Scorpions from Mexico: From Species Diversity to Venom Complexity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Families | Worldwide | Mexico | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genera | Species | Genera | Species | % Genera | % Species | |
| Akravidae | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bothriuridae | 16 | 150 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Buthidae | 92 | 1054 | 2 | 44 | 2 | 4 |
| Caraboctonidae | 5 | 31 | 3 | 9 | 60 | 29 |
| Chactidae | 12 | 178 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| Chaerilidae | 1 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Diplocentridae | 10 | 121 | 3 | 58 | 30 | 48 |
| Euscorpiidae | 4 | 51 | 3 | 8 | 75 | 16 |
| Hemiscorpiidae | 1 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Heteroscorpionidae | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hormuridae | 11 | 81 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Iuridae | 4 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pseudochactidae | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Scorpionidae | 9 | 152 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Scorpiopidae | 6 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Superstitioniidae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 100 |
| Troglotayosicidae | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Typhlochactidae | 4 | 11 | 4 | 11 | 100 | 100 |
| Urodacidae | 2 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vaejovidae | 23 | 201 | 21 | 149 | 91 | 74 |
| Totals | 208 | 2231 | 38 | 281 | 18 | 13 |
Scorpion Taxonomy and Systematics
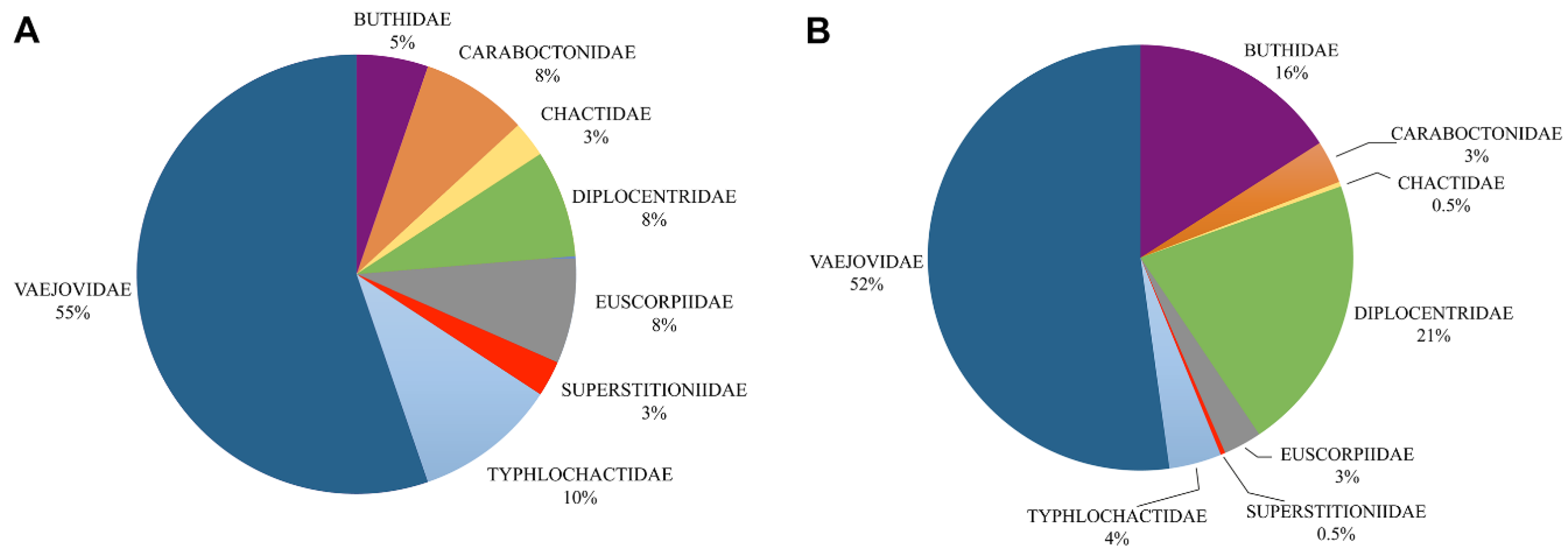
2. Mexican Scorpion Diversity


2.1. Family Buthidae C.L. Koch, 1837
2.2. Family Caraboctonidae Krapelin, 1905
2.3. Family Chactidae Pocock, 1893
2.4. Family Diplocentridae Karsch, 1880
2.5. Family Euscorpiidae Laurie, 1896
2.6. Family Superstitioniidae Stahnke, 1940
2.7. Family Typhlochactidae Mitchell, 1971
2.8. Family Vaejovidae Thorell, 1876
3. Geographical Hotspots and Environmental Variables as Indicators of Explored Areas in Mexico
4. Venomic Studies in Mexico
| Species | # Peptides | Most Relevant | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anuroctonus pococki | 8 | Phaiodotoxin | [43] |
| Centruroides elegans | 12 | CeII8 | [101] |
| Centruroides exilicauda | 17 | Neurotoxin Cex11 | [71] |
| Centruroides gracilis | 4 | Toxin Cg2 | [85] |
| Centruroides infamatus | 1 | Beta toxin Cii1 | [74] |
| Centruroides limpidus | 20 | Cll1, Cll2 | [74,79] |
| Centruroides margaritatus | 1 | Margatoxin | [102] |
| Centruroides noxius | 31 | Noxiustoxin, Cn2 | [56,57,58,59,61,62,63,103] |
