The Choice of Anti-Inflammatory Influences the Elimination of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Small-Sized Molecules
2.2. Medium-Sized Molecules
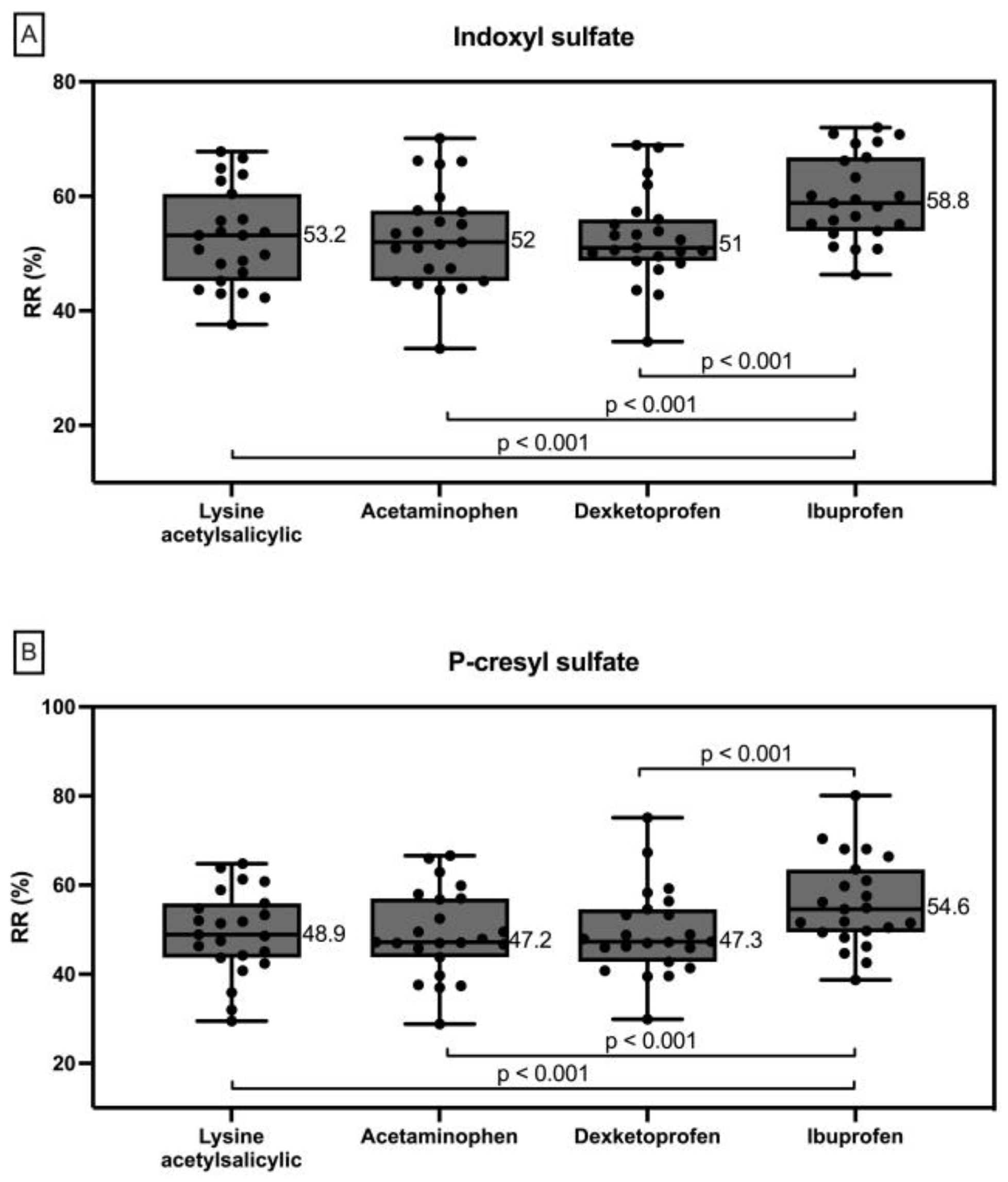
2.3. Protein Bound Uremic Toxins
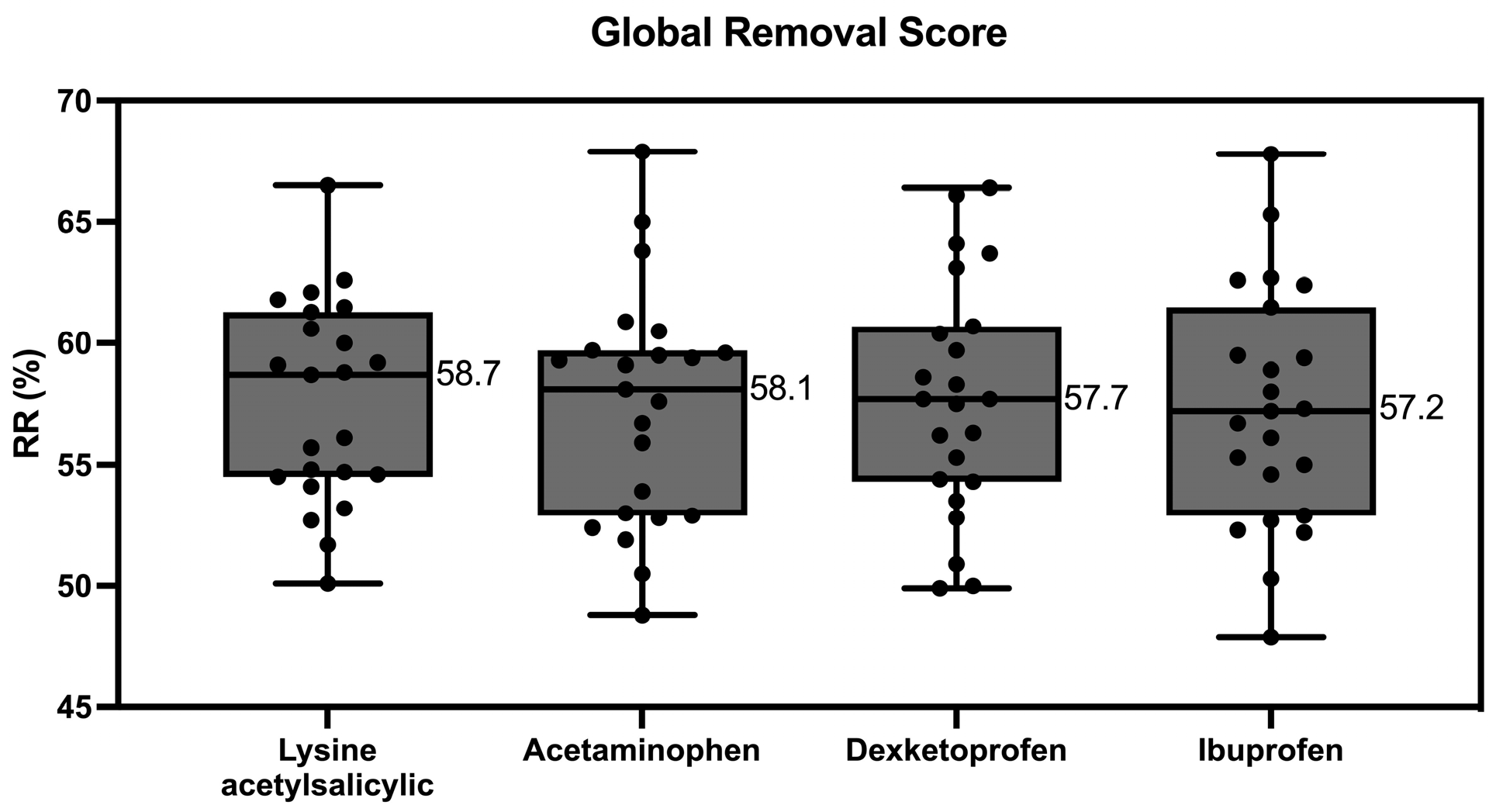
2.4. Global Removal Score
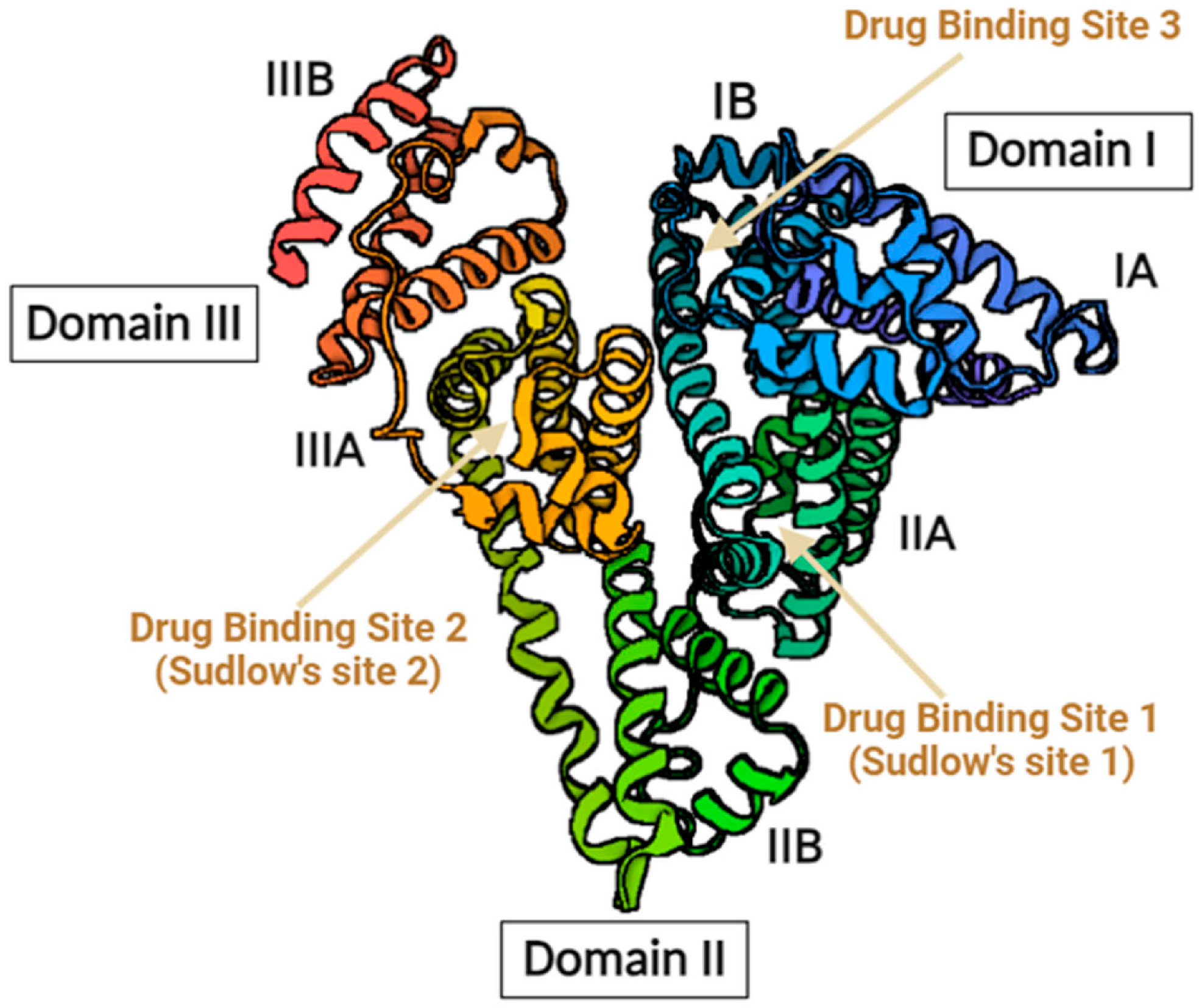
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
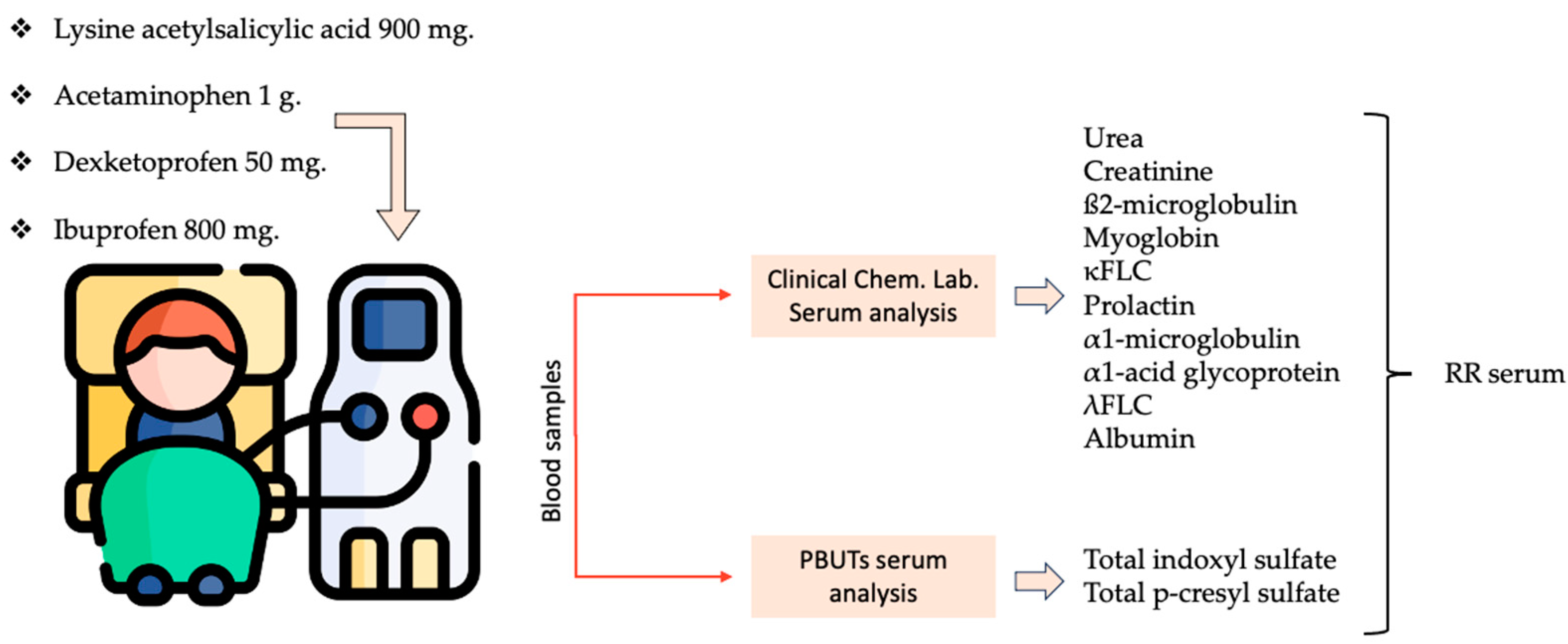
5.1. Study Design
- -
- Lysine acetylsalicylic acid 900 mg.
- -
- Acetaminophen 1 g.
- -
- Dexketoprofen 50 mg.
- -
- Ibuprofen 800 mg.
5.2. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambourg, E.; Colvin, L.; Guthrie, G.; Murugan, K.; Lim, M.; Walker, H.; Boon, G.; Bell, S. The Prevalence of Pain among Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Using Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, S.N.; Jhangri, G.S. Impact of Pain and Symptom Burden on the Health-Related Quality of Life of Hemodialysis Patients. J. Pain. Symptom Manag. 2010, 39, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, S.N. Clinical Pharmacology Considerations in Pain Management in Patients with Advanced Kidney Failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argilés, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on Uremic Toxins: Classification, Concentration, and Interindividual Variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalim, S.; Wald, R.; Yan, A.T.; Goldstein, M.B.; Kiaii, M.; Xu, D.; Berg, A.H.; Clish, C.; Thadhani, R.; Rhee, E.P.; et al. Extended Duration Nocturnal Hemodialysis and Changes in Plasma Metabolite Profiles. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, S.W.; Jung, G.T.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, K.P.; Jo, Y.; Jin, K.; Moon, J.Y. The Medium Cut-Off Membrane Does Not Lower Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins 2022, 14, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, T.; Eloot, S.; Vanholder, R.; Glorieux, G.; Van Der Sande, F.M.; Scheijen, J.L.; Leunissen, K.M.; Kooman, J.P.; Schalkwijk, C.G. Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins, Dicarbonyl Stress and Advanced Glycation End Products in Conventional and Extended Haemodialysis and Haemodiafiltration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieter, D.H.; Hackl, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Chenine, L.; Moragues, H.L.; Lemke, H.D.; Wanner, C.; Canaud, B. Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxin Removal in Haemodialysis and Post-Dilution Haemodiafiltration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Uremic Toxins Work Group List of Uremic Solutes—Uremic Solutes Database. Available online: https://database.uremic-toxins.org/soluteList.php (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Vanholder, R.; Pletinck, A.; Schepers, E.; Glorieux, G. Biochemical and Clinical Impact of Organic Uremic Retention Solutes: A Comprehensive Update. Toxins 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, I.W.; Hsu, K.H.; Hsu, H.J.; Lee, C.C.; Sun, C.Y.; Tsai, C.J.; Wu, M.S. Serum Free P-Cresyl Sulfate Levels Predict Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality in Elderly Hemodialysis Patients—A Prospective Cohort Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bammens, B.; Evenepoel, P.; Keuleers, H.; Verbeke, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y. Free Serum Concentrations of the Protein-Bound Retention Solute p-Cresol Predict Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Ospina, D.; Mas-Fontao, S.; Gracia-Iguacel, C.; Avello, A.; González de Rivera, M.; Mujika-Marticorena, M.; Gonzalez-Parra, E. Displacing the Burden: A Review of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxin Clearance Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, V.; Tao, X.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P. Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins Using Binding Competitors in Hemodialysis: A Narrative Review. Toxins 2021, 13, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madero, M.; Cano, K.B.; Campos, I.; Tao, X.; Maheshwari, V.; Brown, J.; Cornejo, B.; Handelman, G.