Targeting Enterotoxins: Advancing Vaccine Development for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli ETEC
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Mechanism of ETEC Infection
3. Release of ETEC Toxins: The Trigger for Diarrheal Disease
3.1. Heat-Labile Toxin (LT)
3.1.1. LT Toxin Structure and Variants
3.1.2. LT Toxic Mechanism
3.2. Heat-Stable Toxin (ST)
3.2.1. ST Toxin Structure and Subtypes
3.2.2. Toxin Mechanism
3.3. Additional Exotoxins
4. Immunogenicity and Relevance of ETEC Toxins in Host Protection
4.1. Immunomodulatory Effects of LT
4.2. Immunogenic Challenges of ST
4.3. Contrasting Immunogenicity of ETEC Toxins: ST vs. LT
5. Detoxification of LT and ST for Vaccine Development
5.1. LT Detoxification
5.2. ST Detoxification
6. Immune Adjuvants Based on LT
6.1. Mechanisms of LT as an Adjuvant
6.2. LT-Based Adjuvants: Applications
7. Innovative Vaccine Design Against ETEC Infection
| Animal Model | Vaccine/Toxin | Dose | Route | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit | MecVax—multiepitope-fusion-based vaccine composed of STaN12S-mnLTR192G/L211A and CFA/I/II/IV | 25 μg CFA/I/II/IV + 25 μg toxoid fusion STa/LT + 0.2 μg dmLT adjuvant | ID | Specific serum IgG, inhibits adherence and neutralizes STa and CT enterotoxicity | [126,127,128] |
| Mouse | Total ETEC RNA | 30, 50, or 70 μg single dose | IM or Oral | IL-1β secretion, specific serum IgG, IgM, and IgA and mucosal IgA. A 75% protection was achieved with 70 μg orally administered | [129] |
| Mouse | SLS (STa-LTB-STb) recombinant enterotoxin and fimbriae proteins (F4, F5, F6, F18, and F41) | SC | IL-1β and TNF-a secretion, specific serum IgG, 80% protection achieved | [130] | |
| Mouse | Microneedle—LTB subunit | 5 μg, single dose | ID | Specific serum IgA, IL-17A production | [86] |
| Mouse | Chitosan nanoparticles containing LTB, STxB, and CTxB | 4 doses of 70 μg | Oral+IP | Specific serum IgG and IgA and mucosal IgA. A 33% survival was achieved | [116] |
| Mouse | Chitosan nanoparticles containing OMVs | 10 or 50 μg single dose | SC or Oral | Serum IgG and mucosal IgA. Toxin and bacteria neutralization | [117] |
| Mouse | PD alone or PD-O148 conjugate, adjuvanted with aluminum phosphate | 50 μg, 3 doses | SC | O-specific serum IgG titers, protection | [131] |
| Mouse | CFA/I fimbrial antigens, including CfaEB and a CfaE- LTB chimera with dmLT | 10 μg CfaEB with 0.1 μg dmLT | ID, sublingual | IgG1, IgG2a, and fecal IgA antibody responses in ID but not in sublingual | [120] |
7.1. Current Vaccination Clinical Trials Against ETEC
| Vaccine | Composition/Adjuvant | Dose | Route | Phase of Development | Main Findings | Manufacturer and Study ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETVAX | Inactivated, multivalent vaccine containing CFA/I, CS3, CS5, CS6, LT toxoid | 2 doses, 2 weeks apart | Oral | II | Safe. LTB and O78 LPS-specific IgA, IgG | Scandinavian Biopharma AB, NCT05178134 [133] |
| ACE527 | Live attenuated ETEC vaccine+dmLT | 2 or 3 doses | Oral | I/II | Well tolerated and protective with adjuvant (65.9% protective efficacy) | PATH, NCT01739231 [109] |
| dmLT | Attenuated recombinant dmLT from ETEC | 3 doses, 3 weeks apart | Oral, ID, sublingual | I | Safe but low immunogenicity (low specific dmLT-IgA and IgG) | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), NCT02531685 and NCT02052934 [150] |
| CfaE | Subunit recombinant vaccine including CfaE +mLT | 3 doses, 3 weeks apart | Transcutaneous skin patch/ID | I/II | Safe and immunogenic. Vaccine efficacy of 27.8% with a reduction in disease severity | U.S. Army Medical Research and Development Command, NCT01382095 [142], NCT01644565 [151], NCT01922856 [143] |
| CssBA | Subunit recombinant vaccine including C6S +dmLT | 3 doses, 3 weeks apart | IM | I | Safe and well tolerated. Robust IgG and IgA responses with dmLT adjuvant | PATH, NCT03404674 [111] |
| CVD 1208-122 | Live attenuated Shigella flexneri 2a expressing LTB subunit and CFA/I of ETEC | 2 doses, 4 weeks apart | Oral | I | No available data | University of Maryland, NCT04634513 (incomplete) |
| ShigETEC | Live attenuated Shigella flexneri 2a expressing LT and CFA/I of ETEC | 3 doses, 2 weeks apart | Oral | I | No available data | Eveliqure Biotechnologies, NCT05987488 (incomplete), NCT05409196 |
7.2. Emerging Trends in ETEC Vaccination
7.3. Overview of Strategies for ETEC Toxin Neutralization in Vaccine Development
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cassels, F.J.; Khalil, I.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Walker, R.I. Special Issue on Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Vaccines: ETEC Infection and Vaccine-Mediated Immunity. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Elsas, J.D.; Semenov, A.V.; Costa, R.; Trevors, J.T. Survival of Escherichia coli in the Environment: Fundamental and Public Health Aspects. ISME J. 2011, 5, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.D.; Swarthout, J.M.; Worby, C.J.; Chieng, B.; Mboya, J.; Earl, A.M.; Njenga, S.M.; Pickering, A.J. Bacterial Strain Sharing between Humans, Animals, and the Environment among Urban Households. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Balawi, M.; Morsy, F.M. Prenatal versus Postnatal Initial Colonization of Healthy Neonates’ Colon Ecosystem by the Enterobacterium Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00379-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofi, T.; Panayidou, S.; Dieronitou, I.; Michael, C.; Apidianakis, Y. Metabolic Output Defines Escherichia coli as a Health-Promoting Microbe against Intestinal Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, J.; Blum-Oehler, G. In Appreciation of Theodor Escherich. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobman, J.L.; Penn, C.W.; Pallen, M.J. Laboratory Strains of Escherichia coli: Model Citizens or Deceitful Delinquents Growing Old Disgracefully? Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzosa, M.; Pastor, Y.; Irache, J.M.; Gamazo, C. Experimental Vaccination with Nanoparticles Containing Escherichia coli Virulence Factors. In Applications of Nanobiotechnology for Neglected Tropical Disease, 1st ed.; Formiga, F.R., Inamuddin, Seberino, P., Eds.; Elsevier, Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Keddy, K.H.; Smith, A.M. Bacterial Gastroenteritis. In Gastrointestinal Diseases and Their Associated Infections; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Escherichia coli, Diarrheagenic|CDC Yellow Book 2024. Available online: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/escherichia-coli-diarrheagenic (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Yun, Y.