Updated Nematocyst Types in Tentacle of Venomous Box Jellyfish, Chironex indrasaksajiae (Sucharitakul, 2017) and Chiropsoides buitendijki (Horst, 1907) (Cnidaria, Cubozoa) in Thai Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
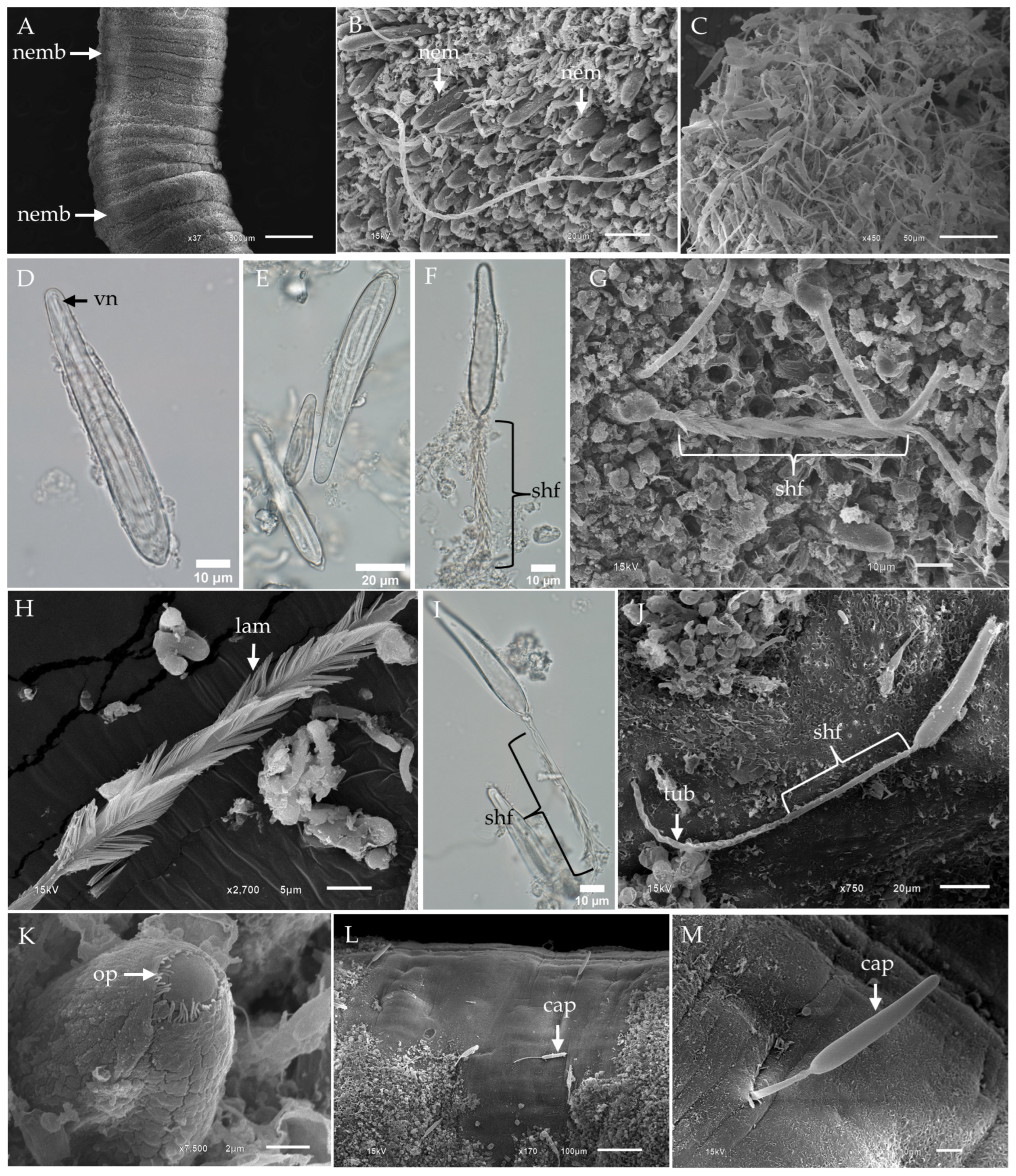
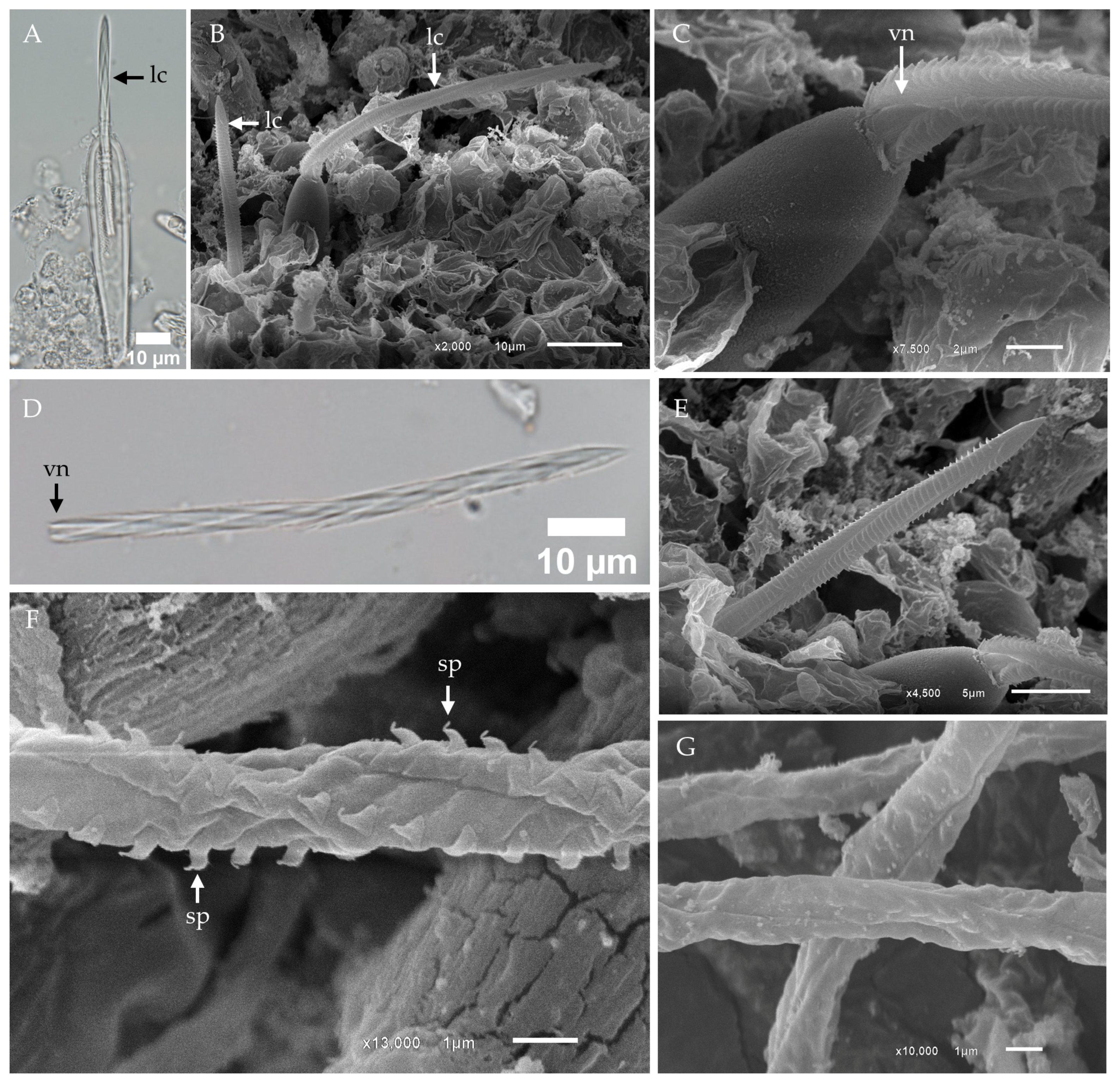
