Abstract
Mycotoxins are a major threat to animal and human health, as well as to the global feed supply chain. Among them, aflatoxins, fumonisins, zearalenone, T-2 toxins, deoxynivalenol, and Alternaria toxins are the most common mycotoxins found in animal feed, with genotoxic, cytotoxic, carcinogenic, and mutagenic effects that concern the animal industry. The chronic negative effects of mycotoxins on animal health and production and the negative economic impact on the livestock industry make it crucial to develop and implement solutions to mitigate mycotoxins. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge of the mycotoxicosis effect in livestock animals as a result of their contaminated diet. In addition, we discuss the potential of five promising phytogenics (curcumin, silymarin, grape pomace, olive pomace, and orange peel extracts) with demonstrated positive effects on animal performance and health, to present them as potential anti-mycotoxin solutions. We describe the composition and the main promising characteristics of these bioactive compounds that can exert beneficial effects on animal health and performance, and how these phytogenic feed additives can help to alleviate mycotoxins’ deleterious effects.
Keywords:
phytogenics; bioactive compounds; mycotoxins; animals; livestock; aquaculture; pet; biosorbents Key Contribution:
This review highlights the potential of five phytogenic compounds—curcumin; silymarin; grape pomace; olive pomace; and orange peel extracts—as effective anti-mycotoxin solutions for improving animal health and performance. These compounds have demonstrated positive effects on animal health and performance, and are presented as viable anti-mycotoxin solutions.
1. Introduction
Mycotoxins are toxic secondary metabolites produced by filamentous fungi, primarily from the genera Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Fusarium [1,2]. These low molecular weight compounds pose a serious threat to the health of both animals and humans. One of the most concerning aspects of mycotoxins in animal production is their physical and chemical properties, which make them highly stable during agricultural processes. This stability allows them to persist in cereal grains throughout harvesting, transportation, and storage, leading to long-term contamination [2]. As a result, mycotoxins can be transferred from feed to livestock and even into dairy products, posing a significant risk to the global feed supply chain. This affects not only feed safety but also animal health and productivity, ultimately impacting human health through animal-derived products, economies, and international trade [2].
The health consequences of mycotoxin exposure can be classified as either acute or chronic, with chronic toxicity posing a particular concern in livestock production. Chronic exposure to mycotoxins can negatively affect animal appetite and lead to a range of metabolic, physiological, and immunological disorders. These disruptions result in reduced production efficiency, including lower feed intake, poor growth rates, decreased egg production, changes in carcass quality, and reduced fertility, ultimately leading to economic losses [3].
The principal mycotoxins contaminating livestock feed include Fusarium-derived toxins such as fumonisins (FBs), trichothecenes [deoxynivalenol (DON) and T-2/HT-2 toxin)], and zearalenone (ZEN), as well as non-Fusarium mycotoxins like ochratoxins (OTs) and aflatoxins (AFs) [4]. They are strictly regulated in parts of the European Union and North America due to their impact on livestock feed contamination. Regulatory bodies overseeing food and agriculture have set maximum permissible limits for each type of mycotoxin in animal feed and food products to prevent mycotoxicosis in livestock [4,5]. In recent years, however, attention has shifted to emerging mycotoxins such as those produced by Alternaria species, particularly alternariol (AOH), alternariol monomethyl ether (AME), and tenuazonic acid (TeA). These toxins have become potential contaminants in livestock feed, prompting increased interest in their biomonitoring and regulation [6].
Environmental conditions play a key role in the growth of mycotoxin-producing fungi. Warm and humid climates, typically found in subtropical and tropical regions, create ideal conditions for fungal proliferation and mycotoxin production [7]. Furthermore, climate change and global warming are altering the climatic patterns of many regions, including those in temperate zones that traditionally experience cooler, drier climates. These changes have led to an increase in mycotoxicosis outbreaks in agricultural commodities and animal feed in these regions, making it crucial to continuously monitor climate trends and food contamination [8]. Controlling the risk of mycotoxin development and mitigating unexpected outbreaks due to climate change and globalization are vital for maintaining feed safety.
Several strategies have been developed to mitigate the detrimental effects of mycotoxins in animal feed and consequently protect animal and human health. These strategies can be broadly classified into pre-harvest and post-harvest measures. Pre-harvest strategies include the use of resistant crop varieties, crop rotation, and the application of fungicides to reduce fungal infection and mycotoxin production [9]. Post-harvest strategies involve proper drying and storage conditions to inhibit fungal growth, the use of chemical and biological agents to degrade or adsorb mycotoxins, and the implementation of rigorous monitoring and regulatory frameworks to ensure feed safety [10].
Among the biological agents used to mitigate the effects of mycotoxins, several studies have demonstrated their efficacy. Notably, PPAR-γ agonists [11,12], quercetin [13], resveratrol [14], sodium butyrate [15], and EPA and DHA [16] have shown novel applications in counteracting the harmful effects induced by mycotoxins. As widely described, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) is a member of the PPAR subfamily [17], and it has been shown to regulate liver alterations (e.g., cardiac fibrosis [17]). Recently, some authors have shown how PPAR-γ can exert a protective effect against mycotoxins by expression of the transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), thus alleviating the progression of cardiac fibrosis induced by these toxic agents [12].
Regarding quercetin, its potential to counteract mycotoxins effects relies on its antioxidant and free radical scavenging properties against DON, which have been recently demonstrated [13,18]. On the other hand, sodium butyrate, a histone deacetylase (HDAC) modulator, has been demonstrated to alleviate mycotoxin-induced liver injury via epigenetic modification [15].
As outlined by Seethaler et. al, long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), including EPA and DHA, have been shown to improve intestinal integrity in both animal studies and clinical trials [19]. An in vitro study conducted by Xiao et al. [16] showed that these fatty acids can promote cell growth, thus improving intestinal barrier function and, at the same time, downregulate the protein expression of necroptosis factors (such as tumor necrosis factor receptor TNFR1).
However, phytogenics—plant-derived products such as essential oils, herbs, and spices—are the most included substances in animal diets due to their potential to mitigate mycotoxin contamination. These phytogenic compounds exhibit antifungal, antioxidant, and immune-modulating properties that can reduce the incidence of mycotoxins and alleviate their negative effects on animal health and productivity [20,21]. Incorporating phytogenics into animal feed not only enhances feed quality and safety but also promotes sustainable, natural solutions to combat mycotoxin contamination.
1.1. Mycotoxins in Animal Feed: Effects on Animal Health and Production
Mycotoxicosis, resulting from mycotoxin exposure through inhalation, ingestion, or direct contact, can severely impact animal health. While it is important to control acute toxicity, it is equally crucial to monitor low-level chronic toxicity, as this can eventually lead to significant disruptions in animal health and production [8]. The co-occurrence of multiple mycotoxins in feed can exacerbate their harmful effects due to synergistic interactions, causing more severe damage than a single mycotoxin alone [8]. However, further research is needed to fully understand the impact of co-contamination and co-exposure to multiple mycotoxins in livestock feed. Currently, most studies focus on the effects of individual mycotoxins, leaving gaps in our knowledge regarding their combined impact on animal health.
Firstly, AFs, produced by the genera Aspergillus, are mycotoxins characterized by rapid absorption and metabolization into their active or detoxified metabolites through the liver [3]. These mycotoxins are known for their genotoxic, hepatotoxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic effects, impacting reproduction and immune systems in both humans and animals, including rodents, poultry, swine, and ruminants. This results in liver damage, decreased productivity, poor eggshell and carcass quality, and increased susceptibility to various diseases [3,22,23,24]. Notably, aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) is widely known as the most toxic AF, linked to liver damage and diseases in both animals (rodents, livestock, and aquaculture species) and humans, including hepatocellular carcinoma [25,26]. Some species are described as the most susceptible to AFB1, such as turkeys, rats, pigs, sheep, and dogs, whereas others such as monkeys, mice, and chickens are considered resistant [27].
OTs, also produced by the Aspergillus and Penicillium species, primarily affect the kidneys, causing nephrotoxicity, kidney enlargement, and tumors in the urinary tract in animals (pigs, poultry, and rodents) and humans [28,29]. They can also disrupt the immune system and fetal development [22]. Ochratoxin A (OTA) is described as dangerous due to the carry-over of this mycotoxin into animal products from swine, poultry, and even ruminants [30,31]. The presence of OTA in milk from ruminant species represents a concern for human health [28].
DON, a trichothecene mycotoxin produced by the Fusarium species, can reduce feed consumption and weight gain, due to symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, and nausea. DON also causes ribotoxic stress and immune suppression. Among all livestock species, swine are the most susceptible species to the toxicity of DON [22]. On the other hand, contamination by T-2 and HT-2 toxins, which are also trichothecene mycotoxins, can lead to oxidative stress through increased lipid peroxidation, and can mainly trigger carcinogenesis, immune depression, neurotransmitter imbalances, hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, weight loss, growth retardation, oral lesions, and reproductive disturbances in humans, poultry, and rodents [32,33]. As observed with DON, swine are among the most susceptible animals regarding the effects of the T-2 toxin [34].
In addition, FBs, also from the Fusarium species, are commonly described as sphingolipid metabolism disruptors as they inhibit ceramide synthase and the acylation of sphinganine and sphingosine, a biomarker positively correlated to hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and carcinogenicity [35]. Additionally, FBs can restrict the mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I and promote the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), lipid peroxidation, and oxidative stress [36]. FBs affect numerous species, such as horses, pigs, sheep, cattle, fish, poultry, nonhuman primates, mink, rabbits, and rodents. However, natural disease outbreaks primarily occur in horses and pigs, with horses showing greater susceptibility [37].
ZEN, which is also produced by the Fusarium species, is characterized as an estrogen-receptor agonist that can trigger negative consequences, such as alterations in the reproductive tract, fertility impairment, hypoestrogenic syndromes, reduced testosterone and spermatogenesis, and finally cancer in reproductive organs. Exposure to ZEN leads to signs of hyperestrogenism, most notably in pigs, though it can also occur in other animal species to a lesser degree [38,39].
Finally, the emerging and concerning Alternaria mycotoxins, of which the most studied are TeA, AME, and AOH, are described as genotoxic, cytotoxic, carcinogenic, and mutagenic toxins correlated to carcinoma colon cells in humans and esophageal cancer in mammalian cells. However, further research is necessary to truly understand the toxic potential and effects that Alternaria toxins can cause to animal and human health, especially given the advice of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in 2012, concerning the high levels of these toxins found in many food products in Europe [40]. Overall, these mycotoxins significantly impact animal health and production, highlighting the need for attention in the livestock industry.
Food and agricultural organizations estimate that 60–80% of feed crops are infected by mycotoxins, with 20% of the crops exceeding the European Union’s (EU) legal food safety limits [41]. Thus, chronic mycotoxicosis in feed crops entails additional costs, such as increased costs for health and veterinary care, regulatory fees, and investment in research costs focusing on relieving the impact and severity of the mycotoxin problem. This has a multi-million economic impact on the livestock industry [42]. Therefore, developing and implementing solutions to control and monitor factors implicated in mycotoxicosis is highly important to alleviate the negative effects in animal production caused by mycotoxicosis. Factors influencing the production and contamination of livestock feeds and foods by mycotoxins are divided into physical factors (environmental conditions), chemical factors (fungicides and fertilizers), biological factors (fungal species, strain specificity, strain variation, and instability of toxigenic properties), and agricultural practices (harvesting, storage, transport, treatments, and sanitation, among others) [42].
1.2. Natural Anti-Mycotoxin Solutions
Currently, different strategies are implemented in farms and agriculture to prevent or mitigate mycotoxicosis, addressing economic losses and factors implicated in reduced animal productivity. These strategies include good agricultural practices such as early harvesting, proper drying, physical treatments, sanitation, proper storage, and insect management. Additionally, chemical and biological controls, such as antifungal treatments and the use of atoxigenic strains, are implemented alongside breeding programs involving genetic bioengineering. Finally, decontaminating livestock feed through the use of feed additives is also a key strategy [42,43].
Feed additives can be categorized into different approaches: biological adsorbents and detoxication techniques, enterosorbents (adsorbent minerals), and anti-mycotoxin dietary compounds [42,43]. Biological adsorbents include bacteria (such as lactic acid bacteria), organic binders (bacteria and yeast cell wall and micronized fibers), and fungal conidia that reduce mycotoxin bioavailability [1]. Other biological methods involve bacteria, fungi strains, yeasts, or bioactive materials like enzymes or polypeptides to biodegrade mycotoxins and alleviate their toxic effects [1,44,45].
Enterosorbents, made from mycotoxin-binding minerals such as bentonites, sepiolites, zeolites, diatomites, aluminosilicates, hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate (HSCAS), and activated carbons, prevent the intestinal absorption of mycotoxins [46]. Their effectiveness depends on properties like charge distribution, polarity, pore size, and surface area [47]. Additionally, they improve the stability of food matrices by enhancing texture, consistency, and moisture control, contributing to better overall palatability and food quality [47]. However, some enterosorbents, like clays, have a non-selective absorption mechanism that can reduce the bioavailability of essential dietary nutrients such as vitamins, amino acids, and minerals [48,49]. The effectiveness of these enterosorbents is also influenced by dosage, incubation medium, and pH conditions [49].
Natural anti-mycotoxin dietary interventions are under development to explore innovative solutions based on nutraceutical, bioactive, and phytogenic compounds with antifungal and beneficial effects against the effects of mycotoxins on animal and human health. In particular, phytogenic feed additives derived from plant materials such as flowers, seeds, leaves, bark, and roots, possess nutraceutical qualities like antimicrobial, antifungal, antiparasitic, and antiviral properties, as well as mycotoxin-binding capabilities [50,51]. Compared to synthetic or chemical solutions and clays, natural feed additives are less toxic, leave no residue, and are nutritionally beneficial for animals while preserving the bioavailability of nutrients [52].
Dietary interventions also include amino acids, minerals, hormones, vitamins, and a wide range of phytogenic compounds. Amino acids play an important role in regulating metabolic pathways and cellular functions. Their antioxidant capacity makes them suitable candidates to protect against mycotoxin-induced oxidative stress [53,54]. Moreover, the immune and physiological functions of amino acids offer promising approaches for animal protection. The most studied amino acids with anti-mycotoxin properties include L-arginine, L-glutamine, and L-carnitine [53,54,55]. On the other hand, minerals like zinc, manganese, and selenium, which possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antiviral properties, are crucial for maintaining the body’s homeostasis and regulating immune functions. Therefore, the use of dietary minerals is a promising strategy against mycotoxins’ negative effects on body homeostasis [56,57,58]. Hormones like melatonin offer protection against mycotoxicosis through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects [59,60]. Vitamins, especially C and E, have been studied for their ability to protect vital organs such as the liver and kidneys from mycotoxin-induced damage, including oxidative stress and DNA damage [61,62,63].
Moreover, phytogenic bioactive compounds are emerging as promising solutions for controlling the toxic effects of mycotoxins in food and feed. These compounds support essential physiological pathways and functions while offering protective properties. Phytogenics derived from plant products like essential oils, herbs, and spices, are increasingly recognized for their antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects, which can inhibit the growth of mycotoxin-producing fungi and reduce contamination in feed [64,65]. They disrupt fungal cell walls and membranes, inducing autophagy and activating the antioxidant system, as well as activating hormone-dependent signaling pathways to prevent fungal spoilage [66]. Phytogenics also interfere with the biosynthesis of mycotoxins or degrade their structures [66]. Moreover, phytogenics exhibit strong anti-inflammatory qualities, which help mitigate the inflammatory responses in organs such as the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract, which are commonly affected by mycotoxins. This reduces tissue damage and improves overall organ function [65,67]. Additionally, their potent antioxidant activity neutralizes free radicals generated by mycotoxins, protecting cells from oxidative stress [65,68]. Therefore, by combining these actions, phytogenics enhance the resilience of animals to mycotoxin-induced toxicity, supporting better health and productivity.
The most well-known phytogenic compounds with anti-mycotoxin effects include phenolic compounds (polyphenols), terpenes, and nitrogen-containing compounds. Phenolic compounds are powerful antioxidants that modulate cellular redox status by eliminating free radicals, chelating metal ions, and promoting the activity of antioxidative enzymes [69]. However, phenol antifungal activity depends on the chemical structure of the polyphenol, aldehydes, acid groups, conjugated double bonds, and the length of CH [70].
On the other hand, terpenes, volatile compounds formed by isoprene molecules, act as radical scavengers from environmental stresses by absorbing free radicals or radiation through double bonds. They also exhibit antifungal properties due to their lipophilic nature, which allows them to enter cells and modify membranes that affect cell permeability and electrochemical potential, preparing them to combat fungi and mycotoxins. Terpenes are mainly found in plant extracts and essential oils [71,72].
Nitrogen-containing compounds, such as glucosinolates, alkaloids, and cyanogenic glucosides, have defensive roles in cells, with some, like alkaloids and glucosinolates, possessing antifungal properties that target enzymes crucial to fungal processes [66,73]. Their main target is the inactivation of critical enzyme reductases, acetate kinases, and oxidases implicated in fungal processes [74].
In addition to their antifungal and antioxidant properties, some phytogenic compounds are emerging as effective biosorbents for binding mycotoxins [75,76]. These biosorbents, made from by-products and waste materials in the food industry, are eco-friendly and economical, containing biomolecules like polysaccharides and proteins with functional groups that bind to mycotoxins and even heavy metals [77]. While research on new biosorbents for mycotoxin removal is increasing, further studies are needed to determine their effectiveness and characteristics. Therefore, given the growing demand for natural alternatives to antibiotics in animal production, phytogenic compounds are gaining widespread acceptance as promising solutions. The following sections will highlight the major biosorbents currently used in animal nutrition, their mechanisms in the adsorption process of mycotoxins, and their implications for animal health and productivity.
2. Phytogenic Biosorbents Used in Animal Nutrition
The contamination of animal feed with mycotoxins poses a significant threat to livestock health and productivity, resulting in significant economic losses in the agriculture sector. Traditional methods for mycotoxin control, such as chemical binders and decontamination processes, have shown limited effectiveness and can cause side effects. In recent years, anti-mycotoxin phytogenic solutions have gained attention as a promising alternative. These natural compounds not only neutralize mycotoxins but also offer additional health benefits. This section focuses on well-established phytogenics already incorporated into animal and human diets, sharing common signaling pathways like antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms that boost their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antifungal activities. Additionally, this section explores these phytogenic anti-mycotoxin solutions and their potential impact on animal health and productivity, offering a comprehensive overview of their role in modern animal husbandry.