| Centruroides sculpturatus | 26 | CsEv1 | [70] |
| Centruroides suffusus | 8 | CssII | [104] |
| Centruroides tecomanus | 37 | Clt1 | [77,105] |
| Hoffmannihadrurus gertschi | 13 | Hadrucalcin, Hadrurin, Hge scorpine | [40,91,98,106] |
| Mesomexovis punctatus | 15 | VpAmp1 | [107,108] |
| Mesomexovis subcristatus | 8 | ViSplp1 | [107] |
| Thorellius intrepidus | 14 | ViCaTx1 | [107] |
| Vaejovis mexicanus | 22 | Vejovine, Vm23, Vm24 | [92,96,97] |

5. Natural History, Behavior and Ecology Studies of Mexican Scorpions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunlop, J.A.; Selden, P.A. Scorpion fragments from the Silurian of Powys, Wales. Arachnology 2013, 16, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddington, J.; Rudkin, D.M.; Dunlop, J.A. A new mid-Silurian aquatic scorpion—One step closer to land? Biol. Lett. 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Francke, O.F.; Prendini, L. Shinning a light into the world’s deepest caves: Phylogenetic systematics of the troglobiotic scorpion genus Alacran Francke, 1982 (Typhlochactidae: Alacraninae). Invertebr. Syst. 2014, 28, 643–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, J.A.; Ojanguren-Affilastro, A.A.; Mattoni, C.I.; Prendini, L. Systematic revision of the Andean scorpion genus Orobothriurus Maury, 1976 (Bothriuridae), with discussion of the altitude record for scorpions. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2011, 359, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.C. Scorpions of Baja California, Mexico, and Adjacent Islands. Occ. Pap. Calif. Acad. Sci. 1980, 135, 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Polis, G.A. The Biology of Scorpions; Stanford University Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1990; p. 587. [Google Scholar]
- Prendini, L. Scorpion diversity and distribution in southern Africa: Pattern and process. In African Biodiversity: Molecules, Organisms, Ecosystems; Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Tropical Biology, Bonn, Germany, 2–6 May 2004; Huber, B.A., Sinclair, B.J., Lampe, K.H., Eds.; Springer Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 25–68. [Google Scholar]
- Prendini, L. Order Scorpiones C.L. Koch, 1850. In Animal Biodiversity: An Outline of Higher-Level Classification and Survey of Taxonomic Richness; Zhang, Z.Q., Ed.; Zootaxa: Auckland, New Zealand, 2011; Volume 3148, pp. 115–177. [Google Scholar]
- Rein-Ove, J. Scorpion Files. Tronheim. Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2014. Available online: http://www.ntnu.no/ub/scorpion-files (accessed on 1 October 2015).
