Aflatoxin B1 Impairs Bone Mineralization in Broiler Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Performance
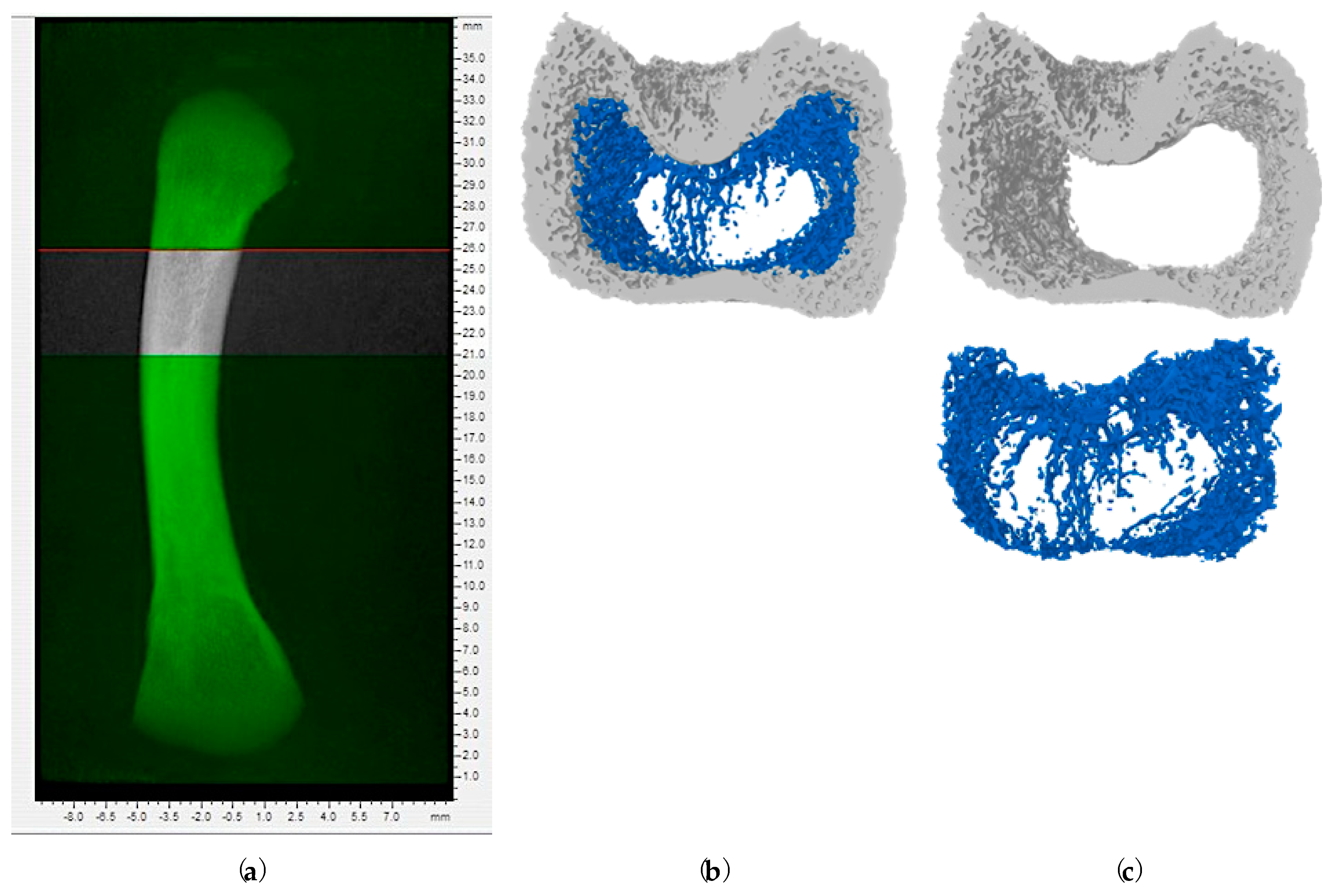
2.2. Bone Microstructural Changes in Response to Increasing Doses of Aflatoxin B1
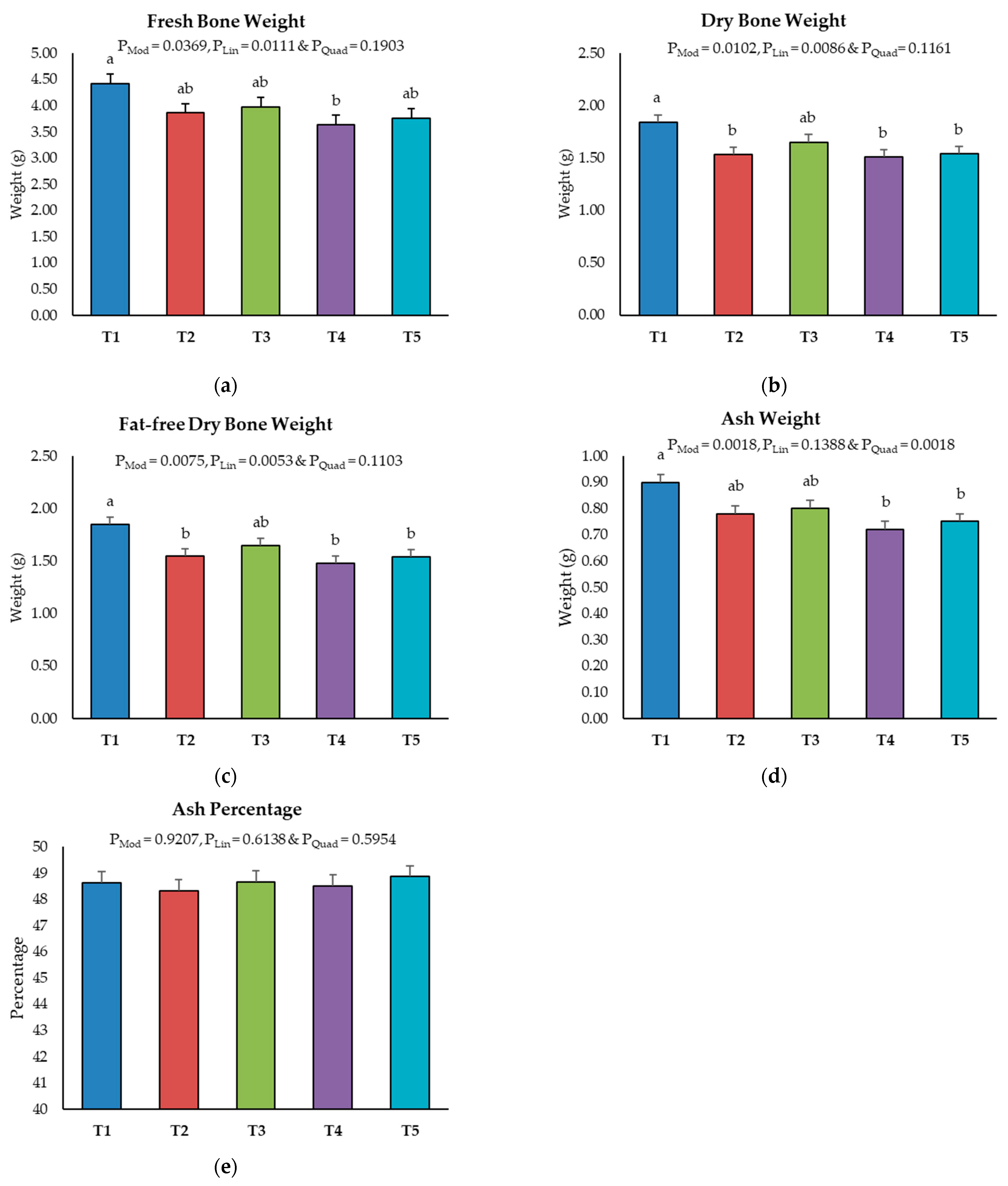
2.3. Bone Ash Content of Tibia Bone
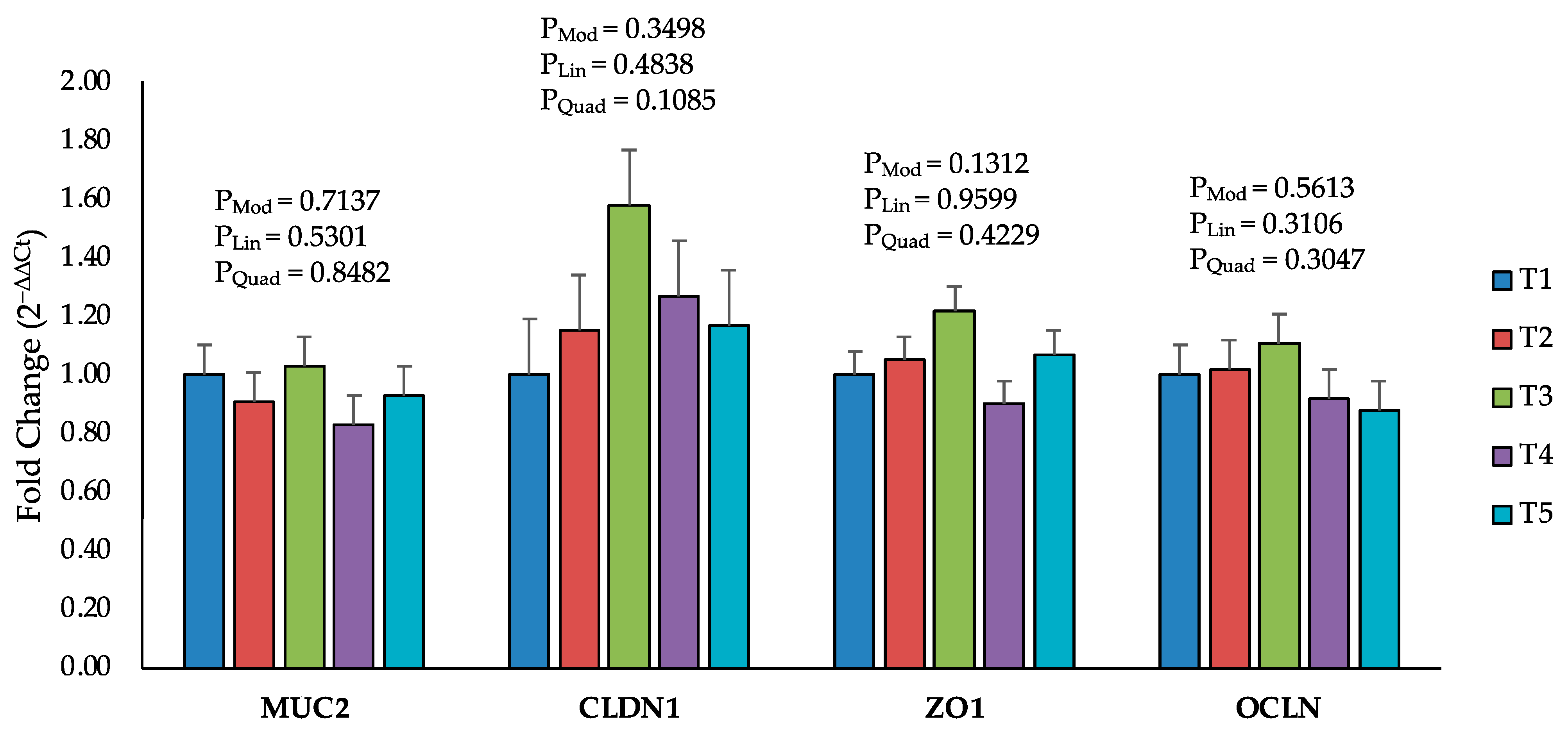
2.4. Changes in the Expression of Calcium and Phosphorus Transporters
2.5. Intestinal Permeability and Tight Junction Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Preparation of Aflatoxin B1 Contaminated Feed
5.2. Birds and Experimental Design
5.3. Intestinal Permeability
5.4. RNA Extraction and Real-Time RT-PCR
5.5. Bone Ash Analysis
5.6. Micro-Computed Tomography (Micro-CT) of Femur Bone
5.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medina, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Magan, N. Effect of Climate Change on Aspergillus Flavus and Aflatoxin B1 Production. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pathak, H.; Bhadauria, S.; Sudan, J. Aflatoxin Contamination in Food Crops: Causes, Detection, and Management: A Review. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2021, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Q. Aflatoxin B1 in Poultry Liver: Toxic Mechanism. Toxicon 2023, 233, 107262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, L.; Xu, W. Aflatoxin B1-Induced Epigenetic Alterations: An Overview. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, T.; Cuéllar, H.; Jaramillo-Juárez, F.; Valdivia, A.G.; Reyes, J. Effects of Aflatoxin B(1) on the Liver and Kidney of Broiler Chickens during Development. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2000, 125, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Aflatoxin B1 Impairs Mitochondrial Functions, Activates ROS Generation, Induces Apoptosis and Involves Nrf2 Signal Pathway in Primary Broiler Hepatocytes. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessari, E.N.C.; Oliveira, C.A.F.; Cardoso, A.L.S.P.; Ledoux, D.R.; Rottinghaus, G.E. Effects of Aflatoxin B1 and Fumonisin B1 on Body Weight, Antibody Titres and Histology of Broiler Chicks. Br. Poult. Sci. 2006, 47, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Yuan, S.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Wang, F.; Cui, H.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, J.; Geng, Y. Effects of Aflatoxin B on Oxidative Stress Markers and Apoptosis of Spleens in Broilers. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Sun, M.; He, Y.; Lei, J.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Bai, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, B. Mycotoxins Binder Supplementation Alleviates Aflatoxin B1 Toxic Effects on the Immune Response and Intestinal Barrier Function in Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R.C.; Chauhan, H.V.S.; Jha, G.J. Suppression of Cell-Mediated Immunity by Purified Aflatoxin B1 in Broiler Chicks. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1991, 28, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, C.; Chang, J.; Yin, Q.; Wang, L.; Jin, S.