Toxicokinetics of Deoxynivalenol in Dezhou Male Donkeys after Oral Administration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Validation Parameters
2.2. Plasma Toxicokinetics Parameters of DON
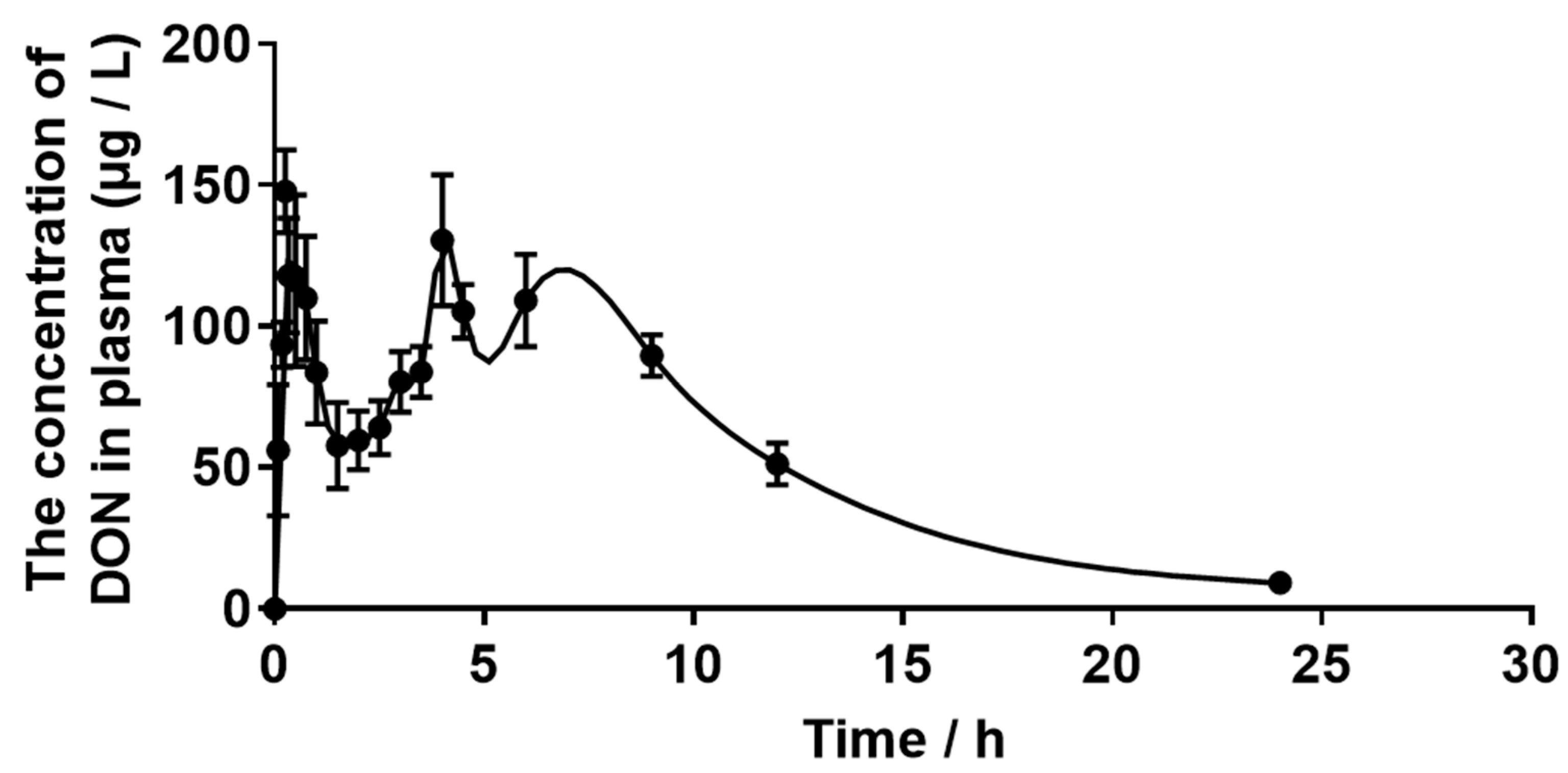
2.3. Plasma Concentration of DON
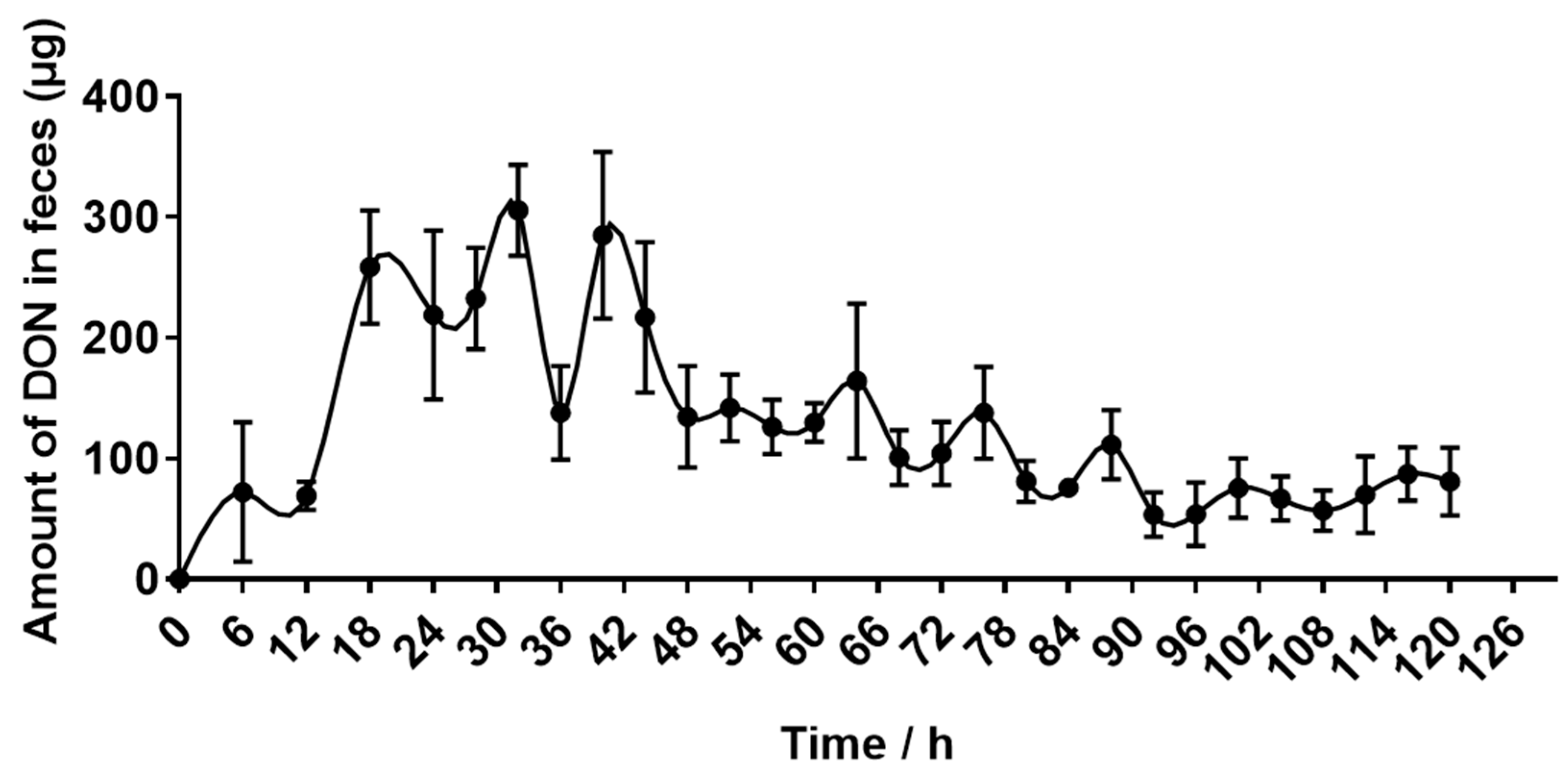
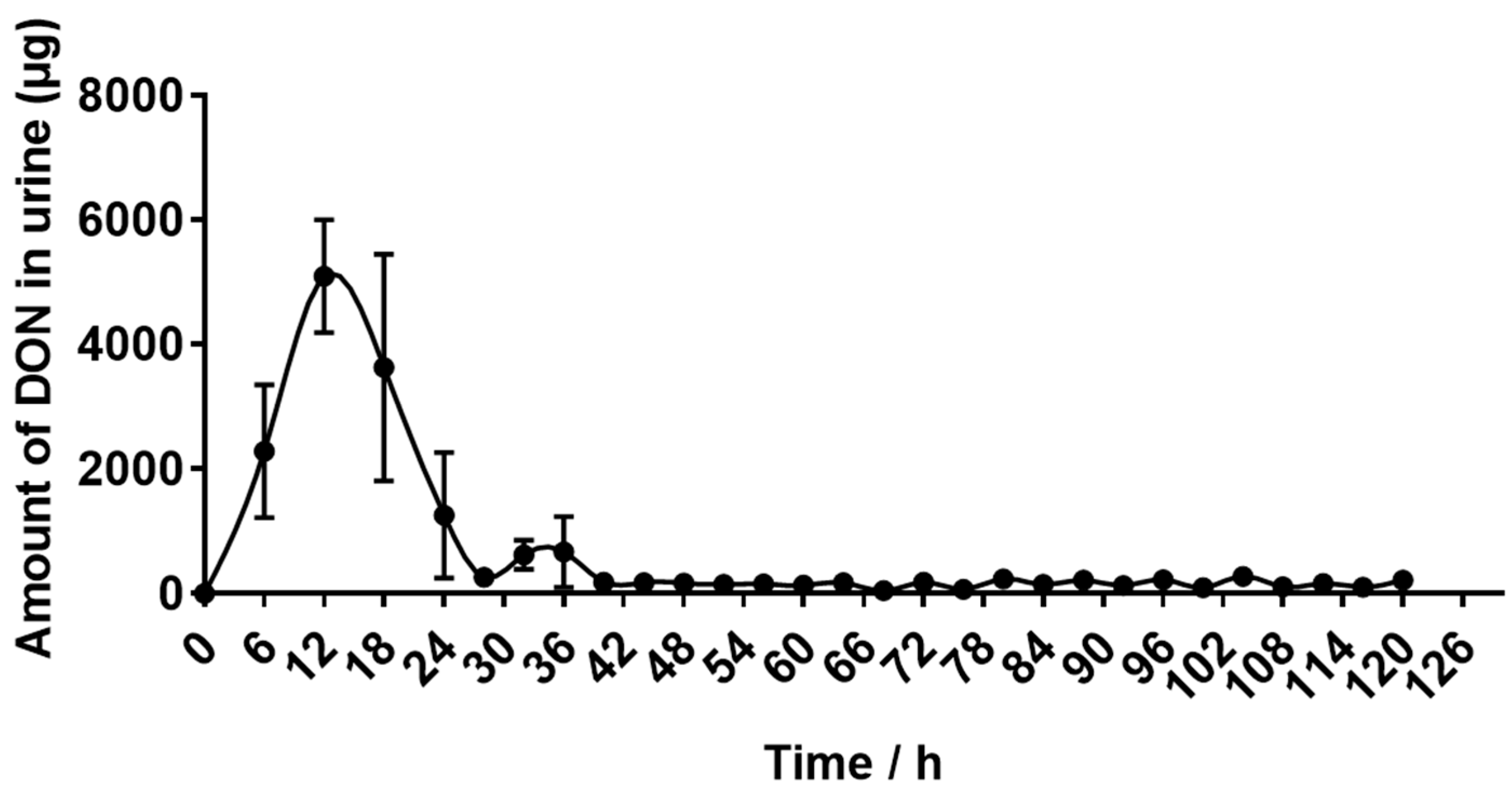
2.4. Recovery of DON Eliminated in Urine and Feces
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Mycotoxins
5.2. Animals and Treatment
5.3. Blood, Plasma, Feces and Urine Collection
5.4. Standard Solutions
5.5. Sample Pretreatment
5.6. HPLC Method Validation
5.7. Quantification of DON by HPLC
5.8. Data Standardization
5.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rotter, B.A.; Prelusky, D.B.; Pestka, J.J. Toxicology of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1996, 48, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestka, J.J. Deoxynivalenol: Toxicity, mechanisms and animal health risks. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2007, 137, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhao, L.H.; Fan, Y.; Jia, Y.X.; Sun, L.; Ma, S.S.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q.G.; Zhang, J.Y. Occurrence of mycotoxins in feed ingredients and complete feeds obtained from the Beijing region of China. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gruber-Dorninger, C.; Jenkins, T.; Schatzmayr, G. Global mycotoxin occurrence in feed: A ten-year survey. Toxins 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, R.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Su, Y.T.; Xie, W.M.; Zhang, N.Y.; Dai, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Rajput, S.A.; Qi, D.S.; et al. Individual and combined occurrence of mycotoxins in feed ingredients and complete feeds in China. Toxins 2018, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Z. Natural occurrence of deoxynivalenol and its acetylated derivatives in Chinese maize and wheat collected in 2017. Toxins 2020, 12, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, S.; Dixit, S.; Dwivedi, P.D.; Pandey, H.P.; Das, M. Influence of temperature and pH on the degradation of deoxynivalenol (DON) in aqueous medium: Comparative cytotoxicity of DON and degraded product. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Effects of mycotoxin-contaminated feed on farm animals-ScienceDirect. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracarense, A.P.; Lucioli, J.; Grenier, B.; Drociunas Pacheco, G.; Moll, W.D.; Schatzmayr, G.; Oswald, I.P. Chronic ingestion of deoxynivalenol and fumonisin, alone or in interaction, induces morphological and immunological changes in the intestine of piglets. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleemput, J.V.; Poelaert, K.C.K.; Laval, K.; Broeck, W.V.D.; Nauwynck, H.J. Deoxynivalenol, but not fumonisin B1, aflatoxin B1 or diesel exhaust particles disrupt integrity of the horse’s respiratory epithelium and predispose it for equine herpesvirus type 1 infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 234, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.H.; Li, X.Y.; Ji, C.; Rong, X.P.; Liu, S.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ma, Q.G. Protective effect of Devosia sp. ANSB714 on growth performance, serum chemistry, immunity function and residues in kidneys of mice exposed to deoxynivalenol. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 92, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Guo, Y.P.; Zhao, L.H.; Fan, Y.; Ji, C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ma, Q.G. Protective effects of Devosia sp. ANSB714 on growth performance, immunity function, antioxidant capacity and tissue residues in growing-finishing pigs fed with deoxynivalenol contaminated diets. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Wang, J.H.; Guo, W.B.; Ling, A.R.; Luo, A.Q.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.L.; Zhao, Z.H. Toxic effects and possible mechanisms of deoxynivalenol exposure on sperm and testicular damage in balb/c mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2289–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, J.; Mu, P.Q.; Lin, R.Q.; Wen, J.K.; Deng, Y.Q. Toxicokinetics and metabolism of deoxynivalenol in animals and humans. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 2639–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dänicke, S.; Valenta, H.; Doll, S. On the toxicokinetics and the metabolism of deoxynivalenol (DON) in the pig. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2004, 58, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osselaere, A.; Devreese, M.; Goossens, J.; Vandenbroucke, V.; De Baere, S.