Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Concentrations Measured in Alaskan Arctic Clams Using ELISA and HPLC Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
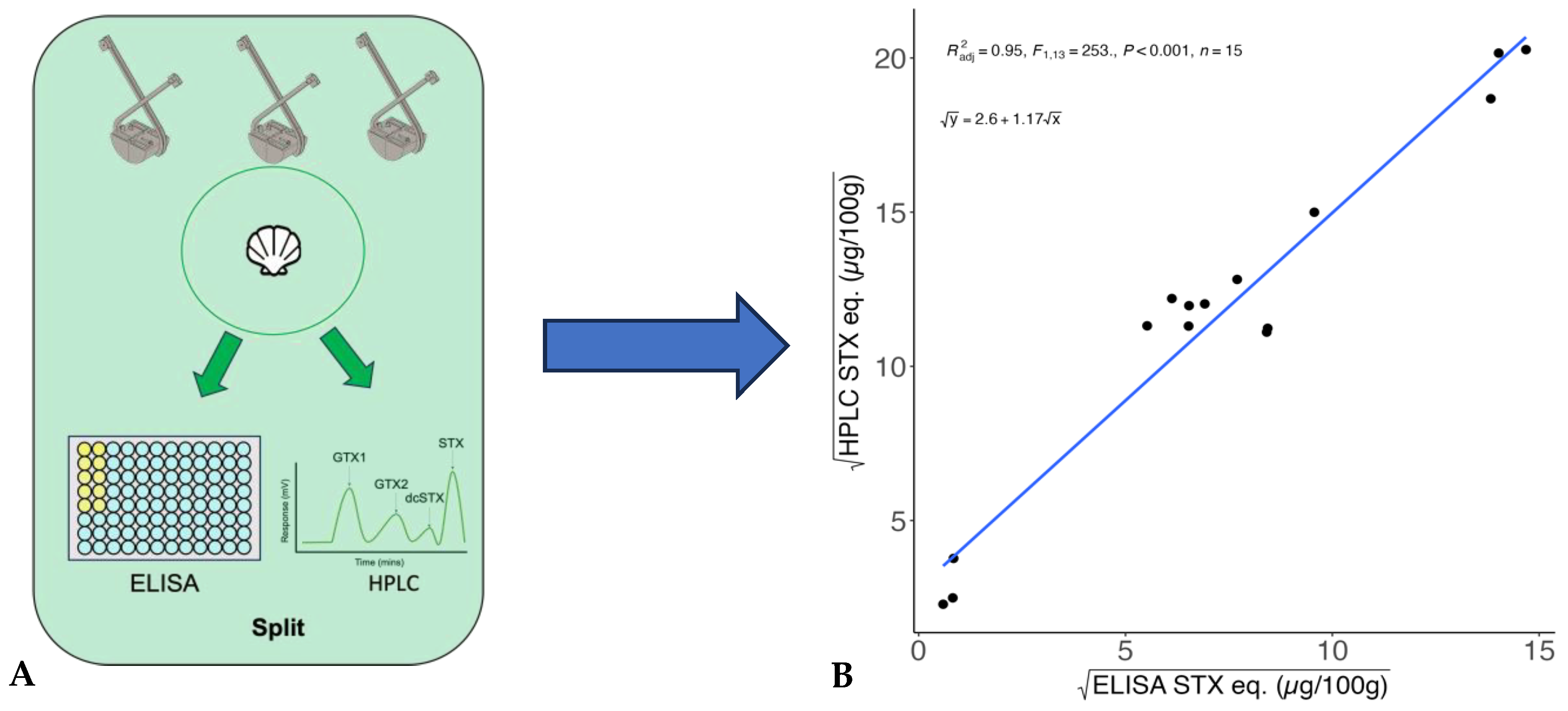
2.1. Correction Model for ELISA STX Eq. Values
| Species | Region | Date | ELISA (μg STX eq./100 g) | HPLC (μg STX eq./100 g) | ELISA% of HPLC | ELISA +/− to HPLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carditidae sp. | Beaufort Sea | 7 August 2022 | 0.35 | 5.21 | 7 | − |
| Siliqua patula | Beaufort Sea | 7 August 2022 | 0.68 | 6.20 | 11 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Bering Strait | 26 July 2022 | 0.71 | 14.22 | 5 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Chukchi Sea | 11 August 2022 | 30.51 | 128.00 | 24 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Bering Strait | 8 August 2019 | 37.47 | 148.80 | 25 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Chukchi Sea | 11 August 2022 | 42.58 | 127.80 | 33 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Chukchi Sea | 11 August 2022 | 42.71 | 143.20 | 30 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Bering Strait | 18 October 2020 | 47.84 | 144.60 | 33 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Beaufort Sea | 7 October 2020 | 59.28 | 164.30 | 36 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Chukchi Sea | 24 November 2022 | 70.79 | 123.40 | 57 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Chukchi Sea | 11 August 2022 | 71.18 | 126.20 | 56 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Bering Strait | 18 October 2020 | 91.49 | 224.90 | 41 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Chukchi Sea | 24 November 2022 | 191.29 | 348.90 | 55 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Chukchi Sea | 24 November 2022 | 196.61 | 406.40 | 48 | − |
| Macoma calcarea | Chukchi Sea | 24 November 2022 | 215.57 | 410.90 | 52 | − |
| Congener | Molecular Weights [g/mol] | Cross-Reactivity (%) | TEF |
|---|---|---|---|
| STX * | 372.2 | 100% | 1.0 |
| NEO | 315.3 | 1.30% | 1.0 |
| GTX1 | 411.4 | <0.2% | 1.0 |
| dcSTX | 256.3 | - | 1.0 |
| GTX4 | 411.4 | <0.2% | 0.7 |
| GTX3 | 395.4 | 23% | 0.6 |
| dcGTX3 | 352.3 | 1.40% | 0.4 |
| GTX2 | 395.4 | 23% | 0.4 |
| dcGTX2 | 352.3 | 1.40% | 0.2 |
| GTX5 | 379.4 | 23% | 0.1 |
| C2 | 475.4 | - | 0.1 |
| C1 | - | - | 0.1 |
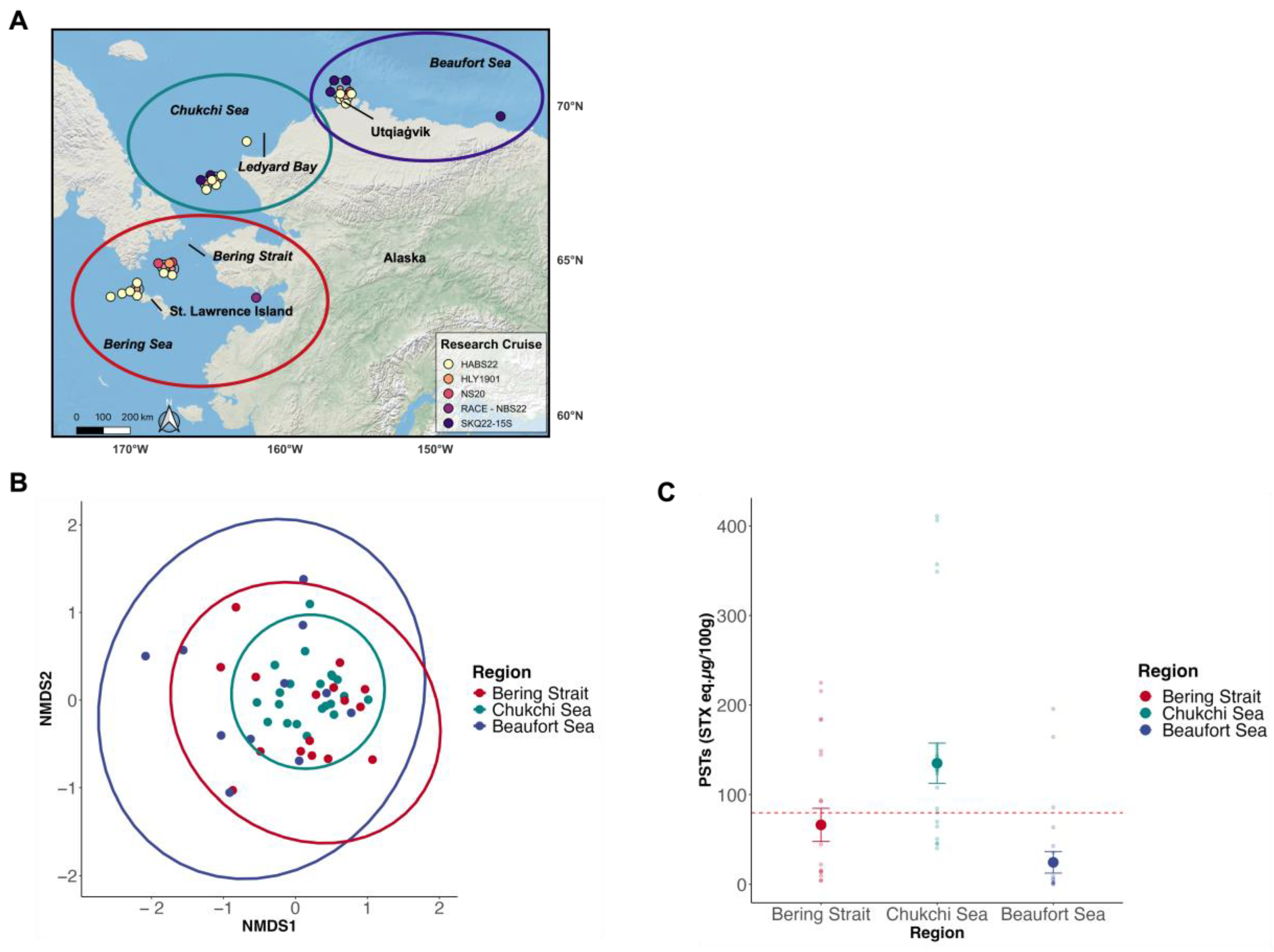
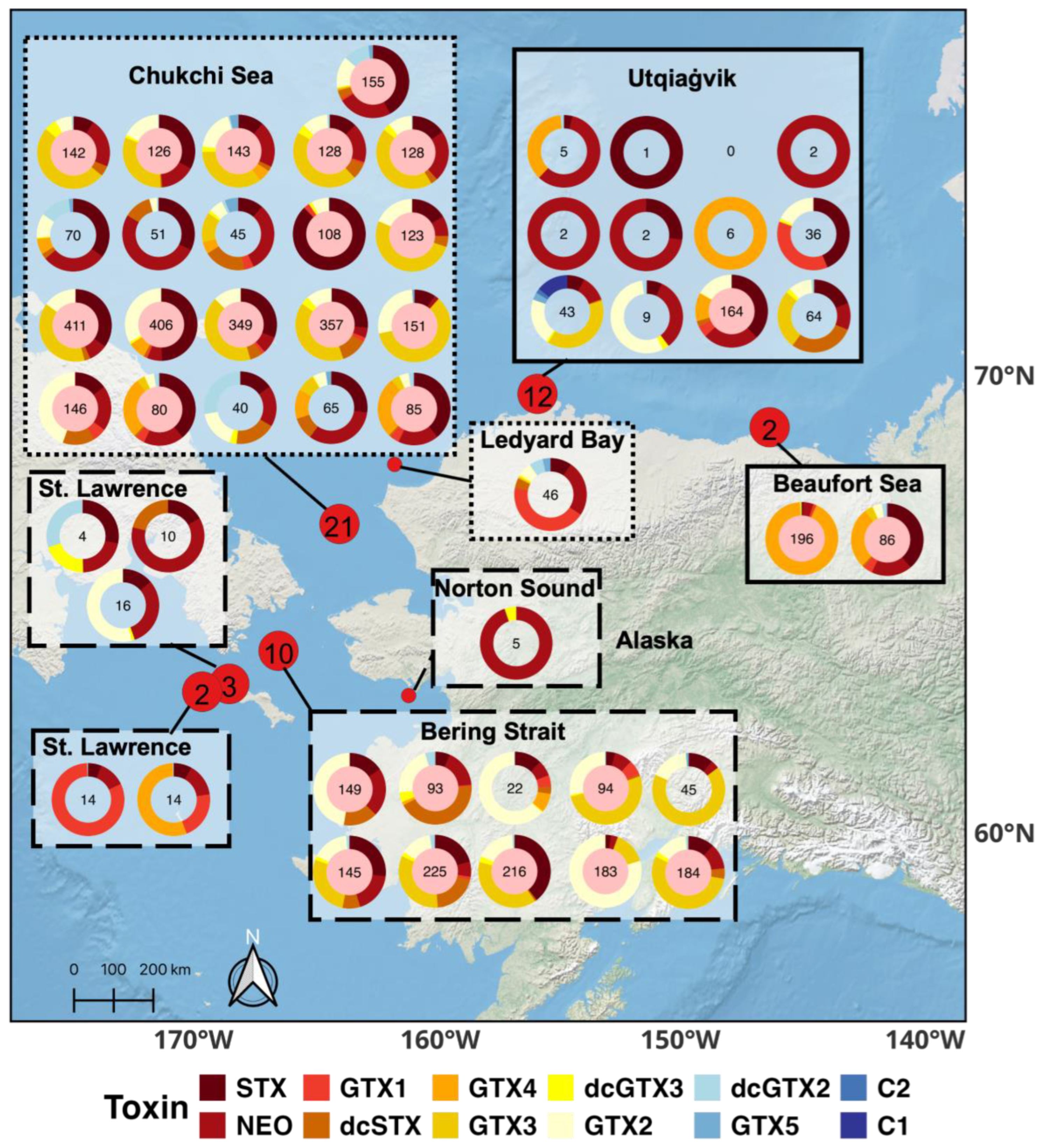
2.2. PST Profiles and Total Toxicities of Alaskan Arctic Clams
3. Discussion
3.1. Linear Model to Estimate Total PST Toxicity from ELISA STX Eq. Measurements
3.2. Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Profiles in Alaskan Arctic Clams
3.3. Total Toxicity of Alaskan Arctic Clams
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Sample Collection
5.2. Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Measurements
5.2.1. Abraxis ELISA
5.2.2. HPLC Methods
5.3. Statistical Analysis
5.3.1. Correction Model—ELISA and HPLC PST Measurements