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, F. Compound Mycotoxin Detoxifier Alleviating Aflatoxin B1 Toxic Effects on Broiler Growth Performance, Organ Damage and Gut Microbiota. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bintvihok, A.; Kositcharoenkul, S. Effect of Dietary Calcium Propionate on Performance, Hepatic Enzyme Activities and Aflatoxin Residues in Broilers Fed a Diet Containing Low Levels of Aflatoxin B1. Toxicon 2006, 47, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxton, H.; Anthony, N.B.; Corr, S.A.; Hutchinson, J.R. The Effects of Selective Breeding on the Architectural Properties of the Pelvic Limb in Broiler Chickens: A Comparative Study across Modern and Ancestral Populations. J. Anat. 2010, 217, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartcher, K.M.; Lum, H.K. Genetic Selection of Broilers and Welfare Consequences: A Review. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2020, 76, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; Bloomfield, S.A.; Ricke, S.C. Effects of Age, Vitamin D3, and Fructooligosaccharides on Bone Growth and Skeletal Integrity of Broiler Chicks. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2425–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, M.Y.; Karnuah, A.B.; Anthony, N.B.; Pesti, G.M.; Aggrey, S.E. The Effects of Broiler Chicken Growth Rate on Valgus, Varus, and Tibial Dyschondroplasia. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, D.V.; Bodine, A.B.; Rehrer, N.J. Metabolic Effects of Low Aflatoxin B1 Levels on Broiler Chicks. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, D.; Rottinghaus, G.; Bermudez, A.; Alonso-Debolt, M. Efficacy of a Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate to Ameliorate the Toxic Effects of Aflatoxin in Broiler Chicks. Poult. Sci. 1999, 78, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shirley, R.; Dibner, J.; Uraizee, F.; Officer, M.; Kitchell, M.; Vazquez-Anon, M.; Knight, C. Comparison of Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate and Yeast Cell Wall on Counteracting Aflatoxicosis in Broiler Chicks. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, N.K.S.; Ledoux, D.R.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Bermudez, A.J.; Chen, Y.C. Efficacy of Turmeric (Curcuma Longa), Containing a Known Level of Curcumin, and a Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate to Ameliorate the Adverse Effects of Aflatoxin in Broiler Chicks. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, P.; Santini, A.; Fattore, L.; Novellino, E.; Ritieni, A. Toxicity of Aflatoxin B1 towards the Vitamin D Receptor (VDR). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 76, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persico, M.; Sessa, R.; Cesaro, E.; Dini, I.; Costanzo, P.; Ritieni, A.; Fattorusso, C.; Grosso, M. A Multidisciplinary Approach Disclosing Unexplored Aflatoxin B1 Roles in Severe Impairment of Vitamin D Mechanisms of Action. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2023, 39, 1275–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvandi, A.M.; Shahba, S.; Mehrzad, J.; Lombardi, G. Metabolic Disruption by Naturally Occurring Mycotoxins in Circulation: A Focus on Vascular and Bone Homeostasis Dysfunction. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 915681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, R.H.; Kirkden, R.D.; Broom, D.M. A Review of the Aetiology and Pathology of Leg Weakness in Broilers in Relation to Welfare. Avian Poult. Biol. Rev. 2002, 13, 45–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierończyk, B.; Rawski, M.; Józefiak, D.; Świątkiewicz, S. Infectious and Non-Infectious Factors Associated with Leg Disorders in Poultry—A Review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2017, 17, 645–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choppa, V.S.R.; Kim, W.K. A Review on Pathophysiology, and Molecular Mechanisms of Bacterial Chondronecrosis and Osteomyelitis in Commercial Broilers. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntur, A.R.; Rosen, C.J. Bone As An Endocrine Organ. Endocr. Pract. 2012, 18, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchacki, K.J.; Roberts, F.; Lovdel, A.; Farquharson, C.; Morton, N.M.; MacRae, V.E.; Cawthorn, W.P. Skeletal Energy Homeostasis: A Paradigm of Endocrine Discovery. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 234, R67–R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, N.C.; Durairaj, V. Avian Bone Physiology and Poultry Bone Disorders. In Sturkie’s Avian Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 549–563. ISBN 978-0-12-819770-7. [Google Scholar]
- Knowles, T.G.; Kestin, S.C.; Haslam, S.M.; Brown, S.N.; Green, L.E.; Butterworth, A.; Pope, S.J.; Pfeiffer, D.; Nicol, C.J. Leg Disorders in Broiler Chickens: Prevalence, Risk Factors and Prevention. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnoli, A.P.; Monge, M.P.; Miazzo, R.D.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Magnoli, C.E.; Merkis, C.I.; Cristofolini, A.L.; Dalcero, A.M.; Chiacchiera, S.M. Effect of Low Levels of Aflatoxin B1 on Performance, Biochemical Parameters, and Aflatoxin B1 in Broiler Liver Tissues in the Presence of Monensin and Sodium Bentonite. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, C.A.; Apajalahti, J.; Yiannikouris, A.; Ojanperä, S.; Kettunen, H. Effects of Low Dietary Aflatoxin B1 on Broiler Liver Concentration without and with Mycosorb® Toxin Binder. J. Appl. Anim. Nutr. 2013, 2, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavangar, P.; Gharahveysi, S.; Rezaeipour, V.; Irani, M. Efficacy of Phytobiotic and Toxin Binder Feed Additives Individually or in Combination on the Growth Performance, Blood Biochemical Parameters, Intestinal Morphology, and Microbial Population in Broiler Chickens Exposed to Aflatoxin B1. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, H.; Kurtoglu, V.; Coskun, B. Preventive Efficacy of Clinoptilolite in Broilers during Chronic Aflatoxin (50 and 100 ppb) Exposure. Res. Vet. Sci. 2000, 69, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; He, X.; Hu, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Hou, D.