Toxicokinetics of a Single Oral Dose of Aflatoxin B1 in Plasma, Feces, and Urine of Male Donkeys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Detection Method Validation
2.2. Plasma Toxicokinetic Parameters of AFB1 and AFM1
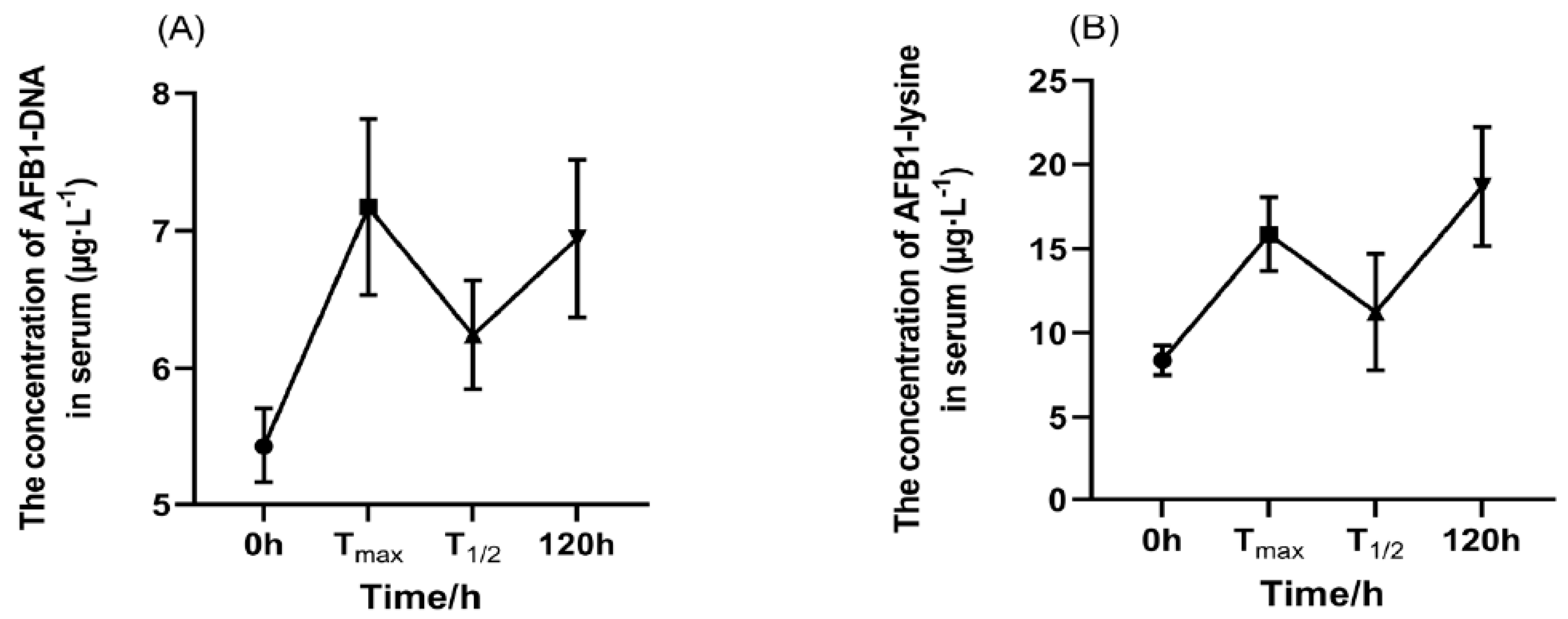
2.3. Plasma Concentration of AFB1 and AFM1
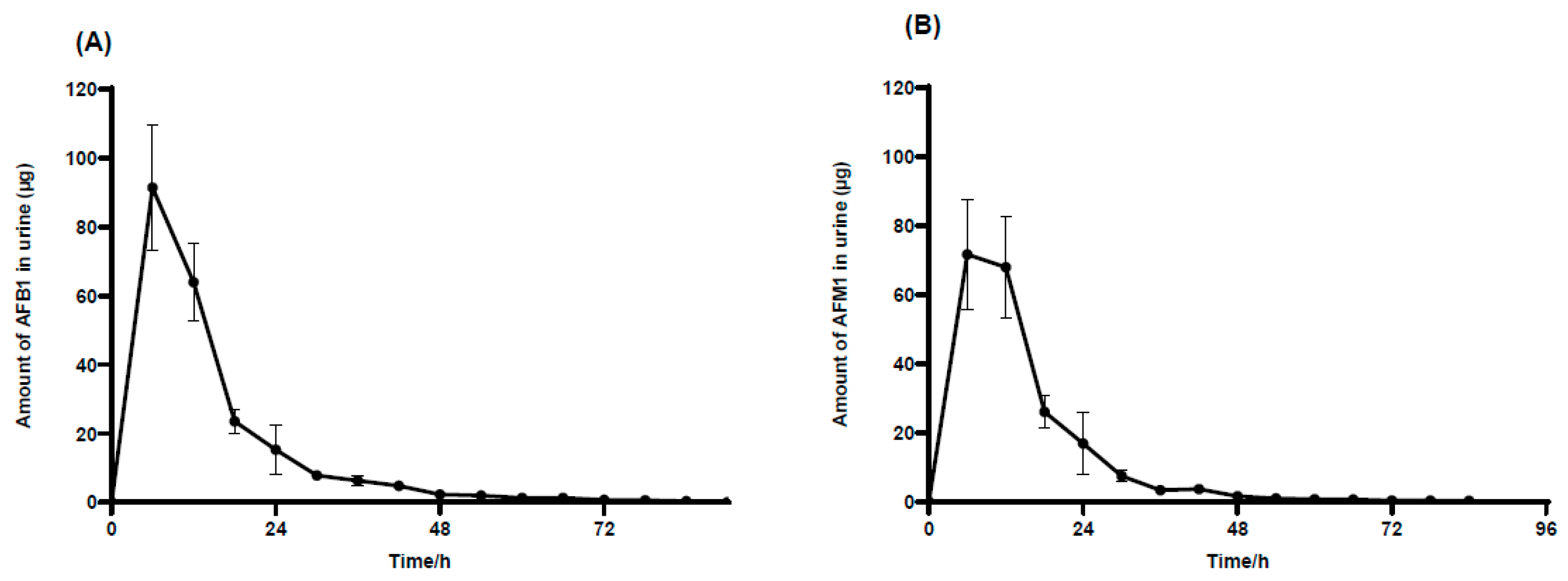
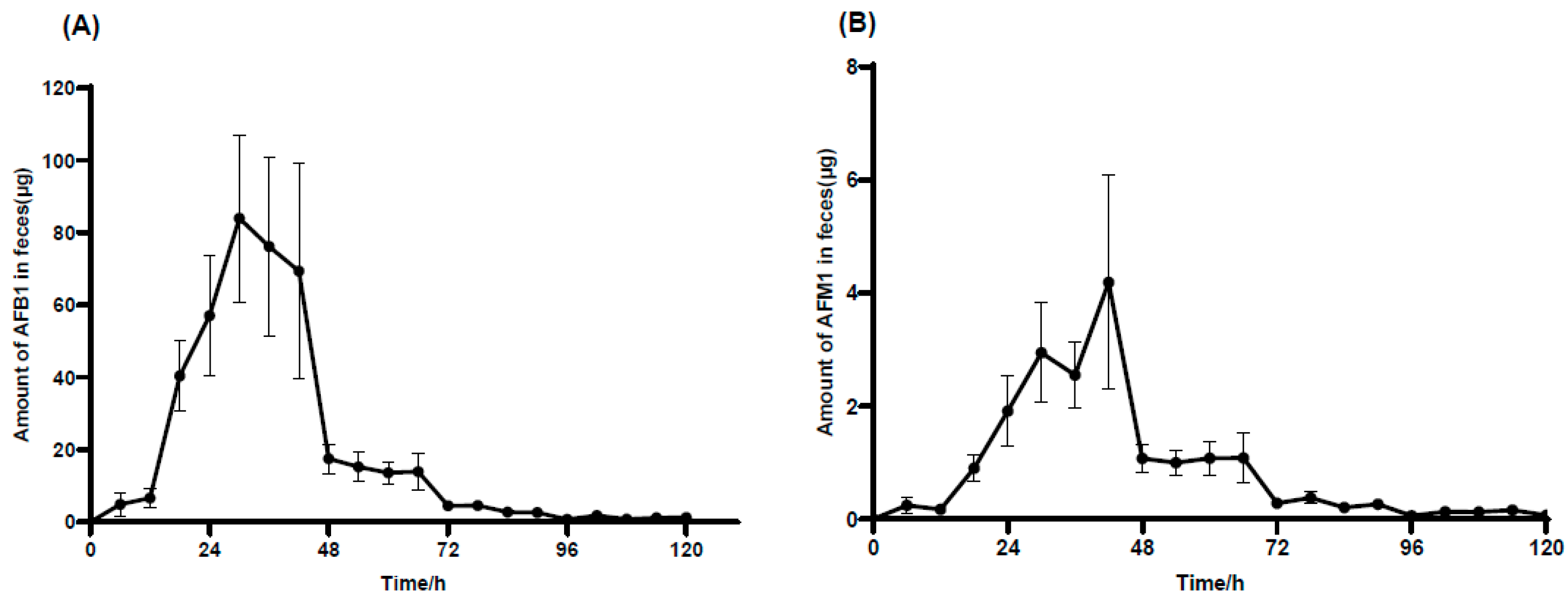
2.4. Recovery of AFB1 and AFM1 in Urine and Feces
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals, Products, and Reagents
5.2. Animal and Treatment
5.3. Sample Collection
5.4. Sample Treatment
5.5. Standard Solutions
5.6. Method Validation
5.7. UPLC-MS/MS Analysis
5.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asao, T.; Büchi, G.; Abdel-Kader, M.M.; Chang, S.B.; Wick, E.L.; Wogan, G.N.; Asao, T.; Büchi, G.; Abdel-Kader, M.M.; Chang, S.B. Aflatoxins B and G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 1706–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asao, T.; Buechi, G.; Abdelkader, M.; Chang, S.; Wick, E.; Wogan, G.; Kader, M.A.; Agerwick, E. The Structures of Aflatoxins B and G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965, 87, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Moschini, M.; Masoero, F. Aflatoxins absorption in the gastro-intestinal tract and in the vaginal mucosa in lactating dairy cows. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 7, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaei, D.; Javanmardi, F.; Khaneghah, A.M. The global overview of the occurrence of mycotoxins in cereals: A three-year survey. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busby, W.F.; Wogan, G.N. Food-borne mycotoxins and alimentary mycotoxicoses. In Food-Borne Infections and Intoxications; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Congcong, L.; Xiangdong, L.; Jiao, W.; Xiangbo, J.; Qiuliang, X. Research progress in toxicological effects and mechanism of aflatoxin B1 toxin. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13850. [Google Scholar]
- Capriotti, A.L.; Caruso, G.; Cavaliere, C.; Foglia, P.; Samperi, R.; Laganà, A. Multiclass mycotoxin analysis in food, environmental and biological matrices with chromatography/mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2012, 31, 466–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiannikouris, A.; Jouany, J.P. Mycotoxins in feeds and their fate in animals: A review. Anim. Res. 2002, 51, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wen, T.; Cao, A.; Wang, J.; Pan, H.; Zhao, R. Bile Acids