-S.; Park, D.-Y.; Oh, I.; Shin, W.-R.; Ahn, G.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H. Pathogenic Factors and Recent Study on the Rapid Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC). Mol. Biotechnol. 2025, 67, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakbin, B.; Brück, W.M.; Rossen, J.W.A. Virulence Factors of Enteric Pathogenic Escherichia coli: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolhion, N. A Milestone in Screening for Adherent-Invasive E. coli Colonization in Patients with Crohn’s Disease? United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 995–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesser, K.J.; Levy, K. Updates on Defining and Detecting Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Pathotypes. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ud-Din, A.; Wahid, S. Relationship among Shigella spp. and Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC) and Their Differentiation. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aesan—Agencia Española de Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/AECOSAN/web/seguridad_alimentaria/subdetalle/Escherichia_coli.htm?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- Khalil, I.; Walker, R.; Porter, C.K.; Muhib, F.; Chilengi, R.; Cravioto, A.; Guerrant, R.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Qadri, F.; Baqar, S.; et al. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Vaccines: Priority Activities to Enable Product Development, Licensure, and Global Access. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4266–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.I.; Troeger, C.; Blacker, B.F.; Rao, P.C.; Brown, A.; Atherly, D.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Engmann, C.M.; Houpt, E.R.; Kang, G.; et al. Morbidity and mortality due to shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: The Global Burden of Disease Study 1990–2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matías, J.; Berzosa, M.; Pastor, Y.; Irache, J.; Gamazo, C. Maternal Vaccination. Immunization of Sows during Pregnancy against ETEC Infections. Vaccines 2017, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.D.; Herbelin, C.J.; Bumbaugh, A.C.; Selander, R.K.; Whittam, T.S. Parallel Evolution of Virulence in Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nature 2000, 406, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainil, J.G.; Bex, F.; Jacquemin, E.; Pohl, P.; Couturier, M.; Kaeckenbeeck, A. Prevalence of Four Enterotoxin (STaP, STaH, STb, and LT) and Four Adhesin Subunit (K99, K88, 987P, and F41) Genes among Escherichia coli Isolates from Cattle. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1990, 51, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harro, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Feller, A.; DeNearing, B.; Cage, A.; Ram, M.; Lundgren, A.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Walker, R.I.; et al. Refinement of a Human Challenge Model for Evaluation of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccines. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.F.; Pye, G.; Bramley, R.; Clark, A.G.; Dyson, T.J.; Hardcastle, J.D. Measurement of Gastrointestinal PH Profiles in Normal Ambulant Human Subjects. Gut 1988, 29, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Park, K.; Yoon, H. Cooperative Interaction between Acid and Copper Resistance in Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, S.L.; Robertson, D.C. Factors Affecting Release of Heat-Labile Enterotoxin by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1979, 23, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, L.; Ali, Z.B.; Nygren, E.; Wang, Z.; Karlsson, S.; Zhu, B.; Quiding-Järbrink, M.; Sjöling, Å. Alkaline PH Is a Signal for Optimal Production and Secretion of the Heat Labile Toxin, LT in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales-Siles, L.; Sjöling, Å. The Different Ecological Niches of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, C.; De Paepe, K.; Galia, W.; De Bodt, J.; Chalancon, S.; Leriche, F.; Ballet, N.; Denis, S.; Alric, M.; Van de Wiele, T.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Modulation of Enterotoxigenic E. coli H10407 Pathogenesis and Interplay with Microbiota in Human Gut Models. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodero, M.D.; Munson, G.P. Cyclic AMP Receptor Protein-Dependent Repression of Heat-Labile Enterotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.M.; Seidler, U.E. Bicarbonate Secretion and Acid/Base Sensing by the Intestine. Pflüg. Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2024, 476, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulke-Abel, J.; In, J.; Yin, J.; Zachos, N.C.; Kovbasnjuk, O.; Estes, M.K.; De Jonge, H.; Donowitz, M. Human Enteroids as a Model of Upper Small Intestinal Ion Transport Physiology and Pathophysiology. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 638–649.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.; Smith, E.M.; Foulke-Abel, J.D.; Barry, E.M. Research in a Time of Enteroids and Organoids: How the Human Gut Model Has Transformed the Study of Enteric Bacterial Pathogens. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1795389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, G.C. Role of Mucus Layers in Gut Infection and Inflammation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Randall, A.; Vickers, T.J.; Molina, D.; Harro, C.D.; DeNearing, B.; Brubaker, J.; Sack, D.A.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Felgner, P.L.; et al. Human Experimental Challenge with Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Elicits Immune Responses to Canonical and Novel Antigens Relevant to Vaccine Development. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Kansal, R.; Bartels, S.R.; Hamilton, D.J.; Shaaban, S.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Adhesin Degradation Accelerates Delivery of Heat-Labile Toxin by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 29771–29779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Pastrana, G.; Rojas-Bautista, M.; Hernández-Pérez, P.; Santiago-Martínez, O.; Gómez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Terrazas-Luna, V.M.; Montes-Yedra, J.; Bautista-Avendaño, A.A.; García-López, E.S.; Leon-Sicairos, N.; et al. Virulence Genes, Antimicrobial Resistance Profile, Phylotyping and Pathotyping of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Children in Southwest Mexico. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadri, F.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Sack, R.B. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Developing Countries: Epidemiology, Microbiology, Clinical Features, Treatment, and Prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mentzer, A.; Svennerholm, A.M. Colonization factors of human and animal-specific enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.; Luo, Q.; Roy, K.; Shabaan, S.; Kumar, P.; Qadri, F.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Contribution of the Highly Conserved EaeH Surface Protein to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli Pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3657–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasko, D.A.; Del Canto, F.; Luo, Q.; Fleckenstein, J.M.; Vidal, R.; Hazen, T.H. Comparative Genomic Analysis and Molecular Examination of the Diversity of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli Isolates from Chile. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, F.M.; Martin, J.; Hazen, T.H.; Vickers, T.J.; Pashos, M.; Okhuysen, P.C.; Gómez-Duarte, O.G.; Cebelinski, E.; Boxrud, D.; del Canto, F.; et al. Conservation and Global Distribution of Non-Canonical Antigens in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haycocks, J.R.J.; Sharma, P.; Stringer, A.M.; Wade, J.T.; Grainger, D.C. The Molecular Basis for Control of ETEC Enterotoxin Expression in Response to Environment and Host. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004605. [Google Scholar]
- Crofts, A.A.; Giovanetti, S.M.; Rubin, E.J.; Poly, F.M.; Gutiérrez, R.L.; Talaat, K.R.; Porter, C.K.; Riddle, M.S.; DeNearing, B.; Brubaker, J.; et al. Enterotoxigenic E. coli Virulence Gene Regulation in Human Infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, e8968–e8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutkan, H.; Kuehn, M.J. Context-Dependent Activation Kinetics Elicited by Soluble versus Outer Membrane Vesicle-Associated Heat-Labile Enterotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3760–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryson, A.; Gonzalez, G.; Al-Atoom, N.; Nashar, N.; Smith, J.R.; Nashar, T. Extracellular Vesicles Are Conduits for E. coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin (LT) and the B-Subunits of LT and Cholera Toxin in Immune Cell-to-Cell Communication. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 177, 106038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klipstein, F.A.; Short, H.B.; Engert, R.F.; Jean, L.; Weaver, G.A. Contamination of the Small Intestine by Enterotoxigenic Coliform Bacteria among the Rural Population of Haiti. Gastroenterology 1976, 70, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klipstein, F.A.; Engert, R.F.; Short, H.B. Enterotoxigenicity of colonising coliform bacteria in tropical sprue and blind-loop syndrome. Lancet 1978, 312, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, A.; Tumala, B.; Vickers, T.J.; Martin, J.C.; Rosa, B.A.; Sabui, S.; Basu, S.; Simoes, R.D.; Mitreva, M.; Storer, C.; et al. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin Drives Enteropathic Changes in Small Intestinal Epithelia. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, J.D.; Isaacson, R.E.; Schifferli, D.M. Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizza, M.; Giuliani, M.M.; Fontana, M.R.; Monaci, E.; Douce, G.; Dougan, G.; Mills, K.H.G.; Rappuoli, R.; Del Giudice, G. Mucosal Vaccines: Non Toxic Derivatives of LT and CT as Mucosal Adjuvants. Vaccine 2001, 19, 2534–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gigosos, R.; García-Fortea, P.; Reina-Doña, E.; Plaza-Martín, E. Effectiveness in Prevention of Travellers’ Diarrhoea by an Oral Cholera Vaccine WC/RBS. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2007, 5, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, L.; Taucher, C. Travel Vaccines: Update. Can. Pharm. J. 2020, 153, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, W.S.; Falkow, S. Amino Acid Sequence Homology between Cholera Toxin and Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin. Nature 1980, 288, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, W. Significance of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Heat-Labile Toxin (LT) Enzymatic Subunit Epitopes in LT Enterotoxicity and Immunogenicity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00849-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Soria-Guerra, R.E.; Moreno-Fierros, L.; Govea-Alonso, D.O.; Herrera-Díaz, A.; Korban, S.S.; Alpuche-Solís, Á.G. Immunogenicity of Nuclear-Encoded LTB:ST Fusion Protein from Escherichia coli Expressed in Tobacco Plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 30, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seriwatana, J.; Echeverria, P.; Taylor, D.N.; Rasrinaul, L.; Brown, J.E.; Peiris, J.S.; Clayton, C.L. Type II Heat-Labile Enterotoxin-Producing Escherichia Coli Isolated from Animals and Humans. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigobelo, E.C.; Gamez, H.J.; Marin, J.M.; Macedo, C.; Ambrosin, J.A.; Ávila, F.A. Virulence Factors of Escherichia coli Isolated from Diarrheic Calves. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2006, 58, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, A.R.M.; Salvadori, M.R.; Coswig, L.T.; Gatti, M.S.V.; Leite, D.S.; Valadares, G.F.; Neto, M.G.; Shocken-Iturrino, R.P.; Blanco, J.E.; Yano, T. Type 2 Heat-Labile Enterotoxin (LT-II)-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Ostriches with Diarrhea. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 105, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celemin, C.; Anguita, J.; Naharro, G.; Suarez, S. Evidence That Escherichia coli Isolated from the Intestine of Healthy Pigs Hybridize with LT-II, ST-Ib and SLT-II DNA Probes. Microb. Pathog. 1994, 16, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, E.C.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Olson, B.H. Occurrence of Genes Associated with Enterotoxigenic and Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in Agricultural Waste Lagoons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, M.V.; Borges, C.A.; Beraldo, L.G.; Maluta, R.P.; Pollo, A.S.; Borzi, M.M.; dos Santos, L.F.; Kariyawasam, S.; Ávila, F.A. de Shigatoxigenic and Atypical Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in Fish for Human Consumption. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amézquita-López, B.A.; Soto-Beltrán, M.; Lee, B.G.; Yambao, J.C.; Quiñones, B. Isolation, Genotyping and Antimicrobial Resistance of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, T.A.; Connell, T.D.; Holmes, R.K.; Whipp, S.C. Evaluation of Heat-Labile Enterotoxins Type IIa and Type IIb in the Pathogenicity of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli for Neonatal Pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.M.; Kuhlmann, F.M. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infections. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2019, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 142–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sack, R.B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1975, 29, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, Z.; Luo, Y.; Cox, E.; Devriendt, B. Heat-Stable Enterotoxins of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Their Impact on Host Immunity. Toxins 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammermueller, J.; Kruth, S.; Prescott, J.; Gyles, C. Detection of Toxin Genes in Escherichia coli Isolated from Normal Dogs and Dogs with Diarrhea. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 59, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Davis, S.M.; Westra, C.; Vickers, T.J.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Molecular Determinants of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxin Secretion and Delivery. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00526-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, H.R. Properties of Guanylate Cyclase and Levels of Cyclic GMP in Rat Small Intestinal Villous and Crypt Cells. FEBS Lett. 1975, 55, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiglmeier, P.R.; Rösch, P.; Berkner, H. Cure and Curse: E. coli Heat-Stable Enterotoxin and Its Receptor Guanylyl Cyclase C. Toxins 2010, 2, 2213–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostedgaard, L.S.; Baldursson, O.; Welsh, M.J. Regulation of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Cl− Channel by Its R Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7689–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, E.; Harel, J.; Dubreuil, D.J. Binding Characteristics of Escherichia coli enterotoxin b (STb) to the Pig Jejunum and Partial Characterization of the Molecule Involved. Microb. Pathog. 1998, 24, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, J.D. EAST1 Toxin: An Enigmatic Molecule Associated with Sporadic Episodes of Diarrhea in Humans and Animals. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereecke, N.; Van Hoorde, S.; Sperling, D.; Theuns, S.; Devriendt, B.; Cox, E. Virotyping and Genetic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Porcine ETEC/STEC Strains and Associated Plasmid Types. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1139312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, L.-P.; Dubreuil, J.D. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Enterotoxin 1 (EAST1): A New Toxin with an Old Twist. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 28, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatsuyanagi, J.; Saito, S.; Kinouchi, Y.; Sato, H.; Morita, M.; Itoh, K. Characteristics of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and E. coli Harboring Enteroaggregative E. coli Heat-Stable Enterotoxin-1 (EAST-1) Gene Isolated from a Water-Borne Outbreak. J. Jpn. Assoc. Infect. Dis. 1996, 70, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Rennie, R.P.; Freer, J.H.; Arbuthnott, J.P. The Kinetics of Erythrocyte Lysis by Escherichia coli Haemolysin. J. Med. Microbiol. 1974, 7, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A.; von Rhein, C.; Bauer, S.; Huüttinger, C.; Goebel, W. Molecular Analysis of Cytolysin A (ClyA) in Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5311–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E.; Schumann, M.; Schneemann, M.; Dony, V.; Fromm, A.; Nagel, O.; Schulzke, J.-D.; Bücker, R. Escherichia coli Alpha-Hemolysin HlyA Induces Host Cell Polarity Changes, Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction and Cell Detachment in Human Colon Carcinoma Caco-2 Cell Model via PTEN-Dependent Dysregulation of Cell Junctions. Toxins 2021, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faubert, C.; Drolet, R. Hemorrhagic Gastroenteritis Caused by Escherichia coli in Piglets: Clinical, Pathological and Microbiological Findings. Can. Vet. J. 1992, 33, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Girardi, P.; Bhuiyan, T.R.; Lundin, S.B.; Harutyunyan, S.; Neuhauser, I.; Khanam, F.; Nagy, G.; Szijártó, V.; Henics, T.; Harandi, A.M.; et al. Anti-Toxin Responses to Natural Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Infection in Adults and Children in Bangladesh. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxt, A.M.; Diaz, Y.; Bacle, A.; Grauffel, C.; Reuter, N.; Aasland, R.; Sommerfelt, H.; Puntervoll, P. Characterization of Immunological Cross-Reactivity between Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxin and Human Guanylin and Uroguanylin. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2913–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, C.F.; Sutton, C.E.; Ross, P.J.; Iwakura, Y.; Pizza, M.; Rappuoli, R.; Lavelle, E.C.; Mills, K.H.G. Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin Promotes Protective Th17 Responses against Infection by Driving Innate IL-1 and IL-23 Production. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5896–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzosa, M.; Nemeskalova, A.; Zúñiga-Ripa, A.; Salvador-Bescós, M.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F.; Gamazo, C.; Irache, J.M. Immune Response after Skin Delivery of a Recombinant Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B Subunit of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Mice. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Sández-Robledo, C.; Bañuelos-Hernández, B.; Angulo, C. Corn-Based Vaccines: Current Status and Prospects. Planta 2017, 245, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soh, H.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Lee, H.H.; Ajjappala, H.; Jang, K.; Park, J.H.; Sim, J.S.; Lee, G.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Han, Y.H.; et al. Expression and Functional Validation of Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B (LTB) and Cholera Toxin B (CTB) Subunits in Transgenic Rice (Oryza sativa). Springerplus 2015, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Tsai, M.