Insights into the Hypertensive Effects of Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom: Purification of an Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Like Peptidase
Abstract
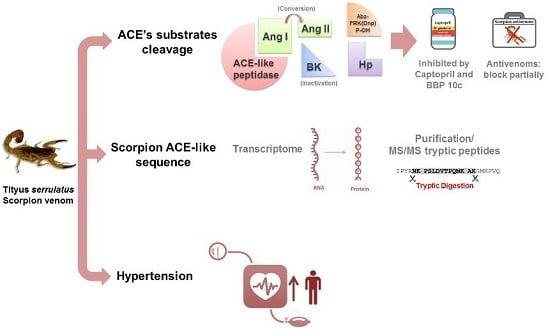
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. FRET Substrates Specific for Carboxy- and Endopeptidases on Tsv
2.2. In Vitro Serum Neutralization Assays Using Abz-FRK(Dnp)P-OH as Substrate
2.3. Effect of Chloride Ion Concentration on Tsv and sACE
2.4. Hydrolysis of ACE Natural Substrates by Tsv
2.5. Inhibition Assay on Reverse Phase Chromatography
2.6. Purification of ACE-Like Peptidase from T. serrulatus Venom
2.7. Sequence Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Venoms and Antivenoms
4.3. Fluorescent Substrate-Specific for Carboxy- and Endopeptidases, and Peptidase Inhibitors
4.4. Effect of Chloride Ion Concentration on Tsv and ACE Activities
4.5. In Vitro Serum Neutralization Assays Using Abz-FRK(Dnp)P-OH
4.6. Cleavage of Biologically Active Peptides and Inhibition by Captopril
4.7. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Ang–I and BK Fragments Produced by Tsv
4.8. Data Analysis
4.9. Purification of ACE-Like Peptidase from Tityus serrulatus Venom
4.10. Purified Protein Characterization
4.10.1. SDS-PAGE—In-Gel Digestion and Mass Spectrometry
4.10.2. Bioinformatic Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lourenço, W.; Cuellar, O. Scorpions, scorpionism, life history strategies and parthenogenesis. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins 1995, 1, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, A.M.; De Marco Almeida, F.; de Lima, M.E.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Bougis, P.E. Individual variability in Tityus serrulatus (scorpiones, buthidae) venom elicited by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupo, P.; Jurca, M.; Azeedo-Marques, M.M.; Oliveira, J.S.; Hering, S.E. Severe scorpion envenomation in Brazil. Clinical, laboratory and anatomopathological aspects. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1994, 36, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, M.C.; Gazzinelli, G.; Diniz, C.R.; Gomez, M.V. Effect of the venom of the scorpion Tityus serrulatus on adrenal gland catecholamines. Toxicon 1968, 5, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, F.; Lanchote, V.L.; Bendhack, L.M.; Giglio, J.R.; Sampaio, S.V.; Arantes, E.C. Effects of voltage-gated Na+ channel toxins from Tityus serrulatus venom on rat arterial blood pressure and plasma catecholamines. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 141, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, P.L.; Fletcher, M.D.; Weninger, K.; Anderson, T.E.; Martin, B.M. Vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) cleavage by a new metalloprotease from the Brazilian scorpion Tityus serrulatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7405–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cologna, C.T.; Marcussi, S.; Giglio, J.R.; Soares, A.M.; Arantes, E.C. Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom and toxins: An overview. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarenga, É.R.; Mendes, T.M.; Magalhaes, B.F.; Siqueira, F.F.; Dantas, A.E.; Barroca, T.M.; Horta, C.C.; Kalapothakis, E. Transcriptome analysis of the Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom gland. Open J. Genet. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta, C.C.; de Freitas Magalhães, B.; Oliveira-Mendes, B.B.; do Carmo, A.O.; Duarte, C.G.; Felicori, L.F.; Machado-de-Ávila, R.A.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Kalapothakis, E. Molecular, immunological, and biological characterization of Tityus serrulatus venom hyaluronidase: New insights into its role in envenomation. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, S.M. The long road of research on snake venom serine proteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, F.S.; Swenson, S. Snake venom metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, A.J.; Chung, R.; Dunlap, W.C.; Morandini, A.C.; Marques, A.C.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Ward, M.; Padilla, G.; da Silva, L.F.; Andreakis, N.; et al. Proteomic characterisation of toxins isolated from nematocysts of the South Atlantic jellyfish Olindias sambaquiensis. Toxicon 2013, 71, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavi-Hemami, H.; Möller, C.; Marí, F.; Purcell, A.W. High molecular weight components of the injected venom of fish-hunting cone snails target the vascular system. J. Proteom. 2013, 91, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, M.P.; Richards, E.H.; Isaac, R.E.; Edwards, J.P. Antibacterial and proteolytic activity in venom from the endoparasitic wasp Pimpla hypochondriaca (hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2003, 49, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De F Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.; de L. M. Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.; Gonçalves-de-Andrade, R.M.; Kobashi, L.S.; Almeida, D.D.; Ho, P.L.; Tambourgi, D.V. Transcriptome analysis of Loxosceles laeta (araneae, sicariidae) spider venomous gland using expressed sequence tags. BMC Genom. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venancio, E.J.; Portaro, F.C.; Kuniyoshi, A.K.; Carvalho, D.C.; Pidde-Queiroz, G.; Tambourgi, D.V. Enzymatic properties of venoms from Brazilian scorpions of Tityus genus and the neutralisation potential of therapeutical antivenoms. Toxicon 2013, 69, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, U.C.; Candido, D.M.; Dorce, V.A.; De L. M. Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I. The transcriptome recipe for the venom cocktail of Tityus bahiensis scorpion. Toxicon 2015, 95, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajado Carvalho, D.; Kuniyoshi, A.K.; Kodama, R.T.; Oliveira, A.K.; Serrano, S.M.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Portaro, F.V. Neuropeptide Y family-degrading metallopeptidases in the Tityus serrulatus venom partially blocked by commercial antivenoms. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 142, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verano-Braga, T.; Dutra, A.A.; León, I.R.; Melo-Braga, M.N.; Roepstorff, P.; Pimenta, A.M.; Kjeldsen, F. Moving pieces in a venomic puzzle: Unveiling post-translationally modified toxins from Tityus serrulatus. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, E.; Rendón-Anaya, M.; Rego, S.C.; Schwartz, E.F.; Possani, L.D. Antarease-like Zn-metalloproteases are ubiquitous in the venom of different scorpion genera. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, M.D.; Possani, L.D.; Fletcher, P.L. Morphological studies by light and electron microscopy of pancreatic acinar cells under the effect of Tityus serrulatus venom. Cell Tissue Res. 1994, 278, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, K.R.; Sturrock, E.D.; Riordan, J.F.; Ehlers, M.R. ACE revisited: A new target for structure-based drug design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagaman, J.R.; Moyer, J.S.; Bachman, E.S.; Sibony, M.; Magyar, P.L.; Welch, J.E.; Smithies, O.; Krege, J.H.; O’Brien, D.A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme and male fertility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2552–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, D. The angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourati Ben Mustapha, S.; Coulet, F.; Eyries, M.; De Larouziere, V.; Ravel, C.; Berthaut, I.; Antoine, J.M.; Soubrier, F.; Mandelbaum, J. In vitro fertilization failure of normozoospermic men: Search for a lack of testicular isozyme of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Basic Clin. Androl. 2013, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, P.P.; Zhan, Q.T.; Le, F.; Zheng, Y.M.; Jin, F. Angiotensin-converting enzymes play a dominant role in fertility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21071–21086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macours, N.; Hens, K. Zinc-metalloproteases in insects: ACE and ECE. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modica, M.V.; Lombardo, F.; Franchini, P.; Oliverio, M. The venomous cocktail of the vampire snail Colubraria reticulata (mollusca, gastropoda). BMC Genom. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgenstern, D.; Rohde, B.H.; King, G.F.; Tal, T.; Sher, D.; Zlotkin, E. The tale of a resting gland: Transcriptome of a replete venom gland from the scorpion Hottentotta judaicus. Toxicon 2011, 57, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, D.D.; Scortecci, K.C.; Kobashi, L.S.; Agnez-Lima, L.F.; Medeiros, S.R.; Silva-Junior, A.A.; De L. M. Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.; de F Fernandes-Pedrosa, M. Profiling the resting venom gland of the scorpion Tityus stigmurus through a transcriptomic survey. BMC Genom. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, M.C.; Melo, R.L.; Cesari, M.H.; Juliano, M.A.; Juliano, L.; Carmona, A.K. Peptidase specificity characterization of C- and N-terminal catalytic sites of angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 8519–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, C.J.; Masuyer, G.; Schwager, S.L.; Akif, M.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Molecular and thermodynamic mechanisms of the chloride-dependent human angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1798–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, K.E.; Ong, F.S.; Blackwell, W.L.; Shah, K.H.; Giani, J.F.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Shen, X.Z.; Fuchs, S.; Touyz, R.M. A modern understanding of the traditional and nontraditional biological functions of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blais, P.-A.; Côté, J.; Morin, J.; Larouche, A.; Gendron, G.; Fortier, A.; Regoli, D.; Neugebauer, W.; Gobeil, F. Hypotensive effects of hemopressin and bradykinin in rabbits, rats and mice: A comparative study. Peptides 2005, 26, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, A.C.; Fernandes, B.L.; Cruz, L.; Ferro, E.S. Bioactive peptides produced by limited proteolysis. In Colloquium Series on Neuropeptides; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–92. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, U.C.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Santos, M.B.V.; Silva, A.P.S.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Imberg, A.S.; Candido, D.M.; Yamanouye, N.; Dorce, V.A.C.; de Azevedo L. M. Junqueira, I. Proteomics endorsed transcriptomics profile of the venom gland from Tityus scorpions. Unpublished work; manuscript in preparation.
