Water Quality, Toxicity and Diversity of Planktonic and Benthic Cyanobacteria in Pristine Ancient Lake Khubsugul (Hövsgöl), Mongolia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
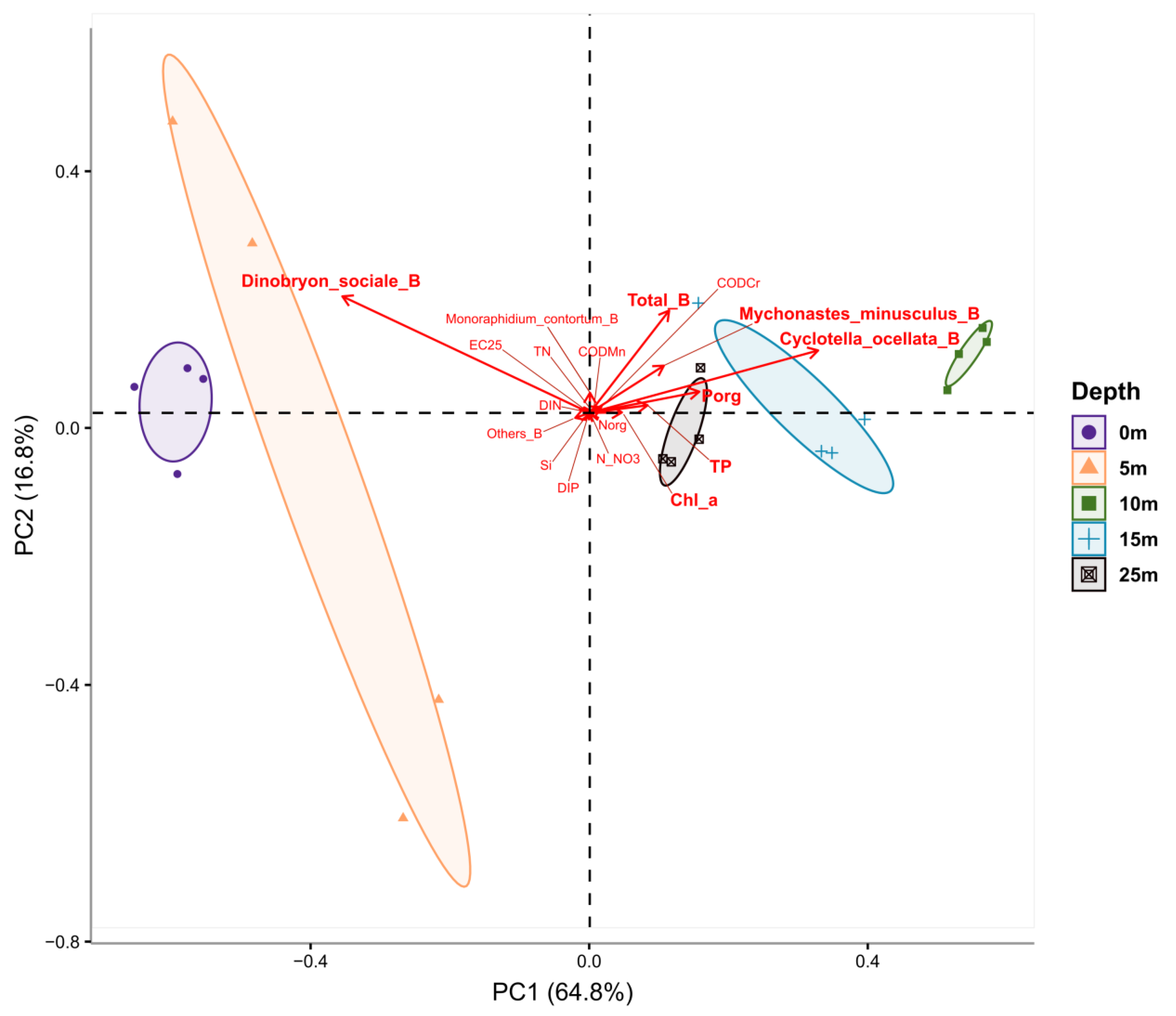
2.1. Hydrophysical and Hydrochemical Parameters
2.2. Chlorophyll a
| Components/ Parameters | Units | Depth, m | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 25 | 0–25 | ||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Ec (25 °C) | µS cm−1 | 171.4 | 1.0 | 182.4 | 2.2 | 179.1 | 1.96 | 182.8 | 1.5 | 133.9 | 1.4 | 169.9 | 1.6 |
| Temperature | °C | 9.1 | 0.06 | 8.4 | 0.1 | 8.4 | 0.15 | 8.0 | 0.1 | 8.0 | 0.1 | 8.38 | 0.1 |
| Oxygen | mg L−1 | 10.98 | 0.04 | 11.31 | 0.03 | 11.39 | 0.04 | 11.42 | 0.02 | 11.75 | 0.03 | 11.37 | 0.03 |
| Si | mg L−1 | 0.82 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 0.01 | 0.81 | 0.01 | 0.81 | 0.02 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 0.80 | 0.02 |
| N-NH4 | mg L−1 | 0.010 | 0.001 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||||||
| N-NO2 | mg L−1 | 0.001 | 0.0006 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| N-NO3 | mg L−1 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.11 | 0.001 |
| DIN 1* | mg L−1 | 0.021 | 0.0015 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.001 |
| Norg * | mg L−1 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.9 | 0.01 |
| TN | mg L−1 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.01 |
| DIP 2 | µg L−1 | 2.3 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 0.4 |
| Porg * | µg L−1 | 0.4 | 0.09 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 0.2 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 1.42 | 0.2 |
| TP | µg L−1 | 2.7 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 4.3 | 0.1 | 4.3 | 0.2 | 3.3 | 0.1 | 3.5 | 0.23 |
| CODCr | mgC L−1 | 1.01 | 0.07 | 0.95 | 0.03 | 1.55 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 0.09 | 1.23 | 0.08 | 1.05 | 0.08 |
| CODMn | mgC L−1 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.02 |
| Chlorophyll a | µg L−1 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.42 | 0.07 | 0.54 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 0.15 | 0.53 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 0.08 |
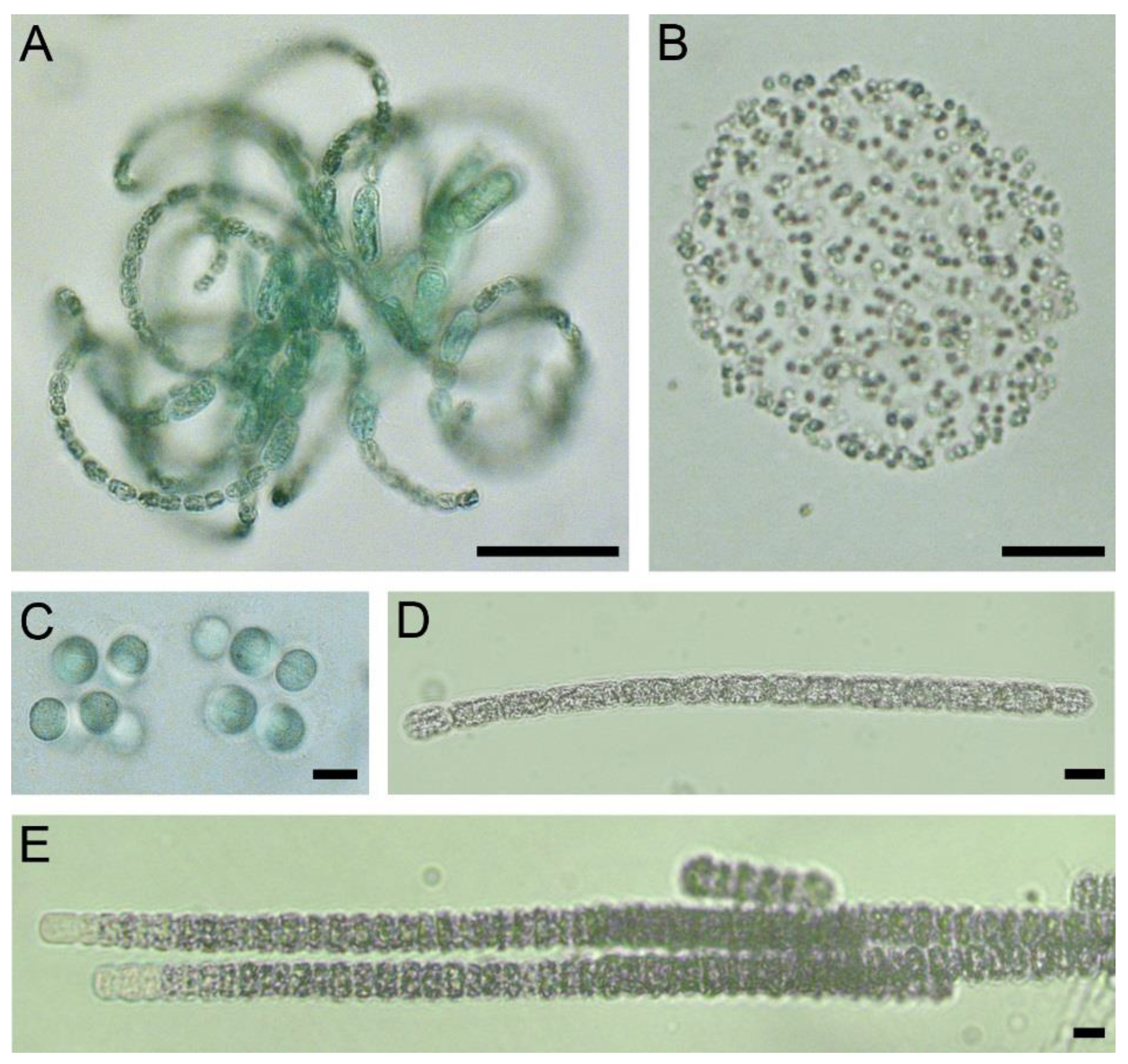
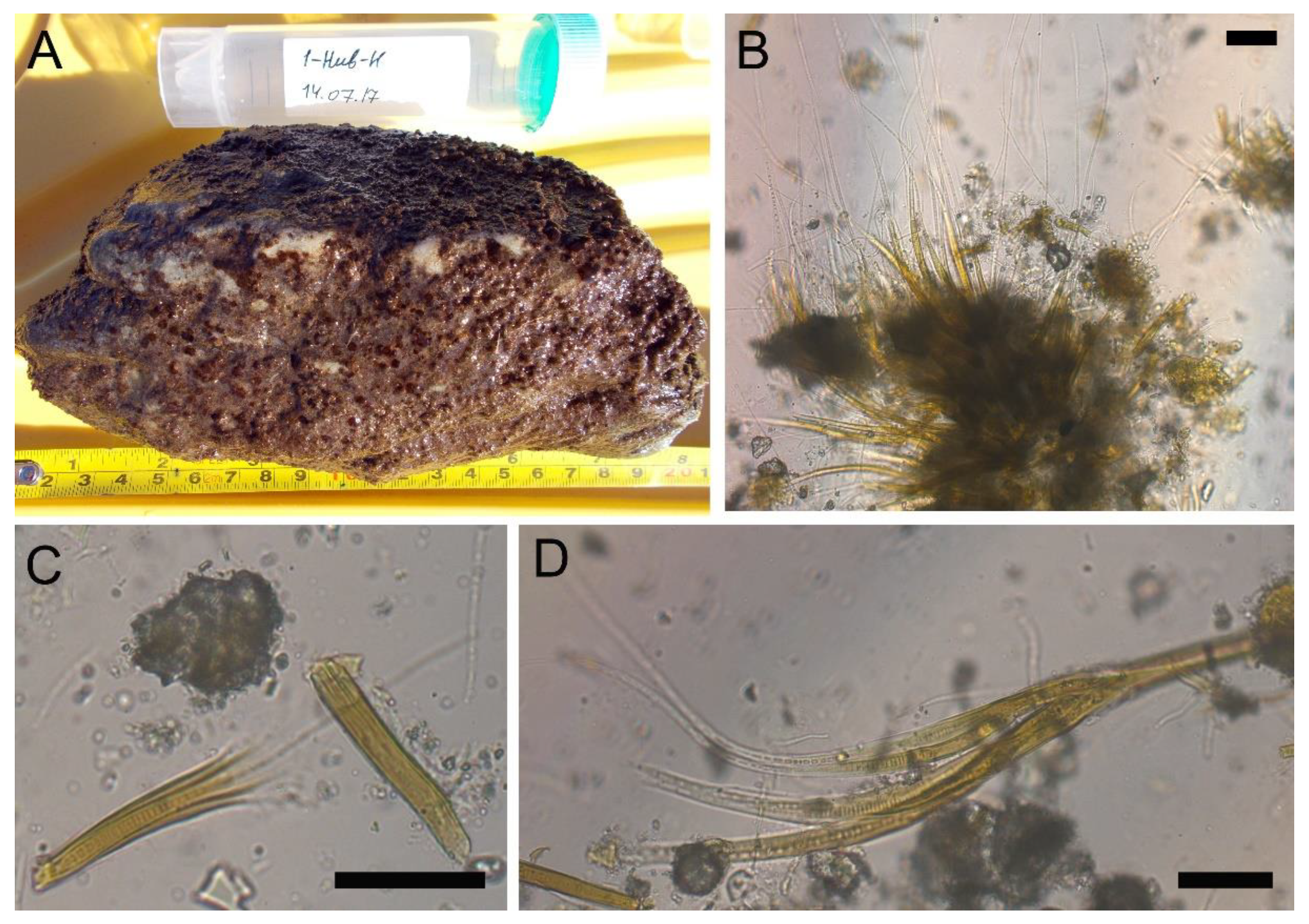
2.3. Microscopy Analysis of Planktonic and Benthic Cyanobacterial Communities
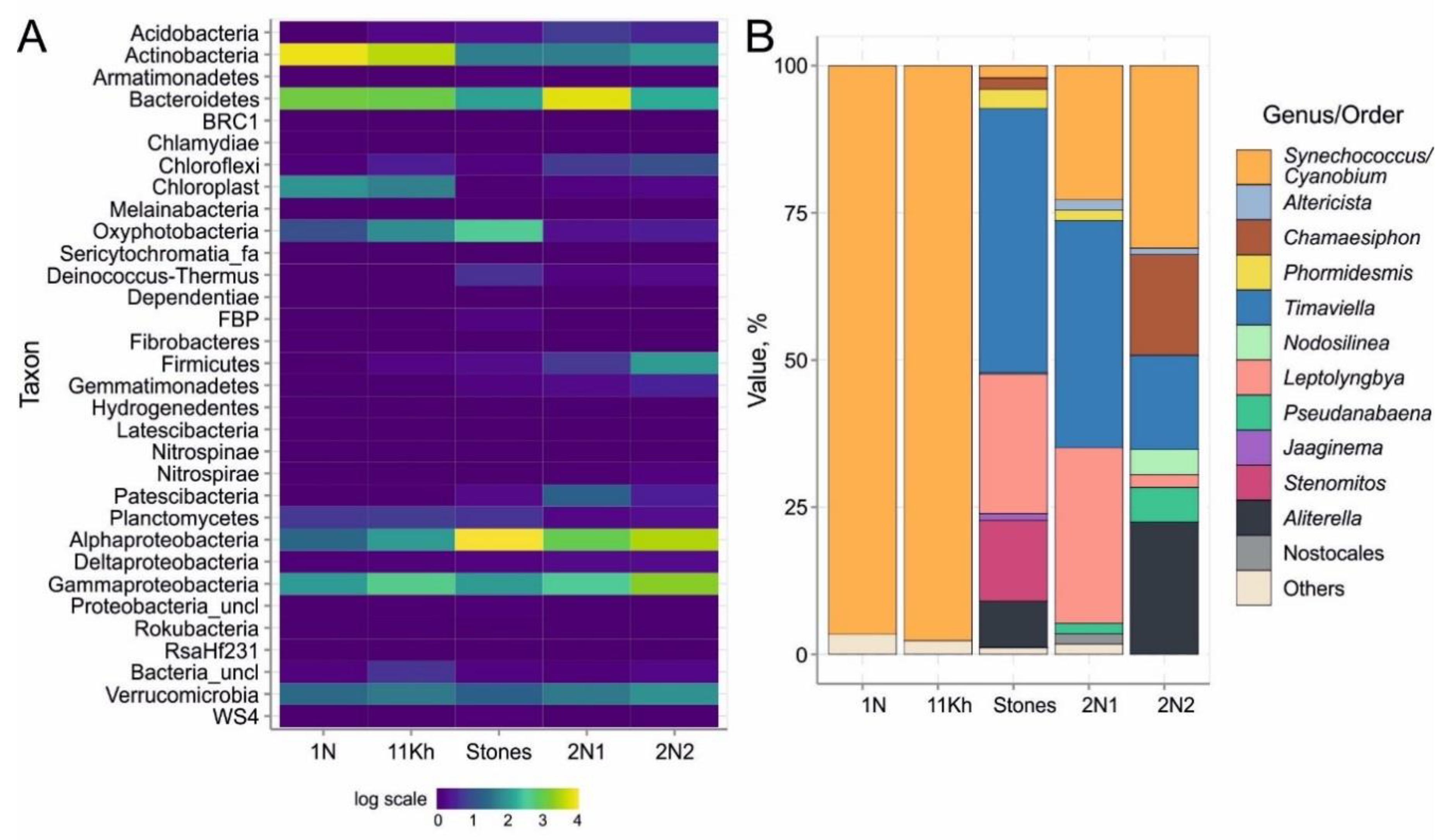
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing of 16S rRNA Gene of Bacterial Community
2.5. Microbial Water Quality Assessment
2.6. High-Throughput Sequencing of 16S rRNA Gene of Pathogenic and Opportunistic Bacteria
2.7. Microcystin Synthetase Genes
2.8. Microcystin Concentration and Microcystin Congeners
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
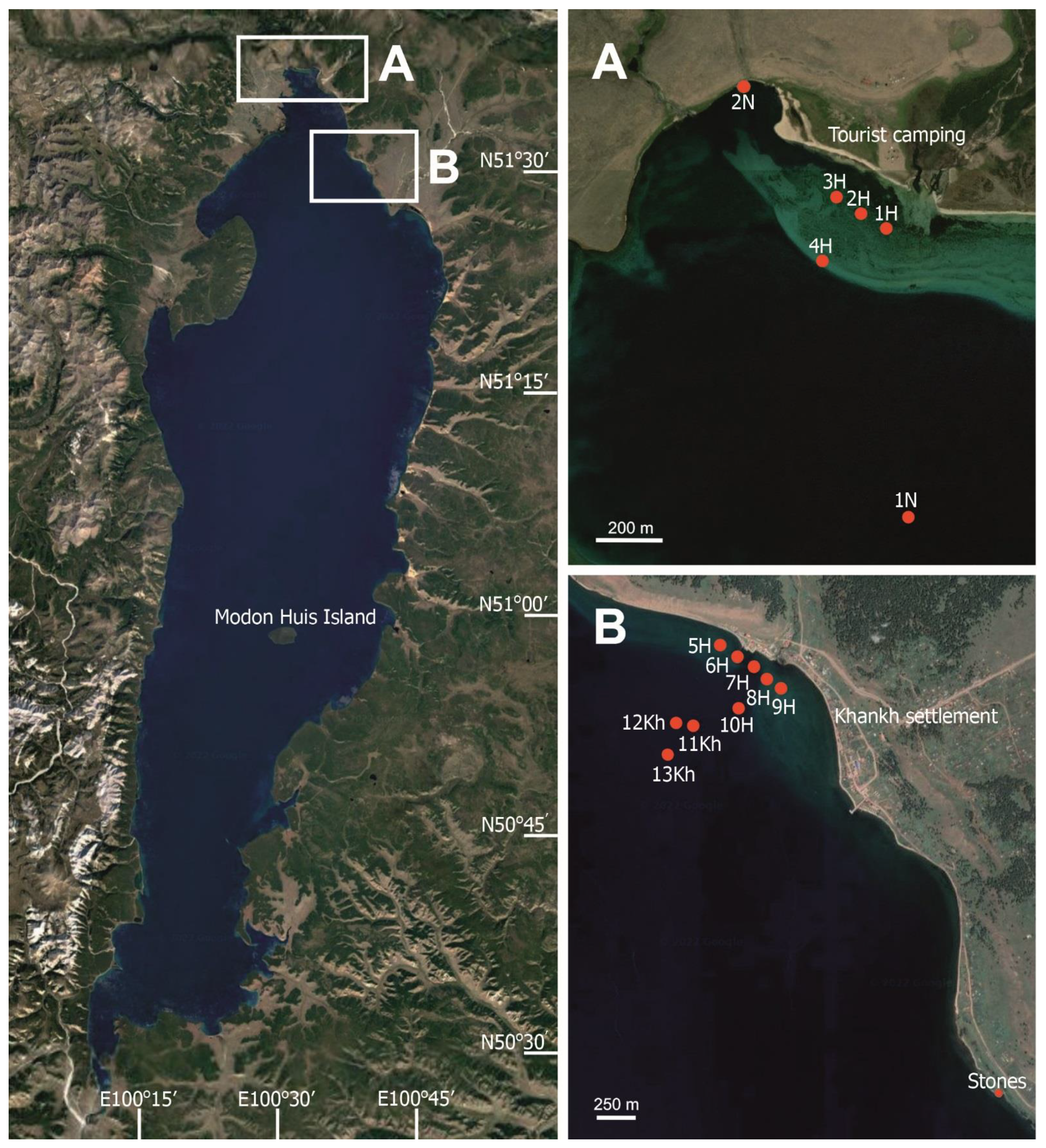
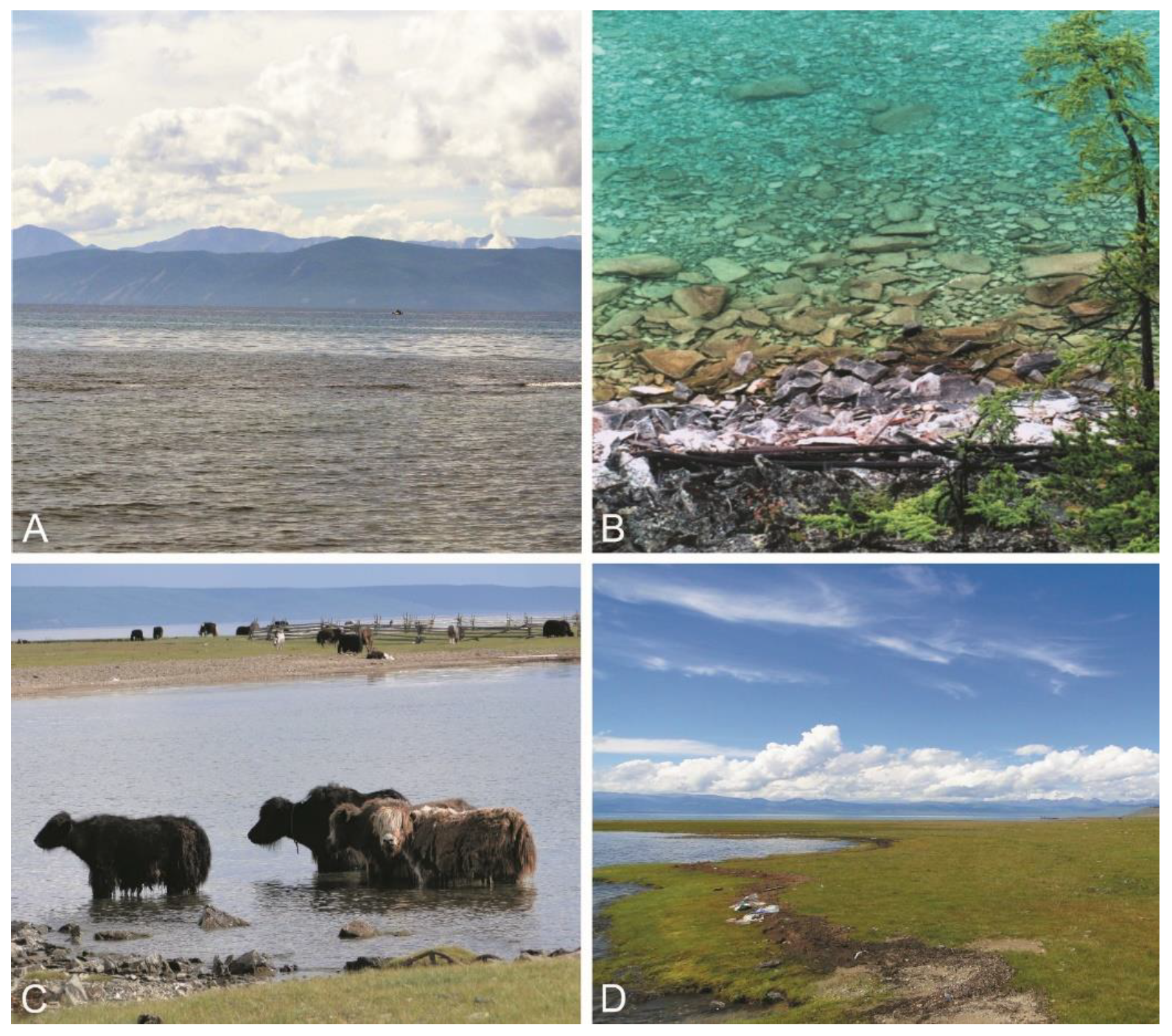
5.1. Site Description
5.2. Sampling
5.3. Sanitary-Microbiological Analysis
5.4. Microscopy
5.5. Molecular Genetic Analysis
5.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
5.7. High Performance Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry
5.8. Hydrochemical Analysis
5.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knoll, A.H.; Barghoorn, E.S. Archean microfossils showing cell division from the Swaziland system of South Africa. Science 1977, 198, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schopf, J.W. Microfossils of the early Archean Apex Chert: New evidence of the antiquity of life. Science 1993, 260, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G.; Kudela, R. Mitigating the expansion of harmful algal blooms across the freshwater-to-marine continuum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5519–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Mitigating toxic planktonic cyanobacterial blooms in aquatic ecosystems facing increasing anthropogenic and climatic pressures. Toxins 2018, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, S.A.; Kelly, L.T.; Bouma-Gregson, K.; Humbert, J.F.; Laughinghouse, H.D.; Lazorchak, J.; McAllister, T.G.; McQueen, A.; Pokrzywinski, K.; Puddick, J.; et al. Toxic benthic freshwater cyanobacterial proliferations: Challenges and solutions for enhancing knowledge and improving monitoring and mitigation. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 1824–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.L.; Karlson, B.; Wulff, A.; Kudela, R.; Trick, C.; Asnaghi, V.; Berdalet, E.; Cochlan, W.; Davidson, K.; De Rijcke, M.; et al. Future HAB science: Directions and challenges in a changing climate. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, R.U.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. Cyanobacterial community succession and associated cyanotoxin production in hypereutrophic and eutrophic freshwaters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhayani, K.; Paliwal, C.; Ghosh, T.; Mishra, S. Nutra-cosmeceutical potential of pigments from microalgae. In Sunscreens: Source, Formulations, Efficacy and Recommendations; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 29–52. [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal, C.; Nesamma, A.A.; Jutur, P.P. Sustainable downstream processing of microalgae for in-dustrial application. In Industrial Scope with High-Value Bio-Molecules from Microalgae; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorus, I.; Falconer, I.R.; Salas, H.J.; Bartram, J. Health risks caused by freshwater cyanobacteria in recreational waters. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2000, 3, 323–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Reinl, K.L.; Lafrancois, B.M.; Brovold, S.; Miller, T.R. A first assessment of cyanobacterial blooms in oligotrophic Lake Superior. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 2984–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinl, K.L.; Sterner, R.W.; Austin, J.A. Seasonality and physical drivers of deep chlorophyll layers in Lake Superior, with implications for a rapidly warming lake. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, N.A.; Tomberg, I.V.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Belykh, O.I.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Fedorova, G.A.; Netsvetaeva, O.G.; Eletskaya, E.V.; Timoshkin, O.A. Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Nostocales) bloom in world’s deepest Lake Baikal (East Siberia): Abundance, toxicity and factors influencing growth. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 1, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.I.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Kuzmin, A.V.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Fedorova, G.A.; Khanaev, I.V.; Sherbakova, T.A.; Timoshkin, O.A. First detection of benthic cyanobacteria in Lake Baikal producing paralytic shellfish toxins. Toxicon 2016, 121, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.I.; Fedorova, G.A.; Kuzmin, A.V.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Timoshkin, O.A.; Sorokovikova, E.G. Microcystins in cyanobacterial biofilms from the littoral zone of Lake Baikal. Moscow Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 2017, 72, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.I.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Kuz’min, A.V.; Mogil’nikova, T.A.; Fedorova, G.A.; Sorokovnikova, E.G. Identification of cyanobacterial producers of shellfish paralytic toxins in Lake Baikal. Mikrobiologiia 2015, 84, 120–122. [Google Scholar]