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P. Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins during Hemodialysis Using a Binding Competitor. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paats, J.; Adoberg, A.; Arund, J.; Dhondt, A.; Fernström, A.; Fridolin, I.; Glorieux, G.; Leis, L.; Luman, M.; Gonzalez-Parra, E.; et al. Serum Levels and Removal by Haemodialysis and Haemodiafiltration of Tryptophan-Derived Uremic Toxins in ESKD Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesaffer, G.; De Smet, R.; Lameire, N.; Dhondt, A.; Duym, P.; Vanholder, R. Intradialytic Removal of Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins: Role of Solute Characteristics and of Dialyser Membrane. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.J.G.; Patel, K.P.; Marquez, I.O.; Plummer, N.S.; Hostetter, T.H.; Meyer, T.W. Effect of Increasing Dialyzer Mass Transfer Area Coefficient and Dialysate Flow on Clearance of Protein-Bound Solutes: A Pilot Crossover Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivias-Motta, E.; Martín-Malo, A.; Buendia, P.; Álvarez-Lara, M.A.; Soriano, S.; Crespo, R.; Carracedo, J.; Ramírez, R.; Aljama, P. Hemodiafiltration with Endogenous Reinfusion Improved Microinflammation and Endothelial Damage Compared with Online-Hemodiafiltration: A Hypothesis Generating Study. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, B.; Toussaint, N.D.; Meyer, T.; Bammens, B.; Verbeke, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Kerr, P.G.; Evenepoel, P. Reduction in Protein-Bound Solutes Unacceptable as Marker of Dialysis Efficacy during Alternate-Night Nocturnal Hemodialysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 34, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, N.; Eloot, S.; Waterloos, M.A.; Van Landschoot, M.; Dhondt, A.; Glorieux, G.; Ledebo, I.; Vanholder, R. Effective Removal of Protein-Bound Uraemic Solutes by Different Convective