Inflammatory Cytokines as Uremic Toxins: “Ni Son Todos Los Que Estan, Ni Estan Todos Los Que Son”
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Inflammation in Chronic Kidney Disease
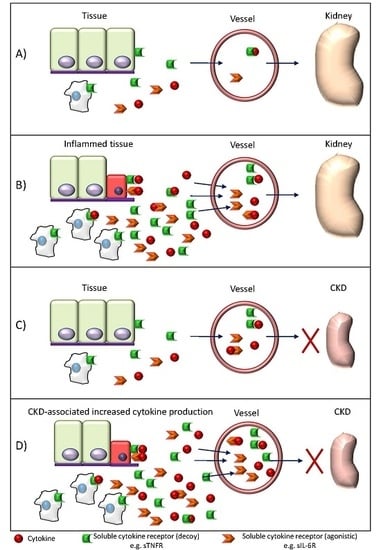
3. Cytokines and Uremic Toxins
4. Cytokines as Uremic Toxins
4.1. IL-1β and IL-18
4.2. IL-6
4.3. TNFα
4.4. IL-8
4.5. IL-10
5. Adipokines
5.1. Adiponectin
5.2. Leptin
5.3. Resistin
6. Which Additional Cytokines Should Be in Listed as Potential Uremic Toxins?
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Naghavi, M.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; Coates, M.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 19802015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.; Covic, A.; Fliser, D.; Fouque, D.; Goldsmith, D.; Kanbay, M.; Mallamaci, F.; Massy, Z.A.; Rossignol, P.; Vanholder, R.; et al. Epidemiology, contributors to, and clinical trials of mortality risk in chronic kidney failure. Lancet 2014, 383, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholder, R.; Glorieux, G. The intestine and the kidneys: A bad marriage can be hazardous. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elewa, U.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Martin-Cleary, C.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. Cardiovascular risk biomarkers in CKD: The inflammation link and the road less traveled. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2012, 44, 1731–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heine, G.H.; Ortiz, A.; Massy, Z.A.; Lindholm, B.; Wiecek, A.; Martínez-Castelao, A.; Covic, A.; Goldsmith, D.; Süleymanlar, G.; London, G.M.; et al. Monocyte subpopulations and cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Benito-Martin, A.; Gonalves, S.; Sanz, A.B.; Ucero, A.C.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Ramos, A.M.; Berzal, S.; Selgas, R.; Ruíz-Ortega, M.; et al. TNF superfamily: A growing saga of kidney injury modulators. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 182958. [Google Scholar]
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argilés, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uremic-Toxins.org. Data Base. Available online: http://www.uremic-toxins.org/DataBase.html (accessed on 20 October 2016).
- Duranton, F.; Cohen, G.; De Smet, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Jankowski, J.; Vanholder, R.; Argiles, A.; Abou Deif, O.; Drueke, T.; Baurmeister, U.; et al. Normal and Pathologic Concentrations of Uremic Toxins. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohan, D.E. Role of collecting duct endothelin in control of renal function and blood pressure. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R659–R668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, A.B.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Gonzalez-Espinoza, L.; Ucero, A.C.; Poveda, J.; Ruiz-Andres, O.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Selgas, R.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. Macrophages and recently identified forms of cell death. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 33, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, J.; Mitra, N.; Kanetsky, P.A.; Devaney, J.; Wing, M.R.; Reilly, M.; Shah, V.O.; Balakrishnan, V.S.; Guzman, N.J.; Girndt, M.; et al. Association between albuminuria, kidney function, and inflammatory biomarker profile in CKD in CRIC. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, A.M.; Ellis, C.D.; Shintani, A.; Booker, C.; Ikizler, T.A. IL-1β Receptor Antagonist Reduces Inflammation in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanino, A.; Okura, T.; Nagao, T.; Kukida, M.; Pei, Z.; Enomoto, D.; Miyoshi, K.; Okamura, H.; Higaki, J. Interleukin-18 deficiency protects against renal interstitial fibrosis in aldosterone/salt-treated mice. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 1727–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahar, S.; Dwarakanath, R.S.; Reddy, M.A.; Lanting, L.; Todorov, I.; Natarajan, R. Angiotensin II enhances interleukin-18 mediated inflammatory gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells: A novel cross-talk in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formanowicz, D.; Wanic-Kossowska, M.; Pawliczak, E.; Radom, M.; Formanowicz, P. Usefulness of serum interleukin-18 in predicting cardiovascular mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease—Systems and clinical approach. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M.J.; Kline, J.; Bauman, J.; Gardner, O.; Jonak, Z.; Koch, K.M.; Murray, S.C.; Weisenbach, J.; Toso, J. A phase I trial evaluating the safety and biological activity of iboctadekin (rhIL-18) in combination with rituximab in patients with CD20+ B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 8566. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Guo, T.; Wang, H.; Mei, H.; Hu, Y. Association between the interleukin-6 genetic polymorphism 174 G/C and thrombosis disorder risk. Medicine 2016, 95, e4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechemia-Arbely, Y.; Barkan, D.; Pizov, G.; Shriki, A.; Rose-John, S.; Galun, E.; Axelrod, J.H. IL-6/IL-6R axis plays a critical role in acute kidney injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoits-Filho, R. Interleukin-6 is an independent predictor of mortality in patients starting dialysis treatment. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2002, 17, 1684–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memoli, B.; Grandaliano, G.; Soccio, M.; Postiglione, L.; Guida, B.; Bisesti, V.; Esposito, P.; Procino, A.; Marrone, D.; Michael, A. In Vivo Modulation of Soluble “Antagonistic” IL-6 Receptor Synthesis and Release in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Axelsson, J.; Machowska, A.; Heimbürger, O.; Bárány, P.; Lindholm, B.; Lindström, K.; Stenvinkel, P.; Qureshi, A.R. Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality Risk in Patients with Advanced CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzzelli, M.; Schweiger, M.; Schreiber, R.; Campos-Olivas, R.; Tsoli, M.; Allen, J.; Swarbrick, M.; Rose-John, S.; Rincon, M.; Robertson, G.; et al. A switch from white to brown fat increases energy expenditure in cancer-associated cachexia. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stouthard, J.M.; Romijn, J.A.; Van der Poll, T.; Endert, E.; Klein, S.; Bakker, P.J.; Veenhof, C.H.; Sauerwein, H.P. Endocrinologic and metabolic effects of interleukin-6 in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, 813–819. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.A.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S. Science in medicine Therapeutic strategies for the clinical blockade of IL-6/gp130 signaling. Cell 2011, 121, 3375–3383. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, D.I.; Holmes, M.V.; Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Engmann, J.E.L.; Shah, T.; Sofat, R.; Guo, Y.; Chung, C.; Peasey, A.; Pfister, R.; et al. The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: A mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet 2012, 379, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Lüscher, T.F. Anti-inflammatory therapies for cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.; Bustos, C.; Alonso, J.; Alcázar, R.; López-Armada, M.J.; Plaza, J.J.; González, E.; Egido, J. Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the pathogenesis of experimental and human glomerulonephritis. Adv. Nephrol. Necker Hosp. 1995, 24, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roach, D.R.; Bean, G.D.; Demangel, C.; France, M.P.; Briscoe, H.; Britton, W.J. TNF Regulates Chemokine Induction Essential for Cell Recruitment, Granuloma Formation, and Clearance of Mycobacterial Infection. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 4620–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.A.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Suárez-Alvarez, B.; Lopez-Larrea, C.; Jakubowski, A.; Blanco, J.; Ramirez, R.; Selgas, R.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; et al. The inflammatory cytokines TWEAK and TNFα reduce renal klotho expression through NFκB. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, Y.; Zhang, X.U.; Wolfe, R.R. Short-term effects of tumor necrosis factor on energy and substrate metabolism in dogs. J. Clin. Invest. 1993, 91, 2437–2445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Aly, Z. Arterial calcification: A tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediated vascular Wnt-opathy. Transl. Res. 2008, 151, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hénaut, L.; Sanz, A.B.; Martin-Sanchez, D.; Carrasco, S.; Villa-Bellosta, R.; Aldamiz-Echevarria, G.; Massy, Z.A.; Sanchez-Nino, M.D.; Ortiz, A. TWEAK favors phosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells through canonical and non-canonical activation of NFκB. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buendía, P.; De Oca, A.M.; Madueño, J.A.; Merino, A.; Martín-Malo, A.; Aljama, P.; Ramírez, R.; Rodríguez, M.; Carracedo, J. Endothelial microparticles mediate inflammation-induced vascular calcification. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Ketteler, M.; Johnson, R.J.; Lindholm, B.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Riella, M.; Heimbürger, O.; Cederholm, T.; Girndt, M. IL-10, IL-6, and TNF-α: Central factors in the altered cytokine network of uremia—The good, the bad, and the ugly. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1216–1233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.D.; Phillips, T.M.; Khetpal, P.; Kimmel, P.L. Cytokine patterns and survival in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2010, 25, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.; Massy, Z.A.; Fliser, D.; Lindholm, B.; Wiecek, A.; Martínez-Castelao, A.; Covic, A.; Goldsmith, D.; Süleymanlar, G.; London, G.M.; et al. Clinical usefulness of novel prognostic biomarkers in patients on hemodialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 8, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Chiarri, M.; Ortíz, A.; Lerma, J.L.; López-Armada, M.J.; Mampaso, F.; González, E.; Egido, J. Involvement of tumor necrosis factor and platelet-activating factor in the pathogenesis of experimental nephrosis in rats. Lab Investig. 1994, 70, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Egido, J.; Gómez-Chiarri, M.; Ortíz, A.; Bustos, C.; Alonso, J.; Gómez-Guerrero, C.; Gómez-Garre, D.; López-Armada, M.J.; Plaza, J.; Gonzalez, E. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the pathogenesis of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1993, 39, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka, H. TNF as a Target of Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 15, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Lee, C.-K.; Cha, H.-S.; Choe, J.-Y.; Park, E.-J.; Kim, J. Effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and chronic kidney disease. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edrees, A.F.; Misra, S.N.; Abdou, N.I. Anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: Correlation of TNF-alpha serum level with clinical response and benefit from changing dose or frequency of infliximab infusions. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2005, 23, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Don, B.R.; Kim, K.; Li, J.; Dwyer, T.; Alexander, F.; Kaysen, G.A. The effect of etanercept on suppression of the systemic inflammatory response in chronic hemodialysis patients. Clin. Nephrol. 2010, 73, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S.J. Molecular mechanisms of soluble cytokine receptor generation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14177–14181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neirynck, N.; Glorieux, G.; Schepers, E.; Verbeke, F.; Vanholder, R. Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and 2 predict outcomes in advanced chronic kidney disease: A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohda, T.; Niewczas, M.A.; Ficociello, L.H.; Walker, W.H.; Skupien, J.; Rosetti, F.; Cullere, X.; Johnson, A.C.; Crabtree, G.; Smiles, A.M. Circulating TNF Receptors 1 and 2 Predict Stage 3 CKD in Type 1 Diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewczas, M.A.; Gohda, T.; Skupien, J.; Smiles, A.M.; Walker, W.H.; Rosetti, F.; Cullere, X.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Doria, A.; Mayadas, T.N.; et al. Circulating TNF Receptors 1 and 2 Predict ESRD in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, Y.; Yabe, D.; Taniguchi, A.; Fukushima, M.; Nakai, Y.; Hosokawa, M.; Okumura, T.; Nin, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Nishimura, F.; et al. Circulating TNF receptor 2 is associated with the development of chronic kidney disease in non-obese Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 99, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, A.C.; Nordquist, L.; Larsson, T.E.; Carrero, J.-J.; Larsson, A.; Lind, L.; Ärnlöv, J. Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 is Associated with Glomerular Filtration Rate Progression and Incidence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Two Community-Based Cohorts of Elderly Individuals. Cardiorenal Med. 2015, 5, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bemelmans, M.H.; Gouma, D.J.; Buurman, W.A. Tissue distribution and clearance of soluble murine TNF receptors in mice. Cytokine 1994, 6, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardam, M.A.; Keystone, E.C.; Menzies, R.; Manners, S.; Skamene, E.; Long, R.V.D. Anti-tumour necrosis factor agents and tuberculosis risk: Mechanisms of action and clinical management. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanowski, K.; Clark, E.G.; Levin, A.; Cook, V.J.; Johnston, J.C. Tuberculosis and chronic kidney disease: An emerging global syndemic. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocci, G.; Goletti, D.; Marino, V.; Matucci, A.; Milano, G.M.; Cantini, F.; Scarpa, R. Cardiovascular outcomes and tumour necrosis factor antagonists in chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease: A focus on rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15 (Suppl. 1), 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Enbrel. Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_Product_Information/human/000262/WC500027361.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2016).
- Brat, D.J.; Bellail, A.C.; Van Meir, E.G. The role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro-Oncology 2005, 7, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, J.; Dominguez, C.; Hamilton, D.; Palena, C. The IL-8/IL-8R Axis: A Double Agent in Tumor Immune Resistance. Vaccines 2016, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panichi, V.; Taccola, D.; Rizza, G.M.; Consani, C.; Ghiadoni, L.; Filippi, C.; Cristofani, R.; Panicucci, E.; Migliori, M.; Sidoti, A.; et al. Interleukin-8 is a powerful prognostic predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in dialytic patients. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2006, 102, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangsgaard, N.; Houtkamp, M.; Schuurhuis, D.H.; Parren, P.W.H.I.; Baadsgaard, O.; Niessen, H.W.M.; Skov, L. Neutralization of IL-8 prevents the induction of dermatologic adverse events associated with the inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, L.; Beurskens, F.J.; Zachariae, C.O.C.; Reitamo, S.; Teeling, J.; Satijn, D.; Knudsen, K.M.; Boot, E.P.; Hudson, D.; Baadsgaard, O.; et al. IL-8 as Antibody Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory Diseases: Reduction of Clinical Activity in Palmoplantar Pustulosis. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oft, M. IL-10: Master switch from tumor-promoting inflammation to antitumor immunity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, W.; Ouyang, X.; Agarwal, A.; Zhang, L.; Long, D.A.; Cruz, P.E.; Roncal, C.A.; Glushakova, O.Y.; Chiodo, V.A.; Atkinson, M.A.; et al. IL-10 Suppresses Chemokines, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in a Model of Chronic Renal Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3651–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naing, A.