A Complete Protocol for Rapid and Low-Cost Fabrication of Polymer Microfluidic Chips Containing Three-Dimensional Microstructures Used in Point-of-Care Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fabrication Protocol
2.1. Design the Shim and Simulate the Milling Tools
2.1.1. Software
2.1.2. Design the Shim
2.1.3. Simulation the Milling Tool
2.2. Micro-Milling the Shim
2.2.1. Preparation
- The Al-plates were immobilized on a flat, smooth surface by applying a layer of double-sided tape (Figure 3a,g).
- Black Decker Duosand (Black Decker, Baltimore, MD, USA) with 800 grit wet and dry sandpaper (P800) was used for 15 minutes at maximal speed (Figure 3b,c).
- Autosol ALUMINUM polishing paste was applied to the aluminum sheet surface and a polishing sponge was attached to the Bosch GEX 125-1 AE machine (Bosch, Gerlingen, Germany), which was then run for 15 min at maximal speed (Figure 3d,e).
- The polishing paste residue was wiped off the aluminum surface with ethanol using cleanroom wipes, and then with cool water to observe a mirror finish (Figure 3h).
- The thickness of the aluminum sheet was measured using an Electronic IP54 Outside Micrometer (Figure 3f).
2.2.2. Milling Steps
- Place a sacrificial layer (PMMA 3 mm thick) at the bottom of the aluminum sheet to protect the milling stage and the milling tip.
- Determine the reference point, which is the centre (x = 0, y =0) of the aluminum sheet.
- Adjust the milling Z-stage position.
- Apply the milling oil.
- Start the milling.
- Change the milling tool.
2.2.3. On-the-Fly Polishing Steps
- Remove the aluminum debris from the surface using a vacuum cleaner, followed by water and a cleanroom paper, until the surface is completely clean. If the surface is not clean, the debris will cause scratches to the surface during polishing.
- Apply the Autosol polishing paste.
- Hand polish the surface of the reaction-chambers (which are formed after bulk-milling) by using a cleanroom wiper (Figure 4e).
- Redo the milling with the polishing paste still on the surface, to simultaneously polish the microarrays.
2.2.4. Cleaning and Finishing
2.3. Polymer Injection Moulding
2.3.1. Alignment Marks
2.3.2. Injection Moulding Parameters and Conditions
3. Application in Pathogen Detection
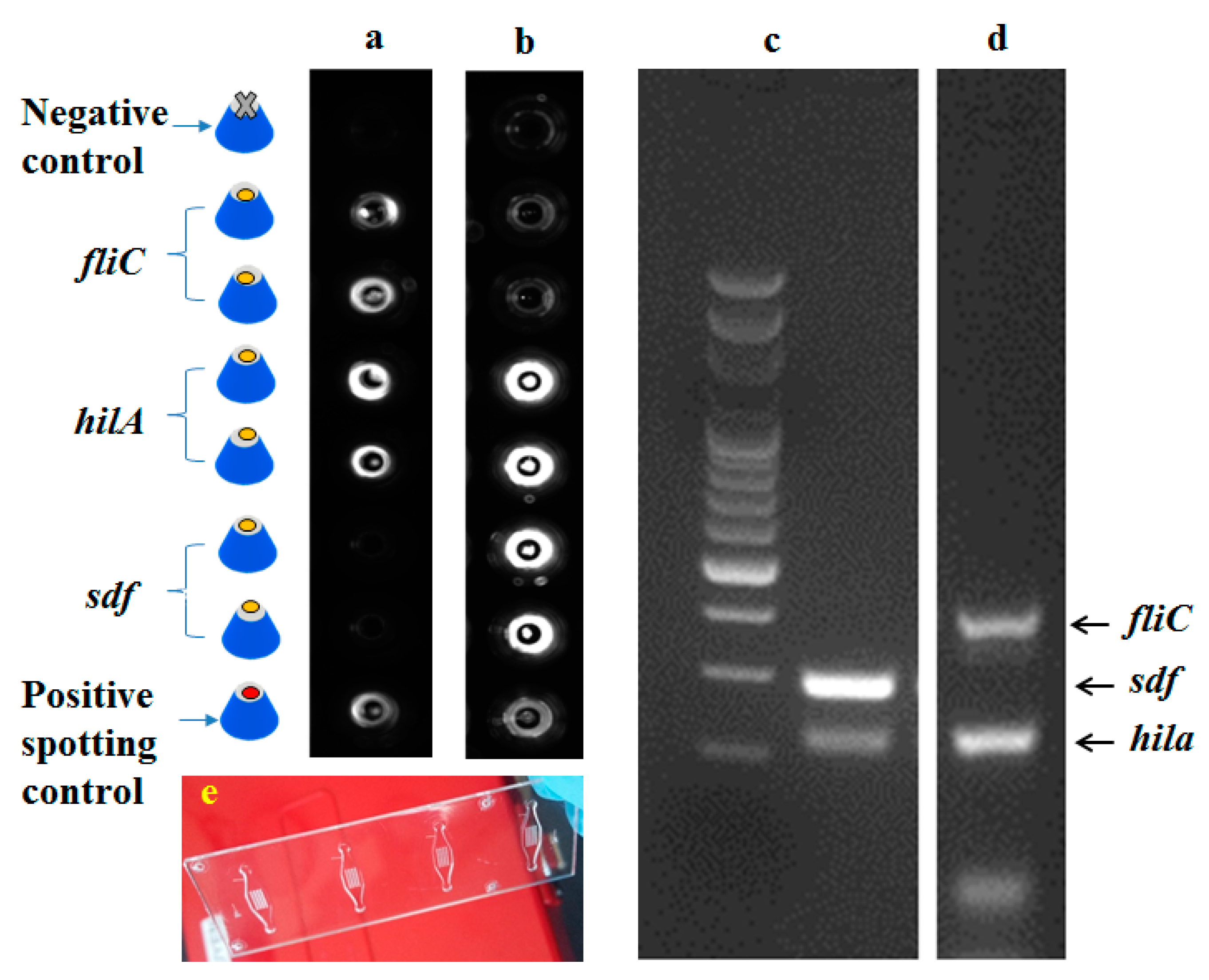
3.1. Detection of Salmonella Subtypes with SP-PCR
3.2. Detection of Salmonella by SP-PCR on SAF Structures
3.3. Discussion on the Possible Point-of-Care Device Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooper, R.M.; Leslie, D.C.; Domansky, K.; Jain, A.; Yung, C.; Cho, M.; Workman, S.; Super, M.; Ingber, D.E. A Microdevice for Rapid Optical Detection of Magnetically Captured Rare Blood Pathogens. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Linh, Q.T.; Hung, T.Q.; Chin, W.H.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D.; Quyen, T.L.; Hung, T.Q.; Chin, W.H.; Wolff, A.; et al. A Lab-on-a-Chip System with Integrated Sample Preparation and Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Rapid and Quantitative Detection of Salmonella Spp. in Food Samples. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neethirajan, S.