Toxigenic Potential of Aspergillus Species Occurring on Maize Kernels from Two Agro-Ecological Zones in Kenya
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Study Sites
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Isolation and Identification of Moulds
2.4. Molecular Characterization
2.4.1. Detection of Aflatoxin Genes aflD (=nor1) and aflQ (=ordA = ord-1)
2.4.2. DNA Extraction
2.4.3. PCR Amplification
2.5. Aflatoxigenicity of the Isolates
2.5.1. Fluorescence on Coconut Agar Medium (CAM)
2.5.2. Aflatoxin Analysis

2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fungal Profile of Maize Kernels from Nandi and Makueni Districts
| Region | Fungal genera | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus sp. | Fusarium sp. | Penicillium sp. | Trichoderma sp. | Others | Total | |
| Makueni | 189 (62) | 71 (23) | 25 (8) | 10 (3) | 12 (4) | 307(100) |
| Nguumo | 70 (73) | 16 (17) | 4 (4) | 1 (1) | 5 (5) | 96 (100) |
| Ukia | 82 (52) | 48 (31) | 17 (11) | 7 (4) | 3 (2) | 157(100) |
| Wote | 37 (69) | 7 (13) | 4 (7) | 2 (4) | 4 (7) | 54 (100) |
| Nandi | 203 (67) | 50 (16) | 18 (6) | 6 (2) | 29 (9) | 306 (100) |
| Kaptumo | 94 (73) | 16 (13) | 6 (5) | 0 (0) | 12 (9) | 128 (100) |
| Kilibwoni | 58 (54) | 27 (25) | 9 (8) | 6 (6) | 7 (7) | 107 (100) |
| Laboret | 51 (72) | 7 (10) | 3 (4) | 0 (0) | 10(14) | 71 (100) |
| Total (Nandi + Makueni) | 392 (64) | 121 (20) | 43 (7) | 16 (3) | 41 (6) | 613 (100) |
3.2. Population Composition of the Genus Aspergillus

| Location | Number of isolates | A. flavus (%) | Strain | A. parasiticus (%) | A. tamarii (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nandi | Kilibwoni | 33 | 64 | L | 21 | 15 |
| Kaptumo | 65 | 55 | L | 9 | 36 | |
| Laboret | 34 | 62 | L | 26 | 12 | |
| No. producing sclerotia (%) | 37 (n = 29) | 19 (n = 4) | 0 | |||
| Makueni | Nguumo | 41 | 95 | S | 5 | 0 |
| Ukia | 42 | 67 | S | 7 | 26 | |
| Wote | 20 | 94 | S | 6 | 0 | |
| No. producing sclerotia (%) | 71(n = 61) | 67 (n = 4) | 0 |

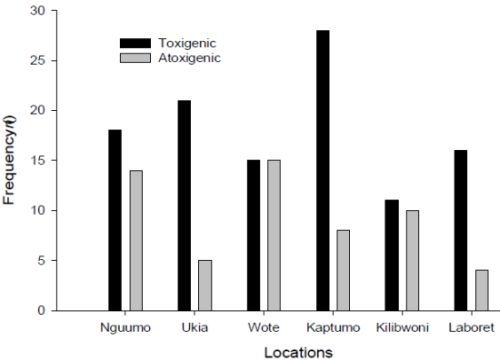
3.3. Molecular Analysis of Aspergillus Strains and Aflatoxin Production on CAM


3.4. Production of Aflatoxins by the Isolates in Vitro
| (a) Makueni isolates | ||||||
| Code | Isolate | AFB1 (µg/kg) | AFB2 (µg/kg) | AFG1 (µg/kg) | AFG2 (µg/kg) | Total Aflatoxin (µg/kg) |
| 1VM326g | A. flavus | 8159 | 2037 | 2 | 0 | 10199 |
| 2VM890g | A.flavus | 19916 | 9564 | 1 | 2 | 29484 |
| Kp-B | A. flavus | 1502 | 343 | 6 | 0 | 1850 |
| 2VM983g | A.flavus | 13143 | 2265 | 20 | 0 | 15427 |
| 2M1204g | A. flavus | 127 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 140 |
| Km-A | A. flavus | 57 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 62.133 |
| 1VM79g | A. flavus | 257 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 332.35 |