- Belykh, O.I.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Butina, T.V. Identification of toxic cyanobacteria in Lake Baikal. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 463, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, L.; Mihali, T.; Moffitt, M.; Kellmann, R.; Neilan, B. On the chemistry, toxicology and genetics of the cyanobacterial toxins, microcystin, nodularin, saxitoxin and cylindrospermopsin. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1650–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plaas, H.E.; Paerl, H.W. Toxic cyanobacteria: A growing threat to water and air quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi, A.; Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Pflugmacher, S. Still challenging: The ecological function of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin–What we know so far. Toxin Rev. 2018, 37, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preece, E.P.; Hardy, F.J.; Moore, B.C.; Bryan, M. A review of microcystin detections in Estuarine and Marine waters: Environmental implications and human health risk. Harmful Algae 2017, 61, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouaïcha, N.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; Labidi, Z.; Djabri, A.; Benayache, N.Y.; Nguyen-Quang, T. Structural diversity, characterization and toxicology of microcystins. Toxins 2019, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janssen, E.M.L. Cyanobacterial peptides beyond microcystins—A review on co-occurrence, toxicity, and challenges for risk assessment. Water Res. 2019, 151, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Welker, M. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; p. 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Giesy, J.P.; Adamovsky, O.; Svirčev, Z.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G.A.; Mijovic, B.; Shi, T.; Tuo, X.; Li, S.-C.; et al. Challenges of using blooms of Microcystis spp. in animal feeds: A comprehensive review of nutritional, toxicological and microbial health evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Cyanobacterial Toxins: Microcystins. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality and Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments. WHO/HEP/ECH/WSH/2020.6; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments. Volume 1: Coastal and Fresh Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; p. 219. ISBN 92-4-154580-1. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 631. ISBN 978-92-4-154995-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dittmann, E.; Neilan, B.A.; Erhard, M.; Von Döhren, H.; Börner, T. Insertional mutagenesis of a peptide synthetase gene that is responsible for hepatotoxin production in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 26, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Asayama, M.; Fujii, K.; Harada, K.; Shirai, M. Genetic analysis of the peptide synthetase genes for a cyclic heptapeptide microcystin in Microcystis spp. J. Biochem. 1999, 126, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Ueda, A.; Asayama, M.; Fujii, K.; Harada, K.I.; Ochi, K.; Shirai, M. Polyketide synthase gene coupled to the peptide synthetase module involved in the biosynthesis of the cyclic heptapeptide microcystin. J. Biochem. 2000, 127, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tillett, D.; Dittmann, E.; Erhard, M.; Von Döhren, H.; Börner, T.; Neilan, B.A. Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: An integrated peptide-polyketide synthetase system. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christiansen, G.; Fastner, J.; Erhard, M.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. Microcystin biosynthesis in Planktothrix: Genes, evolution, and manipulation. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rouhiainen, L.; Vakkilainen, T.; Siemer, B.L.; Buikema, W.; Haselkorn, R.; Sivonen, K. Genes coding for hepatotoxic heptapeptides (microcystins) in the cyanobacterium Anabaena strain 90. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fewer, D.P.; Wahlsten, M.; Österholm, J.; Jokela, J.; Rouhiainen, L.; Kaasalainen, U.; Rikkinen, J.; Sivonen, K. The genetic basis for O-acetylation of the microcystin toxin in cyanobacteria. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rounge, T.B.; Rohrlack, T.; Nederbragt, A.J.; Kristensen, T.; Jakobsen, K.S. A genome-wide analysis of nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene clusters and their peptides in a Planktothrix rubescens strain. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heck, K.; Alvarenga, D.O.; Shishido, T.K.; Varani, A.M.; Dörr, F.A.; Pinto, E.; Rouhiainen, L.; Jokela, J.; Sivonen, K.; Fiore, M.F. Biosynthesis of microcystin hepatotoxins in the cyanobacterial genus Fischerella. Toxicon 2018, 141, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shishido, T.K.; Jokela, J.; Humisto, A.; Suurnäkki, S.; Wahlsten, M.; Alvarenga, D.O.; Sivonen, K.; Fewer, D.P. The biosynthesis of rare homo-amino acid containing variants of microcystin by a benthic cyanobacterium. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, A.; Harel, M.; Kaplan-Levy, R.N.; Hadas, O.; Sukenik, A.; Dittmann, E. The languages spoken in the water body (or the biological role of cyanobacterial toxins). Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, A.; Kinnear, S. Interpreting the possible ecological role(s) of cyanotoxins: Compounds for competitive advantage and/or physiological aide? Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2239–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rantala, A.; Fewer, D.P.; Hisbergues, M.; Rouhiainen, L.; Vaitomaa, J.; Börner, T.; Sivonen, K. Phylogenetic evidence for the early evolution of microcystin synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burford, M.A.; Carey, C.C.; Hamilton, D.P.; Huisman, J.; Paerl, H.W.; Wood, S.A.; Wulff, A. Perspective: Advancing the research agenda for improving understanding of cyanobacteria in a future of global change. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Barnard, M.A. Mitigating the global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Moving targets in a human- and climatically-altered world. Harmful Algae 2020, 96, 101845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barruffa, A.S.; Sposito, V.; Faggian, R. Climate change and cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Adaptation practices for developing countries. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2021, 72, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, S.L.; Brunner, S.L.; Klump, J.V.; Houghton, E.M.; Miller, T.R. Spatial analysis of toxic or otherwise bioactive cyanobacterial peptides in Green Bay, Lake Michigan. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millie, D.F.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Dyble, J.; Pigg, R.; Rediske, R.; Klarer, D.M.; Litaker, R.W.; Tester, P.A. Influence of environmental conditions on late-summer cyanobacterial abundance in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2008, 11, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, K.A.; Sullivan, J.M.; Boyer, G.L. Harmful algal blooms in Sodus Bay, Lake Ontario: A comparison of nutrients, marina presence, and cyanobacterial toxins. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; Miller, C.; Arhonditsis, G.; Boyer, G.L.; Carmichael, W.; Charlton, M.N.; Confesor, R.; Depew, D.C.; Höök, T.O.; Ludsin, S.A.; et al. The re-eutrophication of Lake Erie: Harmful algal blooms and hypoxia. Harmful Algae 2016, 56, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffin, J.D.; Mishra, S.; Kane, D.D.; Bade, D.L.; Stanislawczyk, K.; Slodysko, K.N.; Jones, K.W.; Parker, E.M.; Fox, E.L. Cyanobacterial blooms in the central basin of Lake Erie: Potentials for cyanotoxins and environmental drivers. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Luo, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, J.; Liu, J. Occurrence and spatial distributions of microcystins in Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Clara, T.; Huang, F.; Wei, J.; Yang, F. Identification and characterization of the dominant Microcystis sp. cyanobacteria detected in Lake Dong Ting, China. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2019, 82, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olokotum, M.; Mitroi, V.; Troussellier, M.; Semyalo, R.; Bernard, C.; Montuelle, B.; Okello, W.; Quiblier, C.; Humbert, J.F. A review of the socioecological causes and consequences of cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Victoria. Harmful Algae 2020, 96, 101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozhova, O.M.; Kobanova, G.I. Phytoplankton of Lake Hövsgöl. In The Geology, Biodiversity and Ecology of Lake Hövsgöl; Goulden, C.E., Sitnikova, T., Gelhaus, J., Boldgiv, B., Eds.; Backhuys: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 387–402. ISBN 9789057821622. [Google Scholar]
- Sodnom, N.; Losev, N. Natural Conditions and Resources of Hovsgol Region; Nedra: Moscow, Russia, 1976; pp. 10–355. [Google Scholar]
- Zagorenko, G.F. New Data about several algae of Lake Khubsugul. In Natural Conditions and Resources of Hovsgol Region; Losev, N.F., Tsevgmid, D., Eds.; Irkutsk State University: Irkutsk, Russia, 1972; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zagorenko, G.F.; Kozhova, O.M. Structure and ecological data of summer phytoplankton of Lake Hovsgol in 1971. In Natural Conditions and Resources of Hovsgol Region; Batmunh, J., Losev, N.F., Eds.; Irkutsk State University: Irkutsk, Russia, 1973; pp. 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhova, O.M.; Zagorenko, G.F.; Ladejtschikova, V.K. Peculiarities of annual and season dynamics of phytoplankton in Lake Khubsugul. Hydrobiol. J. 1977, 36, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhov, M.M.; Antipova, H.L.; Vasilyeva, G.L.; Nikolaeva, E.P. On the plankton of Lake Khubsugul (Kosogol). Tr. Limnol. Inst. 1965, 26, 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhova, O.M.; Izmest’eva, L.R.; Erbaeva, E.A. A review of the hydrobiology of Lake Khubsugul (Mongolia). Hydrobiologia 1994, 291, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhova, O.M.; Kobanova, G.I.; Izmestyeva, L.R. Summer Phytoplankton of Lake Khubsugul (Mongolia). Hydrobiol. J. 2000, 36, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindák, F.; Zagorenko, G.F. Contribution to the knowledge of the species composition of summer phytoplankton of Lake Hubsugul, Mongolia. Folia Geobot. Phytotaxon. 1992, 27, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorenko, G.F.; Prozorov, B.A. A new species of the genus Tolypothrix (Scytonemataceae, Cyanophyta) from the Khubsugul Lake in Mongolia. Bot. Zhurnal 1983, 68, 1128–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Belykh, O.I.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Fedotov, A.F. Abundance, morphological diversity, and spatial distribution of autotrophic picoplankton in Lake Hovsgol (Mongolia). Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2005, 8, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likens, G.E. Primary production of inland aquatic ecosystems. In Primary Production of the Biosphere; Leith, H., Whittaker, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SanPin 2.1.5.980-00; On the Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare of the Population (with the Amendments and Additions). Minzdrav of Russia: Moscow, Russia, 1999; p. 164.
