Biological and Enzymatic Characterization of Proteases from Crude Venom of the Ant Odontomachus bauri
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Electrophoretic Profile

2.2. Enzymatic Activities
2.2.1. Azocaseinolytic Activity

2.2.2. Gelatin Zymography


2.2.3. Fibrinogenolytic Activity

2.3. Biological Activities
2.3.1. Hemolytic Activity
2.3.2. Cell Viability Assay

2.3.3. Hemorrhagic and Coagulant Activities
2.3.4. Defibrinating Activity
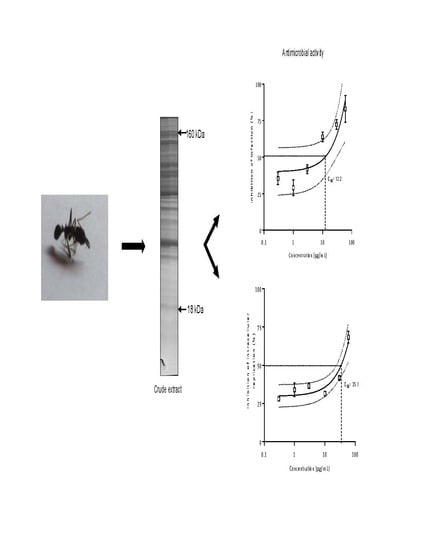
2.3.5. Antimicrobial Activity
| O. bauri Venom Concentration (μg) | Zones of Growth Inhibition, in mm (% Inhibition) | |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | Staphylococcus aureus | |
| 15 | 15 (62.5) | 16 (72.7) |
| 10 | 12 (50.0) | 14 (63.6) |
| 5 | 11 (45.8) | 11 (50.0) |
| 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 1.25 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Positive control * | 24 | 22 |
2.3.6. Antiparasitic Activity