5.3.2. Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Profiles and Total Toxicity Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSTs | Paralytic shellfish toxins |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| TEF | Toxicity equivalency factors |
| STX | Saxitoxin |
| NEO | Neosaxitoxin |
| GTX1–4 | Gonyautoxins 1–4 |
| dcGTX2–3 | Decarbamoyl gonyautoxin 2–3 |
| dcSTX | Decarbamoyl saxitoxin |
| C1–2 | Carbamate toxins |
| Eq. | Equivalents |
| HAB | Harmful algae bloom |
| MBA | Mouse bioassay |
| BDL | Below detectable limit |
| RBA | Receptor binding assay |
References
- Hall, S.; Strichartz, G.; Moczydlowski, E.; Ravindran, A.; Reichardt, P.B. The Saxitoxins. In Marine Toxins; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Volume 418, pp. 3–29. ISBN 9780841217331. [Google Scholar]
- Schantz, E.J.; Ghazarossian, V.E.; Schnoes, H.K.; Strong, F.M.; Springer, J.P.; Pezzanite, J.O.; Clardy, J. Structure of Saxitoxin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 1238–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, K.D.; Sayler, G.S. An Overview on the Marine Neurotoxin, Saxitoxin: Genetics, Molecular Targets, Methods of Detection and Ecological Functions. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 991–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain on a Request from the European Commission on Marine Biotoxins in Shellfish-Saxitoxin Group. EFSA J. 2009, 1019, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Etheridge, S.M.; Roesler, C.S. Effects of Temperature, Irradiance, and Salinity on Photosynthesis, Growth Rates, Total Toxicity, and Toxin Composition for Alexandrium fundyense Isolates from the Gulf of Maine and Bay of Fundy. Deep. Sea Res. Part 2 Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2005, 52, 2491–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Kulis, D.M.; Doucette, G.J.; Gallagher, J.C.; Balech, E. Biogeography of Toxic Dinoflagellates in the Genus Alexandrium from the Northeastern United States and Canada. Mar. Biol. 1994, 120, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schantz, E.J.; Mold, J.D.; Stanger, D.W.; Shavel, J.; Riel, F.J.; Bowden, J.P.; Lynch, J.M.; Wyler, R.S.; Riegel, B.; Sommer, H. Paralytic Shellfish Poison. VI. A Procedure for the Isolation and Purification of the Poison from Toxic Clam and Mussel Tissues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 5230–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC Official Method 959. 08 Paralytic Shellfish Poison, Biological Method. In Official Methods of Analysis of Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Horwitz, W., Ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000; pp. 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Shellfish Prechromatographic Oxidation and Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. First Action 2005, Official Method 2005.06. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; Horwitz, W., Latimer, G.W., Eds.