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Toxicokinetic study and absolute oral bioavailability of deoxynivalenol, T-2 toxin and zearalenone in broiler chickens. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestka, J.J.; Islam, Z.; Amuzie, C.J. Immunochemical assessment of deoxynivalenol tissue distribution following oral exposure in the mouse. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 178, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lake, B.G.; Phillips, J.C.; Walters, D.G.; Bayley, D.L.; Cook, M.W.; Thomas, L.V.; Gilbert, J.; Startin, J.R.; Baldwin, N.C.P.; Bycroft, B.W.; et al. Studies on the metabolism of deoxynivalenol in the rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1987, 25, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, R.A.; Engrola, S.; Aragao, C.; Mackenzie, S.; Bichl, G.; Czabany, T.; Schatzmayr, D. Fate of [3H]-deoxynivalenol in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) juveniles: Tissue distribution and excretion. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2018, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuzie, C.J.; Harkema, J.R.; Pestka, J.J. Tissue distribution and proinflammatory cytokine induction by the trichothecene deoxynivalenol in the mouse: Comparison of nasal vs. oral exposure. Toxicology 2008, 248, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J.J.; Amuzie, C.J. Tissue distribution and proinflammatory cytokine gene expression following acute oral exposure to deoxynivalenol: Comparison of weanling and adult mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prelusky, D.B.; Hamilton, R.M.; Trenholm, H.L. Transmission of residues to eggs following long-term administration of 14C-labelled deoxynivalenol to laying hens. Poult. Sci. 1989, 68, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saint-Cyr, M.J.; Perrin-Guyomard, A.; Manceau, J.; Houée, P.; Delmas, J.; Rolland, J.; Laurentie, M. Risk assessment of deoxynivalenol by revisiting its bioavailability in pig and rat models to establish which is more suitable. Toxins 2015, 7, 5167–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schelstraete, W.; Devreese, M.; Croubels, S. Comparative toxicokinetics of Fusarium mycotoxins in pigs and humans. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyarts, T.; Dänicke, S. Bioavailability of the Fusarium toxin deoxynivalenol (DON) from naturally contaminated wheat for the pig. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 163, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pralatnet, S.; Poapolathep, S.; Imsilp, K.; Tanhan, P.; Isariyodom, S.; Kumagai, S.; Poapolathep, A. The fate and tissue disposition of deoxynivalenol in broiler chickens. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, R.F.; Qu, H.L.; Guo, Y.X.; Zhang, M.J.; Fu, T.Z.; Huang, S.M.; Zhao, L.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q.G. Toxicokinetics of a single oral dose of OTA on Dezhou male donkeys. Toxins 2023, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesonder, R.F.; Ciegler, A.; Rogers, R.F.; Burbridge, K.A.; Bothast, R.J.; Jensen, A.H. Survey of 1977 crop year preharvest corn for vomitoxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 36, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidhauser, M.; Hankele, A.; Ulbrich, S.E. Reconsidering “low-dose”-Impacts of oral estrogen exposure during preimplantation embryo development. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekaert, N.; Devreese, M.; Bergen, T.V.; Schauvliege, S.; Boevre, V.E.; Saeger, S.D.; Vanhaecke, L.; Berthiller, F.; Michlmayr, H.; Malachová, A.; et al. In vivo contribution of deoxynivalenol-3-β-D-glucoside to deoxynivalenol exposure in broiler chickens and pigs: Oral bioavailability, hydrolysis and toxicokinetics. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faeste, C.K.; Ivanova, L.; Sayyari, A.; Hansen, U.; Sivertsen, T.; Uhlig, S. Prediction of deoxynivalenol toxicokinetics in humans by in vitro-to-in vivo extrapolation and allometric scaling of in vivo animal data. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2195–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prelusky, D.B.; Hamilton, R.M.; Trenholm, H.L.; Miller, J.D. Tissue distribution and excretion of radioactivity following administration of 14C-labeled deoxynivalenol to White Leghorn hens. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1986, 7, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azcona-Olivera, J.I.; Ouyang, Y.; Murtha, J.; Chu, F.S.; Pestka, J.J. Induction of cytokine mRNAs in mice after oral exposure to the trichothecene vomitoxin (deoxynivalenol): Relationship to toxin distribution and protein synthesis inhibition. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1995, 133, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagla, V.; Woechtl, B.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Hennig-Pauka, I.; Moll, W.; Adam, G.; Berthiller, F. Metabolism of the masked mycotoxin deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside in pigs. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 229, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Hametner, C.; Nagl, V.; Slavik, V.; Moll, W.; Berthiller, F. Deoxynivalenol (DON) sulfonates as major DON metabolites in rats: From identification to biomarker method development, validation and application. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7911–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, W.; Huang, L.; Pan, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chen, D.; Tao, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Metabolism, distribution, and excretion of deoxynivalenol with combined techniques of radiotracing, high-performance liquid chromatography ion trap time of flight mass spectrometry, and online radiometric detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 288–296. [Google Scholar]
- Pestka, J.J.; Clark, E.S.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Berthiller, F. Sex is a determinant for deoxynivalenol metabolism and elimination in the mouse. Toxins 2017, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binder, E.M.; Tan, L.M.; Chin, L.J.; Handl, J.; Richard, J. Worldwide occurrence of mycotoxins in commodities, feeds and feed ingredients. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2007, 137, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekaert, N.; Devreese, M.; De Mil, T.; Fraeyman, S.; Antonissen, G.; De Baere, S.; De Backer, P.; Vermeulen, A.; Croubels, S. Oral Bioavailability, Hydrolysis, and Comparative Toxicokinetics of 3-Acetyldeoxynivalenol and 15-Acetyldeoxynivalenol in Broiler Chickens and Pigs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8734–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Matrix | Slope | R2 | Range (μg/L)/ (μg/kg) | Sensitivity (μg/L)/(μg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOD | LOQ | ||||
| Plasma | 17.818 | 0.9972 | 25–5000 | 25 | 100 |
