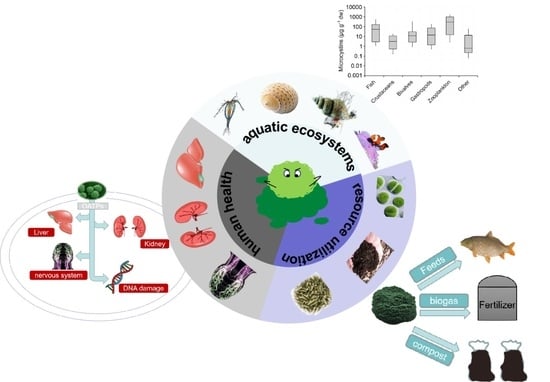
Transmission of Microcystins in Natural Systems and Resource Processes: A Review of Potential Risks to Humans Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
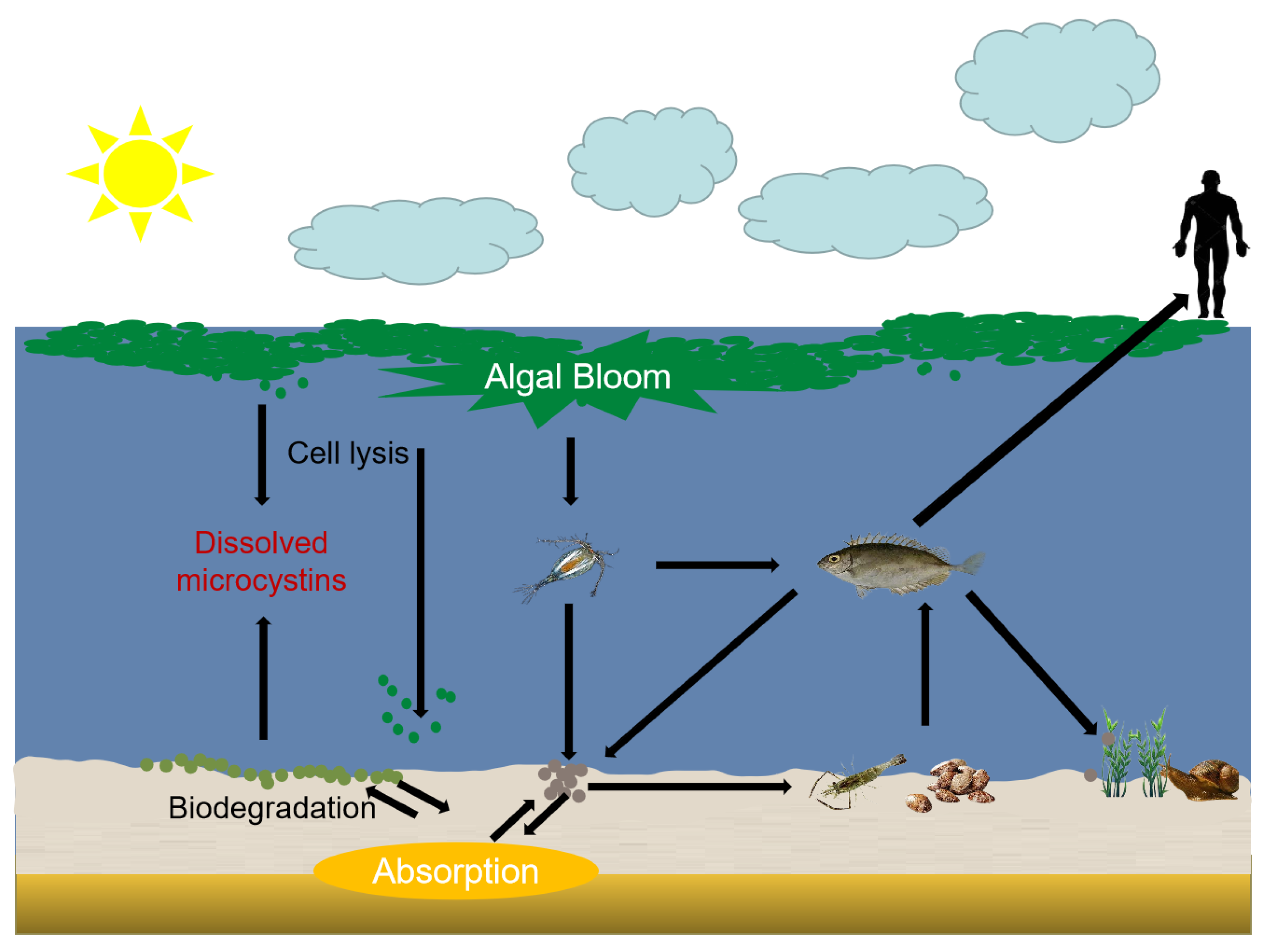
2. Exposure Pathways of MCs in Aquatic Food Chain
2.1. Accumulation of Zooplankton
2.2. Accumulation of Benthic Herbivores
2.3. Accumulation of Gastropod
2.4. Accumulation of Fish
3. Exposure Pathways of MCs in the Process of Resource Utilization
3.1. Cyanobacteria Compost
3.2. Cyanobacteria Biogas Fertilizer
3.3. Raw Material for Feeds
4. The Impact of Algal Toxins on Human Health and the Assessment of Human Health Risks of Cyanobacteria Recycling
4.1. The Harm of MCs to Liver
4.2. The Harm of MCs to Kidney
4.3. The Harm of MCs to Nervous System
4.4. Other Toxicity of MCs
4.5. Conclusions and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y. Environmental controls of harmful cyanobacterial blooms in Chinese inland waters. Harmful Algae 2021, 110, 102127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvinchuk, L.F.; Sharov, A.N.; Chernova, E.N.; Smirnov, V.V.; Berezina, N.A. Mutual links between microcystins-producing cyanobacteria and plankton community in clear and brown northern lakes. Food Webs 2023, 35, e00279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, D.; Giannoutsou, E.; Panteris, E.; Gkelis, S.; Adamakis, I.S. Microcystin-LR and cyanobacterial extracts alter the distribution of cell wall matrix components in rice root cells. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 191, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Tang, Q.; Xu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, C. A comprehensive review on the photocatalytic inactivation of Microcystis aeruginosa: Performance, development, and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2023, 312 Pt 1, 137239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Quijada, L.; Prieto, A.I.; Guzman-Guillen, R.; Jos, A.; Camean, A.M. Occurrence and toxicity of microcystin congeners other than MC-LR and MC-RR: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 106–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žegura, B.; Štraser, A.; Filipič, M. Genotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity of cyanobacterial toxins—A review. Mutat. Res./Rev. Mutat. Res. 2011, 727, 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, P. A review of reproductive toxicity of microcystins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briland, R.D.; Stone, J.P.; Manubolu, M.; Lee, J.; Ludsin, S.A. Cyanobacterial blooms modify food web structure and interactions in western Lake Erie. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Q. Microcystin biosynthesis and toxic effects. Algal Res. 2021, 55, 102277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Lujic, J.; Marinovic, Z.; Subakov-Simic, G.; Dulic, T.; Vazic, T.; Nybom, S.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G.A.; et al. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in fishponds and their effects on fish tissue. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Alamri, S.; Hashem, M. The link between microcystin levels in groundwater and surface Nile water, and assessing their potential risk to human health. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 244, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preece, E.P.; Hobbs, W.; Hardy, F.J.; O’Garro, L.; Frame, E.; Sweeney, F. Prevalence and persistence of microcystin in shoreline lake sediments and porewater, and associated potential for human health risk. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Du, X.; Shi, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Tian, Z.; Shi, L.; Guo, H.; et al. Advances in the toxicology research of microcystins based on Omics approaches. Environ. Int. 2021, 154, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Paul Peter, A.; Chew, K.W.; Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Show, P.L. Resource recovery from industrial effluents through the cultivation of microalgae: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Yuan, Q. Effects of three major nutrient contents, compost thickness and treatment time on larval weight, process performance and residue component in black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Ristow, B.; Rahayu, T.; Putra, N.S.; Widya Yuwono, N.; Nisa, K.; Mategeko, B.; Smetana, S.; Saki, M.; Nawaz, A.; et al. Black soldier fly larvae (BSFL) and their affinity for organic waste processing. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagala-Borowska, I.; Karwaciak, I.; Jaros, D.; Ratajewski, M.; Kokocinski, M.; Jurczak, T.; Remlein, B.; Rudnicka, K.; Pulaski, L.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J. Cyanobacterial cell-wall components as emerging environmental toxicants—Detection and holistic monitoring by cellular signaling biosensors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807 Pt 2, 150645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Xie, L.; Cheng, C.; Su, X.; Zhao, Y. Different environmental factors drive the concentrations of microcystin in particulates, dissolved water, and sediments peaked at different times in a large shallow lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326 Pt B, 116833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beversdorf, L.J.; Rude, K.; Weirich, C.A.; Bartlett, S.L.; Seaman, M.; Kozik, C.; Biese, P.; Gosz, T.; Suha, M.; Stempa, C.; et al. Analysis of cyanobacterial metabolites in surface and raw drinking waters reveals more than microcystin. Water Res. 2018, 140, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavagadhi, S.; Balasubramanian, R. Toxicological evaluation of microcystins in aquatic fish species: Current knowledge and future directions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142–143, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z. An eco-environmental assessment of harmful algal bloom mitigation using modified clay. Harmful Algae 2021, 107, 102067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ger, K.A.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Frost, P.C.; Hansson, L.A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E.; Lurling, M. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotton, B.; Guillard, J.; Anneville, O.; Marechal, M.; Savichtcheva, O.; Domaizon, I. Trophic transfer of microcystins through the lake pelagic food web: Evidence for the role of zooplankton as a vector in fish contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.M.; Nagelkerken, I.; Goldenberg, S.U.; Walden, G.; Leung, J.Y.S.; Connell, S.D. Functional loss in herbivores drives runaway expansion of weedy algae in a near-future ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.L.; Shimizu, K.; Kanazawa, A.; Gao, Y.; Dao, T.S.; Utsumi, M. Microcystin accumulation and biochemical responses in the edible clam Corbicula leana P. exposed to cyanobacterial crude extract. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 44, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, M.; Azevedo, J.; Carvalho, A.P.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Effects of storage, processing and proteolytic digestion on microcystin-LR concentration in edible clams. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofrio, M.D.; Egerton, T.A.; Reece, K.S.; Pease, S.K.D.; Sanderson, M.P.; Iii, W.J.; Yeargan, E.; Roach, A.; DeMent, C.; Wood, A.; et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of phycotoxins and their co-occurrence within nearshore waters. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 101993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, H.; Amrani, A.; Sedrati, F.; Maaref, H.; Leghrib, F.; Benamara, M.; Amara, H.; Wang, Z.; Nasri, H. Histological and chemical damage induced by microcystin-LR and microcystin-RR on land snail Helix aspersa tissues after acute exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharm. 2021, 245, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerabadhran, M.; Manivel, N.; Sarvalingam, B.; Seenivasan, B.; Srinivasan, H.; Davoodbasha, M.; Yang, F. State-of-the-art review on the ecotoxicology, health hazards, and economic loss of the impact of microcystins and their ultrastructural cellular changes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 256, 106417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Shu, Y.; Tian, C.; Wang, C.; Fang, T.; Xiao, B.; Wu, X. Effects of chronic exposure to microcystin-LR on life-history traits, intestinal microbiota and transcriptomic responses in Chironomus pallidivittatus. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibayashi, M.; Furuta, S.; Inoue, E.; Ichise, S.; Takei, N. Dominance of harmful algae, Microcystis spp. and Micrasterias hardyi, has negative consequences for bivalves in a freshwater lake. Harmful Algae 2021, 101, 101967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, M.M.; Godwin, C.M.; Johengen, T.H. The effect of single versus dual nutrient decreases on phytoplankton growth rates, community composition, and Microcystin concentration in the western basin of Lake Erie. Harmful Algae 2023, 123, 102382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Gao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D. Cyanobacteria bloom hazard function and preliminary application in lake taihu, China. Chemosphere 2022, 307 Pt 4, 136122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Q.; Le Manach, S.; Huet, H.; Duvernois-Berthet, E.; Chaouch, S.; Duval, C.; Sotton, B.; Ponger, L.; Marie, A.; Matheron, L.; et al. An integrated omic analysis of hepatic alteration in medaka fish chronically exposed to cyanotoxins with possible mechanisms of reproductive toxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Liang, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhao, X.; Gao, N.; Li, J.; Lu, W.; Cui, K.; Li, H. Benefit-risk assessment of consuming fish and shrimp from a large eutrophic freshwater lake, China. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Dong, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wu, M. Microcystins distribution, bioaccumulation, and Microcystis genotype succession in a fish culture pond. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Luo, W.; Lu, Y.; Giesy, J.P. Bioaccumulation of microcystins (MCs) in four fish species from Lake Taihu, China: Assessment of risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X. Effect of cyanobacteria on immune function of crucian carp (Carassius auratus) via chronic exposure in diet. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, S.Y.; Li, D.W.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, W.D. Toxicity and underlying mechanism of the toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus caribaeus to the fish Oryzias melastigma. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 247, 114223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucault, P.; Gallet, A.; Duval, C.; Marie, B.; Duperron, S. Gut microbiota and holobiont metabolome composition of the medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) are affected by a short exposure to the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 253, 106329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Wu, Q.; Xie, S.; Zou, J. Effects of partial replacement of dietary flour meal with seaweed polysaccharides on the resistance to ammonia stress in the intestine of hybrid snakehead (Channa maculatus ♀ × Channa argus ♂). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Z.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, J. Promotion effect on liver tumor progression of microcystin-LR at environmentally relevant levels in female krasV12 transgenic zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 252, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Xu, H.; Ding, S. Stimulation of high-concentration dissolved nitrogen and reactive phosphorus in Lake Taihu sediments on the initiation and maintenance of cyanobacterial blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851 Pt 2, 158088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Abd Al-Halim, M.A.; Mohammed, S.A. Algae processing by plasma discharge technology: A review. Algal Res. 2023, 70, 102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ye, J.; Shu, T.; Sun, Y.; Li, J. Zooplankton response to the lake restoration in the drinking-water source in Meiliang Bay of subtropical eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnologica 2012, 42, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniyar, C.B.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, D.R. Continuous and Synoptic Assessment of Indian Inland Waters for Harmful Algae Blooms. Harmful Algae 2022, 111, 102160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Li, Y.W.; Liu, B.L.; Zhao, H.M.