Establishment and Comparison of Detection Methods for Ricin and Abrin Based on Their Depurination Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
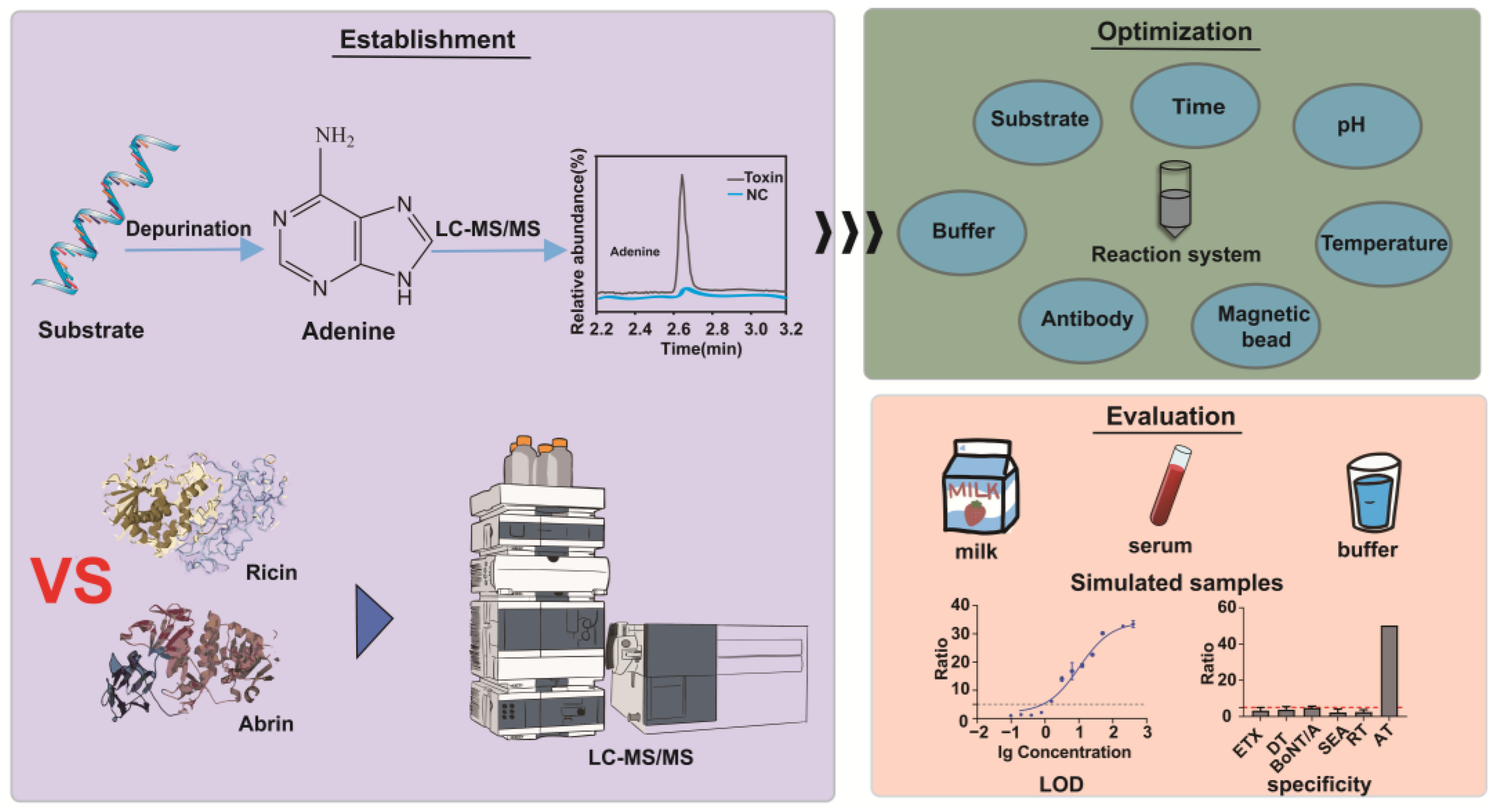
2.1. Evaluation of the Synthetic DNA and RNA Substrates of Ricin and Abrin
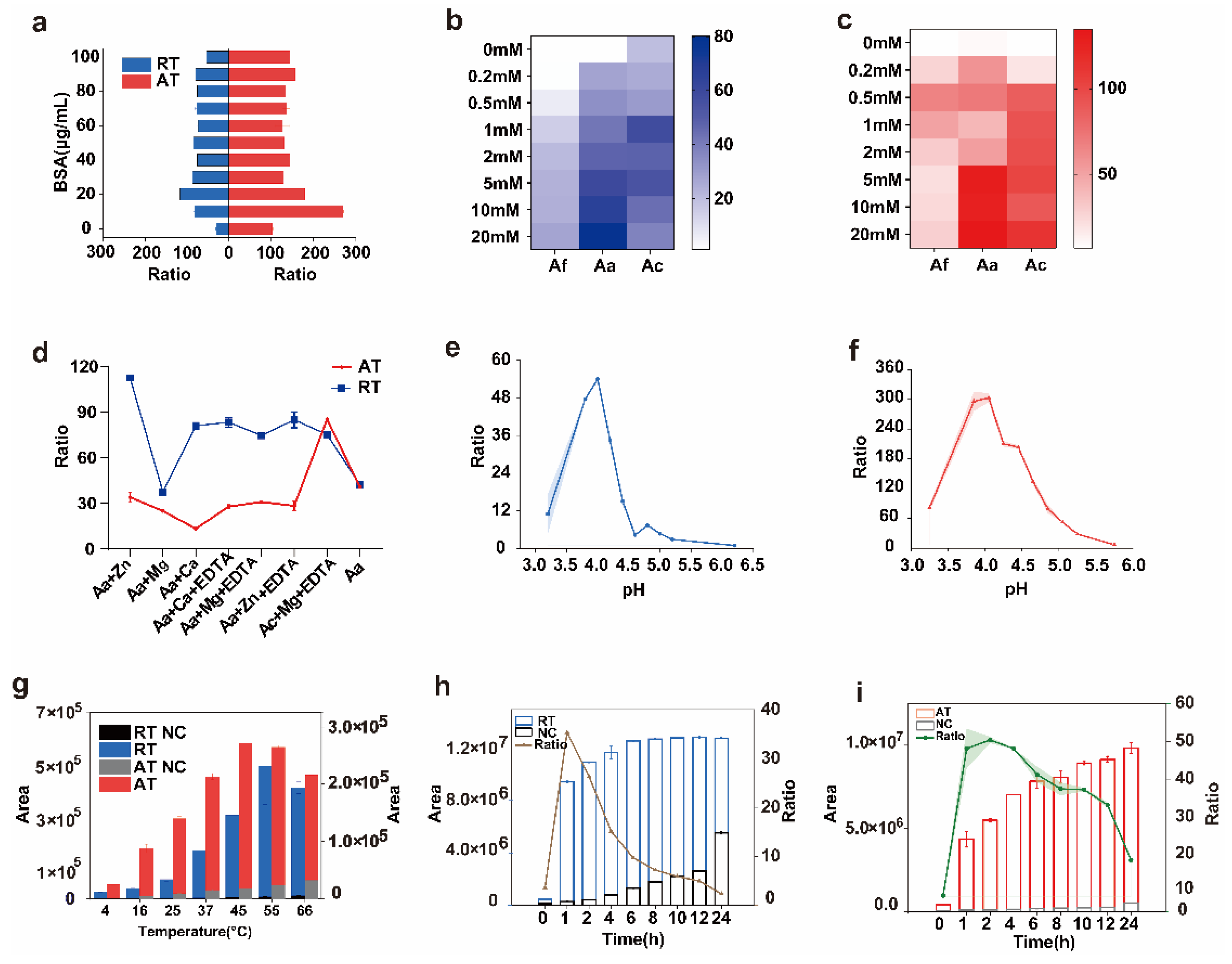
2.2. Optimization of Conditions for Ricin and Abrin Depurination Reactions
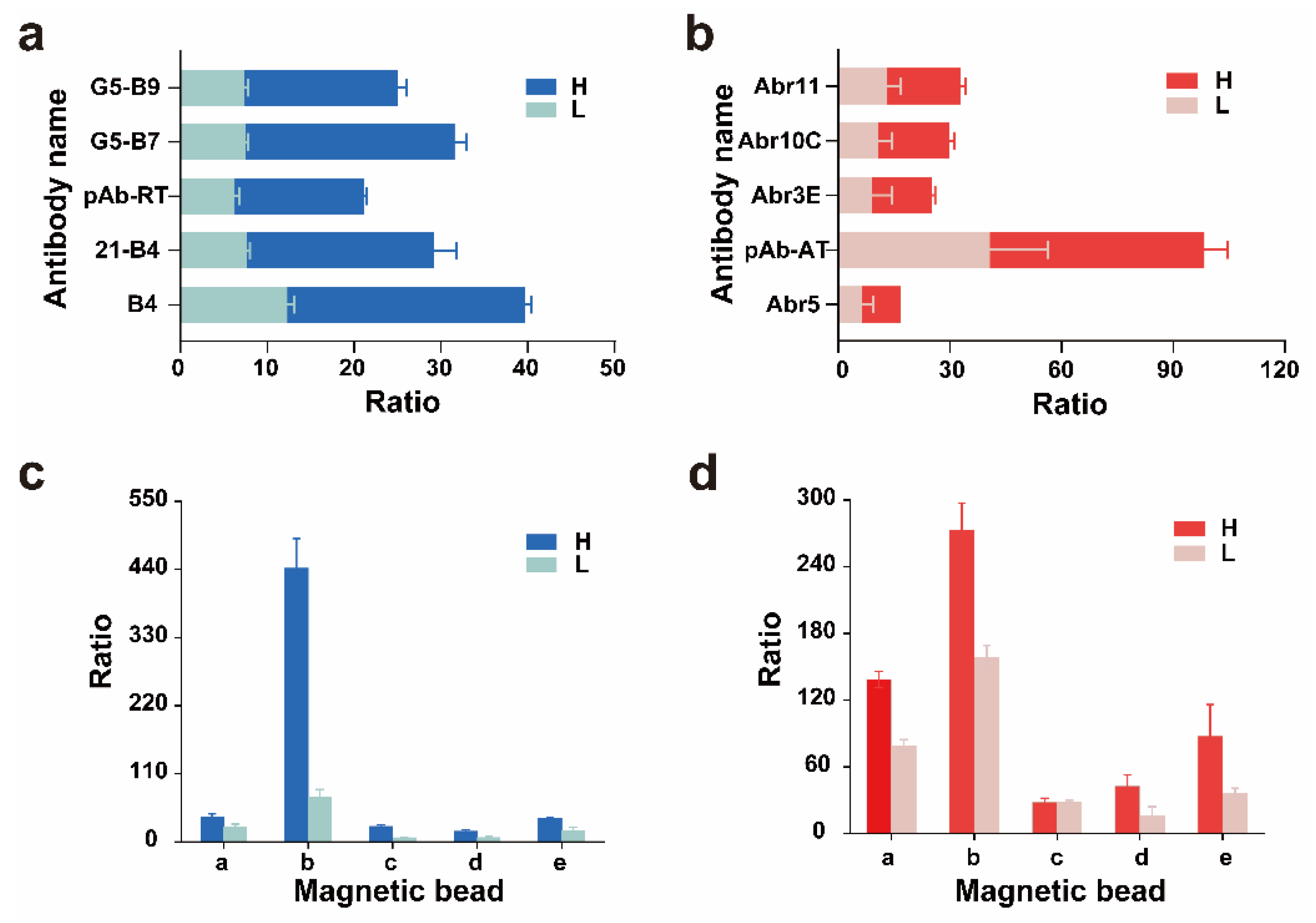
2.3. Selection of Trapping Antibodies and Magnetic Beads
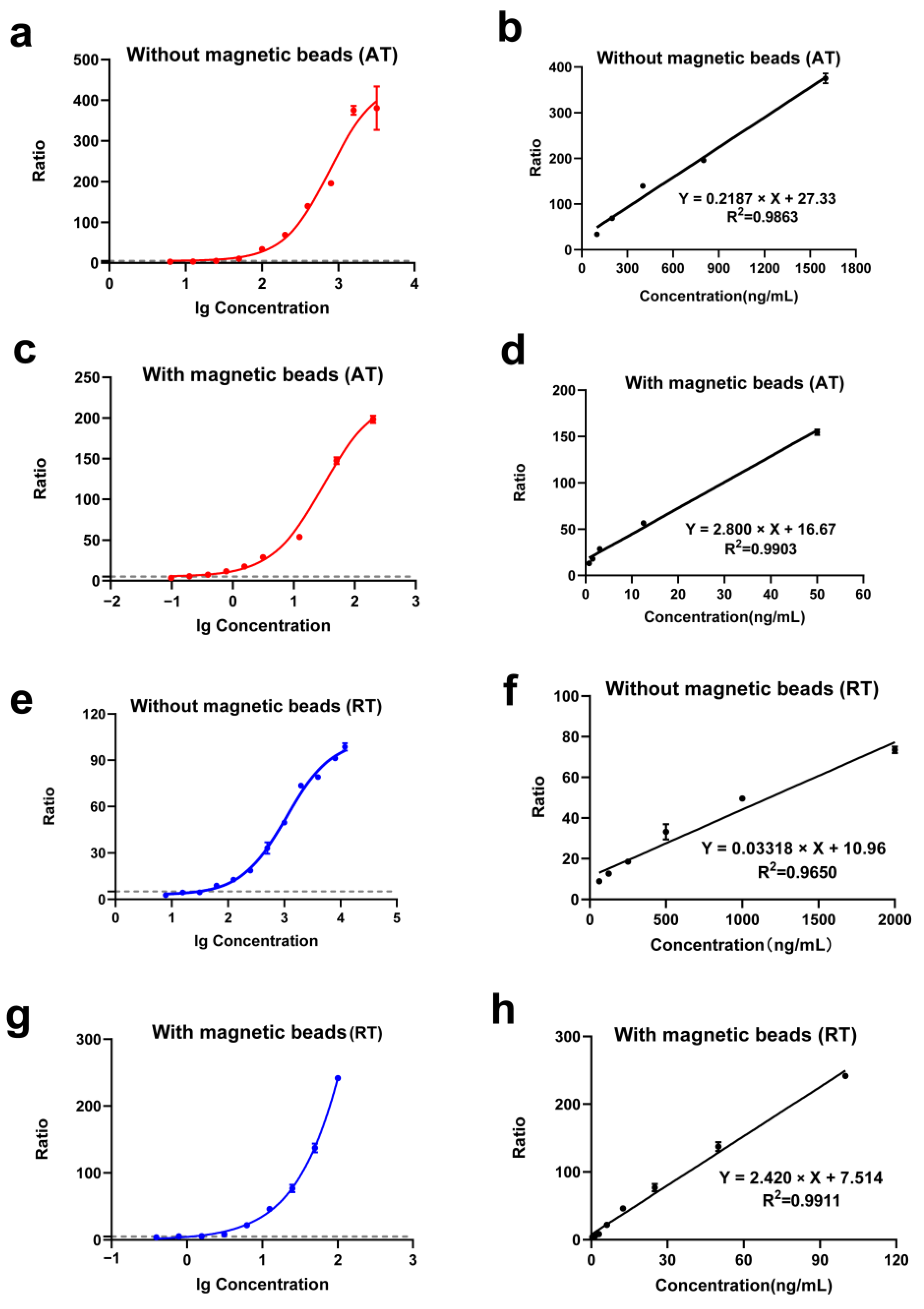
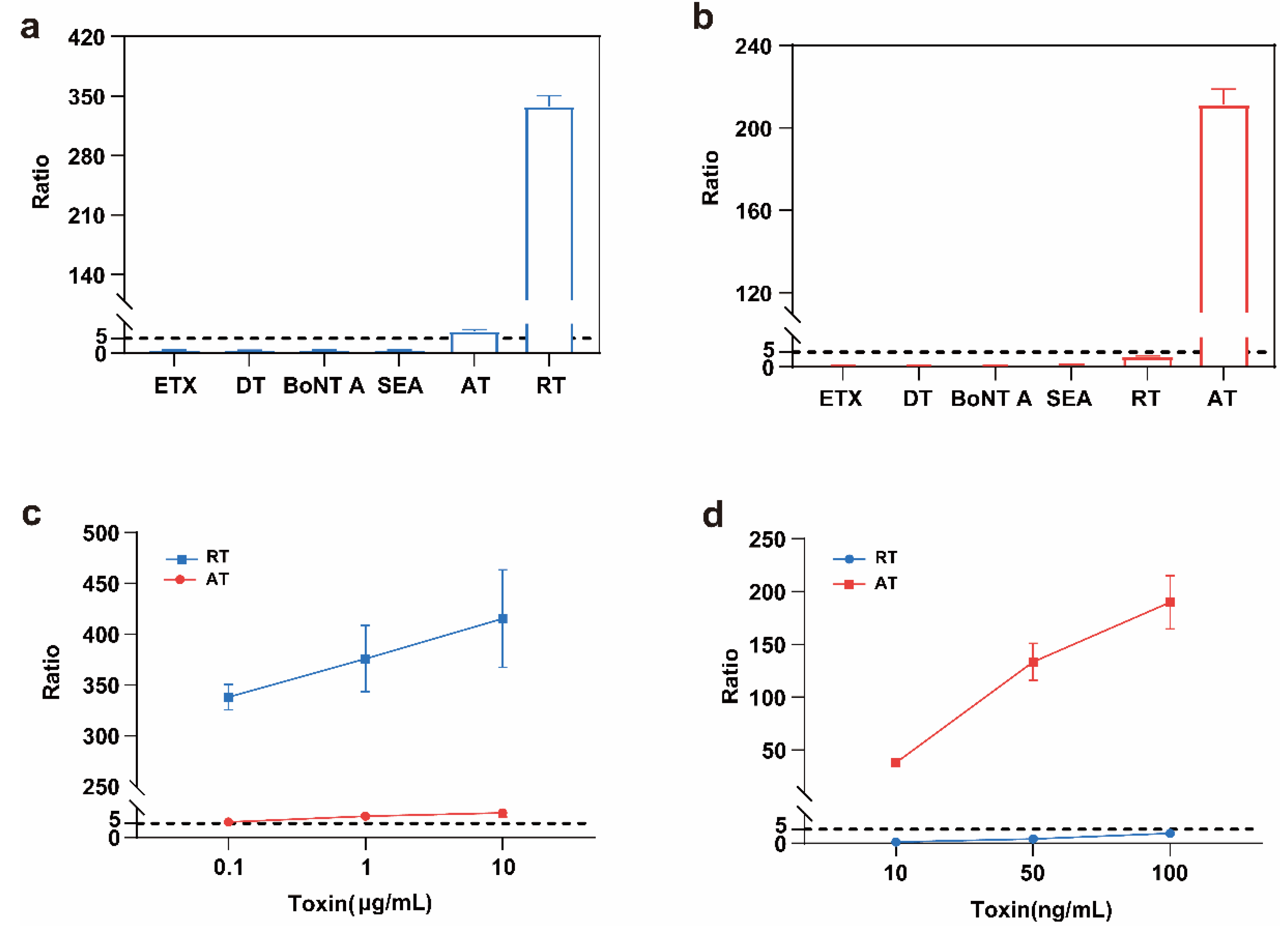
2.4. Linearity Range and Sensitivity of the Detection Method
2.5. Detection of Simulated Samples
2.6. Recovery Rates of the Detection Method
2.7. Specificity of the Detection Method
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Designs and Sequences of the Substrates
4.3. Nanobody Design and Purification
4.4. HPLC–MS/MS Analysis
4.5. Optimization of Reaction Conditions
4.6. Linearity Range and Sensitivity
4.7. Complex Matrices and Recovery Rate Detection
4.8. Evaluation of the Specificity of the Detection Method
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AT | Abrin |
| BoNT A | Botulinum toxin A |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| DT | Diphtheria toxin |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ETX | Clostridium perfringens epsilon toxin |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| MRM | Multireaction monitoring |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffer saline |
| RIP | Ribosome-inactivating protein |
| RT | Ricin |
| SEA | Staphylococcal enterotoxin A |
References