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Autio, K.A.; Ott, P.A.; Patel, M.R.; Wong, D.J.; Falchook, G.S.; Pant, S.; Whiteside, M.; Rasco, D.R.; et al. Safety, antitumor activity, and immune activation of pegylated recombinant human interleukin-10 (AM0010) in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3562–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; van Montfrans, C.; van den Ende, A.; Kaser, A.; van Deventer, S.J.H.; Schreiber, S.; Gregor, M.; Ludwiczek, O.; Rutgeerts, P.; Gasche, C.; et al. Treatment of Crohn’s disease with recombinant human interleukin-10 induces the proinflammatory cytokine interferon gamma. Gut 2002, 50, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.I.; Solak, Y.; Saglam, M.; Cayci, T.; Acikel, C.; Unal, H.U.; Eyileten, T.; Oguz, Y.; Sari, S.; Carrero, J.J.; et al. The relationship between IL-10 levels and cardiovascular events in patients with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.; Sigrist, M.; Romann, A.; Chiarelli, G.; Levin, A. Novel biomarkers do not correlate with severity of vascular stiffness in ckd patients with severe co-morbid disease. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2011, 119, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Irndt, M.A.G.; Lrich, C.H.U.; Aul, H.A.K.; Ester, U.R.S.; Ester, M.A.S.; Saar, H. Uremia-associated immune defect: The IL-10—CRP axis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2003, 63, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teta, D. Adipokines as uremic toxins. J. Ren. Nutr. 2012, 22, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, K.; Nagaraju, S.P.; Rhee, C.M.; Mathe, Z.; Molnar, M.Z. Adipocytokines in renal transplant recipients. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Iwatani, H.; Kihara, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Komura, N.; Fujita, K.; Maeda, N.; Nishida, M.; Katsube, F.; Shimomura, I.; Ito, T.; Funahashi, T. Exacerbation of albuminuria and renal fibrosis in subtotal renal ablation model of adiponectin-knockout mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, F. Regulation of adiponectin multimerization, signaling and function. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Carrero, J.J.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. The complex role of adiponectin in chronic kidney disease. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Tripepi, G.; Benedetto, F.A.; Cutrupi, S.; Parlongo, S.; Malatino, L.S.; Bonanno, G.; Seminara, G.; Rapisarda, F.; et al. Adiponectin, metabolic risk factors, and cardiovascular events among patients with end-stage renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.Z.; Ni, Z.H.; Gu, L.Y.; Lin, A.W.; Fang, W.; Yao, Q.; Lindholm, B.; Qian, J.Q. Adiponectin is related to carotid artery plaque and a predictor of cardiovascular outcome in a cohort of non-diabetic peritoneal dialysis patients. Blood Purif. 2008, 26, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, N.; Kato, A.; Misaki, T.; Sakakima, M.; Fujigaki, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Hishida, A. Association of serum adiponectin levels with all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients. Intern. Med. 2008, 47, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drechsler, C.; Krane, V.; Winkler, K.; Dekker, F.; Wanner, C. Changes in adiponectin and the risk of sudden death, stroke, myocardial infarction, and mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Heiman, M.; DiMarchi, R. Leptin: Structure, Function and Biology. Vitam. Horm. 2005, 71, 345–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heimburger, O.; Lonnqvist, F.; Danielsson, A.; Nordenstrom, J.; Stenvinkel, P. Serum immunoreactive leptin concentration and its relation to the body fat content in chronic renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1997, 8, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Ziyadeh, F.N. The emerging role of transforming growth factor-beta in kidney diseases. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, 829–842. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Mamputu, J.-C.; Wiernsperger, N.; Renier, G. Signaling Pathways Involved in Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression Induced by Leptin. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2227–2234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Honigmann, M.R.; Nath, A.K.; Murakami, C.; García-Cardeña, G.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Sessa, W.C.; Madge, L.A.; Schechner, J.S.; Schwabb, M.B.; Polverini, P.J.; Flores-Riveros, J.R. Biological action of leptin as an angiogenic factor. Science 1998, 281, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallaschofski, H.; Kobsar, A.; Sokolova, O.; Siegemund, A.; Stepan, H.; Faber, R.; Eigenthaler, M.; Lohmann, T. Differences in platelet activation by prolactin and leptin. Horm. Metab. Res. 2004, 36, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlyle, M.; Jones, O.B.; Kuo, J.J.; Hall, J.E. Chronic cardiovascular and renal actions of leptin: Role of adrenergic activity. Hypertension 2002, 39, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, K.; Maeda, T.; Kawane, T.; Matsunuma, A.; Horiuchi, N. Leptin stimulates fibroblast growth factor 23 expression in bone and suppresses renal 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 synthesis in leptin-deficient mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, W.W.; Ding, W.; Gunta, S.S.; Gu, Y.; Tabakman, R.; Klapper, L.N.; Gertler, A.; Mak, R.H. A Pegylated Leptin Antagonist Ameliorates CKD-Associated Cachexia in Mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheung, W.; Yu, P.X.; Little, B.M.; Cone, R.D.; Marks, D.L.; Mak, R.H. Role of leptin and melanocortin signaling in uremia-associated cachexia. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Odamaki, M.; Furuya, R.; Yoneyama, T.; Nishikino, M.; Hibi, I.; Miyaji, K.; Kumagai, H. Association of the serum leptin concentration with weight loss in chronic hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1999, 33, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castaneda-Sceppa, C.; Sarnak, M.J.; Wang, X.; Greene, T.; Madero, M.; Kusek, J.W.; Beck, G.; Kopple, J.D.; Levey, A.S.; Menon, V. Role of adipose tissue in determining muscle mass in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Carmona, A.; Pérez Fontán, M.; Cordido, F.; García Falcón, T.; García-Buela, J. Hyperleptinemia is not correlated with markers of protein malnutrition in chronic renal failure. Nephron 2000, 86, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholze, A.; Rattensperger, D.; Zidek, W.; Tepel, M. Low serum leptin predicts mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5. Obesity 2007, 15, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K. So, is leptin good or bad in chronic kidney disease? Obesity 2007, 15, 1343–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez, J.J.; Bossola, M.; Fernández-Reyes, M.J.; Di Stasio, E.; Tazza, L.; Luciani, G.; Codoceo, R.; Iglesias, P.; Rodríguez, A.; González, E.; et al. Relationship between leptin and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in chronic hemodialysis patients. Nefrologia 2011, 31, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C.; Postorino, M.; Marino, C.; Pizzini, P.; Cutrupi, S.; Tripepi, G. Waist circumference modifies the relationship between the adipose tissue cytokines leptin and adiponectin and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in haemodialysis patients. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 269, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steppan, C.M.; Bailey, S.T.; Bhat, S.; Brown, E.J.; Banerjee, R.R.; Wright, C.M.; Patel, H.R.; Ahima, R.S.; Lazar, M.A. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001, 409, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, J.; Bergsten, A.; Qureshi, A.R.; Heimbürger, O.; Bárány, P.; Lönnqvist, F.; Lindholm, B.; Nordfors, L.; Alvestrand, A.; Stenvinkel, P. Elevated resistin levels in chronic kidney disease are associated with decreased glomerular filtration rate and inflammation, but not with insulin resistance. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 596–604. [Google Scholar]
- Codoñer-Franch, P.; Alonso-Iglesias, E. Resistin: Insulin resistance to malignancy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 438, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, A.; Spadaro, S.; Copetti, M.; Spoto, B.; Salvemini, L.; Pizzini, P.; Frittitta, L.; Mallamaci, F.; Pellegrini, F.; Trischitta, V.; et al. Association between resistin levels and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A new study and a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, B.; Mattace-Raso, F.; Sijbrands, E.; Pizzini, P.; Cutrupi, S.; D’Arrigo, G.; Tripepi, G.; Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F. Resistin and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: Effect modification by adiponectin in end-stage kidney disease patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013, 28 (Suppl. 4), 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubicek, T.; Bartlova, M.; Krajickova, J.; Haluzikova, D.; Mraz, M.; Lacinova, Z.; Kudla, M.; Teplan, V.; Haluzik, M. Increased production of proinflammatory cytokines in adipose tissue of patients with end-stage renal disease. Nutrition 2009, 25, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallquist, C.; Mansouri, L.; Norrbäck, M.; Hylander, B.; Jacobson, S.H.; Lundahl, J. Early Changes in Monocyte Adhesion Molecule Expression and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease—A 5-Year Prospective Study. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 44, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, A.A.; Farag, A.S.; El-Maleek Hassan, D.A.; Abdu, S.M.; Lashin, S.M.; Abdelaziz, N. Role of Interleukin-2 in Uremic Pruritus Among Attendants of AL-Zahraa Hospital Dialysis Unit. Indian J. Dermatol. 2015, 60, 211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaspari, A.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Stern, J.B.; Katz, S.I. Dermatologic changes associated with interleukin 2 administration. JAMA 1987, 258, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.N.; Matthews, G.J.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Shah, R.; Mclaughlin, C.; Patel, P.; Budoff, M.; Chen, J.; Wolman, M.; Go, A.; He, J.; et al. Higher plasma CXCL12 levels predict incident myocardial infarction and death in chronic kidney disease: Findings from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study Investigators. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.; Matthews, G.J.; Shah, R.Y.; McLaughlin, C.; Chen, J.; Wolman, M.; Master, S.R.; Chai, B.; Xie, D.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Serum Fractalkine (CX3CL1) and Cardiovascular Outcomes and Diabetes: Findings from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.A.; Moreno, S.; Rubio-Navarro, A.; Sastre, C.; Blanco-Colio, L.M.; Gómez-Guerrero, C.; Ortiz, A.; Egido, J. Targeting chemokines in proteinuria-induced renal disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gomez, M.V.