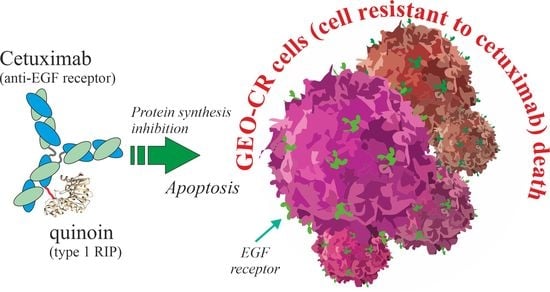
A Novel EGFR Targeted Immunotoxin Based on Cetuximab and Type 1 RIP Quinoin Overcomes the Cetuximab Resistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Quinoin Isolation
2.2. Chemical Linking between Cetuximab and Quinoin by Using SPDP
2.3. Enzymatic Properties of Cetuximab Quinoin Immunocomplex
2.4. In Vitro Effects of Quinoin Cetuximab Immunoconjugate on Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis Using Model Colon Cancer Cells with Acquired Resistance to Cetuximab
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Quinoin, Type 1 RIP Purification
4.3. Immunoconjugate Preparation
4.4. Immunoconjugate Purification
4.5. Analytical Procedures
4.6. Enzymatic Assays
4.7. Cell Lines and Drugs
4.8. Cell Viability Assay
4.9. Apoptosis Assessment
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kim, J.S.; Jun, S.Y.; Kim, Y.S. Critical Issues in the Development of Immunotoxins for Anticancer Therapy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antignani, A.; Fitzgerald, D. Immunotoxins: The role of the toxin. Toxins 2013, 5, 1486–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piro, A.; Tagarelli, A.; Tagarelli, G.; Lagonia, P.; Quattrone, A. Paul Ehrlich: The Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine 1908. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 27, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Mei, S.; Yang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, L. Strategies to mitigate the on- and off-target toxicities of recombinant immunotoxins: An antibody engineering perspective. Antib. Ther. 2022, 5, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khirehgesh, M.R.; Sharifi, J.; Safari, F.; Akbari, B. Immunotoxins and nanobody-based immunotoxins: Review and update. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, E.; Di Maro, A. A new age for biomedical applications of Ribosome Inactivating Proteins (RIPs): From bioconjugate to nanoconstructs. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Weng, A.; Mallinckrodt, B.; Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H.; Thakur, M. Immunotoxins constructed with ribosome-inactivating proteins and their enhancers: A lethal cocktail with tumor specific efficacy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 6584–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olombrada, M.; Lázaro-Gorines, R.; López-Rodríguez, J.C.; Martínez-del-Pozo, Á.; Oñaderra, M.; Maestro-López, M.; Lacadena, J.; Gavilanes, J.G.; García-Ortega, L. Fungal Ribotoxins: A Review of Potential Biotechnological Applications. Toxins 2017, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havaei, S.M.; Aucoin, M.G.; Jahanian-Najafabadi, A. Pseudomonas Exotoxin-Based Immunotoxins: Over Three Decades of Efforts on Targeting Cancer Cells with the Toxin. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 781800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, F.; Aucoin, M.G.; Jahanian-Najafabadi, A. Targeted Diphtheria Toxin-Based Therapy: A Review Article. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavell, D.J.; Flavell, S.U. Plant-Derived Type I Ribosome Inactivating Protein-Based Targeted Toxins: A Review of the Clinical Experience. Toxins 2022, 14, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, N.; Hussain, H.Z.F.; Pedone, P.V.; Ragucci, S.; Di Maro, A. Ribotoxic Proteins, Known as Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis, from Mushrooms and Other Fungi According to Endo’s Fragment Detection. Toxins 2022, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaconu, M.; Kothe, U.; Schlünzen, F.; Fischer, N.; Harms, J.M.; Tonevitsky, A.G.; Stark, H.; Rodnina, M.V.; Wahl, M.C. Structural Basis for the Function of the Ribosomal L7/12 Stalk in Factor Binding and GTPase Activation. Cell 2005, 121, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montanaro, L.; Sperti, S.; Mattioli, A.; Testoni, G.; Stirpe, F. Inhibition by ricin of protein synthesis in vitro. Inhibition of the binding of elongation factor 2 and of adenosine diphosphate-ribosylated elongation factor 2 to ribosomes. Biochem. J. 1975, 146, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stirpe, F. Ribosome-inactivating proteins: From toxins to useful proteins. Toxicon 2013, 67, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, K.; Hudak, K.A. Phylogeny and domain architecture of plant ribosome inactivating proteins. Phytochemistry 2022, 202, 113337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maro, A.; Citores, L.; Russo, R.