- Liang, L.H.; Xia, J.M.; Liu, C.C.; Liu, S.L. Highly toxic type II ribosome-inactivating proteins ricin and abrin and their detection methods: A review. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2021, 38, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.J.; Mantis, N.J. Progress and challenges associated with the development of ricin toxin subunit vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, E.A.E.; Walker, J.L.; O’brien, T.W. Detection of abrin in food using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and electrochemiluminescence technologies. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eric, A.E.G. Toxicity and detection of ricin and abrin in beverages. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Edyta, J.; Michal, C.; Joanna, S.-B.; Michal, B. Biological toxins as the potential tools for bioterrorism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.X.; Hu, C.Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wan, W.; Jin, Z.; Li, Y.; Xin, W.; Kang, L. A self-driven microfluidic chip for ricin and abrin detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, E.; Mossbrugger, I.; Lange, M.; Wölfel, R. Simultaneous detection of ricin and abrin DNA by real-time PCR (qpcr). Toxins 2012, 4, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.; Burkhard, M. Ricin poisoning and forensic toxicology. Drug Test. Anal. 2010, 1, 363–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilford, F.T.; Hope, J. Deficient glutathione in the pathophysiology of mycotoxin-related illness. Toxins 2014, 6, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepaper.cn. (12 December 2016). The Woman Drinking Porridge with Two “Acacia Beans” Was Almost Poisoned: Red Beans Are Highly Toxic, and There Is No Antidote. Available online: https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_1578800 (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Red Star News. (27 March 2025). Eating More Than 20 Acacia, 19 year old Man Nearly Died! The Doctor Reminded. Available online: https://news.qq.com/rain/a/20250327A0634Y00 (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Moshiri, M.; Hamid, F.; Etemad, L. Ricin toxicity: Clinical and molecular aspects. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 4, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Nie, C.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, J.; Kang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.L. Colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic test strip for rapid detection of abrin in food samples. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nandita, S.; Pooja, P.; Vinita, C. Differential toxicity of abrin in human cell lines of different organ origin. Toxicol. In Vitro 2021, 78, 237. [Google Scholar]
- Rasooly, R.; Do, P.; Hernlem, B. CCD Based detector for detection of abrin toxin activity. Toxins 2020, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, K.; Barr, J.R.; Kalb, S.R. Detection of ricin activity and structure by using novel galactose-terminated magnetic bead extraction coupled with mass spectrometric detection. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 631, 114364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.-H.; Yang, Y.; Geng, S.; Cheng, X.; Yu, H.-L.; Liu, C.-C.; Liu, S.-L. Rapid differential detection of abrin isoforms by an acetonitrile- and ultrasound-assisted on-bead trypsin digestion coupled with LC-MS/MS analysis. Toxins 2021, 13, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livet, S.; Worbs, S.; Volland, H.; Simon, S.; Dorner, M.B.; Fenaille, F.; Dorner, B.G.; Becher, F. Development and evaluation of an immuno-MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry approach for quantification of the abrin toxin in complex food matrices. Toxins 2021, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.H.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Yan, L.; Yu, H.L.; Du, B.; Liu, C.C.; Liu, S.L. An in vitro detection method for depurination activity of ricin based on a novel RNA substrate and its application. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Kaitlyn, K.D.; John, R.B.; Suzanne, R.K. Mass spectrometric detection and differentiation of enzymatically active abrin and ricin combined with a novel affinity enrichment Technique. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Baudys, J.; Barr, J.R.; Kalb, S.R. Improved sensitivity for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of active ricin by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6867–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, F.; Duriez, E.; Volland, H.; Tabet, J.C.; Ezan, E. Detection of functional ricin by immunoaffinity and liquid chromatography−tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, H.B.; Brueggemann, E.E.; Hale, M.L. High-performance liquid chromatography–mass selective detection assay for adenine released from a synthetic RNA substrate by ricin A chain. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 330, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, G.; Schneedorf, J.M. A simple, fast and portable method for electrochemical detection of adenine released by ricin enzymatic activity. Toxins 2021, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonova, M.A.; Valyakina, T.I.; Petrova, E.E.; Komaleva, R.L.; Shoshina, N.S.; Samokhvalova, L.V.; Lakhtina, O.E.; Osipov, I.V.; Philipenko, G.N.; Singov, E.K. Development of Xmap assay for detection of six protein toxins. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6326–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, S.; Olsnes, S.; Pihl, A.; Skorve, J.; Abraham, A.K. On the mechanism of protein-synthesis inhibition by abrin and ricin. inhibition of the GTP-hydrolysis site on the 60-S ribosomal subunit. Eur. J. Biochem. 