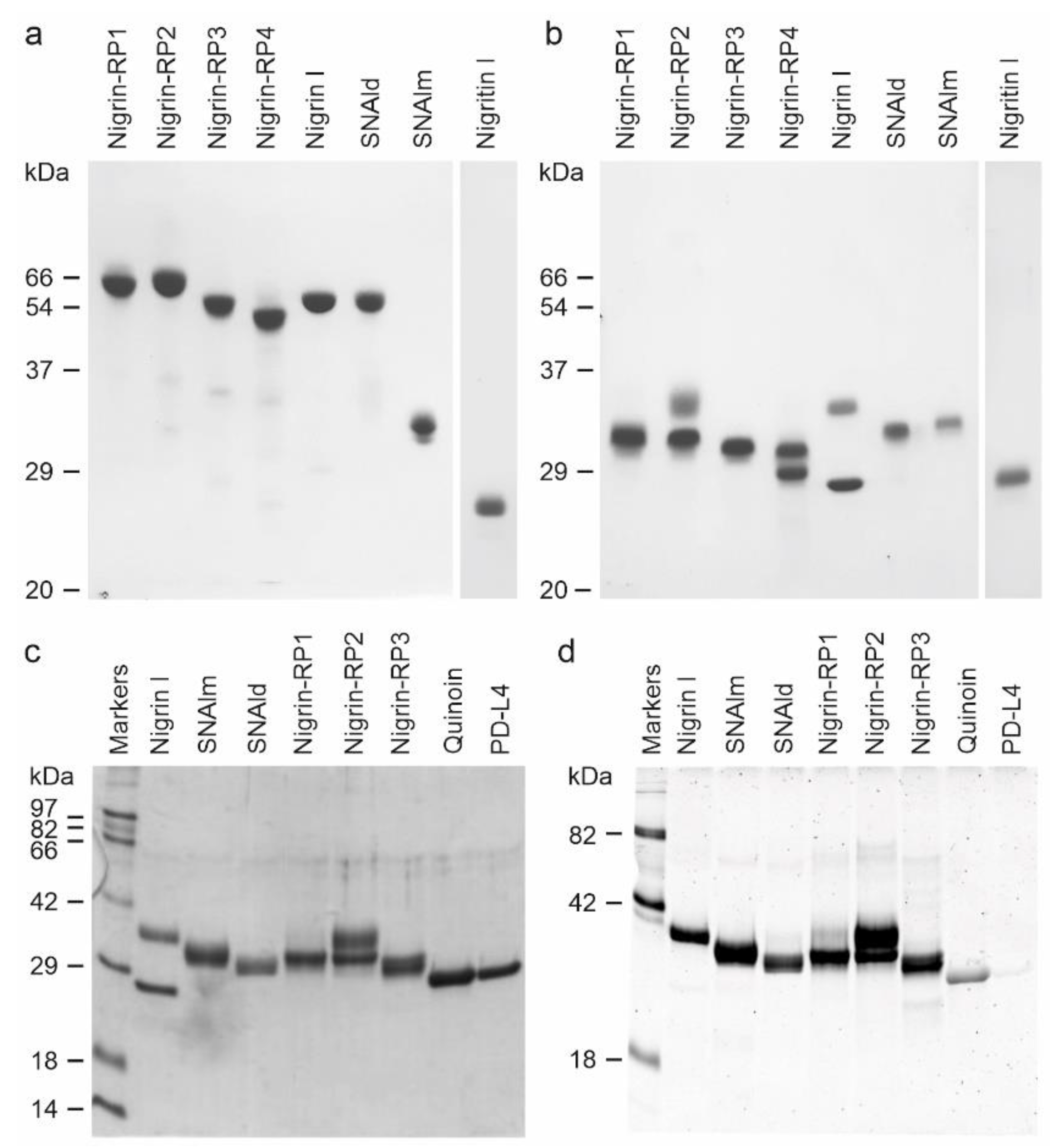
2.1. Isolation of RIPs and Lectins from Elderberry Leaves
2.2. Characterization of RIPs and Lectins from Elderberry Leaves
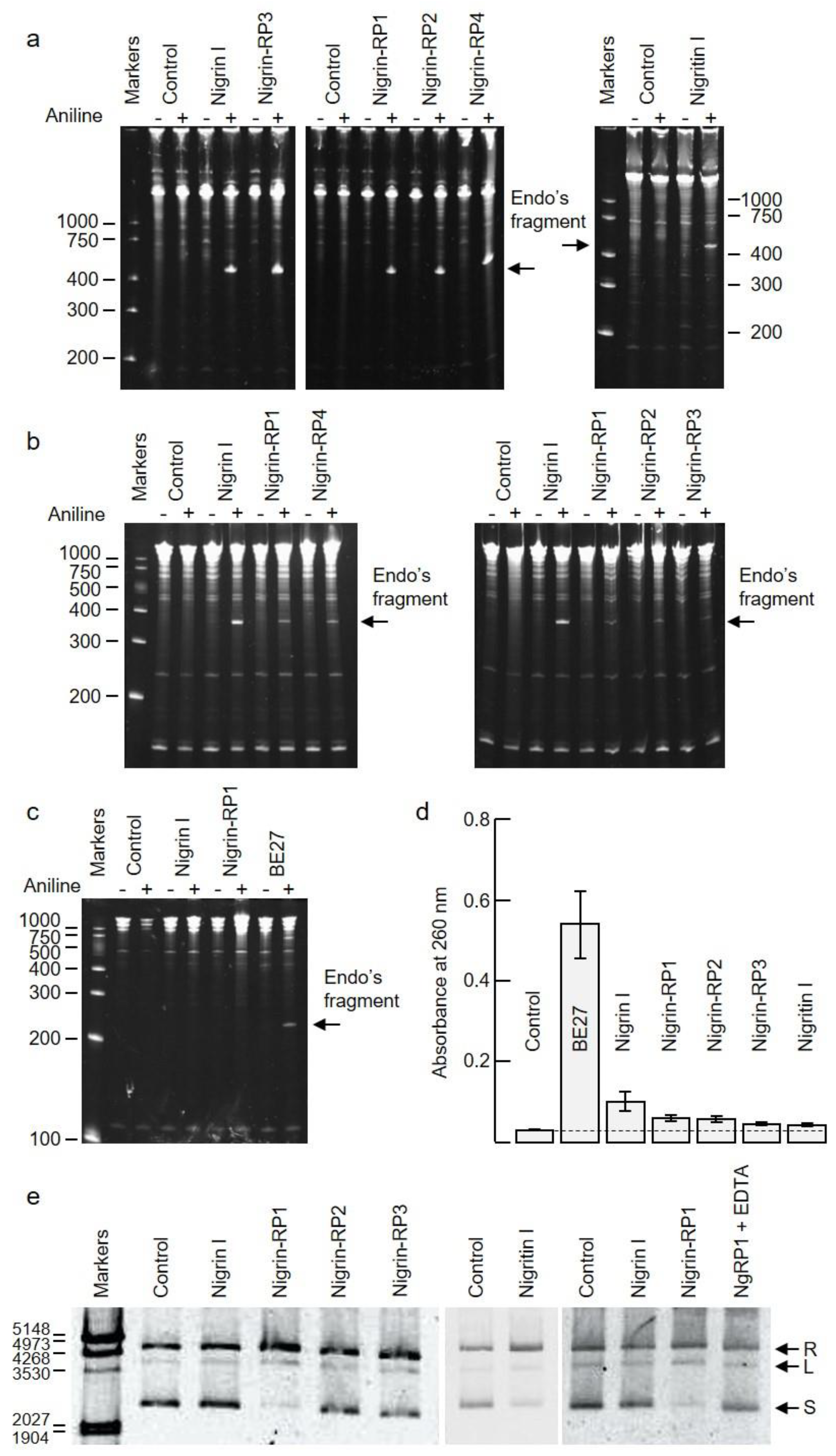
2.3. rRNA N-Glycosylase, Adenine Polynucleotide Glycosylase, and DNA Nicking Activities
2.4. Peptide Mapping of RIPs from S. nigra Leaves by High-Resolution MS/MS
2.5. Carbohydrate Binding Properties of Nigrin l, SNAlm, and SNAld
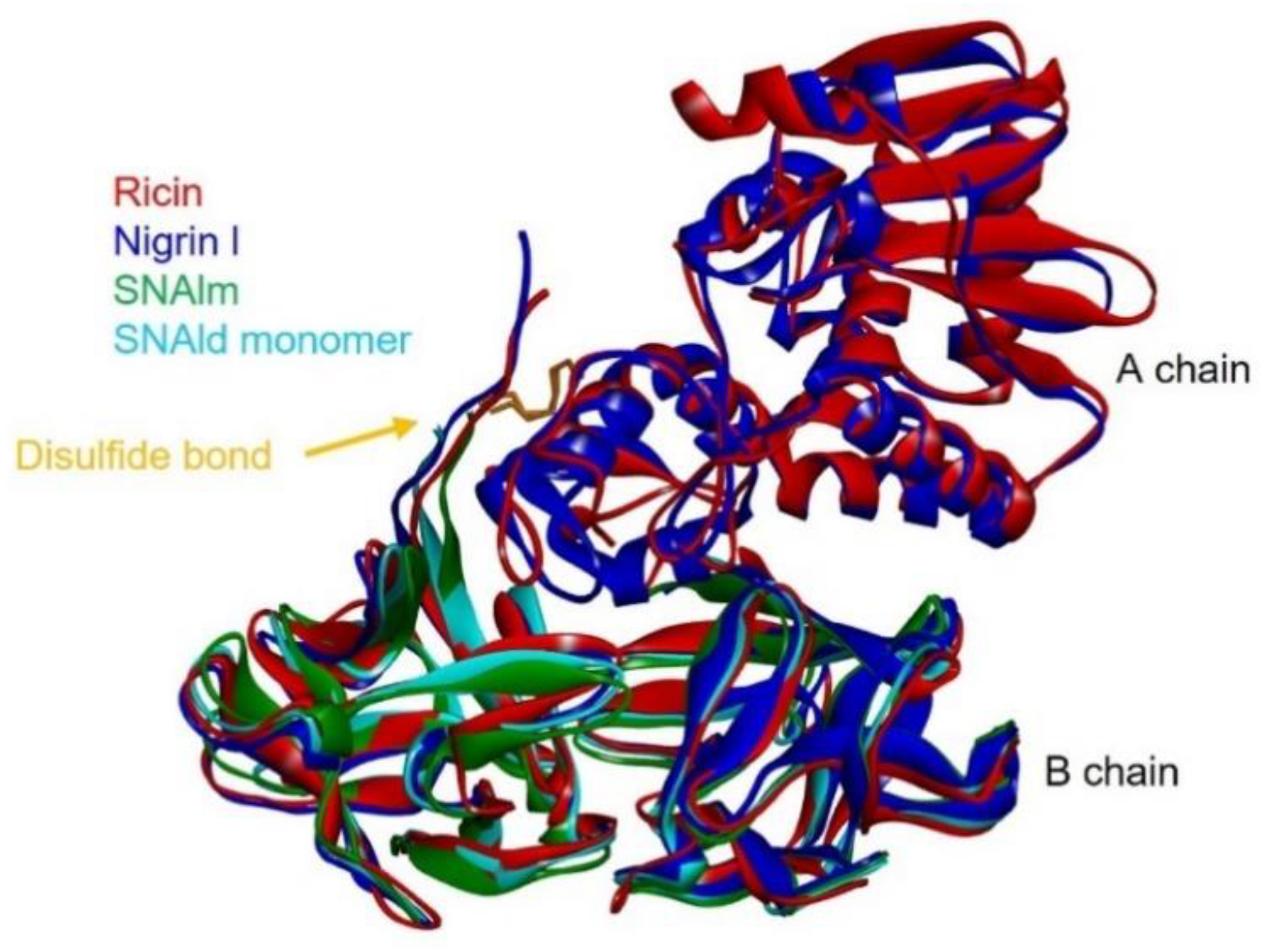
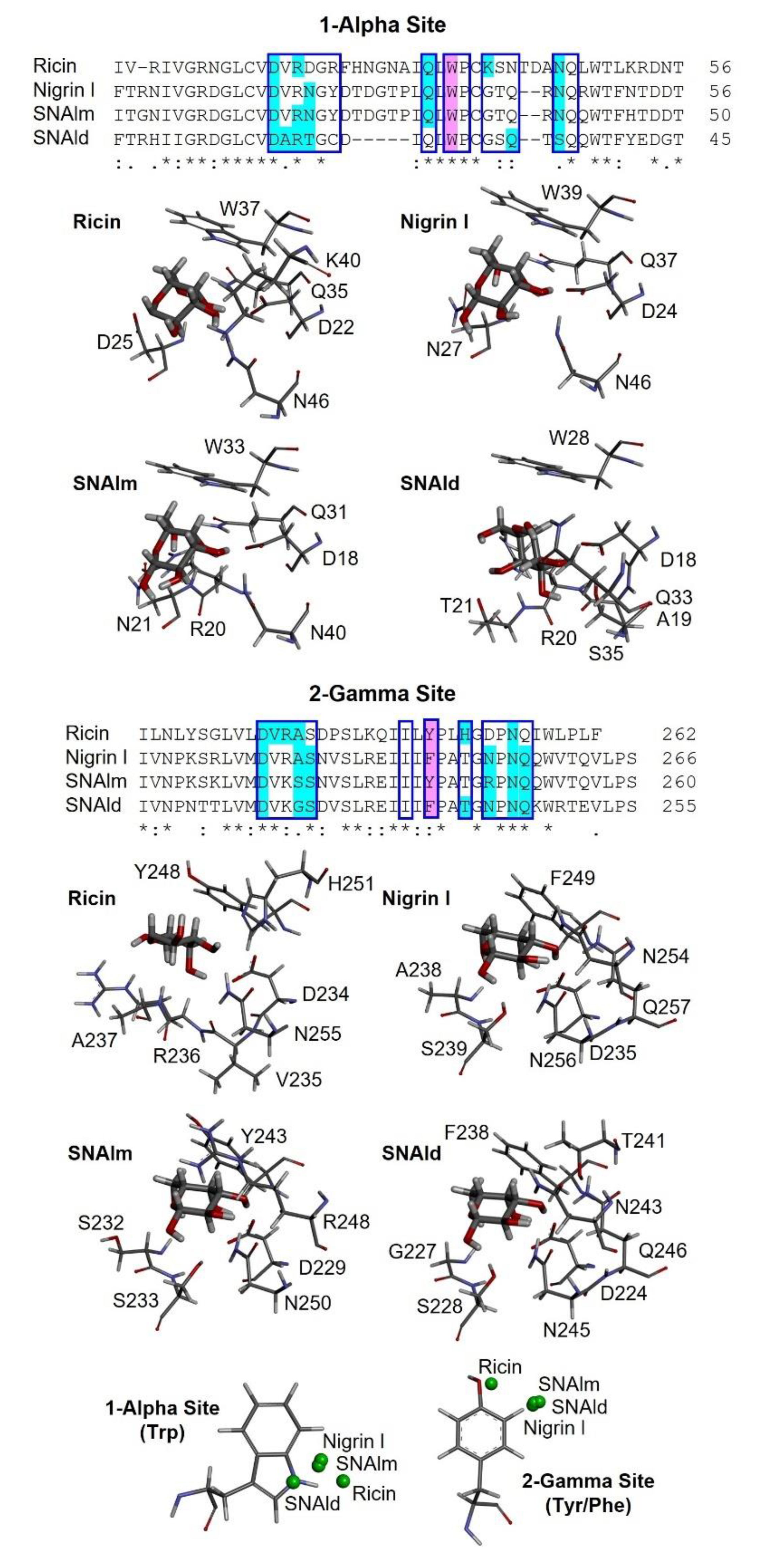
2.6. Structural Analysis of Nigrin l, SNAlm, and SNAld
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.8. Cytotoxic Effect of RIPs from Elderberry Leaves in Cell Cultures
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Cell Lines and Culture
5.3. Methods
5.3.1. Preparation of Crude and Acidified Extracts and Chromatography Using SP-Sepharose
5.3.2. Purification of Nigrin l, SNAlm, and SNAld
5.3.3. Purification of Nigrin-RPs 1, 2, 3, and 4, and Nigritin l
5.3.4. Analytical Procedures
5.3.5. Assays of Cell-Free Protein Synthesis
5.3.6. rRNA N-Glycosylase Assays on Rabbit Reticulocyte, Yeast, Bacterium Lysates, and HeLa Cells
5.3.7. Adenine Polynucleotide Glycosylase Activity on Salmon Sperm DNA and Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) RNA
5.3.8. DNA Cleavage Experiments
5.3.9. Tryptic Digestion and Sample Preparation for MS/MS Analyses
5.3.10. High-Resolution NanoLC–Tandem Mass Spectrometry
5.3.11. Data Processing
5.3.12. Hemagglutination Activity and Carbohydrate Binding Properties
5.3.13. Protein Structure Studies and Graphical Representation
5.3.14. Molecular Docking
5.3.15. Cell Viability and DNA Fragmentation Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M. Ribosome Inactivating Proteins from Plants: Biological Properties and their Use in Experimental Therapy. In Antitumor Potential and Other Emerging Medicinal Properties of Natural Compounds; Fang, E.F., Ng, T.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maro, A.; Citores, L.; Russo, R.; Iglesias, R.; Miguel Ferreras, J.M. Sequence comparison and phylogenetic analysis by the Maximum Likelihood method of ribosome-inactivating proteins from angiosperms. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 85, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreras, J.M.; Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Jimenez, P.; Girbes, T. Use of Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins from Sambucus for the Construction of Immunotoxins and Conjugates for Cancer Therapy. Toxins 2011, 3, 420–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M.; Llorente, A.; Citores, L. Ebulin l Is Internalized in Cells by Both Clathrin-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms and Does Not Require Clathrin or Dynamin for Intoxication. Toxins 2021, 13, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Zhou, Y.K.; Ji, Z.L.; Chen, X.R. The Plant Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins Play Important Roles in Defense against Pathogens and Insect Pest Attacks. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M. Antiviral Activity of Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins. Toxins 2021, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Pedrazzi, M.; Bolognesi, A. Immunotoxins and Other Conjugates Containing Saporin-S6 for Cancer Therapy. Toxins 2011, 3, 697–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zaeytijd, J.; Rouge, P.; Smagghe, G.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Structure and Activity of a Cytosolic Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Rice. Toxins 2019, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parente, A.; Chambery, A.; Di Maro, A.; Russo, R.; Severino, V. Ribosome-inactivating Proteins from Phytolaccaceae. In Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins: Ricin and Related Proteins; Stirpe, F., Lappi, D., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domashevskiy, A.V.; Goss, D.J. Pokeweed Antiviral Protein, a Ribosome Inactivating Protein: Activity, Inhibition and Prospects. Toxins 2015, 7, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreras, J.M.; Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Jimenez, P.; Girbes, T. Sambucus Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins and Lectins. In Toxic Plant Proteins–Plant Cell Monographs, 1st ed.; Lord, J.M., Hartley, M.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 18, pp. 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Stoppa, C.; Bolognesi, A. Large-scale chromatographic purification of ribosome-inactivating proteins. J. Chromatograph. 1987, 408, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreras, J.M.; Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Jimenez, P.; Souza, A.M.; Gayoso, M.J.; Girbes, T. Occurrence and new procedure of preparation of nigrin, an antiribosomal lectin present in elderberry bark. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2798–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M.; Di Maro, A.; Citores, L. Ebulin-RP, a novel member of the Ebulin gene family with low cytotoxicity as a result of deficient sugar binding domains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, E.J.M.; Barre, A.; Rouge, P.; VanLeuven, F.; Peumans, W. Isolation and molecular cloning of a novel type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein with an inactive B chain from elderberry (Sambucus nigra) Bark. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 8353–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Ferreras, J.M. Ribosomal RNA N-glycosylase Activity Assay of Ribosome-inactivating Proteins. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girbes, T.; Barbieri, L.; Ferreras, J.M.; Arias, F.; Rojo, M.; Iglesias, R.; Alegre, C.; Escarmis, C.; Stirpe, F. Effects of ribosome-inactivating proteins on Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens translation systems. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 6721–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Di Maro, A.; Ferreras, J.M. Biological and antipathogenic activities of ribosome-inactivating proteins from Phytolacca dioica L. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Di Maro, A.; Ferreras, J.M. Biological activities of the antiviral protein BE27 from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Planta 2015, 241, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Ferreras, J.M.; Barraco, A.; Ricci, P.; Stirpe, F. Some ribosome-inactivating proteins depurinate ribosomal RNA at multiple sites. Biochem. J. 1992, 286, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbieri, L.; Valbonesi, P.; Bonora, E.; Gorini, P.; Bolognesi, A.; Stirpe, F. Polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins: Effect on DNA, RNA and poly(A). Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Ferreras, J.M.; Iglesias, R.; Polito, L.; Bolognesi, A. Kirkiin: A New Toxic Type 2 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from the Caudex of Adenia kirkii. Toxins 2021, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with Alpha Fold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Pedrazzi, M.; Citores, L.; Ferreras, J.M.; Bolognesi, A. Primary Sequence and 3D Structure Prediction of the Plant Toxin Stenodactylin. Toxins 2020, 12, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiello, S.; Iglesias, R.; Polito, L.; Citores, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Ferreras, J.M.; Bolognesi, A. Sequence, Structure, and Binding Site Analysis of Kirkiin in Comparison with Ricin and Other Type 2 RIPs. Toxins 2021, 13, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutenber, E.; Robertus, J. Structure of ricin B-chain at 2.5-A resolution. Proteins 1991, 10, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, C.