Efficacy and Safety of a New Botulinum Toxin Type A Free of Complexing Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Demographic
| Characteristic | 2U Group (n = 5) | 5U Group (n = 5) | 10U Group (n = 5) | 20U Group (n = 5) | 30U Group (n = 5) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender Male | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | - |
| Age (years) Median | 26 | 31 | 31 | 28 | 27 | 0.7101 * |
| Range | 23–33 | 21–34 | 21–50 | 25–36 | 25–30 | - |
| Body weight (kg) | 74.30 ± 6.79 | 73.24 ± 9.30 | 78.22 ± 7.80 | 80.92 ± 12.93 | 71.22 ± 4.04 | 0.420 * |
| Height (cm) | 179.74 ± 5.79 | 174.72 ± 8.02 | 175.40 ± 3.74 | 174.14 ± 3.46 | 175.04 ± 6.56 | 0.566 * |
| Right preferred foot | 100% (5) | 100% (5) | 100% (5) | 100% (5) | 60% (3) | 0.167 † |
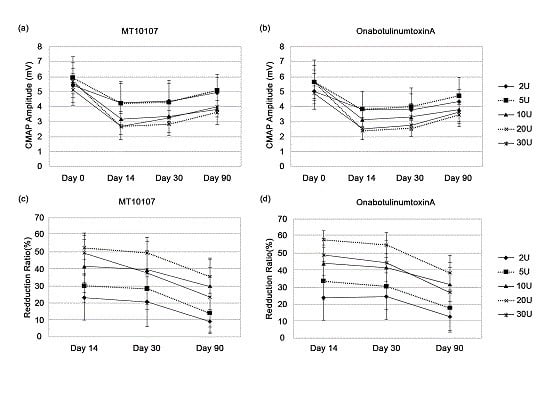
2.2. Efficacy

| Difference a | Day 14 | Day 30 | Day 90 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose Group | Difference a | p | Difference a | p | Difference a | p |
| 2U | −0.75 ± 2.49 | 0.5376 | −3.81 ± 3.17 | 0.0550 | −3.42 ± 3.32 | 0.0825 |
| 5U | −3.44 ± 4.12 | 0.1354 | −2.15 ± 5.12 | 0.4002 | −3.61 ± 12.14 | 0.5430 |
| 10U | −2.10 ± 4.47 | 0.3527 | −2.30 ± 3.58 | 0.2230 | −1.82 ± 6.56 | 0.5685 |
| 20U | −5.49 ± 8.78 | 0.2344 | −5.31 ± 10.03 | 0.3016 | −2.89 ± 7.25 | 0.4228 |
| 30U | 0.31 ± 8.21 | 0.9363 | −6.38 ± 16.93 | 0.4467 | −3.50 ± 14.94 | 0.6277 |
2.3. Spread of Toxin Effects
| Reduction | Day 14 | Day 30 | Day 90 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduction | p | Reduction | p | Reduction | p | |
| MT10107 | ||||||
| 2U | 0.38 ± 0.34 | 0.2500 b | 0.32 ± 1.57 | 0.6694 a | −1.21 ± 1.55 | 0.1560 a |
| 5U | 0.33 ± 0.53 | 0.5000 b | −0.02 ± 0.59 | 0.9518 a | 0.08 ± 3.78 | 0.9625 a |
| 10U | −0.11 ± 0.28 | 0.4326 a | 0.08 ± 0.76 | 0.8266 a | −0.01 ± 1.29 | 0.9829 a |
| 20U | −0.23 ± 0.38 | 0.5000 b | −0.67 ± 1.09 | 0.2500 b | −3.17 ± 2.03 | 0.0251 a |
| 30U | 0.24 ± 0.52 | 0.3579 a | 1.24 ± 3.09 | 0.8750 b | 1.11 ± 4.09 | 0.5763 a |
| OnabotulinumtoxinA | ||||||
| 2U | −0.28 ± 0.45 | 0.5000 b | −0.32 ± 1.31 | 0.6118 a | 3.27 ± 7.09 | 0.3606 a |
| 5U | 0.20 ± 2.32 | 0.8591 a | 0.29 ± 3.61 | 0.8675 a | −0.33 ± 2.27 | 0.7626 a |
| 10U | 4.20 ± 8.27 | 0.2500 b | 2.14 ± 4.35 | 0.3125 b | 1.62 ± 4.60 | 0.6250 b |
| 20U | −0.03 ± 0.70 | 0.6250 b | 0.34 ± 1.32 | 0.6019 a | −1.79 ± 2.65 | 0.2064 a |
| 30U | 2.03 ± 4.18 | 0.2500 b | 2.7 ± 3.71 | 0.0625 b | 1.17 ± 2.28 | 0.3167 a |
| Reduction | Day 14 | Day 30 | Day 90 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduction | p | Reduction | p | Reduction | p | |
| MT10107 | ||||||
| 2U | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.9028 a | 1.71 ± 3.23 | 0.3010 a | 1.62 ± 1.18 | 0.0371 a |
| 5U | 0.81 ± 0.64 | 0.0474 a | 0.89 ± 2.17 | 0.4088 a | −1.28 ± 4.73 | 0.5778 a |
| 10U | 0.64 ± 3.02 | 0.8750 b | 1.15 ± 3.52 | 0.5045 a | −0.45 ± 4.06 | 0.8146 a |
| 20U | 0.69 ± 1.05 | 0.5000 b | 2.04 ± 3.06 | 0.1250 b | −0.23 ± 0.79 | 0.5469 a |
| 30U | 2.22 ± 6.38 | 0.8125 b | 1.46 ± 7.27 | 0.6762 a | 3.24 ± 7.29 | 0.3765 a |
| OnabotulinumtoxinA | ||||||
| 2U | −0.62 ± 0.79 | 0.1545 a | −1.12 ± 1.32 | 0.1299 a | 0.15 ± 3.82 | 0.9351 a |
| 5U | 0.34 ± 0.75 | 0.3678 a | 0.92 ± 2.36 | 0.7500 b | −0.45 ± 4.28 | 0.8240 a |
| 10U | 1.02 ± 2.82 | 1.0000 b | 1.76 ± 2.67 | 0.2500 b | −0.87 ± 2.30 | 0.4444 a |
| 20U | −0.41 ± 1.19 | 1.0000 b | −0.22 ± 1.17 | 0.6946 a | −1.20 ± 1.83 | 0.2174 a |
| 30U | 0.88 ± 1.42 | 0.5000 b | 0.71 ± 1.88 | 0.4441 a | 1.55 ± 1.94 | 0.1468 a |
2.4. Safety
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Study Design
| Dose Gorup | MT10107·100U | BOTOX·50U | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume of Dilution | Volume of Injection | Volume of Dilution | Volume of Injection | |
| 2U Group | 5.0 mL | 0.1 mL | 2.5 mL | 0.1 mL |
| 5U Group | 2.0 mL | 0.1 mL | 1.0 mL | 0.1 mL |
| 10U Group | 1.0 mL | 0.1 mL | 0.5 mL | 0.1 mL |
| 20U Group | 0.5 mL | 0.1 mL | 0.25 mL | 0.1 mL |
| 30U Group | 0.33 mL | 0.1 mL | 0.17 mL | 0.1 mL |
