Process Understanding of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing through Multiphysics Simulation and Inline Metrology
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Literature Review
1.1. Introduction
- – max decrease in roughness;
- – time constant;
- – min achievable roughness;
- – processing time;
1.2. Electrical Conductivity of the Plasma-Gas Layer
1.3. Mechanism during Plasma Electrolytic Polishing
2. Multiphysics Simulation of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing
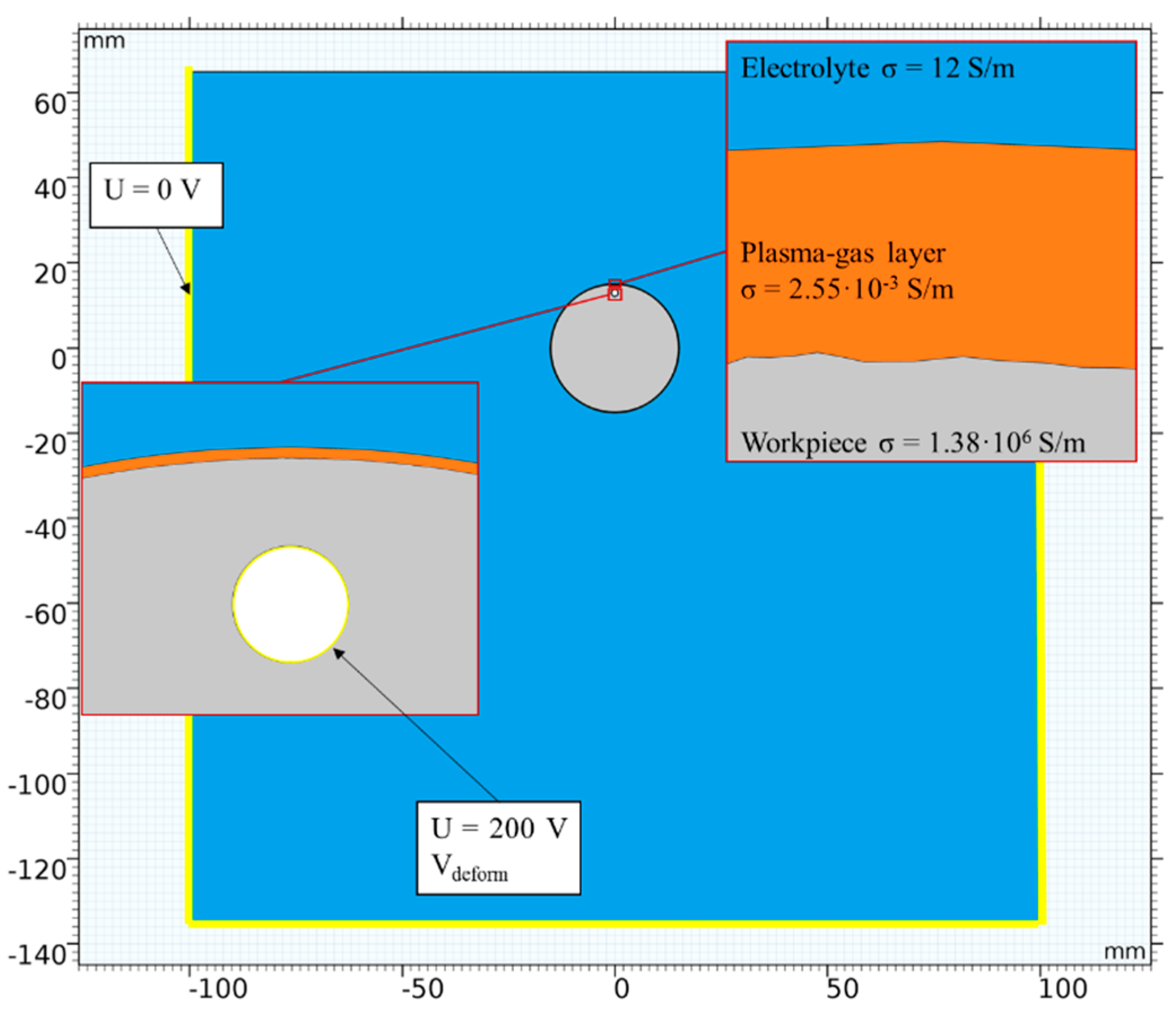
2.1. Geometry
2.2. Model Mesh
2.3. Simulation Results
3. Inline Metrology in Plasma Electrolytic Polishing
Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
- The main voltage drop in PeP occurs in the plasma-gas layer. The current distribution inside plasma-gas layer is determined by the workpiece surface. Thus, a higher current density on the peaks leads to a faster removal of the peaks and to a reduction of roughness.