- Prendini, L.; Wheeler, W.C. Scorpion higher phylogeny and classification, taxonomic anarchy, and standards for peer review in online publishing. Cladistics 2005, 21, 446–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.P.; Fernández, R.; Esposito, L.; González-Santillán, E.; Monod, L. Phylogenomic resolution of scorpions reveals multilevel discordance with morphological phylogenetic signal. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2015, 282, 20142953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francke, O.F. The genus Diplocentrus in the Yucatan Peninsula with description of two new troglobites (Scorpionida, Diplocentridae). Assoc. Mex. Cave Stud. Bull. 1979, 6, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Francke, O.F. Scorpions of the genus Diplocentrus from Oaxaca, Mexico. J. Arachnol. 1977, 4, 145–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sissom, W.D. Systematics, biogeography and paleontology. In The Biology of Scorpions; Polis, G.A., Ed.; Stanford University Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 64–160. [Google Scholar]
- Fet, V.; Sissom, W.D.; Lowe, G.; Braunwalder, M.E. Catalog of the Scorpions of the World (1758–1998); The New York Entomological Society: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 690. [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço, W.; Sissom, W.D. Scorpiones. In Biodiversidad, Taxonomía y Biogeografía de Artrópodos de México: Hacia una Síntesis de su Conocimiento; Llorente-Bousquets, J.E., Soriano, E.G., Papavero, N., Eds.; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México/CONABIO/BAYER: Mexico City, Mexico, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 115–135. [Google Scholar]
- Armas, L.F.; Martín-Frías, E.; Estévez-Ramírez, J. Lista anotada de las especies mexicanas del género Centruroides Marx, 1890 (Scorpiones: Buthidae). Rev. Iber. Aracnol. 2003, 8, 93–98. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Francke, O.F. Biodiversidad de Arthropoda (Chelicerata: Arachnida ex. Acari) en México. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2013, 85, S408–S418. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sissom, W.D.; Hendrixson, B. Scorpion biodiversity and patterns of endemism in northern Mexico. In Biodiversity, Ecosystems and Conservation in Northern Mexico; Cartron, J.L.E., Ceballos, G., Felger, R.S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 122–137. [Google Scholar]
- Soleglad, M.E.; Fet, V. Contributions to scorpion systematics. III. Subfamilies Smeringurinae and Syntropinae (Scorpiones: Vaejovidae). Euscorpius 2008, 71, 1–115. [Google Scholar]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Francke, O.F.; Prendini, L. Phylogeny of the North American scorpion genus Diplocentrus Peters, 1861 (Scorpiones: Diplocentridae) based on morphology, nuclear and mitochondrial DNA. Arthropod Syst. Phylo. 2014, 72, 257–279. [Google Scholar]
- González-Santillán, E.; Prendini, L. Phylogeny of the North American vaejovid scorpion subfamily Syntropinae Kraepelin, 1905, based on morphology, mitochondrial and nuclear DNA. Cladistics 2015, 31, 341–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, F.; Villegas-Guzmán, G.; González-Santillán, E.; Córdova-Tabares, V.; Francke, O.F.; Piedra-Jiménez, D.; Estrada-Ruiz, E.; Luna-Castro, B. New fossil scorpion from the Chiapas Amber Lagerstätte. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-Saavedra, J.; Francke, O.F.; Cano-Camacho, H.; Hernández-Calderón, E. Evidencias morfológicas y moleculares que validan como especie a Centruroides tecomanus (Scorpiones, Buthidae). Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2009, 80, 71–84. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Contreras-Félix, G.A. Two new species of Centruroides Marx 1890 (Scorpiones: Buthidae) from Oaxaca, Mexico. Zootaxa 2013, 3734, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teruel, R.; Kovarik, F.; Baldazo-Monsivais, J.G.; Hoferek, D. A new species of Centruroides of the “nigrovariatus” group (Scorpiones: Buthidae) from southern Mexico. Rev. Iber. Aracnol. 2015, 26, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Francke, O.F.; Teruel, R.; Santibáñez-López, C.E. A new genus and a new species of scorpion (Scorpiones: Buthidae) from southeastern Mexico. J. Arachnol. 2014, 42, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendini, L. Substratum specialization and speciation in southern African scorpions: The Effect Hypothesis revisited. In Scorpions 2001. In Memoriam Gary A. Polis; Fet, V., Selden, P.A., Eds.; British Arachnological Society: London, UK, 2001; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gastil, B.; Minch, J.; Philips, R.P. The geology and ages of islands. In Island Biogeography in the Sea of Cortez; Case, T.J., Cody, M.L., Eds.; University of California Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1983; pp. 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Grismer, L.L. The origin and evolution of the peninsular herpetofauna of Baja California, Mexico. Herpetol. Nat. Hist. 1994, 2, 51–106. [Google Scholar]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Francke, O.F.; Prendini, L. Kolotl, n. gen. (Scorpiones: Diplocentridae), a new scorpion genus from Mexico. Am. Mus. Novit. 2014, 3815, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sissom, W.D. Family Vaejovidae Thorell, 1876. In Catalog of the Scorpions of the World (1758–1998); Fet, V., Sissom, W.D., Lowe, G., Braunwalder, M.E., Eds.; New York Entomological Society: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 503–553. [Google Scholar]