4.3. Efficacy and Safety Parameters
4.4. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rohrich, R.J.; Janis, J.E.; Fagien, S.; Stuzin, J. The cosmetic use of botulinum toxin. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2003, 112, 177S–188S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressler, D. Five-year experience with incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®): The first botulinum toxin drug free of complexing proteins. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frevert, J. Xeomin is free from complexing proteins. Toxicon 2009, 54, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlfarth, K.; Muller, C.; Sassin, I.; Comes, G.; Grafe, S. Neurophysiological double-blind trial of a botulinum neurotoxin type a free of complexing proteins. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2007, 30, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressler, D.; Mander, G.; Fink, K. Measuring the potency labelling of onabotulinumtoxinA(Botox®) and incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) in ad LD50 assay. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, T.; Clarke, K. Potency evaluation of a formulated drug product containing 150-kd botulinum neurotoxin type A. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 32, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chundury, R.V.; Couch, S.M.; Holds, J.B. Comparison of preferences between onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) and incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin) in the treatment of benign essential blepharospasm. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 29, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moers-Carpi, M.; Dirschka, T.; Feller-Heppt, G.; Hilton, S.; Hofmann, K.; Philipp-Dormston, W.; Rutter, A.; Tan, K.; Chapman, M.; Fulford-Smith, A. A randomized, double-blind comparison of 20 units of onabotulinumtoxinA with 30 units of incobotulinumtoxinA for glabellar lines. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2012, 14, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frevert, J.; Dressler, D. Complexing proteins in botulinum toxin type A drugs: A help or a hindrance? Biologics 2010, 4, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, W.H.; Kohl, A.; Brinkmann, S.; Comes, G. Efficacy and tolerability of a botulinum toxin type A free of complexing proteins (NT 201) compared with commercially available botulinum toxin type A (BOTOX) in healthy volunteers. J. Neural Transm. 2005, 112, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloop, R.; Escutin, R.; Matus, J.; Cole, B.; Peterson, G. Dose-response curve of human extensor digitorumbrevis muscle function to intramuscularly injected botulinum toxin type A. Neurology 1996, 46, 1382–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Schwartz, K. Response and immunoresistance to botulinum toxin injections. Neurology 1995, 45, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlfarth, K.; Kampe, K.; Bigalke, H. Pharmacokinetic properties of different formulations of botulinum neurotoxin type A. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, S65–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, H.-M.; Park, J.H.; Song, D.H.; Chung, M.E. Efficacy and Safety of a New Botulinum Toxin Type A Free of Complexing Proteins. Toxins 2016, 8, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010004
Oh H-M, Park JH, Song DH, Chung ME. Efficacy and Safety of a New Botulinum Toxin Type A Free of Complexing Proteins. Toxins. 2016; 8(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Hyun-Mi, Joo Hyun Park, Dae Heon Song, and Myung Eun Chung. 2016. "Efficacy and Safety of a New Botulinum Toxin Type A Free of Complexing Proteins" Toxins 8, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010004
APA StyleOh, H.-M., Park, J. H., Song, D. H., & Chung, M. E. (2016). Efficacy and Safety of a New Botulinum Toxin Type A Free of Complexing Proteins. Toxins, 8(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010004