- PeP can be simulated as an electrochemical machining process. Moreover, future simulations can be undertaken considering only the plasma-gas layer where the interface with the electrolyte acts as a cathode and the workpiece surface as the anode.
- PeP processing time and roughness can be predicted with the simulation.
- Changes in roughness depend on the position along the sample height.
- roughness can be fitted with exponential decay fit, as well as with roughness.
- The changes in roughness for both and depend on the position along the sample’s height. The decrease in roughness for the bottom of the sample is bigger.
- The current efficiency of PeP is comparable to that of ECM, but the current density is lower.
- Passivation in PeP and oxygen formation should be different from a typical electrochemical process because of the plasma-gas layer.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nestler, K.; Böttger-Hiller, F.; Adamitzki, W.; Glowa, G.; Zeidler, H.; Schubert, A. Plasma Electrolytic Polishing-An Overview of Applied Technologies and Current Challenges to Extend the Polishable Material Range. Procedia CIRP 2016, 42, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidler, H.; Boettger-Hiller, F.; Edelmann, J.; Schubert, A. Surface Finish Machining of Medical Parts Using Plasma Electrolytic Polishing. Procedia CIRP 2016, 49, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Синькевич, Ю.В.; Шелег, В.К.; Янковский, И.Н.; Беляев, Г.Я. Электроимпульсное Полирование Сплавов на Основе Железа, Хрома и Никеля (Electropulse Polishing of Alloys Based on Iron, Chromium and Nickel); Белорусский Национальный Технический Университет: Minsk, Belarus, 2014; ISBN 978-985-550-516-8. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelsen, M.; Deutsch, C.; Seitz, H. Electrolytic Plasma Polishing of Pipe Inner Surfaces. Metals 2017, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Куликов, И.С.; Ващенко, С.В.; Каменев, А.Я. Электролитно-Плазменная Обработка Материалов (Electrolytic-Plasma Treatment of Materials); Беларуская Навука: Минск, Belarus, 2010; ISBN 978-985-08-1215-5. [Google Scholar]
- Алексеев, Ю.Г.; Паршуто, А.Э.; Нисс, В.С.; Королев, А.Ю. Способ Электролитно-Плазменной Обработки Стального Изделия (The Method of Electrolyte-Plasma Treatment of Steel Products). BY Patent 21103, 4 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Duradji, V.N.; Kaputkin, D.E.; Duradji, A.Y. Aluminum treatment in the electrolytic plasma during the anodic process. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2017, 10, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Смыслов, А.М.; Таминдаров, Д.Р.; Мингажев, А.Д.; Смыслова, М.К.; Самаркина, А.Б. Способ Электролитно-Плазменного Полирования Деталей из Титановых Сплавов (Method of Electrolyte-Plasma Grinding Parts Made from Titanium Alloys). RU Patent 2495967, 3 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Valiev, R.I.; Khafizov, A.A.; Shakirov, Y.I.; Sushchikova, A.N. Polishing and deburring of machine parts in plasma of glow discharge between solid and liquid electrodes. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 86, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenchukova, V.O.; Nagula, P.K.; Tretinnikov, D.L. About changes in the chemical composition of the electrolyte in the process of electrolytic-plasma treatment of materials. Mater. Methods Technol. 2015, 9, 404–413. [Google Scholar]
- Kashapov, L.N.; Kashapov, N.F.; Kashapov, R.N. Investigation of the influence of plasma-electrolytic processing on the surface of austenitic chromium-nickel steels. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 479, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Дураджи, В.Н.; Капуткин, Д.Е. Способ Электролитно-Плазменной Обработки Поверхности Металлов (Method of electrolytic-plasma treatment of metal surface). RU Patent 2550393, 27 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, A.S.; Zeidler, H.; Schubert, A. Analysis of voltage and current during the Plasma electrolytic Polishing of stainless steel. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference European Society Precision Engineering Nanotechnology, EUSPEN 2017, Hannover, Germany, 29 May–2 June 2017; pp. 2–3, ISBN 9780995775107. [Google Scholar]
