Occurrence of Co-Contamination and Interaction of Multi-Mycotoxins in Dairy Cow Feed in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Performance of the Applied Analytical Method
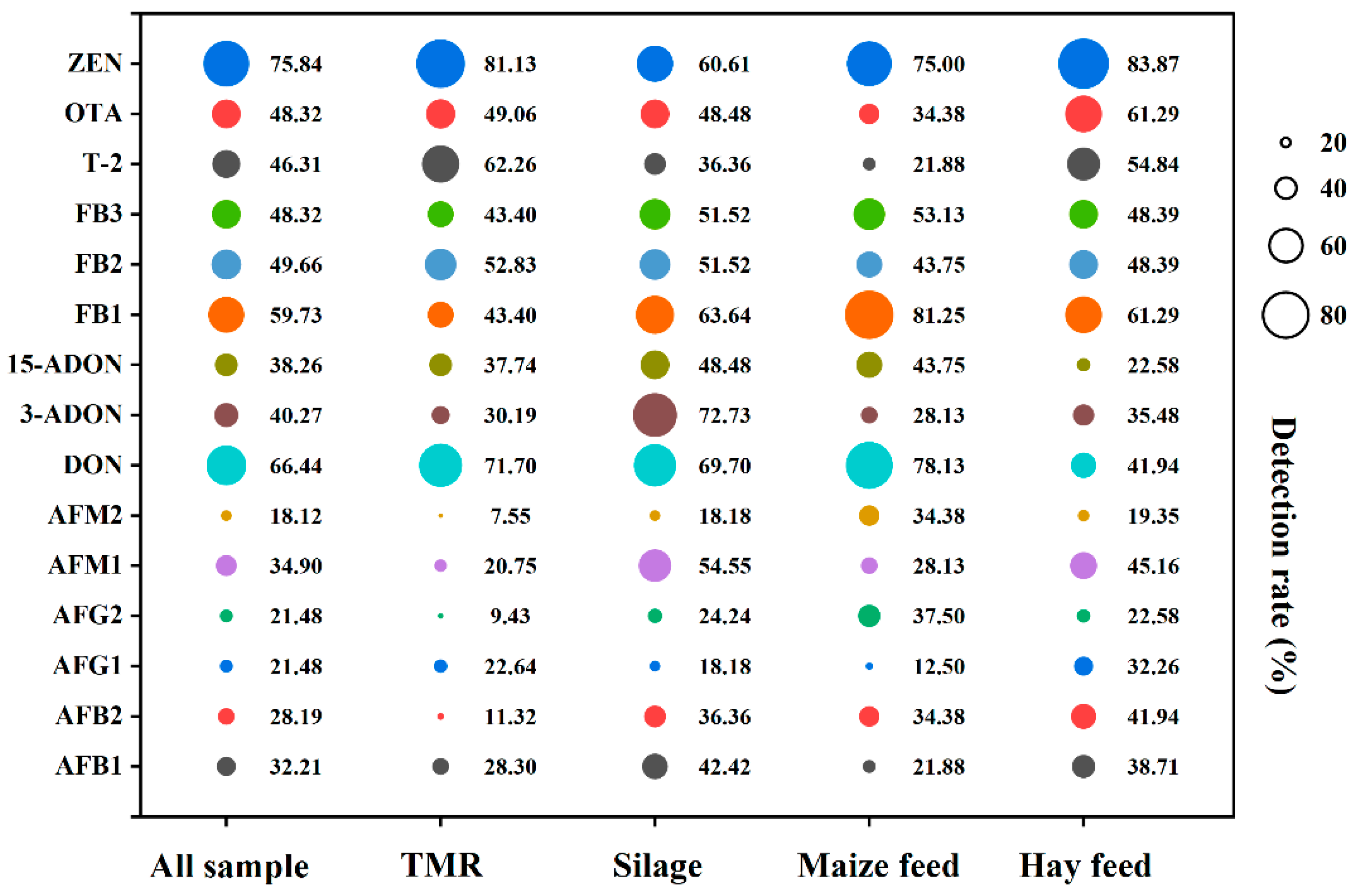
2.2. Occurrence of Multiple Mycotoxins
2.3. Contamination Levels of Mycotoxins
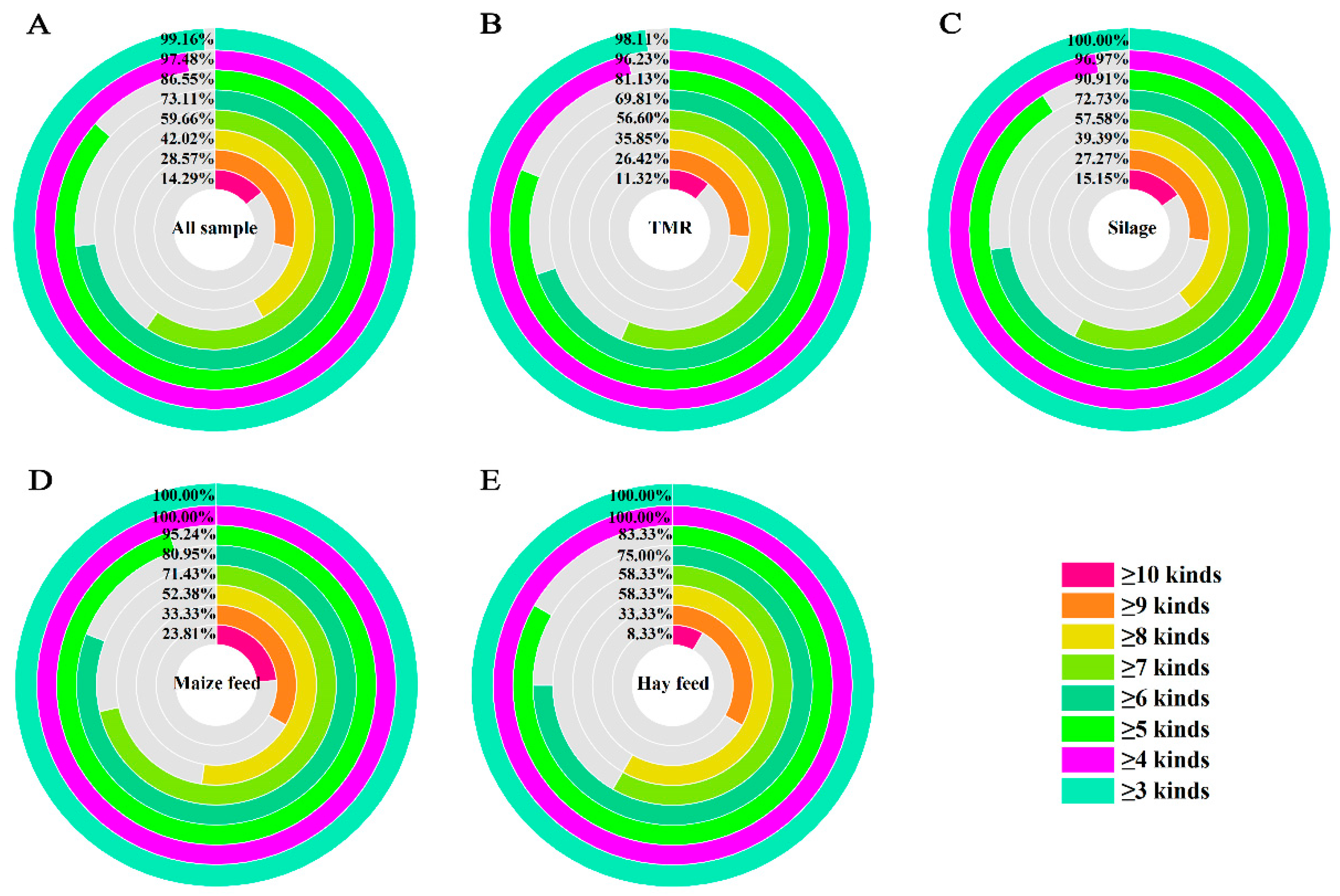
2.4. Combined Contamination of Mycotoxins
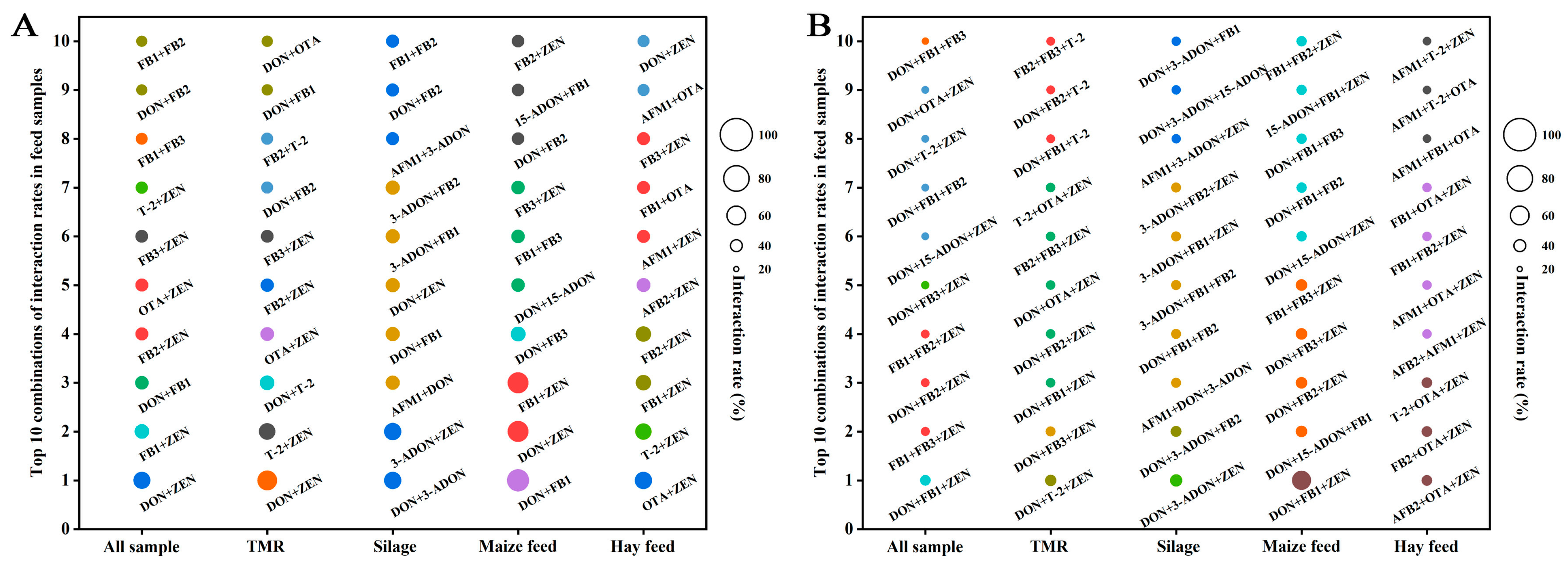
2.5. Correlation Analysis of Mycotoxins
2.6. Interaction Analysis of Mycotoxins
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Sampling
5.2. Chemicals and Reagents
5.3. Sample Extraction
5.4. UPLC-MS/MS Conditions
5.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Xu, H.; Lv, M.; Hu, D.; He, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Y. Challenges to improve the safety of dairy products in China. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 76, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayulu, H. Role of Animal Husbandry Nutrition Science on Feed, Food and Environment Safety. Tech. BioChemMed 2023, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, J.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Ruiz, M.J.; Vila-Donat, P. Multi-mycotoxin occurrence in feed, metabolism and carry-over to animal-derived food products: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 158, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Pereira, C.; CCunha, S.; Fernandes, J.O. Prevalent Mycotoxins in Animal Feed: Occurrence and Analytical Methods. Toxins 2019, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.; Naehrer, K. Prevalence of mycotoxins in feedstuffs and feed surveyed worldwide in 2009 and 2010. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2012, 51, 175–192. [Google Scholar]
- Streit, E.; Naehrer, K.; Rodrigues, I.; Schatzmayr, G. Mycotoxin occurrence in feed and feed raw materials worldwide: Long-term analysis with special focus on Europe and Asia. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2892–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, C.T.; Connolly, L.; Kolawole, O. Potential adverse effects on animal health and performance caused by the addition of mineral adsorbents to feeds to reduce mycotoxin exposure. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink-Gremmels, J. The role of mycotoxins in the health and performance of dairy cows. Vet. J. 2008, 176, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duringer, J.; Roberts, H.L.; Doupovec, B.; Faas, J.; Estill, C.T.; Jiang, D.; Schatzmayr, D. Effects of deoxynivalenol and fumonisins fed in combination on beef cattle: Health and performance indices. World Mycotoxin J. 2020, 13, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ogunade, I.; Vyas, D.; Adesogan, A. Aflatoxin in Dairy Cows: Toxicity, Occurrence in Feedstuffs and Milk and Dietary Mitigation Strategies. Toxins 2021, 13, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xie, M.; Wei, D. Biological Detoxification of Mycotoxins: Current Status and Future Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Solano, B.; González-Peñas, E. Mycotoxin Determination in Animal Feed: An LC-FLD Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Aflatoxins, Ochratoxins and Zearelanone in This Matrix. Toxins 2020, 12, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaičiulienė, G.; Bakutis, B.; Jovaišienė, J.; Falkauskas, R.; Gerulis, G.; Kerzienė, S.; Baliukonienė, V. Prevalence of Mycotoxins and Endotoxins in Total Mixed Rations and Different Types of Ensiled Forages for Dairy Cows in Lithuania. Toxins 2021, 13, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Cheng, T.-L.; Xu, W.; Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Fanning, S.; Li, F. Natural co-occurrence of multi-mycotoxins in unprocessed wheat grains from China. Food Control 2021, 130, 108321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y. Mycotoxins as human carcinogens—The IARC Monographs classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streit, E.; Schatzmayr, G.; Tassis, P.; Tzika, E.; Marin, D.; Taranu, I.; Tabuc, C.; Nicolau, A.; Aprodu, I.; Puel, O.; et al. Current Situation of Mycotoxin Contamination and Co-occurrence in Animal Feed—Focus on Europe. Toxins 2021, 4, 788–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Berindan–Neagoe, I.; Chedea, V.; Balacescu, L.; Brie, I.; Soritau, O.; Socaciu, C.; Irimie, A. Individual And Combined Cytotoxic Effects Of The Major Four Aflatoxins In Different In Vitro Stabilized Systems. J. Food Biochem. 2010, 34, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó-Fodor, J.; Szabó, A.; Kócsó, D.J.; Marosi, K.; Bóta, B.; Kachlek, M.; Mézes, M.; Balogh, K.M.; Kövér, G.; Nagy, I. Interaction between the three frequently co-occurring Fusarium mycotoxins in rats. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 103, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblad, M.; Gidlund, A.; Sulyok, M.; Börjesson, T.; Krska, R.; Olsen, M.; Fredlund, E. Deoxynivalenol and other selected Fusarium toxins in Swedish wheat—Occurrence and correlation to specific Fusarium species. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 167, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizachew, D.; Szonyi, B.; Tegegne, A.; Hanson, J.; Grace, D. Aflatoxin contamination of milk and dairy feeds in the Greater Addis Ababa milk shed, Ethiopia. Food Control 2016, 59, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber-Dorninger, C.; Jenkins, T.; Schatzmayr, G. Global Mycotoxin Occurrence in Feed: A Ten-Year Survey. Toxins 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bbosa, G.S.; Kitya, D.; Lubega, A.; Ogwal-Okeng, J.; Anokbonggo, W.W.; Kyegombe, D.B. Review of the Biological and Health Effects of Aflatoxins on Body Organs and Body Systems. Aflatoxins—Recent Adv. Future Prospect. 2013, 25, 239–265. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi Shad, Z.; Ghavami, M.; Atungulu, G. Occurrence of Aflatoxin in Dairy Cow Feed Ingredients and Total Mixed Ration. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2019, 35, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Blanco, M.; Ramos, A.J.; Prim, M.; Sanchis, V.; Marín, S. Usefulness of the analytical control of aflatoxins in feedstuffs for dairy cows for the prevention of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bervis, N.; Lorán, S.; Juan, T.; Carramiñana, J.J.; Herrera, A.; Ariño, A.; Herrera, M. Field Monitoring of Aflatoxins in Feed and Milk of High-Yielding Dairy Cows under Two Feeding Systems. Toxins 2021, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambacq, E.; Vanhoutte, I.; Audenaert, K.; Gelder, L.; Haesaert, G. Occurrence, prevention and remediation of toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins in silage: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 96, 2284–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Wang, C.; Sun, L.; Xu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Na, N.; Yin, G.; Liu, S.; Xue, Y. Dynamics of Bacterial and Fungal Communities and Metabolites During Aerobic Exposure in Whole-Plant Corn Silages with Two Different Moisture Levels. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 663895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Giuberti, G.; Frisvad, J.; Bertuzzi, T.; Nielsen, K. Review on Mycotoxin Issues in Ruminants: Occurrence in Forages, Effects of Mycotoxin Ingestion on Health Status and Animal Performance and Practical Strategies to Counteract Their Negative Effects. Toxins 2015, 7, 3057–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleadin, J.; Vulić, A.; Zadravec, M.; Lešić, T.; Benič, M.; Tkalec, V.J.; Vahčić, N. Presence of Fusarium mycotoxins in feedstuffs and cow milk sampled from Croatian farms during 2015. Mljekarstvo 2017, 67, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, T.; Hawkey, R.; Higgie, E.; Lee, M.; Mee, E.; Parfitt, D.; Raj, J.; Roderick, S.; Walker, N.; Ward, P.; et al. Silage and total mixed ration hygienic quality on commercial farms: Implications for animal production. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 72, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monbaliu, S.; Van Poucke, C.; Detavernier Cl Dumoulin, F.; Van De Velde, M.; Schoeters, E.; Van Dyck, S.; Averkieva, O.; Van Peteghem, C.; De Saeger, S. Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Feed as Analyzed by a Multi-Mycotoxin LC-MS/MS Method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Z. Natural Occurrence of Deoxynivalenol and Its Acetylated Derivatives in Chinese Maize and Wheat Collected in 2017. Toxins 2020, 12, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Blanco, M.; Marín, S.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.J. Fusarium mycotoxins in total mixed rations for dairy cows. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.A.M.; González Pereyra, M.L.; Keller, K.M.; Alonso, V.A.; Oliveira, A.A.; Almeida, T.X.; Barbosa, T.S.; Nunes, L.M.T.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Rosa, C.A.R. Fungal and mycotoxins contamination in corn silage: Monitoring risk before and after fermentation. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2013, 52, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.T.; Petta, T.