Bicistronic Vector Expression of Recombinant Jararhagin-C and Its Effects on Endothelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
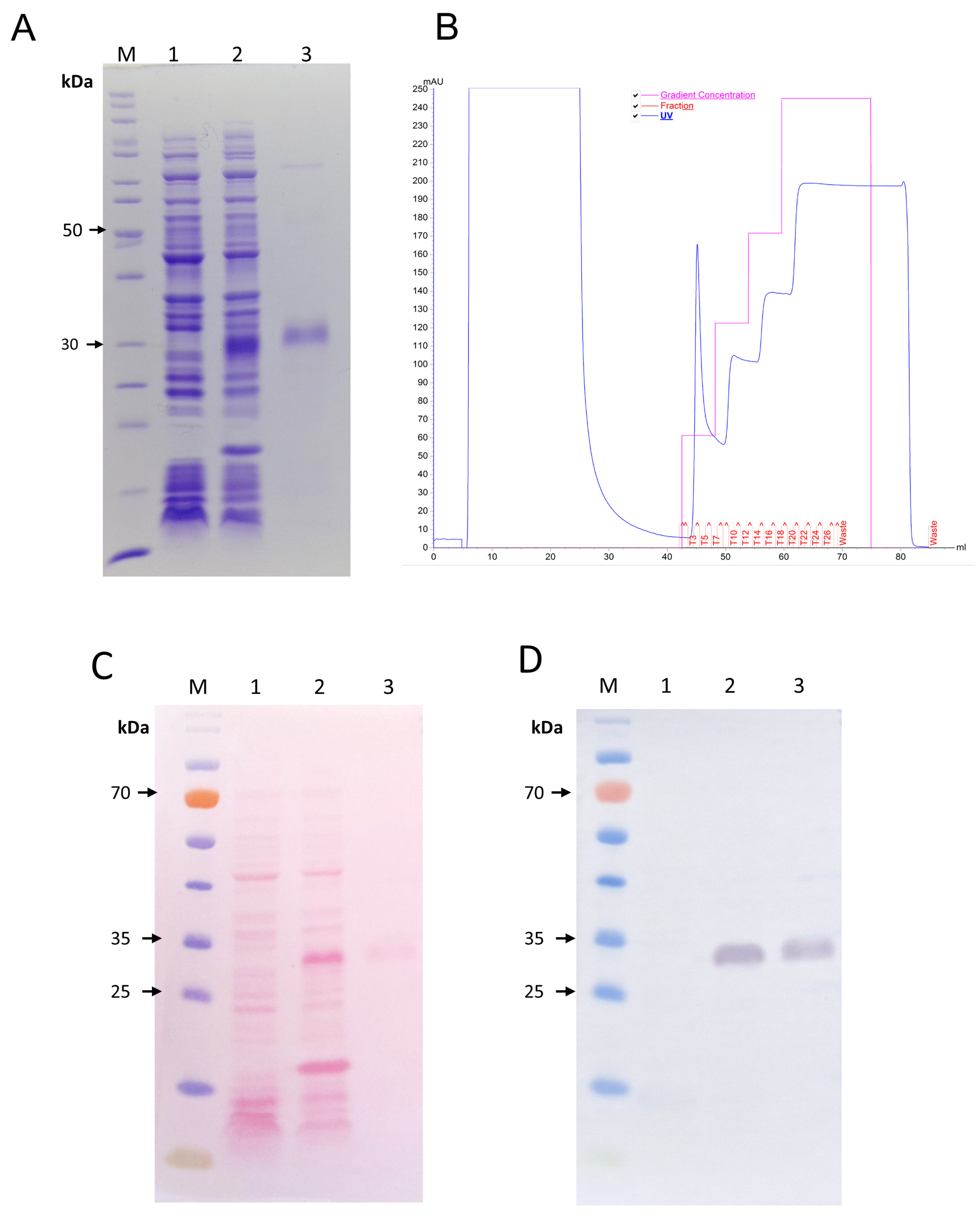
2.1. Expression and Purification of rJar-C
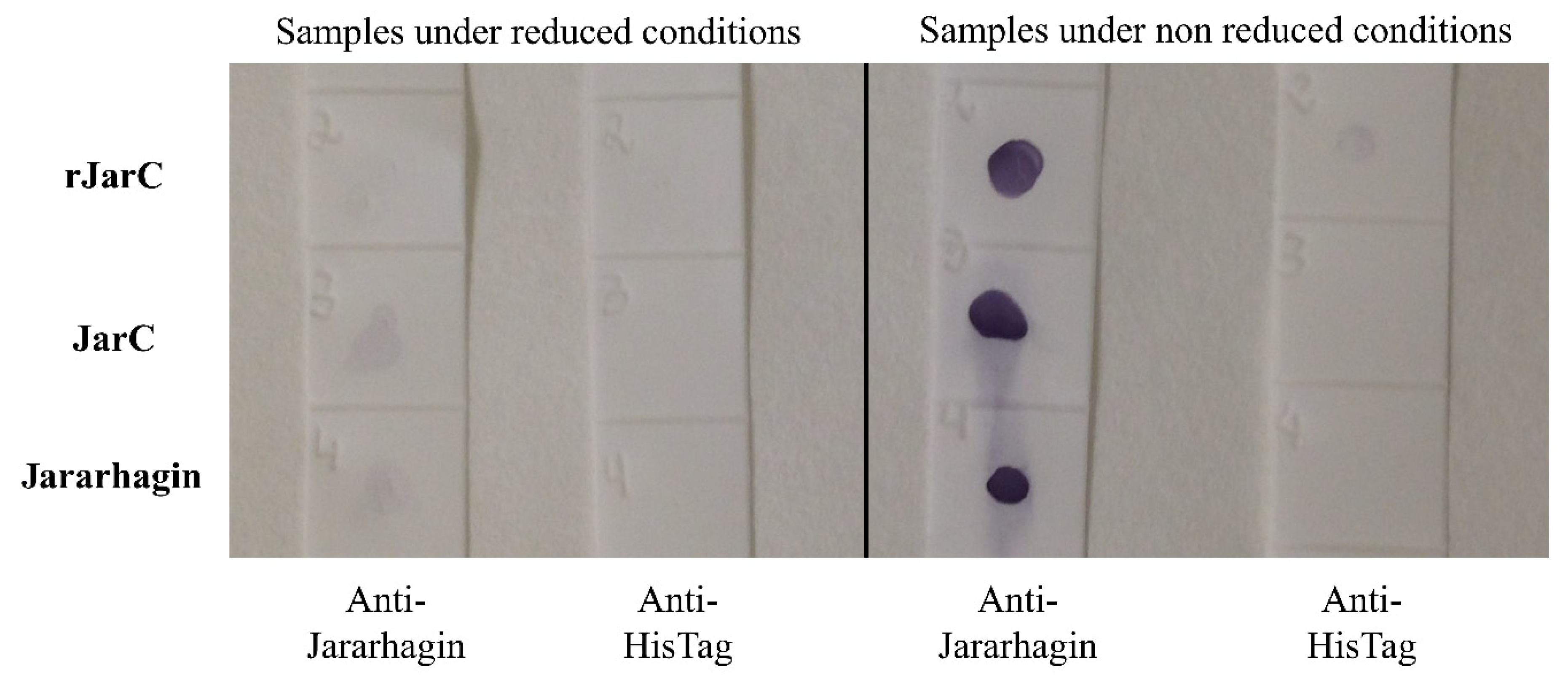
2.2. rJarC Conformation Is Important for Antibody Recognition
2.3. Native and Recombinant JarC Exhibit Non-Toxic Effects on HUVEC Cells
2.4. Native and Recombinant JarC Promote HUVEC Cell Migration on Collagen Substrates
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Material and Methods
5.1. Cloning of JarC into the pSUMOUlp1 Vector
5.2. rJarC Expression in pSUMOUlp1 Vector
5.3. Purification of rJarC
5.4. In-Solution Digestion and Proteomic Analysis
5.5. Western Blot Analysis
5.6. rJarC Detection by Polyclonal Anti-Jararhagin Antibodies (Dot Blot)
5.7. Purification of Native JarC (JarC)
5.8. HUVEC Cell Culture
5.9. Cell Viability Assay
5.10. In Vitro Migration of Endothelial Cells: Wound Healing Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calvete, J.J.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Monleón, D.; Esteve, V.; Celda, B.; Juárez, P.; Sanz, L. Snake venom disintegrins: Evolution of structure and function. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez, P.; Comas, I.; González-Candelas, F.; Calvete, J.J. Evolution of snake venom disintegrins by positive Darwinian selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 2391–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesar, P.H.S.; Braga, M.A.; Trento, M.V.C.; Menaldo, D.L.; Marcussi, S. Snake Venom Disintegrins: An Overview of their Interaction with Integrins. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiguti, A.S.; Zuzel, M.; Theakston, R.D. Snake venom metalloproteinases and disintegrins: Interactions with cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1998, 31, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clissa, P.B.; Della-Casa, M.S.; Zychar, B.C.; Sanabani, S.S. The Role of Snake Venom Disintegrins in Angiogenesis. Toxins 2024, 16, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, Y.; Fujimura, Y.; Miura, S.; Shima, H.; Yoshida, E.; Yoshioka, A.; Hirano, K.; Suzuki, M.; Titani, K. A 28 kDa-protein with disintegrin-like structure (jararhagin-C) purified from Bothrops jararaca venom inhibits collagen- and ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 201, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, M.J.; Desmond, H.P.; Theakston, R.D.; Crampton, J.M. Purification, cloning, and molecular characterization of a high molecular weight hemorrhagic metalloprotease, jararhagin, from Bothrops jararaca venom. Insights into the disintegrin gene family. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 22869–22876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Marcinkiewicz, M.; Niewiarowski, S. Selective recognition of alpha2beta1 integrin by jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase/disintegrin from bBothrops jararaca venom. Thromb. Res. 2001, 102, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, J.S.; Sheppard, D. Cross talk among TGF-β signaling pathways, integrins, and the extracellular matrix. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczyk, M.; Carracedo, S.; Gullberg, D. Integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, B.A.; De Moura, F.B.R.; Tomiosso, T.C.; Corrêa, N.C.R.; Goulart, L.R.; Barcelos, L.S.; Clissa, P.B.; Araújo, F.A. Jararhagin-C, a disintegrin-like protein, improves wound healing in mice through stimulation of M2-like macrophage, angiogenesis and collagen deposition. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, B.A.; Deconte, S.R.; de Moura, F.B.R.; Tomiosso, T.C.; Clissa, P.B.; Andrade, S.P.; Araújo, F.A. Inflammation, angiogenesis and fibrogenesis are differentially modulated by distinct domains of the snake venom metalloproteinase jararhagin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zychar, B.C.; Clissa, P.B.; Carvalho, E.; Alves, A.S.; Baldo, C.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L.; Gonçalves, L.R.C. Modulation of Adhesion Molecules Expression by Different Metalloproteases Isolated from. Toxins 2021, 13, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassini-Vieira, P.; Deconte, S.R.; Tomiosso, T.C.; Campos, P.P.; Montenegro, C.e.F.; Selistre-de-Araújo, H.S.; Barcelos, L.S.; Andrade, S.P.; Araújo, F.e.A. DisBa-01 inhibits angiogenesis, inflammation and fibrogenesis of sponge-induced-fibrovascular tissue in mice. Toxicon 2014, 92, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelo, L.F.G.; Ferreira, B.A.; Deconte, S.R.; Tomiosso, T.C.; Dos Santos, P.K.; Andrade, S.P.; Selistre de Araújo, H.S.; Araújo, F.A. Alternagin-C, a disintegrin-like protein from Bothrops alternatus venom, attenuates inflammation and angiogenesis and stimulates collagen deposition of sponge-induced fibrovascular tissue in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, D.L.; Kane, J.F. Properties of inclusion bodies from recombinant Escherichia coli. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1988, 16, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrió, M.M.; Villaverde, A. Construction and deconstruction of bacterial inclusion bodies. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 96, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, P.F.; Meng, E.; Li, W.Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, L.Y.; Wu, L.; Li, M.J.; Liang, S.P.; Zhang, D.Y. An efficient strategy for heterologous expression and purification of active peptide hainantoxin-IV. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, Q. Soluble expression, purification, and characterization of Gloydius shedaoensis venom gloshedobin in Escherichia coli by using fusion partners. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Duan, H.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Z. The role of thioredoxin and disulfide isomerase in the expression of the snake venom thrombin-like enzyme calobin in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). Protein Expr. Purif. 2004, 38, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.T.; Jeong, B.; Yu, J.; Koo, B.K.; Jo, S.H.; Robinson, R.C.; Choe, H. Soluble prokaryotic expression and purification of crotamine using an N-terminal maltose-binding protein tag. Toxicon 2014, 92, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marblestone, J.G.; Edavettal, S.C.; Lim, Y.; Lim, P.; Zuo, X.; Butt, T.R. Comparison of SUMO fusion technology with traditional gene fusion systems: Enhanced expression and solubility with SUMO. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Cuebas, L.M.; White, M.M. Expression of a biologically-active conotoxin PrIIIE in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Hoege, C.; Pyrowolakis, G.; Jentsch, S. SUMO, ubiquitin′s mysterious cousin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroutka Iii, R.J.; Orcutt, S.J.; Strickler, J.E.; Butt, T.R. SUMO fusion technology for enhanced protein expression and purification in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 705, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokawa-Falcão, L.H.; Caporrino, M.C.; Barbaro, K.C.; Della-Casa, M.S.; Magalhães, G.S. Toxin Fused with SUMO Tag: A New Expression Vector Strategy to Obtain Recombinant Venom Toxins with Easy Tag Removal inside the Bacteria. Toxins 2017, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, V.; Succar, B.B.; de Moraes, J.A.; Saldanha-Gama, R.F.G.; Barja-Fidalgo, C.; Zingali, R.B. Recombinant and Chimeric Disintegrins in Preclinical Research. Toxins 2018, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Línica, A.; Della-Casa, M.S.