2.1. Curcumin Extract
2.1.1. Composition and Main Characteristics
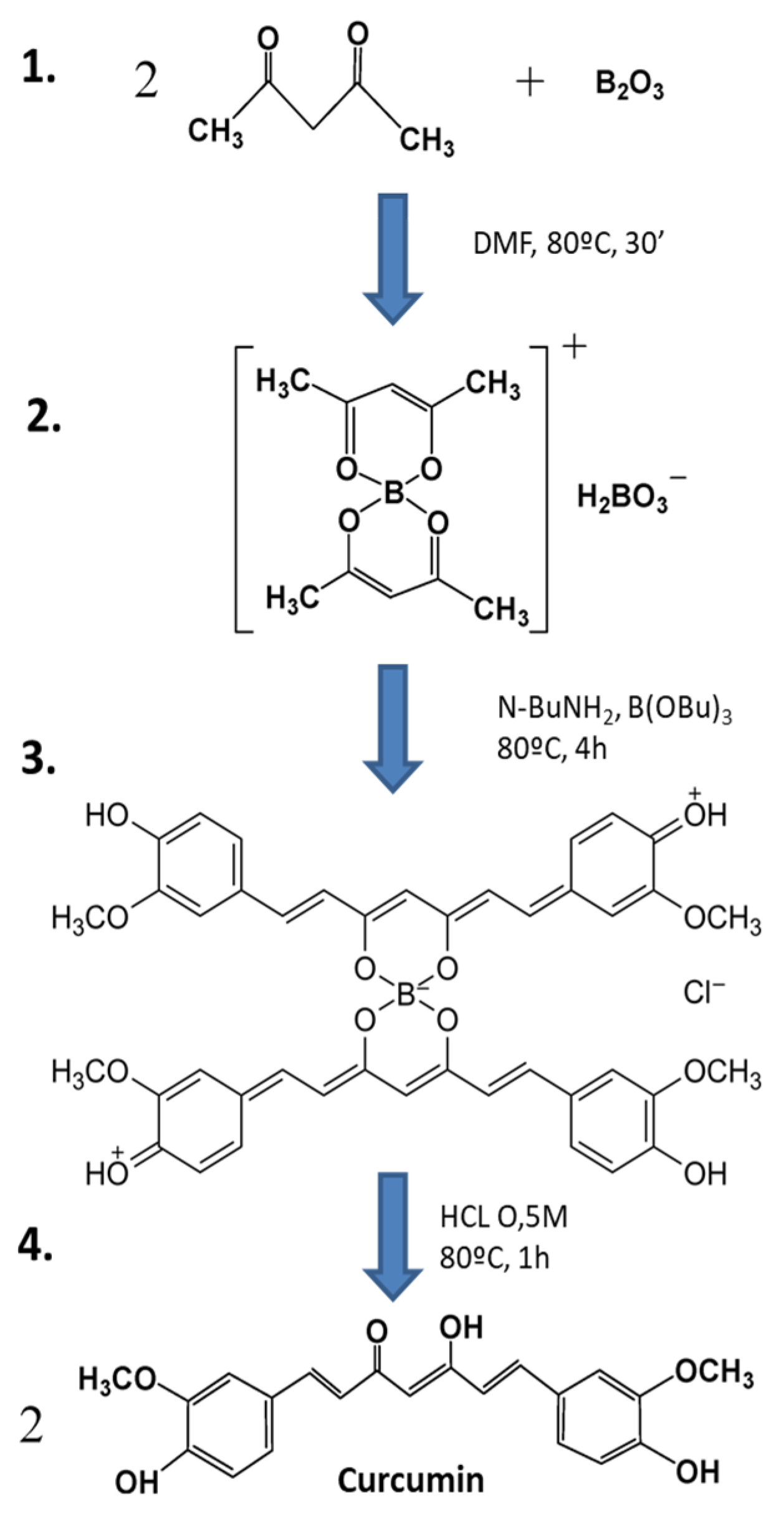
Curcumin ((E, E)-1,7-bis (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione) is the main active component of turmeric (Curcuma longa L), among other curcuminoids, and is classified as a polyphenolic pigment [78]. Traditionally used as a natural homemade remedy in India, curcumin is known for its anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antioxidant, free radical scavenging, and immune-enhancing properties [78]. The synthesis of curcumin has been thoroughly investigated and optimized, as explained in the study by Pabon [79]. The steps to synthesize curcumin are summarized in Figure 1. Its structure is based on two aromatic rings containing o-methoxy phenolic groups, connected by a seven-carbon linker with an α, β-unsaturated β-diketone moiety (Figure 1).
According to regulation 2021/551 of the European Commission [80], the maximum recommended curcumin extract content is limited to 15 mg/kg of feed, with Curcuma essential oils limited to 20 mg/kg for most animals, except calves, where it is limited to 80 mg/kg. Curcumin is a non-toxic dietary compound rapidly and efficiently metabolized and eliminated by mammals, without accumulating in the body [81]. Upon ingestion, curcumin undergoes various biological reactions, including oxidation, nucleophilic addition, hydrolysis, degradation, and enzymatic reactions [81]. However, as a limiting factor, curcumin has low water solubility and is chemically unstable, leading to poor absorption and rapid metabolism [82]. To improve its solubility, stability, and bioavailability, innovative approaches have been developed, such as using olive oil as a solvent [83] or encapsulating curcumin in nanoparticles or nanospheres [84]. Marchiori et al. demonstrated that 10 mg/kg of nano-encapsulated curcumin had similar effects to 30 mg/kg of free dietary curcumin, highlighting the potential of these technologies to improve curcumin’s pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics [85]. Therefore, it is important to consider how curcumin is administered and what form it takes, in order to predict its bioavailability and bioactivity.
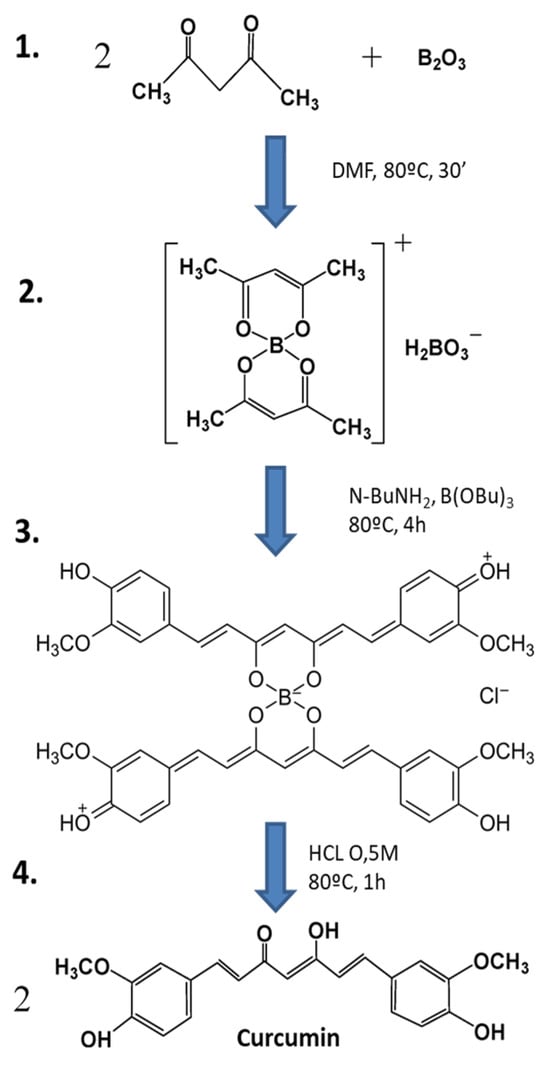
Figure 1.
Synthesis of curcumin by the general method proposed by Pabon [79] (image adapted from Zerazion et al., 2016) [86]. 1. A suspension of B2O3 (3 mmol) and acetylacetone (2 mmol) in 1.5 mL of DMF was stirred for 30 min at 80 °C. 2. To this was added 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (5.4 mmol), followed by the slow addition of n-butylamine solution, and this was stirred at 80 °C for 4 h. 3. The solution was acidified with 0.5 M HCl at 80 °C for 1 h. 4. Curcumin was dried and recrystallized.
Figure 1.
Synthesis of curcumin by the general method proposed by Pabon [79] (image adapted from Zerazion et al., 2016) [86]. 1. A suspension of B2O3 (3 mmol) and acetylacetone (2 mmol) in 1.5 mL of DMF was stirred for 30 min at 80 °C. 2. To this was added 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (5.4 mmol), followed by the slow addition of n-butylamine solution, and this was stirred at 80 °C for 4 h. 3. The solution was acidified with 0.5 M HCl at 80 °C for 1 h. 4. Curcumin was dried and recrystallized.
2.1.2. Mode of Action and Implication on Animal Health and Production
Curcumin has three active sites that undergo oxidation, electron transfer, and hydrogen abstraction [78]. It acts as a reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger by transforming ROS into more stable phenoxyl radicals through hydrogen oxidation at the phenol-OH group of its three active sites [78,86]. As a result, curcumin protects cells from oxidative damage caused by ROS. Additionally, curcumin inhibits necroptosis and inflammation by blocking aflatoxin-activated RIP/MLKL and TLR4/NFκB signaling pathways [87]. The TLR4/NFκB signaling pathway inhibition also alleviates intestinal inflammation by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [87]. Another benefit of curcumin is its ability to photosensitize and inactivate certain fungi and bacteria, reducing their levels [88]. Curcumin also acts as a liver protector and detoxifier by upregulating hepatic genes related to energy production, fatty acid metabolism, detoxification, coagulation, and immunological regulation [89].
Curcumin’s numerous biological effects in animals include anti-pulmonary fibrosis, anti-inflammation, anti-aging, antiviral, antibacterial, anticancer, immunomodulation, cardiovascular protection, and neuroprotection [90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99]. It affects key signaling pathways, such as AMPK, p53, p21, AKT, mTOR, Nrf2/ARE, NF-κβ, NLRP3, MAPKs, c-JUN, PPAR, and Wnt/β-catenin [100].
Studies have shown curcumin’s potential to inhibit the CYP450 enzyme, a key liver enzyme involved in activating aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), thereby protecting the liver and gastrointestinal tract [101,102]. Co-treatment with curcumin counteracts the harmful effects of ochratoxin A (OTA) by mitigating inflammation, reducing nitric oxide levels, and decreasing oxidative stress in the kidneys and liver in rats [103]. In addition, curcumin nanoparticles also help alleviate ZEN-induced hepatotoxicity in rats by ameliorating biochemical and cytogenetic parameters and the histopathological state [104].
In livestock, curcumin has shown significant protective effects against mycotoxicosis. For example, in male broiler chickens, curcumin [103] supplementation (400 mg/kg) reduced oxidative stress and damage in the liver and kidneys caused by 0.02 mg/kg of AFB1 [105,106]. Another study used 444 mg/kg of curcuminoids from turmeric or 300 mg/kg of curcumin with male 180-day-old broilers, demonstrating liver-protective effects and the ability to alleviate immune organ damage caused by the exposure to 1 mg/kg of AFB1 [87,107]. Moreover, the supplementation of 0.2% of curcumin acted as an immunomodulatory and protective agent against the damaging effects of AFB1 (2 ppm) on immune organs in male 151-day-old broiler chicks, such as the thymus, spleen, and bursa of Fabricius, and improved performance indicators like body weight, feed intake, and the feed conversion ratio [108]. Furthermore, 500 mg/kg of curcumin has been shown to protect the intestines of one-day-old broilers from 1 mg/kg of AFB1-induced damage by downregulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway [109]. Curcumin at doses of 150 mg/kg and 450 mg/kg alleviated liver and intestinal damage caused by 100 µg/kg of AFB1 in one-day-old broilers and 5 mg/kg of AFB1 in 120-day-old broilers, respectively, by downregulating CYP450 [101,110]. Additionally, 0.05% of turmeric extract can protect against the toxic effects of 3 ppm of AFB1 in the liver and kidneys of one-day-old broilers [111]. In several studies in one-day-old ducks, 400 and 500 mg/kg of curcumin demonstrated protective effects on the liver and intestine against acute damage induced by 0.06 and 0.1 mg/kg of AFB1. Curcumin suppressed the generation of CYP450 and AFB1-DNA adducts in the liver, and modulated gut microbiota, intestinal NLRP3 inflammasome, and the TLR4/NF-κβ signaling pathways in the intestines of the ducks [112,113]. The beneficial effects of curcumin extend to 28-week-old egg-laying hens and 45-week-old layer Japanese quails, where it has been shown to restore egg production and egg weight following AFB1 exposure (0.5 and 1.5 mg/kg, respectively) [114,115]. Additionally, 50 mg/kg of curcumin and 10 mg/kg of nano-curcumin demonstrated hepatoprotective and antioxidant properties in one-day-old male broilers intoxicated by FBs (600 mg/kg), minimizing the mycotoxicosis effect and increasing BW and ADG [116]. In another study, 400 mg/kg feed curcumin also provided partial protection against 1 mg/kg feed OTA in one-day-old broilers [117]. In addition, in broilers, the toxic effects of 0.5 ppm of OTA on kidneys were alleviated by 2 g/kg of feed curcumin [118]. In one-day-old ducks, OTA caused increased expression of apoptosis-related genes and the TLR4/ NF-κβ signaling pathway, and downregulated mitochondrial transcription factors A, B1, and B in the intestine. However, harmful effects induced by 2 mg/kg of OTA were diminished by 400 mg/kg of curcumin, protecting intestinal integrity and function, regulating gut microbiota, and improving performance parameters [90,119].
Curcumin has shown similar protective effects in swine, mitigating apoptosis and ROS in kidney cells contaminated with FB1, OTA, and DON [120]. A combination of curcumin and other phytogenics with adsorbent additives enhanced immune responses in pigs exposed to mycotoxins [121]. Furthermore, curcumin combined with silymarin and clays has improved reproductive and performance parameters in sows and piglets exposed to multiple mycotoxins. In 366-day-old sows, reproductive parameters and litter characteristics were ameliorated thanks to the supplementation of the multi-component mycotoxin-detoxifying agent and, in 28-day-old weaned piglets, BW and ADG were improved, and mortality and liver and intestinal damage were reduced significantly [122,123].
In an in vitro study with a bovine fetal hepatocyte-derived cell line (BFH12), curcumin mitigated the hepatotoxic effect of AFB1 by increasing antioxidant activity and the anti-inflammatory response. Antioxidant players, MDA concentration, and NQ01 enzyme activity were increased, and CYP3A activity, which plays a role in the bioactivation of AFB1, was reduced by curcumin administration [124]. In an in vivo study with dairy cows in their late lactation period, exposed to 5 µg/kg of AFB1, curcumin did not impact milk yield, milk composition, or somatic cell count. However, the low availability of curcumin in this formulation can be an issue in finding significant effects against mycotoxicosis, and better formulations are needed to maximize its influence on milk production [100]. Takiya et al. used a feeding phytogenic combination, in which curcumin and grape seed were used among other ingredients, in an in vitro study of dairy cows, and obtained benefits in performance parameters and nutrient utilization. Milk yield and fat were greater, and dry matter digestibility also increased [125].
In aquaculture, 400 mg/kg of curcumin alleviated OTA-inhibited myoblast differentiation and myofibrillar development-related proteins in a study with juvenile grass carp contaminated with OTA (1.2 mg/kg), ameliorating muscle toxicity and development, and enhancing growth performance mainly by increasing the weight gain percentage and final body weight. Additionally, Curcuma supplementation upregulated S6K1 and TOR, which are associated with the AKT/TOR signaling pathway, resulting in myoblast proliferation and fusion [126]. Also, 400 mg/kg of curcumin could alleviate 1.2 mg/kg OTA-induced gill and intestinal injuries in juvenile grass carp by reducing OTA residues in the gills and intestine, regulating TLR4 and NFκB signaling pathways, enhancing antioxidant defenses, decreasing oxidative stress, promoting a correct mitochondrial function, and decreasing necrosis and pro-inflammatory factors in the intestine [127,128]. In Red Tilapia, 50–60 mg/kg of nano-curcumin additive in feed increased disease resistance against Aspergillus flavus infection through the amelioration of hepatic damage and inflammation, intestinal dysfunction and morphology, splenic tissues and normal melano-splenic inflammatory macrophages, and improvement of the primary epithelium of the gill lamella and secondary filament in the gill tissue. This health amelioration in Red Tilapia improved growth performance parameters by increasing BW, ADG, FI, and fish survival, and decreasing FCR. Body composition was also ameliorated by nano-curcumin, reducing lipid content and increasing protein content [129]. El-Barbary demonstrated that the supplementation with curcumin in Nile Tilapia injected with AFB1 was effective in improving liver and kidney function and antioxidant activity by increasing the activity of detoxified enzymes and enhancing the detoxification of AFB1 through the suppression of CYP1A in the liver [130,131]. In addition, a diet of 5 g/kg of curcumin additive in feed for Nile Tilapia was effective against 2 ppm AFB1’s effects on growth performance, increasing BW, FI, ADG, and mortality rate, and reducing FCR. The residual AFB1 concentration was also reduced in Nile Tilapia by curcumin supplementation, which means curcumin can be a potential anti-AFB1 additive and protector against AF toxicity in this species [132]. In addition, the promising formulation of dietary Zn(II)-curcumin in shrimps exposed to AFB1 ameliorated hepatopancreas damage by conferring antioxidant and immunological protection [133].
In pets, 6–8 week-old rabbits aflatoxicated with 50 µg of oral AFB1 dissolved in 0.5 mL of olive oil were treated with 25 and 50 µg/kg of BW zinc oxide nanoparticles with curcumin, which conferred hepatoprotective effects by enhancing antioxidant activity, scavenging ROS, and improving hepatic condition [134].
Therefore, curcumin is a highly bioactive compound with significant potential for mitigating mycotoxicosis in livestock and pets. With effective doses ranging between 400 and 500 mg/kg in various studies, curcumin could play a crucial role in new strategies to combat the effects of mycotoxins in animal diets [101,119,135].