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Bordin, K.; Gomes, G.A.; Oliveira, C.A.F. Co-occurrence of mycotoxins in maize food and maize-based feed from small-scale farms in Brazil: A pilot study. Mycotoxin Res. 2019, 35, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Gong, M.; Yin, Y.; Huang, R.; Ruan, Z.; Zhou, T.; Xie, M. Occurrence of mycotoxins in feeds and feed ingredients in China. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2011, 9, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Guo, W.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Abdallah, M.F.; Zhou, X.; Lei, H.; Tu, W.; Wang, H.; et al. Co-contamination and interactions of multiple mycotoxins and heavy metals in rice, maize, soybeans, and wheat flour marketed in Shanghai City. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twarużek, M.; Skrzydlewski, P.; Kosicki, R.; Grajewski, J. Mycotoxins survey in feed materials and feedingstuffs in years 2015–2020. Toxicon 2021, 202, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachariasova, M.; Dzuman, Z.; Veprikova, Z.; Hajkova, K.; Jiru, M.; Vaclavikova, M.; Zachariasova, A.; Pospichalova, M.; Florian, M.; Hajslova, J. Occurrence of multiple mycotoxins in European feedingstuffs, assessment of dietary intake by farm animals. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 193, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckard, S.; Wettstein, F.E.; Forrer, H.-R.; Vogelgsang, S. Incidence of Fusarium Species and Mycotoxins in Silage Maize. Toxins 2011, 3, 949–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusilier, K.; Chilvers, M.I.; Limay-Rios, V.; Singh, M.P. Mycotoxin Co-Occurrence in Michigan Harvested Maize Grain. Toxins 2022, 14, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borutova, R.; Aragon, Y.A.; Nährer, K.; Berthiller, F. Co-occurrence and statistical correlations between mycotoxins in feedstuffs collected in the Asia–Oceania in 2010. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 178, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Han, X.; Li, F. Co-occurrence of multi-mycotoxins in wheat grains harvested in Anhui province, China. Food Control 2019, 96, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Kersten, S.; Meyer, U.; Engelhardt, U.; Dänicke, S. Residues of zearalenone (ZEN), deoxynivalenol (DON) and their metabolites in plasma of dairy cows fed Fusarium contaminated maize and their relationships to performance parameters. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.N.