-X.; Song, Z. The Preventive Effect and Mechanisms of Adsorbent Supplementation in Low Concentration Aflatoxin B1 Contaminated Diet on Subclinical Symptom and Histological Lesions of Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giambrone, J.J.; Diener, U.L.; Davis, N.D.; Panangala, V.S.; Hoerr, F.J. Effects of Purified Aflatoxin on Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 1985, 64, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabiulla, I.; Malathi, V.; Swamy, H.V.L.N.; Naik, J.; Pineda, L.; Han, Y. The Efficacy of a Smectite-Based Mycotoxin Binder in Reducing Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity on Performance, Health and Histopathology of Broiler Chickens. Toxins 2021, 13, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Wang, J.Q.; Jia, S.C.; Chen, Y.K.; Wang, J.P. Effect of Yeast Cell Wall on the Growth Performance and Gut Health of Broilers Challenged with Aflatoxin B1 and Necrotic Enteritis. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Applegate, T.J. Impact of Dietary Branched Chain Amino Acids Concentration on Broiler Chicks during Aflatoxicosis. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Naehrer, K.; Applegate, T.J. Interactive Effects of Dietary Protein Concentration and Aflatoxin B1 on Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Gut Health in Broiler Chicks. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1312–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, B.; Oswald, I. Mycotoxin Co-Contamination of Food and Feed: Meta-Analysis of Publications Describing Toxicological Interactions. World Mycotoxin J. 2011, 4, 285–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Burr, D.B. Bone Modeling and Remodeling. In Basic and Applied Bone Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 75–90. ISBN 978-0-12-416015-6. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, B. Normal Bone Anatomy and Physiology. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, S131–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, N.C.; Huff, G.R.; Huff, W.E.; Balog, J.M. Factors Regulating Bone Maturity and Strength in Poultry. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonare, L.D.; Giannini, S. Bone Microarchitecture as an Important Determinant of Bone Strength. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2004, 27, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenu, C.; Delmas, P.D. Physiology of Bone Remodeling. In Advances in Organ Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 5, pp. 45–64. ISBN 978-0-7623-0390-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins, Y.H.; Choi, J.; Teng, P.-Y.; Yamada, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Kim, W.K. Reduced Bone Formation and Increased Bone Resorption Drive Bone Loss in Eimeria Infected Broilers. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, G.; Dermauw, V.; Bouillon, R. Vitamin D Signaling in Calcium and Bone Homeostasis: A Delicate Balance. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleet, J.C.; Schoch, R.D. Molecular Mechanisms for Regulation of Intestinal Calcium Absorption by Vitamin D and Other Factors. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2010, 47, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proszkowiec-Weglarz, M.; Angel, R. Calcium and Phosphorus Metabolism in Broilers: Effect of Homeostatic Mechanism on Calcium and Phosphorus Digestibility. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2013, 22, 609–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Regmi, P.; Applegate, T.; Chai, L.; Kim, W.K. Osteoimmunology: A Link between Gastrointestinal Diseases and Skeletal Health in Chickens. Animals 2023, 13, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Garlich, J.; Qureshi, M. Vitamin D Deficiency Alters the Immune Responses of Broiler Chicks. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza-Seeber, R.; Latorre, J.D.; Bielke, L.R.; Kuttappan, V.A.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Merino-Guzman, R.; Vicente, J.L.; Donoghue, A.; Cross, D.; et al. Leaky Gut and Mycotoxins: Aflatoxin B1 Does Not Increase Gut Permeability in Broiler Chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.J.; Hernández, E. In Situ Absorption of Aflatoxins in Rat Small Intestine. Mycopathologia 1996, 134, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, S.; Coulombe, R.A. Metabolism of Aflatoxin B1 in Turkey Liver Microsomes: The Relative Roles of Cytochromes P450 1A5 and 3A37. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 254, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Fu, P.; Chen, N.; Gao, N.; Cao, Q.; Yue, K.; Xu, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; et al. Total Flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae Protect Hepatocytes against Aflatoxin B1-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Broiler Chickens. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 230, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Yu, P.; Yang, K.; Cao, D. Aflatoxin B1: Metabolism, Toxicology, and Its Involvement in Oxidative Stress and Cancer Development. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2022, 32, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkerroum, N. Chronic and Acute Toxicities of Aflatoxins: Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Cheng, P.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Hamid, S. Curcumin Successfully Inhibited the Computationally Identified CYP2A6 Enzyme-Mediated Bioactivation of Aflatoxin B1 in Arbor Acres Broiler. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Han, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ishfaq, M.; Liu, R.; Wei, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Effect of Curcumin as Feed Supplement on Immune Response and Pathological Changes of Broilers Exposed to Aflatoxin B1. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, M.F.A.; Merino-Guzman, R.; Latorre, J.D.; Mahaffey, B.D.; Yang, Y.; Teague, K.D.; Graham, L.E.