-L.; Tsai, Y.-G.; Kuo, C.-H.; Hung, C.-H. IL-33 Regulates M1/M2 Chemokine Expression via Mitochondrial Redox-Related Mitophagy in Human Monocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 359, 109915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxt, A.; Aasland, R.; Sommerfelt, H.; Nataro, J.; Puntervoll, P. Heat-Stable Enterotoxin of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli as a Vaccine Target. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, M.; Geens, M.; Schauvliege, S.; Gasthuys, F.; van der Meulen, J.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Goddeeris, B.M.; Niewold, T.; Cox, E. Role of Heat-Stable Enterotoxins in the Induction of Early Immune Responses in Piglets after Infection with Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, M.; Hellemans, A.; Cox, E. Optimization of a Small Intestinal Segment Perfusion Model for Heat-Stable Enterotoxin A Induced Secretion in Pigs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 152, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, E.D.; Govasli, M.L.; Sommerfelt, H.; Puntervoll, P. Development of an Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Based on the Heat-Stable Toxin. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.J.; McNeela, E.; Pizza, M.; Rappuoli, R.; O’Neill, L.; Mills, K.H.G. Modulation of Innate and Acquired Immune Responses by Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin: Distinct Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Nontoxic AB Complex and the Enzyme Activity. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5750–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizza, M.; Fontana, M.R.; Giuliani, M.M.; Domenighini, M.; Magagnoli, C.; Giannelli, V.; Nucci, D.; Hol, W.; Manetti, R.; Rappuoli, R. A Genetically Detoxified Derivative of Heat-Labile Escherichia coli Enterotoxin Induces Neutralizing Antibodies against the A Subunit. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feil, I.K.; Reddy, R.; de Haan, L.; Merritt, E.A.; van den Akker, F.; Storm, D.R.; Hol, W.G.J. Protein Engineering Studies of A-chain Loop 47–56 of Escherichia coli Heat-labile Enterotoxin Point to a Prominent Role of This Loop for Cytotoxicity. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 20, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, M.M.; Del Giudice, G.; Giannelli, V.; Dougan, G.; Douce, G.; Rappuoli, R.; Pizza, M. Mucosal Adjuvanticity and Immunogenicity of LTR72, a Novel Mutant of Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin with Partial Knockout of ADP-Ribosyltransferase Activity. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, R.I.; Steele, D.; Aguado, T. Analysis of Strategies to Successfully Vaccinate Infants in Developing Countries against Enterotoxigenic E. Coli (ETEC) Disease. Vaccine 2007, 25, 2545–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klipstein, F.A.; Engert, R.F.; Houghten, R.A. Mucosal Antitoxin Response in Volunteers to Immunization with a Synthetic Peptide of Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Enterotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1985, 50, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Mateo, K.; Nataro, J.P.; Robertson, D.C.; Zhang, W. Modified Heat-Stable Toxins (HSTa) of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Lose Toxicity but Display Antigenicity after Being Genetically Fused to Heat-Labile Toxoid LT(R192G). Toxins 2011, 3, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, V.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Monreal-Escalante, E.; Murillo-Álvarez, J.I.; Angulo, C. Conjugation of β-Glucans on Heat-Stable Enterotoxin (ST) to Enhance the Immunogenic Response in Mouse Leucocytes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Setty, P.; Boedeker, E.C. Development of Live Attenuated Bacterial Vaccines Targeting Escherichia coli Heat-Labile and Heat-Stable Enterotoxins. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 202, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxt, A.M.; Diaz, Y.; Aasland, R.; Clements, J.D.; Nataro, J.P.; Sommerfelt, H.; Puntervoll, P. Towards Rational Design of a Toxoid Vaccine against the Heat-Stable Toxin of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovska, L.; Lopes, L.; Simmons, C.P.; Pizza, M.; Dougan, G.; Chain, B.M. Modulation of Dendritic Cell Endocytosis and Antigen Processing Pathways by Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin and Mutant Derivatives. Vaccine 2003, 21, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, S.; Nawar, H.F.; Russell, M.W.; Connell, T.D. Differential Binding of Escherichia coli Enterotoxins LT-IIa and LT-IIb and of Cholera Toxin Elicits Differences in Apoptosis, Proliferation, and Activation of Lymphoid Cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, I.; Marinaro, M.; Kiyono, H.; Jackson, R.J.; Nakagawa, I.; Fujihashi, K.; Hamada, S.; Clements, J.D.; Bost, K.L.; McGhee, J.R. Mechanisms for Mucosal Immunogenicity and Adjuvancy of Escherichia coli Labile Enterotoxin. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Lu, T.; Mani, S.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Walker, R.; Sack, D.A.; Zhang, W. Adjuvant Effect of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Double-Mutant Heat-Labile Toxin (DmLT) on Systemic Immunogenicity Induced by the CFA/I/II/IV MEFA ETEC Vaccine: Dose-Related Enhancement of Antibody Responses to Seven ETEC Adhesins (CFA/I, CS1-CS6). Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, E.B.; Lawson, L.B.; Freytag, L.C.; Clements, J.D. Characterization of a Mutant Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin, LT(R192G/L211A), as a Safe and Effective Oral Adjuvant. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harro, C.; Louis Bourgeois, A.; Sack, D.; Walker, R.; DeNearing, B.; Brubaker, J.; Maier, N.; Fix, A.; Dally, L.; Chakraborty, S.; et al. Live Attenuated Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Vaccine with DmLT Adjuvant Protects Human Volunteers against Virulent Experimental ETEC Challenge. Vaccine 2019, 37, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, A.; Bourgeois, L.; Carlin, N.; Clements, J.; Gustafsson, B.; Hartford, M.; Holmgren, J.; Petzold, M.; Walker, R.; Svennerholm, A.