Recent Insights into Sample Pretreatment Methods for Mycotoxins in Different Food Matrices: A Critical Review on Novel Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
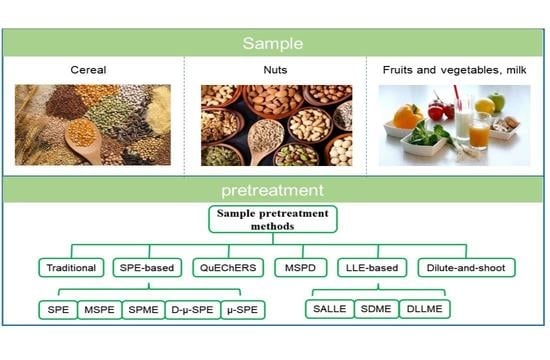
2. Sample Pretreatment Methods
2.1. Traditional Used Methods
2.2. SPE-Based Approaches
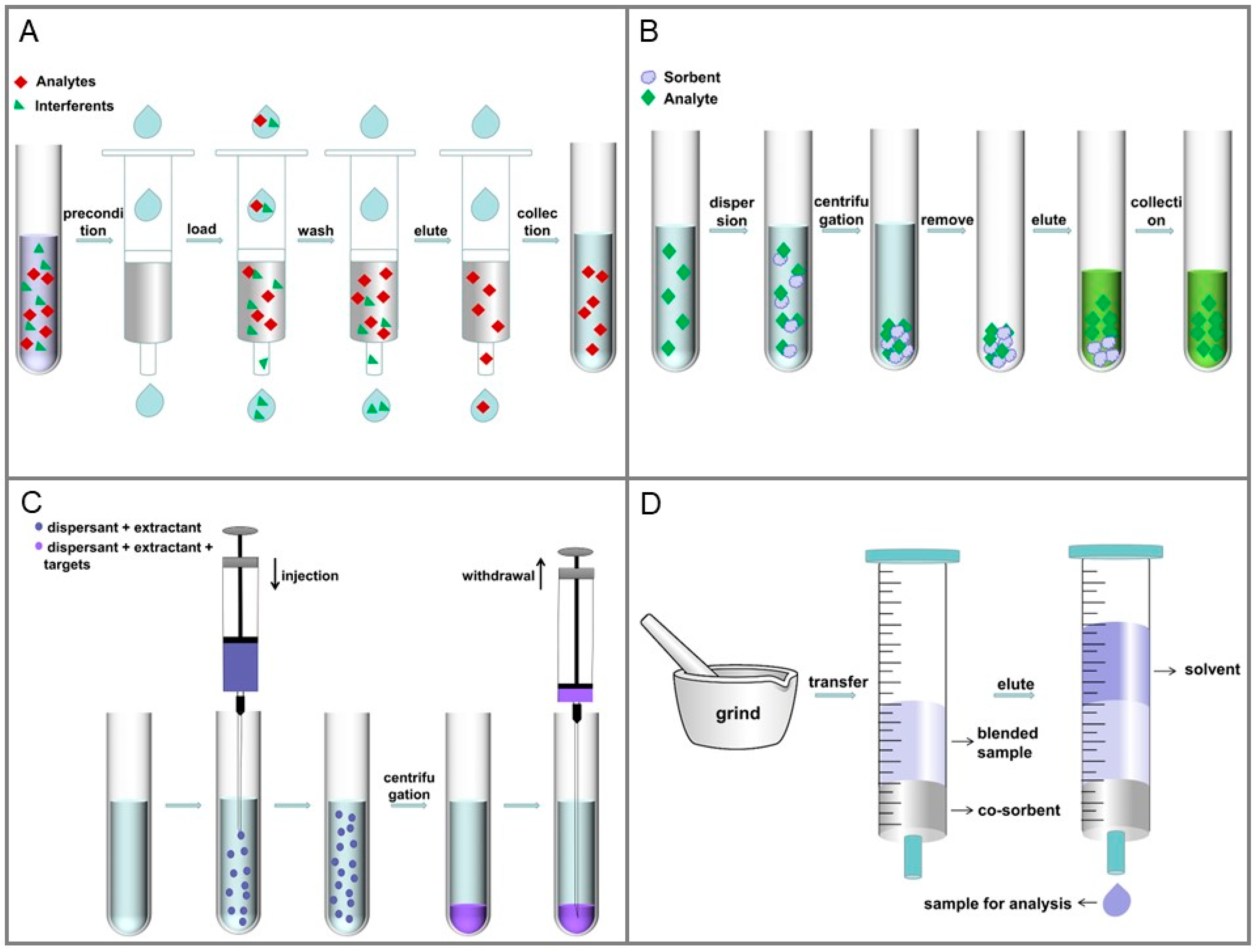
2.2.1. Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE)
Traditional Materials Used in SPE
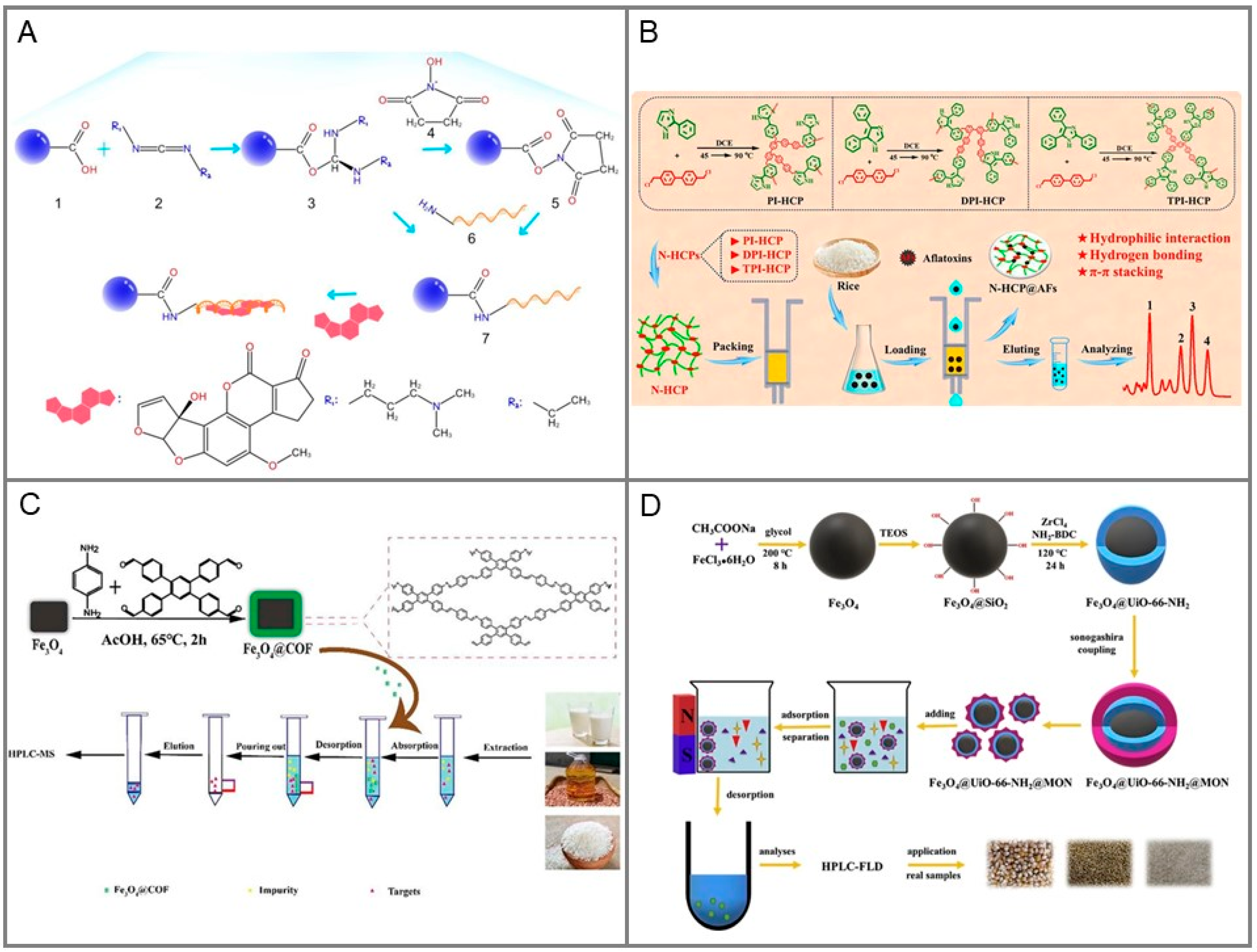
From Traditional to Novel Materials in SPE Columns
A new Perspective of SPE: Online Technology
2.2.2. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction (MSPE)
2.2.3. Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME)
2.2.4. Dispersive Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction (D-μ-SPE)
2.2.5. Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction (μ-SPE)
2.2.6. Summary and Recommendations
2.3. LLE-Based Approaches
2.3.1. Salting-Out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction (SALLE)
2.3.2. Single-Drop Microextraction (SDME)
2.3.3. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction (DLLME)
2.4. QuEChERS
2.5. Matrix Solid Phase Dispersion (MSPD)
2.6. Dilute-And-Shoot
2.7. Hybridization of Different Sample Pretreatment Methods
2.8. Recommendations
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Qiu, J.; Xu, J.; Shi, J. Fusarium Toxins in Chinese Wheat since the 1980s. Toxins 2019, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.W.; Subrahmanyam, S.; Piletsky, S. Analytical methods for determination of mycotoxins: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 632, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide contamination of food-crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascari, X.; Ramos, A.; Marín, S.; Sanchís, V. Mycotoxins and beer. Impact of beer production process on mycotoxin contamination. A review. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, W.; Smith, J.; Simpson, B.; Oldham, J.; Scott, P.M. Aflatoxins in food: Occurrence, biosynthesis, effects on organisms, detection, and methods of control. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1991, 30, 403–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainio, H.; Heseltine, E.; Wilbourn, J. Report on an IARC working group meeting on some naturally occurring substances. Int. J. Cancer 1993, 53, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, J.P.F.; Placinta, C.M.; Macdonald, A.M.C. Fusarium mycotoxins: A review of global implications for animal health, welfare and productivity. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1999, 80, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Xie, S.; Xu, F.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Pan, Y.; Huang, L.; Peng, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Ochratoxin A: Toxicity, oxidative stress and metabolism. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, E.; Hou, H.; Hu, W.; Dong, H.; Li, X. Removing and detoxifying methods of patulin: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Das, M.; Tripathi, A. Occurrence and toxicity of a fusarium mycotoxin, zearalenone. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2710–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Deng, T.; Xiao, Y.; Jin, C.; Lyu, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Yang, H. Emerging Alternaria and Fusarium mycotoxins in tomatoes and derived tomato products from the China market: Occurrence, methods of determination, and risk evaluation. Food Control 2023, 145, 109464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, N.I.; Hussain, S.; Javed, M.; Rehman, H.; Shahzady, T.G.; Parveen, B.; Ali, K.G. Nature of aflatoxins: Their extraction; analysis; control. J. Food Saf. 2018, 38, e12561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Banerjee, K. A Review: Sample Preparation and Chromatographic Technologies for Detection of Aflatoxins in Foods. Toxins 2020, 12, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Liu, F.; Fang, F.; Ding, X.; Han, Q.; Tan, Y.; Peng, C. Solid-phase extraction techniques based on nanomaterials for mycotoxin analysis: An overview for food and agricultural products. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 2273–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-Pérez, J.F.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Hitzler, D.; Castro-Guerrero, F.G.; Gámiz-Gracia, L.; García-Campaña, A.M. Simple determination of aflatoxins in rice by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to chemical post-column derivatization and fluorescence detection. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhou, T.; Wan, Y.; Tan, T. A Simple Strategy Based on Deep Eutectic Solvent for Determination of Aflatoxins in Rice Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Hao, L.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q. Phenyl-imidazole based and nitrogen rich hyper-crosslinked polymer for sensitive determination of aflatoxins. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.P.; Madureira, F.; de Azevedo Vargas, E.; Faria, A.F.; Augusti, R. Development and validation of a multianalyte method for quantification of mycotoxins and pesticides in rice using a simple dilute and shoot procedure and UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizy, J.; Jahani, M.; Beigbabaei, A. Graphene Adsorbent-Based Solid-Phase Extraction for Aflatoxins Clean-Up in Food Samples. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, B.; Hao, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q. Preparation of magnetic hyper-crosslinked polymer for high efficient preconcentration of four aflatoxins in rice and sorghum samples. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Alshehri, S.; Bando, Y.; Yamauchi, Y.; Wu, Q. Design of hyper-cross-linked polymers with tunable polarity for effective preconcentration of aflatoxins in grain. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhang, F. Synthesis of a magnetic covalent organic framework as sorbents for solid-phase extraction of aflatoxins in food prior to quantification by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-Y.; Liu, J.-M.; Wang, Z.-H.; Lv, S.-W.; Zhao, N.; Wang, S. Integration of Fe3O4@UiO-66-NH2@MON core-shell structured adsorbents for specific preconcentration and sensitive determination of aflatoxins against complex sample matrix. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Xu, C.; Jiang, N.; Wang, J.; Ding, C.-F. Poly (methacrylic acid-co-diethenyl-benzene) monolithic microextraction column and its application to simultaneous enrichment and analysis of mycotoxins. Talanta 2018, 178, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S.A.; Sukor, R.; Ismail, M.N.; Selamat, J. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction (DLLME) and LC-MS/MS Analysis for Multi-Mycotoxin in Rice Bran: Method Development, Optimization and Validation. Toxins 2021, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Osboo, R.; Maham, M. Pre-Concentration and Extraction of Aflatoxins from Rice Using Air-Assisted Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 2816–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somsubsin, S.; Seebunrueng, K.; Boonchiangma, S.; Srijaranai, S. A simple solvent based microextraction for high performance liquid chromatographic analysis of aflatoxins in rice samples. Talanta 2018, 176, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Osboo, R.; Maham, M.; Nasrollahzadeh, M. Rapid and sensitive extraction of aflatoxins by Fe3O4/zeolite nanocomposite adsorbent in rice samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gab-Allah, M.A.; Tahoun, I.F.; Yamani, R.N.; Rend, E.A.; Shehata, A.B. Eco-friendly and sensitive analytical method for determination of T-2 toxin and HT-2 toxin in cereal products using UPLC-MS/MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 107, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardani, F.; Mirzajani, R.; Tamsilian, Y.; Kiasat, A.; Farajpour, F.B. A novel immunoaffinity column based metal–organic framework deep eutectic solvents @ molecularly imprinted polymers as a sorbent for the solid phase extraction of aflatoxins AFB1, AFB2, AFG1 and AFG2 from cereals samples. Microchem. J. 2023, 187, 108366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró-Abella, E.; Herrero, P.; Canela, N.; Arola, L.; Ras, R.; Fontanals, N.; Borrull, F. Determination of Trichothecenes in Cereal Matrices Using Subcritical Water Extraction Followed by Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Sun, Y.; He, L.; Zhao, W.; Xiang, G.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, S. A polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes/dual ligands-based magnetic adsorbent for effective extraction of aflatoxins in cereals via multiple interactions. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, J.J.; Cai, Z.; Huang, B.F.; Jin, M.C.; Ren, Y.P. Simultaneous determination of five Alternaria toxins in cereals using QuEChERS-based methodology. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1068–1069, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Peng, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, Z.; Fan, C.; Sun, Y. QuEChERS extraction followed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determination of deoxynivalenol and zearalenone in cereals. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017, 28, 1477–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Tian, M.; Yan, X.; Xiao, W. Isolation of Aflatoxin B1 from Moldy Foods by Solid-Phase Extraction Combined with Bifunctional Ionic Liquid-Based Silicas. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 8427580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoal, F.N.; de Azevedo Silva, D.; von Sperling de Souza, R.; de Oliveira, M.S.; Pereira, D.A.A.; de Souza, S.V.C. A Rapid Single-Extraction Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2, Fumonisin B1, and Zearalenone in Corn Meal by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1631–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltner, F.; Rampl, C.; Rychlik, M.; Zimmermann, T.; Rohe, A. Development and Validation of a Cost-Effective HPLC-FLD Method for Routine Analysis of Fumonisins B1 and B2 in Corn and Corn Products. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gab-Allah, M.A.; Choi, K.; Kim, B. Development of isotope dilution-liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for the accurate determination of type-A trichothecenes in grains. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Iqbal, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, T.; Du, Y. Rapid determination of fumonisin (FB1) by syringe SPE coupled with solid-phase fluorescence spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 226, 117549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Pan, A.; Zhang, C.; Guo, M.; Lou, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, X. Fast extraction of aflatoxins, ochratoxins and enniatins from maize with magnetic covalent organic framework prior to HPLC-MS/MS detection. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Jiang, K.; Fan, Z.; Di Mavungu, J.D.; Dong, M.; Guo, W.; Fan, K.; Campbell, K.