2.2. Silymarin Extract
2.2.1. Composition and Main Characteristics
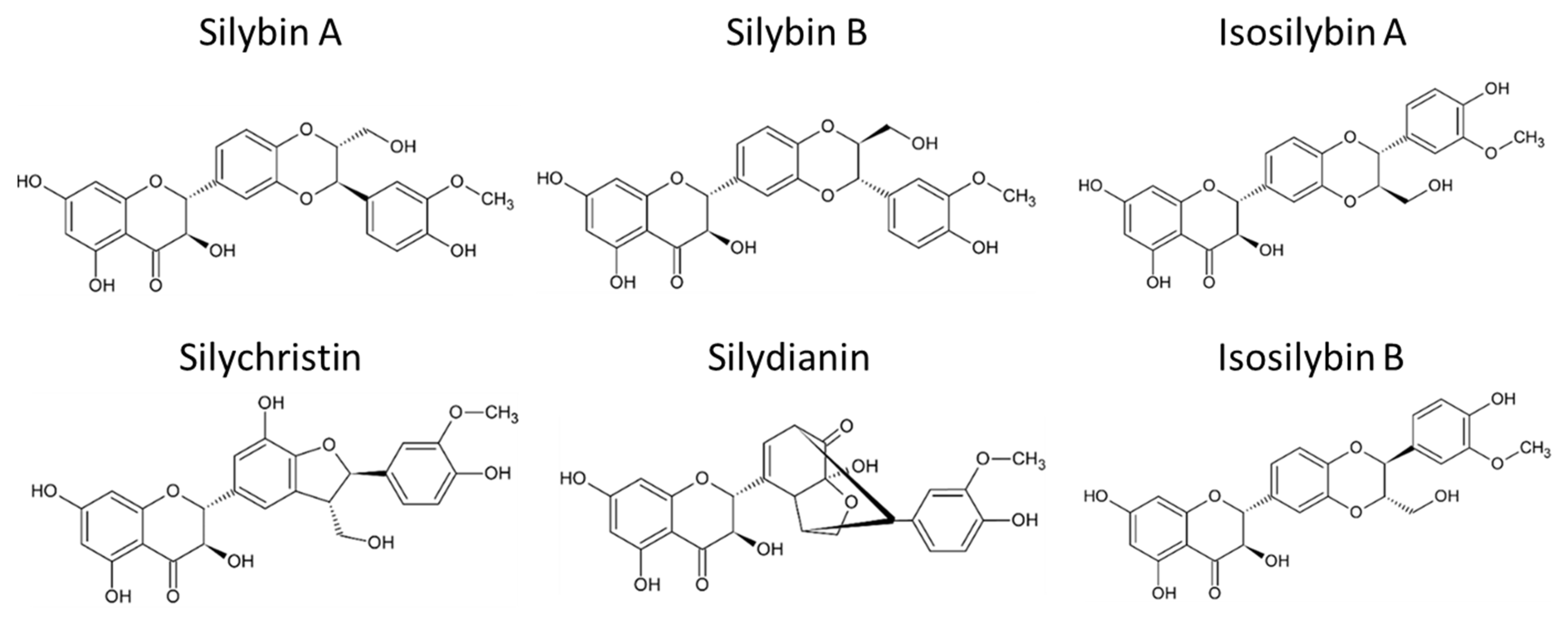
Silymarin (Silybum marianum) is the primary active compound extracted mainly from the seeds of the milk thistle, a thorny herb from the Asteraceae family. It has been widely studied for its potential in treating liver diseases [136,137]. The health benefits of milk thistle are largely attributed to silymarin, a complex composed of several flavonolignans such as silybin A, silybin B, isosilybin A, isosilybin B, silydianin, and silychristin (Figure 2). Additionally, silymarin contains flavonoids like quercetin and polyphenols. Among these, silybins are the most bioactive compounds, comprising 50–60% of silymarin, with the highest bioavailability. Despite its bioactive potential, silymarin is a highly hydrophobic molecule with low bioavailability, largely due to its rapid liver biotransformation and short half-life of six hours [138]. Beyond its hepatoprotective properties, guarding against liver diseases such as toxin-induced liver damage, viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma [139,140], silymarin has also demonstrated antioxidant, antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory, choleretic, immune-stimulating, regenerative, cytoprotective, cardioprotective, neuroprotective, and anti-carcinogenic effects [141].
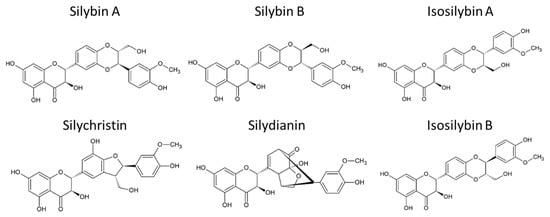
Figure 2.
Chemical structure of main flavonolignans contained in silymarin complex.
Once ingested, both free and conjugated forms of silybin are rapidly metabolized by the body, with a half-life of six hours. Silybin is recognized as a foreign substance and, consequently, metabolized by phase II enzymes [142]. As with curcumin, silymarin is also a bioactive compound with low bioavailability and fast metabolism, and its concentration in plasma is also low, as it is mainly found in the conjugated form. However, upon consumption, silymarin induces reactions such as increased glutathione S-transferase (GST) and quinone reductase (QR) activity in certain organs, thanks to its antioxidant properties [142].
2.2.2. Mode of Action and Implication on Animal Health and Production
Silymarin acts not only as a free radical scavenger but also inhibits enzymes involved in free radical production and maintains mitochondrial electron-transport chain integrity during oxidative stress [142]. It protects mitochondria from reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced protein modifications, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial DNA damage by reducing electron leakage, ROS formation, and inactivating ROS-producing enzymes within the mitochondria [142].
Liver damage induced by various factors can be mitigated through the use of silymarin, a compound that reduces hepatic enzyme levels (ALT, AST, and ALP) by activating ribosomal RNA synthesis, promoting liver regeneration, and preventing fibrosis [143]. Notably, silymarin is capable of deactivating the CYP450 enzyme, which plays a crucial role in detoxifying mycotoxins, thereby reducing glutathione (GSH) consumption in the liver [143].
Given these antioxidant properties, silymarin has been tested for its ability to mitigate the effects of mycotoxins. It inhibits lipid peroxidation and enhances enzymes related to oxidative stress, such as catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), GSH peroxidase, GST, and GSH reductase. Additionally, silymarin protects organs from damage by activating the PI3K-Akt cell survival pathway, preventing apoptosis [144]. For instance, in a preclinical study with mice, silymarin alleviated liver damage caused by FB1 toxicity through its antioxidant effects, reducing the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), as well as the apoptotic rate, thereby conferring a hepatoprotective effect [145].
Silymarin also alleviated ZEN-induced hepatotoxicity and reproductive toxicity by reducing histopathological lesions in the liver, ovaries, and uterus. This effect was attributed to the mTOR signaling pathway regulation and the reduction of oxidative stress and the ZEN-related protein metabolism [146]. In another study, nano-encapsulated silymarin, designed to improve solubility and bioavailability, mitigated DON toxicity by counteracting elevated serum enzyme activity, cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL, cytokines, lipid peroxidation, and nitric oxide (NO), while enhancing antioxidant enzymes such as GPx, SOD, and CAT [147]. Additionally, silymarin protected against FB toxicity by preventing cellular damage, reducing lactate dehydrogenase production, and lowering Tnf-α expression [148].
In various livestock species, silymarin supplementation has demonstrated multiple health benefits. For example, in 14-day-old broilers, silymarin extract countered the adverse effects of 0.8 mg/kg of AFB1 on liver health, improving performance and meat quality [149]. In one-day-old broilers exposed to 250–500 ppb of AFB1, diets containing 0.5–1% of Silybum marianum seeds improved liver status and acted as a hepatoprotective agent [150]. Similarly, seven-day-old broilers affected by 2 ppm of AFB1 and supplemented with 1000 ppm of silymarin showed enhanced villi height and VH:CD ratio, improved absorptive surface area, reduced pathogenic bacteria growth, and ameliorated FI, ADG, and FCR [151]. Armanini et al. observed that 100 mg/kg of silymarin improved productivity, meat quality, oxidative stress, and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in broilers exposed to 0.05 ppm of AFB1 and 20 ppm of FBs [152]. Likewise, in a study with one-day-old broilers contaminated with 8.4 ppb of AFB1 and 24.3 ppb of T-2 toxin, 0.5% silymarin improved performance parameters such as BW, BWG, FI, and FCR [153]. In ducks, a 0.5% milk thistle seed supplementation alleviated liver damage from 4.9 mg/kg of DON and 0.66 mg/kg of ZEN by activating the antioxidant system [154]. Additionally, in one-day-old ducks fed with diets naturally contaminated with ZEN (0.46–0.50 mg/kg of feed) and DON (3.43–3.72 mg/kg of feed), 0.5% milk thistle seed, 0.5% milk thistle seed cake, or 0.1% milk thistle seed oil prevented histological alterations in the liver, spleen, and bursa of Fabricius [155]. Similar protective effects were observed in laying hens, where 1% silymarin supplementation reduced the impact of 1 mg/kg of OTA on performance, increased egg production and quality, and protected the liver and kidneys from oxidative stress [156]. In a study with one-day-old chicks intoxicated with 3 mg/kg of OTA, 1000 mg/kg of silymarin protected the liver and kidneys against oxidative stress induced by mycotoxins [157]. In quails fed with a diet contaminated with 2.2 mg/kg of AFB1, 2000 mg/kg of silymarin alleviated the adverse effects of AFs on performance parameters such as FCR and ADG, and on hepatic function serum biomarkers [158].
In nursery pigs contaminated with 500 ppb of AFB1, a blend of silymarin and other phytogenics protected the liver and intestines from mycotoxin-induced damage, improving liver biomarkers and gut morphology [159]. Additionally, in 25-day-old post-weaned pigs exposed to 0.35 mg/kg of ZEN and 0.5 mg/kg of T-2 toxin, silymarin supplementation reduced mycotoxin residues, enhanced biochemical parameters, and improved growth performance [160]. Similar results were found in piglets exposed to 0.992 mg/kg of ZEN and 0.531 mg/kg of OTA and supplemented with a binding agent combined with silymarin in-feed, improving FCR [161]. Another mycotoxin deactivator blend with silymarin caused an amelioration in the performance parameters by increasing BW, ADG, and FI, and reduced oxidative stress in 24-day-old weaned pigs contaminated with 4.5 mg/kg of DON, 0.5 mg/kg of ZEN, and 18 mg/kg of FBs [162]. As aforementioned, the combination of curcumin extract and silymarin extract with a mix of selected clays to test a novel mycotoxin detoxifier formulation showed protective and ameliorative effects on weaned piglets and sows fed with a diet naturally contaminated with multiple mycotoxins [122,123].
Finally, 600 mg/kg of silymarin supplementation in dairy cows intoxicated with 1 mg/kg of AFB1 mitigated AFB1’s toxic effects, improving renal and liver function, and increased ADG and FI [163]. Additionally, 600 mg/kg BW of silymarin phytosome supplementation in dairy cows exposed to 0.8 mg/kg of AFB1 succeeded in reducing AFM1 carry-over in milk [164]. On the other hand, the supplementation of silymarin succeeded in reverting AFB1 toxic effects, ameliorating rabbit health [165].
Given these findings, silymarin is a promising ingredient for mitigating mycotoxicosis in livestock animals. Some studies suggest that combining silymarin with adsorbent clays may further enhance its detoxifying properties [122,123,166]. To note, the maximum effective dosage of silymarin across livestock studies typically ranges from 5–10 g/kg of diet.
2.3. Grape Pomace Extract
2.3.1. Composition and Main Characteristics
Grapes (Vitis vinifera L.) are the most widely cultivated fruit crop globally, and they are used in the food industry to produce various products, such as wine [167]. During the grape processing for wine production, by-products are generated that possess significant nutritional value. Circular economy practices have opened new avenues for reusing these by-products in various applications, including the development of new food products or nutraceutical ingredients. These ingredients, with their added value, are beneficial for both human and animal consumption [168]. The by-products from wine production, collectively referred to as grape pomace, consist of grape seeds, grape skins, and grape stalks. However, using these by-products directly from waste can introduce toxins and other harmful substances along with health-beneficial compounds [108]. Therefore, it is essential to develop efficient extraction techniques to optimize the recovery of by-products with the best biological and physico-chemical characteristics [168,169].
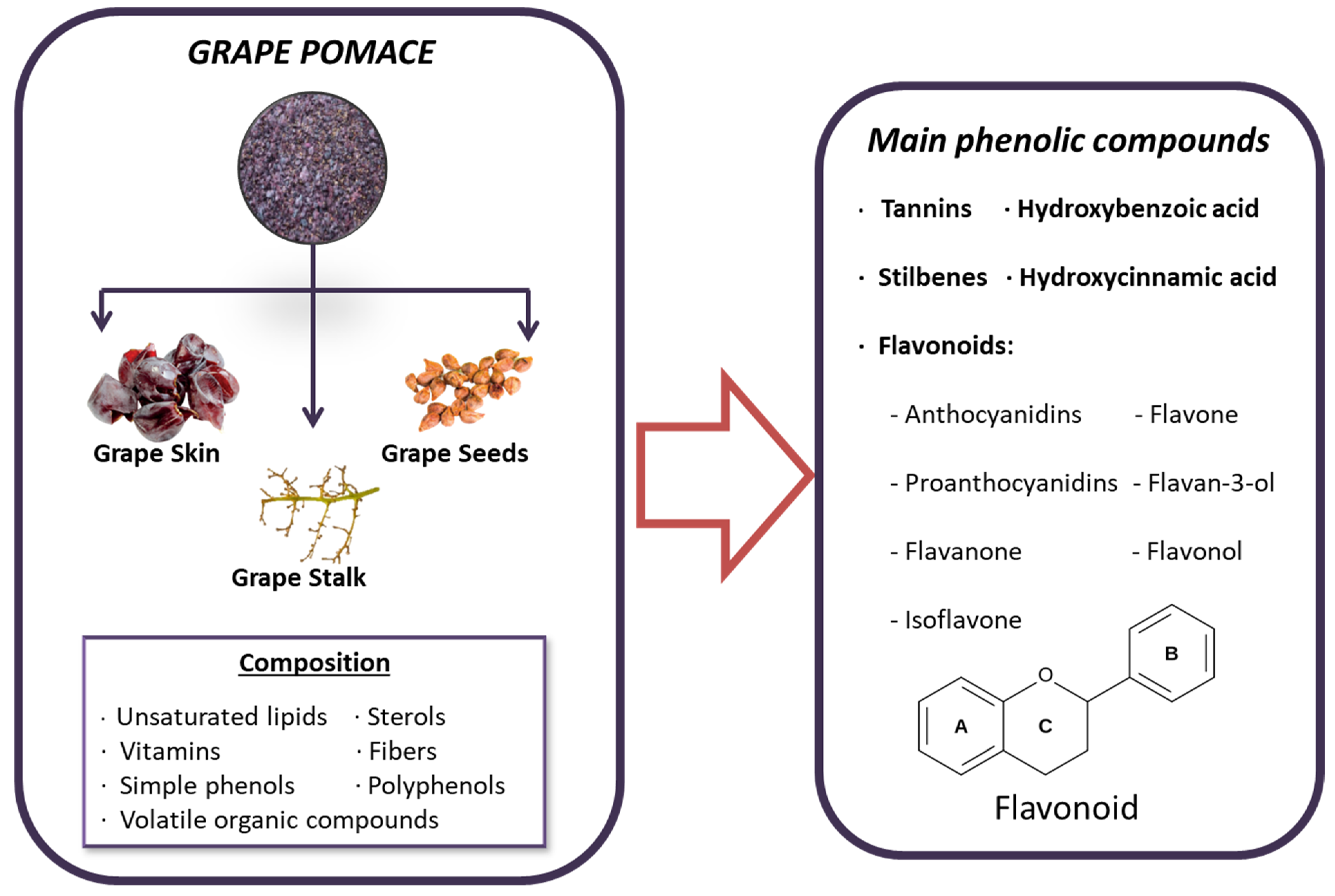
Grape pomace contains a rich variety of beneficial compounds, including unsaturated lipids, sterols, vitamins, antioxidants, fiber, volatile organic compounds and, most notably, phenolic compounds. These phenolic compounds are of particular interest due to their beneficial properties, which include reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, and even possessing anticancer properties [170]. The most significant phenolic compounds found in grape pomace include simple phenols like hydroxycinnamic and hydroxybenzoic acids, as well as polyphenols such as tannins, stilbenes, and flavonoids [171]. Additionally, the phenolic profile can vary depending on the grape variety, which plays an important role in the selection process [171]. In grapes, phenolic compounds are divided into two main categories: non-flavonoids and flavonoids. Flavonoids, characterized by a C6–C3–C6 structure, are prevalent in grapes and are composed of two hydroxylated benzene rings (A and B) linked by a tricarbon chain that forms part of the heterocyclic ring C. These compounds are further categorized into different structural classes based on the oxidation state of ring C, including flavonols, flavan-3-ols (encompassing simple flavan-3-ols and their polymeric form, proanthocyanidins), and anthocyanins [172] (Figure 3). On the other hand, the most abundant non-flavonoids in grapes are hydroxycinnamic acids, such as caftaric acid and coutaric acid [172].
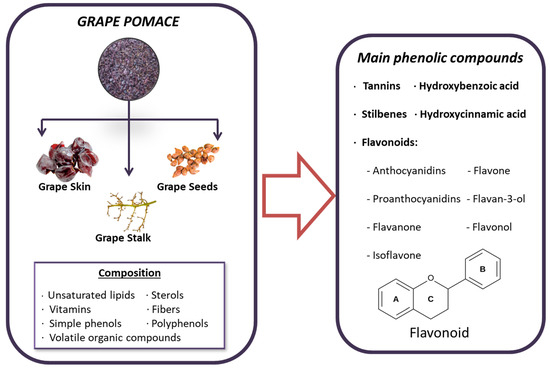
Figure 3.
Composition and principal bioactive components of grape pomace extract.