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M.; Wu, D.; Nandagopal, S.; Lin, F. Microfluidics for Food, Agriculture and Biosystems Industries. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Baldo, M.A.; Messina, G.A.; Sanz, M.I.; Raba, J. Microfluidic Immunosensor with Micromagnetic Beads Coupled to Carbon-Based Screen-Printed Electrodes (SPCEs) for Determination of Botrytis Cinerea in Tissue of Fruits. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2010, 58, 11201–11206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasseri, B.; Soleimani, N.; Rabiee, N.; Kalbasi, A.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Point-of-Care Microfluidic Devices for Pathogen Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmler, M.; Sauer, U.; Schleicher, E.; Preininger, C.; Brandenburg, A. Biochip Point-of-Care Device for Sepsis Diagnostics. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 192, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Bi, H.; Liu, B.; Qiao, L. Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms by Microfluidics Based Analytical Methods. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5512–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourlousse, D.M.; Ahmad, F.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Seyrig, G.; Tiedje, J.M.; Hashsham, S.A. A Polymer Microfluidic Chip for Quantitative Detection of Multiple Water- and Foodborne Pathogens Using Real-Time Fluorogenic Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utko, P.; Persson, F.; Kristensen, A.; Larsen, N.B. Injection Molded Nanofluidic Chips: Fabrication Method and Functional Tests Using Single-Molecule DNA Experiments. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, R.; Pedersen, J.N.; Mir, K.U.; Bilenberg, B.; Kristensen, A. Concentrating and Labeling Genomic DNA in a Nanofluidic Array. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, K.; Ngo, T.A.; Matteucci, M.; Wolff, A. Fabrication of 3D Microstructure Array on Chip for Rapid Pathogen Detection. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 281, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.Q.; Sun, Y.; Poulsen, C.E.; Linh-Quyen, T.; Chin, W.H.; Bang, D.D.; Wolff, A. Miniaturization of a Micro-Optics Array for Highly Sensitive and Parallel Detection on an Injection Moulded Lab-on-a-Chip. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodship, V. Troubleshooting Injection Moulding; iSmithers Rapra Publishing: Shawbury, England, 2004; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, T.Q.; Chin, W.H.; Sun, Y.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. A Novel Lab-on-Chip Platform with Integrated Solid Phase PCR and Supercritical Angle Fluorescence (SAF) Microlens Array for Highly Sensitive and Multiplexed Pathogen Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Zoëga Andreasen, S.; Wolff, A.; Duong Bang, D. From Lab on a Chip to Point of Care Devices: The Role of Open Source Microcontrollers. Micromachines 2018, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perfetto, J.; Ho, J. OPENPCR. Available online: http://openpcr.org (accessed on 19 September 2019).