- González-Santillán, E.; Prendini, L. Redefinition and generic revision of the North American vaejovid scorpion subfamily Syntropinae Kraepelin, 1905, with descriptions of six new genera. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2013, 382, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Santillán, E.; Prendini, L. Systematic revision of the North American syntropine vaejovid scorpions with a subaculear tubercle, Konetontli González-Santillán and Prendini, 2013. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2015, 397, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Possani, L.D.; Schwartz, E.; Rodríguez de la Vega, R. Scorpion Venom; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- Possani, L.D. Structure of scorpion toxins. In Handbook of Natural Toxins; Tu, A.T., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1984; Volume 2, pp. 513–550. [Google Scholar]
- De la Vega, R.; Possani, L.D. Minireview: Current views on scorpion toxins specific for K+-channels. Toxicon 2004, 43, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Vega, R.; Possani, L.D. Overview of scorpion toxins specific for Na+ channels and related peptides: Biodiversity, structure-function relationships and evolution. Toxicon 2005, 46, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytgat, J.; Chandy, K.G.; Garcia, L.M.; Gutman, G.A.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; van de Walt, J.J.; Possani, L.D. A unified nomenclature for short chain peptides isolated from scorpion venoms: Alpha-KTx molecular subfamilies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, E.F.; Capes, E.M.; Diego-García, E.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Fuentes, O.; Possani, L.D.; Valdivia, H.H. Purification, amino acid sequence and functional properties of hadrucalcin, a peptide from Hadrurus gertschi scorpion venom with pharmacological activity on rynodine receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagón, A.C.; Possani, L.D. Utilización de cromatografía por afinidad para la purificación de enzimas de venenos animales. In Proceedings of the First InterAmerican Symposium on Enzyme Biotechnology, Mexico City, Mexico, 1984; pp. 125–132. (In Spanish)
- Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Batista, C.V.F.; Possani, L.D. Phaiodactylipin, a glycosylated heterodimericdo phospholipase A2, from the scorpion Anuroctonus phaiodactylus. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Batista, C.V.F.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Bosmans, F.; Tytgat, J.; Possani, L.D. Phaiodotoxin, a novel structural class of insect-toxin isolated from the venom of the Mexican scorpion Anuroctonus phaiodactylus. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 4753–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, E.; Rendón-Anaya, M.; Rego, S.C.; Schwartz, E.F.; Possani, L.D. Antarease-like Zn-metalloproteases are ubiquitous in the venom of different scorpion genera. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo, E.C.; Anguiano, L.G.; González, J. Acciones del veneno de alacrán sobre el sistema vaso-motor. Rev. Inst. Salubr. Enferm. Trop. 1944, 5, 227–240. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Del Pozo, E.C.; González, J.; Méndez, T.H. Acciones del veneno de alacrán sobre el aparato respiratorio. Rev. Inst. Salubr. Enferm. Trop. 1945, 6, 77–84. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- García, G.P. Étude des Neurotoxines du Venin du Scorpion Mexicain “Centruroides Suffusus Suffusus”. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Nice, Nice, France, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Rochat, H.; Bernard, P.; Couraud, F. Scorpion toxins: Chemistry and mode of action. In Advances in Cytopharmacology; Ceccarelli, B., Clementi, F., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 3, pp. 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Jover, E.; Couraud, F.; Rochat, H. Two types of scorpion neurotoxins characterized by their binding to two separate receptor sites on rat brain synaptosomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 95, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, H.; Rochat, C.; Sampieri, F.; Miranda, F.; Lissitzky, S. The amino acid sequence of neurotoxin II of Androctonus australis Hector. Eur. J. Biochem. 