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animals
4.2. Crude Venom
4.3. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
4.4. Enzymatic Activities
4.4.1. Azocaseinolytic Activity
4.4.2. Effect of pH and Temperature on Azocaseinolytic Activity
4.4.3. Effect of Inhibitors and Ions on Azocaseinolytic Activity
4.4.4. Gelatin Zymography
4.4.5. Temperature Dependent Gelatinolytic Activity
4.4.6. Enzyme Stability
4.4.7. Fibrinogenolytic Activity
4.5. Biological Activities
4.5.1. Hemolytic Activity
4.5.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.5.3. Hemorrhagic Activity
4.5.4. Coagulant Activity
4.5.5. Defibrinating Activity
4.5.6. Antimicrobial activity
4.5.7. Antiparasitic Activity
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spagna, J.C.; Vakis, A.I.; Schmidt, C.A.; Patek, S.N.; Zhang, X.; Tsutsui, N.D.; Suarez, A.V. Phylogeny, scaling, and the generation of extreme forces in trap-jaw ants. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 2358–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesus, M.S.; Rodrigues, W.C.; Barbosa, G.; Trilles, L.; Wanke, B.; Lazera Mdos, S.; Silva, M. Cryptococcus neoformans carried by Odontomachus bauri ants. Mem. Inst. Osvaldo Cruz 2012, 107, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Acosta, A.; Reyes-Lugo, M. Severe human urticaria produced by ant (Odontomachus bauri, Emery 1892) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) venom. Int. J. Dermatol. 2002, 41, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronenberg, W.; Tautz, J.; Hölldobler, B. Fast trap jaws and giant neurons in the ant Odontomachus. Science 1993, 5133, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patek, S.N.; Baio, J.E.; Fisher, B.L.; Suarez, A.V. Multifunctionality and mechanical origins: Ballistic jaw propulsion in trap-jaw ants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12787–12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronenberg, W.; Tautz, J.; Hoildobler, B. Fast Trap Jaws and Giant Neurons in the Ant Odontomachus. Science 1993, 262, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Acosta, A.; Sánchez, E.E.; Navarrete, L.F. Intense allergic reaction in a patient stung by the black ant (Odontomachus bauri). Rev. Cuba. Med. Trop. 2006, 1, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, E.G.; Bueno, O.C.; Yabuki, A.T.; de Jesus, C.M.; Solis, D.R.; Rossi, M.L.; Nogueira Nde, L. General morphology and ultrastructure of the venom apparatus and convoluted gland of the fire ant, Solenopsis saevissima. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billen, J.; Stroobants, Z.; Wenseleers, T.; Hashim, R.; Ito, F. Diversity and morphology of abdominal glands in workers of the ant genus Myopias (Formicidae, Ponerinae). Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2013, 42, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanandy, T.; Gueven, N.; Davies, N.W.; Brown, S.G.G.; Wiese, M.D. Pilosulins: A review of the structure and mode of action of venom peptides from an Australian ant Myrmecia pilosula. Toxicon 2015, 98, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orivel, J.; Redeker, V.; le Caer, J.P.; Krier, F.; Revol-Junelles, A.M.; Longeon, A.; Chaffotte, A.; Dejean, A.; Rossier, J. Ponericins, new antibacterial and insecticidal peptides from the venom of the ant Pachycondyla goeldii. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17823–17829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.D. Exocrine chemistry of the myrmicine ant Zacryptocerus pusillus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2006, 63, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escoubas, P.; King, G.F. Venomics as a drug discovery platform. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2009, 6, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex cocktails: The evolutionary novelty of venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cologna, C.T.; dos Santos Cardoso, J.; Jourdan, E.; Degueldre, M.; Gregory, U.; Nicolas, G.; Trovatti Uetanabaro, A.P.; Costa Neto, E.M.; Thonart, P.; de Pauw, E.; et al. Peptidomic comparison and characterization of the major components of the venom of the giant ant Dinoponera quadriceps collected in four different areas of Brazil. J. Proteomics 2013, 94, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.F.; Hardy, M.C. Spider-Venom Peptides: Structure, pharmacology, and potential for control of insect pests. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.J.; Herzig, V.; King, G.F.; Alewood, P.F. The insecticidal potential of venom peptides. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3665–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilevski, A.A.; Kozlov, S.A.; Egorov, T.A.; Grishin, E.V. Purification and characterization of biologically active peptides from spider venoms. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 615, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouzid, W.; Verdenaud, M.; Klopp, C.; Ducancel, F.; Noirot, C.; Vétillard, A. De Novo sequencing and transcriptome analysis for Tetramorium bicarinatum: A comprehensive venom gland transcriptome analysis from an ant species. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aili, S.R.; Touchard, A.; Escoubas, P.; Padula, M.P.; Orivel, J.; Dejean, A.; Nicholson, G.M. Diversity of peptide toxins from stinging ant venoms. Toxicon 2014, 92, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.; Giralt, E. Three valuable peptides from bee and wasp venoms for therapeutic and biotechnological use: Melittin, apamin and mastoparan. Toxins 2015, 7, 1126–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.R. Hymenoptera Venom Allergens. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 30, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, I.; Davis, J.L.; Rash, L.D.; Anangi, R.; Mobli, M.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J.; King, G.F. Venomics: A new paradigm for natural products-based drug discovery. Amino Acids 2010, 40, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, M.D.; Chataway, T.K.; Davies, N.W.; Milne, R.W.; Brown, S.G.; Gai, W.P.; Heddle, R.J. Proteomic analysis of Myrmecia pilosula (jack jumper) ant venom. Toxicon 2006, 47, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, D.; Zhao, Q.; McMahan, C.; Velasquez, D.; Haskins, W.E.; Sponsel, V.; Cassill, A.; Renthal, R. The major antennal chemosensory protein of red imported fire ant workers. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitworth, S.T.; Blum, M.S.; Travis, J. Proteolytic enzymes from larvae of the fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. Isolation and characterization of four serine endopeptidases. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14430–14434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Choo, Y.M.; Yoon, H.J.; Jia, J.; Cui, Z.; Wang, D.; Kim, D.H.; Sohn, H.D.; Jin, B.R. Fibrin(ogen)olytic activity of bumblebee venom serine protease. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 255, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeller, L. Protein denaturation on p-t axes—Thermodynamics and analysis. Subcell. Biochem. 