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.Y.; Mo, C.H.; Wong, M.H.; Li, Q.X. High ecological and human health risks from microcystins in vegetable fields in southern China. Environ. Int. 2019, 133 Pt A, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Yoshikuni, Y. Metabolic engineering for valorization of macroalgae biomass. Metab. Eng. 2022, 71, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, S.; Zeinalzadeh, K.; Kheirfam, H.; Habibzadeh Azar, B. The impact of cyanobacteria inoculation on soil hydraulic properties at the lab-scale experiment. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 272, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.; Li, J. Current research scenario for microcystins biodegradation—A review on fundamental knowledge, application prospects and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastropetros, S.G.; Pispas, K.; Zagklis, D.; Ali, S.S.; Kornaros, M. Biopolymers production from microalgae and cyanobacteria cultivated in wastewater: Recent advances. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 60, 107999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Yue, L.; Hua, J.; Dong, H.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zhou, J.; Lin, R. Hydrothermal heating with sulphuric acid contributes to improved fermentative hydrogen and methane co-generation from Dianchi Lake algal bloom. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 192, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Peng, Y.; Yu, M.; Deng, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Y.; Wang, G. Severe cyanobacteria accumulation potentially induces methylotrophic methane producing pathway in eutrophic lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292 Pt B, 118443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, G.; He, Q. Methane production in harmful algal blooms collapsed water: The contribution of non-toxic Microcystis aeruginosa outweighs that of the toxic variety. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wu, Y.; Gan, N.; Zheng, L.; Li, T.; Song, L. Growth inhibitory effect of Microcystis on Aphanizomenon flos-aquae isolated from cyanobacteria bloom in Lake Dianchi, China. Harmful Algae 2015, 42, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, M.K.; Vignesh, N.S.; Gayathri, S.; Anjitha, N.; Athira, K.M.; Gunaseelan, S.; Arunkumar, M.; Sanjaykumar, A.; Karthikumar, S.; Ganesh Moorthy, I.M.; et al. Review on rewiring of microalgal strategies for the heavy metal remediation—A metal specific logistics and tactics. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; Petlulu, P.; Tian, Z.; Shi, L.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, S.; Guo, X.; et al. A new identity of microcystins: Environmental endocrine disruptors? An evidence-based review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851 Pt 2, 158262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevzorova, T.; Kutcherov, V. Barriers to the wider implementation of biogas as a source of energy: A state-of-the-art review. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 26, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; Miller, C.; Arhonditsis, G.; Boyer, G.L.; Carmichael, W.; Charlton, M.N.; Confesor, R.; Depew, D.C.; Hook, T.O.; Ludsin, S.A.; et al. The re-eutrophication of Lake Erie: Harmful algal blooms and hypoxia. Harmful Algae 2016, 56, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreña-Caro, D.; Benton, M.G. Cyanobacteria as photoautotrophic biofactories of high-value chemicals. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 28, 335–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Varjani, S.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Sustainable aquaculture and animal feed from microalgae—Nutritive value and techno-functional components. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoti, M.; Gumbo, J.; Jideani, A.I.O. Occurrence of cyanobacteria in water used for food production: A review. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 125, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakairu, G.W.; Nagawa, C.B.; Mbabazi, J. Assessment of cyanobacteria toxins in freshwater fish: A case study of Murchison Bay (Lake Victoria) and Lake Mburo, Uganda. Toxicon 2010, 55, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegand, C.; Pflugmacher, S. Ecotoxicological effects of selected cyanobacterial secondary metabolites: A short review. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2005, 203, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, K.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, L.; Yu, G.; Song, L. Modelling ecosystem structure and trophic interactions in a typical cyanobacterial bloom-dominated shallow Lake Dianchi, China. Ecol. Model. 2014, 291, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, M.C.P.; da Silva Ferrão-Filho, A.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Single and mixed diets of the toxic Cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Raphidiopsis raciborskii differently affect Daphnia feeding behavior. Food Webs 2022, 32, e00245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Kabir, M.; Zuhara, F.T.; Mehjabin, A.; Tasannum, N.; Hoang, A.T.; Kabir, Z.; Mofijur, M. Threats, challenges and sustainable conservation strategies for freshwater biodiversity. Environ. Res. 2022, 214 Pt 1, 113808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoti, M.I.; Edokpayi, J.; Mutileni, N.; Durowoju, O.; Munyai, F.L. Cyanotoxins in groundwater; occurrence, potential sources, health impacts and knowledge gap for public health. Toxicon 2023, 226, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Du, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H. Update on the adverse effects of microcystins on the liver. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, H. Effects of harmful algal blooms on the physiological, immunity and resistance to environmental stress of bivalves: Special focus on paralytic shellfish poisoning and diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 739000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Z. Microcystin pollution in lakes and reservoirs: A nationwide meta-analysis and assessment in China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Xu, L.L.; Chen, L.; He, J.; Wang, Y.K.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Wang, Y.T.; Wu, Q.H.; et al. Acute exposure to microcystins affects hypothalamic-pituitary axes of male rats. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishfaq, P.M.; Mishra, S.; Mishra, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Gayen, S.; Jain, S.K.; Tripathi, S.; Mishra, S.K. Inonotus obliquus aqueous extract prevents histopathological alterations in liver induced by environmental toxicant Microcystin. Curr. Res. Pharm. Drug Discov. 2022, 3, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palikova, M.; Ondrackova, P.; Mares, J.; Adamovsky, O.; Pikula, J.; Kohoutek, J.; Navratil, S.; Blaha, L.; Kopp, R. In vivo effects of microcystins and complex cyanobacterial biomass on rats (Rattus norvegicus var. alba): Changes in immunological and haematological parameters. Toxicon 2013, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Maity, S.; Guchhait, R.; Chatterjee, A.; Biswas, C.; Adhikari, M.; Pramanick, K. Toxic effects of cyanotoxins in teleost fish: A comprehensive review. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 240, 105971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swe, T.; Miles, C.O.; Cerasino, L.; Mjelde, M.; Kleiven, S.; Ballot, A. Microcystis, Raphidiopsis raciborskii and Dolichospermum smithii, toxin producing and non-toxigenic cyanobacteria in Yezin Dam, Myanmar. Limnologica 2021, 90, 125901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, P.; Chen, J.; Liang, G. Distribution of microcystins in various organs (heart, liver, intestine, gonad, brain, kidney and lung) of Wistar rat via intravenous injection. Toxicon 2008, 52, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Yan, M.; Jin, H.; Guo, H.; Han, X. Chronic exposure to MC-LR increases the risks of microcytic anemia: Evidence from human and mice. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, C.; Sun, P.; Ni, T. Response of cyanobacterial bloom risk to nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in large shallow lakes determined through geographical detector: A case study of Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, T.; Liao, Q.; Xiang, J.; Luo, L.; Xiong, X. Pathological and biochemical characterizations of microcystin-LR-induced liver and kidney damage in chickens after acute exposure. Toxicon 2022, 220, 106952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, Q.; Liu, C.; Shen, J.; Yan, W. Microcystin-LR exposure induced nephrotoxicity by triggering apoptosis in female zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, M.G.; Gutierrez-Praena, D.; Prieto, A.I.; Guzman-Guillen, R.; Jos, A.; Camean, A.M. Neurotoxicity induced by microcystins and cylindrospermopsin: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Z.; Diao, W.; Su, M.; Shi, W.; Wan, T.; Han, X. The organic anion transporting polypeptide 1a5 is a pivotal transporter for the uptake of microcystin-LR by gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 182, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez-Quijada, L.; Puerto, M.; Gutierrez-Praena, D.; Llana-Ruiz-Cabello, M.; Jos, A.; Camean, A.M. Microcystin-RR: Occurrence, content in water and food and toxicological studies. A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Du, X.; Liu, H.; Losiewic, M.D.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R.; Tian, Z.; Shi, L.; Guo, H.; et al. The latest advances in the reproductive toxicity of microcystin-LR. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zheng, C.; Shi, X. Effect of paternal exposure to microcystin-LR on testicular dysfunction, reproduction, and offspring immune response in the oriental river prawn (Macrobrachium nipponense). Aquaculture 2021, 534, 736332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Song, T.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Yang, P.; Zhang, X. Effects of dietary toxic cyanobacteria and ammonia exposure on immune function of blunt snout bream (Megalabrama amblycephala). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 78, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, A. Cytotoxicity and intestinal permeability of phycotoxins assessed by the human Caco-2 cell model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, C.L.; Li, D.W.; Li, H.Y.; Li, R.M.; Yang, W.D. Microcystin-LR exposure interfered maintenance of colonic microenvironmental homeostasis in rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 173, 113611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painefilu, J.C.; Gonzalez, C.; Carcamo, J.G.; Bianchi, V.A.; Luquet, C.M. Microcystin-LR modulates multixenobiotic resistance proteins in the middle intestine of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 253, 106327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ni, L.; Cao, T.; Xie, P. Ammonium, microcystins, and hypoxia of blooms in eutrophic water cause oxidative stress and C-N imbalance in submersed and floating-leaved aquatic plants in Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Ding, X.; Zhou, W. Study on ultrasonic treatment for degradation of Microcystins (MCs). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, M.; Xiao, B.; Gu, P. Transmission of Microcystins in Natural Systems and Resource Processes: A Review of Potential Risks to Humans Health. Toxins 2023, 15, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070448
Ren X, Wang Y, Zhang K, Ding Y, Zhang W, Wu M, Xiao B, Gu P. Transmission of Microcystins in Natural Systems and Resource Processes: A Review of Potential Risks to Humans Health. Toxins. 2023; 15(7):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070448
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xueli, Yuting Wang, Kenian Zhang, Yi Ding, Wanqing Zhang, Mengyi Wu, Beiqi Xiao, and Peng Gu. 2023. "Transmission of Microcystins in Natural Systems and Resource Processes: A Review of Potential Risks to Humans Health" Toxins 15, no. 7: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070448
APA StyleRen, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, K., Ding, Y., Zhang, W., Wu, M., Xiao, B., & Gu, P. (2023). Transmission of Microcystins in Natural Systems and Resource Processes: A Review of Potential Risks to Humans Health. Toxins, 15(7), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070448