| 2M1002L | A.flavus | 63390 | 33777 | 17 | 0 | 97184 |
| 1VM403g | A.flavus | 10113 | 3438 | 22 | 0 | 13574 |
| 1VM147g | A. flavus | 898 | 267 | 0 | 0 | 1165 |
| 2M1014g | A. flavus | 702 | 82 | 1 | 0 | 785 |
| 1VM402g | A.flavus | 12032 | 6989 | 17 | 0 | 19038 |
| 2VM892g | A.flavus | 33173 | 14458 | 22 | 0 | 47653 |
| 1VM83y | A. flavus | 1988 | 721 | 203 | 0 | 2912 |
| 3VM482g | A.flavus | 14092 | 8947 | 30 | 0 | 23069 |
| 1VM235g | A. flavus | 459 | 135 | 7 | 0 | 602 |
| 1VM130d | A.flavus | 61878 | 30349 | 22 | 0 | 92249 |
| 1VM175g | A.flavus | 52229 | 15100 | 20 | 0 | 67350 |
| 3VM559g | A. flavus | 1686 | 200 | 7 | 0 | 1893.2 |
| 2M1090g | A. flavus | 516 | 50 | 568 | 64 | 11971 |
| 1VM223g | A.flavus | 32145 | 15245 | 365 | 65 | 47820 |
| 2M1016g | A. flavus | 798 | 229 | 12 | 0 | 1039 |
| 1VM328g | A.flavus | 31797 | 6743 | 54 | 0 | 38594 |
| Km-B | A. flavus | 673 | 81.356 | 12 | 0 | 766 |
| 2VM882g | A.flavus | 30939 | 11627 | 10 | 0 | 42576 |
| 2M1365g | A.flavus | 83491 | 52600 | 16875 | 0 | 152966 |
| 3VM551g | A.flavus | 30637 | 13620 | 21 | 0 | 44278 |
| Um | A. flavus | 1692 | 420 | 8 | 0 | 2120 |
| 2M1383g | A. flavus | 270 | 47 | 7 | 0 | 324 |
| 2M1122g | A. flavus | 5028 | 1008 | 42 | 0 | 6078 |
| 1VM250 | A. flavus | 2719 | 969 | 8 | 0 | 3695 |
| 1VM95yg | A.flavus | 59374 | 29456 | 25 | 0 | 88878 |
| 1VM79Lg | A. flavus | 1073 | 382 | 3 | 0 | 1458 |
| 3VM643g | A.flavus | 339 | 47 | 0 | 0 | 387 |
| 2VM983g | A. parasiticus | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 22 |
| 1VM149g | A.parasiticus | 15139 | 3141 | 28728 | 8411 | 55419 |
| 1VM118g | A. parasiticus | 97 | 6 | 9 | 0 | 112 |
| 2VM983 | A. parasiticus | 45 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 61 |
| (b) Nandi isolates | ||||||
| Code | ISOLATE | AFB1 (µg/kg) | AFB2 (µg/kg) | AFG1 (µg/kg) | AFG2 (µg/kg) | Total Aflatoxin (µg/kg) |
| BM I YG | A.flavus | 42 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 46 |
| BM130YG | A.flavus | 64030 | 16583 | 51 | 0 | 80664 |
| BM112YG | A.flavus | 13775 | 2054 | 48914 | 9624 | 74367 |
| BM 43 G | A.flavus | 898 | 56 | 7 | 0 | 962 |
| BM 12 G | A.flavus | 35 | 0 | 22 | 0 | 57 |
| BM 1 G | A.flavus | 110 | 38 | 3 | 0 | 151 |
| BM 59 G | A.flavus | 21 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 22 |
| BM 1G | A.flavus | 10164 | 2622 | 17 | 0 | 12803 |
| BM 3 YG | A.flavus | 39 | 8 | 49 | 0 | 96 |
| BM 1 G | A.flavus | 57142 | 59231 | 292 | 0 | 116666 |
| BM 3 G | A.flavus | 23 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 33 |
| BM 9 G | A.flavus | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 22 |
| BM 54 YG | A.flavus | 12888 | 9272 | 44 | 0 | 22203 |
| BM 80 G | A.flavus | 6233 | 2857 | 0 | 0 | 9089 |
| BM 1 YG | A.flavus | 91 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 91 |