2.1. Morphological Characterization and Distribution of Nematocysts in the Tentacles of Chironex indrasaksajiae
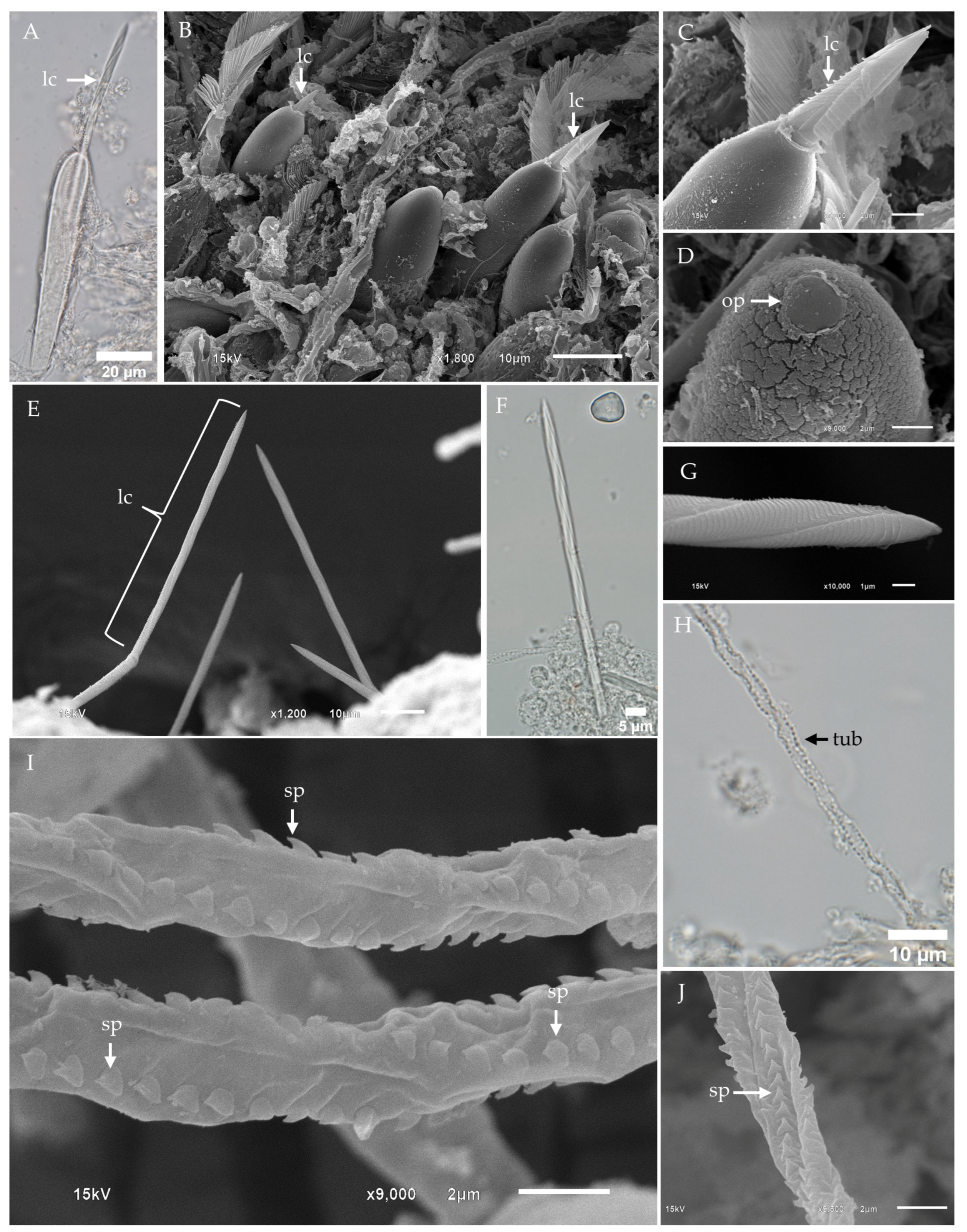
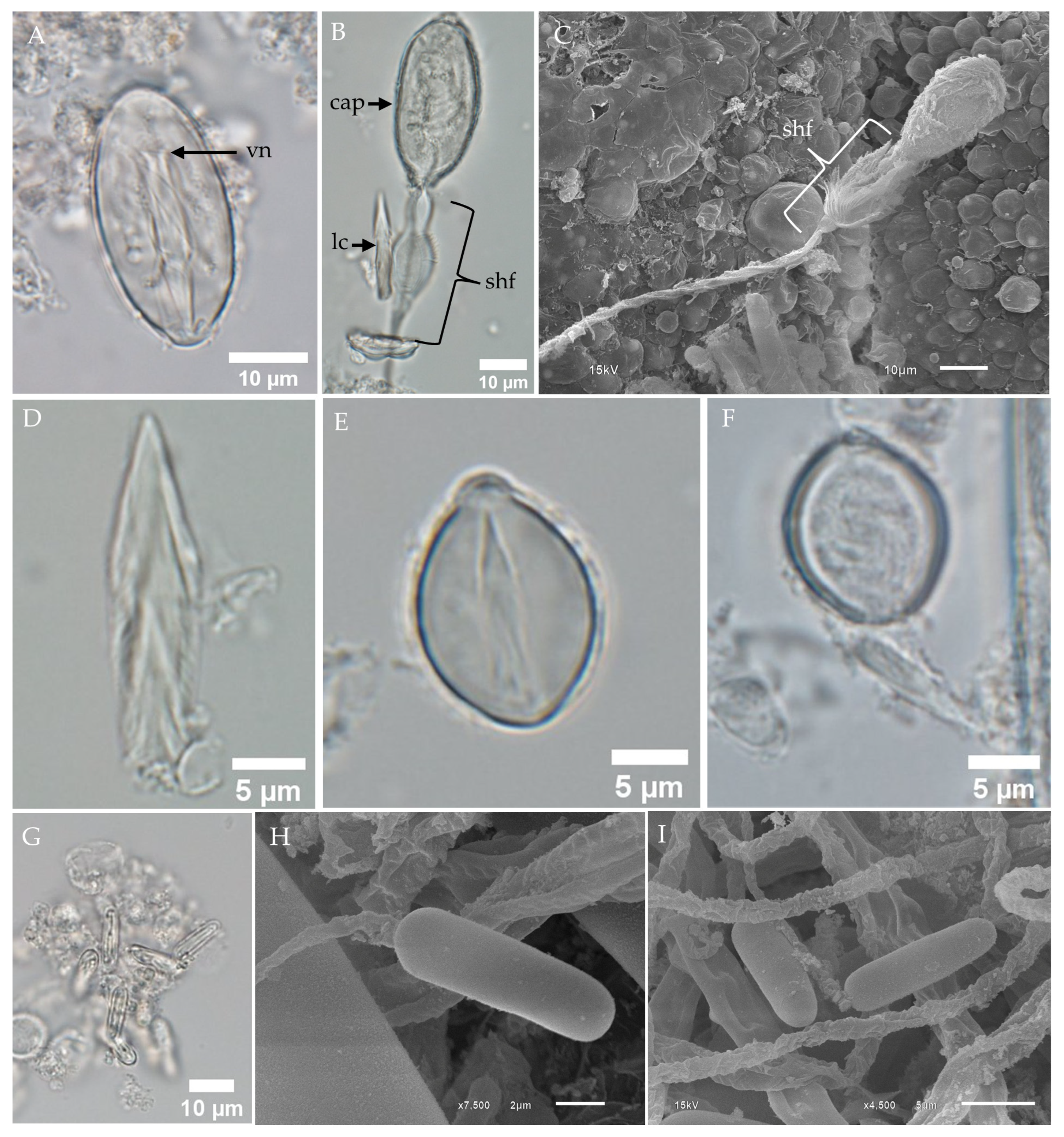
2.2. Morphological Characterization and Distribution of Nematocysts in the Tentacles of Chiropsoides buitendijki
2.3. Comparison of Nematocyst Sizes Between Chironex indrasaksajiae and Chiropsoides buitendijki
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Specimen Collection
5.2. Analyses and Classification of Isolated Nematocysts by Light Microscopy
- Banana-shaped microbasic p-mastigophoresThis nematocyst type is characterized by an elongated capsule, widest at the apical region and tapering toward the distal end. Upon discharge, the shaft length is shorter than the capsule, with a shaft-to-capsule length ratio of less than 1.5. The undischarged shaft features a distinctive V-shaped notch at its base.
