Molecular Diversity and Isoform Evolution in Tityus obscurus Venom: Insights from Proteomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents and Scorpion Venom
5.2. RP-HPLC
5.3. Proteomic Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beraldo-Neto, E.; Vigerelli, H.; Coelho, G.R.; da Silva, D.L.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Pimenta, D.C. Unraveling and Profiling Tityus bahiensis Venom: Biochemical Analyses of the Major Toxins. J. Proteom. 2023, 274, 104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula Santos-da-Silva, A.; Candido, D.M.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Kimura, L.F.; Prezotto-Neto, J.P.; Barbaro, K.C.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Dorce, V.A.C. Some Pharmacological Effects of Tityus obscurus Venom in Rats and Mice. Toxicon 2017, 126, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, U.C.; Nishiyama, M.Y.; Dos Santos, M.B.V.; De Paula Santos-Da-Silva, A.; De Menezes Chalkidis, H.; Souza-Imberg, A.; Candido, D.M.; Yamanouye, N.; Dorce, V.A.C.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.d.L.M. Proteomic Endorsed Transcriptomic Profiles of Venom Glands from Tityus obscurus and T. serrulatus Scorpions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.G.; Bordon, K.D.C.F.; Moreno-González, J.A.; de Almeida, B.R.R.; Pardal, P.P.; de Araújo Lira, A.F.; Cândido, D.M.; Arantes, E.C.; de Lima Procópio, R.E. On the Noxious Black Amazonian Scorpion, Tityus obscurus (Scorpiones, Buthidae): Taxonomic Notes, Biology, Medical Importance and Envenoming Treatment. Toxicon 2023, 228, 107125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.C.; Viana, G.M.M.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Beraldo-Neto, E. Scorpion Peptides and Ion Channels: An Insightful Review of Mechanisms and Drug Development. Toxins 2023, 15, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, K.W. Exploiting the Diversity of Ion Channels: Modulation of Ion Channels for Therapeutic Indications. In Concepts and Principles of Pharmacology: 100 Years of the Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 260, pp. 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Vargas, J.A.; Mourão, C.B.F.; Quintero-Hernández, V.; Possani, L.D.; Schwartz, E.F. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tityus pachyurus and Tityus obscurus Novel Putative Na+-Channel Scorpion Toxins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e0030478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Mata, E.C.G.; Ombredane, A.; Joanitti, G.A.; Kanzaki, L.I.B.; Schwartz, E.F. Antiretroviral and Cytotoxic Activities of Tityus obscurus Synthetic Peptide. Arch. Pharm. 