-M. Safety and Immunogenicity of an Improved Oral Inactivated Multivalent Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Vaccine Administered Alone and Together with DmLT Adjuvant in a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase I Study. Vaccine 2014, 32, 7077–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Gutiérrez, R.L.; Maciel, M.; Poole, S.; Testa, K.J.; Trop, S.; Duplessis, C.; Lane, A.; Riddle, M.S.; Hamer, M.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Intramuscularly Administered CS6 Subunit Vaccine with a Modified Heat-Labile Enterotoxin from Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vaccine 2021, 39, 5548–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsch, M.; Zhou, W.; Rhodes, P.; Bopp, M.; Chen, R.T.; Linder, T.; Spyr, C.; Steffen, R. Use of the Inactivated Intranasal Influenza Vaccine and the Risk of Bell’s Palsy in Switzerland. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-C.; Hsu, W.-T.; Lee, W.-S.; Wang, N.-C.; Chen, T.-J.; Liu, M.-C.; Pai, H.-C.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Chang, M.; Hsieh, S.-M. A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Immunogenicity of an Intranasally Administered Trivalent Inactivated Influenza Vaccine with the Adjuvant LTh(AK): A Phase II Study. Vaccine 2020, 38, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.M. Confronting Challenges to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Development. Front. Trop. Dis. 2021, 2, 709907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, P.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: Intestinal Pathogenesis Mechanisms and Colonization Resistance by Gut Microbiota. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2055943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari Marandi, B.H.; Zolfaghari, M.R.; Kazemi, R.; Motamedi, M.J.; Amani, J. Immunization against Vibrio Cholerae, ETEC, and EHEC with Chitosan Nanoparticle Containing LSC Chimeric Protein. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 134, 103600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noroozi, N.; Mousavi Gargari, S.L.; Nazarian, S.; Sarvary, S.; Rezaei Adriani, R. Immunogenicity of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Outer Membrane Vesicles Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticles. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Diaz-Arévalo, D.; Guan, H.; Zeng, M. Noninvasive Vaccination against Infectious Diseases. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2018, 14, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.Y.; Seo, H.; Sack, D.A.; Zhang, W. Intradermally Administered Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Candidate MecVax Induces Functional Serum Immunoglobulin G Antibodies against Seven Adhesins (CFA/I and CS1 through CS6) and Both Toxins (STa and LT). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0213921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, M.; Bauer, D.; Baudier, R.L.; Bitoun, J.; Clements, J.D.; Poole, S.T.; Smith, M.A.; Kaminski, R.W.; Savarino, S.J.; Norton, E.B. Intradermal or Sublingual Delivery and Heat-Labile Enterotoxin Proteins Shape Immunologic Responses to a CFA/I Fimbria-Derived Subunit Antigen Vaccine against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00460-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, A.M.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Donnelly, R.F. Technology Update: Dissolvable Microneedle Patches for Vaccine Delivery. Med. Devices Evid. Res. 2019, 12, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Preferred Product Characteristics for Vaccines Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-preferred-product-characteristics-for-vaccines-against-enterotoxigenic-escherichia-coli (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Rodgers, A.M.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Kissenpfennig, A.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle Arrays for Vaccine Delivery: The Possibilities, Challenges and Use of Nanoparticles as a Combinatorial Approach for Enhanced Vaccine Immunogenicity. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, I.; Bagwe, P.; Gomes, K.B.; Bajaj, L.; Gala, R.; Uddin, M.N.; D’Souza, M.J.; Zughaier, S.M. Microneedles: A New Generation Vaccine Delivery System. Micromachines 2021, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangla, B.; Jave, S.; Sultan, M.H.; Ahsan, W.; Aggarwal, G.; Kohli, K. Nanocarriers-Assisted Needle-Free Vaccine Delivery Through Oral and Intranasal Transmucosal Routes: A Novel Therapeutic Conduit. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 757761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Garcia, C.; Ruan, X.; Duan, Q.; Sack, D.A.; Zhang, W. Preclinical Characterization of Immunogenicity and Efficacy against Diarrhea from MecVax, a Multivalent Enterotoxigenic E. coli Vaccine Candidate. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e0010621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, I.; Parvej, S.M.D.; Shen, Y.; Li, S.; Lauder, K.L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Protein-Based Vaccine Candidate MecVax Broadly Protects against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Intestinal Colonization in a Rabbit Model. Infect. Immun. 2023, 91, e0027223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.M.; Seo, H.; Zhang, W.; Sack, D.A. A Multi-Epitope Fusion Antigen Candidate Vaccine for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Is Protective against Strain B7A Colonization in a Rabbit Model. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Bai, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Total RNA against ETEC Challenge in a Mouse Model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, L. Protective Efficacy of a Novel Multivalent Vaccine in the Prevention of Diarrhea Induced by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in a Murine Model. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 23, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.J.; Warfel, K.F.; Desai, P.; Li, J.; Lee, J.-J.; Wong, D.A.; Nguyen, P.M.; Qin, Y.; Sobol, S.E.; Jewett, M.C.; et al. A Low-Cost Recombinant Glycoconjugate Vaccine Confers Immunogenicity and Protection against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infections in Mice. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1085887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, J.; Bourgeois, L.; Carlin, N.; Clements, J.; Gustafsson, B.; Lundgren, A.; Nygren, E.; Tobias, J.; Walker, R.; Svennerholm, A.-M. Development and Preclinical Evaluation of Safety and Immunogenicity of an Oral ETEC Vaccine Containing Inactivated E. coli Bacteria Overexpressing Colonization Factors CFA/I, CS3, CS5 and CS6 Combined with a Hybrid LT/CT B Subunit Antigen, Administered Alone and Together with DmLT Adjuvant. Vaccine 2013, 31, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar]