Despite the wide range of health benefits attributed to polyphenols, it remains unclear which specific compounds contribute the most to these effects. Polyphenols must be released from the food matrix and transformed into bioaccessible forms in the gastrointestinal tract to be absorbed into the bloodstream. Most dietary phenolics are poorly absorbed in the small intestine and undergo extensive metabolism by the gut microbiota in the large intestine, producing metabolites that differ structurally from the original compounds [173]. As a result, dietary phenolic compounds generally have low bioavailability, with phenolic acids being the most bioavailable and anthocyanins the least. Anthocyanins, which are primarily found in red grapes, act as natural colorants and are highly stable, making them difficult to digest and absorb [170,174]. In contrast, proanthocyanidins, which are the most abundant phenolic compounds in grape seeds, exhibit better bioavailability [175]. In conclusion, most phenolic compounds in grape pomace are not absorbed in the small intestine, with 90–95% remaining unabsorbed. While some phenolic compounds are directly available, the majority are partially broken down by intestinal enzymes and microorganisms. The resulting metabolites from polyphenol digestion are then absorbed and utilized by the body through passive diffusion or active transport [170]. Regarding the use of dry grape extract in animal nutrition, EFSA has conducted a study on the safety and efficacy of this feed additive. The study concluded that a maximum dosage of 100 mg/kg of feed for animal species poses no safety concerns and is not considered a risk to the environment [176].
Flavonoids are high-quality bioactive molecules with natural antioxidant properties, and hold great potential for use in the food industry. In addition to their antioxidant activity, flavonoids possess anti-inflammatory, estrogenic, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, and antitumor properties, making them valuable in the development of nutraceutical strategies for combating diseases and as functional food additives. Grape pomace, specifically, has been shown to inhibit the growth of certain harmful bacteria, further enhancing its value [156,177].
2.3.2. Mode of Action and Implication on Animal Health and Production
The molecular mechanisms by which flavonoids and non-flavonoids exert their effects are diverse [178]. The antioxidant properties of polyphenols, particularly proanthocyanidins, are associated with the prevention of lipid oxidation. Studies have shown that proanthocyanidins reduce oxidative stress by lowering levels of lipid peroxidation and Nε-carboxymethyl lysine (products of reactive oxygen species activity), and decreasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD and GSH in a diabetic preclinical model [170]. Anthocyanidins, flavonols, and other phenolic compounds present in red grape pomace have been found to decrease ROS levels, TBARS, and carbonyl levels, while increasing GSH levels by promoting the enzymatic activation of glutamyl cysteine synthetase (GCS) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) in muscle cells [179,180]. In cardiovascular diseases, grape pomace rich in proanthocyanidins, anthocyanins, and quercetin has been shown to restore the expression of genes such as eNOS, SOD2, and HO-1, which are involved in reducing hypertension and providing vascular protection [181]. In a preclinical study, grape pomace supplementation has also been found to increase the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, GPx, and glutathione reductase in models of colitis [182].
The multiple benefits of grape pomace have sparked interest in its use as a feed additive in animal nutrition. Grape pomace has demonstrated its ability to act as a biosorbent, capable of adsorbing mycotoxins by hydrophobic interactions such as AFB1 and ZEN, and forming polar non-covalent interactions with OTA and FB1 [183]. Additionally, grape pomace has been observed to exhibit biofungicidal properties against key mycotoxigenic species [184]. As a result, grape pomace presents a cost-effective solution for decontaminating mycotoxin-contaminated feed and offers antioxidant and antimicrobial benefits, making it a promising anti-mycotoxin product. For consideration, the maximum effective dosage of grape extract observed in different studies with livestock animals was around 80–100 g/kg of diet.
Studies on livestock animals have further demonstrated the effectiveness of grape seed extract in mitigating the harmful effects of mycotoxins. In one-day-old broiler chickens, 250 and 500 mg/kg of grape seed extract reduced the oxidative stress in the liver and plasmatic cytokine levels enhanced by 400 mg/kg of FB1. Grape seed extracts also ameliorated jejunal morphology and ileal microbiota homeostasis, and improved BW, FCR, and mortality rates, resulting in better growth performance [177]. Additionally, grape seed extract counteracted AFB1’s effects on the immune function, antioxidant capacity, and liver morphology of one-day-old broiler chickens by reducing AFB1 residues and damage in the liver, resulting in increased serum immunoglobulin levels and antioxidant parameters and improved growth performance, by improving the organ’s relative weight, ADG, and FCR [37,185,186]. Moreover, 200 mg/kg of grape seed extract can improve the immune function of one-day-old broiler chickens by counteracting the influence of 76 ppb of AFB1 in the growth of the thymus gland and the relative weight of the bursa of Fabricius [187]. In addition, 2 mL/L of gallic acid extracted from grape skin improved hematology, serum biochemistry, and histological morphology in the lungs, liver, and ileum in 100-day-old broilers contaminated with 2.7 × 106 spores/mL of Aspergillus flavus [188]. Similar improvements were observed in quails when supplemented with 500 mg/kg of grape seed extract, including relief of the negative effects induced by 1 mg/kg of AFB1, such as oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, liver fibrosis, and sinusoidal dilation. In addition, grape seed extract improved performance parameters in quails such as FCR, BW, and BWG [189].
Furthermore, the supplementation of grape seed extract in a study with piglets exposed to 479 ppb of OTA and 62 ppb of AFB1 reduced portal areas with mononuclear cellular infiltration and periportal fibrosis in the liver, reduced atrophy of the glomerular tufts, and altered the Bowman’s capsule. In this regard, CYP450 expression in the liver was downregulated by grape seed extract resulting in the bioinactivation of these mycotoxins [181]. In a study with piglets fed with a bolus contaminated with FB1, ZEN, OTA, DON, and AFB1, supplementation with grape pomace reduced the gastrointestinal absorption of these mycotoxins; therefore, the mycotoxicosis of these piglets was reduced [190,191]. Moreover, 8% grape seed extract reduced oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in the mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, and liver of four-week-old weaned piglets exposed to 320 μg/kg of AFB1 [192,193]. Similarly, cross-bred TOPIGS-40, contaminated after weaning with 320 ppb of AFB1, were given supplements with 8% grape seed extract, enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines and TBARS levels [194]. In addition, 8% grape pomace feeding in cross-bred pigs (TOPIG-40) exposed to 320 g/kg of AFB1 positively improved BW and kidney status by boosting the tissue’s antioxidant status [195]. Regarding microbiota homeostasis, 8% dietary grape seed administration to four-week-old piglets contaminated with 320 g/kg feed AFB1 caused an increase in the concentration of beneficial microbiota in the large intestine, causing a reduction in diarrhea and an increase in BW [196].
Furthermore, the use of grape pomace in aquatic animals has also shown positive results. For example, the administration of 1 g/kg of tannins to juvenile Chinese sea bass improved intestinal integrity and bacterial homeostasis, leading to enhanced growth performance and a resistance to AFB1 toxicity [197]. Similarly, 0.2% quercetin, another polyphenol found in grape pomace, has been shown to protect against liver and muscle damage in tilapia exposed to 4.8 mg/kg feed T-2 toxin, improving survival and performance parameters [198]. Therefore, quercetin was effective in protecting the liver and the muscle from T-2 toxicity and in enhancing performance parameters.
2.4. Olive Pomace Extract
2.4.1. Composition and Main Characteristics
During the olive oil extraction process, by-products rich in bioactive compounds are generated. Since olive oil production yields only 15–20% of the raw material, the remaining 80–85% consists of olive pomace [199]. Olive pomace is composed of sugars, fibers, polyalcohols, volatile fatty acids, pectins, fats, and various phenolic compounds like hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, secoiridoid derivatives, phenolic acids, and flavonoids [200]. Olive pomace has well-known health benefits for both animals and humans. Similar to grape extracts, olive pomace is a by-product of olive oil processing, making it an eco-friendly practice within the circular economy, adding value to the olive oil industry [201]. Furthermore, the bioactive compounds in olive pomace have attracted significant interest in the pharmaceutical and functional food industries.
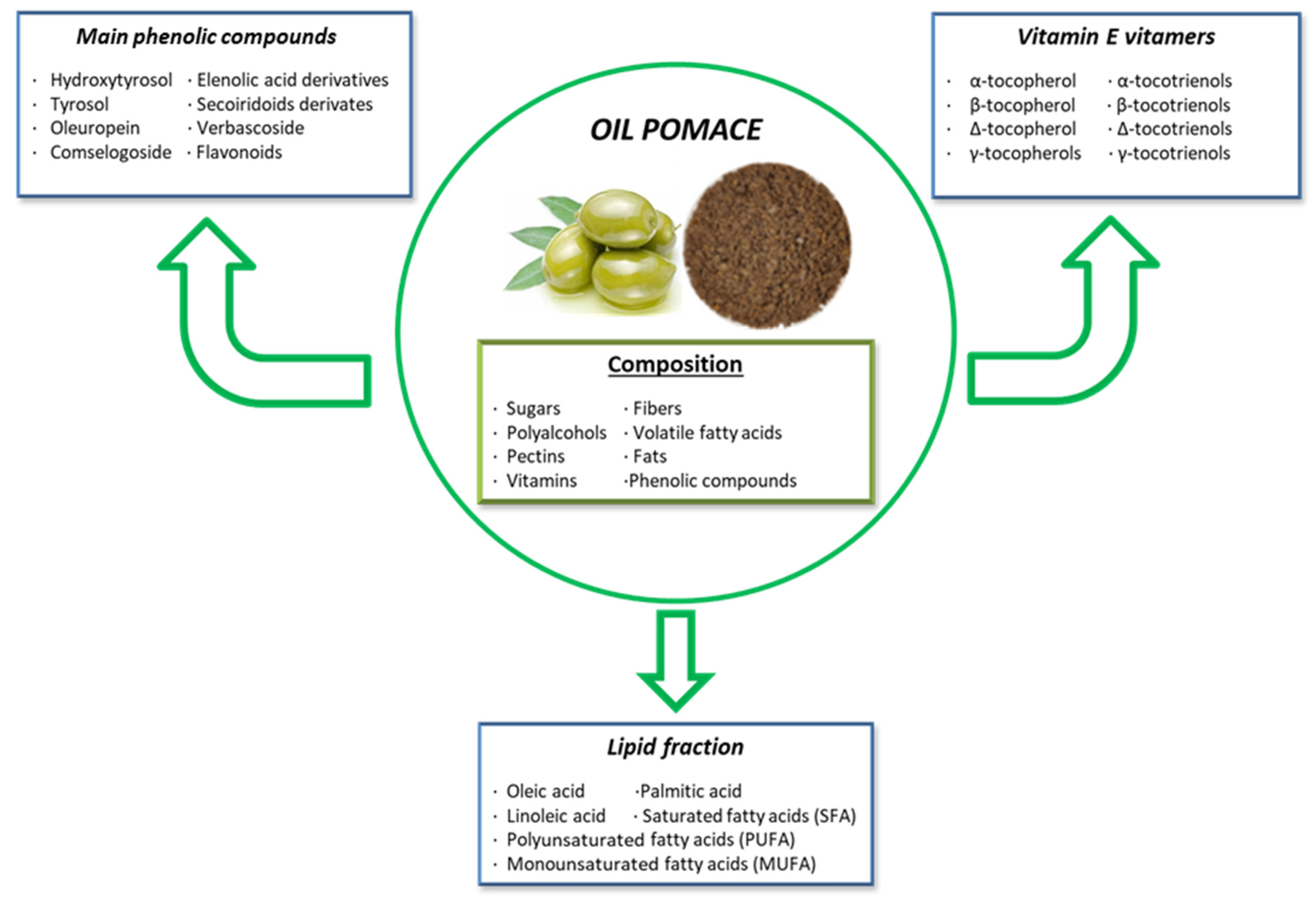
Olive pomace contains crushed olive stones, pulp, skins, and varying amounts of water, depending on the oil extraction method used. It is rich in phytochemicals, including vitamin E vitamers, phenolic compounds, peptides, quercetin, and fats (Figure 4) [202]. The most important vitamin E vitamer is α-tocopherol, the most abundant and biologically active form of vitamin E present in olive pomace. It plays a crucial antioxidant role by scavenging ROS and preventing lipid peroxidation. Apart from α-tocopherol, olive pomace contains seven other important vitamers: β, δ, and γ-tocopherols, and α, β, δ, and γ-tocotrienols [203].
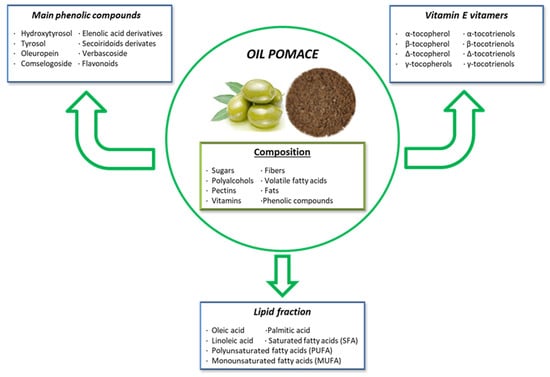
Figure 4.
Composition and principal bioactive components of olive pomace extract.
In terms of fats, olive pomace is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and contains polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). The high MUFA content makes olive pomace less susceptible to oxidation. Oleic acid (C18:1n9cis), the most abundant MUFA in olive pomace, has numerous health benefits for both animals and humans. Additionally, olive pomace contains linoleic acid, which has antibacterial properties [203,204].
Phenolic compounds are another significant bioactive component of olive pomace, with hydroxytyrosol being the most abundant, followed by tyrosol and oleuropein [205]. Hydroxytyrosol, the main product of oleuropein hydrolysis, is one of the most potent natural antioxidants found in olive pomace. It exhibits antioxidant, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties, and it helps regulate lipid profiles while protecting against genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, and proapoptotic effects [200]. Oleuropein, another important secoiridoid phenolic compound, provides antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties due to the hydroxyl groups in its structure, which donate hydrogen to prevent oxidation. Moreover, oleuropein has been studied for its ability to modulate blood pressure, helping to prevent hypertension [206]. Additionally, oleuropein has demonstrated anti-cancer, cardioprotective, neuroprotective, and lipid-regulating effects in metabolic disorders [200,205]. On the other hand, tyrosol, a phenylethanoid compound, exhibits antimicrobial, anti-carcinogenic, anti-atherogenic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties [200,205].
Despite these favorable characteristics of phenolic compounds in olive pomace, their bioavailability and bioaccessibility are low due to their incomplete intestinal absorption and fast biotransformation during digestion, ending up in the excretion of polyphenols from olive pomace [207,208]. During gastrointestinal digestion, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein concentrations remain stable whereas the bioaccessible tyrosol significantly increases compared to the native and undigested sample. However, the bioaccessibility of these polyphenols can be improved by innovative formulation approaches, such as the use of pharmaceutical excipients and advanced formulations for oral administration [208] or through the fermentation of olive pomace [209]. EFSA has found extensive scientific evidence supporting the health benefits of hydroxytyrosol and related polyphenols [210]. Furthermore, EFSA has raised no safety concerns regarding their use in novel food preparations at doses up to 215 mg/kg for humans, and hydroxytyrosol showed no adverse effects in rats at 2000 mg/kg of body weight in acute toxicity studies and 500 mg/kg of body weight in chronic repeated doses [40,210].
2.4.2. Mode of Action and Implications for Animal Health and Production
Olive pomace, rich in valuable bioactive compounds, is increasingly used in developing functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals. Compounds like hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein, and quercetin exhibit anti-cancer activity by promoting apoptosis in cancer cells, thus reducing their viability [211,212,213]. The antioxidant properties of polyphenols in olive pomace stem from their hydroxyl groups, which neutralize reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, making them effective hydrogen donors. Additionally, they can chelate metal ions to reduce free radical production. These hydroxyl groups also disrupt bacterial cell membranes, contributing to antimicrobial activity [203]. Olive pomace has demonstrated high antioxidant capacity, effectively reducing ROS levels in cancer cells [213]. It increases glutathione (GSH) levels, protecting cells from radical-induced damage. In fact, hydroxytyrosol has shown the highest intracellular radical scavenging activity in pre-treated cells. Olive pomace also reduces glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity, altering the cells’ redox state through direct radical scavenging [214]. In vascular diseases, olive pomace exhibits anti-atherogenic effects by decreasing pro-atherogenic factors (iNOS, COX-2) and pro-inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, MMP-2, MMP-9, and MT1-MMP), reducing nitric oxide (NO) production, and improving vascular health [206]. Hydroxytyrosol also downregulates the expression of the vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) and the intracellular cell adhesion molecule (ICAM-1), both of which are involved in inflammation and are activated by NF-κβ [215]. Olive pomace further exerts anti-inflammatory effects by upregulating TIMP-1 and inhibiting the NF-κβ pathway, which modulates TNF-α and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). In a study involving one-day-old broilers, olive pomace reduced gut inflammation by downregulating IL-8, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, and upregulating the anti-inflammatory cytokine TGF-β4 [216]. Additionally, polyphenols in olive pomace were linked to inhibiting the activation of p38 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways, further contributing to its anti-inflammatory effects [217].
Regarding mycotoxin mitigation, studies have shown that olive pomace can inhibit the growth of toxigenic fungi and reduce levels of AFs [218]. Moreover, an in vitro study showed that olive pomace potentially adsorbs AFB1, ZEN, and OTA mycotoxins at 30 mg/mL at different pH levels [219]. Specifically, hydroxytyrosol has exhibited protective effects against oxidative stress induced by OTA in kidneys from rats, by limiting the release of MDA, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and ROS [220]. Olive leaves and branches have also been found to possess anti-mycotoxin biosorbent properties [221], and olive mill wastewater has shown an inhibitory effect on AFB1 production [222].
Quercetin found in olive pomace, as aforementioned in the grape pomace section, has shown protective effects against T-2 toxin-induced damage in tilapia by enhancing antioxidant capacity, protecting liver function, and improving survival rates, weight gain, and the hepatosomatic index [198].
As a low-cost biosorbent, olive pomace can be used to remove mycotoxins from contaminated animal feed. It also holds promise as a feed additive, offering health benefits that enhance the value of anti-mycotoxin products. However, further studies are needed to understand better the beneficial effects of olive pomace on animal health, especially concerning mycotoxicosis. Notably, the maximum effective dosage of olive pomace extract observed in various livestock studies is around 5 g/kg of diet.
