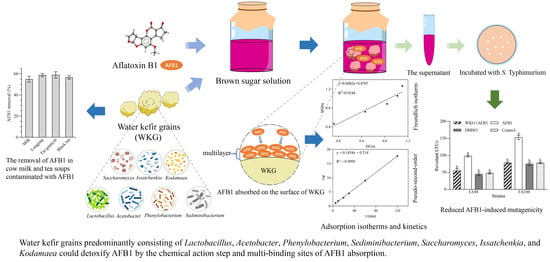
Microbial Composition of Water Kefir Grains and Their Application for the Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Microbial Composition of WKGs
2.2. Adsorption and Desorption of AFB1 by WKGs
2.3. Effects of the Initial Concentrations of AFB1, Inoculation of WKGs, pH Values, and Temperature on the Removal of AFB1 Mediated by WKGs
2.4. The Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics of the Removal of AFB1 by WKGs
2.5. Analysis of AFB1 and AFB1 Metabolites by HPLC–Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-Q-TOF-MS)
2.6. The Ames Test for Mutagenicity
2.7. Removal of AFB1 by WKGs in Cow Milk and Teas Contaminated with AFB1
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Activation of WKGs
5.2. Analysis of Microbial Community Composition
5.3. Removal of AFB1 by WKGs
5.4. Quantification of AFB1 Using HPLC
5.5. Removal of AFB1 by Dead Cells, and Extracellular and Intracellular Extracts
5.6. AFB1 Release from WKGs
5.7. Effect of the Initial Concentration of AFB1, Inoculation of WKGs, pH, and Temperature on the Removal of AFB1
5.8. Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics
5.9. Analysis of AFB1 and AFB1 Metabolites by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS
5.10. Ames Mutagenicity Assay
5.11. Removal of AFB1 in Milk and Tea
5.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide contamination of food-crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25%. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugraha, A.; Khotimah, K.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M. Risk assessment of aflatoxin B1 exposure from maize and peanut consumption in Indonesia using the margin of exposure and liver cancer risk estimation approaches. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, A.; Hua, H.; Shao, T.; Song, P.; Kong, Q.; Luo, T.; Jiang, Y. Aflatoxin B1 induces Src phosphorylation and stimulates lung cancer cell migration. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 6507–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahoum, A.; Verheecke-Vaessen, C.; Bouras, N.; Sabaou, N.; Mathieu, F. Taxonomy of mycelial actinobacteria isolated from Saharan soils and their efficiency to reduce aflatoxin B1 content in a solid-based medium. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Ryu, D. Worldwide occurrence of mycotoxins in cereals and cereal-derived food products: Public health perspectives of their co-occurrence. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7034–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Du, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.; Wang, J. Degradation and detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by tea-derived Aspergillus niger RAF106. Toxins 2020, 12, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, L.; Li, J. Complicated interactions between bio-adsorbents and mycotoxins during mycotoxin adsorption: Current research and future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 96, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaoui, S.; D’Amore, T.; Tarapoulouzi, M.; Agriopoulou, S.; Varzakas, T. Aflatoxins contamination in feed commodities: From occurrence and toxicity to recent advances in analytical methods and detoxification. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustom, I.Y.S. Aflatoxin in food and feed: Occurrence, legislation and inactivation by physical methods. Food Chem. 1997, 59, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyanagi, M.M.d.C.C.; Budiño, F.E.L.; Raj, J.; Vasiljević, M.; Ali, S.; Ramalho, L.N.Z.; Ramalho, F.S.; Corassin, C.H.; Ghantous, G.F.; Oliveira, C.A.F.d. Efficacy of two commercially available adsorbents to reduce the combined toxic effects of dietary Aflatoxins, Fumonisins, and Zearalenone and their residues in the tissues of weaned pigs. Toxins 2023, 15, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avantaggiato, G.; Greco, D.; Damascelli, A.; Solfrizzo, M.; Visconti, A. Assessment of multi-mycotoxin adsorption efficacy of grape pomace. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava-Ramírez, M.D.; Salazar, A.M.; Sordo, M.; López-Coello, C.; Téllez-Isaías, G.; Méndez-Albores, A.; Vázquez-Durán, A. Ability of low contents of biosorbents to bind the food carcinogen aflatoxin B1 in vitro. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, U.; Ain, Q.U.; Yaseen, M.; Santra, S.; Yao, X.; Liu, B. Assessing the aflatoxins mitigation efficacy of blueberry pomace biosorbent in buffer, gastrointestinal fluids and model wine. Toxins 2020, 12, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Durán, A.; Nava-Ramírez, M.J.; Hernández-Patlán, D.; Solís-Cruz, B.; Hernández-Gómez, V.; Téllez-Isaías, G.; Méndez-Albores, A. Potential of kale and lettuce residues as natural adsorbents of the carcinogen aflatoxin B1 in a dynamic gastrointestinal tract-simulated model. Toxins 2021, 13, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, D.; D’Ascanio, V.; Santovito, E.; Logrieco, A.F.; Avantaggiato, G. Comparative efficacy of agricultural by-products in sequestering mycotoxins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 1623–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiannikouris, A.; André, G.; Poughon, L.; François, J.; Dussap, C.G.; Jeminet, G.; Bertin, G.; Jouany, J.P. Chemical and conformational study of the interactions involved in mycotoxin complexation with β-D-Glucans. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Mendoza, A.; Garcia, H.S.; Steele, J.L. Screening of Lactobacillus casei strains for their ability to bind aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankaanpää, P.; Tuomola, E.; El-Nezami, H.; Ahokas, J.; Salminen, S.J. Binding of aflatoxin B1 alters the adhesion properties of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG in a Caco-2 model. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Zhang, G.; Ding, S.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Ren, D.; Chen, P. Lactobacillus plantarum T3 as an adsorbent of aflatoxin B1 effectively mitigates the toxic effects on mice. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, M.; Shi, Z.; Ghassempour, A.; Sedaghat, N.; Ahmadzadeh, M.; Mirabolfathy, M.; Javan-Nikkhah, M. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by Bacillus subtilis UTBSP1 isolated from pistachio nuts of Iran. Food Control 2012, 23, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchkongkaew, A.; Taillandier, P.; Gasaluck, P.; Lebrihi, A. Isolation of Bacillus spp. from Thai fermented soybean (Thua-nao): Screening for aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A detoxification. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Juri, M.G.; Dalcero, A.M.; Magnoli, C.E. In vitro aflatoxin B1 binding capacity by two Enterococcus faecium strains isolated from healthy dog faeces. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogi, C.A.; Armando, R.; Ludueña, R.; de Moreno de LeBlanc, A.; Rosa, C.A.R.; Dalcero, A.; Cavaglieri, L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains retain their viability and aflatoxin B1 binding ability under gastrointestinal conditions and improve ruminal fermentation. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2011, 28, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Hojati, M.; Norouzian, M.A.; Assadi Alamouti, A.; Afzalzadeh, A. In vitro evaluation of binding capacity of different binders to adsorb aflatoxin. Vet. Res. Forum 2021, 12, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Rajabzadeh Shandiz, S.; Ziaratnia, S.M.; Pahlevanloo, A.; Sarabi Jamab, M. Extraction efficiency of β-D-glucan from waste part of bottom mushroom (agaricus bisprous) and its ability to adsorb aflatoxin B1. Res. Innov. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 8, 314–325. [Google Scholar]
- Bzducha-Wróbel, A.; Bryła, M.; Gientka, I.; Błażejak, S.; Janowicz, M. Candida utilis ATCC 9950 cell walls and β(1,3)/(1,6)-Glucan preparations produced using Agro-Waste as a mycotoxins trap. Toxins 2019, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Dong, S.; Luo, X.; Wei, B.; Zhang, C.; Ji, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Meng, G.; Jia, B.; et al. Humic acids alleviate aflatoxin B1-induced hepatic injury by reprogramming gut microbiota and absorbing toxin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 259, 115051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlek, Z.; Bosnir, J.; Kuharic, Z.; Racz, A.; Jurak, I.; Lasic, D.; Markov, K.; Jakopovic, Z.; Frece, J. The influence of binding of selected mycotoxin deactivators and aflatoxin M1 on the content of selected micronutrients in milk. Processes 2022, 10, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinas, M.; Horisberger, M.; Bauer, H. The structural organization of the Tibi grain as revealed by light, scanning and transmission microscopy. Arch. Microbiol. 1980, 128, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureys, D.; De Vuyst, L. Microbial species diversity, community dynamics, and metabolite kinetics of water kefir fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2014, 80, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, J.S.; Yang, N.S.; Chen, M.J. Sugary kefir strain Lactobacillus mali APS1 ameliorated hepatic steatosis by regulation of SIRT-1/Nrf-2 and gut microbiota in rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Wilkinson, S.; Daenen, L.; Arendt, E.K. An update on water kefir: Microbiology, composition and production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 345, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Chang, S.; Guo, Q.; Yan, X.