Insecticidal Effects of Transgenic Maize Bt-Cry1Ab, Bt-Vip3Aa, and Bt-Cry1Ab+Vip3Aa against the Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker) in Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Comparison of Insecticidal Effects of Three Bt Maize Events against the Oriental Armyworm
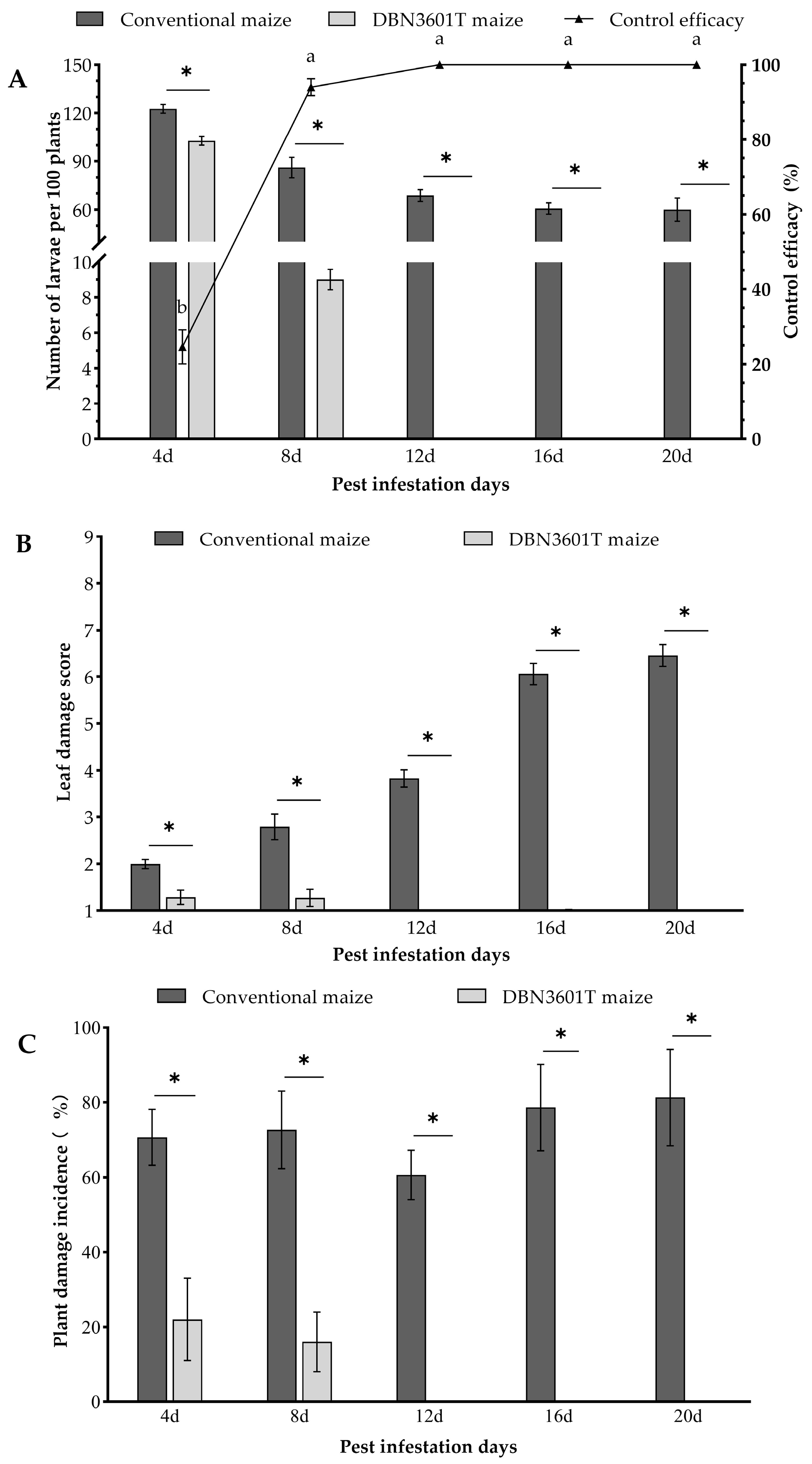
2.2. Field Control Efficacy of DBN3601T Maize on the Oriental Armyworm Larvae in a Mesh Cage
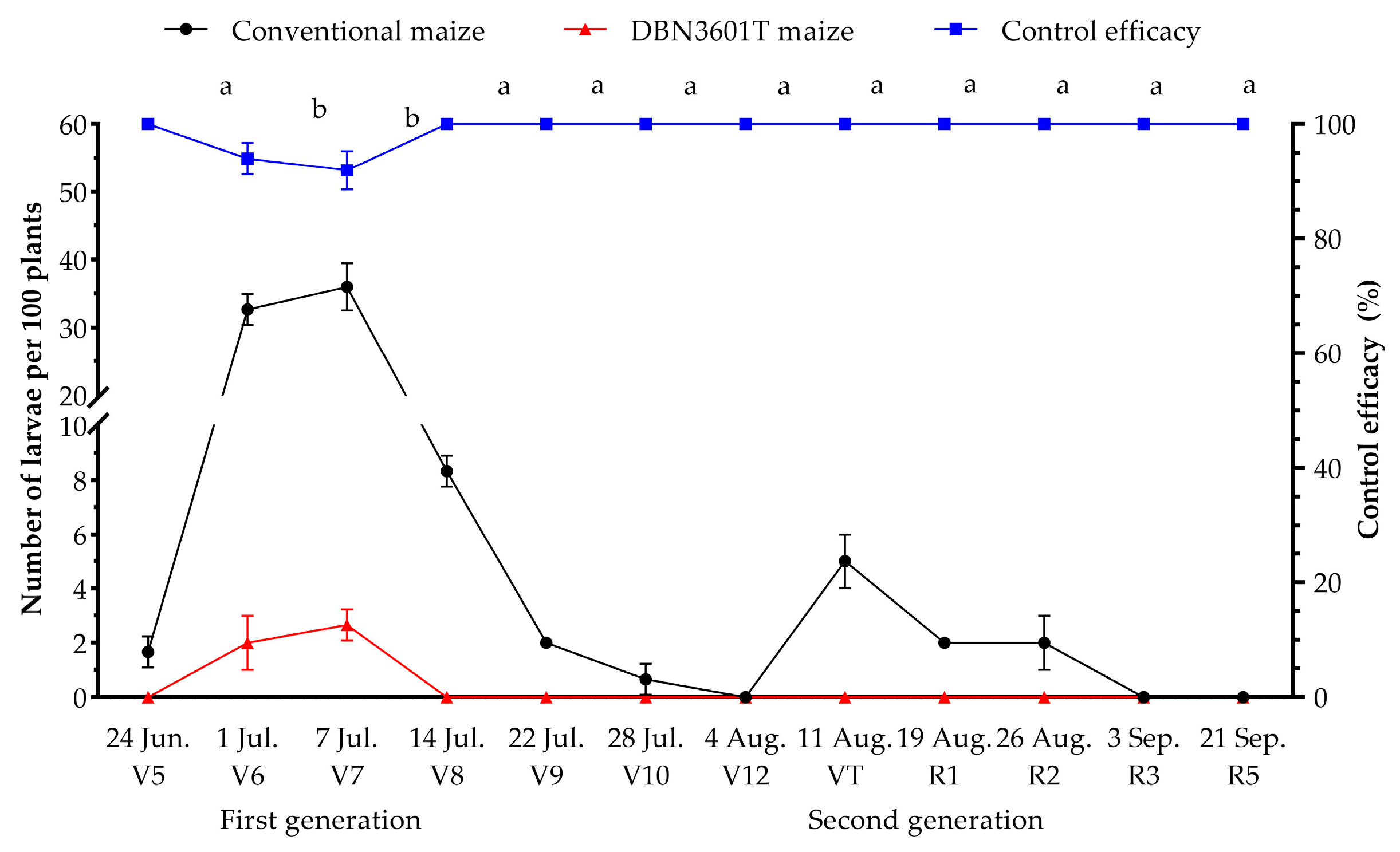
2.3. Naturally Occurring Population Dynamics of Oriental Armyworm in the Bt-(Cry1Ab+Vip3Aa) (Event DBN3601T) Maize Field
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Maize for Testing
5.2. Oriental Armyworm Culture
5.3. Tissue Bioassays and Determination of Insecticidal Protein Expression of Bt Maize
5.4. Field Cage Bioassay
5.5. Control Efficiency Assessment against Naturally Occurring Oriental Armyworm
5.6. Data Processing and Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Li, C.G.; Zeng, J.; Liu, J. Population dynamics of the armyworm in China: A review of the past 60 years′ research. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2014, 51, 890–898. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.; Davies, J. The Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata (Wlk.). Distribution, Biology and Control: A Literature Review; Center for Oversea Pest Research, ODA Miscellaneous Report 59; Center for Oversea Pest: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.F.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.X.; Luo, L.Z. Novel features, occurrence trends and economic impact of the oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker) in China. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2014, 51, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.F.; Hou, P.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Zhang, F.S. Understanding production potentials and yield gaps in intensive maize production in China. Field Crops Res. 2013, 143, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Tang, Q.B.; Li, X.R.; Cheng, D.F.; Xun, Z. Analysis on the migration of first-generation Mythimna separata (Walker) in China in 2013. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.S.; Zhang, H.W.; Liu, D.Z.; Lv, C.Y.; Cang, X.Z.; Sun, X.X.; Song, Y.F.; He, W.; Chu, B.; Zhao, S.Y.; et al. Seasonal migratory activity of Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) across China and Myanmar. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 4975–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.F.; Luo, L.Z.; Zhang, L.; Sappington, T.W.; Hu, Y. Regulation of migration in Mythimna separata (Walker) in China: A review integrating environmental, physiological, hormonal, genetic, and molecular factors. Environ. Entomol. 2011, 40, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, M.; Chi, Y.; Wuriyanghan, H. De novo assembly of the transcriptome for oriental armyworm Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and analysis on insecticide resistance-related genes. J. Insect Sci. 2016, 16, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, R.; Akhtar, Z.R.; Rehman, M.A.; Tariq, M.; Asad, A.; Muhammad, S.; Ur-Rehman, H.; Mukhtar, M.L. Field evolved resistance and inheritance patterns of laboratory selected strains of oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata, against lambda-cyhalothrin and its cross resistance to other insecticides. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 58, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.Y.; Kang, Z.J.; Shi, X.Y.; Gao, X.W. Metabolic adaptation mechanisms of insects to plant secondary metabolites and their implications for insecticide resistance of insects. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2015, 58, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, S.; Shuai, L.; Li, Y.P.; Xu, X.L.; Cheng, W.N.; Yi, W.; Wu, J.X. Insecticide resistance of the field populations of oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker) in Shaanxi and Shanxi provinces of China. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Frankenhuyzen, K. Insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal proteins. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 101, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Wu, K.M.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Guo, Y.Y.; Desneux, N. Widespread adoption of Bt cotton and insecticide decrease promotes biocontrol services. Nature 2012, 487, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon 2007, 49, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, S.; Jin, M.H.; Wu, C.; Chakraborty, P.; Xiao, Y.T. Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein family Vip3A and mode of action against pest Lepidoptera. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhao, S.Y.; Wu, K.M. Susceptibilities of the invasive fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) to the insecticidal proteins of Bt maize in China. Toxins 2022, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.P.; Ji, T.J.; Zhao, S.Y.; Feng, H.Q.; Wu, K.M. High-dose assessment of transgenic insect-resistant maize events against major lepidopteran pests in China. Plants 2022, 11, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardke, J.T.; Leonard, B.R.; Huang, F.; Jackson, R.E. Damage and survivorship of fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on transgenic field corn expressing Bacillus thuringiensis Cry proteins. Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.A.; Hellmich, R.L.; Lewis, L.C. Late-instar European corn borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) tunneling and survival in transgenic corn hybrids. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.M.; Conville, J.; Matthews, P.; Hootman, T.; Himes, J.; Wong, S.; Huang, F.N.; Ni, X.Z.; Chen, J.S.; Bramlett, M. More than 10 years after commercialization, Vip3A-expressing MIR162 remains highly efficacious in controlling major Lepidopteran maize pests: Laboratory resistance selection versus field reality. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 192, 105385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkness, E.C.; Dively, G.; Patton, T.; Morey, A.C.; Hutchison, W.D. Novel Vip3A Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) maize approaches high-dose efficacy against Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) under field conditions: Implications for resistance management. GM Crops 2010, 1, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghrari, K.; Oliveira, S.C.; Nascimento, A.M.; Queiroz, B.; Fatoretto, J.; De Souza, B.H.S.; Fernandes, O.A.; Môro, G.V. The implications of homozygous Vip3Aa20 and Cry1Abmaize on Spodoptera frugiperda control. J. Pest Sci. 2022, 95, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Jehle, J.A. Quantitative analysis of the seasonal and tissue-specific expression of Cry1Ab in transgenic maize Mon810. J. Plant Dis. Protect. 