1975, 59, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Dong, L.; Yue, N.; Lv, J.; Ji, B.; Xia, S.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Innovative ricin toxin detection: Unraveling apurinic/apyrimidinic lyase activity and developing fluorescence sensors. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 3608–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, L.; Jin, D.; Liu, Y. Nanobody—A versatile tool for cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Ding, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, M.; Gao, L.; Chen, Q.; Xie, S.; Liu, A.; Yin, S. Nanobody: A small antibody with big implications for tumor therapeutic strategy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2337–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, G.Q. Structural analysis of impurities in Aciclovir tablets by HPLC-MS/MS. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2024, 41, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-C.; Kang, L.; Hu, T.-M.; Wang, J.-L. Abrin-a a chain expressed as soluble form in escherichia coli from a pcr-synthesized gene is catalytically and functionally active. Biochimie 2004, 86, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P.; Zabetakis, D.; Walper, S.; Liu, J.L.; Bernstein, R.; Calm, A.; Carney, J.P.; O’Brien, T.W.; Walker, J.L. Llama-derived single domain antibodies specific for abrus agglutinin. Toxins 2011, 3, 1405–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, D.J.; Tremblay, J.M.; Mantis, N.J.; Shoemaker, C.B. Stepwise engineering of heterodimeric single domain camelid vhh antibodies that passively protect mice from ricin toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 36538–36547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, C.; Vance, D.J.; Eisele, L.E.