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Comparative analysis of carbohydrate binding properties of Sambucus nigra lectins and ribosome-inactivating proteins. Glycoconj. J. 2014, 31, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercatelli, D.; Bortolotti, M.; Andresen, V.; Sulen, A.; Polito, L.; Gjertsen, B.; Bolognesi, A. Early Response to the Plant Toxin Stenodactylin in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Involves Inflammatory and Apoptotic Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Battelli, M.G.; Calafato, G.; Bolognesi, A. Ricin: An Ancient Story for a Timeless Plant Toxin. Toxins 2019, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.; Phatak, P.; Chauhan, V. Differential toxicity of abrin in human cell lines of different organ origin. Toxicol. In Vitro 2022, 78, 105250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battelli, M.; Citores, L.; Buonamici, L.; Ferreras, J.M.; de Benito, F.; Stirpe, F.; Girbes, T. Toxicity and cytotoxicity of nigrin b, a two-chain ribosome-inactivating protein from Sambucus nigra: Comparison with ricin. Arch. Toxicol. 1997, 71, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Hoshi, K.; Osuka, F.; Gotoh, M.; Saito, T.; Hojo, H.; Suzuki, R.; Ohira, H.; Honda, T.; Hashimoto, Y. Lectin inhibits antigen-antibody reaction in a glycoform-specific manner: Application for detecting alpha 2,6sialylated-carcinoembryonic antigen. Proteomics 2016, 16, 3081–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ito, H. Simple and Rapid Detection of Glycoforms by “Lectin Inhibition” Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2132, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernygorodskyi, S.; Shkolnikov, V.; Suhan, D. Lectin binding patterns in normal, dysplastic and Helicobacter pylori infected gastric mucosa. Exp. Oncol. 2017, 39, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Hoshi, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Honda, T. Glycoform-Specific Visualization in Immunohistochemistry by “Lectin Inhibition”. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2132, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, S.; Kimani, M.; Zhang, Y.; Verhassel, A.; Sternbaek, L.; Wang, T.; Persson, J.; Harkonen, P.; Johansson, E.; Caraballo, R.; et al. Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers against Sialic Acid on Silica-Coated Polystyrene Cores-Assessment of the Binding Behavior to Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, R.; Okimoto, T.; Kodama, M.; Togo, K.; Fukuda, K.; Okamoto, K.; Mizukami, K.; Murakami, K. Changes in Gastric Mucosal Glycosylation Before and After Helicobacter pylori Eradication Using Lectin Microarray Analysis. Turkish J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 33, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptan, E.; Sancar-Bas, S.; Sancakli, A.; Bektas, S.; Bolkent, S. The effect of plant lectins on the survival and malignant behaviors of thyroid cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 6274–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Peumans, W.J.; Van Damme, E.J.M. The Sambucus nigra type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein SNA-I‘ exhibits in planta antiviral activity in transgenic tobacco. FEBS Lett. 2002, 516, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbussche, F.; Desmyter, S.; Ciani, M.; Proost, P.; Peumans, W.J.