A New 3D Cultured Liver Chip and Real-Time Monitoring System Based on Microfluidic Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Cells
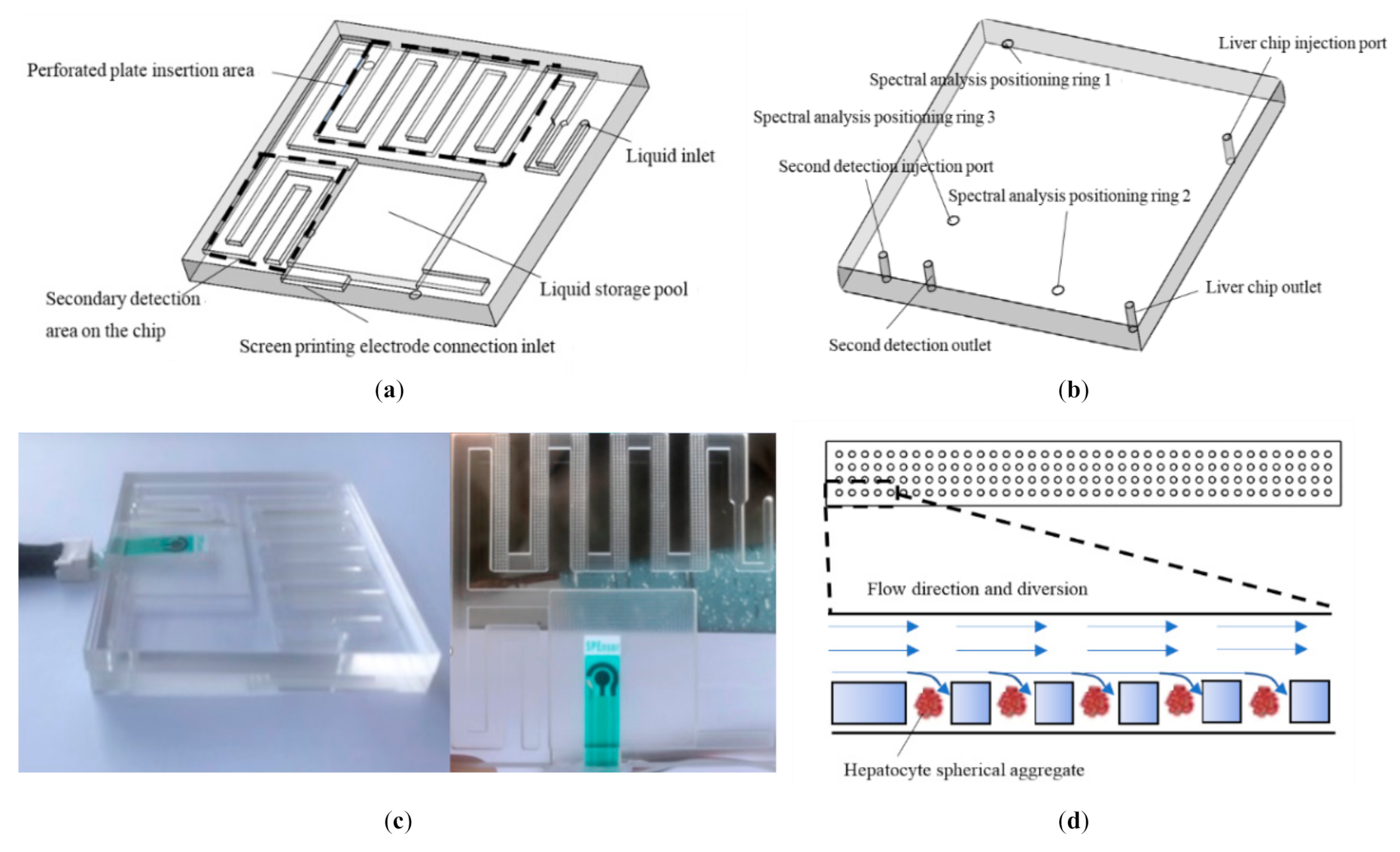
2.2. Development of Liver Chip Based on Microfluidic Technology
2.3. Establishment of Liver Chip Monitoring System
2.4. Experimental Method Based on Liver Chip Monitoring System
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results and Analysis of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.2. Results and Analysis of Near Infrared Spectroscopy
3.3. Results and Analysis of Paracetamol Metabolism
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mani, D.; Kaushik, A.; Husain, A.; Awasthi, H.; Singh, D.P.; Khan, R. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective potential of Swaras and Hima extracts of Tinospora cordifolia and Boerhavia diffusa in Swiss albino mice. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 5658–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.T.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, W.C.; Shieh, P.C.; Chung, M.I.; Huang, G.J.; Romero, F.J. Salvianolic Acid C against Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Attenuating Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis through Inhibition of the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, P.P.; Fan, L.X.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.J.; Li, L.J. Therapeutic potential of menstrual blood stem cells in treating acute liver failure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6190–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Peng, Y.; Chongwu, R.; Pengfei, R.; Zheng, M.; Lin, Z.; Wenliang, Z.; Changjie, J. Pharmacoeconomics of three Therapeutic Schemes for Anti-tuberculosis Therapy Induced Liver Injury in China. Open Med. 2018, 13, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamm, R.; Bashir, R.; Arora, N.; Dar, R.D.; Gillette, M.U.; Griffith, L.G.; Kemp, M.L.; Kinlaw, K.; Levin, M.; Martin, A.C.; et al. Perspective: The promise of multi-cellular engineered living systems. APL Bioeng. 2018, 2, 040901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iti, C.; Mohd, Y.; Madhu, V.; Pratap, S.A. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Groundbreaking Approach for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Pi, Q.; Gong, Z.; Yang, X.; Mak, M.; Wu, Y. Indoor nanoscale particulate matter-induced coagulation abnormality based on a human 3D microvascular model on a microfluidic chip. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stucki, J.D.; Hobi, N.; Galimov, A.; Stucki, A.O.; Schneider-Daum, N.; Lehr, C.-M.; Huwer, H.; Frick, M.; Funke-Chambour, M.; Geiser, T.; et al. Medium throughput breathing human primary cell alveolus-on-chip model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Low, L.A.; Mummery, C.; Berridge, B.R.; Austin, C.P.; Tagle, D.A. Organs-on-chips: Into the next decade. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyett, B.P.; Yu, H.; Strachan, J.; Drummond, C.J.; Conn, C.E. Fusion dynamics of cubosome nanocarriers with model cell membranes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, C.-H.D.; Tanaka, J.; Kaneko, M.; Horade, M.; Ito, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Ohtani, T.; Sakata, Y.; Oh, K.W. An On-Chip RBC Deformability Checker Significantly Improves Velocity-Deformation Correlation. Micromachines 2016, 7, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M. A living system on a chip. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 471, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, G.; Alicia, R.; Alexander, T.; Anna-Klara, A.; Noichl, B.P.; Roland, L.; Lutz, K. Bioprinting Perfusion-Enabled Liver Equivalents for Advanced Organ-on-a-Chip Applications. Genes 2018, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shao, C.; Bian, F.; Zhao, Y. Biomimetic enzyme cascade reaction system in microfluidic electrospray microcapsules. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Deng, R.; Tong, W.H.; Huan, L.; Way, N.C.; Islambadhan, A.; Iliescu, C.; Yu, H. A perfusion incubator liver chip for 3D cell culture with application on chronic hepatotoxicity testing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yosuke, N.; Hiroshi, K.; Yasuyuki, S.; Teruo, F. Bile canaliculi formation by aligning rat primary hepatocytes in a microfluidic device. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 022212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.T.; Lin, R.Z.; Chang, W.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Liu, C.H. Rapid heterogeneous liver-cell on-chip patterning via the enhanced field-induced dielectrophoresis trap. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, W.; Lin, B. A liver-chip-based alcoholic liver disease model featuring multi-non-parenchymal cells. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chae, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Han, W.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, D.W. Cell-printed 3D liver-on-a-chip possessing a liver microenvironment and biliary system. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danny, B.; Sebastian, P.; Elishai, E.; Gahl, L.; Merav, C.; Mathieu, V.; Jan, V.; Magnus, J.; Yaakov, N. Real-time monitoring of metabolic function in liver-on-chip microdevices tracks the dynamics of mitochondrial dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2231–E2240. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Aleman, J.; Shin, S.R.; Kilic, T.; Kim, D.; Shaegh, S.a.M.; Massa, S.; Riahi, R.; Chae, S.; Hu, N.; et al. Multisensor-integrated organs-on-chips platform for automated and continual in situ monitoring of organoid behaviors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2293–E2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, X.G.; Guan, Y.X.; Wang, F.R.; Fang, Z.L. Fabrication of poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) microfluidic chips by a simple hot embossing method. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. Ed. 2003, 24, 1962–1966. [Google Scholar]
- Bhise, N.S.; Manoharan, V.; Massa, S.; Tamayol, A.; Ghaderi, M.; Miscuglio, M.; Lang, Q.; Zhang, Y.S.; Shin, S.R.; Calzone, G.; et al. A liver-on-a-chip platform with bioprinted hepatic spheroids. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; Xie, L.; Shu, F.; Shi, Q.; Shaheen, N. A New 3D Cultured Liver Chip and Real-Time Monitoring System Based on Microfluidic Technology. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11121118
Zhang Y, Yang N, Xie L, Shu F, Shi Q, Shaheen N. A New 3D Cultured Liver Chip and Real-Time Monitoring System Based on Microfluidic Technology. Micromachines. 2020; 11(12):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11121118
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yao, Ning Yang, Liangliang Xie, Fangyu Shu, Qian Shi, and Naila Shaheen. 2020. "A New 3D Cultured Liver Chip and Real-Time Monitoring System Based on Microfluidic Technology" Micromachines 11, no. 12: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11121118
APA StyleZhang, Y., Yang, N., Xie, L., Shu, F., Shi, Q., & Shaheen, N. (2020). A New 3D Cultured Liver Chip and Real-Time Monitoring System Based on Microfluidic Technology. Micromachines, 11(12), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11121118