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Sanz, A.B.; Zheng, B.; Martín-Cleary, C.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Ortiz, A.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B. Targeting inflammation in diabetic kidney disease: early clinical trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 3784, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, E.; Anan, F.; Masaki, T.; Kaneda, K.; Nawata, T.; Eshima, N.; Saikawa, T.; Yoshimatsu, H. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is associated with silent cerebral infarction in patients on haemodialysis. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elewa, U.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Mahillo-Fernández, I.; Martin-Cleary, C.; Sanz, A.B.; Perez-Gomez, M.V.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Ortiz, A. Circulating CXCL16 in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016, 41, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, M.C.; Sanz, A.B.; Mezzano, S.; Blanco, J.; Carrasco, S.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Benito-Martín, A.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. TWEAK (tumor necrosis factor–like weak inducer of apoptosis) activates CXCL16 expression during renal tubulointerstitial inflammation. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, M.C.; Martin-Cleary, C.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Elewa, U.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Carrero, J.J.; Ortiz, A. CXCL16 in kidney and cardiovascular injury. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.I.; Sonmez, A.; Ortiz, A.; Saglam, M.; Kilic, S.; Eyileten, T.; Caglar, K.; Oguz, Y.; Vural, A.; Çakar, M. Soluble TWEAK and PTX3 in nondialysis CKD patients: Impact on endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular outcomes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.J.; Ortiz, A.; Qureshi, A.R.; Martín-Ventura, J.L.; Bárány, P.; Heimbürger, O.; Marrón, B.; Metry, G.; Snaedal, S.; Lindholm, B.; et al. Additive effects of soluble TWEAK and inflammation on mortality in hemodialysis patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.I.; Carrero, J.J.; Ortiz, A.; Martín-Ventura, J.L.; Sonmez, A.; Saglam, M.; Yaman, H.; Yenicesu, M.; Egido, J.; Blanco-Colio, L.M. Soluble TWEAK plasma levels as a novel biomarker of endothelial function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Ortiz, A.; Ramos, A.M. Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, A.B.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Ucero, A.C.; Egido, J.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Ramos, A.M.; Putterman, C.; Ortiz, A. TWEAK and the progression of renal disease: Clinical translation. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2014, 29 (Suppl. 1), i54–i62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.M.; Niu, J.M.; Lei, Q.; Lin, X.H.; Chen, X. Serum levels of the adipokine chemerin in preeclampsia. J. Perinat. Med. 2012, 40, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Qureshi, A.R.; Anderstam, B.; Heimbürger, O.; Bárány, P.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P.; Axelsson, J. Clinical importance of an elevated circulating chemerin level in incident dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2010, 25, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Hsu, S.-P.; Pai, M.-F.; Yang, J.-Y.; Wu, H.-Y.; Peng, Y.S. Reappraisal of effects of serum chemerin and adiponectin levels and nutritional status on cardiovascular outcomes in prevalent hemodialysis patients. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 34128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, K.B.; Nguyen Dinh Cat, A.; Lopes, R.A.M.; Rios, F.J.; Anagnostopoulou, A.; Lobato, N.S.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Tostes, R.C.; Montezano, A.C.; Touyz, R.M. Chemerin Regulates Crosstalk between Adipocytes and Vascular Cells Through Nox. Hypertension 2015, 66, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, J.; Witasp, A.; Carrero, J.J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Suliman, M.E.; Heimbürger, O.; Bárány, P.; Lindholm, B.; Alvestrand, A.; Schalling, M.; et al. Circulating Levels of Visfatin/Pre-B-Cell Colony-Enhancing Factor 1 in Relation to Genotype, GFR, Body Composition, and Survival in Patients With CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Huang, P.H.; Chen, T.H.; Chiang, C.H.; Leu, H.B.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, J.W.; Lin, S.J. Increased circulating visfatin is associated with progression of kidney disease in non-diabetic hypertensive patients. Am. J. Hypertens. 2016, 29, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benito-Martin, A.; Ucero, A.C.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Santamaria, B.; Picatoste, B.; Carrasco, S.; Lorenzo, O.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. Endogenous NAMPT dampens chemokine expression and apoptotic responses in stressed tubular cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Andres, O.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Moreno, J.A.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Ramos, A.M.; Sanz, A.B.; Ortiz, A. Downregulation of kidney protective factors by inflammation: Role of transcription factors and epigenetic mechanisms. Am. J. Phys. Ren. Physiol. 