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Ho, P.L.; Crampton, J.M.; Theakston, R.D. Jararhagin ECD-containing disintegrin domain: Expression in escherichia coli and inhibition of the platelet-collagen interaction. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 369, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, D.A.; Almeida, M.C.; Barros, C.C.; Sanchez, E.F.; Pesquero, P.R.; Lang, E.A.; Samaan, M.; Araujo, R.C.; Pesquero, J.B.; Pesquero, J.L. Leucurogin, a new recombinant disintegrin cloned from Bothrops leucurus (white-tailed-jararaca) with potent activity upon platelet aggregation and tumor growth. Toxicon 2011, 58, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- İncir, İ.; Kaplan, Ö. Escherichia coli in the production of biopharmaceuticals. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assakura, M.T.; Silva, C.A.; Mentele, R.; Camargo, A.C.; Serrano, S.M. Molecular cloning and expression of structural domains of bothropasin, a P-III metalloproteinase from the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Toxicon 2003, 41, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cominetti, M.R.; Terruggi, C.H.; Ramos, O.H.; Fox, J.W.; Mariano-Oliveira, A.; De Freitas, M.S.; Figueiredo, C.C.; Morandi, V.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S. Alternagin-C, a disintegrin-like protein, induces vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) expression and endothelial cell proliferation in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18247–18255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S.; Cominetti, M.R.; Terruggi, C.H.; Mariano-Oliveira, A.; De Freitas, M.S.; Crepin, M.; Figueiredo, C.C.; Morandi, V. Alternagin-C, a disintegrin-like protein from the venom of Bothrops alternatus, modulates alpha2beta1 integrin-mediated cell adhesion, migration and proliferation. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.E.; Lucena, S.E.; Reyes, S.; Soto, J.G.; Cantu, E.; Lopez-Johnston, J.C.; Guerrero, B.; Salazar, A.M.; Rodriguez-Acosta, A.; Galan, J.A.; et al. Cloning, expression, and hemostatic activities of a disintegrin, r-mojastin 1, from the mohave rattlesnake (Crotalus scutulatus scutulatus). Thromb. Res. 2010, 126, e211–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntravat, M.; Helmke, T.J.; Atphaisit, C.; Cuevas, E.; Lucena, S.E.; Uzcategui, N.L.; Sanchez, E.E.; Rodriguez-Acosta, A. Expression, purification, and analysis of three recombinant ECD disintegrins (r-colombistatins) from P-III class snake venom metalloproteinases