DEP-on-a-Chip: Dielectrophoresis Applied to Microfluidic Platforms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Microfluidic Separation Techniques
3. Dielectrophoresis
4. Dielectrophoresis (DEP)-on-a-Chip
4.1. External Electrodes
4.2. Two-Dimensional Electrodes
4.2.1. Parallel and Interdigitated Electrodes
4.2.2. Castellated Electrodes
4.2.3. Other Types of Electrodes
4.3. Three-Dimensional Electrodes
4.3.1. Metal 3D Electrodes
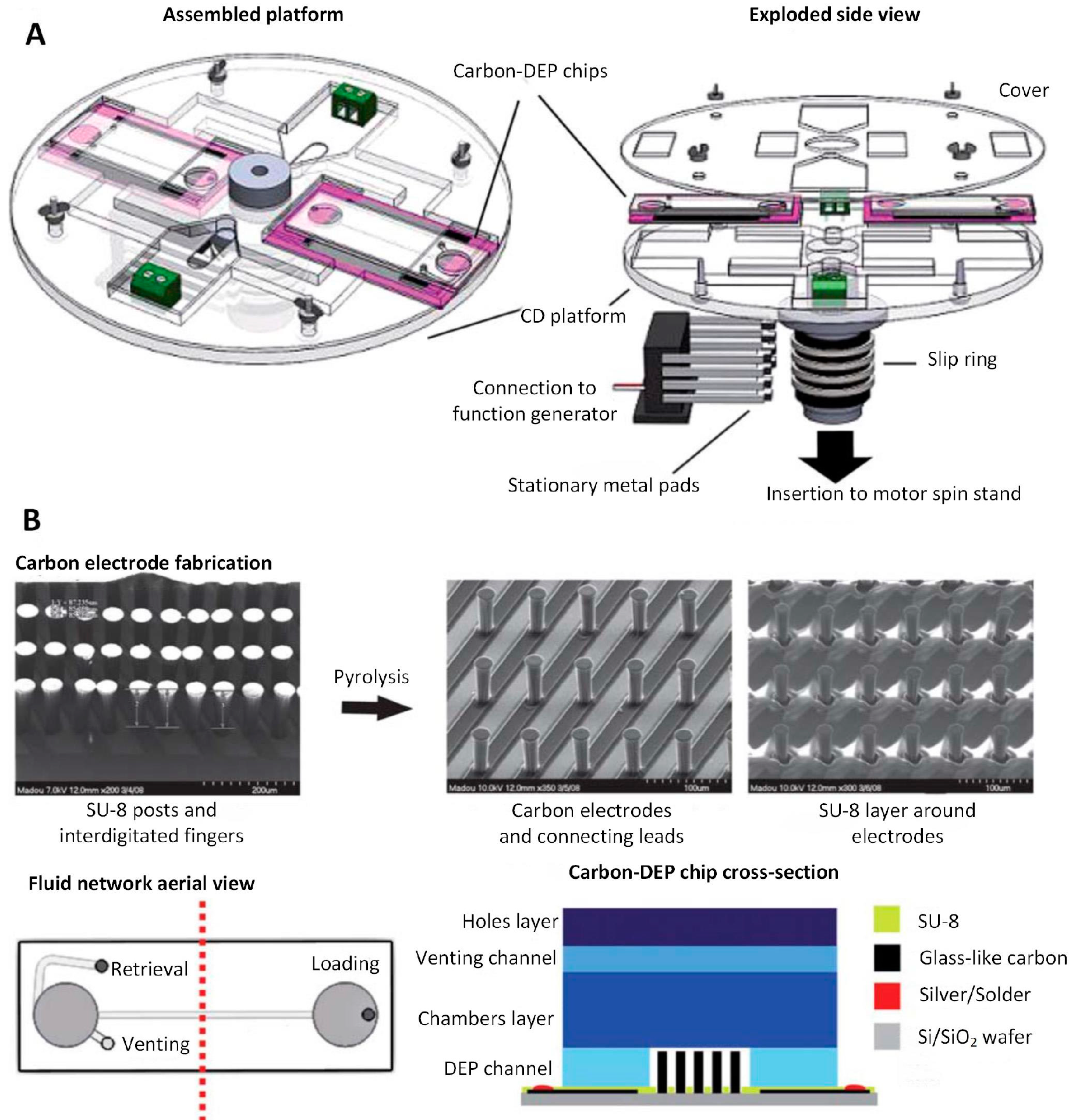
4.3.2. Carbon 3D Electrodes
4.3.3. Polymer 3D Electrodes
4.3.4. Silicon 3D Electrodes
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- West, J.; Becker, M.; Tombrink, S.; Manz, A. Micro total analysis systems: Latest achievements. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4403–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craighead, H. Future lab-on-a-chip technologies for interrogating individual molecules. Nature 2006, 442, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittrich, P.S.; Manz, A. Lab-on-a-chip: Microfluidics in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ali, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Jensen, K.F. Cells on chips. Nature 2006, 442, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenberg, J.; de Rooij, N.F.; Verpoorte, E. Sample pretreatment on microfabricated devices. Talanta 2002, 56, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzacki, S.Z.; Thwar, P.K.; Yang, M.; Ugaz, V.M.; Burns, M.A. Integrated microsystems for controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, G.; Xuan, X. Particle manipulations in non-Newtonian microfluidics: A review. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 500, 182–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roper, M.G.; Easley, C.J.; Landers, J.P. Advances in polymerase chain reaction on microfluidic chips. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3887–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghavi, B.J.; Moore, J.A.; Chavez, J.L.; Hagen, J.A.; Kelley-Loughnane, N.; Chou, C.-F.; Swami, N.S. Aptamer-functionalized nanoparticles for surface immobilization-free electrochemical detection of cortisol in a microfluidic device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salafi, T.; Zeming, K.K.; Zhang, Y. Advancements in microfluidics for nanoparticle separation. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.-G.; Kong, M.-Q.; Zhou, S.; Sheng, Y.-F.; Wang, P.; Yu, T.; Inci, F.; Kuo, W.P.; Li, L.-J.; Demirci, U.; et al. An integrated double-filtration microfluidic device for isolation, enrichment and quantification of urinary extracellular vesicles for detection of bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalili, A.; Samiei, E.; Hoorfar, M. A review of sorting, separation and isolation of cells and microbeads for biomedical applications: Microfluidic approaches. Analyst 2019, 144, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Faqheri, W.; Thio, T.H.G.; Qasaimeh, M.A.; Dietzel, A.; Madou, M. Particle/cell separation on microfluidic platforms based on centrifugation effect: A review. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2017, 21, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazian, M.; Li, W.; Nam-Trung, N. Lab on a chip for continuous-flow magnetic cell separation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Mao, Z.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, P.-H.; Truica, C.I.; Drabick, J.J.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Dao, M.; et al. Acoustic separation of circulating tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4970–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laurell, T.; Petersson, F.; Nilsson, A. Chip integrated strategies for acoustic separation and manipulation of cells and particles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, J.D.; Collins, G.E. Integrated microfluidic device for solid-phase extraction coupled to micellar electrokinetic chromatography separation. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6664–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-L.; Lin, T.-Y.; Fuh, M.-R. Microfluidic chip-based liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry for determination of small molecules in bioanalytical applications: An update. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahore, V.; Kumar, S.; Rogers, C.I.; Jensen, J.K.; Sonker, M.; Woolley, A.T. Pressure-actuated microfluidic devices for electrophoretic separation of pre-term birth biomarkers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlheyer, D.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; van den Berg, A.; Schasfoort, R.B.M. Miniaturizing free-flow electrophoresis—A critical review. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, B.; Li, D. Dielectrophoresis in microfluidics technology. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2410–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, R.E.; Rohani, A.; Farmehini, V.; Swami, N.S. Review: Microbial analysis in dielectrophoretic microfluidic systems. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 966, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abd Rahman, N.; Ibrahim, F.; Yafouz, B. Dielectrophoresis for Biomedical Sciences Applications: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, A.J.; Di Carlo, D. Continuous Scalable Blood Filtration Device Using Inertial Microfluidics. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 107, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Seki, M. Hydrodynamic filtration for on-chip particle concentration and classification utilizing microfluidics. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broyles, B.S.; Jacobson, S.C.; Ramsey, J.M. Sample filtration, concentration, and separation integrated on microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helton, K.L.; Nelson, K.E.; Fu, E.; Yager, P. Conditioning saliva for use in a microfluidic biosensor. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Marukenko, S.A.; Monuki, E.S.; Flanagan, L.A.; Lee, A.P. Dual frequency dielectrophoresis with interdigitated sidewall electrodes for microfluidic flow-through separation of beads and cells. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, M.M.; Jalalian, L.; Ribeiro, S.; Ona, K.; Demirci, U.; Cedars, M.I.; Rosen, M.P. Microfluidic sorting selects sperm for clinical use with reduced DNA damage compared to density gradient centrifugation with swim-up in split semen samples. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeo, J.C.; Kenry; Zhao, Z.; Zhang,, P.; Wang, Z.; Lim, C.T. Label-free extraction of extracellular vesicles using centrifugal microfluidics. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12, 024103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sethu, P. Low-stress Microfluidic Density-gradient Centrifugation for Blood Cell Sorting. Biomed. Microdevices 2018, 20, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feshitan, J.A.; Chen, C.C.; Kwan, J.J.; Borden, M.A. Microbubble size isolation by differential centrifugation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 329, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cui, Y.; Xuan, S.; Gong, X. 3D-printed microfluidic manipulation device integrated with magnetic array. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2018, 22, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, S.; Sun, X.; Feng, Z.; Lei, C.; Zhou, Y. An innovative micro magnetic separator based on 3D micro-copper-coil exciting soft magnetic tips and FeNi wires for bio-target sorting. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2019, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Xu, L.; Ahn, B.; Lee, K.; Oh, K.W. Continuous-flow in-droplet magnetic particle separation in a droplet-based microfluidic platform. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2012, 13, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, U.; Vandevyver, C.; Parashar, V.K.; Gijs, M.A.M. Droplet-based DNA purification in a magnetic lab-on-a-chip. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3062–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, S.B.Q.; Marmottant, P.; Thibault, P. Fast acoustic tweezers for the two-dimensional manipulation of individual particles in microfluidic channels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 114103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baresch, D.; Thomas, J.-L.; Marchiano, R. Observation of a Single-Beam Gradient Force Acoustical Trap for Elastic Particles: Acoustical Tweezers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 024301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Lin, S.