2020, 353, 2000151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, C.V.F.; Del Pozo, L.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Contreras, S.; Becerril, B.; Wanke, E.; Possani, L.D. Proteomics of the Venom from the Amazonian Scorpion Tityus Cambridgei and the Role of Prolines on Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Toxins. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 803, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, N.B.; de Souza, B.M.; Cocchi, F.K.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Dorce, V.A.C.; Palma, M.S. Profiling the Short, Line-ar, Non-Disulfide Bond-Containing Peptidome from the Venom of the Scorpion Tityus obscurus. J. Proteom. 2018, 170, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaaytah, A.; Albalas, Q. Scorpion Venom Peptides with No Disulfide Bridges: A Review. Peptides 2014, 51, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.C.; Corzo, G.; Hahin, R. Scorpion Venom Peptides without Disulfide Bridges. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B.; Delepierre, M.; Tytgat, J. Scorpion Toxins Specific for Na+-Channels. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possani, L.D.; Merino, E.; Corona, M.; Bolivar, F.; Becerril, B. Peptides and Genes Coding for Scorpion Toxins That Affect Ion-Channels. Biochimie 2000, 82, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid-Uribe, J.I.; Veytia-Bucheli, J.I.; Romero-Gutierrez, T.; Ortiz, E.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion Venomics: A 2019 Overview. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2020, 17, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeyan, C.; Martinez, G.; Miranda, F.; Rochat, H.; Lissitzky, S. Disulfide Bonds of Toxin II of the Scorpion Androctonus Australis Hector. Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 47, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chua, P.J.; Bay, B.H.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Scorpion Venoms as a Potential Source of Novel Cancer Therapeutic Compounds. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housley, D.M.; Housley, G.D.; Liddell, M.J.; Jennings, E.A. Scorpion Toxin Peptide Action at the Ion Channel Subunit Level. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 46–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, H.; Castle, N.A.; Pardo, L.A. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels as Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 982–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, H.M.; Mourão, C.B.F.; Tibery, D.V.; Barbosa, E.A.; Campos, L.A.; Schwartz, E.F. To4, the First Tityus obscurus β-Toxin Fully Electrophysiologically Characterized on Human Sodium Channel Isoforms. Peptides 2017, 95, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Bosmans, F.; Tytgat, J. Adaptive Evolution of Scorpion Sodium Channel Toxins. J. Mol. Evol. 2004, 58, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Chan, A.H.C.; Koludarov, I.; Muñoz-Gómez, S.A.; Antunes, A.; Fry, B.G. Evolution Stings: The Origin and Diversification of Scorpion Toxin Peptide Scaffolds. Toxins 2013, 5, 2456–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; He, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Cao, Z. Extreme Diversity of Scorpion Venom Peptides and Proteins Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis: Implication for Proteome Evolution of Scorpion Venom Arsenal. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hmed, B.; Serria, H.T.; Mounir, Z.K. Scorpion Peptides: Potential Use for New Drug Development. J. Toxicol. 2013, 2013, 958797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez De La Vega, R.C.; Possani, L.D. Overview of Scorpion Toxins Specific for Na+ Channels and Related Peptides: Biodiversity, Structure-Function Relationships and Evolution. Toxicon 2005, 46, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, C.V.F.; Román-González, S.A.; Salas-Castillo, S.P.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Gómez-Lagunas, F.; Possani, L.D. Proteomic Analysis of the Venom from the Scorpion Tityus stigmurus: Biochemical and Physiological Comparison with Other Tityus Species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, C.V.F.; D’Suze, G.; Gómez-Lagunas, F.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Encarnación, S.; Sevcik, C.; Possani, L.D. Proteomic Analysis of Tityus discrepans Scorpion Venom and Amino Acid Sequence of Novel Toxins. Proteomics 2006, 6, 3718–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibery, D.V.; Campos, L.A.; Mourão, C.B.F.; Peigneur, S.; Carvalho, A.C.; Tytgat, J.; Schwartz, E.F. Electrophysiological Characterization of Tityus obscurus β Toxin 1 (To1) on Na+-Channel Isoforms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehling, E.G.; Sforça, M.L.; Zanchin, N.I.T.; Oyama, S.; Pignatelli, A.; Belluzzi, O.; Polverini, E.; Corsini, R.; Spisni, A.; Pertinhez, T.A. Looking over Toxin-K + Channel Interactions. Clues from the Structural and Functional Characterization of α-KTx Toxin Tc32, a Kv1.3 Channel Blocker. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beraldo-Neto, E.; Ferreira, V.F.; Vigerelli, H.; Fernandes, K.R.; Juliano, M.A.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Pimenta, D.C. Unraveling Neuroprotection with Kv1.3 Potassium Channel Blockade by a Scorpion Venom Peptide. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayem, N.; Gargouri, Y. Scorpion Venom Phospholipases A2: A Minireview. Toxicon 2020, 184, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, E.B.; de Freitas, L.A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Lebrun, I.; Nencioni, A.L.A. Tb1, a Neurotoxin from Tityus bahiensis Scorpion Venom, Induces Epileptic Seizures by Increasing Glutamate Release. Toxins 2020, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, F.G.; Longhim, H.T.; Cologna, C.T.; Degueldre, M.; De Pauw, E.; Quinton, L.; Arantes, E.C. Proteome of Fraction from Tityus serrulatus Venom Reveals New Enzymes and Toxins. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 25, e148218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobzhansky, T. Nothing in Biology Makes Sense except in the Light of Evolution. Am. Biol. Teach. 1973, 35, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
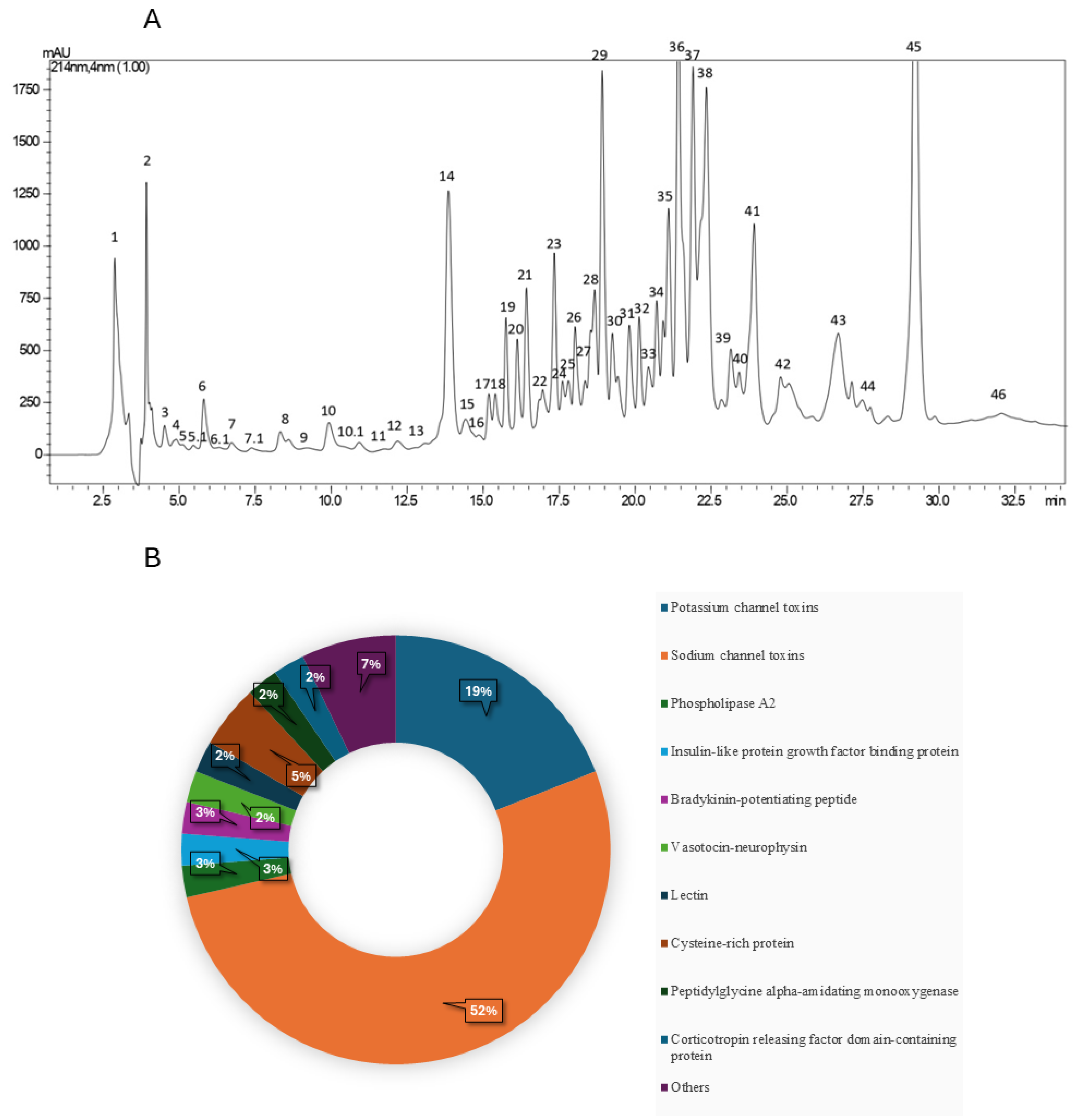
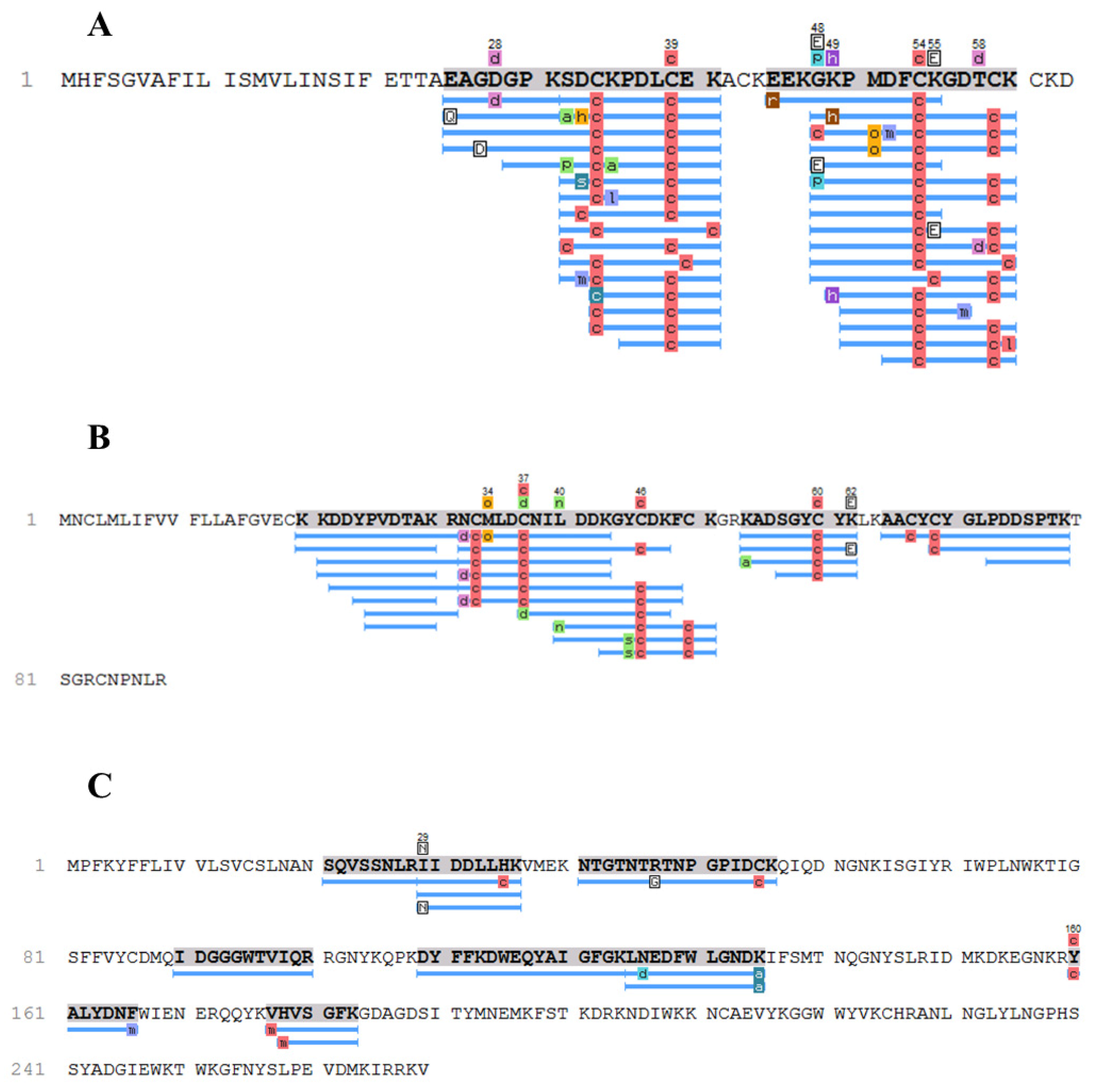

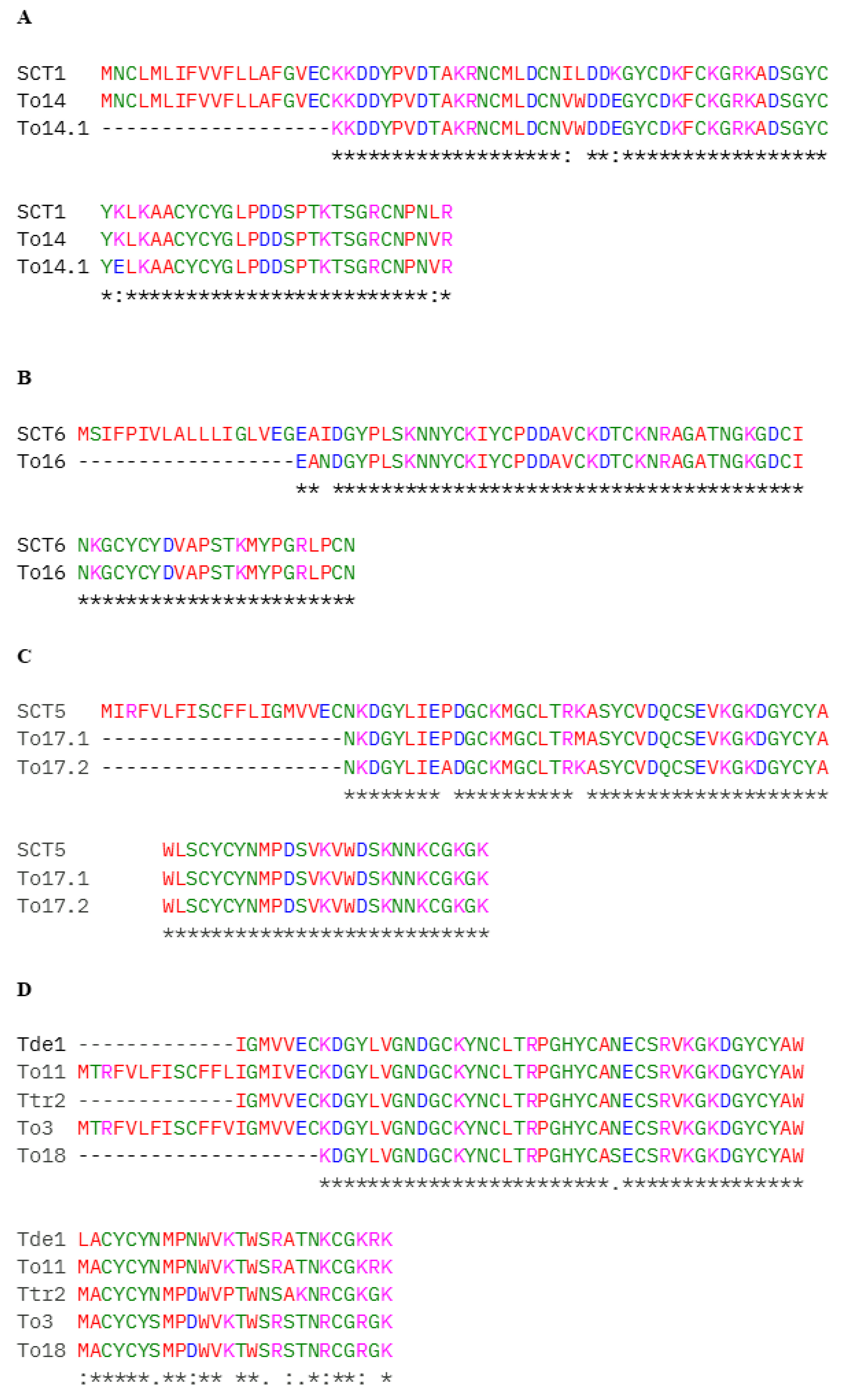
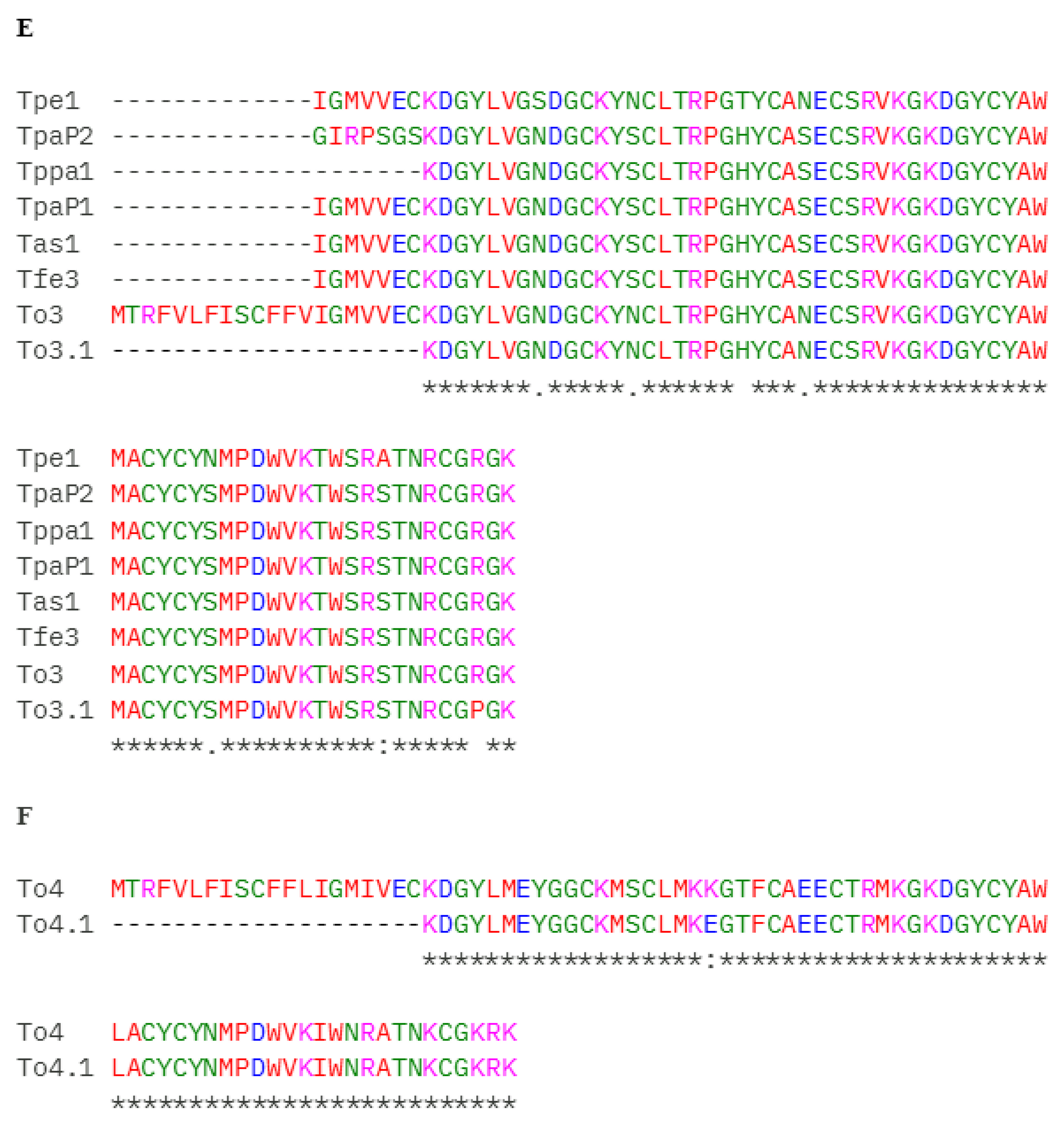

| Fraction | Description | Access | Amino Acid Substitution | New Isoform Names |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | Potassium channel toxin 1 | A0A1E1WVU5 | G48E K55E | ToP1 |
| 28 | Sodium channel toxin 1, Toxin To14-Substitution found in a conserved fragment | A0A1E1WVY8, H1ZZI3 | K62E | To14.1 |
| 31 | Sodium channel toxin 6 | A0A1E1WW05 | I21N | To16 |
| 36/37 | Sodium channel toxin 5 | A0A1E1WWE3 | K40M (Fraction 36) P29A (Fraction 36 and 37) | To17.1 (P29A; K40M)–found in fraction 36 To17.2 (P29A)–found in fraction 37 |
| 36/38 | Neurotoxin Ttr2, Neurotoxin Tde1, Toxin To3, Toxin To11–Substitution found in a conserved fragment | A0A7L4XVE5, A0A7L4XVB3, P60213, H1ZZI0 | N32S N45S | To18 |
| 37 | Neurotoxin TpaP2, Neurotoxin TpaP1, Neurotoxin Tas1, Neurotoxin Tfe3, Toxin Tppa1, Neurotoxin Tpe1, Toxin To3-Substitution found in a conserved fragment | A0A7L4XT36, A0A7L4XS46, A0A7L4XS27, A0A7L4XUN7, C0HLZ0, A0A7L4XS62, P60213 | R71P R64P R84P | To3.1 |
| 40 | Beta-toxin To4 | P60215 | K39E | To4.1 |