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes-based magnetic solid-phase extraction for the determination of zearalenone and its derivatives in maize by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 2017, 79, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.B.; de Castro Gomes Vieira, C.M.; Orlando, R.M.; Faria, A.F. Simultaneous determination of fumonisins B1 and B2 in different types of maize by matrix solid phase dispersion and HPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahoun, I.; Gab-Allah, M.; Yamani, R.; Shehata, A. Development and validation of a reliable LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of deoxynivalenol and T-2 toxin in maize and oats. Microchem. J. 2021, 169, 106599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Guo, W.; Fan, K.; Han, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Nie, D. MIL-101(Cr)@Fe3O4 nanocomposites as magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the determination of multiple mycotoxins in agricultural products by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 2023, 146, 109540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Jiao, T.; Ali, S.; Xu, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q. Dispersive micro solid phase extraction based ionic liquid functionalized ZnO nanoflowers couple with chromatographic methods for rapid determination of aflatoxins in wheat and peanut samples. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Xu, D.; Wang, S.; Uchiyama, K. Inkjet-Based Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Method Coupled with UHPLC–MS/MS for the Determination of Aflatoxins in Wheat. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3027–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; An, J.; Sun, Y.; He, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, S. A simple and low-cost sample preparation for the effective extraction, purification and enrichment of aflatoxins in wheat by combining with ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 106036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; De Ruyck, K.; Uka, V.; Gámiz-Gracia, L.; García-Campaña, A.; De Saeger, S.; Diana Di Mavungu, J. In-house validation of a rapid and efficient procedure for simultaneous determination of ergot alkaloids and other mycotoxins in wheat and maize. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5567–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarolo, K.; Ferreira, C.; Kupski, L.; Badiale-Furlong, E. Optimization of Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Method for Extraction of Aflatoxins from Cornmeal. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 3342–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Development and evaluation of a rapid immunomagnetic extraction for effective detection of zearalenone in agricultural products. Food Control 2020, 110, 106973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, A.V.; de Moraes, M.H.P.; dos Santos, R.P.; Souza, Y.P.; da Nóbrega, A.W. Determination of Mycotoxins in Cereal-Based Porridge Destined for Infant Consumption by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 4049–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, F.; Li, P. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxins, fumonisin B1, T-2 and cyclopiazonic acid in agri-products by immunomagnetic solid-phase extraction coupled with UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, N.; Sereshti, H. Electrospun polymer composite nanofiber-based in-syringe solid phase extraction in tandem with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with HPLC-FD for determination of aflatoxins in soybean. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, J.-J.; Lai, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-C. Using Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled with Reactive Carbon Fiber Ionization-Mass Spectrometry for the Detection of Aflatoxin B1 from Complex Samples. Separations 2022, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara-Durán, J.; Moreno-González, D.; García-Reyes, J.; Molina-Díaz, A. Use of a modified QuEChERS method for the determination of mycotoxin residues in edible nuts by nano flow liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H.; Wei, Q. A novel fluorescence biosensor based on CRISPR/Cas12a integrated MXenes for detecting Aflatoxin B1. Talanta 2023, 252, 123773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Chu, C.; Warner, E.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Chai, K.; Cao, J.; Peng, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Rapid microwave-assisted dispersive micro-solid phase extraction of mycotoxins in food using zirconia nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1561, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ma, Y.; Gan, B.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y. Development of QuEChERS clean-up based on EMR-lipid for simultaneous analysis of 9 mycotoxins, acaylamide and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in biscuit by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2023, 409, 135265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Yuste, A.; Walravens, J.; Urraca, J.L.; Abou-Hany, R.A.G.; Descalzo, A.B.; Orellana, G.; Rychlik, M.; De Saeger, S.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Analysis of alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether in foodstuffs by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; Peng, T.; Wang, J.; Yao, K.; Sun, S.; Shao, B.; Tang, J. Design of Multifunctional Nanostructure for Ultrafast Extraction and Purification of Aflatoxins in Foodstuffs. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10556–10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Su, X.; Wang, H. Simultaneous Determination of Aflatoxin B1, Bisphenol A, and 4-Nonylphenol in Peanut Oils by Liquid-Liquid Extraction Combined with Solid-Phase Extraction and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.-Z.; Liu, P.; Su, X.-C.; Liao, Y.-H.; Lei, N.-S.; Liang, Y.-H.; Zhou, S.-H.; Lin, W.-S.; Chen, J.; Feng, Y.-Q.; et al. Low-cost humic acid-bonded silica as an effective solid-phase extraction sorbent for convenient determination of aflatoxins in edible oils. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 970, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Adsorption of aflatoxins and ochratoxins in edible vegetable oils with dopamine-coated magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wan, L.; Bai, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Liao, X. Quantification of mycotoxins in vegetable oil by UPLC-MS/MS after magnetic solid-phase extraction. Food Addit. Contaminants. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2017, 34, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Fu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, X. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Aflatoxin B1, B2, G1 and G2 in Vegetable Oils Using Bare Fe3O4 as Magnetic Sorbents Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2020, 58, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Guan, J.; Dong, H.; Chen, J.; Liang, M.; Zhou, C.; Xian, Y.; Xu, X. Simultaneous determination of twelve mycotoxins in edible oil, soy sauce and bean sauce by PRiME HLB solid phase extraction combined with HPLC-Orbitrap HRMS. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1001671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhou, X. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2, and M1 in dairy products by high-performance liquid chromatography/fluorescence. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9840–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuib, N.; Makahleh, A.; Salhimi, S.; Saad, B. Determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products using high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence with post column photochemical derivatization. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1510, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yue, Z.; Fan, H.; Wu, S. Preparation and application of aptamer-functionalized sorbent for the analysis of ultra-trace aflatoxin M1 and analogues in milk. Microchem. J. 2021, 166, 106179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Huang, Q.; Fan, K.; Wu, L.; Nie, D.; Guo, W.; Wu, Y.; Han, Z. Reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticle composite-based solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of 9 mycotoxins in milk. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Sálamo, J.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M. Core-shell poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles for the extraction of estrogenic mycotoxins from milk and yogurt prior to LC–MS analysis. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campone, L.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Celano, R.; Pagano, I.; Di Sanzo, R.; Carabetta, S.; Russo, M.; Rastrelli, L. Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in milk samples from Italy analysed by online-SPE UHPLC-MS/MS. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebbi, A.; Nemati, M.; Mogaddam, M.A.; Farajzadeh, M.; Lotfipour, F. Dispersive micro–solid–phase extraction of aflatoxins from commercial soy milk samples using a green vitamin–based metal–organic framework as an efficient sorbent followed by high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry determination. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1673, 463099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsoy, N.; Sırtbaşı, B.; Şimşek, S.; Elik, A.; Altunay, N. Optimization and application of ultrasound-assisted sugar based deep eutectic solvent dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination and extraction of aflatoxin M1 in milk samples. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, J.-J.; Cong, J.-M.; Cai, Z.-X.; Zhang, J.-S.; Wang, J.-L.; Ren, Y.-P. Optimization for quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe extraction of mycotoxins and veterinary drugs by response surface methodology for application to egg and milk. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1532, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.M.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Gámiz-Gracia, L. Determination of Fusarium toxins in functional vegetable milks applying salting-out-assisted liquid–liquid extraction combined with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.M.; Moreno-González, D.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Gámiz-Gracia, L. Determination of Aflatoxins in Yogurt by Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction and HPLC with Photo-Induced Fluorescence Detection. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Cañás, I.; González-Jartín, J.M.; Alvariño, R.; Alfonso, A.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Detection of mycotoxins in cheese using an optimized analytical method based on a QuEChERS extraction and UHPLC-MS/MS quantification. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 135182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Fernández, D.; Rocío-Bautista, P.; Moreno-González, D.