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Analysis of the in planta antiviral activity of elderberry ribosome-inactivating proteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi-Noghabi, S.; Van Damme, E.J.M.; Smagghe, G. Carbohydrate-binding activity of the type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein SNA-I from elderberry (Sambucus nigra) is a determining factor for its insecticidal activity. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi-Noghabi, S.; Van Damme, E.J.M.; Smagghe, G. Expression of Sambucus nigra agglutinin (SNA-I’) from elderberry bark in transgenic tobacco plants results in enhanced resistance to different insect species. Transgen. Res. 2009, 18, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girbes, T.; Citores, L.; Ferreras, J.M.; Rojo, M.; Iglesias, R.; Munoz, R.; Arias, F.; Calonge, M.; Garcia, J.; Mendez, E. Isolation and partial characterization of nigrin-b, a nontoxic novel type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein from the bark of Sambucus nigra L. Plant Mol. Biol. 1993, 22, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, E.J.M.; Barre, A.; Rouge, P.; VanLeuven, F.; Peumans, W. Characterization and molecular cloning of Sambucus nigra agglutinin V (nigrin b), a GalNAc-specific type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein from the bark of elderberry (Sambucus nigra). Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 237, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, E.J.M.; Roy, S.; Barre, A.; Citores, L.; Mostafapous, K.; Rouge, P.; VanLeuven, F.; Girbes, T.; Goldstein, I.; Peumans, W. Elderberry (Sambucus nigra) bark contains two structurally different Neu5Ac(alpha 2,6)Gal/GalNAc-binding type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 245, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Benito, F.; Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M.; Camafeita, E.; Mendez, E.; Girbes, T. Isolation and partial characterization of a novel and uncommon two-chain 64-kDa ribosome-inactivating protein from the bark of elder (Sambucus nigra L). FEBS Lett. 1997, 413, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, E.J.M.; Barre, A.; Rouge, P.; VanLeuven, F.; Peumans, W. The NeuAc(alpha-2,6)Gal/GalNAc-binding lectin from elderberry (Sambucus nigra) bark, a type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein with an unusual specificity and structure. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 235, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, H.; Peumans, W.; Goldstein, I. Isolation and characterization of a 2nd lectin (SNA-II) present in elderberry (Sambucus nigra L) bark. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 277, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Benito, F.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M.; Citores, L.; Camafeita, E.; Mendez, E.; Girbes, T. Constitutive and inducible type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) in elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.). FEBS Lett. 1998, 428, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citores, L.; de Benito, F.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M.; Jimenez, P.; Argueso, P.; Farias, G.; Mendez, E.; Girbes, T. Isolation and characterization of a new non-toxic two-chain ribosome-inactivating protein from fruits of elder (Sambucus nigra L). J. Exp. Bot. 1996, 47, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peumans, W.; Roy, S.; Barre, A.; Rouge, P.; van Leuven, F.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Elderberry (Sambucus nigra) contains truncated Neu5Ac(alpha-2,6)Gal/GalNAc-binding type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins. FEBS Lett. 1998, 425, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, E.J.M.; Roy, S.; Barre, A.; Rouge, P.; Van Leuven, F.; Peumans, W. The major elderberry (Sambucus nigra) fruit protein is a lectin derived from a truncated type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein. Plant J. 1997, 12, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Munoz, R.; Ferreras, J.M.; Jimenez, P.; Girbes, T. Elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) seed proteins inhibit protein synthesis and display strong immunoreactivity with rabbit polyclonal antibodies raised against the type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein nigrin b. J. Exp. Bot. 1994, 45, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peumans, W.; Kellens, J.; Allen, A.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Isolation and characterization of a seed lectin from elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) and its relationship to the bark lectins. Carbohydr. Res. 1991, 213, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, I.; Koretska, N.; Palchykovska, L.; Nehrutska, V. Lectins from Sambucus nigra L. inflorescences: Isolation and investigation of biological activity using procaryotic test-systems. Ukr. Biokhimicheskii Zhurnal 1999, 79, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Karpova, I.; Lylo, V.; Macewicz, L.; Kotsarenko, K.; Palchkovska, L.; Ruban, T.; Lukash, L. Lectins of Sambucus nigra as biologically active and DNA-protective substances. Acta Hortic. 