| BM 78 YG | A.flavus | 31 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 42 |
| BM 1 YG | A.flavus | 119 | 25 | 1 | 0 | 145 |
| BM 14 G | A.flavus | 3771 | 2488 | 9826 | 7798 | 23883 |
| BM 69 G | A.flavus | 16 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 22 |
| BM 1 G | A.flavus | 40 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 46 |
| BM 1 YG | A.flavus | 200 | 43 | 4 | 0 | 247 |
| BM 1 G | A.flavus | 10058 | 1217 | 17 | 0 | 11292 |
| BM 49 G | A.flavus | 64 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 77 |
| BM 1 Y | A.flavus | 108 | 9 | 207 | 0 | 325 |
| BM 1 G | A.flavus | 12960 | 4661 | 7 | 0 | 17628 |
| BM 55 YG | A.flavus | 13288 | 8072 | 54 | 0 | 21413 |
| BM 1 YG | A.flavus | 77 | 18487 | 68 | 0 | 18632 |
| BM 1 YG | A.flavus | 2923 | 25 | 514 | 0 | 3463 |
| BM 2 YG | A.flavus | 806 | 488 | 9 | 0 | 1304 |
| BM 3 YG | A.flavus | 42 | 13 | 7 | 0 | 63 |
| BM 4 YG | A.flavus | 216 | 53 | 0 | 0 | 269 |
| BM 2 G | A.flavus | 33 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 44 |
| BM 1 G | A.flavus | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
| BM 1 YG | A.flavus | 19 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 24 |
| BM 1 G | A.flavus | 41 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 46 |
| BM 2 G | A.flavus | 139 | 18 | 63 | 0 | 221 |
| BM 38 YG | Aparasiticus | 10763 | 2876 | 24 | 0 | 13662 |
| BM 39 G | A.parasiticus | 11077 | 832 | 1288 | 0 | 13197 |
| BM 1 YG | A.parasiticus | 603 | 208 | 1699 | 7798 | 10308 |
| BM 1 G | A.parasiticus | 991 | 292 | 5982 | 2717 | 9982 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Conflict of Interest
Acknowledgements
References
- Nyoro, J.K.; Kirimi, L.; Jayne, T.S. Competitiveness of Kenya and Ugandan maize production: challenges for the future; Tegemeo Working Paper Series, No. 10; Egerton University: Kenya, 2004; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ngindu, A.; Kenya, P.R.; Ochieng, D.M.; Omondi, T.M.; Ngare, W.; Gatei, D. Outbreak of acute hepatitis caused by aflatoxin poisoning in Kenya. Lancet 1982, 1, 1346–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Probst, C.; Njapau, H.; Cotty, P.J. Outbreak of an acute aflatoxicosis in Kenya in 2004: identification of the causal agent. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2762–2764. [Google Scholar]
- Kesley, G. Aflatoxin Contamination of maize in Africa. Biosecurity Blog. 2010. Available online: http://www.fas.org/blog/nutshell/2010/06/aflatoxin-contamination-of-maize-in-africa/ (accessed on 12 April 2012).
- World Health Organization, Some naturally occurring substances: food items and constituents, heterocyclic aromatic amines and mycotoxins, Monograph 56; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1993.
- FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization), Agro-ecological Zoning guidelines, FAO Soils Bulletin 73; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1996.
- Cochran, W.G. Sampling Techniques, 2nd ed; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Traisat, H. Mycotoxin prevention and control in food grains. In Sampling, sample handling and preparation in grains and cereals; Semple, R.L., Frio, A.S., Hicks, P.A., Lozare, J.V., Eds.; UNDP/FAO Regional Network Inter-Country Cooperation on Preharvest Technology and Quality Control of Foodgrains (REGNET) and the ASEAN Grain Postharvest Programme: Bankok, Thailand, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, P.E.; Tousson, T.A.; Marasas, W.F.O. Fusarium FusariumSpecies: An Illustrated Manual for Identification; Pennsylvania State University Press: University Park, Pennsylvania, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, J.I.; Hocking, A.D. Fungi and Food Spoilage; Blackie Academic and Professional: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Leslie, J.F.; Summerell, B.A. The Fusarium Laboratory Manual; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Klich, M.A. Biogeography of Aspergillus species in soil and litter. Mycologia 2002, 94(1), 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.I.; Hockings, I.; Glend, I. An improved medium for the detection of Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus. J. Appl. Bact. 1983, 54, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotty, P.J. Virulence and cultural characteristics of two Aspergillus flavus strains pathogenic on cotton. Phytopathology 1989, 79(7), 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chang, P.K.; Cary, J.W.; Ehrlich, K.C.; Montalbano, B.; Dyer, J.M.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cleveland, T.E. Characterization of the critical amino acids of an Aspergillus parasiticus cytochrome P450 monooxygenase encoded by ordA involved in aflatoxin B1, G1, B2, and G2 biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 4834–4841. [Google Scholar]
- Papa, K.E. Norsolorinic acid mutant of Aspergillus flavus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1982, 128, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.W. Loss of norsolorinic acid and aflatoxin production by a mutant of Aspergillus parasiticus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1981, 124, 429–432. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, T.E. Conversion of dihydro-O-methylsterigmatocystin to aflatoxin B2 by Aspergillus parasiticus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1989, 18, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.; Armando, V.; Zofia, K.; Nelson, L. A polyphasic approach to the identification of aflatoxigenic and non-aflatoxigenic strains of Aspergillus section Flavi isolated from Portuguese almonds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 129, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.J.; Pamies, P.; Dobson, A.D.W. The use of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for monitoring aflatoxin production in Aspergillus parasiticus 439. International. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 56, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, S.K.; McCammon, S. Detection of toxigenic isolates of Aspergillus flavus and related species on coconut cream agar. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1994, 76(1), 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, E.F.; Posada, F.; Peterson, W.S.; Gianfagna, J.T.; Chaves, F. Penicillium species endophytic in coffee plants and Ochratoxin A production. Mycologia 2006, 98(1), 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedsgaard, J. Micro-scale extraction procedure for standardized screening of fungal metabolite production in cultures. J. Chromatogr. 1997, 760, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 8 April 2012).