1972, 28, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, K.P.; Watt, D.D.; Lazdunski, M. Classification of Na channel receptors specific for scorpion toxins. Pflüg. Arch. (Eur. J. Phsysiol.) 1983, 387, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B.; Delepierre, M.; Tytgat, J. Scorpion toxins specific for Na+-channels. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possani, L.D.; Ramirez, G.A.; Fletcher, P.L., Jr.; Gurrola, M.A.H. Isolation of two mammalian toxins from the venom of the Mexican scorpion Centruroides elegans (Thorell). FEBS Lett. 1978, 91, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possani, L.D.; Fletcher, P.L., Jr.; Alagon, A.C.; Julia, J.Z. Purification and characterization of a mammalian toxin from venom of the Mexican scorpion Centruroides limpidus tecomanus Hoffmann. Toxicon 1980, 18, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, M.A.R.; Possani, L.D.; Ramírez, G.A.; Fletcher, P.L., Jr. Purification and characterization of two mammalian toxins from the venom of the Mexican scorpion Centruroides noxius Hoffmann. Toxicon 1980, 18, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possani, L.D.; Dent, M.A.R.; Martin, B.M.; Maelicke, A.; Svendsen, I. The amino terminal sequence of several toxins from the venom of the Mexican scorpion Centruroides noxius Hoffmann. Carlsberg Res. Commun. 1981, 46, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, E.; Wanke, E.; Prestipino, G.; Possani, L.D.; Maelicke, A. Selective blockage of voltage-dependent K+ channels by a novel scorpion toxin. Nature 1982, 296, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, E.; Prestipino, G.; Wanke, E.; Possani, L.D.; Maelicke, A. Selective action of scorpion neurotoxins on the ionic currents of the squid giant axon. Toxicon 1983, 3, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possani, L.D.; Martin, B.; Svendsen, I. The primary structure of Noxiustoxin: A K+ channel blocking peptide from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides noxius Hoffmann. Carlsberg Res. Commun. 1982, 47, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, D.A.; Morais-Cabral, J.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Kuo, A.; Gulbis, J.M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.R.; MacKinnon, R. The structure of potassium channel: Molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 1998, 280, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamudio, F.; Saavedra, R.; Martin, B.M.; Gurrola-Briones, G.; Herion, P.; Possani, L.D. Amino acid sequence an immunological characterization with monoclonal antibodies of two toxins from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides noxius Hoffmann. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 204, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintar, A.; Possani, L.D.; Delepierre, M. Solution structure of toxin 2 from Centruroides noxius Hoffmann, a beta scorpion neurotoxin acting on sodium channels. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 287, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavon, E.; Sacco, T.; Restano-Cassulini, R.; Gurrola, G.B.; Tempia, F.; Possani, L.D.; Wanke, E. Resurgent current and voltage sensor-trapping enhanced activation of a β-scorpion toxin solely in Nav1.6 sodium channel: Significance in mice Purkinje neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20326–20337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Aranda, E.S.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Possani, L.D. The use of synthetic peptides can be a misleading approach to generate vaccines against scorpion toxins. Vaccine 1995, 13, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Aranda, E.S.; Selisko, B.; York, E.J.; Gurrola, G.B.; Stewart, J.M.; Possani, L.D. Mapping of an epitope recognized by a neutralizing monoclonal antiboby specific to toxin Cn2 from the scorpion Centruroides noxius, using discontinuous synthetic peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaño-Umbarila, L.; Juárez-González, R.V.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Ortiz-León, M.; Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B. A strategy for the generation of specific human antibodies by directed evolution and phage display. An example of a single-chain antibody fragment that neutralizes a major component of scorpion venom. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 2591–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaño-Umbarila, L.; Contreras-Ferrat, G.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Morelos-Juárez, C.; Corzo, G.; Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B. Exploiting cross-reactivity to neutralize two different scorpion venoms with one single chain antibody fragment. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 6143–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canul-Tec, J.C.; Riaño-Umbarila, L.; Rudinño-Pinera, E.; Becerril, B.; Possani, L.D.; Torres-Larios, A. Structural basis of neutralization of the major toxic component from the scorpion Centruroides noxius Hoffmann by a human-derived single chain antibody fragment. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20892–20900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babin, D.R.; Watt, D.D.; Goos, S.M.; Mlenjek, R.V. Amino acid sequence of neurotoxic protein variants from the venom of Centruroides sculpturatus Ewing. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1974, 164, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, M.; Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Merino, E.; Zurita, M.; Possani, L.D. Genes and peptides from the scorpion Centruroides sculpturatus Ewing, that recognize Na+-channels. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Dávila, S.; Licea, A.; Corona, M.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Garcia-Valdes, J.; Boyer, L.; Possani, L.D. Biochemical, genetic and physiological characterization of venoms components from two species of scorpions: Centruroides exilicauda Wood and Centruroides sulpturatus Ewing. Biochimie 2004, 86, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagon, A.C.; Guzmán, H.S.; Martin, B.M.; Ramírez, A.N.; Carbone, E.; Possani, L.D. Isolation and characterization of two toxins from the Mexican scorpion Centruroides limpidus limpidus Karsch. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1988, 89, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.N.; Martín, B.M.; Gurrola, G.B.; Possani, L.D. Isolation and characterization of a novel toxin from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides limpidus limpidus Karsch. Toxicon 1994, 32, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehesa-Davila, M.; Ramírez, A.N.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Gurrola, G.; Lievano, A.; Darszon, A.; Possani, L.D. Structural and functional comparison of toxins from the venom of the scorpions Centruroides infamatus infamatus, Centruroides limpidus limpidus and Centruroides noxius. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1996, 113B, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possani, L.D.; Martín, B.M.; Svendsen, I.; Rode, G.S.; Erickson, B.W. Scorpion Toxins from Centruroides noxius and Tityus serrulatus: Primary Structures and Sequence Comparison by metric analysis. Biochem. J. 1985, 229, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatani, A.; Kirsh, G.E.; Possani, L.D.; Brown, A.M. Effects of two new world scorpion toxins on single channel and whole cell cardiac sodium channels. Am. J. Physiol. 1988, 254, H443–H451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, A.N.; Gurrola, G.B.; Martín, M.B.; Possani, L.D. Isolation of several toxins from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides limpidus tecomanus Hoffmann. Toxicon 1988, 26, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrola, G.B.; Moreno-Hagelsieb, G.; Zamudio, F.Z.; García, M.; Soberon, X.; Possani, L.D. The disulfide bridge of toxin 2 from the scorpion Centruroides noxius. FEBS Lett. 1994, 347, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, F.; Delepierre, M.; Ramírez, A.N.; Balderas, C.; Possani, L.D. Primary and NMR three-dimensional structure determination of a novel crustacean toxin from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides limpidus limpidus Karsch. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 11135–11149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, B.M.; Ramírez, A.N.; Gurrola, G.B.; Nobile, M.; Prestipino, G.; Possani, L.D. Novel K+-channel blocking toxins from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides limpidus limpidus Karsch. Biochem. J. 1994, 304, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino-Solís, G.; Riaño-Umbarila, L.; Becerril, B.; Possani, L.D. Antidotes against venomous animals: State of the art and prospectives. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo-López, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, M.; Possani, L.D.; Tseng, G.N. Mapping the binding site of a HERG-specific peptide toxin (ErgTx) to the channel´s outer vestibule. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 16403–16411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, M.; Gurrola, G.B.; Merino, E.; Restano-Cassulini, R.; Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; García, B.; Ramírez-Domínguez, M.E.; Coronas, F.I.V.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Wanke, E.; et al. A large number of novel Ergtoxin-like genes and ERG K+-channels blocking peptides from scorpions of the genus Centruroides. FEBS Lett. 2002, 532, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril, B.; Corona, M.; García, C.; Bolívar, F.; Possani, L.D. Cloning of genes encoding scorpion toxins: An interpretive review. J. Toxicol. 1995, 14, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possani, L.D.; Merino, E.; Corona, M.; Bolívar, F.; Becerril, B. Peptides and genes coding for scorpion toxins that affect ion-channels. Biochimie 2000, 82, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huys, I.