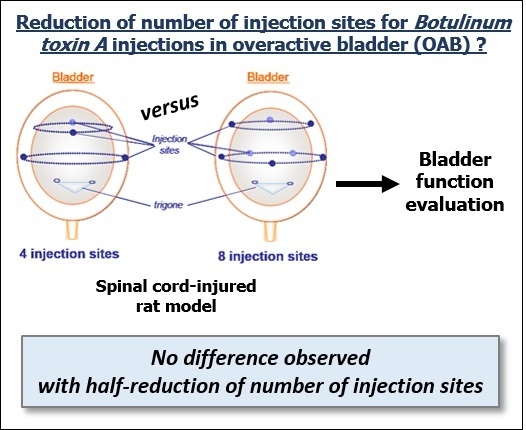
Does Reduction of Number of Intradetrusor Injection Sites of aboBoNTA (Dysport®) Impact Efficacy and Safety in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Intradetrusor Injections of aboBoNT-A 22.5U in Four or Eight Sites in Rats 19 Days after SCI-Induced NDO
| Treatment | Saline (Aggregated) | AboBoNTA 22.5U | Corresponding Clinically Relevant Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Injection Sites | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 | |
| Maximal amplitude, mmHg | 30.3 ± 1.4 | 30.0 ± 1.9 | 23.2 ± 1.2 ### | 22.7 ± 0.9 ### | Maximal pressure at contraction (P Max) |
| Voiding efficiency, % | 87.2 ± 4.9 | 87.3 ± 3.9 | 90.9 ± 4.7 | 88.2 ± 4.6 | Post-void residual volume in bladder |
| Infused volume, µL (Bladder capacity) | 801.1 ± 45.6 | 898.9 ± 69.6 | 1186.6 ± 101.2 ## | 999.2 ± 81.9 | bladder storage capacity |
| Compliance, mL/mmHg | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.25 ± 0.03 ## | 0.21 ± 0.02 | Compliance (index, mL or cm H2O) |
| NVC amplitude, mmHg | 5.9 ± 0.8 | 5.1 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.3 # | 3.9 ± 0.2 ## | Pressure at first involuntary contraction |
| NVC frequency, nb per min | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | - |
| NVC volume threshold, % | 49.5 ± 8.1 | 40.8 ± 7.3 | 58.7 ± 6.1 | 52.0 ± 5.7 | Bladder volume at first contraction |

2.2. Effects of Treatments on Body Weight
| Treatment | AboBoNTA 22.5 U | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of injection sites | Four | Eight |
| AUC BWL at day one post-injection (% × day) | −3.4 ± 0.2 | −3.4 ± 0.2 |
| AUC BWL from day one to day two post-injection (% × day) | −10.3 ± 0.5 | −9.7 ± 0.5 |
| AUC BWL from day one to day tree post-injection (% × day) | −19.8 ± 1.2 | −17.2 ± 1.3 |
| AUC BWL from day one to day four post-injection (% × day) | −33.5 ± 2.1 | −27.8 ± 2.3 |
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Experimental Section
5.1. General Experimental Design
5.2. Saline or aboBoNTA Intradetrusor Injections

5.3. Cystometry Experiments in Conscious Spinal-Cord-Injured Rats
5.4. Statistical Analysis
5.5. Drugs and Chemicals
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schurch, B.; Stohrer, M.; Kramer, G.; Schmid, D.M.; Gaul, G.; Hauri, D. Botulinum-A toxin for treating detrusor hyperreflexia in spinal cord injured patients: A new alternative to anticholinergic drugs? Preliminary results. J. Urol. 2000, 164, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.P.; Franks, M.E.; McNeil, B.K.; Ghosh, R.; de Groat, W.C.; Chancellor, M.B.; Somogyi, G.T. Effect of botulinum toxin A on the autonomic nervous system of the rat lower urinary tract. J. Urol. 2003, 169, 1896–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, M.; Somogyi, G.T.; Kiss, S.; Boone, T.B.; Smith, C.P. Botulinum toxin A inhibits ATP release from bladder urothelium after chronic spinal cord injury. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Chancellor, M.B.; Kuo, H.C. Urinary nerve growth factor levels are elevated in patients with detrusor overactivity and decreased in responders to detrusor botulinum toxin-A injection. Eur. Urol. 2009, 56, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.P.; Boone, T.B.; de Groat, W.C.; Chancellor, M.B.; Somogyi, G.T. Effect of stimulation intensity and botulinum toxin isoform on rat bladder strip contractions. Brain Res. Bull. 2003, 61, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolidis, A.; Dasgupta, P.; Fowler, C.J. Proposed mechanism for the efficacy of injected botulinum toxin in the treatment of human detrusor overactivity. Eur. Urol. 2006, 49, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, A.; Somogyi, G.T.; Boone, T.B.; Smith, C.P. Central inhibitory effect of intravesically applied botulinum toxin A in chronic spinal cord injury. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, A.; Wyndaele, J.J.; Andersson, K.E.; Fry, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Zabbarova, I.; De, W.S. Researching bladder afferents—determining the effects of β3-adrenergic receptor agonists and botulinum toxin type-A. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Tyagi, P.; Huang, C.C.; Yoshimura, N.; Wu, M.; Kaufman, J.; Chancellor, M.B. Urodynamic and immunohistochemical evaluation of intravesical botulinum toxin A delivery using liposomes. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F.; Herschorn, S.; Aliotta, P.; Brin, M.; Thompson, C.; Lam, W.; Daniell, G.; Heesakkers, J.; Haag-Molkenteller, C. Efficacy and safety of onabotulinumtoxinA in patients with urinary incontinence due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehren, I.; Volz, D.; Farrelly, E.; Berglund, L.; Brundin, L.; Hultling, C.; Lafolie, P. Efficacy and impact of botulinum toxin A on quality of life in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: A randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2007, 41, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, D.; Gousse, A.; Keppenne, V.; Sievert, K.D.; Thompson, C.; Lam, W.; Brin, M.F.; Jenkins, B.; Haag-Molkenteller, C. Phase 3 efficacy and tolerability study of onabotulinumtoxinA for urinary incontinence from neurogenic detrusor overactivity. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herschorn, S.; Gajewski, J.; Ethans, K.; Corcos, J.; Carlson, K.; Bailly, G.; Bard, R.; Valiquette, L.; Baverstock, R.; Carr, L.; Radomski, S. Efficacy of botulinum toxin A injection for neurogenic detrusor overactivity and urinary incontinence: A randomized, double-blind trial. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovner, E.; Dmochowski, R.; Chapple, C.; Thompson, C.; Lam, W.; Haag-Molkenteller, C. OnabotulinumtoxinA improves urodynamic outcomes in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2013, 32, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurch, B.; de Seze, M.; Denys, P.; Chartier-Kastler, E.; Haab, F.; Everaert, K.; Plante, P.; Perrouin-Verbe, B.; Kumar, C.; Fraczek, S.; Brin, M.F. Botulinum toxin type a is a safe and effective treatment for neurogenic urinary incontinence: Results of a single treatment, randomized, placebo controlled 6-month study. J. Urol. 2005, 174, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangera, A.; Andersson, K.E.; Apostolidis, A.; Chapple, C.; Dasgupta, P.; Giannantoni, A.; Gravas, S.; Madersbacher, S. Contemporary management of lower urinary tract disease with botulinum toxin A: A systematic review of botox (onabotulinumtoxinA) and dysport (abobotulinumtoxinA). Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, S.; Mohammadian, R.; Aminsharifi, A.; Ariafar, A.; Vaghedashti, J.; Yazdani, M.; Yadollahi, M.; Emadmarvasti, V.; Baharikhoob, A. Success rate and patients' satisfaction following intradetrusor dysport injection in patients with detrusor overactivity: A comparative study of idiopathic and neurogenic types of detrusor overactivity. Urol. J. 2014, 11, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.P.; Gangitano, D.A.; Munoz, A.; Salas, N.A.; Boone, T.B.; Aoki, K.R.; Francis, J.; Somogyi, G.T. Botulinum toxin type A normalizes alterations in urothelial ATP and NO release induced by chronic spinal cord injury. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temeltas, G.; Tikiz, C.; Dagci, T.; Tuglu, I.; Yavasoglu, A. The effects of botulinum-A toxin on bladder function and histology in spinal cord injured rats: Is there any difference between early and late application? J. Urol. 2005, 174, 2393–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, P.Y.; Johnson, C.S.; Wrathall, J.R. Comparison of the effects of complete and incomplete spinal cord injury on lower urinary tract function as evaluated in unanesthetized rats. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 208, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr-Roussel, D.; Oger, S.; Pignol, B.; Pham, E.; Le, M.A.; Chabrier, P.E.; Caisey, S.; Compagnie, S.; Picaut, P.; Bernabe, J.; et al. Minimal effective dose of dysport and botox in a rat model of neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.L.; de Groat, W.C. The role of capsaicin-sensitive afferent fibers in the lower urinary tract dysfunction induced by chronic spinal cord injury in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 187, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, J.; Kramer, G.; Jakse, G. Comparing two types of botulinum-A toxin detrusor injections in patients with severe neurogenic detrusor overactivity: A case-control study. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, R.; Jones, D.; Borrego, J.A. Comparing two botulinum toxin type A formulations using manufacturers’ product summaries. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2007, 32, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsenmeyer, T.A. Use of botulinum toxin in individuals with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: State of the art review. J. Spin. Cord Med. 2013, 36, 402–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsenty, G.; Denys, P.; Amarenco, G.; de Seze, M.; Game, X.; Haab, F.; Kerdraon, J.; Perrouin-Verbe, B.; Ruffion, A.; Saussine, C.; et al. Botulinum toxin A (Botox) intradetrusor injections in adults with neurogenic detrusor overactivity/neurogenic overactive bladder: A systematic literature review. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F. Targets for botulinum toxin in the lower urinary tract. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2014, 33, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolidis, A.; Popat, R.; Yiangou, Y.; Cockayne, D.; Ford, A.P.; Davis, J.B.; Dasgupta, P.; Fowler, C.J.; Anand, P. Decreased sensory receptors P2X3 and TRPV1 in suburothelial nerve fibers following intradetrusor injections of botulinum toxin for human detrusor overactivity. J. Urol. 2005, 174, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannantoni, A.; di Stasi, S.M.; Nardicchi, V.; Zucchi, A.; Macchioni, L.; Bini, V.; Goracci, G.; Porena, M. Botulinum-A toxin injections into the detrusor muscle decrease nerve growth factor bladder tissue levels in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 2341–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannantoni, A.; Conte, A.; Farfariello, V.; Proietti, S.; Vianello, A.; Nardicchi, V.; Santoni, G.; Amantini, C. Onabotulinumtoxin-A intradetrusorial injections modulate bladder expression of NGF, TrkA, p75 and TRPV1 in patients with detrusor overactivity. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 68, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.; Yunoki, T.; Naito, S.; Yoshimura, N. Differential effects of botulinum neurotoxin A on bladder contractile responses to activation of efferent nerves, smooth muscles and afferent nerves in rats. J. Urol. 2012, 188, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehnert, U.; Boy, S.; Schmid, M.; Reitz, A.; von, H.A.; Hodler, J.; Schurch, B. A morphological evaluation of botulinum neurotoxin A injections into the detrusor muscle using magnetic resonance imaging. World J. Urol. 2009, 27, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, A.; Cruz, F.; Cruz, C.D.; Avelino, A. Spread of onabotulinumtoxinA after bladder injection. Experimental study using the distribution of cleaved SNAP-25 as the marker of the toxin action. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsenty, G.; Carsenac, A.; Boy, S.; Reitz, A.; Bardot, P.; Tournebise, H. Botulinum toxin-A (BTA) in the treatmentof neurogenic detrusor overactivity incontinence (NDOI)d a prospective randomized study to compare 30 vs. 10 injection sites (abstract 890). Eur. Urol. 2007, 6, 245–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.H.; Chen, S.F.; Kuo, H.C. Different number of intravesical onabotulinumtoxinA injections for patients with refractory detrusor overactivity do not affect treatment outcome: A prospective randomized comparative study. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Castaneda, J.; Jankovic, J.; Comella, C.; Dashtipour, K.; Fernandez, H.H.; Mari, Z. Diffusion, spread, and migration of botulinum toxin. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, H.F.; Zhu, Z.; Thach, T.Q.; Ruegg, C.L. Characterization of diffusion and duration of action of a new botulinum toxin type A formulation. Toxicon 2011, 58, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, H.; Duran, Y.; Dilege, E.; Mihmanli, M.; Seymen, H.; Demirkol, M.O. Effect on gastric emptying and weight reduction of botulinum toxin-A injection into the gastric antral layer: An experimental study in the obese rat model. Obes. Surg. 2005, 15, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Popolo, G. Botulinum-A toxin in the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2001, 20, 522–524. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, H.C. Urodynamic evidence of effectiveness of botulinum A toxin injection in treatment of detrusor overactivity refractory to anticholinergic agents. Urology 2004, 63, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grise, P.; Ruffion, A.; Denys, P.; Egon, G.; Chartier, K.E. Efficacy and tolerability of botulinum toxin type A in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity and without concomitant anticholinergic therapy: Comparison of two doses. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Laet, K.; Wyndaele, J.J. Adverse events after botulinum A toxin injection for neurogenic voiding disorders. Spin. Cord 2005, 43, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huynh Le Maux, A.; Pignol, B.; Behr-Roussel, D.; Blachon, J.-L.; Chabrier, P.-E.; Compagnie, S.; Picaut, P.; Bernabé, J.; Giuliano, F.; Denys, P. Does Reduction of Number of Intradetrusor Injection Sites of aboBoNTA (Dysport®) Impact Efficacy and Safety in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity? Toxins 2015, 7, 5462-5471. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124896
Huynh Le Maux A, Pignol B, Behr-Roussel D, Blachon J-L, Chabrier P-E, Compagnie S, Picaut P, Bernabé J, Giuliano F, Denys P. Does Reduction of Number of Intradetrusor Injection Sites of aboBoNTA (Dysport®) Impact Efficacy and Safety in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity? Toxins. 2015; 7(12):5462-5471. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124896
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuynh Le Maux, Amélie, Bernadette Pignol, Delphine Behr-Roussel, Jean-Luc Blachon, Pierre-Etienne Chabrier, Sandrine Compagnie, Philippe Picaut, Jacques Bernabé, François Giuliano, and Pierre Denys. 2015. "Does Reduction of Number of Intradetrusor Injection Sites of aboBoNTA (Dysport®) Impact Efficacy and Safety in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity?" Toxins 7, no. 12: 5462-5471. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124896
APA StyleHuynh Le Maux, A., Pignol, B., Behr-Roussel, D., Blachon, J.-L., Chabrier, P.-E., Compagnie, S., Picaut, P., Bernabé, J., Giuliano, F., & Denys, P. (2015). Does Reduction of Number of Intradetrusor Injection Sites of aboBoNTA (Dysport®) Impact Efficacy and Safety in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity? Toxins, 7(12), 5462-5471. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124896