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Dilute-and-shoot versus clean-up approaches: A comprehensive evaluation for the determination of mycotoxins in nuts by UHPLC-MS/MS. LWT 2022, 169, 113976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapınar, H.S.; Balıkçıoğlu, A. Boron-doped activated carbon nanocomposite as a selective adsorbent for rapid extraction of aflatoxins in nut samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 112, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapınar, H.S.; Bilgiç, A. A new magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2-APTMS-CPA adsorbent for simple, fast and effective extraction of aflatoxins from some nuts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 105, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, A.R.S.; Barros, S.; Pena, A.; Silva, A.S. Development and Validation of QuEChERS Followed by UHPLC-ToF-MS Method for Determination of Multi-Mycotoxins in Pistachio Nuts. Molecules 2021, 26, 5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Dong, Y.; Yuan, X.; Fan, L.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L. Fast determination of 14 mycotoxins in chestnut by dispersive solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Xian, Y.; Xiao, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; He, J. Development and comparison of single-step solid phase extraction and QuEChERS clean-up for the analysis of 7 mycotoxins in fruits and vegetables during storage by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Hazer, B.; Elik, A.; Altunay, N. Synthesized of poly(vinyl benzyl dithiocarbonate-dimethyl amino ethyl methacrylate) block copolymer as adsorbent for the vortex-assisted dispersive solid phase microextraction of patulin from apple products and dried fruits. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Determination of patulin in apple juice by single-drop liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.; Mañes, J.; Font, G.; Juan-García, A. Determination of mycotoxins in fruit berry by-products using QuEChERS extraction method. LWT 2017, 86, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ji, M. Determination of Ochratoxin A contamination in grapes, processed grape products and animal-derived products using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectroscopy system. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadok, I.; Szmagara, A.; Staniszewska, M.M. The validated and sensitive HPLC-DAD method for determination of patulin in strawberries. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadok, I.; Szmagara, A.; Krzyszczak, A. Validated QuEChERS-based UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS method for the postharvest control of patulin (mycotoxin) contamination in red-pigmented fruits. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, E.; Ladányi, M.; Fodor, P.; Soros, C. Comparison of QuEChERS and “dilute and shoot” extraction methods for multi-mycotoxin analysis of samples from button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) cultivation. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2021, 56, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Berardis, S.; De Paola, E.L.; Montevecchi, G.; Garbini, D.; Masino, F.; Antonelli, A.; Melucci, D. Determination of four Alternaria alternata mycotoxins by QuEChERS approach coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in tomato-based and fruit-based products. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Deng, T.; Xiao, Y.; Jin, C.; Lyu, W.; Wang, W.; Tang, B.; Wu, Z.; Yang, H. Evaluation of Alternaria toxins in fruits, vegetables and their derivatives marketed in China using a QuEChERS method coupled with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Analytical methods and occurrence. Food Control 2023, 147, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amde, M.; Temsgen, A.; Dechassa, N. Ionic liquid functionalized zinc oxide nanorods for solid-phase microextraction of aflatoxins in food products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 91, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.L.; Francis, K.A.; Johnson, J.T.; Gaskill, C.L. Quantitation of fumonisin B(1) and B(2) in feed using FMOC pre-column derivatization with HPLC and fluorescence detection. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, P.; Tienstra, M.; Mol, H.; Herrmann, S.S.; Rasmussen, P.H.; Frandsen, H.L.; Poulsen, M.E. Development of a new generic extraction method for the analysis of pesticides, mycotoxins, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in representative animal feed and food samples. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, G.D.T.M.; Domínguez-González, R.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Ultrasound assisted combined molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective micro-solid phase extraction and determination of aflatoxins in fish feed using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1609, 460431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Jang, S.; Jo, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Yun, H.; Jeong, M.; Moon, J.; Na, T.; Cho, H. Optimization of the QuEChERS-Based Analytical Method for Investigation of 11 Mycotoxin Residues in Feed Ingredients and Compound Feeds. Toxins 2021, 13, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facorro, R.; Llompart, M.; Dagnac, T. Combined (d)SPE-QuEChERS Extraction of Mycotoxins in Mixed Feed Rations and Analysis by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2020, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, J.; Barba, F.J.; Font, G.; Ferrer, E. Mycotoxin Incidence in Some Fish Products: QuEChERS Methodology and Liquid Chromatography Linear Ion Trap Tandem Mass Spectrometry Approach. Molecules 2019, 24, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, J.