- SanPiN 1.2.3685-21; Hygienic Standards and Requirements for Ensuring the Safety and (or) Harmlessness of Environmental Factors for Humans. Minzdrav of Russia: Moscow, Russia, 2021; p. 469.
- MUK 4.2.1884-04. 4.1; Control Methods. Biological and Microbiological Factors. Sanitary-Microbiological and Sanitary-Parasitological Analysis of Surface Water Bodies. Standartinform: Moscow, Russia, 2004; p. 108.
- Cruz, A.T.; Cazacu, A.C.; Allen, C.H. Pantoea agglomerans, a plant pathogen causing human disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller, H.E.; Brenner, D.J.; Fanning, G.R.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Kampfer, P. Emended description of Buttiauxella agrestis with recognition of six new species of Buttiauxella and two new species of Kluyvera: Buttiauxella ferragutiae sp. nov., Buttiauxella gaviniae sp. nov., Buttiauxella brennerae sp. nov., Buttiauxella izardii sp. nov., Buttiauxella noackiae sp. nov., Buttiauxella warmboldiae sp. nov., Kluyvera cochleae sp. nov., and Kluyvera georgiana sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, T.; Chowdhury, G.; Pazhani, G.P.; Shinoda, S. Vibrio fluvialis: An emerging human pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saraoui, T.; Leroi, F.; Björkroth, J.; Pilet, M.F. Lactococcus piscium: A psychrotrophic lactic acid bacterium with bioprotective or spoilage activity in food—A review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clements, K.D.; Sutton, D.C.; Choat, J.H. Occurrence and characteristics of unusual protistan symbionts from surgeonfishes (Acanthuridae) of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Biol. 1989, 102, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Zhao, D.L.; Shen, L.L.; Jing, C.L.; Zhang, C.S. Application and mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis in biological control of plant disease. In Role of Rhizospheric Microbes in Soil: Stress Management and Agricultural Sustainability; Meena, V.S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alebouyeh, M.; Gooran, O.P.; Azimi-Rad, M.; Tajbakhsh, M.; Tajeddin, E.; Jahani, S.S.; Nazemalhosseini, M.E.; Zali, M.R. Fatal sepsis by bacillus circulans in an immunocompromised patient. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2011, 3, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waters, J.L.; Ley, R.E. The human gut bacteria Christensenellaceae are widespread, heritable, and associated with health. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egan, M.; Dempsey, E.; Ryan, C.A.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. The Sporobiota of the Human Gut. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1863134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Dong, X. Cellulosilyticum ruminicola gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the rumen of yak, and reclassification of Clostridium lentocellum as Cellulosilyticum lentocellum comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerritsen, J.; Umanets, A.; Staneva, I.; Hornung, B.; Ritari, J.; Paulin, L.; Rijkers, G.T.; de Vos, W.M.; Smidt, H. Romboutsia hominis sp. nov., the first human gut-derived representative of the genus romboutsia, isolated from ileostoma effluent. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3479–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumas-Bilak, E.; Carlier, J.P.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Mory, F.; Teyssier, C.; Gay, B.; Campos, J.; Marchandin, H. Acidaminococcus intestini sp. nov., isolated from human clinical samples. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2314–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Auria, G.; Galán, J.C.; Rodríguez-Alcayna, M.; Moya, A.; Baquero, F.; Latorre, A. Complete genome sequence of Acidaminococcus intestini RYC-MR95, a gram-negative bacterium from the phylum Firmicutes. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 7008–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivacheva, M.A.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Krasnopeev, A.Y.; Potapov, S.A.; Choydash, B.; Belykh, O.I. Microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in the benthos of Lake Baikal. Bull. Irkutsk. State Univ. Ser. Biol. 2016, 17, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Jungblut, A.D.; Neilan, B.A. Molecular identification and evolution of the cyclic peptide hepatotoxins, microcystin and nodularin, synthetase genes in three orders of cyanobacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2006, 185, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanenko, V.D.; Oksijuk, O.P.; Zhukinsky, V.N.; Stolberg, F.V.; Lavrik, V.I. Ecological Impact Assessment of Hydrotechnical Constructions on Water Bodies; Naukova Dumka: Kijev, Ukraina, 1990; p. 291. [Google Scholar]
- Bogoyavlensky, B. (Ed.) Atlas of Lake Hubsugul; GUGK: Moscow, Russia, 1989; p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasova, E.N.; Mamontova, E.A.; Mamontov, A.A.; Goreglyad, A.V.; Tsypukova, S.S.; Tkatchenko, L.L. The spatial and time change ability of chemical composition of water of Lake Hovsgol (Mongolia). Environ. Chem. 2017, 26, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasova, E.N. Components of trophic status in water of Lake Baikal, the Lake Hovsgol and the Lake Teletskoe. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 1998, 5, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Goulden, C.E.; Sitnikova, T.Y.; Gelhaus, J.; Boldgiv, B. The Geology, Biodiversity and Ecology of Lake Hövsgöl (Mongolia); Backhuys: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2006; p. 525. ISBN 9789057821622. [Google Scholar]
- Sorokovikova, L.M.; Tomberg, I.V.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Molozhnikova, E.V.; Khodzher, T.V. Low water level in the Selenga River and reduction of silica input to Lake Baikal. Inland Waters 2019, 9, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 48216-001; Integrated Livelihoods Improvement and Sustainable Tourism in Khuvsgul Lake National Park Project. MON 9873. Water Quality Monitoring Program for Khuvsgul Lake National Park–Final Consultant Report. Asian Development Bank: UlaanBaatar, Mongolia, 2020; p. 703.