| Feces | 14.066 | 0.9963 | 25–5000 | 25 | 100 |
| Urine | 16.774 | 0.9990 | 25–20,000 | 25 | 100 |
| Spike Level (μg/L)/(μg/kg) | Average Recovery (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | Feces | Urine | |
| 25 | 86.91 | 78.16 | 87.58 |
| 100 | 84.85 | 88.84 | 75.02 |
| 500 | 83.17 | 88.63 | 93.04 |
| 1000 | 87.03 | 73.30 | 92.54 |
| 5000 | 90.82 | 78.58 | 93.18 |
| 20,000 | — | — | 86.25 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Body weight (kg) | 131.00 ± 1.05 |
| Single oral dose of DON (μg·kg·BW−1) | 500 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.07 ± 0.74 |
| Cmax (μg·L−1) | 174.30 ± 14.27 |
| T1/2Elim (h) | 5.81 ± 0.77 |
| AUC (μg·L−1·h) | 1540 ± 195.50 |
| Cl (L·kg·BW−1·h−1) | 0.35 ± 0.057 |
| Vd (L·kg·BW−1) | 2.82 ± 0.35 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| DON intake (mg) | 65.50 ± 0.52 |
| DON excretion through feces (mg) | 4.42 ± 0.35 |
| DON excretion through feces (%) | 6.74 ± 0.51 |
| DON excretion through urine (mg) | 13.12 ± 1.69 |
| DON excretion through urine (%) | 19.98 ± 2.46 |
| Absorption rate (%) | 93.26 ± 0.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, R.; Qu, H.; Guo, Y.; Ji, C.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, L.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q. Toxicokinetics of Deoxynivalenol in Dezhou Male Donkeys after Oral Administration. Toxins 2023, 15, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070426
Kang R, Qu H, Guo Y, Ji C, Cheng J, Wang Y, Huang S, Zhao L, Ji C, Ma Q. Toxicokinetics of Deoxynivalenol in Dezhou Male Donkeys after Oral Administration. Toxins. 2023; 15(7):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070426
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Ruifen, Honglei Qu, Yanxin Guo, Chuanliang Ji, Jie Cheng, Yantao Wang, Shimeng Huang, Lihong Zhao, Cheng Ji, and Qiugang Ma. 2023. "Toxicokinetics of Deoxynivalenol in Dezhou Male Donkeys after Oral Administration" Toxins 15, no. 7: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070426
APA StyleKang, R., Qu, H., Guo, Y., Ji, C., Cheng, J., Wang, Y., Huang, S., Zhao, L., Ji, C., & Ma, Q. (2023). Toxicokinetics of Deoxynivalenol in Dezhou Male Donkeys after Oral Administration. Toxins, 15(7), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070426