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Ferrer, E.; Mañes, J. Identification and Quantification of Enniatins and Beauvericin in Animal Feeds and Their Ingredients by LC-QTRAP/MS/MS. Metabolites 2019, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerpoel, C.; Vidal, A.; di Mavungu, J.D.; Huybrechts, B.; Tangni, E.K.; Devreese, M.; Croubels, S.; De Saeger, S. Development and validation of an LC–MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of citrinin and ochratoxin a in a variety of feed and foodstuffs. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1580, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armutcu, C.; Uzun, L.; Denizli, A. Determination of Ochratoxin A traces in foodstuffs: Comparison of an automated on-line two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatography and off-line immunoaffinity-high-performance liquid chromatography system. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1569, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhotská, I.; Gajdošová, B.; Solich, P.; Šatínský, D. Molecularly imprinted vs. reversed-phase extraction for the determination of zearalenone: A method development and critical comparison of sample clean-up efficiency achieved in an on-line coupled SPE chromatography system. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3265–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campone, L.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Celano, R.; Pagano, I.; Russo, M.; Rastrelli, L. Rapid and automated on-line solid phase extraction HPLC–MS/MS with peak focusing for the determination of ochratoxin A in wine samples. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jartín, J.M.; Alfonso, A.; Rodríguez, I.; Sainz, M.J.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. A QuEChERS based extraction procedure coupled to UPLC-MS/MS detection for mycotoxins analysis in beer. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Cui, P.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Han, S.; Zhou, Y. Simultaneous Determination of Four Aflatoxins in Dark Tea by Multifunctional Purification Column and Immunoaffinity Column Coupled to Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11481–11488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Tao, F.; Zhou, Y. Determination of four aflatoxins on dark tea infusions and aflatoxin transfers evaluation during tea brewing. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zou, B.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, W.; Huang, T.; Zong, Q.; Wang, S.-Y. Rapid qualitative and quantitative analysis of aflatoxin B1 in Pu-erh tea by liquid chromatography-isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry coupled with the QuEChERS purification method. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4776–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueslati, S.; Ben Yakhlef, S.; Vila-Donat, P.; Pallarés, N.; Ferrer, E.; Barba, F.J.; Berrada, H. Multi-mycotoxin determination in coffee beans marketed in Tunisia and the associated dietary exposure assessment. Food Control 2022, 140, 109127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainudin, B.H.; Iskandar, M.I.; Sharif, S.; Ahmad, A.A.; Safian, M.F. Validation of quick and highly specific quantitation method of mycotoxin in cocoa beans by high resolution multiple reaction monitoring technique for reference materials analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmangui, A.; Jayasinghe, G.; Driss, M.R.; Touil, S.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Bouabdallah, S.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Assessment of trace levels of aflatoxins AFB1 and AFB2 in non-dairy beverages by molecularly imprinted polymer based micro solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods Adv. Methods Appl. 2021, 13, 3433–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miró-Abella, E.; Herrero, P.; Canela, N.; Arola, L.; Borrull, F.; Ras, R.; Fontanals, N. Determination of mycotoxins in plant-based beverages using QuEChERS and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Yao, K.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, P.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Liang, D.; Ke, Y.; Jiang, H. Determination of aflatoxin and zearalenone analogs in edible and medicinal herbs using a group-specific immunoaffinity column coupled to ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1092, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Huang, P.; Luan, L.; Fan, K.; Guo, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Han, Z. Iron (II, III) oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite as solid-phase extraction sorbent followed by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for simultaneous determination of zearalenone and type A trichothecenes in Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma (Danshen). J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1482, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Gajbhiye, N.A.; Basak, B.B.; Manivel, P. High-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for simultaneous detection of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1 and G2 in Indian medicinal herbs using QuEChERS-based extraction procedure. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 622–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-D.; Suh, J.H.; Feng, S.; Eom, T.; Kim, J.; Hyun, S.M.; Kim, J.; Wang, Y.; Han, S.B. Comprehensive analysis of multi-class mycotoxins in twenty different species of functional and medicinal herbs using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 2019, 96, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró-Abella, E.; Herrero, P.; Canela, N.; Arola, L.; Ras, R.; Borrull, F.; Fontanals, N. Optimised extraction methods for the determination of trichothecenes in rat faeces followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1105, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Deng, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Gong, Y.Y.; Wu, Y. High-throughput and sensitive determination of urinary zearalenone and metabolites by UPLC-MS/MS and its application to a human exposure study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5301–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, P.C.M.C.; Jager, A.V.; Tonin, F.G.; Petta, T.; Di Gregório, M.C.; Cossalter, A.-M.; Pinton, P.; Oswald, I.P.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Oliveira, C.A.F. Determination of fumonisin B1 levels in body fluids and hair from piglets fed fumonisin B1-contaminated diets. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.F.; Escrivá, L.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Moltó, J.C.; Berrada, H. Determination of trichothecenes in chicken liver using gas chromatography coupled with triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry. LWT 2018, 93, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajewska, M.; Łojko, M.; Cendrowski, K.; Sawicki, W.; Kowalkowski, T.; Buszewski, B.; Gadzała-Kopciuch, R. The determination of zearalenone and its major metabolites in endometrial cancer tissues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.; Li, Z.; Mao, X.; Wan, Y.; Qiu, H. Deep eutectic solvent-based liquid-phase microextraction for detection of plant growth regulators in edible vegetable oils. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3511–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liang, M.; Xian, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Hou, X.; Wu, Y. Development and validation of a multianalyte method for quantification of aflatoxins and bongkrekic acid in rice and noodle products using PRiME-UHPLC-MS/MS method. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldano, C.; Mahmood, A.; Dujardin, E. Production, properties and potential of graphene. Carbon 2010, 48, 2127–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, M.D.; Park, S.; Zhu, Y.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-Based Ultracapacitors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.-J.; Kong, F.-Y.; Chen, Z.-D.; Fan, D.-H.; Fang, H.-L.; Wang, W. Reduced graphene oxide-Hemin-Au nanohybrids: Facile one-pot synthesis and enhanced electrocatalytic activity towards the reduction of hydrogen peroxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Latorre, C.; Barciela-García, J.; García-Martín, S.; Peña-Crecente, R.M.; Otárola-Jiménez, J. Magnetic solid-phase extraction using carbon nanotubes as sorbents: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 892, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Seow, J.Y.R.; Skinner, W.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.-L. Metal–organic frameworks: Structures and functional applications. Mater. Today 2019, 27, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H. Direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry combined with single-drop liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction for the rapid analysis of multiple phytohormones in fruit juice. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; He, Z.; Ma, Y.; Uchiyama, K.; Lin, J.M. A novel approach for precisely controlled multiple cell patterning in microfluidic chips by inkjet printing and the detection of drug metabolism and diffusion. Analyst 2016, 141, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Stajnbaher, D.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Matrix | Analytes | Cartridge/Sorbent | Precondition | Wash | Elution | Recovery | RSD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rice and fragrant rice | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | PI-HCP column | MeOH, acetone and H2O | / | acetone | 82.2–113% | <9.1% | [18] |
| rice and noodle products | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | HLB or PRiME HLB column (collect filtrate directly) | n.d. | MeOH/H2O (20/80, v/v) | MeOH | 80.5–106.6% | 2.4–7.2% | [19] |
| rice and wheat | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | graphene | n.d. | / | ACN:H2O:MeOH: acetic acid(59.4:9.9:29.7:1 v/v) | 70.61–113.30% | <6.13% | [20] |
| cereal products | HT-2 and T-2 | IAC | pure H2O | n.d. | ethanol | 78.6–98.6% | 1.2–6.8% | [30] |
| cereals | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | MIL(Al)-53-DES@MIPs | n.d. | distilled H2O | ACN-H2O (9:1, v/v) | 95.3–98.5% | 1.3–4.4% | [31] |
| corn and peanut | AFB1 | Sil@HIm-Im column | n.d. | ACN and H2O | MeOH/acetic acid (2.0% vol.) | 80.0–103.3% | 2.37–6.58% | [36] |
| corn and corn products | FB1 and FB2 | SAX cartridge | MeOH and MeOH/H2O (75/25, v/v) | MeOH/H2O (75/25, v/v) and MeOH | 1% formic acid in MeOH | 79.4–98% | 3.5–55.7% | [38] |
| foodstuffs | AOH and AME | MIPs column | MeOH and phosphate buffer (50 mmol/L, pH = 8.2) | ACN/water (5:95, v/v), ACN/water (15:85, v/v) | 1% TFA in MeOH | 92.5–106.2% | <20% | [60] |
| peanut oils | AFB1 | Carb/PSA column | n.d. | normal hexane | MeOH-dichloromethane (2/8, v/v) | 87.7–105.1% | 2.2–7.9% | [62] |
| edible oils | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | HAS column | acetone/H2O (8/2, v/v) and n-hexane | iso-propanol | acetone/H2O (8/2, v/v) | 85–100% | <11% | [63] |
| milk and dairy products | AFM1 | IAC | n.d. | distilled H2O | MeOH | 85.2–107.0% | ≤7 % | [69] |