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; García-Gómez, B.I.; Vandenberghe, I.; van Beeumen, J.; Dyason, K.; Clynen, E.; Zhu, S.; van der Walt, J.; Possani, L.D.; et al. A subfamily of acidic α-K+ toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Vega, R.; Schwartz, E.F.; Possani, L.D. Mining on scorpion venom biodiversity. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero-Hernández, V.; Ortiz, E.; Rendón-Anaya, M.R.; Schwartz, E.F.; Becerril, B.; Corzo, G.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion and spider venom peptides: Gene cloning and peptide expression. Toxicon 2011, 58, 644–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero-Hernández, V.; Jiménez-Vargas, J.M.; Gurrola, G.B.; Valdivia, H.H.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion venom components that affect ion-channels function. Toxicon 2013, 76, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedraza-Escalona, M.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion β-toxins and voltage-gated sodium channels: Interactions and toxicity effects. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2013, 18, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Larios, A.; Gurrola, G.B.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Possani, L.D. Hadrurin, a new antimicrobial peptide from the venom of the scorpion Hadrurus aztecus. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5023–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Aponte, C.A.; Silva-Sánchez, J.; Quintero-Hernández, V.; Rodríguez-Romero, A.; Balderas, C.; Possani, L.D.; Gurrola, G.B. Vejovine, a new antibiotic from the scorpion venom of Vaejovis mexicanus. Toxicon 2011, 57, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diego-García, E.; Schwartz, E.F.; D’Suze, G.; Roman-González, S.A.; Batista, C.V.; García, B.I.; de la Vega, R.; Possani, L.D. Wide phylogenetic distribution of Scorpine and long-chain beta-KTx-like peptides in scorpion venoms: Identification of “orphan” components. Peptides 2007, 28, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, M.; Coronas, F.V.I.; Merino, E.; Becerril, B.; Gutiérrez, R.; Rebolledo-Antúnez, S.; García, D.E.; Possani, L.D. A novel class of peptide found in scorpion venom with neurodepressant effects in peripheral and central nervous system of the rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1649, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Segovia, L.; Corona, M.; Possani, L.D. Sequence analysis and phylogenetic relationships of genes encoding heterodimeric phospholipases A2 from the venom of the scorpion Anuroctonus phaiodactylus. Gene 2007, 396, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurrola, G.B.; Hernández-López, R.; de la Vega, R.; Varga, Z.; Batista, C.F.; Salas-Castillo, S.; Panyi, G.; Del Rio Portilla, F.; Possani, L.D. Structure, function and chemical synthesis of Vaejovis mexicanus peptide 24: A novel potent blocker of Kv1.3 potassium channels of human T lymphocytes. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 4049–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, Z.; Gurrola, G.B.; Papp, F.; de la Vega, R.; Pedraza-Alva, G.; Tajhya, R.B.; Gaspar, R.; Cárdenas, L.; Rosenstein, Y.; Beeton, C.; et al. Vm24, a natural immunosuppressant peptide potently and selectively blocks Kv1.3 potassium channels of human T cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, E.F.; Schwartz, C.A.; Gómez-Lagunas, F.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Possani, L.D. HgeTx1, the first K+-channel specific toxin characterized from the venom of the scorpion Hadrurus gertschi Soleglad. Toxicon 2006, 48, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Carreto, S.; Quintero-Hernández, V.; Jiménez-Vargas, J.M.; Corzo, G.; Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B.; Ortiz, E. Gene cloning and functional characterization of four novel antimicrobial-like peptides from scorpions of the family Vaejovidae. Peptides 2012, 34, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Carreto, S.; Jiménez-Vargas, J.M.; Rivas-Santiago, B.; Corzo, G.; Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B.; Ortiz, E. Peptides from the scorpion Vaejovis punctatus with broad antimicrobial activity. Peptides 2015, 73, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandendriessche, T.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Zamudio, Z.F.; Possani, L.D.; Tytgat, J. Isolation and characterization of two novel scorpion toxins: The alpha-toxin-like Cell8, specific for Nav1.7 channels and the classical anti-mammalian Cell9, specific for Nav1.4 channels. Toxicon 2010, 56, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Calvo, M.; Leonard, R.J.; Novick, J.; Stevens, S.P.; Schmalhofer, W.