- Kantele, A.; Riekkinen, M.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Pakkanen, S.H.; Pietilä, J.-P.; Patjas, A.; Eriksson, M.; Khawaja, T.; Klemets, P.; Marttinen, K.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of ETVAX®, an Oral Inactivated Vaccine against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Diarrhoea: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial amongst Finnish Travellers to Benin, West Africa. J. Travel Med. 2023, 30, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, F.; Akhtar, M.; Bhuiyan, T.R.; Chowdhury, M.I.; Ahmed, T.; Rafique, T.A.; Khan, A.; Rahman, S.I.A.; Khanam, F.; Lundgren, A.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the Oral, Inactivated, Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine ETVAX in Bangladeshi Children and Infants: A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase 1/2 Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.; Anderson, J.D.; Bagamian, K.H.; Baqar, S.; Giersing, B.; Hausdorff, W.P.; Marshall, C.; Porter, C.K.; Walker, R.I.; Bourgeois, A.L. Vaccine Value Profile for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Vaccine 2023, 41, S95–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.M.; Muhsen, K.; Tennant, S.M.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Sow, S.O.; Sur, D.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Saha, D.; Adegbola, R.; et al. Colonization Factors among Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Children with Moderate-to-Severe Diarrhea and from Matched Controls in the Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, S.T.; Maciel, M.; Dinadayala, P.; Dori, K.E.; McVeigh, A.L.; Liu, Y.; Barry, E.; Grassel, C.; Prouty, M.G.; Renauld-Mongénie, G.; et al. Biochemical and Immunological Evaluation of Recombinant CS6-Derived Subunit Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Candidates. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00788-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudrak, B.; Kuehn, M.J. Heat-Labile Enterotoxin: Beyond G M1 Binding. Toxins 2010, 2, 1445–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, J.D.; Sack, D.A.; Harris, J.R.; Chakraborty, J.; Neogy, P.K.; Stanton, B.; Huda, N.; Khan, M.U.; Kay, B.A.; Khan, M.R.; et al. Cross-Protection by B Subunit-Whole Cell Cholera Vaccine Against Diarrhea Associated with Heat-Labile Toxin-Producing Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: Results of a Large-Scale Field Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 158, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, H.; Siitonen, A.; Kataja, M.J.; Kyrönseppa, H.; Simula, I.; Mattila, L.; Oksanen, P.; Cadoz, M. Prevention of Travellers’ Diarrhoea by Oral B-Subunit/Whole-Cell Cholera Vaccine. Lancet 1991, 338, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamazo, C.; Pastor, Y.; Larrañeta, E.; Berzosa, M.; Irache, J.M.; Donnelly, R.F. Understanding the Basis of Transcutaneous Vaccine Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2019, 10, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, M.S.; Maciel, M.; Porter, C.K.; Poole, S.T.; Gutierrez, R.L.; Gormley, R.; Laird, R.M.; Sebeny, P.J.; Dori, K.E.; Greenleaf, M.E.; et al. A First in Human Clinical Trial Assessing the Safety and Immunogenicity of Transcutaneously Delivered Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Fimbrial Tip Adhesin with Heat-Labile Enterotoxin with Mutation R192G. Vaccine 2020, 38, 7040–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, R.L.; Porter, C.K.; Harro, C.; Talaat, K.; Riddle, M.S.; DeNearing, B.; Brubaker, J.; Maciel, M.; Laird, R.M.; Poole, S.; et al. Efficacy Evaluation of an Intradermally Delivered Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli CF Antigen I Fimbrial Tip Adhesin Vaccine Coadministered with Heat-Labile Enterotoxin with LT(R192G) against Experimental Challenge with Enterotoxigenic E. coli H10407 in Healthy Adult Volunteers. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Kaminski, R.W.; Porter, C.; Choy, R.K.M.; White, J.A.; Fleckenstein, J.M.; Cassels, F.; Bourgeois, L. Vaccines for Protecting Infants from Bacterial Causes of Diarrheal Disease. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqar, S.; Bonavia, A.; Louis Bourgeois, A.; Campo, J.J.; Clifford, A.; Hanevik, K.; Hasso-Agopsowicz, M.; Hausdorff, W.; Kaminski, R.; MacLennan, C.A.; et al. The 2022 Vaccines Against Shigella and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (VASE) Conference: Summary of Breakout Workshops. Vaccine 2024, 42, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, R.M.; Ma, Z.; Dorabawila, N.; Pequegnat, B.; Omari, E.; Liu, Y.; Maue, A.C.; Poole, S.T.; Maciel, M.; Satish, K.; et al. Evaluation of a Conjugate Vaccine Platform against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC), Campylobacter Jejuni and Shigella. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6695–6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, P.H.Q.S.; Bolick, D.T.; Ledwaba, S.E.; Kolling, G.L.; Costa, D.V.S.; Oriá, R.B.; Lima, A.Â.M.; Barry, E.M.; Guerrant, R.L. A Bivalent Vaccine Confers Immunogenicity and Protection against Shigella flexneri and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infections in Mice. npj Vaccines 2020, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harutyunyan, S.; Neuhauser, I.; Mayer, A.; Aichinger, M.; Szijártó, V.; Nagy, G.; Nagy, E.; Girardi, P.; Malinoski, F.J.; Henics, T. Characterization of ShigETEC, a Novel Live Attenuated Combined Vaccine against Shigellae and ETEC. Vaccines 2020, 8, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, P.; Harutyunyan, S.; Neuhauser, I.; Glaninger, K.; Korda, O.; Nagy, G.; Nagy, E.; Szijártó, V.; Pall, D.; Szarka, K.; et al. Evaluation of the Safety, Tolerability and Immunogenicity of ShigETEC, an Oral Live Attenuated Shigella-ETEC Vaccine in Placebo-Controlled Randomized Phase 1 Trial. Vaccines 2022, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, D.I.; Pasetti, M.F.; Brady, R.; Buskirk, A.D.; Wahid, R.; Dickey, M.; Cohen, M.; Baughman, H.; El-Khorazaty, J.; Maier, N.; et al. A Phase 1 Dose Escalating Study of Double Mutant Heat-Labile Toxin LTR192G/L211A (DmLT) from Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) by Sublingual or Oral Immunization. Vaccine 2019, 37, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, R.L.; Riddle, M.S.; Porter, C.K.; Maciel, M.; Poole, S.T.; Laird, R.M.; Lane, M.; Turiansky, G.W.; Jarell, A.; Savarino, S.J. A First in Human Clinical Trial Assessing the Safety and Immunogenicity of Two Intradermally Delivered Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli CFA/I Fimbrial Tip Adhesin Antigens with and without Heat-Labile Enterotoxin with Mutation LT(R192G). Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, W. Vaccines against Gastroenteritis, Current Progress and Challenges. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1486–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Pang, S.; Wu, W.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.; Zhu, G. A Multivalent Vaccine Candidate Targeting Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Fimbriae for Broadly Protecting against Porcine Post-Weaning Diarrhea. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, I.; Parvej, S.M.D.; Li, S.; Lauder, K.L.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W. Polyvalent Protein Adhesin MEFA-II Induces Functional Antibodies against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Adhesins CS7, CS12, CS14, CS17, and CS21 and Heat-Stable Toxin (STa). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0068323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Moxley, R.A.; Zhang, W. Mapping the Neutralizing Epitopes of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 (F4) Fimbrial Adhesin and Major Subunit FaeG. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00329-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawadi, Z.; Alsultan, A.; Alsallami, D.; Alnomasy, S.; Alqasmi, M.; Almufarriji, F.; Alotaibi, B.; Mazhari, B.; Alenazy, R. Designing a Multiepitope MRNA—Based Vaccine against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infection in Calves: Immuno-Informatics and Molecular Modelling Approach. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rando, H.M.; Lordan, R.; Kolla, L.; Sell, E.; Lee, A.J.; Wellhausen, N.; Naik, A.; Kamil, J.P. COVID-19 Review Consortium The Coming of Age of Nucleic Acid Vaccines during COVID-19. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, A.J.; Jiang, A.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wooster, R.; Anderson, D.G. The Clinical Progress of MRNA Vaccines and Immunotherapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, R.I.; Bourgeois, A.L. Oral Inactivated Whole Cell Vaccine for Mucosal Immunization: ETVAX Case Study. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1125102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westcott, M.M.; Blevins, M.; Wierzba, T.F.; Morse, A.E.; White, K.R.; Sanders, L.A.; Sanders, J.W. The Immunogenicity and Properties of a Whole-Cell ETEC Vaccine Inactivated with Psoralen and UVA Light in Comparison to Formalin. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Pathotype | Incidence | Duration of Illness | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| ETEC | 220 million cases annually, 75 million episodes in children under 5 in LMICs | 1–5 days | Watery diarrhea, sometimes severe, could be accompanied by fever and vomiting |
| STEC (EHEC) | 2.5 million cases annually; linked to major outbreaks in industrialized countries | 5–7 days | Mild to severe watery diarrhea, may progress to bloody diarrhea. Can advance to HUS |
| EPEC | Responsible for 81 million cases annually in LMICs | 12 days | Mild to severe watery diarrhea, can be persistent |
| EAEC | Limited epidemiological data | 3–14 days | Watery diarrhea with mucus, occasionally bloody |
| EIEC | Less frequent; associated with regions with poor hygiene | 4–7 days | Watery diarrhea, may progress to bloody (dysentery-like syndrome) |
| DAEC | Limited epidemiological data | Unknown | Watery diarrhea in children (3–5 years) |
| AIEC | Limited epidemiological data, associated with Crohn’s disease | Unknown | Intestinal inflammation |
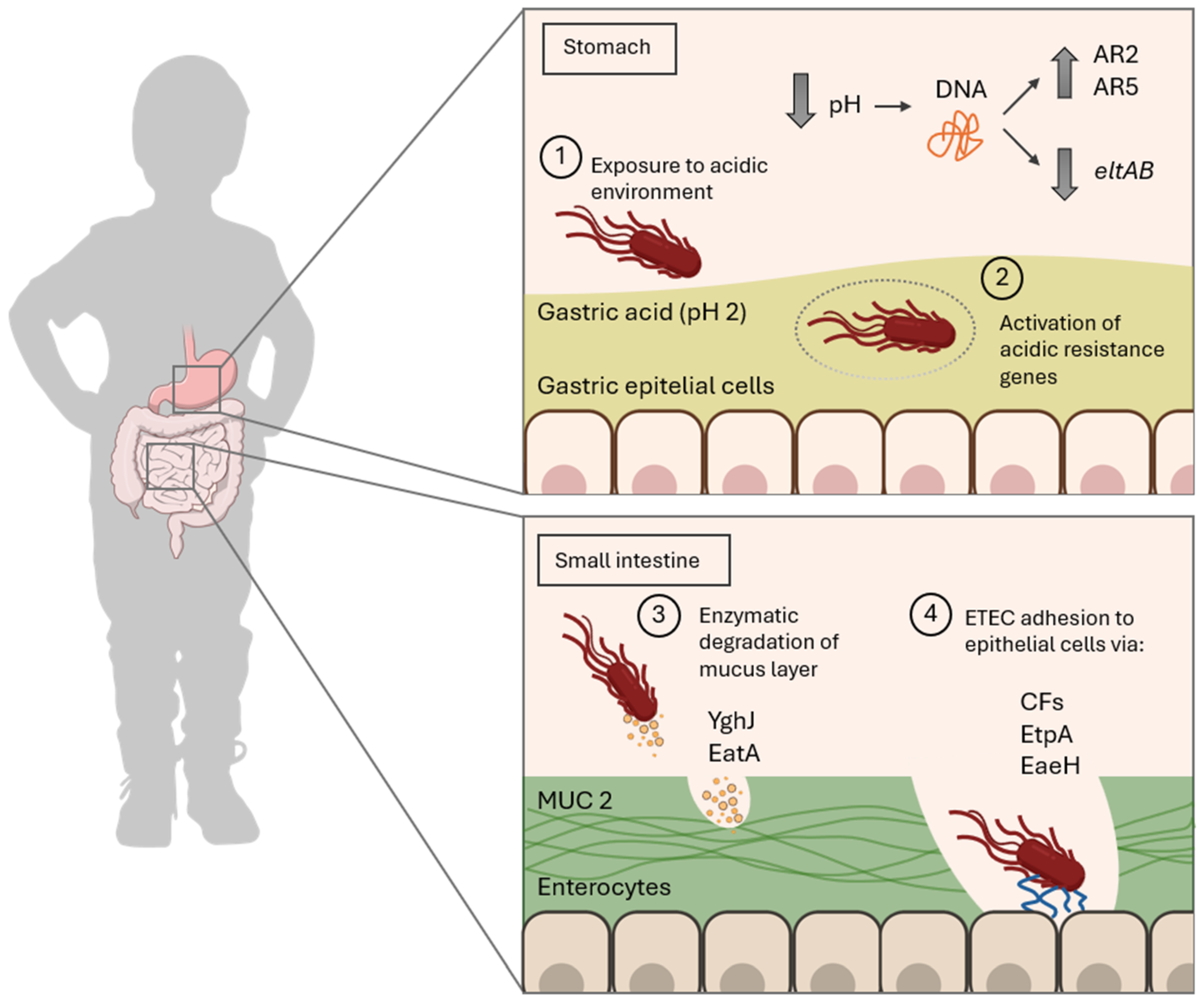
| Stage of the Infection Cycle | Virulence Factor or System | Genes Involved | Function and Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survival in the Acidic Environment | AR1 | Unknown | Activated by the alternative sigma factor σS, regulates the expression of genes involved in the AR2 system. |
| AR2 (GDAR) | gadABC, gadEWX, ybaST | Neutralizes acidic pH through glutamate decarboxylation to GABA, helping maintain cellular stability. | |
| Penetration of the Mucus Layer | YghJ (SsIE) | yghJ | Mucinase secreted by T2SS that degrades MUC2. |
| EatA | eatA | SPATE autotransporter protein that degrades MUC2 and EtpA. | |
| SepA | sepA | Homolog of EatA in Shigella flexneri, degrades MUC2 in the colon and facilitates invasion. | |
| Adherence to Intestinal Epithelium | Colonization factors (CFs) | cfaA, cfaB, cs1, cs2, cs3 | Fimbriae interacting with glycoproteins, fibronectin, and sulfatides on enterocytes. |
| EtpA | etpA | Adhesin that connects flagella to GalNAc on host glycoproteins. | |
| EaeH | eaeH | Outer membrane protein involved in adhesion. | |
| Toxin Secretion | LT (heat-labile toxin) | eltA, eltB | AB5 toxin. Increase intracellular cAMP levels. |
| ST (heat-stable toxin) | estA, estB | Toxins that increase intracellular cGMP by activating guanylate cyclase C. | |
| EAST-1 (enteroaggregative heat-stable enterotoxin) | astA | Increase intracellular cGMP. | |
| HlyA (hemolysin A) | hlyCABD | Generate pores in the host cell membrane. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salvador-Erro, J.; Pastor, Y.; Gamazo, C. Targeting Enterotoxins: Advancing Vaccine Development for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli ETEC. Toxins 2025, 17, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020071
Salvador-Erro J, Pastor Y, Gamazo C. Targeting Enterotoxins: Advancing Vaccine Development for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli ETEC. Toxins. 2025; 17(2):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020071
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalvador-Erro, Josune, Yadira Pastor, and Carlos Gamazo. 2025. "Targeting Enterotoxins: Advancing Vaccine Development for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli ETEC" Toxins 17, no. 2: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020071
APA StyleSalvador-Erro, J., Pastor, Y., & Gamazo, C. (2025). Targeting Enterotoxins: Advancing Vaccine Development for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli ETEC. Toxins, 17(2), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020071