| milk | AFM1 | AFM1-aptamer modified microspheres | n.d. | 5% MeOH-H2O | 10 mM Mg2+ and ACN-MeOH-H2O (v/v, 2:1:1) | 85.3–109.9% | 2.6–6.7% | [70] |
| milk | 9 mycotoxins | rGO/Au column | / | MeOH/H2O (5/95, v/v) | MeOH/ACN/formic acid (50/49/1, v/v/v) | 70.2–111.2% | 2.0–14.9% | [71] |
| nuts | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | AC-B column | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 89.3–96.1% | 0.3–7.0 % | [81] |
| fruits and vegetables | 7 mycotoxins | HLB SPE cartridge | n.d. | 1% formic acid in H2O | MeOH | 81.1–116% | 3–6.2% | [85] |
| feed | FB1 and FB2 | IAC | n.d. | 0.01 M PBS | MeOH and distilled, deionized | FB1: 75.1–109%; FB2: 96–115.2% | 1.0–16.7% | [96] |
| animal feed and food | 11 mycotoxins | EZ-Pop NP column | acetone | / | ACN | 70–120% | <20% | [97] |
| beer, red wine, corn, and Turkish coffee | OTA | IAC | n.d. | PBS (pH: 7.4) | MeOH/HAC (98:2, v/v) | 104.34–107.33% | 0.21–1.31% | [104] |
| dark tea | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | MFC-IAC | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 77.5–93% | 2.2–11% | [108] |
| edible and medicinal herbs | 6 AFs and 6 ZEAs | IAC | n.d. | PBS and 5 mL H2O | MeOH | 64.7–112.1% | <13.7% | [115] |
| human urine | ZEA, α-ZEL, β-ZEL, α-ZAL, β-ZAL, ZAN | 96-well μElution | MeOH and H2O | H2O and 50% MeOH | H2O | 87.9–100% | <7% | [120] |
| pig hair | FB1 | SAX clean-up column | MeOH and MeOH:H2O (3:1, v/v) | MeOH:H2O (3:1, v/v), MeOH | MeOH:acetic acid 0.5% | 70–106% | 1.0–5.0% | [121] |
| Matrix | Analytes | Sorbent | Volume/mg | Adsorption Time/min | Elution | Recovery | RSD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rice and sorghum | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | MHCP-TPE | 30 | 10 | ACN | 81.9–117.0% | <8.0% | [21] |
| rice and maize | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | M-OP10-DCX | 25 | 10 | ACN | 82.8–115% | <8% | [22] |
| milk, edible oil and rice | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | M-COF | 2 | 2 | ACN | 76.4–112.5% | <15% | [23] |
| corn, rice and millet | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | Fe3O4@UiO-66-NH2@MON | 10 | 10 | ACN | 87.3–101.8% | 2.2–3.0% | [24] |
| rice | AFs | Fe3O4/zeolite nanocomposite | 50 | 1 | MeOH | 80–104% | 1.8–7.2% | [29] |
| cereals | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | Fe3O4@POSS@PIL-PSt | 80 | 5 | ACN | 87–120% | 3.2–11.2% | [33] |
| maize | AFs, OTs and enniatins | Fe3O4/COF-TpBD | 5 | 0.5 | ACN/H2O/ acetic acid (85:10:5) | 73.8–105.3% | <8.5% | [41] |
| maize | ZEA and its derivatives | MWCNT-MNPs | 20 | 3 | acetone containing 0.5% formic acid | 75.8–104.1% | ≤14% | [42] |
| maize, wheat, watermelon andmelon | AFB1, B2, G1, G2, OTA, OTB, T-2, HT-2 and DAS | MIL-101(Cr)@Fe3O4 | 25 | 4 | acetone containing 1% formic acid | 83.5–108.5% | 1.6–10.4% | [45] |
| cornmeal | ZEN | immunomagnetic chitosan | 100 | 1 | MeOH | 91.7–104.3% | 2.9% | [51] |
| foodstuffs | AFB1, B2, G1, G2, AFM1, and AFM2 | AF-mAb/CTS/Fe3O4 | 0.3 mL | 0.5 | MeOH | 63–118% | ≤ 16.3% | [61] |
| edible vegetable oils | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | PDA@Fe3O4-MWCNTs | 50 | 10 | ACN/water/acetic acid (84:15:1) | 70.15–89.25% | ≤6.4% | [64] |
| vegetable oil | FB1, ZON and OTA | Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2 | 5 | 10 | ACN/MeOH (1:1) containing 1% formic acid | 85.0–94.7% | 3.1–5.3% | [65] |
| vegetable oils | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | bare Fe3O4 nanoparticles | 10 | 10 | n-hexane | 82.6–106.2% | ≤9.8% | [66] |
| milk and yogurt | 6 mycotoxins | core-shell poly(dopamine) | 60 | 0.5 | MeOH | 70–120% | ≤16% | [72] |
| nuts | AFB1, B2, G1, G2 | Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2-APTMS-CPA | 10 | 2 | MeOH | 87.7–97.5 % | <7.1% | [82] |
| Salviae miltiorrhiza Radix et Rhizoma (Danshen) | ZEA, T-2, HT-2, NEO, DAS | Fe3O4/MWCNTs | 20 | n.d. | acetone containing 0.5% formic acid | 73.7–91.9% | 2.1–13.3% | [116] |
| Pretreatment Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPE-based approaches | SPE |
|
|
| MSPE |
|
| |
| SPME |
|
| |
| D-μ-SPE |
|
| |
| μ-SPE | Avoid fiber degradation and carryover phenomenon. | The sorbent floats or sticks to the wall. | |
| LLE-based approaches | SALLE |
| Mixed with a lot of neutral salt. |
| SDME |
|
| |
| DLLME |
|
| |
| QuEChERS | Quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe. |
| |
| MSPD |
| Limited adsorption capacity | |
| Dilute-and-shoot |
| Low recovery and accuracy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, B.; Feng, X. Recent Insights into Sample Pretreatment Methods for Mycotoxins in Different Food Matrices: A Critical Review on Novel Materials. Toxins 2023, 15, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15030215
Bian Y, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Wei B, Feng X. Recent Insights into Sample Pretreatment Methods for Mycotoxins in Different Food Matrices: A Critical Review on Novel Materials. Toxins. 2023; 15(3):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15030215
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Yu, Yuan Zhang, Yu Zhou, Binbin Wei, and Xuesong Feng. 2023. "Recent Insights into Sample Pretreatment Methods for Mycotoxins in Different Food Matrices: A Critical Review on Novel Materials" Toxins 15, no. 3: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15030215
APA StyleBian, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Y., Wei, B., & Feng, X. (2023). Recent Insights into Sample Pretreatment Methods for Mycotoxins in Different Food Matrices: A Critical Review on Novel Materials. Toxins, 15(3), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15030215