- Khodzher, T.V.; Domysheva, V.M.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Golobokova, L.P. Methods for monitoring the chemical composition of Lake Baikal water. In Novel Methods for Monitoring and Managing Land and Water Resources in Siberia; Mueller, L., Sheudshen, A.K., Eulenstein, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 113–132. [Google Scholar]
- Khodzher, T.V.; Domysheva, V.M.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Sakirko, M.V.; Tomberg, I.V. Current chemical composition of Lake Baikal water. Inland Waters 2017, 7, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyungerel, B. Reflection of the global warming in the change of the Lake Khuvsgul. Bull. Buryat State Univ. Biol. Geogr. 2011, 4, 190–192. [Google Scholar]
- Bezuijen, M.R.; Russell, M.; Zomer, R.J.; Enkhtaivan, D. Building the Climate Change Resilience of Mongolia’s Blue Pearl: A Case Study of Khuvsgul Lake National Park; Asian Development Bank: Manila, Philippines, 2020; p. 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jeong, J.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, H.; Simon Wang, S.Y.; Linderholm, H.W.; Fang, K.; Wu, X.; Chen, D. Abrupt shift to hotter and drier climate over inner East Asia beyond the tipping point. Science 2020, 370, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandintsetseg, B.; Greene, J.S.; Goulden, C.E. Trends in extreme daily precipitation and temperature near Lake Hövsgöl, Mongolia. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboal, M.; Puig, M.Á. Intracellular and dissolved microcystin in reservoirs of the river Segura basin, Murcia, SE Spain. Toxicon 2005, 45, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; El-Sharouny, H.M.; Ali, W.S.M. Microcystin production in benthic mats of cyanobacteria in the Nile River and irrigation canals, Egypt. Toxicon 2006, 47, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokovikova, E.G.; Belykh, O.I.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Kotsar, O.V.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Timoshkin, O.A.; Parfenova, V.V. Diversity of cyanobacterial species and phylotypes in biofilms from the littoral zone of Lake Baikal. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorofeyuk, N.I.; Tsetsegma, D. Algae Flora in Mongolia; Ulzijkhutag, N., Gunin, P.D., Eds.; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 2002; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Barboza, G.F.O.; Gorlach-Lira, K.; Sassi, C.F.C.; Sassi, R. Microcystins production and antibacterial activity of cyanobacterial strains of Synechocystis, Synechococcus and Romeria from water and coral reef organisms (Brazil). Rev. Biol. Trop. 2017, 65, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gagunashvili, A.N.; Andrésson, Ó.S. Distinctive characters of Nostoc genomes in cyanolichens. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivonen, K.; Namikoshi, M.; Evans, W.R.; Färdig, M.; Carmichael, W.W.; Rinehart, K.L. Three new microcystins, cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxins, from Nostoc sp. strain 152. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1992, 5, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivonen, K.; Carmichael, W.W.; Namikoshi, M.; Rinehart, K.L.; Dahlem, A.M.; Niemela, S.I. Isolation and characterization of hepatotoxic microcystin homologs from the filamentous freshwater cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain 152. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2650–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dodds, W.K.; Gudder, D.A.; Mollenhauer, D. The ecology of Nostoc. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.C.; Monroe, E.A.; Eisman, E.B.; Gerwick, L.; Sherman, D.H.; Gerwick, W.H. The unique mechanistic transformations involved in the biosynthesis of modular natural products from marine cyanobacteria. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 1048–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, I.; Jokela, J.; Fewer, D.P.; Wahlsten, M.; Rikkinen, J.; Sivonen, K. Discovery of rare and highly toxic microcystins from lichen-associated cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain IO-102-I. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5756–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinteich, J.; Puddick, J.; Wood, S.A.; Hildebrand, F.; Laughinghouse, H.D.; Pearce, D.A.; Dietrich, D.R.; Wilmotte, A. Toxic cyanobacteria in Svalbard: Chemical diversity of microcystins detected using a liquid chromatography mass spectrometry precursor ion screening method. Toxins 2018, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, S.A.; Mountfort, D.; Selwood, A.I.; Holland, P.T.; Puddick, J.; Cary, S.C. Widespread Distribution and Identification of Eight Novel Microcystins in Antarctic Cyanobacterial Mats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7243–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinteich, J.; Wood, S.A.; Puddick, J.; Schleheck, D.; Kupper, F.C.; Dietrich, D. Potent toxins in Arctic environments--presence of saxitoxins and an unusual microcystin variant in Arctic freshwater ecosystems. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 206, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quiblier, C.; Wood, S.; Echenique-Subiabre, I.; Heath, M.; Villeneuve, A.; Humbert, J.-F. A review of current knowledge on toxic benthic freshwater cyanobacteria—ecology, toxin production and risk management. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5464–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mats, V.D. The sedimentary fill of the Baikal Basin: Implications for rifting age and geodynamics. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2012, 53, 936–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuz’min, M.I.; Yarmolyuk, V.V. Mountain growth and climatic variations in the Earth’s history. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2006, 47, 4–20. [Google Scholar]
- Fedotov, A.P.; De Batist, M.; Pouls, T. Tectonic evolution of the southwestern wall of the Baikal Rift Zone. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2006, 410, 1053–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logatchev, N.A.; Antoshenko-Olenev, I.V.; Bazarov, D.B.; Galkin, V.I.; Goldurev, G.S.; Endrikhinskij, A.S.; Zolatorev, A.G.; Sizikov, A.I.; Ufimzev, G.F. The Uplands of the West Baikal and Trans-Baikal Regions; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1974; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Zubkov, I.N.; Kuzmin, A.V.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Belykh, O.I.; Smirnov, V.I.; Ivanov, A.V.; Shagun, V.A.; Grachev, M.A.; Fedorova, G.A. Method for Determination of Saxitoxins Using Hplc-Ms with 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine Precolumn Derivatization. Proc. Univ. Appl. Chem. Biotechnol. 2018, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshkin, O.A.; Moore, M.V.; Kulikova, N.N.; Tomberg, I.V.; Malnik, V.V.; Shimaraev, M.N.; Troitskaya, E.S.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Zaitseva, E.P.; et al. Groundwater contamination by sewage causes benthic algal outbreaks in the littoral zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia). J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovskaya, G.I. Ecological monitoring of phytoplankton in Lake Baikal. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2000, 3, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.C.; Weathers, K.C.; Cottingham, K.L. Gloeotrichia echinulata blooms in an oligotrophic lake: Helpful insights from eutrophic lakes. J. Plankton Res. 2008, 30, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winter, J.G.; Desellas, A.M.; Fletcher, R.; Heintsch, L.; Morley, A.; Nakamoto, L.; Utsumi, K. Algal blooms in Ontario, Canada: Increases in reports since 1994. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2011, 27, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callieri, C.; Bertoni, R.; Contesini, M.; Bertoni, F. Lake level fluctuations boost toxic cyanobacterial “oligotrophic blooms”. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmaso, N.; Capelli, C.; Shams, S.; Cerasino, L. Expansion of bloom-forming Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) to the deep lakes south of the Alps: Colonization patterns, driving forces and implications for water use. Harmful Algae 2015, 50, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimptsch, J.; Woelfl, S.; Osorio, S.; Valenzuela, J.; Moreira, C.; Ramos, V.; Castelo-Branco, R.; Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, V. First record of toxins associated with cyanobacterial blooms in oligotrophic North Patagonian lakes of Chile-a genomic approach. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2016, 101, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19458: 2006; Water Quality—Sampling for Microbiological Analysis. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; p. 18.
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Band 19/1. Cyanoprocaryota. Teil/Part 1: Chroococcales; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; p. 554. ISBN 9783827408907. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Bd. 19/2. Cyanoprokaryota. Teil/Part 2: Oscillatoriales; Büdel, B., Krienitz, L., Gärtner, G., Schagerl, M., Eds.; Springer: Munchen, Germany, 2005; p. 759. ISBN 9783827421111. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 19/3. Cyanoprokaryota. Teil/Part 3: Heterocytous genera; Büdel, B., Gärtner, G., Krienitz, L., Schagerl, M., Eds.; Springer Spektrum: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; p. 1149. ISBN 978-3-8274-0932-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belykh, O.I.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Fedorova, G.A.; Kaluzhnaya, O.V.; Korneva, E.S.; Sakirko, M.V.; Sherbakova, T.A. Presence and genetic diversity of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria (Anabaena and Microcystis) in Lake Kotokel (Russia, Lake Baikal Region). Hydrobiologia 2011, 671, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Limnological Analyses; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 429. ISBN 978-0-387-98928-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bolleter, W.T.; Bushman, C.J.; Tidwell, P.W. Spectrophotometric Determination of Ammonia as Indophenol. Anal. Chem. 1961, 33, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8467: 1993; Water Quality—Determination of Permanganate Index. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993; p. 4.
- Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package ‘Corrplot’: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. (Version 0.92). Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Wickham, H. The split-apply-combine strategy for data analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 40, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


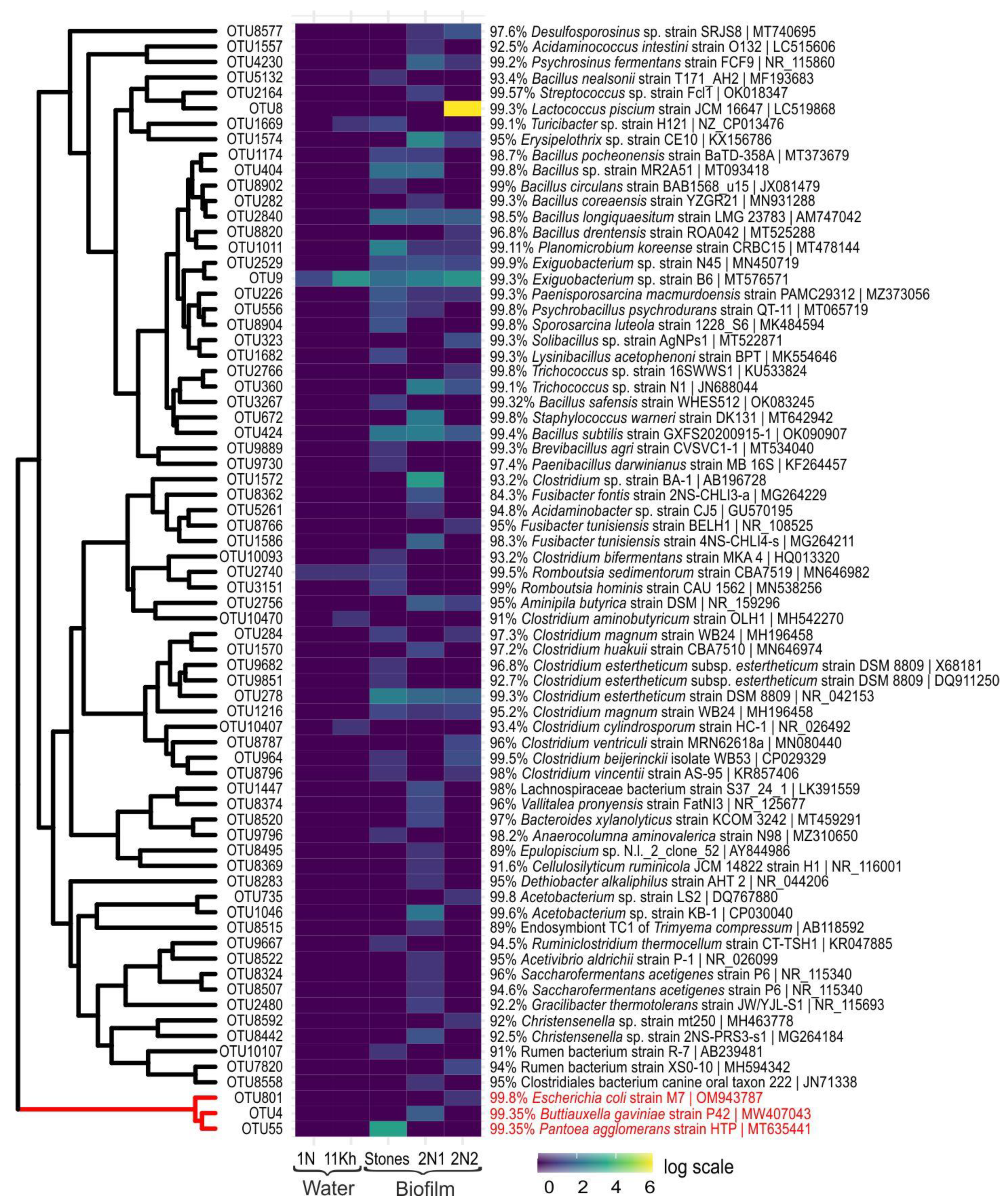

| No | Species by Microscopy | Number of OTUs 1 | Closest Homologue in GenBank | Identity, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anabaenasp. | - | - | - |
| 2 | Calothrix parietina | 2 | C. parietina 2T10 | 99.1, 97.7 |
| 3 | Chamaesiphon subglobosus | 1 | C. subglobosus PCC 7430 | 99.1 |
| 4 | Chamaesiphon polonicus | 2 | C. polonicus SAG 32.87 | 99.1, 99.7 |
| 5 | Chroococcus minutus | 12 | Pseudocapsa sp. Ru3-14/Aliterella gigantea PJ102 | 97.2–99.1 |
| 6 | Chroococcus sp. | 12 | Pseudocapsa sp. Ru3-14/Aliterella gigantea PJ102 | 97.2–99.1 |
| 7 | Coelosphaerium kuetzingianum | - | - | - |
| 8 | Dolichospermum lemmermannii | - | - | - |
| 9 | Gloeobacter sp. | 1 | Gloeobacter kilaueensis JS1 | 99.3 |
| 10 | Leibleinia epiphytica | 15 | Timaviella circinata GR4/T. edaphica Golos-9-1/Timaviella sp. Us-6-3 | 97.5–99.1 |
| 11 | Leptolyngbya sp. | 6 | Leptolyngbya sp. CENA293 | 95.7–97.5 |
| 12 | Limnococcus limneticus | - | - | - |
| 13 | Nostoc sp. | 1 | Nostoc sp. LEGE 04357 | 100 |
| 14 | Oscillatoria sp. | - | - | - |
| 15 | Planktothrixsp. | - | - | - |
| 16 | Pseudanabaena galeata | 2 | Pseudanabaena frigida ULC067 | 99.8, 97.8 |
| 17 | Pseudanabaenasp. | - | - | - |
| 18 | Snowella rosea | - | - | - |
| 19 | S. lacustris | - | - | - |
| 20 | Tolypothrix mongolica | - | - | - |
| 21 | Trichodesmium lacustre | - | - | - |
| 22 | Tychonema tenue | 1 | Tychonema sp. SAG 23.89/M. pseudautumnalis Ak1609/P. autumnale CCALA 143 | 100 |
| 23 | Rivularia coadunata | 1 | Rivularia sp. VP4-08 | 99.1 |
| 24 | - | 2 | Altericista variichlora CALU 1173 | 98.7, 98.9 |
| 25 | - | 1 | Shackletoneilla antarctica ANT.L18.1 | 99.6 |
| 26 | - | 1 | Nodosilinea sp. 19D10hp | 99.8 |
| 27 | - | 1 | Jaaginema geminatum SAG 1459-8 | 100 |
| 28 | - | 1 | Pseudanabaena foetida TNS-AL-57779 | 100 |
| 29 | - | 6 | Stenomitos frigidus ANT.LMA.1, ACT684 | 98–100 |
| 30 | - | 3 | Phormidesmis priestleyi ANT.LPR2.6 | 99.1–100 |
| 31 | - | 1 | Scytonematopsis contorta HA4292-MV4 | 99.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belykh, O.I.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tomberg, I.V.; Fedorova, G.A.; Kuzmin, A.V.; Krasnopeev, A.Y.; Suslova, M.Y.; Potapov, S.A.; Belykh, T.I.; Norovsuren, J.; et al. Water Quality, Toxicity and Diversity of Planktonic and Benthic Cyanobacteria in Pristine Ancient Lake Khubsugul (Hövsgöl), Mongolia. Toxins 2023, 15, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15030213
Belykh OI, Sorokovikova EG, Tomberg IV, Fedorova GA, Kuzmin AV, Krasnopeev AY, Suslova MY, Potapov SA, Belykh TI, Norovsuren J, et al. Water Quality, Toxicity and Diversity of Planktonic and Benthic Cyanobacteria in Pristine Ancient Lake Khubsugul (Hövsgöl), Mongolia. Toxins. 2023; 15(3):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15030213
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelykh, Olga I., Ekaterina G. Sorokovikova, Irina V. Tomberg, Galina A. Fedorova, Anton V. Kuzmin, Andrey Yu. Krasnopeev, Maria Yu. Suslova, Sergey A. Potapov, Tatiana I. Belykh, Jadambaa Norovsuren, and et al. 2023. "Water Quality, Toxicity and Diversity of Planktonic and Benthic Cyanobacteria in Pristine Ancient Lake Khubsugul (Hövsgöl), Mongolia" Toxins 15, no. 3: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15030213
APA StyleBelykh, O. I., Sorokovikova, E. G., Tomberg, I. V., Fedorova, G. A., Kuzmin, A. V., Krasnopeev, A. Y., Suslova, M. Y., Potapov, S. A., Belykh, T. I., Norovsuren, J., Galachyants, A. D., & Tikhonova, I. V. (2023). Water Quality, Toxicity and Diversity of Planktonic and Benthic Cyanobacteria in Pristine Ancient Lake Khubsugul (Hövsgöl), Mongolia. Toxins, 15(3), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15030213