Promote Hepatic Biotransformation and Excretion of Aflatoxin B1 in Broiler Chickens. Toxins 2023, 15, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, A. Mycotoxins: Risks in plant, animal and human systems. AAHE-ERIC/High. Educ. Res. Rep. 2003, 9, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Lian, S.; Shen, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, C. Recombinant porcine beta defensin 2 alleviates inflammatory responses induced by Escherichia coli in IPEC-J2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziriyan, M.; Banaee, M.; Haghi, B.N.; Mohiseni, M. Effects of dietary exposure to aflatoxins on some plasma biochemical indices of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2018, 17, 487–502. [Google Scholar]
- Battacone, G.; Nudda, A.; Cannas, A.; Borlino, A.C.; Bomboi, G.; Pulina, G. Excretion of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk of Dairy Ewes Treated with Different Doses of Aflatoxin B1. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2667–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcuera, L.A.; Vettorazzi, A.; Arbillaga, L.; González-Peñas, E.; López de Cerain, A. An approach to the toxicity and toxicokinetics of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A after simultaneous oral administration to fasted F344 rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3440–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Z.A.; Hsieh, D.P.H. The comparative metabolism and toxicokinetics of aflatoxin B1 in the monkey, rat, and mouse. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1980, 55, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysewski, S.J.; Pier, A.C.; Baetz, A.L.; Cheville, N.F. Experimental equine aflatoxicosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1982, 65, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laura, G.; Walter, M.; Tecla, C.; Claudia, S.; Stefania, C.; Luciano, P. AFM1 in Milk: Physical, Biological, and Prophylactic Methods to Mitigate Contamination. Toxins 2015, 7, 4330–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Jinap, S.; Pirouz, A.A.; Faizal, A.R.A. Aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products, occurrence and recent challenges: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londoño, V.A.G.; Boasso, A.C.; Paula, M.C.Z.d.; Garcia, L.P.; Scussel, V.M.; Resnik, S.; Pacín, A. Aflatoxin M1 survey on randomly collected milk powder commercialized in Argentina and Brazil. Food Control 2013, 34, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyasathaporn, W.; Nakprasert, W. Seasonal patterns of aflatoxin Ml contamination in commercial pasteurised milk from different areas in Thailand. Food Addit. Contam. 