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Mantis, N.J. Differential neutralizing activities of a single domain camelid antibody (VHH) specific for ricin toxin’s binding subunit (RTB). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.P.; Liu, J.L.; Hale, M.L.; Bernstein, R.D.; Moore, M.; Swain, M.D.; Goldman, E.R. Development of antiricin single domain antibodies toward detection and therapeutic reagents. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9604–9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walper, S.A.; Brozozog Lee, P.A.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Comparison of single domain antibody immobilization strategies evaluated by surface plasmon resonance. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 388, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Toxin | Matrices | Calibration Curve | R2 | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | Linearity Range (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrin | PBS | Y = 0.1931X + 9.972 | 0.9800 | 0.579 | 6.25 | 6.25–400 |
| Milk | Y = 0.1414X + 11.23 | 0.9550 | 1.204 | 6.25 | 6.25–400 | |
| Serum | Y = 0.1078X + 6.167 | 0.9526 | 1.458 | 3.125 | 3.125–200 | |
| Ricin | PBS | Y = 0.8550X + 7.995 | 0.9762 | 1.717 | 3.125 | 3.125–200 |
| Milk | Y = 0.3322X + 15.72 | 0.9653 | 3.984 | 12.5 | 12.5–200 | |
| Serum | Y = 0.1775X + 13.75 | 0.9332 | 3.978 | 6.25 | 6.25–100 |
| PBS | Milk | Serum | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxin | Spiked Concentration (ng/mL) | Detection Concentration (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | Detection Concentration (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | Detection Concentration (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) |
| Abrin | 50 | 48.3 | 96.6 | 54.2 | 108.4 | 50.4 | 100.7 |