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M. Sequence comparison and phylogenetic analysis by the Maximum Likelihood method of ribosome-inactivating proteins from angiosperms. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 85, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, E.V.; Robins-Browne, R.M. Effect of Shiga toxin and Shiga-like toxins on eukaryotic cells. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-S.; Yang, J.-H.; Liu, W.-Y. Isolation and enzymatic characterization of lamjapin, the first ribosome-inactivating protein from cryptogamic algal plant (Laminaria japonica A). Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 4746–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.; Boston, R.S. RIBOSOME-Inactivating Proteins: A Plant Perspective. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 52, 785–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, E.J.M.; Hao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Barre, A.; Vandenbussche, F.; Desmyter, S.; Rougé, P.; Peumans, W.J. Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins: A Family of Plant Proteins That Do More Than Inactivate Ribosomes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2001, 20, 395–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirpe, F.; Gilabert-Oriol, R. Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins: An Overview. In Plant Toxins; Carlini, C.R., Ligabue-Braun, R., Gopalakrishnakone, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 153–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhou, Y.K.; Ji, Z.L.; Chen, X.R. The Plant Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins Play Important Roles in Defense against Pathogens and Insect Pest Attacks. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landi, N.; Ruocco, M.R.; Ragucci, S.; Aliotta, F.; Nasso, R.; Pedone, P.V.; Di Maro, A. Quinoa as source of type 1 ribosome inactivating proteins: A novel knowledge for a revision of its consumption. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, N.; Ragucci, S.; Citores, L.; Clemente, A.; Hussain, H.Z.F.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M.; Di Maro, A. Isolation, Characterization and Biological Action of Type-1 Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins from Tissues of Salsola soda L. Toxins 2022, 14, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Saporin-S6: A useful tool in cancer therapy. Toxins 2013, 5, 1698–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragucci, S.; Bulgari, D.; Landi, N.; Russo, R.; Clemente, A.; Valletta, M.; Chambery, A.; Gobbi, E.; Faoro, F.; Di Maro, A. The Structural Characterization and Antipathogenic Activities of Quinoin, a Type 1 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Quinoa Seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, R.; Ragucci, S.; Castaldo, S.; Oliva, M.A.; Landi, N.; Pedone, P.V.; Arcella, A.; Di Maro, A. Cytotoxicity Effect of Quinoin, Type 1 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Quinoa Seeds, on Glioblastoma Cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfaro Alfaro, Á.E.; Murillo Castillo, B.; Cordero García, E.; Tascón, J.; Morales, A.I. Colon Cancer Pharmacogenetics: A Narrative Review. Pharmacy 2022, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normanno, N.; Tejpar, S.; Morgillo, F.; De Luca, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Ciardiello, F. Implications for KRAS status and EGFR-targeted therapies in metastatic CRC. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, R.G.; Wolf, M.; Peeters, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Siena, S.; Freeman, D.J.; Juan, T.; Sikorski, R.; Suggs, S.; Radinsky, R.; et al. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troiani, T.; Martinelli, E.; Napolitano, S.; Vitagliano, D.; Ciuffreda, L.P.; Costantino, S.; Morgillo, F.; Capasso, A.; Sforza, V.; Nappi, A.; et al. Increased TGF-α as a mechanism of acquired resistance to the anti-EGFR inhibitor cetuximab through EGFR-MET interaction and activation of MET signaling in colon cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6751–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troiani, T.; Napolitano, S.; Vitagliano, D.; Morgillo, F.; Capasso, A.; Sforza, V.; Nappi, A.; Ciardiello, D.; Ciardiello, F.; Martinelli, E. Primary and acquired resistance of colorectal cancer cells to anti-EGFR antibodies converge on MEK/ERK pathway activation and can be overcome by combined MEK/EGFR inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3775–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hermanson, G.T. Chapter 20—Antibody Modification and Conjugation. In Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Hermanson, G.T., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 867–920. [Google Scholar]