- Мукаева, В.Р. Управление Технологическим Процессом Электролитно-плазменного Полирования на Основе Контроля Шероховатости пов. по Импедансным Спектрам (Management of Processing Procedure of Electrolytic-Plasma Polishing on the Base of Control of Surface Roughness by Impedance Spectra). Ph.D. Thesis, Ufa State Aviation Technical University, Ufa, Russia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Кревсун, Э.П.; Куликов, И.С.; Каменев, А.Я.; Ермаков, В.Л. Устройство для Электролитно-Плазменного Полирования Металлического Изделия (Device for Electrolytic-Plasma Polishing of Metal Product). BY Patent 13937, 4 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Алексеев, Ю.Г.; Кособуцкий, A.A.; Кoрoлев, A.Ю.; Нисс, В.С.; Кучерявый, В.Д.; Повжик, А.А. Особенности процессов размерной обработки металлических изделий электролитно-плазменным методом (Features of the processes of dimensional processing of metal products by electrolytic-plasma method). Литье и Металлургия 2005, 4, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Ablyaz, T.R.; Muratov, K.R.; Radkevich, M.M.; Ushomirskaya, L.A.; Zarubin, D.A. Electrolytic Plasma Surface Polishing of Complex Components Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Russ. Eng. Res. 2018, 38, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Попов, А.И.; Тюхтяев, М.И.; Радкевич, М.М.; Новиков, В.И. Анализ тепловых явлений при струйной фокусированной электролитно-плазменной обработке (The analysis of thermal phenomena occuring under jet focused electrolytic plasma processing). Научно-Технические Ведомости Cанкт-Петербургского Государственного Политехнического Университета 2017, 4, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Попов, А.И.; Радкевич, М.М.; Кудрявцев, В.Н.; Захаров, С.В.; Кузьмичев, И.С. Установка для Электролитно-Плазменной Обработки Турбинных Лопаток (Plant for Electrolyte-Plasma Treatment of Turbine Blades). RU Patent 2623555, 24 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Алексеев, Ю.Г.; Королев, А.Ю.; Нисс, В.С.; Паршуто, А.Э. Электролитно-плазменная обработка внутренних поверхностей трубчатых изделий (Electrolytic-Plasma Treatment of Inner Surface of Tubular Products). Наука и Техника 2016, 15, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Кургузов, С.А.; Залетов, Ю.Д.; Косматов, В.И.; Гусева, О.С.; Шевцова, И.Н. Электролитно-плазменная очистка поверхности стального металлопроката (Electrolytic and plasma cleaning of the surface of steel rolled metal product). Электротехнические Системы и Комплексы 2016, 2, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Новоселов, М.В.; Шиллинг, Н.Г.; Рудавин, А.А.; Радкевич, М.М.; Попов, А.И. Оценка возможности полирования нержавеющих сталей струйной электролитно-плазменной обработкой (Assessment of a possibility polishing of stainless steels jet electrolytic and plasma processing). Вестник ПНИПУ 2018, 20, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, H.H. Anode Effect in Aqueous Electrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1950, 97, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Гирговьев, А.И.; Ширяева, С.О.; Морозов, В.В. О некоторых закономерностях формирования электрического тока в окрестности опущенного в электролит нагретого электрода (About some regularities of the electric current formation in the vicinity of a heated electrode lowered into the electrolyte). Электронная Обработка Материалов 2004, 5, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Плотников, Н.В.; Смыслов, А.М.; Таминдаров, Д.Р. К вопросу о модели электролитно-плазменного полирования поверхности (To a question on model of electrolytic-plasma polishing). Вестник УГАТУ 2013, 17, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Дураджи, В.Н. Особенности установления электрогидродинамического режима, используемого для полирования металлов в электролитной плазме (Features of the establishment of the electrohydrodynamic regime used for polishing metals in electrolytic plasma). Металлообработка 2013, 3, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Vana, D.; Podhorsky, S.; Hurajt, M.; Hanzen, V. Surface Properties of the Stainless Steel X10 CrNi 18/10 after Aplication of Plasma Polishing in Electrolyte. Int. J. Mod. Eng. Res. 2013, 3, 788–792. [Google Scholar]