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2006; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Oshima, Y. Postcolumn Derivatization Liquid Chromatographic Method for Paralytic Shellfish Toxins. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Fire, S.E.; Leighfield, T.A.; Mikulski, C.M.; Doucette, G.J. Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Shellfish by Receptor Binding Assay: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gigirey, B.; Rodríguez-Velasco, M.L.; Otero, A.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. A Comparative Study for PSP Toxins Quantification by Using MBA and HPLC Official Methods in Shellfish. Toxicon 2012, 60, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.R.; Baugh, K.A.; Wright, B.; RaLonde, R.; Nance, S.L.; Tatarenkova, N.; Etheridge, S.M.; Lefebvre, K.A. Comparative Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins (PSTs) Using Five Different Toxin Detection Methods in Shellfish Species Collected in the Aleutian Islands, Alaska. Toxicon 2009, 54, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Tarnovius, S.; Hatfield, R.G.; Alves, M.T.; Broadwater, M.; Van Dolah, F.; Garcia-Mendoza, E.; Medina, D.; Salhi, M.; Goya, A.B.; et al. Application of Six Detection Methods for Analysis of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Shellfish from Four Regions within Latin America. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana-Viera, S.; Lara-Martin, P.A. Analysis of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Seafood by Liquid Chromatography: A Critical Review of the Methodologies Developed. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 37, e00190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; McNabb, P.S.; Harwood, D.T.; Selwood, A.I.; Boundy, M.J. Single-Laboratory Validation of a Multitoxin Ultra- Performance LC-Hydrophilic Interaction LC-MS/MS Method for Quantitation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalve Shellfish. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boundy, M.J.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T.; McNabb, P.S.; Turner, A.D. Development of a Sensitive and Selective Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method for High Throughput Analysis of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins Using Graphitised Carbon Solid Phase Extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1387, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patria, F.P.; Pekar, H.; Zuberovic-Muratovic, A. Multi-Toxin Quantitative Analysis of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Tetrodotoxins in Bivalve Mollusks with Ultra-Performance Hydrophilic Interaction LC-MS/MS-An in-House Validation Study. Toxins 2020, 12, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garet, E.; González-Fernández, Á.; Lago, J.