-C.S.; Kiraly, B.; Yue, H.; Li, S.; Chiang, I.K.; Shi, J.; Benkovic, S.J.; Huang, T.J. On-chip manipulation of single microparticles, cells, and organisms using surface acoustic waves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11105–11109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Li, P.; Lin, S.-C.S.; Stratton, Z.S.; Nama, N.; Guo, F.; Slotcavage, D.; Mao, X.; Shi, J.; Costanzo, F.; et al. Surface acoustic wave microfluidics. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3626–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstadt, N.; Yager, P.; Hoffman, A.S.; Stayton, P.S. A smart microfluidic affinity chromatography matrix composed of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-coated beads. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 2943–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, D.P.; Blanes, L.; Wilson, A.B.; Wilbanks, T.; Killeen, K.; Grimm, R.; Wenzel, R.; Major, D.; Macka, M.; Clarke, D.; et al. Microfluidic high performance liquid chromatography-chip hyphenation to inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1497, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, I.M.; Trisiripisal, P.; Sarvaiya, H.A. Microfluidic liquid chromatography system for proteomic applications and biomarker screening. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5513–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, S.; De Vos, J.; Dores-Sousa, J.L.; Wouters, B.; Desmet, G.; Eeltink, S. Prototyping of thermoplastic microfluidic chips and their application in high-performance liquid chromatography separations of small molecules. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1523, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redman, E.A.; Mellors, J.S.; Starkey, J.A.; Ramsey, J.M. Characterization of Intact Antibody Drug Conjugate Variants Using Microfluidic Capillary Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2220–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, K.; Klein, J.A.; Haserick, J.R.; Leon, D.R.; Costello, C.E.; McComb, M.E.; Zaia, J. Microfluidic Capillary Electrophoresis Mass Spectrometry for Analysis of Monosaccharides, Oligosaccharides, and Glycopeptides. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6645–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roper, M.G.; Shackman, J.G.; Dahlgren, G.M.; Kennedy, R.T. Microfluidic chip for continuous monitoring of hormone secretion from live cells using an electrophoresis-based immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubery, T.Z.; Srivastava, S.K.; Dutta, P. Dielectrophoretic separation of bioparticles in microdevices: A review. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 691–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viefhues, M.; Eichhorn, R. DNA dielectrophoresis: Theory and applications a review. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 1483–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X. Recent advances in direct current electrokinetic manipulation of particles for microfluidic applications. Electrophoresis 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshmanesh, K.; Nahavandi, S.; Baratchi, S.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-zadeh, K. Dielectrophoretic platforms for bio-microfluidic systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1800–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alazzam, A.; Mathew, B.; Alhammadi, F. Novel microfluidic device for the continuous separation of cancer cells using dielectrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regtmeier, J.; Eichhorn, R.; Viefhues, M.; Bogunovic, L.; Anselmetti, D. Electrodeless dielectrophoresis for bioanalysis: Theory, devices and applications. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2253–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Madadi, H.; Casals-Terre, J.; Sellares, J. Hydrodynamic and direct-current insulator-based dielectrophoresis (H-DC-iDEP) microfluidic blood plasma separation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 4733–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Artemiou, A.; Minerick, A.R. Direct current insulator-based dielectrophoretic characterization of erythrocytes: ABO-Rh human blood typing. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, D. Separation of Janus droplets and oil droplets in microchannels by wall-induced dielectrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1501, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, N.; Darabi, J.; Voglewede, P.; Guo, F.; Bayoumi, A. An analysis of interdigitated electrode geometry for dielectrophoretic particle transport in micro-fluidics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, H.; Hojjat, Y.; Soleimani, M. Interdigitated electrode design and optimization for dielectrophoresis cell separation actuators. J. Electrostat. 2017, 86, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Rosano, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Garson, C.J.; Prabhakarpandian, B.; Pant, K.; Klarmann, G.J.; Perantoni, A.; Alvarez, L.M.; Lai, E. Continuous-flow sorting of stem cells and differentiation products based on dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, X.; Jia, Y.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, H. A Simplified Microfluidic Device for Particle Separation with Two Consecutive Steps: Induced Charge Electro-osmotic Prefocusing and Dielectrophoretic Separation. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9583–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Yobas, L. Dielectrophoretic isolation of cells using 3D microelectrodes featuring castellated blocks. Analyst 2015, 140, 3397–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, T.N.G.; Jiang, A.Y.L.; Vyas, P.D.; Flanagan, L.A. Separation of neural stem cells by whole cell membrane capacitance using dielectrophoresis. Methods 2018, 133, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Lin, X.; Su, Y.; Dong, H.; Wu, J. Screen-printed microfluidic dielectrophoresis chip for cell separation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, S.; Tang, S.-Y.; Tan, S.H.; Guo, J.; Xia, H.; Nam-Trung, N.; Li, W. Tunable particle separation in a hybrid dielectrophoresis (DEP)-inertial microfluidic device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 267, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, L.; Ajami, N.J.; Adachi, J.A.; Gascoynecde, P.R.C.; Petrosino, J.F. Isolation and concentration of bacteria from blood using microfluidic membraneless dialysis and dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Pethig, R. Electrode design for negative dielectrophoresis. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1991, 2, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dalton, C.; Crabtree, H.J.; Nilsson, G.; Kaler, K.V.I.S. Continuous dielectrophoretic cell separation microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Bashir, R. Dielectrophoretic separation and manipulation of live and heat-treated cells of Listeria on microfabricated devices with interdigitated electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 86, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Banada, P.P.; Chatni, M.R.; Lim, K.S.; Bhunia, A.K.; Ladisch, M.; Bashir, R. A multifunctional micro-fluidic system for dielectrophoretic concentration coupled with immuno-capture of low numbers of Listeria monocytogenes. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demierre, N.; Braschler, T.; Muller, R.; Renaud, P. Focusing and continuous separation of cells in a microfluidic device using lateral dielectrophoresis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 132, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerswald, J.; Knapp, H.F. Quantitative assessment of dielectrophoresis as a micro fluidic retention and separation technique for beads and human blood erythrocytes. Microelectron. Eng. 2003, 67, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascoyne, P.R.C.; Vykoukal, J.V. Dielectrophoresis-based sample handling in general-purpose programmable diagnostic instruments. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.-T.; Lin, R.-Z.; Chang, W.-Y.; Chang, H.-Y.; Liu, C.-H. Rapid heterogeneous liver-cell on-chip patterning via the enhanced field-induced dielectrophoresis trap. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Y.; Bessette, P.H.; Qian, J.R.; Meinhart, C.D.; Daugherty, P.S.; Soh, H.T. Marker-specific sorting of rare cells using dielectrophoresis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15757–15761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, U.; Qian, J.; Kenrick, S.A.; Daugherty, P.S.; Soh, H.T. Multitarget Dielectrophoresis Activated Cell Sorter. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8656–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pommer, M.S.; Zhang, Y.; Keerthi, N.; Chen, D.; Thomson, J.A.; Meinhart, C.D.; Soh, H.T. Dielectrophoretic separation of platelets from diluted whole blood in microfluidic channels. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshmanesh, K.; Zhang, C.; Tovar-Lopez, F.J.; Nahavandi, S.; Baratchi, S.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Mitchell, A. Dielectrophoretic manipulation and separation of microparticles using curved microelectrodes. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3707–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Park, J.K. Microfluidic system for dielectrophoretic separation based on a trapezoidal electrode array. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, T.P.; Issadore, D.; Westervelt, R.M. Integrated circuit/microfluidic chip to programmably trap and move cells and droplets with dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, B.; Ozer, M.B.; Cagatay, E.; Buyukkocak, S. An integrated acoustic and dielectrophoretic particle manipulation in a microfluidic device for particle wash and separation fabricated by mechanical machining. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 014112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Duarte, R.; Camacho-Alanis, F.; Renaud, P.; Ros, A. Dielectrophoresis of lambda-DNA using 3D carbon electrodes. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.; Yu, L.; Tay, F.E.H.; Chen, B. Bidirectional field-flow particle separation method in a dielectrophoretic chip with 3D electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.; Tresset, G.; Xu, G. Dielectrophoretic field-flow method for separating particle populations in a chip with asymmetric electrodes. Biomicrofluidics 2009, 3, 044104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Iliescu, C.; Xu, G.; Tay, F.E.H. Sequential field-flow cell separation method in a dielectrophoretic chip with 3-D electrodes. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2007, 16, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Iliescu, C.; Xu, G.L.; Samper, V.; Tay, F.E.H. Fabrication of a dielectrophoretic chip with 3D silicon electrodes. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.; Tresset, G.; Xu, G. Continuous field-flow separation of particle populations in a dielectrophoretic chip with three dimensional electrodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 234104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.; Yu, L.; Xu, G.; Tay, F.E.H. A dielectrophoretic chip with a 3-D electric field gradient. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali, S.; Cetin, B.; Oliaei, S.N.B.; Karpat, Y. Fabrication of continuous flow microfluidics device with 3D electrode structures for high throughput DEP applications using mechanical machining. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, H. Continuous dielectrophoretic particle separation using a microfluidic device with 3D electrodes and vaulted obstacles. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, W. Dielectrophoretic separation of microalgae cells in ballast water in a microfluidic chip. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Duarte, R.; Gorkin, R.A., III; Abi-Samra, K.; Madou, M.J. The integration of 3D carbon-electrode dielectrophoresis on a CD-like centrifugal microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Chang, H.; Neuzil, P. DEP-on-a-Chip: Dielectrophoresis Applied to Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines 2019, 10, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060423
Zhang H, Chang H, Neuzil P. DEP-on-a-Chip: Dielectrophoresis Applied to Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines. 2019; 10(6):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060423
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haoqing, Honglong Chang, and Pavel Neuzil. 2019. "DEP-on-a-Chip: Dielectrophoresis Applied to Microfluidic Platforms" Micromachines 10, no. 6: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060423
APA StyleZhang, H., Chang, H., & Neuzil, P. (2019). DEP-on-a-Chip: Dielectrophoresis Applied to Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines, 10(6), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060423