- Neurath, A.R.; Strick, N. Enzyme-linked fluorescence immunoassays using beta-galactosidase and antibodies covalently bound to polystyrene plates. J. Virol. Methods 1981, 3, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Ferreras, J.M. Ribosomal RNA N-glycosylase Activity Assay of Ribosome-inactivating Proteins. Bio. Protoc. 2017, 7, e2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chambery, A.; Pisante, M.; Di Maro, A.; Di Zazzo, E.; Ruvo, M.; Costantini, S.; Colonna, G.; Parente, A. Invariant Ser211 is involved in the catalysis of PD-L4, type I RIP from Phytolacca dioica leaves. Proteins 2007, 67, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Chen, C.; Nie, J.; Jiao, B. Can EGFR be a therapeutic target in breast cancer? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellisola, G.; Fracasso, G.; Ippoliti, R.; Menestrina, G.; Rosén, A.; Soldà, S.; Udali, S.; Tomazzolli, R.; Tridente, G.; Colombatti, M. Reductive activation of ricin and ricin A-chain immunotoxins by protein disulfide isomerase and thioredoxin reductase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, W.L.; Weyergang, A.; Berg, K.; Tønnesen, H.H.; Selbo, P.K. Targeted delivery and enhanced cytotoxicity of cetuximab-saporin by photochemical internalization in EGFR-positive cancer cells. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianjun, S. Roles of Cellular Redox Factors in Pathogen and Toxin Entry in the Endocytic Pathways. In Molecular Regulation of Endocytosis; Brian, C., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Landi, N.; Pacifico, S.; Ragucci, S.; Iglesias, R.; Piccolella, S.; Amici, A.; Di Giuseppe, A.M.A.; Di Maro, A. Purification, characterization and cytotoxicity assessment of Ageritin: The first ribotoxin from the basidiomycete mushroom Agrocybe aegerita. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maro, A.; Terracciano, I.; Sticco, L.; Fiandra, L.; Ruocco, M.; Corrado, G.; Parente, A.; Rao, R. Purification and characterization of a viral chitinase active against plant pathogens and herbivores from transgenic tobacco. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 147, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Zhang, C.; Wu, S.; Gu, X.; Cai, Y.; Xu, C.; Chen, Z.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; You, X.; et al. Recombinant cucurmosin-based immunotoxin targeting HER-2 with potent in vitro anti-cancer cytotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Di Maro, A.; Ferreras, J.M. Biological and antipathogenic activities of ribosome-inactivating proteins from Phytolacca dioica L. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Maro, A.; Chambery, A.; Daniele, A.; Casoria, P.; Parente, A. Isolation and characterization of heterotepalins, type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins from Phytolacca heterotepala leaves. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Landi, N.; Ciaramella, V.; Ragucci, S.; Chambery, A.; Ciardiello, F.; Pedone, P.V.; Troiani, T.; Di Maro, A. A Novel EGFR Targeted Immunotoxin Based on Cetuximab and Type 1 RIP Quinoin Overcomes the Cetuximab Resistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Toxins 2023, 15, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010057
Landi N, Ciaramella V, Ragucci S, Chambery A, Ciardiello F, Pedone PV, Troiani T, Di Maro A. A Novel EGFR Targeted Immunotoxin Based on Cetuximab and Type 1 RIP Quinoin Overcomes the Cetuximab Resistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Toxins. 2023; 15(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleLandi, Nicola, Vincenza Ciaramella, Sara Ragucci, Angela Chambery, Fortunato Ciardiello, Paolo V. Pedone, Teresa Troiani, and Antimo Di Maro. 2023. "A Novel EGFR Targeted Immunotoxin Based on Cetuximab and Type 1 RIP Quinoin Overcomes the Cetuximab Resistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells" Toxins 15, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010057
APA StyleLandi, N., Ciaramella, V., Ragucci, S., Chambery, A., Ciardiello, F., Pedone, P. V., Troiani, T., & Di Maro, A. (2023). A Novel EGFR Targeted Immunotoxin Based on Cetuximab and Type 1 RIP Quinoin Overcomes the Cetuximab Resistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Toxins, 15(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010057