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Comparative Evaluation of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay and Reference Methods for the Detection of Shellfish Hydrophilic Toxins in Several Presentations of Seafood. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, S.E.; Browning, J.A.; Durden, W.N.; Stolen, M.K. Comparison of During-Bloom and Inter-Bloom Brevetoxin and Saxitoxin Concentrations in Indian River Lagoon Bottlenose Dolphins, 2002–2011. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 218, 105371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemert, C.; Schoen, S.K.; Litaker, R.W.; Smith, M.M.; Arimitsu, M.L.; Piatt, J.F.; Holland, W.C.; Ransom Hardison, D.; Pearce, J.M. Algal Toxins in Alaskan Seabirds: Evaluating the Role of Saxitoxin and Domoic Acid in a Large-Scale Die-off of Common Murres. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Quakenbush, L.; Frame, E.; Huntington, K.B.; Sheffield, G.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Bryan, A.; Kendrick, P.; Ziel, H.; Goldstein, T.; et al. Prevalence of Algal Toxins in Alaskan Marine Mammals Foraging in a Changing Arctic and Subarctic Environment. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Fachon, E.; Bowers, E.K.; Kimmel, D.G.; Snyder, J.A.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Kibler, S.; Ransom Hardison, D.; Anderson, D.M.; et al. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Alaskan Arctic Food Webs during the Anomalously Warm Ocean Conditions of 2019 and Estimated Toxin Doses to Pacific Walruses and Bowhead Whales. Harmful Algae 2022, 114, 102205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.R.; Christopher Holland, W.; Keeler, D.M.; Ransom Hardison, D.; Wayne Litaker, R. Improved Accuracy of Saxitoxin Measurement Using an Optimized Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Toxins 2019, 11, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.M.; Fachon, E.; Pickart, R.S.; Lin, P.; Fischer, A.D.; Richlen, M.L.; Uva, V.; Brosnahan, M.L.; McRaven, L.; Bahr, F.; et al. Evidence for Massive and Recurrent Toxic Blooms of Alexandrium catenella in the Alaskan Arctic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107387118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Chen, H.; Qiu, J.; Lin, H.; Gu, H. Determination of Multiple Toxins in Whelk and Clam Samples Collected from the Chukchi and Bering Seas. Toxicon 2016, 109, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Lin, S.; Chen, M.; Hong, J.; Liu, C. Prevalence of Phycotoxin Contamination in Shellfish from the Northern Bering Sea and the Chukchi Sea. Toxicon 2019, 167, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielson, S.L.; Ahkinga, O.; Ashjian, C.; Basyuk, E.; Cooper, L.W.; Eisner, L.; Farley, E.; Iken, K.B.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Juranek, L.; et al. Manifestation and Consequences of Warming and Altered Heat Fluxes over the Bering and Chukchi Sea Continental Shelves. Deep. Sea Res. Part 2 Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2020, 177, 104781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Campbell, K.; Bradbury, A.; Elliott, C.T.; Harwood, D.T.; Murray, S.A.; Ugalde, S.C.; Wilson, K.; Burgoyne, M.