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Bielke, L.R.; et al. Optimizing Fluorescein Isothiocyanate Dextran Measurement As a Biomarker in a 24-h Feed Restriction Model to Induce Gut Permeability in Broiler Chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; Donalson, L.M.; Herrera, P.; Woodward, C.L.; Kubena, L.F.; Nisbet, D.J.; Ricke, S.C. Research Note: Effects of Different Bone Preparation Methods (Fresh, Dry, and Fat-Free Dry) on Bone Parameters and the Correlations Between Bone Breaking Strength and the Other Bone Parameters. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 1663–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, J.; Teng, P.-Y.; Tompkins, Y.H.; Jordan, B.; Kim, W.K. Effects of Phytase and Coccidial Vaccine on Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Bone Mineralization, and Intestinal Gene Expression of Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Liu, G.; White, D.L.; Tompkins, Y.H.; Kim, W.K. Graded Levels of Eimeria Challenge Altered the Microstructural Architecture and Reduced the Cortical Bone Growth of Femur of Hy-Line W-36 Pullets at Early Stage of Growth (0–6 Wk of Age). Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Kim, W.K. The Application of Micro-CT in Egg-Laying Hen Bone Analysis: Introducing an Automated Bone Separation Algorithm. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5175–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Goo, D.; Sharma, M.K.; Ko, H.; Liu, G.; Paneru, D.; Choppa, V.S.R.; Lee, J.; Kim, W.K. Effects of Different Eimeria Inoculation Doses on Growth Performance, Daily Feed Intake, Gut Health, Gut Microbiota, Foot Pad Dermatitis, and Eimeria Gene Expression in Broilers Raised in Floor Pens for 35 Days. Animals 2023, 13, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Items 2 | Treatment Groups 3 | SEM | p-Values 4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | PModel | PLinear | PQuadratic | ||
| 0–8 days | |||||||||
| BW (g) | 212 | 208 | 207 | 198 | 200 | 6 | 0.4675 | 0.0867 | 0.8741 |
| BWG (g) | 166 | 162 | 161 | 152 | 154 | 6 | 0.4640 | 0.0856 | 0.8772 |
| FI (g) | 197 | 198 | 195 | 195 | 190 | 5 | 0.8832 | 0.3644 | 0.6818 |
| FCR (g/g) | 1.19 | 1.22 | 1.21 | 1.32 | 1.24 | 0.06 | 0.5331 | 0.2490 | 0.5993 |
| 9–19 days | |||||||||
| BW (g) | 705 | 707 | 699 | 693 | 688 | 16 | 0.9083 | 0.3473 | 0.8347 |
| BWG (g) | 493 | 499 | 492 | 495 | 488 | 15 | 0.9898 | 0.7618 | 0.7738 |
| FI (g) | 857 | 860 | 859 | 852 | 853 | 23 | 0.9990 | 0.8431 | 0.9025 |
| FCR (g/g) | 1.74 | 1.72 | 1.75 | 1.72 | 1.76 | 0.06 | 0.9846 | 0.8204 | 0.8157 |
| 0–19 days | |||||||||
| BWG (g) | 659 | 661 | 653 | 647 | 641 | 16 | 0.9076 | 0.3462 | 0.8335 |
| FI (g) | 1053 | 1058 | 1053 | 1048 | 1044 | 24 | 0.9946 | 0.7007 | 0.8378 |
| FCR (g/g) | 1.60 | 1.60 | 1.62 | 1.62 | 1.63 | 0.05 | 0.9831 | 0.5514 | 0.9858 |
| Bone Region | Parameters 2 | Unit | Treatment Groups 3 | p-Values 4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | SEM | PModel | PLinear | PQuadratic | |||
| Total | BMC | g | 0.077 a | 0.071 ab | 0.069 ab | 0.062 b | 0.063 b | 0.003 | 0.0212 | 0.0015 | 0.523 |