| 44 | Lectin | A0A1E1WVN0 | I29N | ToLectin |
| Uniprot Code | Fraction | −10lgP | Peptides | Unique Peptides | Nomenclatures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A1E1WVU5 | 9 | 101.62 | 4 | 4 | Potassium channel toxin 1 |
| 10 | 69.91 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 10.1 | 96.76 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 11 | 66.12 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 12 | 57.29 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 13 | 87.12 | 6 | 6 | ||
| 14 | 136.08 | 8 | 7 | ||
| 15 | 63.29 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 16 | 81.43 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 17 | 50.51 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 18 | 53.03 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 22 | 89.28 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 25 | 54.52 | 1 | 1 | ||
| P60211 | 16 | 55.44 | 2 | 2 | Potassium channel toxin alpha-KTx 18.1 |
| 17 | 50.45 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 18 | 97.36 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 25 | 91.97 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 26 | 129.16 | 4 | 4 | ||
| A0A1E1WVV4 | 17 | 52.38 | 3 | 3 | Potassium channel toxin 2 |
| 34 | 90.36 | 7 | 7 | ||
| 35 | 155.09 | 10 | 9 | ||
| 37 | 70.93 | 3 | 2 | ||
| 38 | 68.52 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 40 | 60.24 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 42 | 60.59 | 4 | 4 | ||
| A0A1E1WVQ0 | 18 | 56.64 | 2 | 2 | Potassium channel toxin 3 |
| 20 | 54.75 | 3 | 3 | ||
| P0DQU5 | 24 | 122.54 | 4 | 4 | Potassium channel toxin (Tityus metuendus) |
| A0A1E1WVZ4 | 24 | 128.59 | 4 | 4 | Potassium channel toxin 5 |
| 25 | 130.52 | 3 | 3 | ||
| A0A1E1WVV5 | 27 | 55.05 | 2 | 2 | Potassium channel toxin 6 |
| 28 | 65.77 | 4 | 4 | ||
| A0A1E1WVU0 | 44 | 109.72 | 6 | 6 | Potassium channel toxin 7 |
| 45 | 115.22 | 6 | 6 | ||
| A0A2I9LP49 Q0GY43 A0A1E1WVV4 (Identification of conserved region) | 33 | 97.84 | 2 | 2 | KTx (Centruroides hentzi) Potassium channel toxin TdiKIK (Tityus discrepans) Potassium channel toxin 2 |
| 36 | 103.19 | 4 | 4 | ||
| P0DQU5 A0A1E1WVP6 (Identification of conserved region) | 23 | 141.08 | 6 | 6 | Potassium channel toxin (Tityus metuendus) Potassium channel toxin 4 |
| A0A1E1WVV4 Q0GY43 (Identification of conserved region) | 41 | 79.15 | 4 | 4 | Potassium channel toxin 2 Potassium channel toxin TdiKIK (Tityus discrepans) |
