Evaluation of Performance and Tunability of a Co-Flow Inertial Microfluidic Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Microfabrication
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Flow Experiments
2.4. Cell Culture
3. Results and Discussion
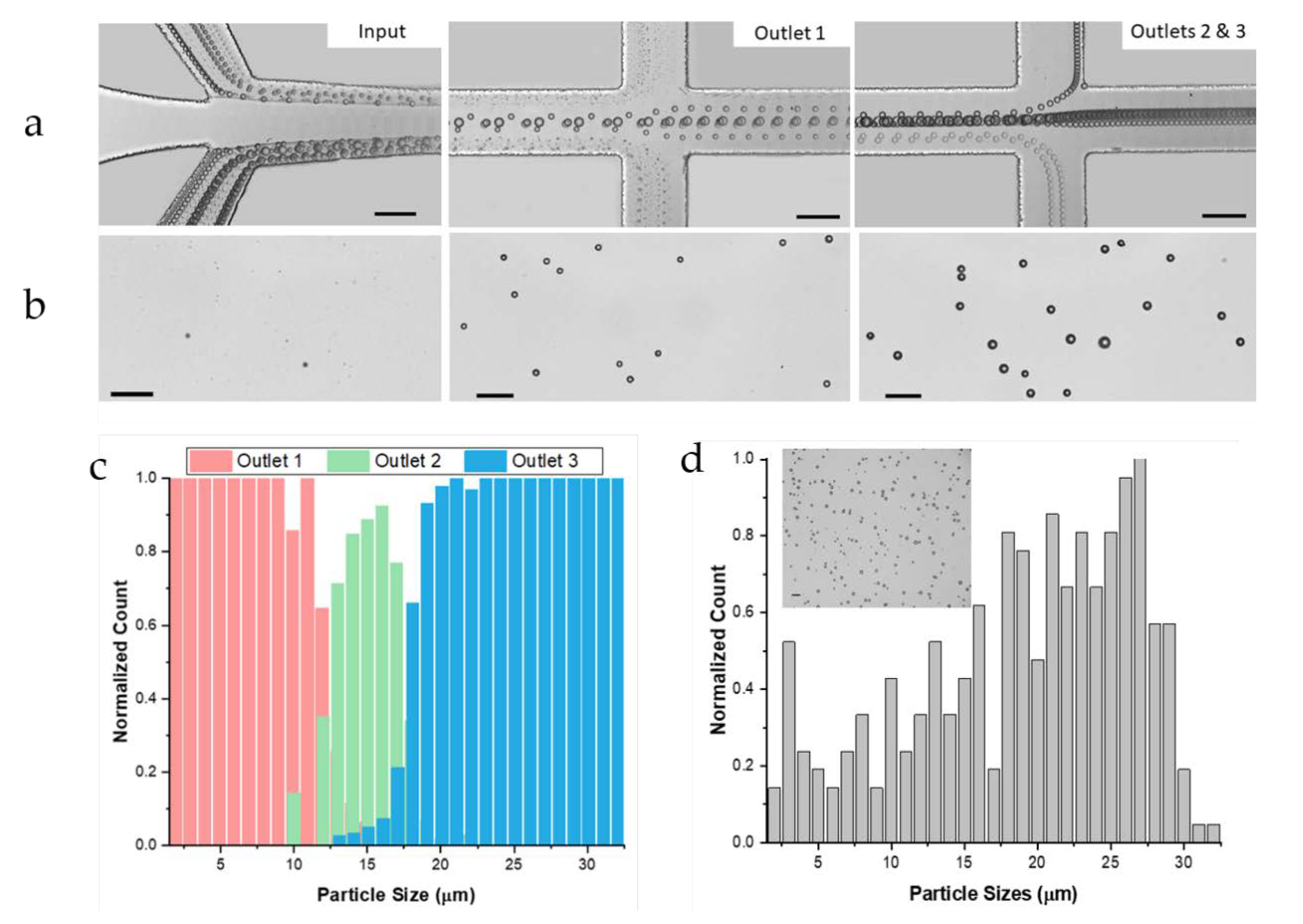
3.1. Inertial Focusing and Hydrodynamic Separation
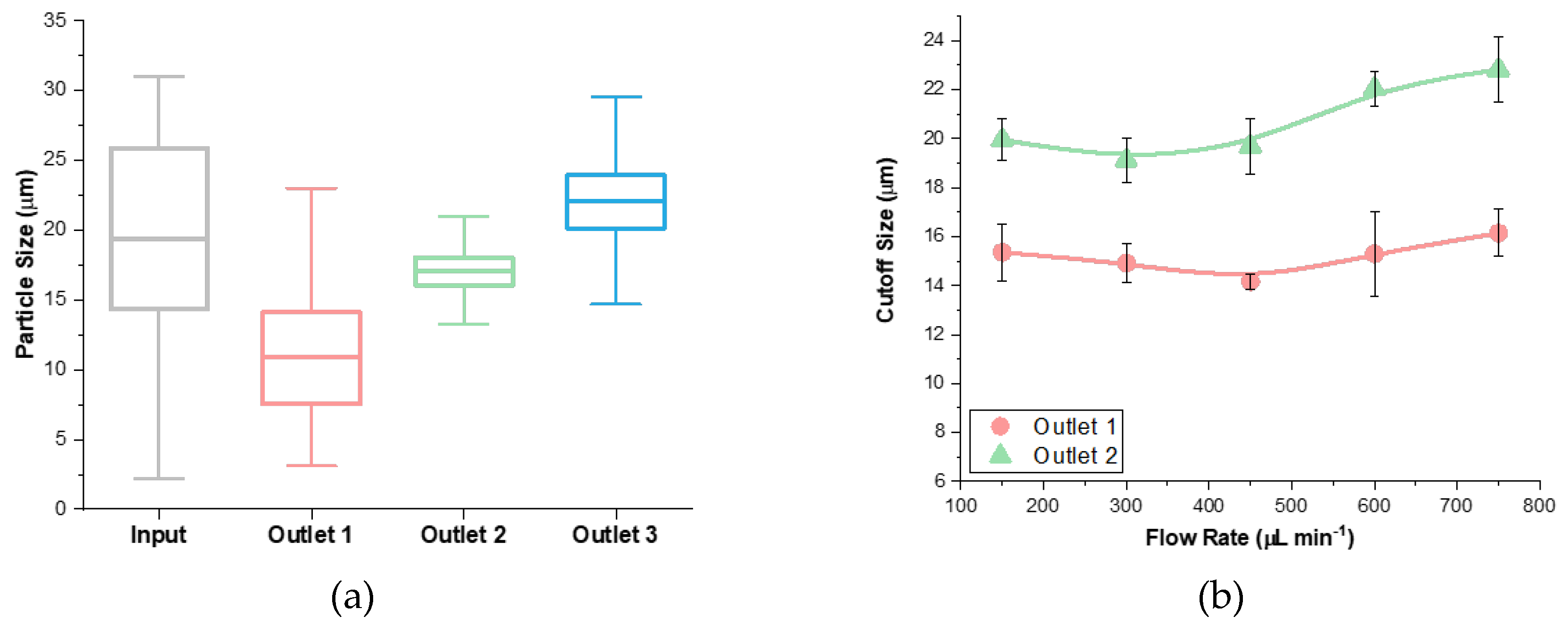
3.2. Analysis of Flow Rate