| BMD | g/cm3 | 0.280 | 0.272 | 0.273 | 0.277 | 0.262 | 0.010 | 0.8026 | 0.3726 | 0.7833 | |
| TV | mm3 | 275 a | 260 ab | 254 ab | 226 b | 240 ab | 10 | 0.0412 | 0.0063 | 0.3953 | |
| BV | mm3 | 109 a | 99 ab | 96 ab | 85 b | 90 ab | 5 | 0.0406 | 0.0045 | 0.2972 | |
| BV/TV | % | 39.62 | 38.34 | 37.71 | 37.89 | 37.47 | 1.62 | 0.9011 | 0.3782 | 0.6894 | |
| Po.V(cl) | mm3 | 0.245 | 0.217 | 0.204 | 0.129 | 0.146 | 0.030 | 0.0642 | 0.0069 | 0.8076 | |
| Po.V(op) | mm3 | 165.7 | 160.0 | 158.4 | 140.5 | 150.1 | 8.5 | 0.3087 | 0.0781 | 0.665 | |
| PP | % | 60.38 | 61.66 | 62.29 | 62.11 | 62.53 | 1.62 | 0.9011 | 0.3782 | 0.6894 | |
| Cortical | BMC | g | 0.057 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.045 | 0.048 | 0.003 | 0.0907 | 0.0175 | 0.2361 |
| BMD | g/cm3 | 0.475 | 0.491 | 0.495 | 0.515 | 0.517 | 0.010 | 0.0922 | 0.0075 | 0.7665 | |
| TV | mm3 | 120 a | 105 ab | 102 ab | 89 b | 94 b | 6 | 0.0189 | 0.0020 | 0.2178 | |
| BV | mm3 | 99 a | 89 ab | 87 ab | 76 b | 83 ab | 5 | 0.0429 | 0.0075 | 0.1968 | |
| BV/TV | % | 82.4 b | 85.0 ab | 85.0 ab | 86.3 ab | 88.1 a | 1.0 | 0.0337 | 0.0023 | 0.9663 | |
| Po.V(cl) | mm3 | 0.237 a | 0.197 ab | 0.191 ab | 0.115 b | 0.139 ab | 0.029 | 0.0500 | 0.0060 | 0.5907 | |
| Po.V(op) | mm3 | 21.06 a | 15.58 ab | 15.06 ab | 12.80 b | 10.93 b | 1.57 | 0.0067 | 0.0004 | 0.4195 | |
| PP | % | 17.58 a | 15.00 ab | 15.04 ab | 13.66 ab | 11.88 b | 1.04 | 0.0337 | 0.0023 | 0.9663 | |
| Trabecular | BMC | g | 0.018 a | 0.017 ab | 0.016 ab | 0.015 ab | 0.012 b | 0.001 | 0.0331 | 0.0026 | 0.2792 |
| BMD | g/cm3 | 0.120 a | 0.116 ab | 0.114 ab | 0.113 ab | 0.090 b | 0.006 | 0.0214 | 0.0043 | 0.1336 | |
| TV | mm3 | 146 | 146 | 144 | 129 | 138 | 8 | 0.5477 | 0.2219 | 0.8596 | |
| BV | mm3 | 7.38 | 8.06 | 6.44 | 6.80 | 5.04 | 0.86 | 0.2328 | 0.0531 | 0.4096 | |
| BV/TV | % | 5.08 | 5.4 | 4.56 | 5.09 | 3.71 | 0.54 | 0.2607 | 0.0976 | 0.3414 | |
| Tb.Th | mm | 0.122 | 0.151 | 0.134 | 0.148 | 0.125 | 0.017 | 0.6706 | 0.954 | 0.2572 | |
| Conn.Dn | mm−3 | 9.42 | 7.71 | 6.01 | 8.06 | 7.98 | 0.79 | 0.0809 | 0.3224 | 0.0259 | |
| Tb.N | mm−1 | 0.438 | 0.348 | 0.289 | 0.370 | 0.371 | 0.041 | 0.1821 | 0.3946 | 0.0463 | |
| Ingredients, % | Starter | Grower |
|---|---|---|
| Corn | 58.50 | 63.72 |
| Soybean Meal (48% CP) | 34.75 | 29.70 |
| Soybean Oil | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Dicalcium Phosphate | 2.08 | 1.35 |
| Limestone | 1.02 | 1.06 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.33 | 0.32 |
| L-Lysine HCl | 0.24 | 0.27 |
| L-Threonine | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| Common Salt | 0.40 | 0.35 |
| Vitamin Premix 1 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Mineral Premix 2 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Sand | 1.88 | 2.13 |
| Chromic Oxide | 0.00 | 0.30 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Calculated Values, % | ||
| D.M. 3 | 87.63 | 87.20 |
| M.E., Kcal/g 4 | 2.90 | 2.95 |
| Crude Protein | 21.50 | 19.50 |
| Calcium | 0.96 | 0.80 |
| Available Phosphorus | 0.54 | 0.40 |