| Uniprot Code | Fraction | −10lgP | Peptides | Unique Peptides | Nomenclatures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A1E1WVY8 | 27 | 181.71 | 8 | 2 | Sodium channel toxin 1 |
| 28 | 214.72 | 16 | 4 | ||
| 29 | 226.21 | 23 | 23 | ||
| 30 | 133.51 | 6 | 6 | ||
| 32 | 93.47 | 4 | 2 | ||
| 33 | 93.05 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 45 | 77.25 | 3 | 3 | ||
| H1ZZI3 | 27 | 171.58 | 7 | 1 | To14 |
| 28 | 197.58 | 13 | 1 | ||
| A0A1E1WW26 | 32 | 104.32 | 5 | 1 | Sodium channel toxin 2 |
| 33 | 83.85 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 34 | 118.95 | 6 | 3 | ||
| 35 | 103.35 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 36 | 92.28 | 3 | 2 | ||
| P84685 | 31 | 90.79 | 4 | 1 | Toxin To6 |
| 32 | 104.61 | 9 | 0 | ||
| A0A1E1WWK1 | 30 | 55.15 | 3 | 1 | Sodium channel toxin 3 |
| 32 | 102.86 | 8 | 2 | ||
| 33 | 111.43 | 7 | 3 | ||
| 34 | 151.33 | 10 | 7 | ||
| 35 | 99.58 | 5 | 2 | ||
| 36 | 104.82 | 6 | 0 | ||
| P84688 | 33 | 87.55 | 5 | 1 | Toxin To7 |
| A0A1E1WVS3 | 31 | 104.72 | 5 | 0 | Sodium channel toxin 4 |
| 35 | 90.77 | 5 | 2 | ||
| 36 | 110.45 | 6 | 1 | ||
| 37 | 93.43 | 6 | 6 | ||
| C9X4K8 | 33 | 72.30 | 4 | 2 | Toxin TdNa10 (Tityus discrepans) |
| A0A1E1WWE3 | 33 | 51.33 | 3 | 3 | Sodium channel toxin 5 |
| 35 | 91.93 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 36 | 166.13 | 13 | 11 | ||
| 37 | 157.93 | 9 | 8 | ||
| A0A1E1WW05 | 28 | 83.99 | 3 | 3 | Sodium channel toxin 6 |
| 29 | 57.99 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 30 | 93.69 | 5 | 3 | ||
| 31 | 168.89 | 6 | 3 | ||
| 32 | 161.52 | 13 | 6 | ||
| 33 | 120.15 | 6 | 4 | ||
| 34 | 83.96 | 5 | 2 | ||
| 35 | 81.58 | 3 | 1 | ||
| 36 | 72.73 | 4 | 1 | ||
| H1ZZI1 | 37 | 67.47 | 2 | 2 | Toxin To12 |
| 38 | 128.28 | 9 | 9 | ||
| 39 | 135.94 | 9 | 9 | ||
| 40 | 58.92 | 3 | 3 | ||
| P60215 | 39 | 51.90 | 1 | 1 | Beta-toxin To4 |
| 40 | 56.16 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 41 | 101.27 | 5 | 3 | ||
| H1ZZI4 | 36 | 146.85 | 6 | 6 | Toxin To15 |
| 37 | 169.34 | 5 | 5 | ||
| 38 | 152.72 | 7 | 7 | ||
| 39 | 154.87 | 7 | 7 | ||
| A0A1E1WVT2 | 45 | 107.00 | 5 | 5 | Sodium channel toxin 7 |
| P84693 | 46 | 64.98 | 5 | 5 | Toxin To5 |
| P60214 | 38 | 129.59 | 5 | 1 | Beta-mammal/insect toxin To1 |
| 39 | 139.60 | 5 | 1 | ||
| 40 | 91.86 | 6 | 3 | ||
| P84631 | 38 | 126.31 | 5 | 1 | Tpa2 (Tityus pachyurus) |
| 39 | 133.87 | 5 | 1 | ||
| 40 | 85.63 | 4 | 1 | ||
| P60213 | 36 | 108.69 | 6 | 1 | Toxin To3 |
| A0A7L4XT36 | 35 | 70.32 | 2 | 1 | Neurotoxin Tpe1 (Tityus perijanensis) |
| 37 | 91.44 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 38 | 54.05 | 1 | 1 | ||