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Comparative Performance of Four Immunological Test Kits for the Detection of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Tasmanian Shellfish. Toxicon 2017, 125, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, K.; Johnson, S.; Turner, A.D. Application of Rapid Test Kits for the Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs from Great Britain. Toxicon 2016, 119, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachon, E.; Pickart, R.S.; Sheffield, G.; Pate, E.; Pathare, M.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Muhlbach, E.; Horn, K.; Spada, N.N.; Rajagopalan, A.; et al. Tracking a Large-scale and Highly Toxic Arctic Algal Bloom: Rapid Detection and Risk Communication. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2025, 10, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Shumway, S.E. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs: Occurrence, Transfer Kinetics, and Biotransformation. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1998, 6, 315–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Lee, J.H.; Cembella, A.D.; Anderson, D.M. Uptake Kinetics of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins from the Dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense in the Mussel Mytilus Edulis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 63, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsuike, M.; Oikawa, H.; Matsuno, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Imai, I. The Physiological Adaptations and Toxin Profiles of the Toxic Alexandrium fundyense on the Eastern Bering Sea and Chukchi Sea Shelves. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The Globally Distributed Genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted Roles in Marine Ecosystems and Impacts on Human Health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einarsson, S.V.; Lowry, K.E.; Lin, P.; Pickart, R.S.; Ashjian, C.J.; Chappell, P.D. Alexandrium on the Alaskan Beaufort Sea Shelf: Impact of Upwelling in a Warming Arctic. Harmful Algae 2022, 120, 102346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.M.; Fachon, E.; Hubbard, K.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Lin, P.; Pickart, R.; Richlen, M.; Sheffield, G.; Van Hemert, C. Harmful Algal Blooms in the Alaskan Arctic an Emerging Threat As the Ocean Warms. Oceanography 2022, 35, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y.U.; Bolch, C.J.