2.5. Orange Peel Extract
2.5.1. Composition and Main Characteristics
For a long time, oranges (Citrus sinensis, Citrus × aurantium, or other varieties) were primarily used in the food industry for human and animal consumption, as well as for juice production. This process generated significant amounts of waste, including orange seeds and peels, which typically went untreated or were discarded. However, the food and animal industries are now recognizing the beneficial health properties of bioactive compounds found in orange peel, which contains a phenolic concentration more than 15% higher than the pulp. These compounds can be utilized in new feed additives and nutraceutical formulas. As a result, orange peel has gained renewed value, aligning with circular economy practices by repurposing orange by-products, thanks to the promising health benefits its components offer [223,224].
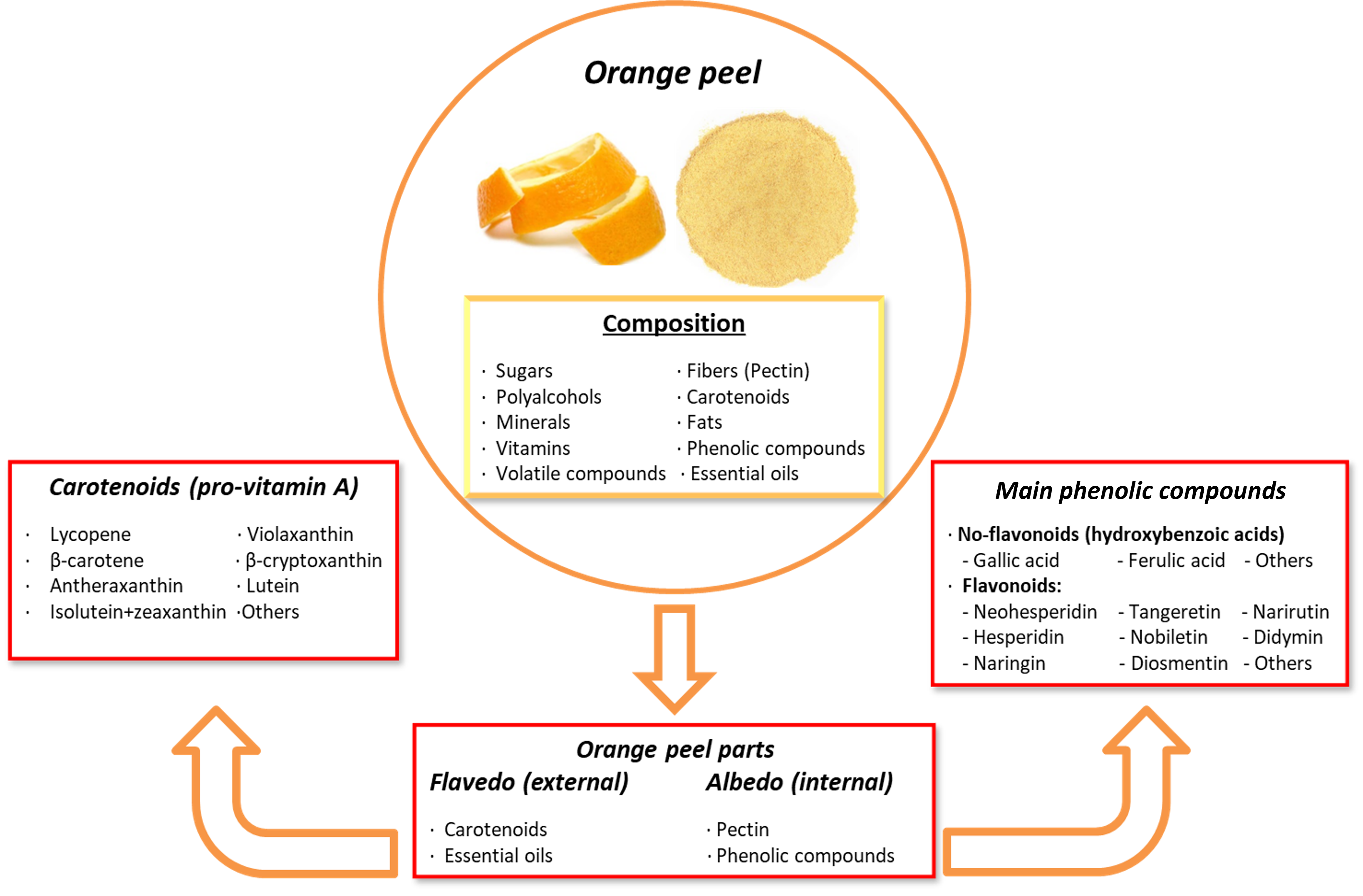
Orange peel contains several phytochemicals of high interest due to their health-promoting and disease-preventing properties. These include vitamin C, folic acid, potassium, pectin, polyphenols, volatile compounds, minerals, dietary fibers, essential oils, and carotenoids. The outer layer, known as the flavedo, is rich in carotenoids and essential oils, while the inner layer, called the albedo, is rich in pectin and phenolic compounds. The phenolic compounds in orange peel include both non-flavonoids and flavonoids, such as polymethoxylated flavones (PMFs), C- or O-glycosylated flavones, O-glycosylated flavanones, and flavonols [87,225,226]. The most abundant citrus flavonoids in the orange peel are neohesperidin, hesperidin, naringin, nobiletin, narirutin, didymin, sinensetin, eriocitrin, 3′, 4′, 5, 5′, 6, 7-hexamethoxyflavone, diosmetin, and tangeretin [227].
The main health benefits attributed to the phenolic compounds in orange peel include antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, anti-proliferative, and antiviral activities. They also contribute to improved capillary fragility and the prevention of platelet aggregation, helping to mitigate various chronic diseases [224]. Glycosylated flavanones, such as hesperidin, naringin, and neohesperidin, are the most abundant polyphenols in orange peel. These polyphenols have shown significant antioxidant and anti-cancer effects in multiple studies, as they stabilize free radicals by donating protons or electrons. However, their oral bioavailability is limited due to the conjugation of their hydroxyl groups and low water solubility, leaving many of the polyphenols unabsorbed and persisting in the colon [59,226]. Despite this low bioavailability, some strategies may enhance this characteristic through enzymatic modifications or the design of delivery systems [109].
In addition to polyphenols, orange peel is a rich source of carotenoids. They are lipophilic non-phenolic compounds that act as natural pigments and offer health benefits through antioxidant and pro-vitamin A activities [228]. Carotenoids are precursors to vitamin A (retinol) that play a critical role in metabolism and chronic disease prevention [229]. These compounds are classified into carotenes, which contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms, and xanthophylls, which contain oxygenated groups, such as hydroxyl, epoxy, and carboxyl groups [225]. The most abundant carotenoids in orange peel include β-carotene, lycopene, isolutein + zeaxanthin, violaxanthin, antheraxanthin, lutein, and β-cryptoxanthin, among others (Figure 5). Carotenoids have been associated with reducing the risk of cancer, osteoporosis, age-related muscular degeneration, cataracts, sunburn-induced skin damage, and cardiovascular diseases [230]. On the other hand, pectin, which is a non-phenolic soluble fiber, appears to ameliorate digestive complications, reduce cholesterol levels, and act as a protective agent against cancer and cardiovascular diseases [231]. Nevertheless, the presence of pectin and its lipophilic characteristics may interfere with carotenoid bioaccessibility. Adjustments to the molecular structure of carotenoids or encapsulation techniques may improve their bioaccessibility and bioavailability in the gastrointestinal tract [232].
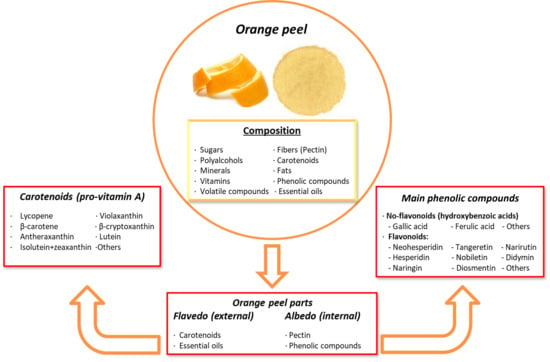
Figure 5.
Composition and principal bioactive components of orange peel extract.
2.5.2. Mode of Action and Implication on Animal Health and Production
The health benefits of the bioactive compounds in orange peel depend on their molecular structures and mechanisms of action. For example, hesperidin and neohesperidin, key flavonoids in orange peel, exhibit radical-scavenging activity [231], suppress ROS and IL-5 via Nrf2 protein expression, activate the ERK/JNK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, and induce HO-1 protein expression by upregulating the transcription factor PPARγ [233]. Hesperidin is especially effective as a ROS scavenger and metal-chelating agent [234,235]. Additionally, hesperidin supports endothelial cell integrity, which is vital for proper vascular function [235]. Hesperidin also shows potential as a feed additive for poultry, as it reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine production and mitigates the effects of influenza A (H1N1) by suppressing MAPK signaling pathways and upregulating p38 and JNK expression, which enhances cell-autonomous immunity [229,230].
Naringin, another key flavonoid, reduces oxidative stress, lowers cholesterol levels, increases SOD activity, and promotes hepatic depuration of LDL cholesterol in rats. This results in improvements in metabolic disorders [236]. Naringin also regulates pro-inflammatory markers such as IL-6, IL-8, iNOS, Nrf2, COX-2, and TNF-α, acting as a potent anti-inflammatory agent in rats [237]. Importantly, naringin functions as an anticancer agent by inhibiting cell proliferation, triggering apoptosis, and diminishing the migration and invasion of specific tumor cells, thereby influencing cell motility [237]. According to several studies in human cells, naringin inhibits cell proliferation, triggers apoptosis, and decreases tumor cell migration and invasion. It achieves this by interrupting EGFR signaling and halting the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phases, as well as by inhibiting VEGF, FAK (PTK2), MMPs, and Zxb1, all of which play roles in tumor development [238].
One of the main carotenoids found in orange peel, β-cryptoxanthin, has been shown in mice to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and TGF-β1, as well as collagen type Iα1 and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 [239]. Additionally, β-cryptoxanthin has protective effects against DNA damage and lipid peroxidation in humans [240]. It also enhances alkaline phosphatase activity and calcium content in the metaphyseal tissue and cortical bone of rats, thereby protecting against osteoporosis by inhibiting bone resorption [241].
Pectin, another important component of orange peel, has numerous health benefits for gut microbiota and gut health. It enhances beneficial bacterial populations, improves digestive and liver enzyme activities, and promotes nutrient absorption. Pectin also serves as an immunomodulator by stimulating the production of antibodies and macrophages [242], making pectin a promising feed additive for improving livestock productivity.
Furthermore, in combination with clays, orange peel has shown enhanced stability in the gastrointestinal tract, increasing the adsorption of mycotoxins such as AFB1, OTA, and FB1 in in vitro studies [243]. Orange peel has also demonstrated the ability to sequester AFB1, OTA, and ZEN [221]. Additionally, orange peel extract exhibited antifungal properties against Aspergillus flavus, a pathogenic fungus linked to various mycotoxicoses in the feed industry [244]. For instance, in an in vitro study, orange peel extract efficiently adsorbed 90% of the AFB1 under gastrointestinal tract conditions [245].
Dietary lycopene (200 and 400 mg/kg), a carotenoid found in orange peel extract, has been shown to alleviate 100 µg/kg of AFB1 toxicity in the gut and the liver of one-day-old broilers by enhancing antioxidant capacity and function and improving inflammatory status, leading to better intestinal health [246]. Lycopene also inhibited hepatic CYP450, which is responsible for liver damage [246,247]. Moreover, 200 mg/kg of dietary lycopene improved growth performance and meat quality in one-day-old broilers exposed to 100 µg/kg of AFB1 [248]. Additionally, dietary lycopene alleviated the toxic effects of DON and ZEN in swine by activating the OXPHOS signaling pathway and enhancing mitochondrial function in intestinal epithelial cells [83,249]. Lycopene also promoted Nrf2 pathway expression, reducing autophagy and apoptosis, thereby mitigating oxidative damage to Sertoli cells caused by ZEN [250].
Overall, polyphenols found in orange peel extract have demonstrated their effectiveness against mycotoxicosis, positioning orange peel extract as an affordable and renewable agro-waste material for mycotoxin adsorption and toxicity reduction. However, further in vivo studies are needed to confirm the beneficial effects of orange peel extract in livestock and pets affected by mycotoxins.
The different interventions using curcumin, silymarin, grape and olive pomace, and orange peel extracts against mycotoxicosis in livestock, aquaculture, and pet species proposed in this paper have been gathered in Supplementary Table S1.
3. Conclusions
In conclusion, mycotoxins pose a significant threat to animal and human health, as well as to the global feed supply chain. The chronic effects of mycotoxins on animal health and production, as well as the economic impact on the livestock industry, make it crucial to develop and implement solutions to control and monitor factors implicated in mycotoxicosis. Additionally, natural anti-mycotoxin solutions, such as biological adsorbents, enterosorbents, and natural dietary interventions, are being developed to prevent or mitigate mycotoxicosis and its detrimental effects on animal and human health. Thus, further research on the use of phytogenic feed additives in foodstuffs contaminated by mycotoxins is essential for finding better, cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and generally safe solutions against mycotoxicosis in animal feed. However, the main limitations of using such products lie in the bioaccessibility and bioavailability that can be studied to discover better formulations and conformations of these bioactive compounds. Moreover, the combination of phytogenics with mycotoxin binders is a promising strategy that can enhance their combined effects against mycotoxins. Even though, in this review, we focused on five promising phytogenics with demonstrated positive effects on animal performance and health to present them as potential anti-mycotoxin solutions, many more bioactive compounds yet to be studied could be useful as treatments against the effects of mycotoxins. Finally, most of the studies on anti-mycotoxin phytogenics in the animal industry are focused on livestock and aquaculture species, setting aside companion animals, whose number is growing exponentially worldwide and who are also threatened by the negative effects of mycotoxins, which are especially prevalent in cats and dogs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/toxins16100434/s1, Table S1: Studies with phytogenic interventions targeting different livestock, aquaculture, and pet species compromised by mycotoxins.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.R.; validation, I.R.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Q.-V.; writing—review and editing, S.Q.-V., O.C., R.C.M., A.D.B. and I.R.; supervision, I.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author S.Q.-V was employed by the company Bionte Nutrition. The remaining authors R.C.M., O.C., A.D.B. and I.R. declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Mavrommatis, A.; Giamouri, E.; Tavrizelou, S.; Zacharioudaki, M.; Danezis, G.; Simitzis, P.E.; Zoidis, E.; Tsiplakou, E.; Pappas, A.C.; Georgiou, C.A.; et al. Impact of Mycotoxins on Animals’ Oxidative Status. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Feng, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Liu, D. Mycotoxins in Livestock Feed in China—Current Status and Future Challenges. Toxicon 2022, 214, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryden, W.L. Mycotoxin Contamination of the Feed Supply Chain: Implications for Animal Productivity and Feed Security. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 173, 134–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, O.; Siri-Anusornsak, W.; Petchkongkaew, A.; Elliott, C. A Systematic Review of Global Occurrence of Emerging Mycotoxins in Crops and Animal Feeds, and Their Toxicity in Livestock. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Du, H.; Kebede, H.; Liu, Y.; Xing, F. Contamination Status of Major Mycotoxins in Agricultural Product and Food Stuff in Europe. Food Control 2021, 127, 108120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichinger, G.; Del Favero, G.; Warth, B.; Marko, D. Alternaria Toxins—Still Emerging? Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4390–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navale, V.; Vamkudoth, K.R.; Ajmera, S.; Dhuri, V. Aspergillus Derived Mycotoxins in Food and the Environment: Prevalence, Detection, and Toxicity. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1008–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kępińska-Pacelik, J.; Biel, W. Mycotoxins—Prevention, Detection, Impact on Animal. Processes 2021, 9, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlin, G.N.; Cairns, J.E.; Das, B. Rapid Breeding and Varietal Replacement Are Critical to Adaptation of Cropping Systems in the Developing World to Climate Change. Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 12, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magan, N.; Hope, R.; Cairns, V.; Aldred, D. Post-Harvest Fungal Ecology: Impact of Fungal Growth and Mycotoxin Accumulation in Stored Grain. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2003, 109, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Dong, H.; Yang, T. Effects of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-α Agonist on Growth Performance, Blood Profiles, Gene Expression Related to Liver Fat Metabolism in Broilers Fed Diets Containing Corn Naturally Contaminated with Mycotoxins. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1103185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Hu, S.; Guo, P.; Zhu, X.; Ren, Z.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X. PPAR-γ with Its Anti-Fibrotic Action Could Serve as an Effective Therapeutic Target in T-2 Toxin-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis of Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Yang, P.L. Quercetin Inhibits the Proliferation and Aflatoxins Biosynthesis of Aspergillus flavus. Toxins 2019, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, P.; Al-mukhaizeem, N.A.R.; Bin Morebah, S.H.; Fouad, D.; Elobeid, M. Protective Effect of Resveratrol against Toxicity Induced by the Mycotoxin, Zearalenone in a Rat Model. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 146, 111840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Q.; Li, K.; Qu, H.; Hu, P.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.Y.; Cai, D.; et al. Sodium Butyrate Ameliorates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Porcine Liver via NR4A2-Mediated Histone Acetylation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10427–10437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Liu, C.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Odle, J.; Lin, X.; Hu, C.A.A.; Liu, Y. EPA and DHA Attenuate Deoxynivalenol-Induced Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cell Injury and Protect Barrier Function Integrity by Inhibiting Necroptosis Signaling Pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.G.; Yuan, Y.P.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.C.; Wang, S.S.; Tang, Q.Z. Piperine Attenuates Pathological Cardiac Fibrosis via PPAR-γ/AKT Pathways. EBioMedicine 2017, 18, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagatur, N.K.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Poda, S.; Kadirvelu, K.; Hashem, A.; Mudili, V.; Siddaiah, C. Quercetin Mitigates the Deoxynivalenol Mycotoxin Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells by Modulating the Oxidative Stress Mediators. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethaler, B.; Lehnert, K.; Yahiaoui-Doktor, M.; Basrai, M.; Vetter, W.; Kiechle, M.; Bischoff, S.C. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Improve Intestinal Barrier Integrity—Albeit to a Lesser Degree than Short-Chain Fatty Acids: An Exploratory Analysis of the Randomized Controlled LIBRE Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 2779–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, G.R.; Ledoux, D.R.; Naehrer, K.; Berthiller, F.; Applegate, T.J.; Grenier, B.; Phillips, T.D.; Schatzmayr, G. Prevalence and Effects of Mycotoxins on Poultry Health and Performance, and Recent Development in Mycotoxin Counteracting Strategies. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1298–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, C.; Baser, K.; Windisch, W. Essential Oils and Aromatic Plants in Animal Feeding—A European Perspective. A Review. Flavour Fragr. J. 2010, 25, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuchi, C.G.; Ondari, E.N.; Ogbonna, C.U.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Baran, K.; Okpala, C.O.R.; Korzeniowska, M.; Guiné, R.P.F. Mycotoxins Affecting Animals, Foods, Humans, and Plants: Types, Occurrence, Toxicities, Action Mechanisms, Prevention, and Detoxification Strategies—A Revisit. Foods 2021, 10, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, C.; Ranjbar Shamsi, R.; Amiri, B.; Kakebaraie, S.; Jalili, F.; Nasta, T.Z. Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effects of Aflatoxin on the Reproductive System: Focus on Cell Cycle Dynamics and Apoptosis in Testicular Tissue. Toxicology 2024, 504, 153773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, J.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, H.; Tian, G.; Chen, D.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Yu, J.; Mao, X.; Huang, Z.; et al. Effects of Chronic Exposure to Low Levels of Dietary Aflatoxin B1 on Growth Performance, Apparent Total Tract Digestibility and Intestinal Health in Pigs. Animals 2021, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabeer, S.; Asad, S.; Jamal, A.; Ali, A. Aflatoxin Contamination, Its Impact and Management Strategies: An Updated Review. Toxins 2022, 14, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological Properties and Their Involvement in Cancer Development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, R.G.; Rădulescu, A.L.; Georgescu, S.E.; Dinischiotu, A. Aflatoxins in Feed: Types, Metabolism, Health Consequences in Swine and Mitigation Strategies. Toxins 2022, 14, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battacone, G.; Nudda, A.; Pulina, G. Effects of Ochratoxin A on Livestock Production. Toxins 2010, 2, 1796–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mally, A.; Hard, G.C.; Dekant, W. Ochratoxin A as a Potential Etiologic Factor in Endemic Nephropathy: Lessons from Toxicity Studies in Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2254–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouany, J.P.; Yiannikouris, A.; Bertin, G. Risk Assessment of Mycotoxins in Ruminants and Ruminant Products. Options Méditerranéennes A 2009, 85, 205–224. [Google Scholar]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.C.; Nielsen, E.; et al. Risks for Animal Health Related to the Presence of Ochratoxin A (OTA) in Feed. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e08375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik, E.; Niemcewicz, M.; Podogrocki, M.; Ceremuga, M.; Stela, M.; Bijak, M. T-2 Toxin—The Most Toxic Trichothecene Mycotoxin: Metabolism, Toxicity, and Decontamination Strategies. Molecules 2021, 26, 6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, M.S.; Mirocha, C.J. Necrotic Oral Lesions in Chickens Fed Diacetoxyscirpenol, T—2 Toxin, and Crotocin. Poult. Sci. 1978, 57, 807–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific Opinion on the Risks for Animal and Public Health Related to the Presence of T-2 and HT-2 Toxin in Food and Feed. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Ding, W.-L.; Xu, B.-W.; Rehman, M.U.; Liu, K.-L.; He, Y.-F.; Li, S.-Y.; Jian, F.-C.; Huang, S.-C. Aflatoxin B1 as a Complicit in Intestinal Damage Caused by Eimeria Ovinoidalis in Lambs: Novel Insights to Reveal Parasite-Gut Battle. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domijan, A.-M. Fumonisin B1: A Neurotoxic Mycotoxin/Fumonizin B1: Neurotoksični Mikotoksin. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2012, 63, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM); Knutsen, H.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L. Risks for Animal Health Related to the Presence of Fumonisins, Their Modified Forms and Hidden Forms in Feed. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinedine, A.; Soriano, J.M.; Moltó, J.C.; Mañes, J.R. Review on the Toxicity, Occurrence, Metabolism, Detoxification Regulations and Intake of Zearalenone: An Oestrogenic Mycotoxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink-Gremmels, J.; Malekinejad, H. Clinical Effects and Biochemical Mechanisms Associated with Exposure to the Mycoestrogen Zearalenone. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific Opinion on the Risks for Animal and Public Health Related to the Presence of Alternaria Toxins in Feed and Food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide Contamination of Food-Crops with Mycotoxins: Validity of the Widely Cited ‘FAO Estimate’ of 25%. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zain, M.E. Impact of Mycotoxins on Humans and Animals. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2010, 15, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Patial, V. Food Mycotoxins: Dietary Interventions Implicated in the Prevention of Mycotoxicosis. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 1717–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Donat, P.; Marín, S.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.J. A Review of the Mycotoxin Adsorbing Agents, with an Emphasis on Their Multi-Binding Capacity, for Animal Feed Decontamination. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Kiarie, E.G.; Yiannikouris, A.; Sun, L.; Karrow, N.A. Nutritional Impact of Mycotoxins in Food Animal Production and Strategies for Mitigation. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gregorio, M.C.; De Neeff, D.V.; Jager, A.V.; Corassin, C.H.; de Pinho Carão, A.C.; de Albuquerque, R.; Azevedo, A.C.; Oliveira, C.A.F. Mineral Adsorbents for Prevention of Mycotoxins in Animal Feeds. Toxin Rev. 2014, 33, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan Miladinovic, D.; Ayoola, O. Influence of the Animal Feed Binders on Optimal Nutritional and Physical Qualities of the Animal Feed Pellets and Feed Production Capacity—A Literature Review. Master’s Thesis, NMBU—Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Ås, Norway, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jouany, J.P. Methods for Preventing, Decontaminating and Minimizing the Toxicity of Mycotoxins in Feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 342–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihal, A.; Rodríguez-Prado, M.; Calsamiglia, S. The Efficacy of Mycotoxin Binders to Control Mycotoxins in Feeds and the Potential Risk of Interactions with Nutrient: A Review. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S.A.; Reinders, R.D. Antibacterial Activity of Selected Plant Essential Oils against Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 36, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezabih Yitbarek, M. Phytogenics as Feed Additives in Poultry Production: A Review. Int. J. Extensive Res. 2015, 3, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, S.R.; Zulkifli, I.; Hair Bejo, M.; Farida, A.; Somchit, M.N. Acute Toxicity Study and Phytochemical Screening of Selected Herbal Aqueous Extract in Broiler Chickens. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 4, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ren, W.; Duan, J.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Li, T.; Yin, Y.; Wu, G. Dietary Arginine Supplementation Enhances Intestinal Expression of SLC7A7 and SLC7A1 and Ameliorates Growth Depression in Mycotoxin-Challenged Pigs. Amino Acids 2013, 46, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, W.; Yao, K.; Zhou, T.; Yin, J.; Li, T.; Yang, L.; He, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H. Effects of Dietary Arginine and Glutamine on Alleviating the Impairment Induced by Deoxynivalenol Stress and Immune Relevant Cytokines in Growing Pigs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidin, Z.U.; Khan, M.Z.; Khatoon, A.; Saleemi, M.K.; Khan, A. Protective Effects of L-Carnitine upon Toxicopathological Alterations Induced by Ochratoxin A in White Leghorn Cockerels. Toxin Rev. 2016, 35, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Protective and Detoxifying Effects Conferred by Selenium against Mycotoxins and Livestock Viruses: A Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 956814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gzyl-Malcher, B.; Rudolphi-Skórska, E.; Sieprawska, A.; Filek, M. Manganese Protects Wheat from the Mycotoxin Zearalenone and Its Derivatives. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, G.D.; Vitorino, V.; Bortoluzzi, A.J.; Scussel, V.M. Effect of Zinc Compounds on Fusarium Verticillioides Growth, Hyphae Alterations, Conidia, and Fumonisin Production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 3395–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, K.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. Melatonin Alleviates β-Zearalenol and HT-2 Toxin-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in Bovine Ovarian Granulosa Cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, M.; Wu, S.; Bao, W. Melatonin Ameliorates the Toxicity Induced by Deoxynivalenol in Murine Ovary Granulosa Cells by Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Su, Y.; Chang, S.; Sun, Y.; Meng, X.; Shan, A. Vitamin C Protects Piglet Liver against Zearalenone-Induced Oxidative Stress by Modulating Expression of Nuclear Receptors PXR and CAR and Their Target Genes. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3675–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, L.; Dhivya, R.; Dhanasekaran, D.; Periasamy, V.S.; Alshatwi, A.A.; Akbarsha, M.A. Hepatotoxic Effect of Ochratoxin A and Citrinin, alone and in Combination, and Protective Effect of Vitamin E: In Vitro Study in HepG2 Cell. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 83, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, A.A.M.; Firgany, A.E.-D.L. Vitamin E Supplementation Ameliorates Aflatoxin B1-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Acta Histochem. 2015, 117, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, M.; Paciolla, C.; Logrieco, A.F.; Mulè, G. Plant Bioactive Compounds in Pre- and Postharvest Management for Aflatoxins Reduction. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.; Syed, B. Phytogenic Feed Additives in Animal Nutrition. In Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of the World; Máthé, Á., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 403–423. ISBN 978-94-017-9809-9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xing, M.; Chen, T.; Tian, S.; Li, B. Effects and Mechanisms of Plant Bioactive Compounds in Preventing Fungal Spoilage and Mycotoxin Contamination in Postharvest Fruits: A Review. Food Chem. 2023, 415, 135787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiouni, S.; Tellez-Isaias, G.; Latorre, J.D.; Graham, B.D.; Petrone-Garcia, V.M.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Yalçın, S.; El-Wahab, A.A.; Visscher, C.; May-Simera, H.L. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidative Phytogenic Substances against Secret Killers in Poultry: Current Status and Prospects. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windisch, W.; Schedle, K.; Plitzner, C.; Kroismayr, A. Use of Phytogenic Products as Feed Additives for Swine and Poultry. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86 (Suppl. S14), E140–E148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.; Dixit, M. Role of Polyphenols and Other Phytochemicals on Molecular Signaling. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 504253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cao, H.; Zhang, D. Structure-Activity Relationships of Cinnamaldehyde and Eugenol Derivatives against Plant Pathogenic Fungi. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 97, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Huang, B.; Luo, X.; Zeng, H.; Ban, X.; He, J.; Wang, Y. The Control of Aspergillus flavus with Cinnamomum Jensenianum Hand-Mazz Essential Oil and Its Potential Use as a Food Preservative. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Blanco, S.; Fernández, J.; López-Ibáñez, S.; Miguélez, E.M.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. Plant Phytochemicals in Food Preservation: Antifungal Bioactivity: A Review. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Rampal, G.; Pal Vig, A. Evaluation of Antifungal and Antioxidative Potential of Hydrolytic Products of Glucosinolates from Some Members of Brassicaceae Family. J. Plant Breed. Crop Sci. 2011, 3, 218–228. [Google Scholar]
- Nazareth, T.M.; Bordin, K.; Manyes, L.; Meca, G.; Mañes, J.; Luciano, F.B. Gaseous Allyl Isothiocyanate to Inhibit the Production of Aflatoxins, Beauvericin and Enniatins by Aspergillus Parasiticus and Fusarium Poae in Wheat Flour. Food Control 2016, 62, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, T.; Güray, T.; Yilmazer, D.T.; Tunali Akar, S. Biosorptive Detoxification of Zearalenone Biotoxin by Surface-Modified Renewable Biomass: Process Dynamics and Application. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 1850–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, E.; Scarcia, Y.; Parlavecchia, M. Removal of Ochratoxin A from Liquid Media Using Novel Low-Cost Biosorbents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 34484–34494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranya, N.; Nakeeran, E.; Giri Nandagopal, M.S.; Selvaraju, N. Optimization of Adsorption Process Parameters by Response Surface Methodology for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Annona Reticulata Linn Peel Microparticles. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2094–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarsini, K.I. The Chemistry of Curcumin: From Extraction to Therapeutic Agent. Molecules 2014, 19, 20091–20112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabon, H.J.J. A Synthesis of Curcumin and Related Compounds. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays Bas 1964, 83, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC) Directive 2003/1831/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2003 on Additives in Animal Feed. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2003/1831/oj (accessed on 19 September 2016).
- Liczbiński, P.; Michałowicz, J.; Bukowska, B. Molecular Mechanism of Curcumin Action in Signaling Pathways: Review of the Latest Research. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1992–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharat, M.; McClements, D.J. Recent Advances in Colloidal Delivery Systems for Nutraceuticals: A Case Study—Delivery by Design of Curcumin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 557, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, F.; Gu, S.; Cao, C.; Xiao, Y.; Bao, W.; Wang, H. Lycopene Alleviates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Toxicity in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Mediating Mitochondrial Function. Toxicology 2024, 506, 153880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Min, T. Curcumin, Curcumin Nanoparticles and Curcumin Nanospheres: A Review on Their Pharmacodynamics Based on Monogastric Farm Animal, Poultry and Fish Nutrition. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiori, M.S.; Oliveira, R.C.; Souza, C.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Ribeiro, Q.M.; Wagner, R.; Gündel, S.S.; Ourique, A.F.; Kirinus, J.K.; Stefani, L.M. Curcumin in the Diet of Quail in Cold Stress Improves Performance and Egg Quality. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 254, 1141925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerazion, E.; Rosa, R.; Ferrari, E.; Veronesi, P.; Leonelli, C.; Saladini, M.; Ferrari, A.M. Phytochemical Compounds or Their Synthetic Counterparts? A Detailed Comparison of the Quantitative Environmental Assessment for the Synthesis and Extraction of Curcumin. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, R.; Xia, S.; Wei, G.; Ishfaq, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Protective Role of Curcumin on Aflatoxin B1-Induced TLR4/RIPK Pathway Mediated-Necroptosis and Inflammation in Chicken Liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temba, B.A.; Fletcher, M.T.; Fox, G.P.; Harvey, J.; Okoth, S.A.; Sultanbawa, Y. Curcumin-Based Photosensitization Inactivates Aspergillus flavus and Reduces Aflatoxin B1 in Maize Kernels. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarru, L.P.; Settivari, R.S.; Antoniou, E.; Ledoux, D.R.; Rottinghaus, G.E. Toxicological and Gene Expression Analysis of the Impact of Aflatoxin B1 on Hepatic Function of Male Broiler Chicks. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-Y.; Peng, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.-H.; Yang, Y.; Zhai, S.-S. Curcumin Attenuates Liver Inflammation in Ducks Fed Corn Contaminated with Ochratoxin A Possibly by Regulating Intestinal Microbiota and Inhibiting Toll like Receptor 4/Nuclear Factor Kappa-B Signaling Pathway. Livest. Sci. 2023, 277, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Talebi, M.; Samargahndian, S. Curcumin and cardiovascular diseases: Focus on Cellular Targets and Cascades. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 136, 111214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, H.; Shakeri, A.; Rashidi, B.; Jalili, A.; Banikazemi, Z.; Sahebkar, A. Phytosomal Curcumin: A Review of Pharmacokinetic, Experimental and Clinical Studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Bordoloi, D.; Padmavathi, G.; Monisha, J.; Roy, N.K.; Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, the Golden Nutraceutical: Multitargeting for Multiple Chronic Diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1325–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Wang, Y.; Sharma, G.; Shen, J.; Velkov, T.; Xiao, X. Polymyxins–Curcumin Combination Antimicrobial Therapy: Safety Implications and Efficacy for Infection Treatment. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Lin, J.; Li, H.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Velkov, T.; Shen, J. The Natural Product Curcumin as an Antibacterial Agent: Current Achievements and Problems. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Tian, E.; Hao, Z.; Tang, S.; Wang, Z.; Sharma, G.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J. Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity and Protective Effects of Curcumin: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, B.; Hoyer, D.; Shen, J.; Velkov, T.; Tang, S. Curcumin Attenuates Colistin-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity in Mice. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Xiao, X.; Tang, S. Curcumin Attenuates Quinocetone Induced Apoptosis and Inflammation via the Opposite Modulation of Nrf2/HO−1 and NF-kB Pathway in Human Hepatocyte L02 Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 95, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Cappai, R.; Tang, S.; Li, D.; Xie, S.; Xiao, X.; Velkov, T. Curcumin Attenuates Colistin-Induced Neurotoxicity in N2a Cells via Anti-Inflammatory Activity, Suppression of Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 55, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolami, F.; Barbarossa, A.; Badino, P.; Ghadiri, S.; Cavallini, D.; Zaghini, A.; Nebbia, C. Effects of Turmeric Powder on Aflatoxin M1 and Aflatoxicol Excretion in Milk from Dairy Cows Exposed to Aflatoxin B1 at the EU Maximum Tolerable Levels. Toxins 2022, 14, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Ishfaq, M.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Fazlani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X. Curcumin Ameliorates Duodenal Toxicity of AFB1 in Chicken through Inducing P-Glycoprotein and Downregulating Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 7035–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Han, M.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, P.; Hussain, M.A.; Zhang, X. Dual Role of Dietary Curcumin Through Attenuating AFB1-Induced Oxidative Stress and Liver Injury via Modulating Liver Phase-I and Phase-II Enzymes Involved in AFB1 Bioactivation and Detoxification. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longobardi, C.; Damiano, S.; Andretta, E.; Prisco, F.; Russo, V.; Pagnini, F.; Florio, S.; Ciarcia, R. Curcumin Modulates Nitrosative Stress, Inflammation, and DNA Damage and Protects against Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiel, A.A.M.; El-Denshary, E.S.; El-Nekeety, A.A.; Al-Yamani, M.F.; Gad, A.S.; Hassan, N.S.; Abdel-Wahhab, M.A. Ameliorative Effects of Curcumin Nanoparticles on Hepatotoxicity Induced by Zearalenone Mycotoxin. Glob. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 9, 234–245. [Google Scholar]