2016, 311, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuta, T.; Komaba, H.; Takagi, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Hyodo, T.; Nagaoka, M.; Tanaka, R.; Iwao, S.; Ishida, M.; et al. A Prospective Multicenter Randomized Controlled Study on Interleukin-6 Removal and Induction by a new Hemodialyzer with Improved Biocompatibility in Hemodialysis Patients: A Pilot Study. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2016, 20, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.C.; Uchino, S.; Fealy, N.; Baldwin, I.; Panagiotopoulos, S.; Goehl, H.; Morgera, S.; Neumayer, H.H.; Bellomo, R. Super high flux hemodialysis at high dialysate flows: An ex vivo assessment. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2004, 27, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Morgera, S.; Slowinski, T.; Melzer, C.; Sobottke, V.; Vargas-Hein, O.; Volk, T.; Zuckermann-Becker, H.; Wegner, B.; Müller, J.M.; Baumann, G.; et al. Renal Replacement Therapy with High-Cutoff Hemofilters: Impact of Convection and Diffusion on Cytokine Clearances and Protein Status. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraiolo, B.L.; Moore, J.A.; Crase, D.; Gribling, P.; Wilking, H.; Baughman, R.A. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha in mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1988, 16, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deaciuc, I.V.; Alappat, J.M.; McDonough, K.H.; D’Souza, N.B. Effect of chronic alcohol consumption by rats on tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 clearance in vivo and by the isolated, perfused liver. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 52, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimers, J.; Wogensen, L.D.; Welinder, B.; Hejnaes, K.R.; Poulsen, S.S.; Nilsson, P.; Nerup, J. The pharmacokinetics, distribution and degradation of human recombinant interleukin 1 beta in normal rats. Scand. J. Immunol. 1991, 34, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferraiolo, B.L.; McCabe, J.; Hollenbach, S.; Hultgren, B.; Pitti, R.; Wilking, H. Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rats. Effects of size and number of doses and nephrectomy. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1989, 17, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beutler, B.A.; Milsark, I.W.; Cerami, A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: Production, distribution, and metabolic fate in vivo. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 3972–3977. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klapproth, J.; Geiger, T.; Heinrich, P.C. Fate and biological action of human recombinant interleukin l Beta in the rat in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 1989, 19, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castell, J.V.; Geiger, T.; Gross, V.; Andus, T.; Walter, E.; Hirano, T.; Kishimoto, T.; Heinrich, P.C. Plasma clearance, organ distribution and target cells of interleukin-6/hepatocyte-stimulating factor in the rat. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 177, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, R.E.; Forbes, M.A.; Hallam, S.; Jenkins, A.; Wadhwa, M.; Dilger, P.; Meager, A.; Thorpe, R.; Bowmer, C.J.; Joffe, J.K.; et al. Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with subcutaneous interleukin 2: Evidence for non-renal clearance of cytokines. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 1842–1848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poveda, J.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Glorieux, G.; Sanz, A.B.; Egido, J.; Vanholder, R.; Ortiz, A. P-Cresyl sulphate has pro-inflammatory and cytotoxic actions on human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2014, 29, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Campbell, K.L.; Johnson, D.W.; Stanton, T.; Vesey, D.A.; Coombes, J.S.; Weston, K.S.; Hawley, C.M.; McWhinney, B.C.; Ungerer, J.P. Protein-bound uremic toxins, inflammation and oxidative stress: A cross-sectional study in stage 3–4 chronic kidney disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibotto, G.; Sofia, A.; Procopio, V.; Villaggio, B.; Tarroni, A.; Di Martino, M.; Cappelli, V.; Gandolfo, M.T.; Aloisi, F.; De Cian, F.; et al. Peripheral tissue release of interleukin-6 in patients with chronic kidney diseases: Effects of end-stage renal disease and microinflammatory state. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oettinger, C.W.; Bland, L.A.; Oliver, J.C.; Arduino, M.J.; McAllister, S.K.; Favero, M.S. The effect of uremia on tumor necrosis factor-alpha release after an in vitro whole-blood endotoxin challenge. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1994, 4, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stinghen, A.E.M.; Gonçalves, S.M.; Martines, E.G.; Nakao, L.S.; Riella, M.C.; Aita, C.A.; Pecoits-Filho, R. Increased plasma and endothelial cell expression of chemokines and adhesion molecules in chronic kidney disease. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2009, 111, c117–c126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminzadeh, M.A.; Pahl, M.V.; Barton, C.H.; Doctor, N.S.; Vaziri, N.D. Human uraemic plasma stimulates release of leptin and uptake of tumour necrosis factor-α in visceral adipocytes. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 3626–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbacher, E.; Koppe, L.; Zarrouki, B.; Pillon, N.J.; Fouque, D.; Soulage, C.O. Human uremic plasma and not urea induces exuberant secretion of leptin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Ren. Nutr. 2011, 21, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolito, M.D.; Du, X.; Zong, H.; Catucci, A.; Maiuri, L.; Trivisano, T.; Pettoello-Mantovani, M.; Campanozzi, A.; Raia, V.; Pessin, J.E.; et al. Urea-induced ROS generation causes insulin resistance in mice with chronic renal failure. Insulin 2010, 120, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, A.B.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Ramos, A.M.; Moreno, J.A.; Santamaria, B.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. NF-κB in Renal Inflammation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poveda, J.; Tabara, L.C.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Martin-Cleary, C.; Sanz, A.B.; Selgas, R.; Ortiz, A.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D. TWEAK/Fn14 and non-canonical NF-kappaB signaling in kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, L.M.; López-Otín, C.; Bjorkman, P.J. Biochemical characterization and crystalization of human Zn-alpha2-glycoprotein, a soluble class I major histocompatibility complex homolog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997, 94, 4626–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, C.C.; Koppe, L.; Alix, P.M.; Kalbacher, E.; Croze, M.L.; Hadj-Aissa, A.; Fouque, D.; Guebre-Egziabher, F.S.C. The relationship between renal function and plasma concentration of the cachectic factor zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein (ZAG) in adult patients with chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Normal Concentration * (ng/L) | Uremic Concentration (ng/L) * | Relative Increase | MW (kD) | Targeting at Clinical Development Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines | |||||
| Interleukin-1β | 160 | 236 ± 92 | 1.5 | 32 | In use |
| Interleukin-18 | 142 ± 48 | 202 ± 169 | 1.4 | 20 | Yes |
| Interleukin-6 | 4.0 | 5.9 ± 2.0 | 1.5 | 24.5 | In use |
| Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNFα) | 7.0 | 21.6 ± 24.5 | 3.0 | 26 | In use |
| Interleukin-8 | 1.64 ± 1.85 | 20.2 ± 25.1 | 10.9 | 8 | Yes |
| Anti-inflammatory cytokines | |||||
| Interleukin-10 | 7.10 ± 1.50 | 10.60 ± 6.00 | 1.5 | 18 | Yes |
| Adipokines | |||||
| Adiponectin | 8,700,000 ± 4,800,000 | 16,600,000 ± 6,600,000 | 2.0 | 28 | No |
| Leptin | 8400 ± 6700 | 37,600 ± 25,100 | 4.5 | 16 | In use |
| Resistin | 15,100 ± 700 | 47,300 (35,300–62,200) | 3.1 | 12.5 | No |
| Comparator | |||||
| β2-microglobulin | 1,900,000 ± 1,600,000 | 30,200,000 ± 7,800,000 | 15.9 | 11.8 | NA |
| Those Already in | Evidence for role in Human CKD-Associated Abnormalities | Comment | Consider Removing from List of Potential Uremic Toxins * | Comment | Consider Adding to List of Potential Uremic Toxins | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | Anakinra: IL-1β promotes inflammation | Increased decoy receptors may be protective | IL-10 | Anti-inflammatory effect | IL-6R | Associated to mortality, facilitates IL-6 signaling |
| IL-18 | Only observational | Adiponectin | Insufficient evidence in humans | IL-2 | Causes pruritus, associated to pruritus | |
| IL-6 | Only observational | Increased soluble receptor may increase some effects | Leptin | Insufficient evidence in humans | sTNFR1, sTNFR2 | Associated to mortality, may sensitize to tuberculosis in humans |
| TNFα | Anti-TNF: TNF may contribute to CKD progression and malnutrition | Increased decoy receptors may be protective | Resistin | Insufficient evidence in humans | CXCL12 | Associated to mortality, |
| IL-8 | Only observational | CX3CL1 | Associated to mortality, | |||
| IL-10 | Only observational | |||||
| Adiponectin | Inconclusive observational | Association with mortality inconsistent and related with either low or high levels | ||||
| Leptin | Inconclusive observational | Low leptin levels associated with mortality in some populations | ||||
| Resistin | Inconclusive observational | Association with mortality inconsistent |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castillo-Rodríguez, E.; Pizarro-Sánchez, S.; Sanz, A.B.; Ramos, A.M.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Martin-Cleary, C.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Ortiz, A. Inflammatory Cytokines as Uremic Toxins: “Ni Son Todos Los Que Estan, Ni Estan Todos Los Que Son”. Toxins 2017, 9, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9040114
Castillo-Rodríguez E, Pizarro-Sánchez S, Sanz AB, Ramos AM, Sanchez-Niño MD, Martin-Cleary C, Fernandez-Fernandez B, Ortiz A. Inflammatory Cytokines as Uremic Toxins: “Ni Son Todos Los Que Estan, Ni Estan Todos Los Que Son”. Toxins. 2017; 9(4):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9040114
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastillo-Rodríguez, Esmeralda, Soledad Pizarro-Sánchez, Ana B. Sanz, Adrian M. Ramos, Maria Dolores Sanchez-Niño, Catalina Martin-Cleary, Beatriz Fernandez-Fernandez, and Alberto Ortiz. 2017. "Inflammatory Cytokines as Uremic Toxins: “Ni Son Todos Los Que Estan, Ni Estan Todos Los Que Son”" Toxins 9, no. 4: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9040114
APA StyleCastillo-Rodríguez, E., Pizarro-Sánchez, S., Sanz, A. B., Ramos, A. M., Sanchez-Niño, M. D., Martin-Cleary, C., Fernandez-Fernandez, B., & Ortiz, A. (2017). Inflammatory Cytokines as Uremic Toxins: “Ni Son Todos Los Que Estan, Ni Estan Todos Los Que Son”. Toxins, 9(4), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9040114