| A0A7L4XT36 | 38 | 109.79 | 5 | 3 | Neurotoxin TpaP2 (Tityus pachyuru) |
| C0HLM1 | 32 | 56.98 | 3 | 1 | Tma3 (Tityus macrochirus) |
| A0A7L4XVR8 | 36 | 57.36 | 3 | 0 | Neurotoxin Tpe3 (Tityus perijanensis) |
| A0A1E1WVS3 A0A1E1WWK1 (Identification of conserved region) | 31 | 104.72 (A0A1E1WVS3) | 5 | 0 | Sodium channel toxin 4 Sodium channel toxin 3 |
| 31 | 103.89 (A0A1E1WVS3) | 5 | 0 | ||
| A0A1E1WVY8 H1ZZI3 (Identification of conserved region) | 31 | 103.88 | 3 | 3 | Sodium channel toxin 1 To14 |
| 34 | 77.91 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 41 | 75.63 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 43 | 67.29 | 2 | 2 | ||
| P60213 H1ZZI0 A0A7L4XVE5 A0A7L4XVB3 (Identification of conserved region) | 35 | 110.59 | 5 | 2 | Toxin To3 Toxin To11 Neurotoxin Ttr2 (Tityus trinitatis) Neurotoxin Tde1 (Tityus dedoslargos) |
| 37 | 115.81 | 4 | 1 | ||
| C9X4K6 H1ZZH8 (Identification of conserved region) | 36 | 117.88 | 5 | 5 | Toxin TdNa8 (Tityus discrepans) Toxin To9 |
| A0A7L4XT36 C0HLZ0 A0A7L4XS46 A0A7L4XS27 A0A7L4XUN7 C0HLZ1 A0A7L4XVD1 Q1I169 A0A7L4XUV3 (Identification of conserved region) | 35 | 101.88 | 3 | 1 | Neurotoxin TpaP2 (Tityus pachyurus) Toxin Tppa1 (Tityus pachyurus) Neurotoxin TpaP1 (Tityus pachyurus) Neurotoxin Tas1 (Tityus asthenes) Neurotoxin Tfe3 (Tityus festae) Toxin Tppa2 (Tityus pachyurus) Neurotoxin TpaP5 (Tityus pachyurus) Toxin Td5 (Fragment) (Tityus discrepans) Neurotoxin Tfe2 (Tityus festae) |
| 37 | 121.07 | 4 | 1 | ||
| 39 | 107.73 | 5 | 3 | ||
| 40 | 88.60 | 3 | 2 | ||
| C0HLZ0 A0A7L4XT36 A0A7L4XS46 A0A7L4XS27 A0A7L4XUN7 (Identification of conserved region) | 36 | 101.63 | 6 | 1 | Toxin Tppa1 (Tityus pachyurus) Neurotoxin TpaP2 (Tityus pachyurus) Neurotoxin TpaP1 (Tityus pachyurus) Neurotoxin Tas1 (Tityus asthenes) Neurotoxin Tfe3 (Tityus festae) |
| Uniprot Code | Fraction | −10lgP | Peptides | Unique Peptides | Nomenclatures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A1E1WVX0 | 7.1 | 74.09 | 4 | 4 | Bradykinin-potentiating peptide |
| 22 | 65.80 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 25 | 61.81 | 4 | 4 | ||
| A0A1E1WVN4 | 26 | 139.09 | 6 | 6 | Insulin-like protein growth factor binding protein |
| 27 | 107.94 | 5 | 5 | ||
| 30 | 84.10 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 31 | 106.35 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 32 | 113.77 | 5 | 5 | ||
| 33 | 79.19 | 4 | 3 | ||
| 34 | 55.88 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 41 | 56.67 | 1 | 1 | ||