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; García, M.L. Purification, characterization and biosynthesis of margatoxin, a component of Centruroides margaritatus venom that selectively inhibits voltage-dependent potassium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 18866–18874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rendon-Anaya, M.; Delaye, L.; Possani, L.D.; Herrera-Estrella, A. Global transcriptome analysis of the scorpion Centruroides noxius: New toxin families and evolutionary insights from an ancestral scorpion species. PLoS ONE 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada, G.; García, B.I.; Schiavon, E.; Ortiz, E.; Cestele, S.; Wanke, E.; Possani, L.D.; Corzo, G. Four disulfide-bridged scorpion beta neurotoxin CssI: Heterologous expression and proper folding in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1170, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Velázquez, L.L.; Quintero-Hernández, V.; Romero-Gutiérrez, M.T.; Coronas, F.I.V.; Possani, L.D. Mass fingerprinting of the venom and transcriptome of venom gland of scorpion Centruroides tecomanus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, E.F.; Diego-García, E.; de la Vega, R.; Possani, L.D. Transcriptome analysis of the venom gland of the Mexican scorpion Hadrurus gertschi (Arachnida: Scorpiones). BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero-Hernández, V.; Ramírez-Carreto, S.; Romero-Guitiérrez, M.T.; Valdez-Velázquez, L.; Becerril, B.; Possani, L.D.; Ortiz, E. Transcriptome analysis of scorpion species belonging to the Vaejovis genus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, O.F. Observations on the reproductive biology and life history of Megacormus gertschi Díaz (Scorpiones, Chactidae, Megacorminae). J. Arachnol. 1979, 7, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Fet, V.; Selden, P.A. Scorpions 2001: In memoriam Gary A. Polis; British Arachnological Society: London, UK, 2001; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Saavedra, J. Ecología y Distribución del Género Centruroides Marx 1890 (Scorpiones: Buthidae) en la Depresión del Balsas, Michoacán, México. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Querétaro, Querétaro, Mexico, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Saavedra, J.; Francke, O.F.; Suzán, H. Actividad superficial y utilización del hábitat por Centruroides balsasensis Ponce y Francke (Scorpiones: Buthidae). Biológicas 2006, 8, 130–137. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Contreras-Garduño, J.; Peretti, A.V.; Córdoba-Aguilar, A. Evidence that mating plug is related to null female mating activity in the scorpion Vaejovis punctatus. Ethology 2006, 112, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jiménez, M.L.; Palacios-Cardiel, C. Scorpions of desert oases in the southern Baja California Peninsula. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 74, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, C.A.; Jones, R.W.; Silva-Hurtado, C.; Sáyago-Vázquez, I. Scorpions are a food item of American Black Bears in Sonora, Mexico. West. N. Am. Nat. 2009, 69, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano-Ravell, A.F.; Ponce-Saavedra, J.; Francke, O.F. Ciclo de vida de Hadrurus gertschi Soleglad (Scorpiones, Iuridae) en una localidad del Estado de Guerrero, Mexico. Rev. Iber. Aracnol. 2011, 19, 133–145. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Quijano-Ravell, A.F.; Ponce-Saavedra, J.; Francke, O.F. Densidad, distribución espacial y biomasa de Hadrurus gertschi Soleglad (Scorpiones, Iuridae) en una localidad de Guerrero, Mexico. Rev. Iber. Aracnol. 2012, 20, 35–43. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Quijano-Ravell, A.F.; Francke, O.F.; Ponce-Saavedra, J.; Villaseñor-Ramos, M.A. Caracterización de las madrigueras de Hadrurus gertschi Solegald (Scorpiones: Iuridae) en una localidad de Guerrero, México. Rev. Iber. Aracnol. 2012, 20, 45–55. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Quijano-Ravell, A.F.; Ponce-Saavedra, J. Comparación de los tamaños de camada usando crías y embriones en Centruroides ornatus Pocock, 1902 (Scorpiones: Buthidae) en Michoacán, México. Entomol. Mex. 2015, 2, 59–65. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Francke, O.F.; Ureta, C.; Possani, L.D. Scorpions from Mexico: From Species Diversity to Venom Complexity. Toxins 2016, 8, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010002
Santibáñez-López CE, Francke OF, Ureta C, Possani LD. Scorpions from Mexico: From Species Diversity to Venom Complexity. Toxins. 2016; 8(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantibáñez-López, Carlos E., Oscar F. Francke, Carolina Ureta, and Lourival D. Possani. 2016. "Scorpions from Mexico: From Species Diversity to Venom Complexity" Toxins 8, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010002
APA StyleSantibáñez-López, C. E., Francke, O. F., Ureta, C., & Possani, L. D. (2016). Scorpions from Mexico: From Species Diversity to Venom Complexity. Toxins, 8(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010002