- Atehnkeng, J.; Ojiambo, P.S.; Donner, M.; Ikotun, T.; Sikoras, R.; Cotty, P.J.; Bandyopadhyay, R. Distribution and toxigenicity of Aspergillus species isolated from maize kernels from three agroecological zones in Nigeria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 122, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.K.; Zablotowicz, R.M.; Locke, M.A. Spatial variability of Aspergillus flavus soil populations under different crops and corn grain infestation and mycotoxins. Can. J. Botany 2004, 82, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zablotowicz, R.M.; Abbas, H.K.; Locke, M.A. Population ecology of Aspergillus flavus associated with Mississippi Delta Soils. Food Addit Contam. 2007, 24, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, C.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Price, L.E.; Cotty, P.J. Identification of atoxigenic Aspergillus flavus isolates to reduce aflatoxin contamination of maize in Kenya. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brian, G.R.; Georgina, D.R.; Wilkinson, J.R.; Yu, J.; Abbas, H.K.; Bhatnagar, D; Cleveland, T.E.; Nierman, W.; Payne, G.A. The effect of elevated temperature on gene transcription and aflatoxin biosynthesis. Mycologia 2007, 99(2), 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egel, D.S.; Cotty, P.J.; Elias, K.S. Relationships among isolates of Aspergillus section Flavi that vary in aflatoxin production. Phytopathology 1994, 84, 96–912. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, K.C.; Chang, P.K.; Yu, J.; Cotty, P.J. Aflatoxin biosynthesis cluster gene cypA is required for G aflatoxin formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6518–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotty, P.J.; Cardwell, K.F. Divergence of West African and North American communities of Aspergillus section Flavi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 65(5), 2264–2266. [Google Scholar]
- Cardwell, K.F.; Cotty, P.J. Distribution of Aspergillus section Flavi among field soils from the four agroecological zones of the Republic of Benin, West Africa. Plant Dis. 2002, 86(4), 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.D.; Diener, U.L.; Eldridge, D.W. Production of Aflatoxins B1 and G1 by Aspergillus flavus in a Semisynthetic Medium. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 14(3), 378–380. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, H.K.; Zablotowicz, R.M.; Weaver, M.A.; Horn, B.W.; Xie, W.; Shier, W.T. Comparison of cultural and analytical methods for determination of aflatoxin production by Mississippi Delta Aspergillus isolates. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlpin, C.E. Synnema and sclerotium production in Aspergillus caelatus and the influence of substrate composition on their development in selected strains. Mycologia 2004, 96, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B.W.; Dorner, J.W. Effect of competition and adverse culture conditions on aflatoxin production by Aspergillus flavus through successive generations. Mycologia 2002, 94(5), 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, K.; Raha, S. Deteriorative changes of maize, groundnut and soybean seeds by fungi in storage. Mycopathologia 2002, 155, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, R.B.; Corra, B.; Possi, C.R. Mycoflora and occurrence of fumonisins in freshly harvested and stored hybrid maize. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2000, 36, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Bii, F.; Wanyoike, W.; Nyende, A.B.; Gituru, R.W.; Bii, C. Fumonisin contamination of maize (Zea mays) in aflatoxin ‘hot’ zones in Eastern Province of Kenya. Afr. J. Health Sci. 2012, 20, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Muthomi, J.W.; Njenga, L.N.; Gathumbi, J.K.; Cheminingwa, G.N. The occurrence of aflatoxins in maize and distribution of mycotoxin-producing fungi in Eastern Kenya. Plant Path. 2009, 8, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Okoth, S.; Nyongesa, B.; Ayugi, V.; Kang'ethe, E.; Korhonen, H.; Joutsjoki, V. Toxigenic Potential of Aspergillus Species Occurring on Maize Kernels from Two Agro-Ecological Zones in Kenya. Toxins 2012, 4, 991-1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4110991
Okoth S, Nyongesa B, Ayugi V, Kang'ethe E, Korhonen H, Joutsjoki V. Toxigenic Potential of Aspergillus Species Occurring on Maize Kernels from Two Agro-Ecological Zones in Kenya. Toxins. 2012; 4(11):991-1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4110991
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkoth, Sheila, Beatrice Nyongesa, Vincent Ayugi, Erastus Kang'ethe, Hannu Korhonen, and Vesa Joutsjoki. 2012. "Toxigenic Potential of Aspergillus Species Occurring on Maize Kernels from Two Agro-Ecological Zones in Kenya" Toxins 4, no. 11: 991-1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4110991
APA StyleOkoth, S., Nyongesa, B., Ayugi, V., Kang'ethe, E., Korhonen, H., & Joutsjoki, V. (2012). Toxigenic Potential of Aspergillus Species Occurring on Maize Kernels from Two Agro-Ecological Zones in Kenya. Toxins, 4(11), 991-1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4110991