- Синькевич, Ю.В. Концепт. модель коммутационного механизма электрич. проводимости парогазовой оболочки в режиме электроимпульсного полирования (Conceptual Model of Commutation Mechanism for Electric Conductivity of Vapor-Gas Envelope in Electro-Impulse Polishing Mode). Наука и Техника 2016, 15, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Воленко, А.П.; Бойченко, О.В.; Чиркунова, Н.В. Электролитно-плазменная обработка металлических изделий (Electrolyte-plasma treatment of metals). Вектор Науки ТГУ 2012, 4, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Suo, L.C.; Guan, L.L.; Fu, Y.L. Analytical Study on Mechanism of Electrolysis and Plasma Polishing. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 472–475, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zong, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, S. Influence of Voltage on Electrolysis and Plasma Polishing. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Manufacturing Engineering and Intelligent Materials (ICMEIM 2017), Guangzhou, China, 25–26 February 2017; Volume 100, no. Icmeim. pp. 10–15, ISBN 978-94-6252-317-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Suo, L.C.; Fu, Y.L.; Guan, L.L. Study on Material Removal Rate of Electrolysis and Plasma Polishing. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Shenyang, China, 6–8 June 2012; pp. 917–922, ISBN 9783037853702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Парфенов, Е.В.; Ерохин, А.Л.; Невьянцева, Р.Р.; Мукаева, В.Р.; Горбатков, М.В. Управление электролитно-плазменными и электрохимическими технологическими процессами на основе контроля состояния объекта методом импедансной спектроскопии (Control of electrolytic-plasma and electrochemical processes based on control of condition of object by impedance spectroscopy). In Proceedings of the Xii Всероссийское Совещание по Проблемам Управления Вспу-2014, Moscow, Russia, 16–19 June 2014; pp. 4348–4359. [Google Scholar]
- Parfenov, E.V.; Farrakhov, R.G.; Mukaeva, V.R.; Gusarov, A.V.; Nevyantseva, R.R.; Yerokhin, A. Electric field effect on surface layer removal during electrolytic plasma polishing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Иванова, Н.П.; Синькевич, Ю.В.; Шелег, В.К.; Янковский, И.Н. Механизм анодного растворения коррозионностойких и конструкц. углерод. сталей в условиях электроимпульсного полирования (The mechanism of anodic dissolution of corrosion-resistant and structural carbon steels under conditions of electropulse polishing). Наука и Техника 2013, 1, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Смыслов, А.М.; Смыслова, М.К.; Мингажев, А.Д.; Селиванов, К.С. Многоэтапная электролитно-плазменная обработка изделий из титана и титановых сплавов (Multistage electrolytic-plasma processing of products from titanium and titanium alloys). Вестник УГАТУ 2009, 13, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Иванова, Н.П.; Синькевич, Ю.В.; Шелег, В.К.; Янковский, И.Н. Исследование морфологии и химического состава электроимпульсно полированной поверхности углеродистых и коррозионностойких сталей (Study of the morphology and chemical composition of electropulse polished surface of carbon and corrosion-resistant steels). Наука и Техника 2012, 6, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Danilov, I.; Hackert-Oschätzchen, M.; Schaarschmidt, I.; Zinecker, M.; Schubert, A. Transient Simulation of the Removal Process in Plasma Electrolytic Polishing of Stainless Steel. In Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2018, Lausanne, Switzerland, 22–24 October 2018; Available online: https://www.comsol.com/paper/download/573171/danilov_paper.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- Sjodin, B. How to Generate Random Surfaces in COMSOL Multiphysics®|COMSOL Blog. Available online: https://www.comsol.com/blogs/how-to-generate-random-surfaces-in-comsol-multiphysics/ (accessed on 24 May 2018).