| dLYS | 1.26 | 1.16 |
| dMET | 0.65 | 0.61 |
| Gene 1 | Accession Number | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Housekeeping Genes | |||
| GAPDH | NM_204305.2 | GCTAAGGCTGTGGGGAAAGT | TCAGCAGCAGCCTTCACTAC |
| ACTB | NM_205518.2 | CAACACAGTGCTGTCTGGTGGTA | ATCGTACTCCTGCTTGCTGATCC |
| Vitamin D Receptor | |||
| VDR | NM_205098.2 | GCAGCAGAAAGTCATCGACA | TGCTGAATTTGCTTCTCACG |
| Ca and P Transporters | |||
| CALB1 | NM_205513.2 | AAGCAGATTGAAGACTCAAAGC | CTGGCCAGTTCAGTAAGCTC |
| CaSR | XM_416491.8 | CTGCTTCGAGTGTGTGGACT | GATGCAGGATGTGTGGTTCT |
| NCX1 | NM_001398209.1 | TCACTGCAGTCGTGTTTGTG | AAGAAAACGTTCACGGCATT |
| NaPi-Ⅱb | NM_204474.3 | AAAGTGACGTGGACCATG | GAGACCGATGGCAAGATCAG |
| PMCA1b | NM_001168002.4 | TTAATGCCCGGAAAATTCAC | TCCACCAAACTGCACGATAA |
| Tight Junction Proteins | |||
| MUC2 | NM_001318434.1 | ATGCGATGTTAACACAGGACTC | GTGGAGCACAGCAGACTTTG |
| CLDN1 | NM_001013611.2 | TGGAGGATGACCAGGTGAAGA | CGAGCCACTCTGTTGCCATA |
| ZO1 | XM_015278981.2 | CAACTGGTGTGGGTTTCTGAA | TCACTACCAGGAGCTGAGAGGTAA |
| OCLN | XM_025144248.1 | GTCTGTGGGTTCCTCATCGT | GTTCTTCACCCACTCCTCCA |
| Abbreviation | Variable | Description of Variables | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMC | Bone mineral content | Measure the bone mineral content of the tissue | g |
| BMD | Bone mineral density | Measure the bone mineral content per unit of volume | g/cm3 |
| TV | Tissue volume | Volume of the entire region of interest | mm3 |
| BV | Bone volume | Volume of the bone segment | mm3 |
| BV/TV | Bone volume fraction | Bone volume segment volume as a fraction of tissue volume from the region of interest | % |
| Po.V(cl) | Volume of closed pores | Volume of closed pore space | mm3 |
| Po.V(op) | Volume of open pores | Volume of open pore space | mm3 |
| PP | Porosity percentage | The volume of pores by total volume of bone | % |
| Tb.Th | Trabecular thickness | Mean thickness of trabeculae measured using 3-D methods | mm |
| Conn.Dn | Connectivity density | A measure of the degree of connectivity of trabeculae normalized by TV | mm−3 |
| Tb.N | Trabecular number | Average number of trabeculae per unit of length | mm−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paneru, D.; Sharma, M.K.; Shi, H.; Wang, J.; Kim, W.K. Aflatoxin B1 Impairs Bone Mineralization in Broiler Chickens. Toxins 2024, 16, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020078
Paneru D, Sharma MK, Shi H, Wang J, Kim WK. Aflatoxin B1 Impairs Bone Mineralization in Broiler Chickens. Toxins. 2024; 16(2):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020078
Chicago/Turabian StylePaneru, Deependra, Milan Kumar Sharma, Hanyi Shi, Jinquan Wang, and Woo Kyun Kim. 2024. "Aflatoxin B1 Impairs Bone Mineralization in Broiler Chickens" Toxins 16, no. 2: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020078
APA StylePaneru, D., Sharma, M. K., Shi, H., Wang, J., & Kim, W. K. (2024). Aflatoxin B1 Impairs Bone Mineralization in Broiler Chickens. Toxins, 16(2), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020078