Strategies: A Prospective Trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, N.; Eloot, S.; Schepers, E.; Lemke, H.D.; Dhondt, A.; Glorieux, G.; Van Landschoot, M.; Waterloos, M.A.; Vanholder, R. Comparison of Removal Capacity of Two Consecutive Generations of High-Flux Dialysers during Different Treatment Modalities. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloot, S.; Dhondt, A.; Van Landschoot, M.; Waterloos, M.A.; Vanholder, R. Removal of Water-Soluble and Protein-Bound Solutes with Reversed Mid-Dilution versus Post-Dilution Haemodiafiltration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 3278–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, S.; Vega, A.; Quiroga, B.; Arroyo, D.; Panizo, N.; Reque, J.E.; López-Gómez, J.M. Protein-Bound Toxins: Added Value in Their Removal with High Convective Volumes. Nefrol. (Engl. Ed.) 2016, 36, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, B.; Cao, X.; Xiang, F.; Zou, J.; Ding, X. Acute Effect of One Session of Hemodiafiltration with Endogenous Reinfusion on Uremic Toxins and Inflammatory Mediators. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2020, 43, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Noguchi, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kadowaki, D.; Kotani, S.; Nakajima, M.; Miyamura, S.; Ishima, Y.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Interaction between Two Sulfate-Conjugated Uremic Toxins, p-Cresyl Sulfate and Indoxyl Sulfate, during Binding with Human Serum Albumin. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghan Niestanak, V.; Unsworth, L.D. Detailing Protein-Bound Uremic Toxin Interaction Mechanisms with Human Serum Albumin in the Pursuit of Designing Competitive Binders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuman, J.; Zunszain, P.A.; Petitpas, I.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Otagiri, M.; Curry, S. Structural Basis of the Drug-Binding Specificity of Human Serum Albumin. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tonelli, M.; Unsworth, L.D. Indoxyl and p-Cresol Sulfate Binding with Human Serum Albumin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 635, 128042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P.; Ho, C.H.; Henrie, M.; Stroup, E.; Handelman, G. Improved Dialytic Removal of Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins with Use of Albumin Binding Competitors: An in Vitro Human Whole Blood Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, V.; Thijssen, S.; Tao, X.; Fuertinger, D.H.; Kappel, F.; Kotanko, P. In Silico Comparison of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxin Removal by Hemodialysis, Hemodiafiltration, Membrane Adsorption, and Binding Competition. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.M.; Skjodt, N.M. Choosing the Right Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug for the Right Patient. A Pharmacokinetic Approach. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2000, 38, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardikasari, S.A.; Katona, G.; Csóka, I. Serum Albumin in Nasal Drug Delivery Systems: Exploring the Role and Application. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Cao, W.; Shen, Z.; Wang, N.; Leng, J.; Zou, N.; Shang, E.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Improved Dialysis Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins by Salvianolic Acids. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, F. Improved Dialytic Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins by Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in Chronic Kidney Disease Rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.S.C.; Faria, M. Adsorption- and Displacement-Based Approaches for the Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins 2023, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.S.; Shah, A.D. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in End-Stage Kidney Disease: Dangerous or Underutilized? Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2021, 22, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, J.; Wehle, B. No Change in Corrected Β2-Microglobulin Concentration after Cuprophane Haemodialysis. Lancet 1987, 14, 628–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduell, F.; Rodas, L.; Broseta, J.J.; Gomez, M.; Xipell, M.; Guillen, E.; Montagud-Marrahi, E.; Arias-Guillén, M.; Fontseré, N.; Vera, M.; et al. Medium Cut-Off Dialyzer versus Eight Hemodiafiltration Dialyzers: Comparison Using a Global Removal Score. Blood Purif. 2019, 48, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | AAS | Paracetamol | Dexketoprofen | Ibuprofen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood processed (L) | 122.7 ± 7.5 | 120.9 ± 7.5 | 120.8 ± 8.2 | 121.2 ± 7.1 |
| Recirculation (%) | 16 ± 5 | 14.7 ± 4.4 | 14.7 ± 4.5 | 16.1 ± 4.8 |
| Real dialysis time (min) | 289 ± 12 | 287.6 ± 11.3 | 288.6 ± 11.5 | 288.5 ± 12.4 |
| Arterial pressure (mmHg) | −204 ± 36 | −200 ± 38 | −213 ± 32 | −205 ± 33 |
| Venous pressure (mmHg) | 195 ± 27 | 199 ± 31 | 193 ± 31 | 196 ± 28 |
| TMP (mmHg) | 183 ± 38 | 185 ± 39 | 181 ± 48 | 182 ± 46 |
| Initial hematocrit (%) | 30 ± 5 | 29.1 ± 4.8 | 29.8 ± 5.1 | 29.2 ± 4.7 |
| Final hematocrit (%) | 34.7 ± 5.5 | 34.3 ± 5.8 | 34.2 ± 5.5 | 33.3 ± 6.1 |
| Initial weight (kg) | 69.8 ± 12.1 | 70.1 ± 12.3 | 69.9 ± 12.2 | 69.9 ± 12.2 |
| Final weight (kg) | 68 ± 12 | 68.2 ± 12.1 | 68.1 ± 12.1 | 68 ± 12 |
| Weight gain (kg) | 1.74 ± 0.83 | 1.93 ± 0.75 | 1.84 ± 0.91 | 1.8 ± 0.6 |
| Replacement volume (L) | 30.6 ± 4.2 | 31.1 ± 3.8 | 30.7 ± 4.7 | 31.4 ± 4.9 |
| Molecule | AAS | Paracetamol | Dexketoprofen | Ibuprofen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea RR (60 Da) | 84.5 ± 3.1 | 85.5 ± 3.6 | 85.6 ± 2.9 | 85.3 ± 3.4 |
| Creatinine RR (113 Da) | 78.6 ± 4.1 | 78.9 ± 4.3 | 79.3 ± 3.8 | 78.5 ± 3.7 |
| ß2-microglobulin RR (11,800 Da) | 84.8 ± 3.9 | 85.1 ± 3.5 | 85.2 ± 3.1 | 84.8 ± 3.9 |
| Myoglobin RR (17,200 Da) | 73.2 ± 8.1 | 73.1 ± 7.5 | 72.8 ± 8.1 | 73.1 ± 7.6 |
| κFLC RR (22,500 Da) | 69.7 ± 6.5 | 69.5 ± 6.8 | 69.2 ± 7.3 | 68.8 ± 7.2 |