- Cheung, H.S.; Wang, F.L.; Ondetti, M.A.; Sabo, E.F.; Cushman, D.W. Binding of peptide substrates and inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Importance of the COOH-terminal dipeptide sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tatei, K.; Cai, H.; Ip, Y.T.; Levine, M. Race: A drosophila homologue of the angiotensin converting enzyme. Mech. Dev. 1995, 51, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, R.E. Neuropeptide-degrading endopeptidase activity of locust (Schistocerca gregaria) synaptic membranes. Biochem. J. 1988, 255, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijffels, G.; Fitzgerald, C.; Gough, J.; Riding, G.; Elvin, C.; Kemp, D.; Willadsen, P. Cloning and characterisation of angiotensin-converting enzyme from the dipteran species, haematobia irritans exigua, and its expression in the maturing male reproductive system. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 237, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoofs, L.; Veelaert, D.; De Loof, A.; Huybrechts, R.; Isaac, E. Immunocytochemical distribution of angiotensin I-converting enzyme-like immunoreactivity in the brain and testis of insects. Brain Res. 1998, 785, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, R.E.; Bland, N.D.; Shirras, A.D. Neuropeptidases and the metabolic inactivation of insect neuropeptides. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 162, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, K.R.; Vakil, A.E. Elevation of plasma angiotensin levels in dogs by indian red scorpion (Buthus tamulus) venom & its reversal by administration of insulin+tolazoline. Indian J. Med. Res. 1988, 88, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bawaskar, H.S.; Bawaskar, P.H. Scorpion sting: Update. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2012, 60, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofer, S.; Shahak, E.; Gueron, M. Scorpion envenomation and antivenom therapy. J. Pediatr. 1994, 124, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucaretchi, F.; Fernandes, L.C.; Fernandes, C.B.; Branco, M.M.; Prado, C.C.; Vieira, R.J.; De Capitani, E.M.; Hyslop, S. Clinical consequences of Tityus bahiensis and Tityus serrulatus scorpion stings in the region of campinas, southeastern Brazil. Toxicon 2014, 89, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peach, M.J.; Cline, W.H.; Watts, D.T. Release of adrenal catecholamines by angiotensin. Ii. Circ Res 1966, 19, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diz, D.I. Another chapter in the understanding of angiotensin-catecholamine interactions relevant to blood pressure control. Exp. Physiol. 2014, 99, 1595–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reaux, A.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Angiotensin III: A central regulator of vasopressin release and blood pressure. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 12, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verano-Braga, T.; Figueiredo-Rezende, F.; Melo, M.N.; Lautner, R.Q.; Gomes, E.R.; Mata-Machado, L.T.; Murari, A.; Rocha-Resende, C.; Elena de Lima, M.; Guatimosim, S.; et al. Structure-function studies of Tityus serrulatus hypotensin-I (TsHpt-i): A new agonist of b(2) kinin receptor. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahloul, M.; Chabchoub, I.; Chaari, A.; Chtara, K.; Kallel, H.; Dammak, H.; Ksibi, H.; Chelly, H.; Rekik, N.; Ben Hamida, C.; et al. Scorpion envenomation among children: Clinical manifestations and outcome (analysis of 685 cases). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, I.Y.; Cezari, M.H.S.; Nakaie, C.R.; Boschcov, P.; Ito, A.S.; Juliano, M.; Juliano, L. Internally quenched fluorogenic protease substrates: Solid-phase synthesis and fluorescence spectroscopy of peptides containing ortho-aminobenzoyl/dinitrophenyl groups as donor-acceptor pairs. Lett. Pept. Sci. 1994, 1, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhang, K.; Hendrie, C.; Liang, C.; Li, M.; Doherty-Kirby, A.; Lajoie, G. Peaks: Powerful software for peptide de novo sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 2337–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, L.; Shan, B.; Chen, W.; Xie, M.; Yuen, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lajoie, G.A.; Ma, B. PEAKS DB: De novo sequencing assisted database search for sensitive and accurate peptide identification. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, M111.010587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havlis, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Peptide | Fragment Sequence | Fragment Identification | MW | Venom Specific Activity (µM/µg/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angiotensin I | DRVY | Ang(1–4) | 551.2 | 0.050 |
| IHPFHL | Ang(5–10) | 762.4 | ||
| HPFHL | Ang(6–10) | 649.3 | ||
| DRVYIHP | Ang(1–7) | 898.4 | ||
| DRVYIHPF | Ang II | 1045.4 | ||
| RVYIHPF | Ang III | 930.5 | ||
| FHL | Ang(8–10) | 415.2 | ||
| Bradykinin | RPPGF | BK(1–5) | 572.3 | 0.045 |
| RPPGFSP | BK(1–7) | 756.3 | ||
| PGFSPFR | BK(3–9) | 806.4 | ||
| Hemopressin | PVNFKFL | Hemo(1–7) | 863.4 | 0.400 |
| PVNFKF | Hemo(1–6) | 750.4 | ||
| PVNFK | Hemo(1–5) | 603.3 | ||
| KFLSH | Hemo(5–9) | 630.35 | ||
| FLSH | Hemo(6–9) | 502.25 |
| Peptide | Inhibitory Activity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA | Captopril 100 nM | Captopril 1 µM | |
| Angiotensin-I | 100 | 8.2 | 48.6 |
| Bradykinin | 100 | 36.3 | 60.0 |
| Dynorphin A | 100 | 0.0 | 1.8 |
| Hemopressin | 100 | 37.8 | 8.9 |
| Proteins | TesticularACE Homo sapiens (AAA60611.1) | T. serrulatus (TserSP00939) | T. bahiensis (JAG85170) | T. obscurus (Tobs01141) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| testicularACE Homo sapiens (AAA60611.1) | 39.18% | 23.12% | 39.18% | |
| T. serrulatus (TserSP00939 ) | 46.39% | 67.21% | 90.34% | |
| T. bahiensis (JAG85170) | 28.16% | 67.34% | 61.22% | |
| T obscurus (Tobs01141) | 46.53% | 92.51% | 62.31% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cajado-Carvalho, D.; Kuniyoshi, A.K.; Duzzi, B.; Iwai, L.K.; Oliveira, Ú.C.d.; Junqueira de Azevedo, I.D.L.M.; Kodama, R.T.; Portaro, F.V. Insights into the Hypertensive Effects of Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom: Purification of an Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Like Peptidase. Toxins 2016, 8, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120348
Cajado-Carvalho D, Kuniyoshi AK, Duzzi B, Iwai LK, Oliveira ÚCd, Junqueira de Azevedo IDLM, Kodama RT, Portaro FV. Insights into the Hypertensive Effects of Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom: Purification of an Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Like Peptidase. Toxins. 2016; 8(12):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120348
Chicago/Turabian StyleCajado-Carvalho, Daniela, Alexandre Kazuo Kuniyoshi, Bruno Duzzi, Leo Kei Iwai, Úrsula Castro de Oliveira, Inácio De Loiola Meirelles Junqueira de Azevedo, Roberto Tadashi Kodama, and Fernanda Vieira Portaro. 2016. "Insights into the Hypertensive Effects of Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom: Purification of an Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Like Peptidase" Toxins 8, no. 12: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120348
APA StyleCajado-Carvalho, D., Kuniyoshi, A. K., Duzzi, B., Iwai, L. K., Oliveira, Ú. C. d., Junqueira de Azevedo, I. D. L. M., Kodama, R. T., & Portaro, F. V. (2016). Insights into the Hypertensive Effects of Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom: Purification of an Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Like Peptidase. Toxins, 8(12), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120348