2007, 2, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Jehle, J.A. Expression of Cry3Bb1 in transgenic corn MON88017. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9990–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Y.; Abbas, N.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.L. Selection for resistance, life history traits and the biochemical mechanism of resistance to thiamethoxam in the maize armyworm, Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Phytoparasitica 2018, 46, 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo, S.E. Impacts of Bt crops on non-target organisms and insecticide use patterns. CAB Rev. Perspect. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 2009, 4, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, B.J.; Zhao, M.; Liang, G.M.; Guo, Y.Y. Insecticidal activity of four different Bt toxins against six important Lepidopteran Pests. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2017, 33, 774. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.X.; Hu, C.X.; Jia, H.R.; Wu, Q.L.; Shen, X.J.; Zhao, S.Y.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Wu, K.M. Case study on the first immigration of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda invading into China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Liu, D.Z.; Sun, X.X.; Li, G.P.; Wu, K.M. Performance of the domestic Bt corn event expressing pyramided Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa19 against the invasive Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) in China. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, G. Oviposition and larval dispersal of the common armyworm, Mythimna convecta (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Aust. J. Ecol. 1991, 16, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Chang, X.Y.; He, K.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Bai, S.X. Resistance evaluation of transgenic Bt maize to oriental armyworm. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 2007, 34, 225–228. [Google Scholar]
- Trtikova, M.; Wikmark, O.G.; Zemp, N.; Widmer, A.; Hilbeck, A. Transgene expression and Bt protein content in transgenic Bt maize (MON810) under optimal and stressful environmental conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Wang, J.; Luo, S.; Peng, Z.S.; Guo, J.W.; Xin, M.G. Spatial and temporal distribution of Bt proteins in Bt maize leaves. Food Agric. Immunol. 2021, 32, 450–459. [Google Scholar]
- Jehangir, N.; Ali, S. The insecticidal efficacy and performance of Bt cotton under variable abiotic stresses—A review on recent findings. Plant Stress 2023, 8, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, T.; Buntin, G.D. Effect of Bacillus thuringiensis transgenic corn for lepidopteran control on nontarget arthropods. Environ. Entomol. 2005, 34, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Carrière, Y. Surge in insect resistance to transgenic crops and prospects for sustainability. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rensburg, J. First report of field resistance by the stem borer, Busseola fusca (Fuller) to Bt-transgenic maize. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2007, 24, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, C.; Bernardi, O.; Salmeron, E.; Sorgatto, R.J.; Dourado, P.M.; Crivellari, A.; Carvalho, R.A.; Willse, A.; Martinelli, S.; Head, G.P. Field-evolved resistance to Cry1Ab maize by Spodoptera frugiperda in Brazil. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.N.; Qureshi, J.A.; Meagher, R.L., Jr.; Reisig, D.D.; Head, G.P.; Andow, D.A.; Ni, X.Z.; Kerns, D.; Buntin, G.D.; Niu, Y. Cry1F resistance in fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda: Single gene versus pyramided Bt maize. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dively, G.P.; Venugopal, P.D.; Finkenbinder, C. Field-evolved resistance in corn earworm to Cry proteins expressed by transgenic sweet corn. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0169115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvapandiyan, A.; Arora, N.; Rajagopal, R.; Jalali, S.K.; Venkatesan, T.; Singh, S.P.; Bhatnagar, R.K. Toxicity analysis of N-and C-terminus-deleted vegetative insecticidal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2001, 67, 5855–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Brévault, T.; Carrière, Y. Insect resistance to Bt crops: Lessons from the first billion acres. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, B.D.; Hellmich, R.L. Understanding successful resistance management: The European corn borer and Bt corn in the United States. GM Crops Food 2012, 3, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.L.; Zhao, J.-Z.; Roush, R.T.; Shelton, A.M. Insect resistance management in GM crops: Past, present and future. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.; García-Benítez, C.; Ortego, F.; Farinós, G.P. Monitoring insect resistance to Bt maize in the European Union: Update, challenges, and future prospects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, J.R.; Andow, D.A.; Horikoshi, R.J.; Sorgatto, R.J.; Fresia, P.; Dos Santos, A.C.; Omoto, C. Field-evolved resistance to Cry1F maize by Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Brazil. Crop Prot. 2014, 64, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.N.; Leonard, B.R.; Cook, D.R.; Lee, D.R.; Andow, D.A.; Baldwin, J.L.; Tindall, K.V.; Wu, X.Y. Frequency of alleles conferring resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis maize in Louisiana populations of the southwestern corn borer. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2007, 122, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, T.; Buuk, C.; Gloyna, K.; Ortego, F.; Farinós, G.P. Ten years of MON810 resistance monitoring of field populations of Ostrinia nubilalis in Europe. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 142, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, B.D.; Spencer, T.; Crespo, A.L.; Storer, N.P.; Head, G.P.; Owens, E.D.; Guyer, D. Ten years of Bt resistance monitoring in the European corn borer: What we know, what we don’t know, and what we can do better. Am. Entomol. 2007, 53, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.N. Resistance of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, to transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1F corn in the Americas: Lessons and implications for Bt corn IRM in China. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguet, D.; Desquilbet, M.; Lemarié, S. Regulating insect resistance management: The case of non-Bt corn refuges in the US. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 76, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Fabrick, J.A.; Carrière, Y. Global patterns of insect resistance to transgenic Bt crops: The first 25 years. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, G.P.; Greenplate, J. The design and implementation of insect resistance management programs for Bt crops. GM Crops Food 2012, 3, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ji, J.; Zhu, X.; Huangfu, N.; Xue, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Niu, L.; Chen, R. Chromosome level genome assembly of oriental armyworm Mythimna separata. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.; Vijayakumar, R.; Linga, V.; Sivakumar, G. Susceptibility of oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae and pupae to native entomopathogenic nematodes. J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 144, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elgawad, M.M. Optimizing entomopathogenic nematode genetics and applications for the integrated management of horticultural pests. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.R.; Torres, A.F.; Truzi, C.C.; Vieira, N.F.; Vacari, A.M.; De Bortoli, S.A. Artificial corn-based diet for rearing Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Insect Sci. 2019, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nleya, T.; Chungu, C.; Kleinjan, J. Corn Growth and Development. In Best Management Practices; South Dakota University: Brookings, SD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Agricultural Standard. Available online: https://www.sdtdata.com/fx/fmrule/tsLibCard/116264.html (accessed on 28 January 2024).


| Growth Stage | Tissue | Cry1Ab (μg/g) | Vip3Aa (μg/g) | Total Bt Protein (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V5 | Leaf | 64.68 ± 1.09 | 5.01 ± 0.09 | 69.69 ± 1.18 a |
| R1 | Silk | 5.83 ± 0.30 | 1.50 ± 0.01 | 7.32 ± 0.31 b |
| R2 | Kernel | 9.85 ± 0.70 | 1.84 ± 0.05 | 11.69 ± 0.75 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, K. Insecticidal Effects of Transgenic Maize Bt-Cry1Ab, Bt-Vip3Aa, and Bt-Cry1Ab+Vip3Aa against the Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker) in Southwest China. Toxins 2024, 16, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030134
Zhang Z, Yang X, Wang W, Wu K. Insecticidal Effects of Transgenic Maize Bt-Cry1Ab, Bt-Vip3Aa, and Bt-Cry1Ab+Vip3Aa against the Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker) in Southwest China. Toxins. 2024; 16(3):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030134
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhenghao, Xianming Yang, Wenhui Wang, and Kongming Wu. 2024. "Insecticidal Effects of Transgenic Maize Bt-Cry1Ab, Bt-Vip3Aa, and Bt-Cry1Ab+Vip3Aa against the Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker) in Southwest China" Toxins 16, no. 3: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030134
APA StyleZhang, Z., Yang, X., Wang, W., & Wu, K. (2024). Insecticidal Effects of Transgenic Maize Bt-Cry1Ab, Bt-Vip3Aa, and Bt-Cry1Ab+Vip3Aa against the Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker) in Southwest China. Toxins, 16(3), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030134