| Prolactin RR (23,000 Da) | 71.4 ± 9.1 | 70.6 ± 8.9 | 71 ± 9 | 70.2 ± 8.4 |
| α1-microglobulin RR (33,000 Da) | 25.8 ± 9.2 | 25.3 ± 11.3 | 27 ± 10 | 26.5 ± 11.1 |
| α1-acid glycoprotein (41,000 Da) | 13.2 ± 7.6 | 12.1 ± 7.6 | 12.9 ± 5.8 | 12.6 ± 6.5 |
| λFLC RR (45,000 Da) | 47.6 ± 7.9 | 45.6 ± 9.1 | 46.7 ± 11.1 | 46.8 ± 9.8 |
| Albumin RR (66,000 Da) | 7.5 ± 5.9 | 7.4 ± 4.9 | 8.2 ± 5.1 | 8.3 ± 5.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escudero-Saiz, V.J.; Cuadrado-Payán, E.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M.; Casals, G.; Rodas, L.M.; Fontseré, N.; Salgado, M.d.C.; Bastida, C.; Rico, N.; Broseta, J.J.; et al. The Choice of Anti-Inflammatory Influences the Elimination of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins 2024, 16, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16120545
Escudero-Saiz VJ, Cuadrado-Payán E, Rodriguez-Garcia M, Casals G, Rodas LM, Fontseré N, Salgado MdC, Bastida C, Rico N, Broseta JJ, et al. The Choice of Anti-Inflammatory Influences the Elimination of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins. 2024; 16(12):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16120545
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscudero-Saiz, Víctor Joaquín, Elena Cuadrado-Payán, María Rodriguez-Garcia, Gregori Casals, Lida María Rodas, Néstor Fontseré, María del Carmen Salgado, Carla Bastida, Nayra Rico, José Jesús Broseta, and et al. 2024. "The Choice of Anti-Inflammatory Influences the Elimination of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins" Toxins 16, no. 12: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16120545
APA StyleEscudero-Saiz, V. J., Cuadrado-Payán, E., Rodriguez-Garcia, M., Casals, G., Rodas, L. M., Fontseré, N., Salgado, M. d. C., Bastida, C., Rico, N., Broseta, J. J., & Maduell, F. (2024). The Choice of Anti-Inflammatory Influences the Elimination of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins, 16(12), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16120545