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Adsorption removal of ochratoxin A from milk by Tibetan kefir grains and its mechanism. LWT 2022, 169, 114024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel-Seydim, Z.B.; Gökırmaklı, Ç.; Greene, A.K. A comparison of milk kefir and water kefir: Physical, chemical, microbiological and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, M.B.; Santos, D.C.d.; Oliveira Filho, J.G.d.; Ores, J.d.C.; Takeuchi, K.P.; Lemes, A.C. A review of nondairy kefir products: Their characteristics and potential human health benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1536–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Rezaei, K.; Khodaiyan, F.; Rahmani, A. Optimisation of aflatoxin B1 reduction in pistachio nuts by kefir grains using statistical experimental methods. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crop. Foods 2016, 8, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriansyah, P.N.A.; Rahayu, W.P.; Kusumaningrum, H.D.; Kawamura, O. Aflatoxin M1 reduction by microorganisms isolated from kefir grains. Int. Food Res. J. 2022, 29, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Khodaiyan, F.; Rezaei, K.; Rahmani, A. Modelling of aflatoxin G1 reduction by kefir grain using response surface methodology. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Taheur, F.; Fedhila, K.; Chaieb, K.; Kouidhi, B.; Bakhrouf, A.; Abrunhosa, L. Adsorption of aflatoxin B1, zearalenone and ochratoxin A by microorganisms isolated from Kefir grains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 251, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi Touranlou, F.; Noori, S.M.; Salari, A.; Afshari, A.; Hashemi, M. Application of kefir for reduction of contaminants in the food industry: A systematic review. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 146, 105748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraç, C.; Camızcı, G. Adsorptive removal of patulin from apple juice via sulfhydryl-terminated magnetic bead-based separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglioni, P.T.; Becker-Algeri, T.; Drunkler, D.; Badiale-Furlong, E. Aflatoxin B1 and M1 in milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 829, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.A.M.; Kalschne, D.L.; Wochner, K.F.; Moreira, M.C.C.; Drunkler, D.A. Feasibility of L. plantarum and prebiotics on aflatoxin b1 detoxification in cow milk. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cai, F.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Yao, B.; Xu, J. Prediction, evaluation, confirmation, and elimination of matrix effects for lateral flow test strip based rapid and on-site detection of aflatoxin B1 in tea soups. Food Chem. 2020, 328, 127081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zeng, R.; Wang, Q.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Aflatoxin B1 and sterigmatocystin: Method development and occurrence in tea. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2022, 15, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmeen, R.; Hashmi, A.S.; Athar, M.; Tayyab, M.; Anjum, A.A. Molecular characterization of Lactobacillus from broiler and in-vitro detoxification of aflatoxin B1. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2021, 31, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Mao, H.; Hu, C.; Tron, T.; Lin, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Molecular docking studies and in vitro degradation of four aflatoxins (AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, and AFG2) by a recombinant laccase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Guo, H.; Guo, C.; Zheng, J.; Yue, T.; Yuan, Y. One-step preparation of nano-Fe3O4 modified inactivated yeast for the adsorption of patulin. Food Control 2018, 86, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, S.; Luo, X.; Song, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ma, W.; et al. Rapid biodegradation of aflatoxin B1 by metabolites of Fusarium sp. WCQ3361 with broad working temperature range and excellent thermostability. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prettl, Z.; Dési, E.; Lepossa, A.; Kriszt, B.; Kukolya, J.; Nagy, E. Biological degradation of aflatoxin B1 by a Rhodococcus pyridinivorans strain in by-product of bioethanol. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 224, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.R.; Vipin, A.V.; Hariprasad, P.; Appaiah, K.A.A.; Venkateswaran, G. Biological detoxification of aflatoxin b1 by Bacillus licheniformis cfr1. Food Control 2016, 71, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, M.; Hu, J.; Wan, K.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Zeng, R.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y. Isolation and characterization of Lactobacillus paracasei 85 and Lactobacillus buchneri 93 to absorb and biotransform zearalenone. Toxics 2022, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Q. Antifungal properties and AFB1 detoxification activity of a new strain of Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fochesato, A.S.; Cuello, D.; Poloni, V.; Galvagno, M.A.; Dogi, C.A.; Cavaglieri, L.R. Aflatoxin B1 adsorption/desorption dynamics in the presence of Lactobacillus rhamnosus RC007 in a gastrointestinal tract-simulated model. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartiainen, S.; Yiannikouris, A.; Apajalahti, J.; Moran, C.A. Comprehensive evaluation of the efficiency of yeast cell wall extract to adsorb ochratoxin A and mitigate accumulation of the toxin in broiler chickens. Toxins 2020, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiannikouris, A.; André, G.; Buléon, A.; Jeminet, G.; Canet, I.; François, J.; Bertin, G.; Jouany, J.P. Comprehensive conformational study of key interactions involved in zearalenone complexation with β-D-Glucans. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaf, J.C.; Atoui, A.; Khoury, A.E.; Chokr, A.; Louka, N. A comparative study of procedures for binding of aflatoxin M1 to Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; Zhang, J.Z.H. Computational search for aflatoxin binding proteins. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 685, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Taheur, F.; Mansour, C.; Mechri, S.; Laaouar, H.; Safta Skhiri, S.; Bouricha, M.; Jaouadi, B.; Mzoughi, R.; Zouari, N. Protective effects of dietary Kefir against aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity in Nile tilapia fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2300–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escrivá, L.; Font, G.; Manyes, L. In vivo toxicity studies of fusarium mycotoxins in the last decade: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Ji, C.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Ma, Q.; Niu, T. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and other microbes selected using coumarin medium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wu, C.; Shen, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, R. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by salt tolerant Tetragenococcus halophilus CGMCC 3792. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Hao, S.; Mu, P.; Deng, F.; Deng, Y. Aflatoxin B1 degradation and detoxification by Escherichia coli CG1061 isolated from chicken cecum. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekpour, A.; Bayati, S. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxins in pistachio using ultrasonically stabilized chloroform/water emulsion and HPLC. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; El-Nezami, H.; Haskard, C.A.; Gratz, S.; Puong, K.Y.; Salminen, S.; Mykkänen, H. Kinetics of adsorption and desorption of aflatoxin B1 by viable and nonviable bacteria. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Fang, Q.; Liao, Z.; Xu, C.; Liang, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.; Wang, J. Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by a potential probiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens WF2020. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 891091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Langmuir | Freundlich | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| qm (µg g−1) | 25.773 | Kf (µg g−1) | 1.601 |
| KL (mL µg−1) | 0.094 | n | 1.644 |
| R2 | 0.529 | R2 | 0.924 |
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Intraparticle Diffusion | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | 0.067 | k2 (g µg−1 min−1) | 0.099 | k3 (g µg−1 min−1/2) | 0.392 |
| qe (µg g−1) | 2.733 | qe (µg g−1) | 6.878 | b | 4.456 |
| R2 | 0.710 | R2 | 0.9995 | R2 | 0.663 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, W.; Liao, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.; Wang, J. Microbial Composition of Water Kefir Grains and Their Application for the Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1. Toxins 2024, 16, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020107
Ouyang W, Liao Z, Yang X, Zhang X, Zhu X, Zhong Q, Wang L, Fang X, Wang J. Microbial Composition of Water Kefir Grains and Their Application for the Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1. Toxins. 2024; 16(2):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020107
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Weidong, Zhenlin Liao, Ximiao Yang, Xiao Zhang, Xiaoxuan Zhu, Qingping Zhong, Li Wang, Xiang Fang, and Jie Wang. 2024. "Microbial Composition of Water Kefir Grains and Their Application for the Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1" Toxins 16, no. 2: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020107
APA StyleOuyang, W., Liao, Z., Yang, X., Zhang, X., Zhu, X., Zhong, Q., Wang, L., Fang, X., & Wang, J. (2024). Microbial Composition of Water Kefir Grains and Their Application for the Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1. Toxins, 16(2), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020107