2015, 72, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouzid, W.; Klopp, C.; Verdenaud, M.; Ducancel, F.; Vétillard, A. Profiling the venom gland transcriptome of Tetramorium bicarinatum (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): The first transcriptome analysis of an ant species. Toxicon 2013, 70, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ye, F.P.; Wang, J.; Liao, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.S.; Lee, W.H. Purification, characterization and gene cloning of Da-36, a novel serine protease from Deinagkistrodon acutus venom. Toxicon 2013, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, H.; Kim, K.S. Improvement of Interfacial Protein Stability by CHAPS. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, D.; Majumdar, S.; Mukherjee, A.K. Mechanism of in vivo anticoagulant and haemolytic activity by a neutral phospholipase A(2) purified from Daboia russelii russelii venom: Correlation with clinical manifestations in Russell’s Viper envenomed patients. Toxicon 2013, 76, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, B.M.; da Silva, A.V.; Resende, V.M.; Arcuri, H.A.; dos Santos Cabrera, M.P.; Ruggiero Neto, J.; Palma, M.S. Characterization of two novel polyfunctional mastoparan peptides from the venom of the social wasp Polybia paulista. Peptides 2009, 30, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, M.A.; de Souza, B.M.; Marques, M.R.; Palma, M.S. Structural and biological characterization of two novel peptides from the venom of the neotropical social wasp Agelaia pallipes pallipes. Toxicon 2004, 44, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchard, A.; Labriere, N.; Roux, O.; Petitclerc, F.; Orivel, J.; Escoubas, P.; Koh, J.M.S.; Nicholson, G.M.; Dejean, A. Venom toxicity and composition in three Pseudomyrmex ant species having different nesting modes. Toxicon 2014, 88, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nget-Hong, T.; Gnanajothy, P. Comparative study of the enzymatic, hemorrhagic, procoagulant and anticoagulant activities of some animal venoms. Camp. Biochem. Physiol. 1992, 36, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; You, D.; Xu, X.; Han, W.; Lu, Y.; Lai, R.; Meng, Q. An anticoagulant serine protease from the wasp venom of Vespa magnifica. Toxicon 2008, 51, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa Jde, O.; Fonseca, K.C.; Mamede, C.C.; Beletti, M.E.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Soares, A.M.; Arantes, E.C.; Hirayama, S.N.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S.; Fonseca, F.; et al. Bhalternin: Functional and structural characterization of a new thrombin-like enzyme from Bothrops alternatus snake venom. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A.; Chaves, F.; Diaz, C.; Escalante, T. Experimental pathology of local tissue damage induced by Bothrops asper snake venom. Toxicon 2009, 54, 958–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Lai, R. The mastoparanogen from wasp. Peptides 2006, 27, 3053–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Ghosh, P.; de, T.; Gomes, A.; Gomes, A.; Dungdung, S.R. In vivo and in vitro antileishmanial activity of Bungarus caeruleus snake venom through alteration of immunomodulatory activity. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 135, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanphorlin, L.M.; Cabral, H.; Arantes, E.; Assis, D.; Juliano, L.; Juliano, M.A.; Da-Silva, R.; Gomes, E.; Bonilla-Rodriguez, G.O. Purification and characterization of a new alkaline serine protease from the thermophilic fungus Myceliophthora sp. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heussen, C.; Dowdle, E.B. Electrophoretic analysis of plasminogen activators in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate and copolymerized substrates. Anal. Biochem. 1980, 102, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, W.; Prentice, C.R.M. The proteolytic action of ancrod on human fibrinogen and its polypeptide chains. Thromb. Res. 1973, 2, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, M.C.; Furtado, M.F.; Travaglia-Cardoso, S.R.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Serrano, S.M.T. Sex-based individual variation of snake venom proteome among eighteen Bothrops jararaca siblings. Toxicon 2006, 47, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denson, K.W.; Russell, F.E.; Almagro, D.; Bishop, R.C. Characterization of the coagulant activity of some snake venoms. Toxicon 1972, 10, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene, J.A.; Roy, A.; Rojas, G.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Cerdas, L. Comparative study on coagulant, defibrinating, fibrinolytic and fibrinogenolytic activities of Costa Rican crotaline snake venoms and their neutralization by a polyvalent antivenom. Toxicon 1989, 27, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagmur, G.; Ercal, B.D.; Mengeloglu, Z.; Sariguzel, F.M.; Berk, E.; Saglam, D. Is rapid antibacterial susceptibility testing medium reliable for routine laboratory practices? Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 31, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, T.C.; Silva, D.A.; Rostkowska, C.; Bela, S.R.; Ferro, E.A.; Magalhaes, P.M.; Mineo, J.R. Toxoplasma gondii: Effects of Artemisia annua L. on susceptibility to infection in experimental models in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 122, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones-Brando, L.; D’Angelo, J.; Posner, G.H.; Yolken, R. In Vitro Inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii by Four New Derivatives of Artemisinin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 4206–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, M.F.; Mota, C.M.; Miranda, V.D.S.; Oliveira Cunha, A.D.; Silva, M.C.; Naves, K.S.C.; Oliveira, F.D.; Silva, D.A.d.O.; Mineo, T.W.P.; Santiago, F.M. Biological and Enzymatic Characterization of Proteases from Crude Venom of the Ant Odontomachus bauri. Toxins 2015, 7, 5114-5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124869
Silva MF, Mota CM, Miranda VDS, Oliveira Cunha AD, Silva MC, Naves KSC, Oliveira FD, Silva DAdO, Mineo TWP, Santiago FM. Biological and Enzymatic Characterization of Proteases from Crude Venom of the Ant Odontomachus bauri. Toxins. 2015; 7(12):5114-5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124869
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Mariana Ferreira, Caroline Martins Mota, Vanessa Dos Santos Miranda, Amanda De Oliveira Cunha, Maraísa Cristina Silva, Karinne Spirandelli Carvalho Naves, Fábio De Oliveira, Deise Aparecida de Oliveira Silva, Tiago Wilson Patriarca Mineo, and Fernanda Maria Santiago. 2015. "Biological and Enzymatic Characterization of Proteases from Crude Venom of the Ant Odontomachus bauri" Toxins 7, no. 12: 5114-5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124869
APA StyleSilva, M. F., Mota, C. M., Miranda, V. D. S., Oliveira Cunha, A. D., Silva, M. C., Naves, K. S. C., Oliveira, F. D., Silva, D. A. d. O., Mineo, T. W. P., & Santiago, F. M. (2015). Biological and Enzymatic Characterization of Proteases from Crude Venom of the Ant Odontomachus bauri. Toxins, 7(12), 5114-5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124869