| 100 | 98.5 | 98.5 | 118.8 | 118.8 | 114.4 | 114.3 | |
| 200 | 187.7 | 93.9 | 219.1 | 109.5 | 248.3 | 124.1 | |
| Ricin | 50 | 56.9 | 113.6 | 60.9 | 121.8 | 52.5 | 105.1 |
| 100 | 100.7 | 100.7 | 119.9 | 119.1 | 117.6 | 117.6 | |
| 200 | 165.3 | 82.6 | 196.7 | 101.1 | 169.8 | 84.9 | |
| Target Compound | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Production (m/z) | Fragmentor (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenine | 136 | 92 119 | 20 | 25 20 |
| Acyclovir | 226.1 | 134.9 152.05 | 12 | 18 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, L.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Lv, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Kang, L.; Xin, W. Establishment and Comparison of Detection Methods for Ricin and Abrin Based on Their Depurination Activities. Toxins 2025, 17, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040177
Dong L, Liu T, Li J, Wang C, Lv J, Wang J, Wang J, Gao S, Kang L, Xin W. Establishment and Comparison of Detection Methods for Ricin and Abrin Based on Their Depurination Activities. Toxins. 2025; 17(4):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040177
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Lina, Tingting Liu, Jiaxin Li, Cen Wang, Jing Lv, Jing Wang, Jinglin Wang, Shan Gao, Lin Kang, and Wenwen Xin. 2025. "Establishment and Comparison of Detection Methods for Ricin and Abrin Based on Their Depurination Activities" Toxins 17, no. 4: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040177
APA StyleDong, L., Liu, T., Li, J., Wang, C., Lv, J., Wang, J., Wang, J., Gao, S., Kang, L., & Xin, W. (2025). Establishment and Comparison of Detection Methods for Ricin and Abrin Based on Their Depurination Activities. Toxins, 17(4), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040177