- Oval-shaped microbasic p-rhopaloidsThese nematocysts have an oval-shaped capsule. The discharged shaft length is shorter than the capsule length, maintaining a shaft-to-capsule length ratio of less than 1.5. The undischarged shaft has a V-shaped notch at its base, while the discharged shaft displays prominent swellings.
- Small sub-spherical microbasic p-rhopaloidsThis type features a small, sub-spherical capsule. Similarly to oval-shaped p-rhopaloids, the discharged shaft is shorter than the capsule length, with a shaft-to-capsule length ratio of less than 1.5. The undischarged shaft has a V-shaped notch at its base, and the discharged shaft exhibits prominent swellings.
- Rod-shaped isorhizasRod-shaped isorhizas are defined by their rod-shaped capsules, lacking a well-defined shaft. The discharged tubule maintains a uniform diameter or tapers slightly toward the distal end.
5.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gershwin, L.-A.; De Nardi, M.; Winkel, K.D.; Fenner, P.J. Marine stingers: Review of an under-recognized global coastal management issue. Coast. Manag. 2010, 38, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaikruea, L. Differences in clinical manifestations between cases stung by single-tentacle and multiple-tentacle box jellyfish over two decades. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathirapongsasuti, N.; Khonchom, K.; Poonsawat, T.; Pransilpa, M.; Ongsara, S.; Detsri, U.; Bungbai, S.; Lawanangkoon, S.-A.; Pattanaporkrattana, W.; Trakulsrichai, S. Rapid and accurate species-specific PCR for the identification of lethal chironex box jellyfish in Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osathanunkul, M.; Sawongta, N.; Sathirapongsasuti, N.; Poonsawat, T.; Detsri, U.; Aungtonya, C.; Suwannapoom, C. Distinguishing venomous jellyfish species via high resolution melting analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1019473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, P.J. Dangers in the ocean: The traveler and marine envenomation. I. jellyfish. J. Travel Med. 1998, 5, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibballs, J. Australian venomous jellyfish, envenomation syndromes, toxins and therapy. Toxicon 2006, 48, 830–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.A.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Raising awareness on the clinical and forensic aspects of jellyfish stings: A worldwide increasing threat. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulware, D.R. A randomized, controlled field trial for the prevention of jellyfish stings with a topical sting inhibitor. J. Travel Med. 2006, 13, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Liu, K.-T.; Chen, J.-B.; Yan, Z.-H.; Danso, B.; Wang, M.-K.; Peng, Z.-Y.; Xiao, L. Jellyfish stings: A review of skin symptoms, pathophysiology, and management. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2024, 30, e944265-1–e944265-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardent, P. The cnidarian cnidocyte, a hightech cellular weaponry. Bioessays 1995, 17, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass-Simon, G.; Scappaticci, J.A.A. The behavioral and developmental physiology of nematocysts. Can. J. Zool. 2002, 80, 1772–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, A.; Özbek, S. The nematocyst: A molecular map of the cnidarian stinging organelle. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babonis, L.S.; Enjolras, C.; Reft, A.J.; Foster, B.M.; Hugosson, F.; Ryan, J.F.; Daly, M.; Martindale, M.Q. Single-cell atavism reveals an ancient mechanism of cell type diversification in a sea anemone. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaposi, K.L.; Mitchell, M.L.; Courtney, R.L.; Seymour, J.E. Variability of cnidae within a small clonal sea anemone (Isactinia sp.). Invertebr. Biol. 2023, 142, e12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruntu, C.P.; Darwisito, S.; Angmalisang, P.A.; Rumengan, A.P. The nematocysts of some Scleractinian coral species from the Sulawesi Sea, Indonesia. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2022, 15, 2460–2470. [Google Scholar]