| A0A1E1WVS0 | 38 | 81.05 | 3 | 3 | Vasotocin-neurophysin |
| 39 | 98.97 | 5 | 4 | ||
| 40 | 99.56 | 5 | 5 | ||
| 41 | 100.00 | 6 | 6 | ||
| C9X4G4 | 41 | 73.72 | 2 | 2 | Uncharacterized protein |
| 45 | 53.74 | 1 | 1 | ||
| A0A1E1WVN8 | 43 | 118.06 | 6 | 6 | Venom protein |
| A0A1E1WVN0 | 44 | 85.20 | 5 | 5 | Lectin |
| A0A1E1WVV0 | 44 | 99.99 | 3 | 3 | Cysteine-rich protein 1 |
| 45 | 82.54 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 46 | 65.75 | 1 | 1 | ||
| A0A1E1WVY9 | 46 | 71.48 | 1 | 1 | Cysteine-rich protein 2 |
| A0A1E1WVQ8 | 44 | 91.07 | 3 | 3 | Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase |
| A0A1E1WVM2 | 9 | 61.08 | 2 | 2 | Corticotropin-releasing factor domain-containing protein |
| 44 | 63.83 | 1 | 1 | ||
| A0A1E1WWE7 | 44 | 77.26 | 4 | 4 | Phospholipase A2 (Fragment) |
| 45 | 87.46 | 4 | 4 | ||
| A0A1E1WWD3 A0A1D3IY23 (Identification of conserved region) | 31 | 75.56 | 2 | 2 | Venom toxin Peptide ToAcP |
| 32 | 75.71 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 34 | 119.70 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 35 | 125.48 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 36 | 78.92 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 40 | 86.38 | 2 | 2 | ||
| A0A1E1WVR3 A0A1E1WVN2 (Identification of conserved region) | 43 | 66.12 | 1 | 1 | Secreted protein (Fragment) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panchera, K.C.; Mendes, L.C.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Beraldo-Neto, E. Molecular Diversity and Isoform Evolution in Tityus obscurus Venom: Insights from Proteomic Analysis. Toxins 2025, 17, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050210
Panchera KC, Mendes LC, Nencioni ALA, Pimenta DC, Beraldo-Neto E. Molecular Diversity and Isoform Evolution in Tityus obscurus Venom: Insights from Proteomic Analysis. Toxins. 2025; 17(5):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050210
Chicago/Turabian StylePanchera, Kemellyn Cristina, Lais Campelo Mendes, Ana Leonor Abrahão Nencioni, Daniel Carvalho Pimenta, and Emídio Beraldo-Neto. 2025. "Molecular Diversity and Isoform Evolution in Tityus obscurus Venom: Insights from Proteomic Analysis" Toxins 17, no. 5: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050210
APA StylePanchera, K. C., Mendes, L. C., Nencioni, A. L. A., Pimenta, D. C., & Beraldo-Neto, E. (2025). Molecular Diversity and Isoform Evolution in Tityus obscurus Venom: Insights from Proteomic Analysis. Toxins, 17(5), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050210