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Toxin Composition of Resting Cysts of Alexandrium tamarense(Dinophyceae). Toxicon 1992, 30, 1539–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, A.; Smith, B.C.; Wikfors, G.H.; Quilliam, M. Grazing on Toxic Alexandrium fundyense Resting Cysts and Vegetative Cells by the Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Keafer, B.A.; Kleindinst, J.L.; McGillicuddy, D.J.; Martin, J.L.; Norton, K.; Pilskaln, C.H.; Smith, J.L.; Sherwood, C.R.; Butman, B. Alexandrium fundyense Cysts in the Gulf of Maine: Long-Term Time Series of Abundance and Distribution, and Linkages to Past and Future Blooms. Deep. Sea Res. Part 2 Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 103, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, S.R.; Litaker, R.W.; Matweyou, J.A.; Hardison, D.R.; Wright, B.A.; Tester, P.A. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Butter Clams (Saxidomus gigantea) from the Kodiak Archipelago, Alaska. Harmful Algae 2022, 111, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas, M.L.; Amorim, A.; Vale, P.; Gomes, S.S.; Botelho, M.J.; Rodrigues, S.M. Prolonged Toxicity of Scrobicularia plana after PSP Events and Its Relation to Gymnodinium catenatum Cyst Consumption and Toxin Depuration. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Medina-Elizalde, J.; García-Mendoza, E.; Turner, A.D.; Sánchez-Bravo, Y.A.; Murillo-Martínez, R. Transformation and Depuration of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in the Geoduck Clam Panopea globosa from the Northern Gulf of California. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; Van Nostrand Reinhold Company: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Charapata, P.; Clark, C.T.; Miller, N.; Kienle, S.S.; Costa, D.P.; Goebel, M.E.; Gunn, H.; Sperou, E.S.; Kanatous, S.B.; Crocker, D.E.; et al. Whiskers Provide Time-Series of Toxic and Essential Trace Elements, Se:Hg Molar Ratios, and Stable Isotope Values of an Apex Antarctic Predator, the Leopard Seal. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Riet, J.; Gibbs, R.S.; Muggah, P.M.; Rourke, W.A.; MacNeil, J.D.; Quilliam, M.A. Liquid Chromatography Post-Column Oxidation (PCOX) Method for the Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Mussels, Clams, Oysters, and Scallops: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1154–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio Team: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- QGIS.org. QGIS Geographic Information System; QGIS Software: Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R.; Huyvaert, K.P. AIC Model Selection and Multimodel Inference in Behavioral Ecology: Some Background, Observations, and Comparisons. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2011, 65, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N. A Protocol for Conducting and Presenting Results of Regression-Type Analyses. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313502495_Vegan_Community_Ecology_Package (accessed on 21 January 2025).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R.V. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means. 2024. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/emmeans/ (accessed on 21 January 2025).