2012, 5, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y. Mycotoxins as human carcinogens—The IARC Monographs classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosnider, H.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Banziger, M.; Bhat, R.V.; Breiman, R.; Brune, M.N.; DeCock, K.; Dilley, A.; Groopman, J.; Hell, K.; et al. Workgroup report: Public health strategies for reducing aflatoxin exposure in developing countries. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensler, T.W.; Roebuck, B.D.; Wogan, G.N.; Groopman, J.D. Aflatoxin: A 50-Year Odyssey of Mechanistic and Translational Toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120, S28–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaib, F.M.; Jolly, P.E.; Ehiri, J.E.; Jiang, Y.; Ellis, W.O.; Stiles, J.K.; Yatich, N.J.; Funkhouser, E.; Person, S.D.; Wilson, C.; et al. Association between Anemia and Aflatoxin B1 Biomarker Levels among Pregnant Women in Kumasi, Ghana. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, D.; Gallagher, E.P. Mechanisms of Aflatoxin Carcinogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 1994, 34, 135–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitomer, N.C.; Awuor, A.O.; Widdowson, M.A.; Daniel, J.H.; Sternberg, M.R.; Rybak, M.E.; Mbidde, E.K. Human aflatoxin exposure in Uganda: Estimates from a subset of the 2011 Uganda AIDS indicator survey (UAIS). Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeton, J.T.; Eddy, S. Chemical and physical characteristics of meat. In Encyclopedia of Meat Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, H.Z.; Grace, M.T.; Ndivho, N.; Nthabiseng, S.A.; Letlhogonolo, S.; Monnye, M. The Possibility of Including Donkey Meat and Milk in the Food Chain: A Southern African Scenario. Animals 2022, 12, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenqiong, C.; Jing, X.; Honglei, Q.; Qiugang, M.; Mingxia, Z.; Mengmeng, L.; Yandong, Z.; Tianqi, W.; Jingrong, G.; Huanfen, Y.; et al. Differential proteomic analysis to identify potential biomarkers associated with quality traits of Dezhou donkey meat using a data-independent acquisition (DIA) strategy. LWT 2022, 166, 113792. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, W.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Yan, M.; Zhu, M.; Gao, J.; Wang, C.; Ma, Q.; et al. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Reveals Dynamic Metabolite Changes during Early Postmortem Aging of Donkey Meat. Foods 2024, 13, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, S.; Meena, G.S.; Gautam, P.B.; Rai, D.C.; Kumari, S. A comprehensive review on donkey milk and its products: Composition, functionality and processing aspects. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 4, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Qu, H.; Guo, Y.; Ji, C.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, L.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q. Toxicokinetics of Deoxynivalenol in Dezhou Male Donkeys after Oral Administration. Toxins 2023, 15, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Qu, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fu, T.; Huang, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q. Toxicokinetics of a Single Oral Dose of OTA on Dezhou Male Donkeys. Toxins 2023, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Kang, R.; Feng, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Ji, C.; Chai, W.; Ma, Q. Toxicokinetics of Zearalenone following Oral Administration in Female Dezhou Donkeys. Toxins 2024, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Chiang, J.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Tsai, C.H. Decreased fracture incidence with traditional Chinese medicine therapy in patients with osteoporosis: A nationwide population-based cohort study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Feng, S.; Liping, G.; Baojian, H.; Daoyuan, L.; Lianli, C. Species-specific identification of collagen components in Colla corii asini using a nano-liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry proteomics approach. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4443–4454. [Google Scholar]
- Jubert, C.; Mata, J.; Bench, G.; Dashwood, R.; Pereira, C.; Tracewell, W.; Turteltaub, K.; Williams, D.; Bailey, G. Effects of Chlorophyll and Chlorophyllin on Low-Dose Aflatoxin B1 Pharmacokinetics in Human Volunteers. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Lootens, O.; Kabeta, T.; Reckelbus, D.; Furman, N.; Cao, X.; Zhang, S.; Antonissen, G.; Croubels, S.; De Boevre, M.; et al. Exploration of Cytochrome P450-Related Interactions between Aflatoxin B1 and Tiamulin in Broiler Chickens. Toxins 2024, 16, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoero, F.; Gallo, A.; Moschini, M.; Piva, G.; Diaz, D. Carryover of aflatoxin from feed to milk in dairy cows with low or high somatic cell counts. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2007, 1, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastaki, S.A.; Osman, N.; Kochiyil, J.; Shafiullah, M.; Padmanabhan, R.; Abdulrazzaq, Y.M. Toxicokinetics of Aflatoxin in Pregnant Mice. Int. J. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, E. A textbook of the diseases of cattle, horses, sheep, pigs and goats. In Veterinary Medicine, 10th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Applebaum, R.S.; Brackett, R.E.; Wiseman, D.W.; Marth, E.H. Responses of Dairy Cows to Dietary Aflatoxin: Feed Intake and Yield, Toxin Content, and Quality of Milk of Cows Treated with Pure and Impure Aflatoxin. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross-Steinmeyer, K.; Eaton, D.L. Dietary modulation of the biotransformation and genotoxicity of aflatoxin B1. Toxicology 2012, 299, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakritz, J.; Winder, B.S.; Noorouz-Zadeh, J.; Huang, T.L.; Buckpitt, A.R.; Hammock, B.D.; Plopper, C.G. Hepatic and pulmonary enzyme activities in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, C.; Garner, R.; Montesano, R.; Tursi, F. Aflatoxin B1 binding to plasma albumin and liver DNA upon chronic administration to rats. Carcinogenesis 1986, 7, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, A.; Tonin, F.; Souto, P.; Privatti, R.; Oliveira, C. Determination of Urinary Biomarkers for Assessment of Short-Term Human Exposure to Aflatoxins in So Paulo, Brazil. Toxins 2011, 6, 1996–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccoy, L.F.; Scholl, P.F.; Schleicher, R.L.; Groopman, J.D.; Powers, C.D.; Pfeiffer, C.M. Analysis of aflatoxin B1-lysine adduct in serum using isotope-dilution liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 19, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustemeyer, S.M.; Lamberson, W.R.; Ledoux, D.R.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Cammack, K.M. Effects of dietary aflatoxin on the health and performance of growing barrows. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 3624–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, S.; Taubel, M.; Juvonen, R.O.; Viluksela, M.; Turner, P.C.; Mykkanen, H.; El-Nezami, H. Lactobacillus rhamnosus Strain GG Modulates Intestinal Absorption, Fecal Excretion, and Toxicity of Aflatoxin B1 in Rats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7398–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, A.; Belío, R.; Ramos, J.J.; Sanz, M.C.; Sáez, T. Aflatoxins and their Metabolites in the Tissues, Faeces and Urine from Lambs Feeding on an Aflatoxin-Contaminated Diet. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 74, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmin, S.; Morgavi, D.P.; Yiannikouris, A.; Boudra, H. Effectiveness of modified yeast cell wall extracts to reduce aflatoxin B1 absorption in dairy ewes. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5611–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloni, F.; Cortinovis, C. Toxicological effects of aflatoxins in horses. Vet. J. 2011, 188, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Su, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y. Simultaneous detection of 21 kinds of mycotoxins and their metabolites in animal plasma with impurity adsorption purification followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 231–237. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


| Matrix | Spiked Concentration (µg·L−1)/(µg·kg−1) | Items (%) | AFB1 (%) | AFM1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine | 2 | Rrecovery | 85.6 | 80.8 |
| RSD | 10.3 | 7.6 | ||
| 10 | Rrecovery | 92.7 | 81.8 | |
| RSD | 9.9 | 5.5 | ||
| 100 | Rrecovery | 101.7 | 100.9 | |
| RSD | 6.9 | 3.7 | ||
| Feces | 2 | Rrecovery | 88.5 | 90.8 |
| RSD | 11.4 | 13.6 | ||
| 10 | Rrecovery | 90.1 | 93.7 | |
| RSD | 9.6 | 8.2 | ||
| 100 | Rrecovery | 86.6 | 83.3 | |
| RSD | 11.4 | 6.4 | ||
| Plasma | 1 | Rrecovery | 81.7 | 96.2 |
| RSD | 9.6 | 10.3 | ||
| 10 | Rrecovery | 88.7 | 83.7 | |
| RSD | 5.4 | 7.2 | ||
| 50 | Rrecovery | 92.6 | 97.5 | |
| RSD | 4.8 | 7.6 |
| Toxicokinetic Parameters | Value of AFB1 | Value of AFM1 |
|---|---|---|
| Body weight (kg) | 124.25 ± 2.75 | |
| AFB1 (µg·kg−1·BW) | 100 | |
| Cmax (µg·L−1) | 15.6 ± 6.88 | 0.72 ± 0.33 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.38 ± 0.89 | 2.25 ± 1.57 |
| T1/2Elim (h) | 6.65 ± 2.84 | 5.85 ± 3.00 |
| AUC0-t (µg·L−1·h) | 79.6 ± 23.9 | 3.84 ±1.98 |
| AUC0-inf (µg·L−1·h) | 82.6 ± 24.3 | 5.50 ± 2.93 |
| Cl (L·kg·BW−1·h−1) | 163 ± 52.2 | 3210 ± 2450 |
| Vd (L·kg−1·BW) | 1440 ± 417 | 22,400 ± 14,800 |
| Parameters | Mass Value (µg) |
|---|---|
| AFB1 intake | 12,420 ± 270 |
| Absorption rate (%) | 96.56 ± 1.45 |
| AFB1 excretion via urine | 210.86 ± 46.39 |
| AFM1 excretion via urine | 195.20 ± 66.62 |
| Total AFB1 excretion through urine (%) | 3.28 ± 0.92 |
| AFB1 excretion via feces | 409.30 ± 172.57 |
| AFM1 excretion via feces | 17.89 ± 8.40 |
| Total AFB1 excretion through feces (%) | 3.44 ± 1.45 |
| Toxicokinetic Parameters | Donkey | Cow | Rhesus Monkey | Broiler Chickens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1(µg·kg−1·BW) | 100 | 40 | 50 | 2000 |