- Rachamim, T.; Morgenstern, D.; Aharonovich, D.; Brekhman, V.; Lotan, T.; Sher, D. The dynamically evolving nematocyst content of an anthozoan, a scyphozoan, and a hydrozoan. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, N.; Štibler, U.K.; Eismann, B.; Mercker, M.; Bergheim, B.G.; Linn, A.; Tuchscherer, P.; Engel, U.; Redl, S.; Marciniak-Czochra, A. Non-muscle myosin II drives critical steps of nematocyst morphogenesis. Iscience 2023, 26, 106291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, S.; Balasubramanian, P.G.; Holstein, T.W. Cnidocyst structure and the biomechanics of discharge. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitatani, R.; Yamada, M.; Kamio, M.; Nagai, H. Length is associated with pain: Jellyfish with painful sting have longer nematocyst tubules than harmless jellyfish. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, R.G.; Webster, A.C.; Lewis, S.R.; Welsford, M. Interventions for the symptoms and signs resulting from jellyfish stings. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 6, CD009688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwick, R.; Callanan, V.; Williamson, J. Nematocyst Inhibition in Chironex fleckeri. Med. J. Aust. 1980, 1, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña, F.H.; Excoffon, A.C.; Zamponi, M.O.; Ricci, L. Importance of nematocysts in taxonomy of acontiarian sea anemones (Cnidaria, Actiniaria): A statistical comparative study. Zool. Anz. 2003, 242, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegolon, L.; Heymann, W.C.; Lange, J.H.; Mastrangelo, G. Jellyfish stings and their management: A review. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 523–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, S.; Killi, N. Nematocysts types and morphological features of some scyphozoa species in the Southwest Turkey. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Fautin, D.G. Structural diversity, systematics, and evolution of cnidae. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekimova, I.A.; Vorobyeva, O.A.; Mikhlina, A.L.; Schepetov, D.M.; Vortsepneva, E.V.; Antokhina, T.I.; Malakhov, V.V. Nematocyst sequestration within the family Fionidae (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia) considering ecological properties and evolution. Front. Zool. 2022, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, A.; Östman, C.; Santín, A.; Marambio, M.; Narda, M.; Gili, J.-M. Cnidome and morphological features of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) throughout the different life cycle stages. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 714503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Xue, W.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Li, P. Updated descriptions of the nematocysts of the scyphozoan jellyfish Cyanea nozakii Kishinouye, 1891 (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa). Toxicon 2020, 187, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershwin, L.-A. Nematocysts of the Cubozoa. Zootaxa 2006, 1232, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassara, E.; Mikšík, I.; Pompach, P.; Mariottini, G.L.; Xiao, L.; Giovine, M.; Pozzolini, M. Proteomic Analysis and Biochemical Characterization of the Nematocyst Extract of the Hydrozoan Velella velella. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.-Y.; Wang, M.-K.; Hou, X.-C.; Wang, Z.-F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Danso, B.; Wei, D.-B.; Shou, Z.-Y.; Xiao, L. Comparative Analysis of Tentacle Extract and Nematocyst Venom: Toxicity, Mechanism, and Potential Intervention in the Giant Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killi, N.; Bonello, G.; Mariottini, G.L.; Pardini, P.; Pozzolini, M.; Cengiz, S. Nematocyst types and venom effects of Aurelia aurita and Velella velella from the Mediterranean sea. Toxicon 2020, 175, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doonan, L.B.; Lynham, S.; Quinlan, C.; Ibiji, S.C.; Winter, C.E.; Padilla, G.; Jaimes-Becerra, A.; Morandini, A.C.; Marques, A.C.; Long, P.F. Venom composition does not vary greatly between different nematocyst types isolated from the primary tentacles of Olindias sambaquiensis (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). Biol. Bull. 2019, 237, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strömberg, S.M.; Östman, C. The cnidome and internal morphology of Lophelia pertusa (Linnaeus, 1758) (Cnidaria, Anthozoa). Acta Zool. 2017, 98, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pica, D.; Puce, S. Investigation of nematocysts in stylasterids (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa: Stylasteridae). Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garese, A.; Carrizo, S.; Acuña, F.H. Biometry of sea anemone and corallimorpharian cnidae: Statistical distribution and suitable tools for analysis. Zoomorphology 2016, 135, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parracho, T.; Morais, Z. Catostylus tagi: Partial rDNA sequencing and characterisation of nematocyte structures using two improvements in jellyfish sample preparation. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heins, A.; Glatzel, T.; Holst, S. Revised descriptions of the nematocysts and the asexual reproduction modes of the scyphozoan jellyfish Cassiopea andromeda (Forskål, 1775). Zoomorphology 2015, 134, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebring, A.; Helmholz, H.; Sötje, I.; Lassen, S.; Prange, A.; Tiemann, H. A new method for the separation of different types of nematocysts from Scyphozoa and investigation of proteinaceous toxins utilizing laser catapulting and subsequent mass spectrometry. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 12, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, A.A.; Kuroiwa, J.M.; Oliver, L.M.; Kunkel, D.D. The ultrastructure of nematocysts from the fishing tentacle of the Hawaiian bluebottle, Physalia utriculus (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa, Siphonophora). Hydrobiologia 2002, 489, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, A.A.; Kuroiwa, J.M.; Oliver, L.M.; Chung, J.J.; Kunkel, D.D. Ultrastructure of a novel eurytele nematocyst of Carybdea alata Reynaud (Cubozoa, Cnidaria). Cell Tissue Res. 2002, 308, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, C. A guideline to nematocyst nomenclature and classification, and some notes on the systematic value of nematocysts. Sci. Mar. 2000, 64, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucharitakul, P.; Chomdej, S.; Achalawitkun, T.; Arsiranant, I. Description of Chironex indrasaksajiae Sucharitakul sp. nov. (Cnidaria, Cubozoa, Chirodropida): A new species of box jellyfish from the Gulf of Thailand. Phuket. Mar. Biol. Cent. Res. Bull. 2017, 74, 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gershwin, L. Comments on Chiropsalmus (Cnidaria: Cubozoa: Chirodropida): A preliminary revision of the Chiropsalmidae, with descriptions of two new genera and two new species. Zootaxa 2006, 1231, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aungtonya, C.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wutthituntisil, N. The genus Chiropsoides (Chirodropida: Chiropsalmidae) from the Andaman Sea, Thai waters. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucharitakul, P.; Chomdej, S.; Achalawitkun, T.; Aongsara, S.; Arsiranant, I.; Paiphongpheaw, P.; Chanachon, K. Chirodropid box jellyfish in the Gulf of Thailand. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaikruea, L.; Siriariyaporn, P.; Wutthanarungsan, R.; Smithsuwan, P. Review of fatal and severe cases of box jellyfish envenomation in Thailand. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2015, 27, NP1639–NP1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaikruea, L.; Siriariyaporn, P. Severe dermatonecrotic toxin and wound complications associated with box jellyfish stings 2008–2013. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 2015, 42, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifkin, J.; Endean, R. The structure and function of the nematocysts of Chironex fleckeri Southcott, 1956. Cell Tissue Res. 1983, 233, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, S.P.; Costello, J.H. Functional characteristics of nematocysts found on the scyphomedusa Cyanea capillata. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2007, 351, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E. The functions of nematocysts in prey capture by epipelagic siphonophores (Coelenterata, Hydrozoa). Biol. Bull. 1984, 166, 310–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, A.; Fishman, L.; Loya, Y.; Zlotkin, E. Delivery of a nematocyst toxin. Nature 1995, 375, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabulut, A.; McClain, M.; Rubinstein, B.; Sabin, K.Z.; McKinney, S.A.; Gibson, M.C. The architecture and operating mechanism of a cnidarian stinging organelle. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasanga, T.; Santidherakul, S.; Wunnapuk, K.; Phuackchantuck, R.; Thaikruea, L.; Achalawitkun, T.; Rungraung, P. Nematocyst Types and Characteristics in the Tentacles of Gershwinia thailandensis and Morbakka sp. (Cubozoa: Carybdeida) from the Gulf of Thailand. Biology 2024, 13, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstein, T.; Tardent, P. An ultrahigh-speed analysis of exocytosis: Nematocyst discharge. Science 1984, 223, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, G.M.; Isbister, G.K.; Lawrie, P.M.; Treston, G.T.; Currie, B.J. Prospective study of jellyfish stings from tropical Australia, including the major box jellyfish Chironex fleckeri. Med. J. Aust. 2001, 175, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkis, N.A.; Maalouf, G.J.; Mahmassani, D.M. Jellyfish stings: A practical approach. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2015, 26, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaikruea, L.; Santidherakul, S. The public health impact of a new simple practical technique for collection and transfer of toxic jellyfish specimens and for nematocyst identification. J. Public Health Policy 2018, 39, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuña, F.H.; Ricci, L.; Excoffon, A.C.; Zamponi, M.O. A novel statistical analysis of cnidocysts in acontiarian sea anemones (Cnidaria, Actiniaria) using generalized linear models with gamma errors. Zool. Anz. 2004, 243, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Species | Chironex indrasaksajiae | Chiropsoides buitendijki | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Nematocyst | Capsule Length (µm) | Capsule Wide (µm) | Capsule Length (µm) | Capsule Wide (µm) | |
| Banana-shaped microbasic p-mastigophores | Range (Min–Max) | 30.26–102.56 | 6.42–17.01 | 72.17–98.37 | 10.73–18.48 |
| Mean ± SD | 58.05 ± 15.46 ab | 9.74 ± 1.88 cd | 85.22 ± 4.21 ab | 13.84 ± 1.48 cd | |
| (n) | (n = 323) | (n = 206) | |||
| Oval-shaped microbasic p-rhopaloids | Range (Min–Max) | 30.27–43.50 | 15.89–24.66 | 30.71–41.10 | 15.25–23.72 |
| Mean ± SD | 36.79 ± 3.22 | 19.85 ± 2.17 | 36.03 ± 1.99 | 18.23 ± 2.27 | |
| (n) | (n =42) | (n = 83) | |||
| Small sub-spherical microbasic p-rhopaloids | Range (Min–Max) | 11.02–15.50 | 8.85–14.51 | 13.92–19.50 | 10.03–14.75 |
| Mean ± SD | 13.28 ± 0.95 | 10.84 ± 1.10 | 15.70 ± 0.95 | 11.93 ± 0.84 | |
| (n) | (n = 37) | (n = 67) | |||
| Rod-shaped isorhizas | Range (Min–Max) | 10.70–14.95 | 4.01–7.78 | 12.25–16.06 | 3.37–5.14 |
| Mean ± SD | 12.93 ± 0.93 | 4.80 ± 0.57 | 14.13 ± 0.83 | 3.97 ± 0.30 | |
| (n) | (n = 72) | (n = 121) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yasanga, T.; Wunnapuk, K.; Phuackchantuck, R.; Thaikruea, L.; Achalawitkun, T.; Rungraung, P.; Santidherakul, S. Updated Nematocyst Types in Tentacle of Venomous Box Jellyfish, Chironex indrasaksajiae (Sucharitakul, 2017) and Chiropsoides buitendijki (Horst, 1907) (Cnidaria, Cubozoa) in Thai Waters. Toxins 2025, 17, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010044
Yasanga T, Wunnapuk K, Phuackchantuck R, Thaikruea L, Achalawitkun T, Rungraung P, Santidherakul S. Updated Nematocyst Types in Tentacle of Venomous Box Jellyfish, Chironex indrasaksajiae (Sucharitakul, 2017) and Chiropsoides buitendijki (Horst, 1907) (Cnidaria, Cubozoa) in Thai Waters. Toxins. 2025; 17(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleYasanga, Thippawan, Klintean Wunnapuk, Rochana Phuackchantuck, Lakkana Thaikruea, Thunyaporn Achalawitkun, Purinat Rungraung, and Sineenart Santidherakul. 2025. "Updated Nematocyst Types in Tentacle of Venomous Box Jellyfish, Chironex indrasaksajiae (Sucharitakul, 2017) and Chiropsoides buitendijki (Horst, 1907) (Cnidaria, Cubozoa) in Thai Waters" Toxins 17, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010044
APA StyleYasanga, T., Wunnapuk, K., Phuackchantuck, R., Thaikruea, L., Achalawitkun, T., Rungraung, P., & Santidherakul, S. (2025). Updated Nematocyst Types in Tentacle of Venomous Box Jellyfish, Chironex indrasaksajiae (Sucharitakul, 2017) and Chiropsoides buitendijki (Horst, 1907) (Cnidaria, Cubozoa) in Thai Waters. Toxins, 17(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010044