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zheng, N. Aflatoxin M1 cytotoxicity against human intestinal Caco-2 cells is enhanced in the presence of other mycotoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Zhang, N.; Qi, D. In vitro investigation of individual and combined cytotoxic effects of aflatoxin B1 and other selected mycotoxins on the cell line porcine kidney 15. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mycotoxins | Linearity Range (μg/kg) | R2 | LOQ (μg/kg) | LOD (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | 0.1–100 | 0.9985 | 0.1 | 0.06 |
| AFB2 | 0.1–100 | 0.9965 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| AFG1 | 0.1–100 | 0.9924 | 0.1 | 0.04 |
| AFG2 | 0.1–100 | 0.9949 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| AFM1 | 0.1–200 | 0.9976 | 0.1 | 0.07 |
| AFM2 | 0.1–200 | 0.9992 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| DON | 10–200 | 0.9988 | 10 | 5.3 |
| 3-ADON | 5–200 | 0.9969 | 5 | 2.4 |
| 15-ADON | 5–200 | 0.9921 | 5 | 2.5 |
| FB1 | 1–200 | 0.9952 | 1 | 0.48 |
| FB2 | 5–200 | 0.9934 | 5 | 2.6 |
| FB3 | 5–200 | 0.9926 | 5 | 2.1 |
| T-2 | 0.1–200 | 0.9969 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| OTA | 0.2–200 | 0.9988 | 0.2 | 0.16 |
| ZEN | 0.5–200 | 0.9979 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Mycotoxins | TMR (%) | Silage (%) | Maize Feed (%) | Hay Feed (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | 70.7 ± 2.6 | 82.1 ± 2.9 | 98.3 ± 7.1 | 110.2 ± 9.8 |
| AFB2 | 96.9 ± 7.8 | 110.2 ± 2.3 | 112.5 ± 8.6 | 90 ± 7.3 |
| AFG1 | 77.3 ± 9.3 | 113.6 ± 4.5 | 117.4 ± 9.1 | 149.1 ± 5.4 |
| AFG2 | 88.6 ± 6.8 | 86.9 ± 8.4 | 89.6 ± 6.3 | 79.7 ± 6.1 |
| AFM1 | 149.8 ± 4.1 | 78.3 ± 3.1 | 99.4 ± 4.1 | 89.9 ± 2.8 |
| AFM2 | 106.3 ± 6.7 | 113.4 ± 2.6 | 87.5 ± 4.2 | 73.8 ± 2.6 |
| DON | 80.2 ± 5.1 | 86.3 ± 1.9 | 149.4 ± 8.9 | 118.1 ± 5.8 |
| 3-ADON | 98.7 ± 1.9 | 108.7 ± 4.5 | 110.8 ± 7.7 | 108.4 ± 4.7 |
| 15-ADON | 110.2 ± 7.6 | 1.8.2 ± 5.9 | 79.7 ± 5.6 | 116.3 ± 6.7 |
| FB1 | 117.8 ± 2.5 | 118.4 ± 5.4 | 82.9 ± 4.2 | 107.5 ± 5.9 |
| FB2 | 80.9 ± 5.4 | 110.1 ± 7.1 | 88.8 ± 6.7 | 80.9 ± 4.8 |
| FB3 | 90.8 ± 3.7 | 89.5 ± 4.8 | 112.6 ± 2.1 | 90.4 ± 6.1 |
| T-2 | 110.5 ± 4.1 | 97.6 ± 0.9 | 89.5 ± 3.5 | 118.8 ± 6.2 |
| OTA | 107.1 ± 9.4 | 99.7 ± 4.8 | 88.3 ± 2.7 | 103.5 ± 7.2 |
| ZEN | 99.4 ± 4.6 | 94.6 ± 6.2 | 91.6 ± 9.8 | 82.9 ± 9.1 |