| Cmax (µg·L−1) | 15.6 ± 6.88 | 13.8 ± 0.9 | - | 9.8 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.38 ± 0.89 | 0.58 ± 0.17 | 4 | 0.25 |
| T1/2Elim (h) | 6.65 ± 2.84 | 15.52 ± 0.51 | 0.61 | - |
| AUC0-inf (µg·L−1·h) | 82.6 ± 24.3 | 2.16 ± 0.36 | - | 1.6 |
| Cl (L·kg·BW−1·h−1) | 163 ± 52.2 | - | 1.25 | - |
| Vd (L·kg−1·BW) | 1440 ± 417 | - | - | - |
| Instrument | UPLC; Waters ACQUITY | ||
| Chromatographic column | BEH Shield RP18 column 100 mm × 2.1 mm i.d., dp 1.7 µm | ||
| Gradient elution program | Time (min) | A: 0.1% FA and 0.1 mM AmAc in water (%) | B: MeOH containing 0.1% FA (%) |
| 0 | 95 | 5 | |
| 0.5 | 95 | 5 | |
| 1.5 | 50 | 50 | |
| 2.5 | 20 | 80 | |
| 3.5 | 20 | 80 | |
| 4 | 2 | 98 | |
| 5 | 2 | -- | |
| 5.5 | 95 | 5 | |
| 6 | 95 | 5 | |
| Oven temperature | 40 °C | ||
| Flow velocity | 0.3 mL·min−1 | ||
| Inoculability quantity | 1 μL | ||
| Ion source | ESI+ | ||
| Capillary voltage | 0.6 kV | ||
| Cone voltage | 42 V | ||
| MRM transitions | 313.1 > 285.0 * and 313.1 > 241.2 for AFB1 (CE 22 and 36) 329.2 > 229.1 * and 329.2 > 259.0 for AFM1 (CE 26 and 24) 330.1 > 301.0 * and 330.1 > 255.1 for 13C17-AFB1 (CE 25 and 36) | ||
| Source temperature | 150 °C | ||
| Desolvation temperature | 500 °C | ||
| Desolvation gas flow | 900 L·h−1 | ||
| Cone gas | 150 L·h−1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; Qu, H.; Li, P.; Dong, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Jia, B.; Ma, Q. Toxicokinetics of a Single Oral Dose of Aflatoxin B1 in Plasma, Feces, and Urine of Male Donkeys. Toxins 2025, 17, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040206
Feng Y, Li M, Zheng Y, Qu H, Li P, Dong B, Wang Y, Liu G, Jia B, Ma Q. Toxicokinetics of a Single Oral Dose of Aflatoxin B1 in Plasma, Feces, and Urine of Male Donkeys. Toxins. 2025; 17(4):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040206
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yulong, Min Li, Yunduo Zheng, Honglei Qu, Pengshuai Li, Boying Dong, Yantao Wang, Guangyuan Liu, Bin Jia, and Qiugang Ma. 2025. "Toxicokinetics of a Single Oral Dose of Aflatoxin B1 in Plasma, Feces, and Urine of Male Donkeys" Toxins 17, no. 4: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040206
APA StyleFeng, Y., Li, M., Zheng, Y., Qu, H., Li, P., Dong, B., Wang, Y., Liu, G., Jia, B., & Ma, Q. (2025). Toxicokinetics of a Single Oral Dose of Aflatoxin B1 in Plasma, Feces, and Urine of Male Donkeys. Toxins, 17(4), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040206