- Damiano, S.; Jarriyawattanachaikul, W.; Girolami, F.; Longobardi, C.; Nebbia, C.; Andretta, E.; Lauritano, C.; Dabbou, S.; Avantaggiato, G.; Schiavone, A. Curcumin Supplementation Protects Broiler Chickens Against the Renal Oxidative Stress Induced by the Dietary Exposure to Low Levels of Aflatoxin B1. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 822227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amminikutty, N.; Spalenza, V.; Jarriyawattanachaikul, W.; Badino, P.; Capucchio, M.T.; Colombino, E.; Schiavone, A.; Greco, D.; D’Ascanio, V.; Avantaggiato, G. Turmeric Powder Counteracts Oxidative Stress and Reduces AFB1 Content in the Liver of Broilers Exposed to the EU Maximum Levels of the Mycotoxin. Toxins 2023, 15, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, N.K.S.; Ledoux, D.R.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Bermudez, A.J.; Chen, Y.C. Antioxidant Efficacy of Curcuminoids from Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) Powder in Broiler Chickens Fed Diets Containing Aflatoxin B1. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Cruz, B.; Hernandez-Patlan, D.; Petrone, V.M.; Pontin, K.P.; Latorre, J.D.; Beyssac, E.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Merino-Guzman, R.; Owens, C.; Hargis, B.M. Evaluation of Cellulosic Polymers and Curcumin to Reduce Aflatoxin B1 Toxic Effects on Performance, Biochemical, and Immunological Parameters of Broiler Chickens. Toxins 2019, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, S.; Yang, W.; Huang, Q.; Ho, C.-T. The Biological Fate and Bioefficacy of Citrus Flavonoids: Bioavailability, Biotransformation, and Delivery Systems. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3307–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.-Y.; Qi, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, M.-K.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Gu, C.-Q.; Rajput, S.; Krumm, C.; Qi, D.-S. Curcumin Prevents Aflatoxin B1 Hepatoxicity by Inhibition of Cytochrome P450 Isozymes in Chick Liver. Toxins 2016, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami-Ahangaran, M.; Rangsaz, N.; Azizi, S. Evaluation of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) Effect on Biochemical and Pathological Parameters of Liver and Kidney in Chicken Aflatoxicosis. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 54, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Pang, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Dietary Curcumin Alleviated Aflatoxin B1-Induced Acute Liver Damage in Ducks by Regulating NLRP3–Caspase-1 Signaling Pathways. Foods 2021, 10, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Hu, T.; He, Y.; Zhong, G.; Wu, S.; Jiang, X.; Rao, G.; You, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Tang, Z. Curcumin Attenuates Aflatoxin B1-Induced Ileum Injury in Ducks by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome and Regulating TLR4/NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Mycotoxin Res. 2024, 40, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manafi, M.; Khosravinia, H. Effects of Aflatoxin on the Performance of Broiler Breeders and Its Alleviation through Herbal Mycotoxin Binder. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 15, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Manafi, M. Toxicity of Aflatoxin B1 on Laying Japanese Quails (Coturnix coturnix Japonica). J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, G.M.; Griss, L.G.; Fortuoso, B.F.; Silva, A.D.; Fracasso, M.; Lopes, T.F.; Schetinger, M.R.S.; Gundel, S.; Ourique, A.F.; Carneiro, C. Feed Contaminated by Fumonisin (Fusarium spp.) in Chicks Has a Negative Influence on Oxidative Stress and Performance, and the Inclusion of Curcumin-Loaded Nanocapsules Minimizes These Effects. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 148, 104496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kövesi, B.; Worlanyo, A.P.; Kulcsár, S.; Ancsin, Z.; Erdélyi, M.; Zándoki, E.; Mézes, M.; Balogh, K. Curcumin Mitigates Ochratoxin A-Induced Oxidative Stress and Alters Gene Expression in Broiler Chicken Liver and Kidney. Acta Vet. Hung. 2024, 72, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, D.; Gupta, M.K.; Singh, K.K.; Kumar, S. Ameliorative Effect of Powdered Rhizome of Curcuma Longa on Ochratoxin A Induced Nephrotoxicity in Broilers. Indian J. Vet. Pathol. 2017, 41, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, D.; Wang, W.C.; Lin, C.X.; Fouad, A.M.; Chen, W.; Xia, W.G.; Wang, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W.H.; Yan, S.J. Effects of curcumin on performance, Intestinal Barrier and Mitochondrial Function in Ducks Fed Corn Contaminated with Ochratoxin A. Animal 2019, 13, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledur, P.C.; Santurio, J.M. Cytoprotective Effects of Curcumin and Silymarin on PK-15 Cells Exposed to Ochratoxin A, Fumonisin B1 and Deoxynivalenol. Toxicon 2020, 185, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, D.M.; Kim, Y.I.; Parnsen, W.; Kim, S.W. Phytobiotics with Adsorbent to Mitigate Toxicity of Multiple Mycotoxins on Health and Growth of Pigs. Toxins 2021, 13, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatsiros, V.G.; Eliopoulos, C.; Voulgarakis, N.; Arapoglou, D.; Riahi, I.; Sadurní, M.; Papakonstantinou, G.I. Effects of a Multi-Component Mycotoxin-Detoxifying Agent on Oxidative Stress, Health and Performance of Sows. Toxins 2023, 15, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatsiros, V.G.; Papakonstantinou, G.I.; Voulgarakis, N.; Eliopoulos, C.; Marouda, C.; Meletis, E.; Valasi, I.; Kostoulas, P.; Arapoglou, D.; Riahi, I. Effects of a Curcumin/Silymarin/Yeast-Based Mycotoxin Detoxifier on Redox Status and Growth Performance of Weaned Piglets under Field Conditions. Toxins 2024, 16, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauletto, M.; Giantin, M.; Tolosi, R.; Bassan, I.; Barbarossa, A.; Zaghini, A.; Dacasto, M. Curcumin Mitigates AFB1-Induced Hepatic Toxicity by Triggering Cattle Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: A Whole Transcriptomic In Vitro Study. Antioxidants 2019, 9, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takiya, C.S.; Ribeiro, V.C.; Almeida, C.V.; Bugoni, M.; Vittorazzi, P.C.; Chesini, R.G.; Grigoletto, N.T.S.; Freitas, A.C.; Vieira, D.J.C.; Souza, A.H. Feeding Phytogenic Ingredients Combined or Not with Lithothamnium Calcareum and a Mycotoxin Binder to Lactating Cows: Effects on Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Physiological Parameters, and Nitrogen Excretion. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2023, 303, 115718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Feng, L.; Jiang, W.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Ren, H.; Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; Mi, H.; Zhou, X. Unveiling the Emerging Role of Curcumin to Alleviate Ochratoxin A-Induced Muscle Toxicity in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Jiang, W.-D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Ren, H.-M.; Jin, X.-W.; Feng, L.; Zhou, X.-Q. Dietary Curcumin Alleviates Intestinal Damage Induced by Ochratoxin A in Juvenile Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Necroptosis and Inflammatory Responses. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 18, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Jiang, W.-D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Ren, H.-M.; Jin, X.-W.; Shi, H.-Q.; Feng, L.; Zhou, X.-Q. New Perspectives on the Mechanism of Curcumin in the Gill Mucosal Immune Barrier Damaged by Ochratoxin A in Juvenile Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2024, 583, 740629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, E.-S.H.; Alaidaroos, B.A.; Jastaniah, S.D.; Munir, M.B.; Shafi, M.E.; Abd El-Aziz, Y.M.; Bazina, W.K.; Ibrahim, S.B.; Eissa, M.E.H.; Paolucci, M. Dietary Effects of Nano Curcumin on Growth Performances, Body Composition, Blood Parameters and Histopathological Alternation in Red Tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) Challenged with Aspergillus flavus. Fishes 2023, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Barbary, M.I. Impact of Garlic and Curcumin on the Hepatic Histology and Cytochrome P450 Gene Expression of Aflatoxicosis Oreochromis niloticus Using RT-PCR. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 18, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Barbary, M.I. Detoxification and Antioxidant Effects of Garlic and Curcumin in Oreochromis niloticus Injected with Aflatoxin B1 with Reference to Gene Expression of Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) by RT-PCR. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 42, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyat, M.S.; Ayyat, A.M.N.; Al-Sagheer, A.A.; El-Hais, A.E.-A.M. Effect of Some Safe Feed Additives on Growth Performance, Blood Biochemistry, and Bioaccumulation of Aflatoxin Residues of Nile Tilapia Fed Aflatoxin-B1 Contaminated Diet. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-Y.; Niu, J.; Yin, P.; Mei, X.-T.; Liu, Y.-J.; Tian, L.-X.; Xu, D.-H. Detoxification and Immunoprotection of Zn(II)-Curcumin in Juvenile Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Feed with Aflatoxin B1. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 80, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atef, H.A.; Mansour, M.K.; Ibrahim, E.M.; Sayed El-Ahl, R.M.H.; Al-Kalamawey, N.M.; El Kattan, Y.A.; Ali, M.A. Efficacy of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Curcumin in Amelioration the Toxic Effects in Aflatoxicated Rabbits. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 795–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Chai, X.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, H.; Feng, X. Curcumin Mitigates Oxidative Damage in Broiler Liver and Ileum Caused by Aflatoxin B1-Contaminated Feed through Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Animals 2024, 14, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickova, D.; Ostry, V.; Toman, J.; Malir, F. Presence of Mycotoxins in Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Food Supplements: A Review. Toxins 2020, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottai, M.E.S. Genetic Parameter Variations Among Milk Thistle, Silybum marianum Varieties and Varietal Sensitivity to Infestation with Seedhead Weevil, Larinus latus Herbst. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2006, 8, 862–866. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, R.; Gupta, G.D. Preparation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Silymarin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Capasso, R.; Milic, N.; Capasso, F. Milk Thistle in Liver Diseases: Past, Present, Future. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Izzo, A.A.; Milić, N.; Cicala, C.; Santini, A.; Capasso, R. Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum): A Concise Overview on Its Chemistry, Pharmacological, and Nutraceutical Uses in Liver Diseases. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanoudi, S.; Alavi, M.S.; Karimi, G.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) as an Antidote or a Protective Agent against Natural or Chemical Toxicities: A Review. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 43, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F. Silymarin as a Natural Antioxidant: An Overview of the Current Evidence and Perspectives. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 204–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, A.; Tedesco, D.E.A. Restoring Activity of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L.) on Serum Biochemical Parameters, Oxidative Status, Immunity, and Performance in Poultry and Other Animal Species, Poisoned by Mycotoxins: A Review. Animals 2023, 13, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Sarkar, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Sil, P.C. Silymarin Protects Mouse Liver and Kidney from Thioacetamide Induced Toxicity by Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species and Activating PI3K-Akt Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozmen, M.; Devrim, A.K.; Tunca, R.; Bayezit, M.; Dag, S.; Essiz, D. Protective Effects of Silymarin on Fumonisin B1-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 15, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xiao, Z.-H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, N.-Y.; Khalil, M.M.; Gu, C.-Q.; Qi, D.-S.; Sun, L.-H. Dietary Silymarin Supplementation Alleviates Zearalenone-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Reproductive Toxicity in Rats. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Wahhab, M.A.; El-Nekeety, A.A.; Salman, A.S.; Abdel-Aziem, S.H.; Mehaya, F.M.; Hassan, N.S. Protective Capabilities of Silymarin and Inulin Nanoparticles against Hepatic Oxidative Stress, Genotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Deoxynivalenol in Rats. Toxicon 2018, 142, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Riley, R.T.; Sharma, R.P. Pharmacological Antagonism of Fumonisin B1 Cytotoxicity in Porcine Renal Epithelial Cells (LLC-PK1): A Model for Reducing Fumonisin-Induced Nephrotoxicity In Vivo. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 90, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedesco, D.; Tameni, M.; Steidler, S.; Galletti, S.; Pierro, F. Effect of Silymarin and Its Phospholipid Complex against AFM1 Excretion in an Organic Dairy Herd. Milchwissenschaft 2003, 58, 416–419. [Google Scholar]
- Makki, O.F.; Omidi, A.; Afzali, N.; Sarir, H.; Frouzanmehr, M. Efficacy of Silybum marianum Seeds in Ameliorating the Toxic Effects of Aflatoxin B1 in Broilers. Iran. J. Toxicol. 2014, 8, 977–982. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanian, E.; Mahdavi, A.H.; Asgary, S.; Jahanian, R. Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Silymarin on Performance, Intestinal Morphology and Ileal Bacterial Count in Aflatoxin-challenged Broiler Chicks. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101, e43–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanini, E.H.; Boiago, M.M.; Cécere, B.G.D.O.; Oliveira, P.V.; Teixeira, C.J.S.; Strapazzon, J.V.; Bottari, N.B.; Silva, A.D.; Fracasso, M.; Vendruscolo, R.G. Protective Effects of Silymarin in Broiler Feed Contaminated by Mycotoxins: Growth Performance, Meat Antioxidant Status, and Fatty Acid Profiles. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulwahid, M.T.; Oleiwi, A.F. Ameliorating Effects of Silymarin against Mycotoxin and Its Effect on Some Production and Hematological Parameters of Broilers. J. Genet. Environ. Resour. Conserv. 2021, 9, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Egresi, A.; Süle, K.; Szentmihályi, K.; Blázovics, A.; Fehér, E.; Hagymási, K.; Fébel, H. Impact of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) on the Mycotoxin Caused Redox-Homeostasis Imbalance of Ducks Liver. Toxicon 2020, 187, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencze-Nagy, J.; Strifler, P.; Horváth, B.; Such, N.; Farkas, V.; Dublecz, K.; Pál, L. Effects of Dietary Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Supplementation in Ducks Fed Mycotoxin-Contaminated Diets. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, Y.; Hassan, R.; El-soud, S.; Eldebani, N. The Protective Role of Silymarin to Ameliorate the Adverse Effects of Ochratoxin-A in Laying Hens on Productive Performance, Blood Biochemistry, Hematological and Antioxidants Status. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2022, 24, eRBCA-2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoev, S.D.; Mircheva, T.; Denev, S.; Chobanova, S.; Ivanov, V. The Protective Effect of Silymarin against Ochratoxin A Induced Histopathological and Biochemical Changes in Chicks. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2021, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Khaleghipour, B.; Khosravinia, H.; Toghiyani, M.; Azarfar, A. Effects of Silymarin on Productive Performance, Liver Function and Serum Biochemical Profile in Broiler Japanese Quail Challenged with Dietary Aflatoxins. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasconi, L.; Dazuk, V.; Molosse, V.L.; Cécere, B.G.O.; Deolindo, G.L.; Mendes, R.E.; Gloria, E.M.; Ternus, E.M.; Galli, G.M.; Paiano, D. Nursery Pigs Fed with Feed Contaminated by Aflatoxin B1 (Aspergillus flavus) and Anti-Mycotoxin Blend: Pathogenesis and Negative Impact on Animal Health and Weight Gain. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 186, 106474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, J.; Vasiljević, M.; Tassis, P.; Farkaš, H.; Männer, K. Efficacy of a Multicomponent Mycotoxin Detoxifying Agent on Concurrent Exposure to Zearalenone and T-2 Mycotoxin in Weaned Pigs. Livest. Sci. 2020, 242, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassis, P.; Raj, J.; Floros, D.; Mittas, N.; Ntarampa, N.; Farkas, H.; Polizopoulou, Z.; Vasilievic, M. Efficacy of a Multicomponent Binding Agent against Combined Exposure to Zearalenone and Ochratoxin A in Weaned Pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1357723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.V.; Fontes, D.O.; Benfato, M.D.S.; Hackenhaar, F.S.; Salomon, T.; Jacob, D.V.; Prévéraud, D.; Araujo, W.A.G.; Glória, E.M.; Domingos, R.L. Mycotoxin Deactivator Improves Performance, Antioxidant Status, and Reduces Oxidative Stress in Nursery Pigs Fed Diets Containing Mycotoxins. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, O.; Khan, J.A.; Khan, M.S.; Omer, M.O.; Chishti, G.A.; Sohail, M.L.; Saleem, M.U. Comparative Efficacy of Silymarin and Choline Chloride (Liver Tonics) in Preventing the Effects of Aflatoxin B1 in Bovine Calves. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, D.; Steidler, S.; Galletti, S.; Tameni, M.; Sonzogni, O.; Ravarotto, L. Efficacy of Silymarin-Phospholipid Complex in Reducing the Toxicity of Aflatoxin B1 in Broiler Chicks. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marietto-Gonçalves, G.A.; Brito, M.B.; Fiorentin, E.L.; Tonin, A.A. Silymarin and Methionine Application on Treatment of Liver Chronic Diseases by Aflatoxicosis in Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculi)—Case Report. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 26, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekinejad, P.; Afzali, N.; Mohammadi, A.; Sarir, H. Protective Effects of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Seeds and Sodium Bentonite in Ameliorating the Toxic Effects of Aflatoxin B1 in Broiler Chicks. Arch. Med. Lab. Sci. 2015, 1, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, T.; Schieber, A.; Kammerer, D.R.; Carle, R. Residues of Grape (Vitis vinifera L.) Seed Oil Production as a Valuable Source of Phenolic Antioxidants. Food Chem. 2008, 112, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, T.; Sousa, P.; Gonçalves, J.; Hontman, N.; Teixeira, J.; Câmara, J.S.; Perestrelo, R. Grape Pomace as a Renewable Natural Biosource of Value-Added Compounds with Potential Food Industrial Applications. Beverages 2024, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonić, B.; Jančíková, S.; Dordević, D.; Tremlová, B. Grape Pomace Valorization: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Foods 2020, 9, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenlu Yang, H.W.; Han, Y.; Tian, X.; Sajid, M.; Mehmood, S.; Li, H. Phenolic Composition of Grape Pomace and Its Metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 64, 4865–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinrod, A.J.G.; Shah, I.M.; Surek, E.; Barile, D. Uncovering the Promising Role of Grape Pomace as a Modulator of the Gut Microbiome: An in-Depth Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochorova, L.; Prusova, B.; Jurikova, T.; Mlcek, J.; Adamkova, A.; Baron, M.; Sochor, J. The Study of Antioxidant Components in Grape Seeds. Molecules 2020, 25, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Sánchez, I.; Esteban-Fernández, A.; Llano, D.; Sanz-Buenhombre, M.; Guadarrana, A.; Salazar, N.; Gueimonde, M.; Los Reyes-Gavilánc, C.G.; Martín Gómez, L.; García Bermejo, M.L. Supplementation with Grape Pomace in Healthy Women: Changes in Biochemical Parameters, Gut Microbiota and Related Metabolic Biomarkers. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 45, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; O’Hair, J.; Stewart, A.C.; O’Keefe, S.F.; Neilson, A.P.; Kim, Y.-T.; McGuire, M.; Lee, A.; Wilder, G.; Huang, H. Compositional Characterization of Different Industrial White and Red Grape Pomaces in Virginia and the Potential Valorization of the Major Components. Foods 2019, 8, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unusan, N. Proanthocyanidins in Grape Seeds: An Updated Review of Their Health Benefits and Potential Uses in the Food Industry. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 67, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances Used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). Safety and Efficacy of Dry Grape Extract When Used as a Feed Flavouring for All Animal Species and Categories. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.A.; Eid, Y.Z.; El-Hassan, E.A.A.; Farouk, M.; Gorgy, M.A.; El, M.; Basuney, H.A. Ameliorative Impacts of Grape Seed Extract on Growth Performance, Immune Response, Antioxidant Capacity and Biochemical Constituents in Broilers Exposed to Fumonisin B1. Egypt. J. Nutr. Feed. 2023, 26, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedea, V.S.; Macovei Ștefan, O.; Bocșan, I.C.; Măgureanu, D.C.; Levai, A.M.; Buzoianu, A.D.; Pop, R.M. Grape Pomace Polyphenols as a Source of Compounds for Management of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation—A Possible Alternative for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs? Molecules 2022, 27, 6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Malki, A.L.; Sayed, A.A.R.; El Rabey, H.A. Proanthocyanidin Attenuation of Oxidative Stress and NF-κB Protects Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice against Diabetic Nephropathy. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 769409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutzourelas, N.; Stagos, D.; Housmekeridou, A.; Karapouliou, C.; Kerasioti, E.; Aligiannis, N.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Kouretas, D. Grape Pomace Extract Exerts Antioxidant Effects through an Increase in GCS Levels and GST Activity in Muscle and Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pino-García, R.; Rivero-Pérez, M.D.; González-SanJosé, M.L.; Croft, K.D.; Muñiz, P. Antihypertensive and Antioxidant Effects of Supplementation with Red Wine Pomace in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2444–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussenna, A.; Cholet, J.; Goncalves-Mendes, N.; Joubert-Zakeyh, J.; Fraisse, D.; Vasson, M.; Texier, O.; Felgines, C. Polyphenol-rich Grape Pomace Extracts Protect against Dextran Sulfate Sodium-induced Colitis in Rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 96, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avantaggiato, G.; Greco, D.; Damascelli, A.; Solfrizzo, M.; Visconti, A. Assessment of Multi-Mycotoxin Adsorption Efficacy of Grape Pomace. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 62, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorni, P.; Bulla, G.; Leni, G.; Soldano, M.; Tacchini, M.; Guerrini, A.; Sacchetti, G.; Bertuzzi, T. Enhancement of Agri-Food by-Products: Green Extractions of Bioactive Molecules with Fungicidal Action against Mycotoxigenic Fungi and Their Mycotoxins. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1196812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali Rajput, S.; Sun, L.; Zhang, N.; Mohamed Khalil, M.; Gao, X.; Ling, Z.; Zhu, L.; Khan, F.; Zhang, J.; Qi, D. Ameliorative Effects of Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract on Growth Performance, Immune Function, Antioxidant Capacity, Biochemical Constituents, Liver Histopathology and Aflatoxin Residues in Broilers Exposed to Aflatoxin B1. Toxins 2017, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.; Candresse, T.; Dormannsné Simon, E.; Gilioli, G.; Grégoire, J.-C.; John Jeger, M.; Evtimova Karadjova, O.; Lövei, G.; Makowski, D.; Manceau, C.; et al. Guidance on a Harmonised Framework for Pest Risk Assessment and the Identification and Evaluation of Pest Risk Management Options by EFSA. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almusawi, A.S.; Jasim, W.K.; Kadhim, L.I. Effects of Dietary Grape Seed Extract on Physiological Parameters, Antioxidant Activity and Immunological Status of Broiler Chicks Exposed to Aflatoxin. Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2019, 13, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, M.; Bolu, S. Effects of Gallic Acid (Isolated from Grape Rind) on Serum Biochemistry, Histology and Haematology of Aspergillus flavus Challenged Broilers. Ethiop. J. Environ. Stud. Manag. 2014, 7, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Shams, G.; Fadil, H.A.; Edrees, N.; Abonorag, M.; El-Sabbagh, N.; Ahmed, E.A. Ameliorative Effect of GSPE Against AFB1 Induced Immunotoxicity and Hepatotoxicity in Japanese Quail. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2022, 10, 712–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, R.G.; Bulgaru, C.; Untea, A.; Vlassa, M.; Filip, M.; Hermenean, A.; Marin, D.; Tăranu, I.; Georgescu, S.E.; Dinischiotu, A. The Effectiveness of Dietary Byproduct Antioxidants on Induced CYP Genes Expression and Histological Alteration in Piglets Liver and Kidney Fed with Aflatoxin B1 and Ochratoxin A. Toxins 2021, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambacorta, L.; Pinton, P.; Avantaggiato, G.; Oswald, I.P.; Solfrizzo, M. Grape Pomace, an Agricultural Byproduct Reducing Mycotoxin Absorption: In Vivo Assessment in Pig Using Urinary Biomarkers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6762–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, D.E.; Bulgaru, C.V.; Laurentiu, M.; Pistol, G.C.; Gras, M.A.; Taranu, I. Effect of the Grape Seed Meal Administration on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Spleen of Piglets Fed Aflatoxin B1. Arch. Zootech. 2019, 22, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, D.E.; Bulgaru, C.V.; Anghel, C.A.; Pistol, G.C.; Dore, M.I.; Palade, M.L.; Taranu, I. Grape Seed Waste Counteracts Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity in Piglet Mesenteric Lymph Nodes. Toxins 2020, 12, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, I.; Marin, D.E.; Palade, M.; Pistol, G.C.; Chedea, V.S.; Gras, M.A.; Rotar, C. Assessment of the Efficacy of a Grape Seed Waste in Counteracting the Changes Induced by Aflatoxin B1 Contaminated Diet on Performance, Plasma, Liver and Intestinal Tissues of Pigs after Weaning. Toxicon 2019, 162, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palade, L.M.; Pertea, A.-M.; Taranu, I. Response of Antioxidant Status in Kidney of Pigs Exposed to Aflatoxin B1 to Dietary Grape Seed Meal. Arch. Zootech. 2021, 24, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosu, I.A.; Pistol, G.C.; Taranu, I.; Marin, D.E. The Impact of Dietary Grape Seed Meal on Healthy and Aflatoxin B1 Afflicted Microbiota of Pigs after Weaning. Toxins 2019, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, C.; Chen, X.; Huang, W. Condensed Tannins Protect against Aflatoxin B1-Induced Toxicity in Lateolabrax Maculatus by Restoring Intestinal Integrity and Regulating Bacterial Microbiota. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Qiu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Lu, P.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Gooneratne, R. Protective Effect of Antioxidant-Enriched Diets on T-2-Toxin-Induced Damage in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2019, 506, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovacchino, L.; Preziuso, S.M.; Serio, M.G.; Mucciarella, M.R.; Loreto, G.; Lanza, B. Double Extraction of Olive Oil in Large Oil Mills of Southern Italy: Effects on Extraction Efficiency, Oil Quality, and Economy of the Process. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 119, 1600161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, J.; Gonçalves, I.; Cardoso, J.; Dias, M.I.; Santos, P.M.P.; Margaça, F.M.A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Barros, L.; Cabo Verde, S. Effects of Electron Beam Radiation on the Phenolic Composition and Bioactive Properties of Olive Pomace Extracts. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antónia Nunes, M.; Costa, A.S.G.; Bessada, S.; Santos, J.; Puga, H.; Alves, R.C.; Freitas, V.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Olive Pomace as a Valuable Source of Bioactive Compounds: A Study Regarding Its Lipid- and Water-Soluble Components. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullón, P.; Gullón, B.; Astray, G.; Carpena, M.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Valorization of By-Products from Olive Oil Industry and Added-Value Applications for Innovative Functional Foods. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.A.; Palmeira, J.D.; Melo, D.; Machado, S.; Lobo, J.C.; Costa, A.S.G.; Alves, R.C.; Ferreira, H.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of a New Olive Pomace Functional Ingredient. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.; Jackman, J.; Valle-González, E.; Cho, N.-J. Antibacterial Free Fatty Acids and Monoglycerides: Biological Activities, Experimental Testing, and Therapeutic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madureira, J.; Margaça, F.M.A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Verde, S.C.; Barros, L. Applications of Bioactive Compounds Extracted from Olive Industry Wastes: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 21, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, M.P.; Lempereur, P.; Salembier, J.-P.; Maes, N.; Albert, A.; Jansen, O.; Pincemail, J. Supplementation Effect of a Combination of Olive (Olea europea L.) Leaf and Fruit Extracts in the Clinical Management of Hypertension and Metabolic Syndrome. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.F.S.; Martins, J.T.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Vicente, A.A.; Pinheiro, A.C. Advances in Nutraceutical Delivery Systems: From Formulation Design for Bioavailability Enhancement to Efficacy and Safety Evaluation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 270–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, K.; Jurišić Dukovski, B.; Vitali Cepo, D. Influence of Pomace Matrix and Cyclodextrin Encapsulation on Olive Pomace Polyphenols’ Bioaccessibility and Intestinal Permeability. Nutrients 2020, 12, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Nawaz, A.; Hano, C.; Walayat, N.; Lorenzo, J.M. Strategies to Increase the Value of Pomaces with Fermentation. Fermentation 2021, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck, D.; Bresson, J.-L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Ildico Hirsch-Ernst, K.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Safety of Hydroxytyrosol as a Novel Food Pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 258/97. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Jin, H.; Yang, R.; Jiang, C.; Shao, D.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J. Prediction of New Targets and Mechanisms for Quercetin in the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Colon Cancer, and Rectal Cancer. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5339–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzolini, J.; Peppicelli, S.; Andreucci, E.; Bianchini, F.; Scardigli, A.; Romani, A.; Marca, G.; Nediani, C.; Calorini, L. Oleuropein, the Main Polyphenol of Olea Europaea Leaf Extract, Has an Anti-Cancer Effect on Human BRAF Melanoma Cells and Potentiates the Cytotoxicity of Current Chemotherapies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quero, J.; Ballesteros, L.F.; Ferreira-Santos, P.; Velderrain-Rodriguez, G.R.; Rocha, C.M.R.; Pereira, R.N.; Teixeira, J.A.; Martin-Belloso, O.; Osada, J.; Rodríguez-Yoldi, M.J. Unveiling the Antioxidant Therapeutic Functionality of Sustainable Olive Pomace Active Ingredients. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, K.; Vinković Vrček, I.; Pavičić, I.; Čepo, D.V. Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Olive Pomace Extracts: Impact of Gastrointestinal Digestion and Cyclodextrin Encapsulation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafehi, H.; Ververis, K.; Karagiannis, T.C. Mechanisms of Action of Phenolic Compounds in Olive. J. Diet. Suppl. 2012, 9, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Encinas, J.; Blanch, M.; Pastor, J.J.; Mereu, A.; Ipharraguerre, I.R.; Menoyo, D. Effects of a Bioactive Olive Pomace Extract from Olea Europaea on Growth Performance, Gut Function, and Intestinal Microbiota in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, D.; Aliakbarian, B.; Casazza, A.A.; Ferrari, N.; Spinella, G.; Pane, B.; Cafueri, G.; Perego, P.; Palombo, D. Effects of Polyphenol Extract from Olive Pomace on Anoxia-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction. Microvasc. Res. 2012, 83, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Razek, A.; Badr, A.; Shehata, M. Characterization of Olive Oil By-Products: Antioxidant Activity, Its Ability to Reduce Aflatoxigenic Fungi Hazard and Its Aflatoxins. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2017, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.S.; Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O. Prevalent Mycotoxins in Animal Feed: Occurrence and Analytical Methods. Toxins 2019, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, R.; Palma, E.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cordaro, M.; Impellizzeri, D.; Caro, C.; Calzetta, L.; Cuzzocrea, S. Protective Effect of Hydroxytyrosol Against Oxidative Stress Induced by the Ochratoxin in Kidney Cells: In Vitro and in Vivo Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, D.; D’Ascanio, V.; Santovito, E.; Logrieco, A.F.; Avantaggiato, G. Comparative Efficacy of Agricultural By-products in Sequestering Mycotoxins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 1623–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavaro, S.L.; D’Antuono, I.; Cozzi, G.; Haidukowski, M.; Cardinali, A.; Logrieco, A.F. Inhibition of Aflatoxin B1 Production by Verbascoside and Other Olive Polyphenols. World Mycotoxin J. 2016, 9, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Sanchez, M.; Cardona Alzate, C.A.; Solarte-Toro, J.C. Orange Peel Waste as a Source of Bioactive Compounds and Valuable Products: Insights Based on Chemical Composition and Biorefining. Biomass 2024, 4, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Hiri, N.; Ioannou, I.; Ghoul, M.; Boudhrioua, M. Proximate Chemical Composition of Orange Peel and Variation of Phenols and Antioxidant Activity during Convective Air Drying. J. New Sci. 2015, 15, 881–890. [Google Scholar]
- Murador, D.C.; Salafia, F.; Zoccali, M.; Martins, P.L.G.; Ferreira, A.G.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Rosso, V.V.; Giuffrida, D. Green Extraction Approaches for Carotenoids and Esters: Characterization of Native Composition from Orange Peel. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-M.; Tait, A.R.; Kitts, D.D. Flavonoid Composition of Orange Peel and Its Association with Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Putra, N.R.; Rizkiyah, D.N.; Abdul Aziz, A.H.; Irianto, I.; Qomariyah, L. Orange Pomace and Peel Extraction Processes towards Sustainable Utilization: A Short Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, K.; Chowdhury, D.; Baruah, P.K. Development of β-carotene Loaded Nanoemulsion Using the Industrial Waste of Orange (Citrus reticulate) Peel to Improve in Vitro Bioaccessibility of Carotenoids and Use as Natural Food Colorant. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, F.; Arain, M.A.; Rajput, N.; Alagawany, M.; Soomro, J.; Umer, M.; Soomro, F.; Wang, Z.; Ye, R.; Liu, J. Health Benefits of Carotenoids and Potential Application in Poultry Industry. A Review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meléndez-Martínez, A.J.; Vicario, I.M.; Heredia, F.J. Review: Analysis of Carotenoids in Orange Juice. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’hiri, N.; Ioannou, I.; Ghoul, M.; Mihoubi Boudhrioua, N. Phytochemical Characteristics of Citrus Peel and Effect of Conventional and Nonconventional Processing on Phenolic Compounds: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 33, 587–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Prasad, P.; Lokesh, V.; Shang, X.; Shin, J.; Keum, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-H. Carotenoids: Dietary Sources, Extraction, Encapsulation, Bioavailability, and Health Benefits—A Review of Recent Advancements. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-L.; Chen, S.-Y.; Ho, C.-Y.; Yen, G.-C. Citrus Flavonoids Suppress IL-5 and ROS through Distinct Pathways in PMA/Ionomycin-Induced EL-4 Cells. Food Funct. 2019, 11, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabil, M.; Donia, T.; Mohamed, T.M. Antioxidant Effect of Hesperidin Isolated from Orange Peels. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2016, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sa’Ayinzat, F.E.; Bawa, E.K.; Ogwu, D.; Hesperidin-Sources, A.J.O. Chemistry, Extraction, Measurement and Biologic Effects on Reproduction in Animals: A Review. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Husb. 2021, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, D.; Kar, B.; Pattnaik, G. Preventive Role of Naringin in Diabetes Mellitusand and Its Mechanism of Action: A Review. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 7806–7812. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Qi, Q.-L.; Wang, M.-T.; Li, Q.-Y. Therapeutic Potential of Naringin: An Overview. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 3203–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabrauskiene, J.; Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Lazauskas, R.; Bernatoniene, J. Naringin and Naringenin: Their Mechanisms of Action and the Potential Anticancer Activities. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Nagashimada, M.; Zhan, L.; Nagata, N.; Kobori, M.; Sugiura, M.; Ogawa, K.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T. Prevention and Reversal of Lipotoxicity-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance and Steatohepatitis in Mice by an Antioxidant Carotenoid, β-Cryptoxanthin. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegele, A.D.; Gillette, C.; O’Neill, C.; Wolfe, P.; Heimendinger, J.; Sedlacek, S.; Thompson, H.J. Plasma Xanthophyll Carotenoids Correlate Inversely with Indices of Oxidative DNA Damage and Lipid Peroxidation. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 421–425. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, M. β-Cryptoxanthin and bone metabolism: The preventive role in osteoporosis. J. Health Sci. 2008, 54, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Mazandarani, M.; Paknejad, H.; Doan, H.; El-Haroun, E.R. The Potential Benefits of Orange Peels Derived Pectin on Serum and Skin Mucus Immune Parameters, Antioxidant Defence and Growth Performance in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 103, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, U.; Ain, Q.U.; Yaseen, M.; Fan, X.; Yao, X.; Tong, Z.; Liu, B. Modification of Bentonite with Orange Peels Extract and Its Application as Mycotoxins’ Binder in Buffered Solutions and Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Benohoud, M.; Galani Yamdeu, J.H.; Gong, Y.Y.; Orfila, C. Green Extraction of Polyphenols from Citrus Peel By-Products and Their Antifungal Activity against Aspergillus flavus. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, M.A.; Ahmed, F.; Kamal, M.; Khan, S.; Aghar, M.A. Effectiveness of Citrus Fruit Peel as a Biosorbent for the Mitigation of Aflatoxins In Vitro. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2022, 39, 1987–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.T.; Wan, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z. Dietary Lycopene Supplementation Could Alleviate Aflatoxin B1 Induced Intestinal Damage through Improving Immune Function and Anti-Oxidant Capacity in Broilers. Animals 2021, 11, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Ji, H.; Ma, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, N.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z. Lycopene Alleviates Aflatoxin B1 Induced Liver Damage through Inhibiting Cytochrome 450 Isozymes and Improving Detoxification and Antioxidant Systems in Broiler Chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 21, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Chen, Q.; Yang, H.; Wan, X. Effects of Lycopene on the Growth Performance, Meat Quality, and Antioxidant Capacity of Broiler Chickens Challenged with Aflatoxin B1. J. Food Sci. 2023, 89, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lu, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, X.; Wang, T. Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Development, Zinc Metabolism and Biodistribution of Minerals (Zn, Fe, Cu, Mn) in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhao, J.; Ma, L.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Rahman, S.U.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Lycopene Attenuates Zearalenone-Induced Oxidative Damage of Piglet Sertoli Cells through the Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2 Related Factor 2 Signaling Pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).