| Comparison (A:B) | Toxin | Mean Percent (%) Contribution | Standard Deviation (%) | Mean Percent Abundance (%) Group A | Mean Percent Abundance (%) Group B | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | NEO | 16 | 15 | 21 | 34 | 0.01 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | GTX2 | 11 | 11 | 23 | 10 | 0.03 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | GTX4 | 11 | 17 | 4 | 21 | 0.02 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | STX | 10 | 11 | 14 | 22 | 0.43 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | GTX3 | 10 | 11 | 18 | 5 | 0.90 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | GTX1 | 5 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 0.37 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | dcSTX | 4 | 6 | 7 | 2 | 0.38 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | dcGTX2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0.79 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | dcGTX3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.45 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | C1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | NA * |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | GTX5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.99 |
| Bering Strait:Beaufort | C2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA * |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | NEO | 15 | 14 | 18 | 34 | 0.04 |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | STX | 13 | 11 | 27 | 22 | 0.03 |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | GTX4 | 11 | 16 | 4 | 21 | 0.02 |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | GTX3 | 11 | 10 | 21 | 5 | 0.64 |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | GTX2 | 7 | 6 | 14 | 10 | 0.92 |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | dcSTX | 4 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 0.77 |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | GTX1 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 0.81 |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | GTX5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.19 |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | C1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | NA * |
| Chukchi:Beaufort | C2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA * |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | GTX3 | 12 | 10 | 21 | 18 | 0.08 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | GTX2 | 10 | 9 | 14 | 23 | 0.09 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | STX | 9 | 8 | 27 | 14 | 0.86 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | NEO | 9 | 10 | 18 | 21 | 0.98 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | GTX1 | 5 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 0.38 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | dcSTX | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 0.18 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | GTX4 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 0.98 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | dcGTX2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 0.17 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | dcGTX3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.06 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | GTX5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.33 |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | C1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA * |
| Chukchi:Bering Strait | C2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charapata, P.; Bowers, E.K.; Hardison, D.R.; Kibler, S.; Anderson, D.M.; Fachon, E.; Lefebvre, K.A. Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Concentrations Measured in Alaskan Arctic Clams Using ELISA and HPLC Methods. Toxins 2025, 17, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020060
Charapata P, Bowers EK, Hardison DR, Kibler S, Anderson DM, Fachon E, Lefebvre KA. Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Concentrations Measured in Alaskan Arctic Clams Using ELISA and HPLC Methods. Toxins. 2025; 17(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharapata, Patrick, Emily K. Bowers, Donnie Ransom Hardison, Steve Kibler, Donald M. Anderson, Evangeline Fachon, and Kathi A. Lefebvre. 2025. "Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Concentrations Measured in Alaskan Arctic Clams Using ELISA and HPLC Methods" Toxins 17, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020060
APA StyleCharapata, P., Bowers, E. K., Hardison, D. R., Kibler, S., Anderson, D. M., Fachon, E., & Lefebvre, K. A. (2025). Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Concentrations Measured in Alaskan Arctic Clams Using ELISA and HPLC Methods. Toxins, 17(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020060