affecting platelet aggregation and SK-MEL-28 cell adhesion. Toxicon 2016, 122, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minea, R.; Helchowski, C.; Rubino, B.; Brodmann, K.; Swenson, S.; Markland, F., Jr. Development of a chimeric recombinant disintegrin as a cost-effective anti-cancer agent with promising translational potential. Toxicon 2012, 59, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Rifkin, D.B. Autocrine activities of basic fibroblast growth factor: Regulation of endothelial cell movement, plasminogen activator synthesis, and DNA synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 107, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.F.; Hoi, P.M.; Wu, G.S.; Xu, Z.T.; Tan, W.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, L.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.T. Anti-angiogenic effect of furanodiene on HUVECs in vitro and on zebrafish in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferraz, K.F.; De Lucca Caetano, L.H.; Orefice, D.P.; Calabria, P.A.L.; Della-Casa, M.S.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Beraldo-Neto, E.; Sanabani, S.S.; Magalhães, G.S.; Clissa, P.B. Bicistronic Vector Expression of Recombinant Jararhagin-C and Its Effects on Endothelial Cells. Toxins 2024, 16, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16120524
Ferraz KF, De Lucca Caetano LH, Orefice DP, Calabria PAL, Della-Casa MS, Freitas-de-Sousa LA, Beraldo-Neto E, Sanabani SS, Magalhães GS, Clissa PB. Bicistronic Vector Expression of Recombinant Jararhagin-C and Its Effects on Endothelial Cells. Toxins. 2024; 16(12):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16120524
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerraz, Karla Fernanda, Lhiri Hanna De Lucca Caetano, Daniele Pereira Orefice, Paula Andreia Lucas Calabria, Maisa Splendore Della-Casa, Luciana Aparecida Freitas-de-Sousa, Emidio Beraldo-Neto, Sabri Saeed Sanabani, Geraldo Santana Magalhães, and Patricia Bianca Clissa. 2024. "Bicistronic Vector Expression of Recombinant Jararhagin-C and Its Effects on Endothelial Cells" Toxins 16, no. 12: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16120524
APA StyleFerraz, K. F., De Lucca Caetano, L. H., Orefice, D. P., Calabria, P. A. L., Della-Casa, M. S., Freitas-de-Sousa, L. A., Beraldo-Neto, E., Sanabani, S. S., Magalhães, G. S., & Clissa, P. B. (2024). Bicistronic Vector Expression of Recombinant Jararhagin-C and Its Effects on Endothelial Cells. Toxins, 16(12), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16120524