- Lim, G.S.; Chang, J.S.; Lei, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, K.; Wong, S. A Lab-on-a-Chip System Integrating Tissue Sample Preparation and Multiplex RT-QPCR for Gene Expression Analysis in Point-of-Care Hepatotoxicity Assessment. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4032–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Species | Target Gene | PCR Primers’ Sequences (5’–3’) |
|---|---|---|
| Salmonella spp. | hilA | hilA-F: GCG ACG CGG AAG TTA ACG AAG A |
| hilA–R: Cy3-CAC GAT AGA GTA ATG CAG ACT CTC GGA TTG AAC CTG ATC | ||
| hilA-solid phase surface probe: TTT TTT TTT TCC CCC CCC CCA AGA GCA TCG TTA | ||
| CAT TGA AAC ACT GTA CGG ACA GGG CTA TCG GTT TAA TCG TCC GGT CG | ||
| S. Enteritidis | sdf | sdf-F: AAA TGT GTT TTA TCT GAT GCA AGA GG |
| sdf-R: Cy3-TCT AAT GAA CTA CGT TCG TTC TTC TGG TAC TTA CGA TGA C | ||
| sdf-solid phase surface probe: TTT TTT TTT TCC CCC CCC CCA TCA AAA AGG TTT AGT AAA TCA GCC TGT TGT CTG CTC ACC ATT CGC CAG CCA CCA CCT TC | ||
| S. Typhimurium | fliC | fliC-F: CCC CGC TTA CAG GTG GAC TAC |
| fliC-R: Cy3-CTG CAG CGG GTT TTC GGT GGT TGT | ||
| fliC-solid phase surface probe : TTT TTT TTT TCC CCC CCC CCA CTT ACG CTG CAA GTA AAG CCG AAG GTC ACA ACT TTA AAG CAC AGC CTG ATC TGG CGG AA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.; Chidambara Vinayaka, A.; Duong Bang, D.; Wolff, A. A Complete Protocol for Rapid and Low-Cost Fabrication of Polymer Microfluidic Chips Containing Three-Dimensional Microstructures Used in Point-of-Care Devices. Micromachines 2019, 10, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10090624
Nguyen T, Chidambara Vinayaka A, Duong Bang D, Wolff A. A Complete Protocol for Rapid and Low-Cost Fabrication of Polymer Microfluidic Chips Containing Three-Dimensional Microstructures Used in Point-of-Care Devices. Micromachines. 2019; 10(9):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10090624
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Trieu, Aaydha Chidambara Vinayaka, Dang Duong Bang, and Anders Wolff. 2019. "A Complete Protocol for Rapid and Low-Cost Fabrication of Polymer Microfluidic Chips Containing Three-Dimensional Microstructures Used in Point-of-Care Devices" Micromachines 10, no. 9: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10090624
APA StyleNguyen, T., Chidambara Vinayaka, A., Duong Bang, D., & Wolff, A. (2019). A Complete Protocol for Rapid and Low-Cost Fabrication of Polymer Microfluidic Chips Containing Three-Dimensional Microstructures Used in Point-of-Care Devices. Micromachines, 10(9), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10090624






