Insight into the Mode of Action of Celangulin V on the Transmembrane Potential of Midgut Cells in Lepidopteran Larvae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
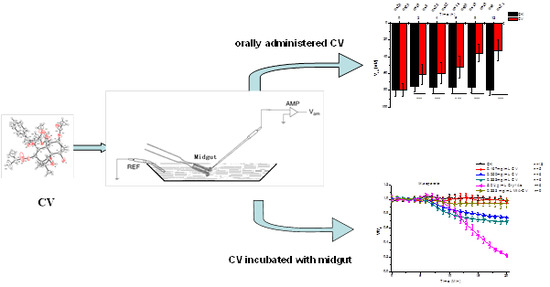
2.1. Effects of CV Ingestion on Midgut Transmembrane Potentials
2.2. Direct Effects of CV on Midgut Transmembrane Potentials
2.3. Effects of CV on V-ATPase Activity in Midguts of M. Separata Larvae
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insects
4.2. Solutions
4.3. Test Toxins and Chemicals
4.4. Treatment
4.5. Membrane Potential Measurements
4.6. V-ATPase Activity Measurements
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perry, T.; Batterham, P.; Daborn, P.J. The biology of insecticidal activity and resistance. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayan, F.E.; Cantrell, C.L.; Duke, S.O. Natural products in crop protection. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 4022–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathana, S.S.; Kalaivani, K.; Sehoon, K.; Murugan, K. The toxicity and behavioural effects of neem limonoids on Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenée), the rice leaffolder. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triggle, D.J.; Mitchell, J.M.; Filler, R. The Pharmacology of Physostigmine. CNS Drug Rev. 1998, 4, 87–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.Z.; Nomuraa, Y.; Satar, G.; Hu, Z.N.; Nauen, R.; He, S.Y.; Zhorove, B.S.; Dong, K. Molecular evidence for dual pyrethroid-receptor sites on a mosquito sodium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11785–11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagagu, S. Chloronicotinyl insecticides-discovery, application and future perspective. Rev. Toxicol. 1997, 1, 75–129. [Google Scholar]
- Casida, J.E.; Schuler, F. The insecticide target in the PSST subunit of complex I. Pest Manag. Sci. 2001, 57, 932–940. [Google Scholar]
- Sattelle, D.B.; Cordova, D.; Cheek, T.R. Insect ryanodine receptors: molecular targets for novel pest control chemicals. Invertebr. Neurosci. 2008, 8, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copping, L.G.; Duke, S.O. Natural products that have been used commercially as crop protection agents. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 524–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.J.; Hu, Z.N.; Liu, H.X.; Qi, Z.J. Insecticidal mechanisms of the major active components from the Chinese bittersweet, Celastrus angulatus and their application. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2005, 48, 770–777. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.M.; Wu, W.J.; Zhang, J.W.; Konishi, Y. The dihydro-β-agarofuran sesquiterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 1153–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.J.; Liu, H.X.; Ji, Z.Q.; Hu, Z.N.; Qi, Z.J. Research and development on the botanical insecticide of 0.2% celangulins emulsifiable concentrate. Agrochemicals 2001, 40, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.J.; Li, S.B.; Zhu, J.B.; Liu, H.X. New sequiterpenoid Celangulin V: Isolation and determination. Acta Univ. Agric. Boreali-Occident. 1994, 22, 116–117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.W.; Cui, L.H.; Li, L.B.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Z.N.; Wu, W.J. Synthesis and insecticidal activities of novel nitrogenous derivatives of celangulin-V. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.Y.; Liu, H.X.; Wu, W.J.; Wang, J.L. Study on the functioning mechanism of celangulin V. Acta Univ. Agric. Boreali-Occident. 2001, 29, 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.J.; Ji, Z.Q.; Hu, Z.N. Natural products and digestive poisons. Agrochemicals 1997, 36, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.J.; Xue, X.P.; Wu, W.J.; Zhang, J.W.; Yang, R.Y. Preparation of monoclonal antibody against Celangulin V and immunolocalization of receptor in the Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata Walker (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7600–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.J.; Shi, B.J.; Hu, Z.N.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wu, W.J. Ultrastructural effects of Celangulin V on midgut cells of the oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata walker (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.N.; Qi, Z.J.; Zhang, J.W.; Wu, W.J. Separation of binding protein of Celangulin V from the Midgut of Mythimna separate Walker by affinity chromatography. Toxins 2015, 7, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.N.; Qi, Z.J.; Li, Q.L.; Wu, W.J. Validation of the Target Protein of Insecticidal Dihydroagarofuran Sesquiterpene Polyesters. Toxins 2016, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Hu, Z.N.; Wu, W.J. Different Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Cry1Ab on Midgut Cell Transmembrane Potential of Mythimna separata and Agrotis ipsilon Larvae. Toxins 2015, 7, 5448–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyronnet, O.; Vachon, V.; Brousseau, R.; Baines, D.; Schwartz, J.-L.; Laprade, R. Effect of Bacillus thuringiensis toxins on the membrane potential of lepidopteran insect midgut cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fortier, M.; Vachon, V.; Kirouac, M.; Schwartz, J.