| Mycotoxins (μg/kg) | TMR (n = 53) | Silage (n = 33) | Maize Feed (n = 32) | Hay Feed (n = 31) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Range | Average | Range | Average | Range | Average | Range | |
| AFB1 | 0.20 | 0.12~1.33 | 3.53 | 0.16~53.69 | 0.10 | 0.13~0.72 | 0.38 | 0.13~4.35 |
| AFB2 | 0.64 | 0.67~12.29 | 2.16 | 0.32~26.32 | 0.81 | 0.06~8.58 | 0.46 | 0.08~6.21 |
| AFG1 | 0.92 | 0.38~14.32 | 0.44 | 0.48~8.62 | 0.25 | 0.44~3.28 | 0.41 | 0.14~2.71 |
| AFG2 | 0.13 | 0.49~2.12 | 0.39 | 0.13~3.83 | 1.14 | 0.08~14.55 | 0.27 | 0.14~5.42 |
| AFM1 | 2.97 | 0.53~36.22 | 9.52 | 0.14~57.37 | 8.88 | 0.13~93.99 | 3.32 | 0.19~47.76 |
| AFM2 | 0.25 | 0.28~6.49 | 1.74 | 0.16~18.52 | 1.38 | 0.13~16.27 | 0.36 | 0.12~3.79 |
| DON | 32.63 | 0.16~328.25 | 10.14 | 0.26~75.35 | 36.75 | 0.14~348.69 | 10.82 | 6.36~58.79 |
| 3-ADON | 14.05 | 0.69~285.90 | 77.65 | 0.14~725.78 | 23.12 | 0.36~476.24 | 6.81 | 0.76~94.82 |
| 15-ADON | 11.41 | 2.42~149.94 | 13.68 | 0.13~142.18 | 16.30 | 2.11~137.88 | 4.39 | 2.94~54.94 |
| FB1 | 142.81 | 1.18~1347.28 | 62.40 | 1.15~743.30 | 58.28 | 2.37~430.79 | 70.24 | 0.24~584.06 |
| FB2 | 7.16 | 0.35~58.52 | 13.21 | 0.25~252.47 | 7.03 | 0.13~69.87 | 21.38 | 0.34~186.69 |
| FB3 | 5.04 | 0.42~45.89 | 8.08 | 0.13~53.92 | 12.20 | 1.38~63.87 | 12.14 | 0.42~100.83 |
| T-2 | 1.25 | 0.12~27.74 | 0.20 | 0.12~1.37 | 0.66 | 0.22~16.19 | 1.04 | 0.13~11.88 |
| OTA | 0.59 | 0.14~6.19 | 1.63 | 0.14~29.48 | 3.03 | 0.17~85.43 | 2.53 | 0.38~53.22 |
| ZEN | 70.61 | 0.63~696.18 | 14.86 | 2.32~61.14 | 11.82 | 0.08~51.67 | 13.94 | 0.27~198.33 |
| Amount of Toxins | Number of Combinations | Toxin Combination (Top 3 Combinations in Terms of Interaction Rate) | Frequency | Interaction Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 kinds | 1321 | DON + FB1 + FB2 + ZEN | 29 | 19.46 |
| DON + FB1 + FB3 + ZEN | 27 | 18.12 | ||
| FB1 + FB2 + FB3 + ZEN | 26 | 17.45 | ||
| 5 kinds | 2440 | DON + FB1 + FB2 + FB3 + ZEN | 19 | 12.75 |
| DON + 15-ADON + FB1 + FB2 + ZEN | 17 | 11.41 | ||
| DON + 15-ADON+ FB2 + T-2 + ZEN | 16 | 10.74 | ||
| 6 kinds | 2790 | DON + 15-ADON + FB2 + FB3 + T-2 + ZEN | 13 | 8.72 |
| DON + FB1 + FB2 + FB3 + T-2 + ZEN | 12 | 8.05 | ||
| DON + 15-ADON + FB1 + FB2 + FB3 + T-2 | 11 | 7.38 | ||
| 7 kinds | 2022 | DON + 15-ADON + FB1 + FB2 + FB3 + T-2 + ZEN | 10 | 6.71 |
| DON + 15-ADON + FB2 + FB3 + T-2 + OTA + ZEN | 8 | 5.37 | ||
