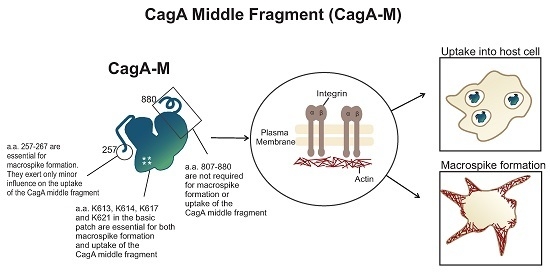
The Middle Fragment of Helicobacter pylori CagA Induces Actin Rearrangement and Triggers Its Own Uptake into Gastric Epithelial Cells
Abstract
Share and Cite
Tohidpour, A.; Gorrell, R.J.; Roujeinikova, A.; Kwok, T. The Middle Fragment of Helicobacter pylori CagA Induces Actin Rearrangement and Triggers Its Own Uptake into Gastric Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2017, 9, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9080237
Tohidpour A, Gorrell RJ, Roujeinikova A, Kwok T. The Middle Fragment of Helicobacter pylori CagA Induces Actin Rearrangement and Triggers Its Own Uptake into Gastric Epithelial Cells. Toxins. 2017; 9(8):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9080237
Chicago/Turabian StyleTohidpour, Abolghasem, Rebecca J. Gorrell, Anna Roujeinikova, and Terry Kwok. 2017. "The Middle Fragment of Helicobacter pylori CagA Induces Actin Rearrangement and Triggers Its Own Uptake into Gastric Epithelial Cells" Toxins 9, no. 8: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9080237
APA StyleTohidpour, A., Gorrell, R. J., Roujeinikova, A., & Kwok, T. (2017). The Middle Fragment of Helicobacter pylori CagA Induces Actin Rearrangement and Triggers Its Own Uptake into Gastric Epithelial Cells. Toxins, 9(8), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9080237