- Böttger-Hiller, F.; Nestler, K.; Zeidler, H.; Glowa, G.; Lampke, T. Plasma electrolytic polishing of metalized carbon fibers. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2016, 3, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

























| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage | 250 V, 300 V, 350 V |
| Electrolyte | Ammonium sulfate |
| Electrolyte concentration (wt %) | 5% |
| Electrolyte temperature | 70 °C, 80 °C, 90 °C |
| Samples material | Stainless steel (1.4021) |
| Initial roughness () | 0.63 µm, 0.32 µm |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| N | Spatial frequency resolution | 2000 |
| b | Spectral exponent | 0.5 |
| A | Scale parameter in y coordinate | 0.001 |
| s | Phase coefficient | from 0 to 1 |
| g1 | Gaussian random function | |
| u1 | Uniform random function |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage | 200 V |
| Anode conductivity | 1.38×107 mS/cm |
| Electrolyte conductivity | 120 mS/cm |
| Plasma-gas layer conductivity | 2.55×10−2 mS/cm |
| Plasma-gas layer thickness | 0.15 mm |
| Anode relative permittivity | 1 |
| Electrolyte relative permittivity | 55 |
| Plasma-gas layer relative permittivity | 1 |
| Parameter | Electrolyte and Plasma-Gas Layer | Workpiece |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum element size | 20 mm | 20 mm |
| Minimum element size | 0.005 mm | 0.005 mm |
| Maximum element growth rate | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| Curvature factor | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Resolution of narrow regions | 1 | 1 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage | 250 V |
| Pre-set temperature of electrolyte | 75 °C |
| Electrolyte salt | Ammonium sulphate |
| Electrolyte salt concentration | 5% of mass |
| Samples material | steel 1.4301 (AISI 304) |
| Initial roughness | (0.15 ± 0.02) µm (0.63 ± 0.08) µm |
| Initial roughness | (0.10 ± 0.02) µm (0.14 ± 0.02) µm |
| Parameter | Initial Roughness | Minimum Achievable Roughness | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top | Bottom | ||
| 0.15 µm | 0.083 µm | 0.045 µm | |
| 0.63 µm | 0.414 µm | 0.221 µm | |
| 0.10 µm | 0.033 µm | 0.028 µm | |
| 0.14 µm | 0.055 µm | 0.032 µm | |
| Chemical Element | Fe | Cr | Ni | N | Mn | Si | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass fraction c in % | 68.8 | 18 | 10 | 0.1 | 2 | 1 | 0.1 |
| Valence z | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Molar Mass M in g/mol | 55.85 | 51.996 | 58.7 | 14.007 | 54.94 | 28.09 | 12.01 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Danilov, I.; Hackert-Oschätzchen, M.; Zinecker, M.; Meichsner, G.; Edelmann, J.; Schubert, A. Process Understanding of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing through Multiphysics Simulation and Inline Metrology. Micromachines 2019, 10, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10030214
Danilov I, Hackert-Oschätzchen M, Zinecker M, Meichsner G, Edelmann J, Schubert A. Process Understanding of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing through Multiphysics Simulation and Inline Metrology. Micromachines. 2019; 10(3):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10030214
Chicago/Turabian StyleDanilov, Igor, Matthias Hackert-Oschätzchen, Mike Zinecker, Gunnar Meichsner, Jan Edelmann, and Andreas Schubert. 2019. "Process Understanding of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing through Multiphysics Simulation and Inline Metrology" Micromachines 10, no. 3: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10030214
APA StyleDanilov, I., Hackert-Oschätzchen, M., Zinecker, M., Meichsner, G., Edelmann, J., & Schubert, A. (2019). Process Understanding of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing through Multiphysics Simulation and Inline Metrology. Micromachines, 10(3), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10030214