| DON + FB1 + FB2 + FB3 + T-2+ OTA + ZEN | 8 | 5.37 | ||
| 8–11 kinds | 1299 | DON + 3-ADON + 15-ADON + FB1 + FB2 + FB3 + T-2 + ZEN | 6 | 4.03 |
| DON + 15-ADON + FB1 + FB2 + FB3 + T-2 + OTA + ZEN | 6 | 4.03 | ||
| DON + 3-ADON + 15-ADON + FB1 + FB2 + FB3 + T-2 + OTA | 4 | 2.68 |
| Mycotoxins | Retention Period (min) | Parent Ion (m/z) | Daughter Ion (m/z) | Impulse Voltage (ev) | Ion Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | 3.32 | 313.24 | 241.16 */284.97 | 36/22 | ES+ |
| AFB2 | 3.17 | 315.22 | 287.14 */259.12 | 28/26 | ES+ |
| AFG1 | 2.83 | 329.22 | 273.12 */229.17 | 38/22 | ES+ |
| AFG2 | 3.04 | 331.23 | 284.99 */241.10 | 42/24 | ES+ |
| AFM1 | 3.18 | 329.22 | 243.08 */199.86 | 42/26 | ES+ |
| AFM2 | 3.03 | 331.22 | 189.05 */245.09 | 40/30 | ES+ |
| DON | 1.99 | 297.1 | 249.1 */231.1 | 13/10 | ES+ |
| 3-ADON | 2.71 | 339.23 | 231.16 */213.15 | 16/12 | ES+ |
| 15-ADON | 2.66 | 356.03 | 339.02 */320.94 | 12/6 | ES+ |
| FB1 | 2.97 | 722.39 | 334.38 */352.38 | 38/34 | ES+ |
| FB2 | 3.41 | 706.39 | 336.39 */354.39 | 36/32 | ES+ |
| FB3 | 3.23 | 706.39 | 336.39 */354.39 | 36/32 | ES+ |
| T-2 | 4.78 | 484.35 | 305.18 */185.13 | 14/18 | ES+ |
| OTA | 2.90 | 404.29 | 239.03 */221.03 | 34/22 | ES+ |
| ZEN | 4.19 | 317.24 | 175.05 */131.03 | 26/24 | ES− |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J. Occurrence of Co-Contamination and Interaction of Multi-Mycotoxins in Dairy Cow Feed in China. Toxins 2025, 17, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030137
Zhu Z, Cheng H, Wang J, Ma J, Wang J, Wang H, Zhou X, Yang J. Occurrence of Co-Contamination and Interaction of Multi-Mycotoxins in Dairy Cow Feed in China. Toxins. 2025; 17(3):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030137
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zuoyin, Haisheng Cheng, Jie Wang, Junmei Ma, Jianhua Wang, Hongyang Wang, Xinli Zhou, and Junhua Yang. 2025. "Occurrence of Co-Contamination and Interaction of Multi-Mycotoxins in Dairy Cow Feed in China" Toxins 17, no. 3: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030137
APA StyleZhu, Z., Cheng, H., Wang, J., Ma, J., Wang, J., Wang, H., Zhou, X., & Yang, J. (2025). Occurrence of Co-Contamination and Interaction of Multi-Mycotoxins in Dairy Cow Feed in China. Toxins, 17(3), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030137