-L.; Laprade, R. Differential Effects of Ionic Strength, Divalent Cations and pH on the Pore-forming Activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Insecticidal Toxins. J. Membr. Biol. 2005, 208, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnepf, E.; Crickmore, N.; van Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.; Feitelson, J.; Zeigler, D.R.; Dean, D.H. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 775–806. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fortier, M.; Vachon, V.; Frutos, R.; Schwartz, J.L.; Laprade, R. Effect of Insect Larval Midgut Proteases on the Activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry Toxins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6208–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, M.; Oltean, D.I.; Gomez, I.; Pullikuth, A.K.; Soberon, M.; Bravo, A.; Gill, S.S. Heliothis virescens and Manduca sexta lipid rafts are involved in Cry1A toxin binding to the midgut epithelium and subsequent pore formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 13863–13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.; Gómez, I.; Conde, J.; Muñoz-Garay, C.; Sánchez, J.; Miranda, R.; Zhuang, M.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Oligomerization triggers binding of a Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab pore-forming toxin to aminopeptidase N receptor leading to insertion intomembrane microdomains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1667, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Gahan, L.J.; Gould, F.L.; Heckel, D.G.; Adang, M.J. The HevCaLP protein mediates binding specificity of the Cry1A class of Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in Heliothis virescens. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 14299–14305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, J.A.; Harvey, W.R. Role of midgut electrogenic K+ pump potential difference in regulating lumen K+ and pH in larval Lepidoptera. J. Exp. Biol. 1988, 140, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, M.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; McNall, R.J.; Andacht, T.; Adang, M.J. Identification of novel Cry1Ac binding proteins in midgut membranes from Heliothis virescens using proteomic analyses. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Qi, Z.J.; Qi, M.; Hu, Z.N.; Wu, W.J. Effects of Periplocoside P from Periploca sepium on the Midgut Transmembrane Potential of Mythimna separata Larvae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, H.; Putzenlechner, M.; Zeiske, W.; Klein, U. A vacuolar-type proton pump energizes H+/K+-antiport in an animal plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 15340–15347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, H.; Beyenbach, K.W.; Huss, M.; Vitavska, O. Vacuolar-type proton pumps in insect epithelia. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.A.F.; Moussa, S.; Taylora, M.D.; Adang, M.J. Manduca sexta (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae) cadherin fragments function as synergists for Cry1A and Cry1C Bacillus thuringiensis toxins against noctuid moths Helicoverpa zea, Agrotis ipsilon and Spodoptera exigua. Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiburcy, F.; Beyenbach, K.W.; Wieczorek, H. Protein kinase A-dependent and-independent activation of the V-ATPase in Malpighian tubules of Aedes aegypti. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, H.; Cioffi, M.; Klein, U.; Harvey, W.R.; Schweikl, H.; Wolfersberger, M.G. Isolation of goblet cell apical membrane from tobacco hornworm midgut and purification of its vacuolar-type ATPase. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 192, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






| Time | Vt/mV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO | CV + DMSO | CV–MIA + DMSO | 32 K | Cry1Ab + 32 K | |
| 0 | 56.6 | 57.1 | 60.3 | 57.0 | 57.0 |
| 2 | 52.6 | 31.7 | 58.9 | 53.2 | 6.0 |
| 4 | 55.7 | 30.0 | 53.5 | 54.5 | 0 |
| 6 | 55.4 | 23.4 | 57.3 | 52.1 | 0 |
| 8 | 58.1 | 8.1 | 56.5 | 50.7 | 0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, M.; Wu, W.; Hu, Z. Insight into the Mode of Action of Celangulin V on the Transmembrane Potential of Midgut Cells in Lepidopteran Larvae. Toxins 2017, 9, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120393
Wang Y, Zhang J, Feng M, Wu W, Hu Z. Insight into the Mode of Action of Celangulin V on the Transmembrane Potential of Midgut Cells in Lepidopteran Larvae. Toxins. 2017; 9(12):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120393
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yingying, Jiwen Zhang, Mingxing Feng, Wenjun Wu, and Zhaonong Hu. 2017. "Insight into the Mode of Action of Celangulin V on the Transmembrane Potential of Midgut Cells in Lepidopteran Larvae" Toxins 9, no. 12: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120393
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, J., Feng, M., Wu, W., & Hu, Z. (2017). Insight into the Mode of Action of Celangulin V on the Transmembrane Potential of Midgut Cells in Lepidopteran Larvae. Toxins, 9(12), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120393