2015, 1061, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekaert, W.; Nsimbalubaki, M.; Peeters, B.; Peumans, W. A lectin from elder (Sambucus nigra L.) bark. Biochem. J. 1984, 221, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, M.; Citores, L.; Arias, F.; Ferreras, J.M.; Jimenez, P.; Girbes, T. cDNA molecular cloning and seasonal acumulation of an ebulin 1-related dimeric lectin of dwarf elder (Sambucus ebulus L.) leaves. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citores, L.; de Benito, F.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M.; Argueso, P.; Jimenez, P.; Mendez, E.; Girbes, T. Presence of polymerized and free forms of the non-toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein ebulin and a structurally related new homodimeric lectin in fruits of Sambucus ebulus L. Planta 1998, 204, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Ferreras, J.M.; Perez, Y.; Jimenez, P.; Gayoso, M.J.; Olsnes, S.; Tamburino, R.; Di Maro, A.; Parente, A.; et al. Sialic acid-binding dwarf elder four-chain lectin displays nucleic acid N-glycosidase activity. Biochimie 2010, 92, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Too, P.; Ma, M.; Mak, A.; Wong, Y.; Tung, C.; Zhu, G.; Au, S.; Wong, K.; Shaw, P. The C-terminal fragment of the ribosomal P protein complexed to trichosanthin reveals the interaction between the ribosome-inactivating protein and the ribosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, B.; Tumer, N. Ricin uses arginine 235 as an anchor residue to bind to P-proteins of the ribosomal stalk. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; Di Maro, A.; Severino, V.; Chambery, A.; Berisio, R. Crystal Structure of PD-L1, a Ribosome Inactivating Protein from Phytolacca dioica L. Leaves with the Property to Induce DNA Cleavage. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.; Schaeffer, R.; et al. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, J.; Day, P.; Monzingo, A.; Ernst, S.; Robertus, J.; Iglesias, R.; Perez, Y.; Ferreras, J.M.; Citores, L.; Girbes, T. 2.8-angstrom crystal structure of a nontoxic type-II ribosome-inactivating protein, ebulin 1. Proteins 2001, 43, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girbes, T.; Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M.; Munoz, R.; Rojo, M.; Arias, F.; Garcia, J.; Mendez, E.; Calonge, M. Ebulin l, a nontoxic novel type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein from Sambucus ebulus L. leaves. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 18195–18199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalb, V.J.; Bernlohr, R. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 82, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1974, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maro, A.; Chambery, A.; Daniele, A.; Casoria, P.; Parente, A. Isolation and characterization of heterotepalins, type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins from Phytolacca heterotepala leaves. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Inbar, Y.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H. PatchDock and SymmDock: Servers for rigid and symmetric docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W363–W367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.; Thiessen, P.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.; Belew, R.; Goodsell, D.; Olson, A. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated Docking with Selective Receptor Flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Minimum Concentration Inhibiting Hemagglutination (mM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates l | Nigrin l | SNAlm | SNAld |
| D-galactose | 50 | 6.25 | 100 |
| Lactose | 12.5 | 1.56 | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iglesias, R.; Russo, R.; Landi, N.; Valletta, M.; Chambery, A.; Di Maro, A.; Bolognesi, A.; Ferreras, J.M.; Citores, L. Structure and Biological Properties of Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins and Lectins from Elder (Sambucus nigra L.) Leaves. Toxins 2022, 14, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090611
Iglesias R, Russo R, Landi N, Valletta M, Chambery A, Di Maro A, Bolognesi A, Ferreras JM, Citores L. Structure and Biological Properties of Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins and Lectins from Elder (Sambucus nigra L.) Leaves. Toxins. 2022; 14(9):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090611
Chicago/Turabian StyleIglesias, Rosario, Rosita Russo, Nicola Landi, Mariangela Valletta, Angela Chambery, Antimo Di Maro, Andrea Bolognesi, José M. Ferreras, and Lucía Citores. 2022. "Structure and Biological Properties of Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins and Lectins from Elder (Sambucus nigra L.) Leaves" Toxins 14, no. 9: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090611
APA StyleIglesias, R., Russo, R., Landi, N., Valletta, M., Chambery, A., Di Maro, A., Bolognesi, A., Ferreras, J. M., & Citores, L. (2022). Structure and Biological Properties of Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins and Lectins from Elder (Sambucus nigra L.) Leaves. Toxins, 14(9), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090611