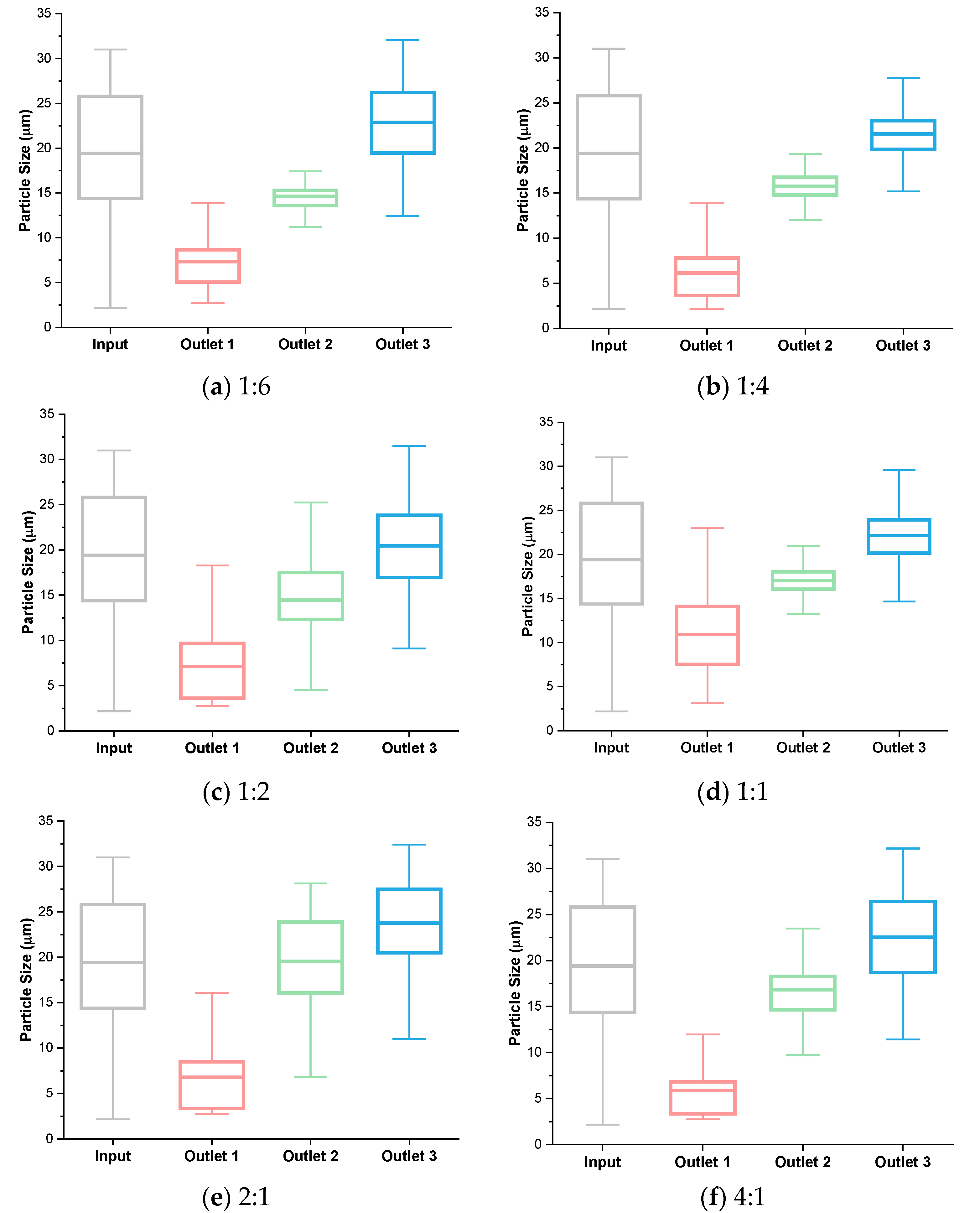
3.3. Analysis of Flow Rate Ratio
3.4. Analysis of Resistance Ratio
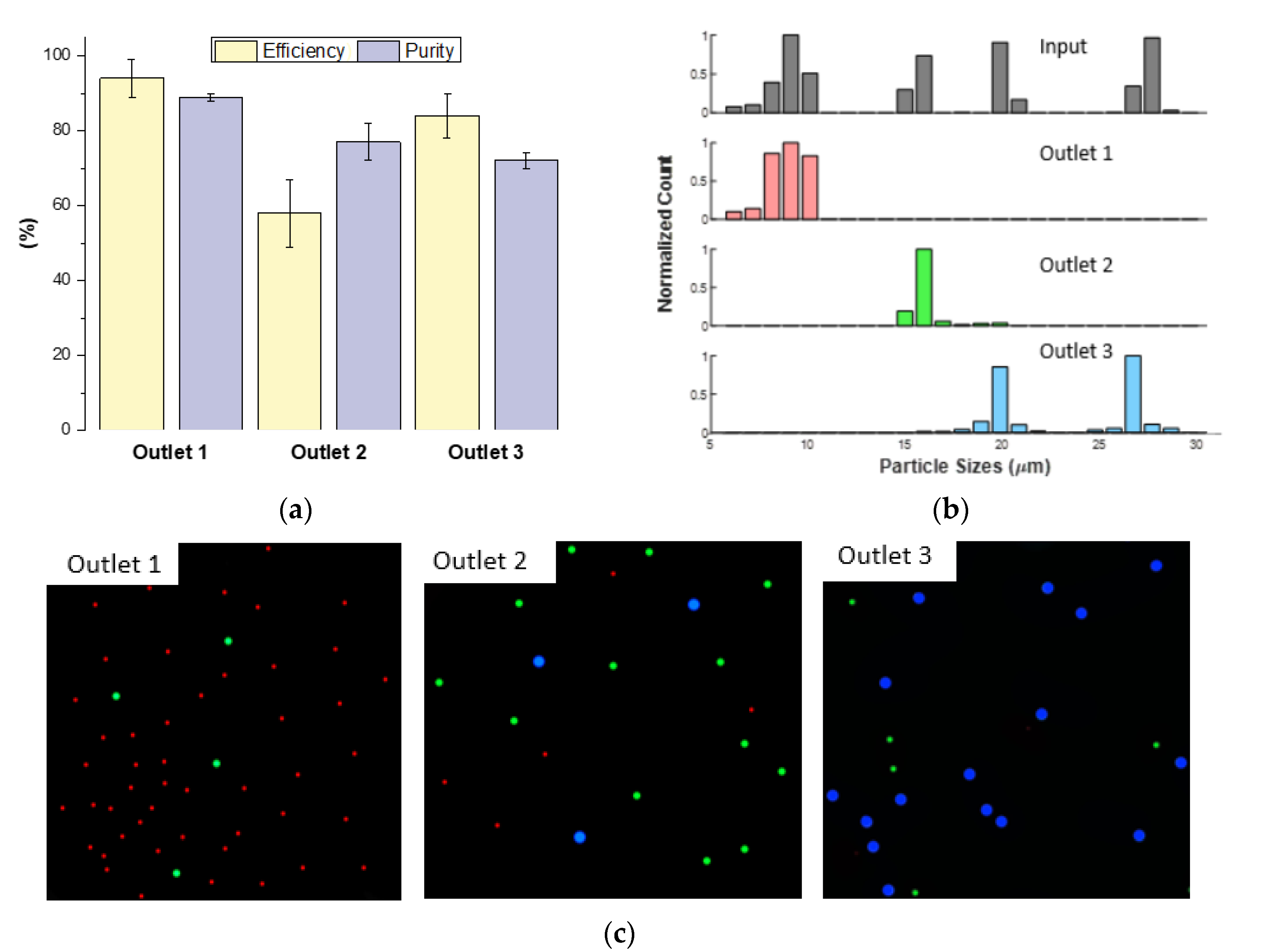
3.5. Separation of a Complex Particle Mixture
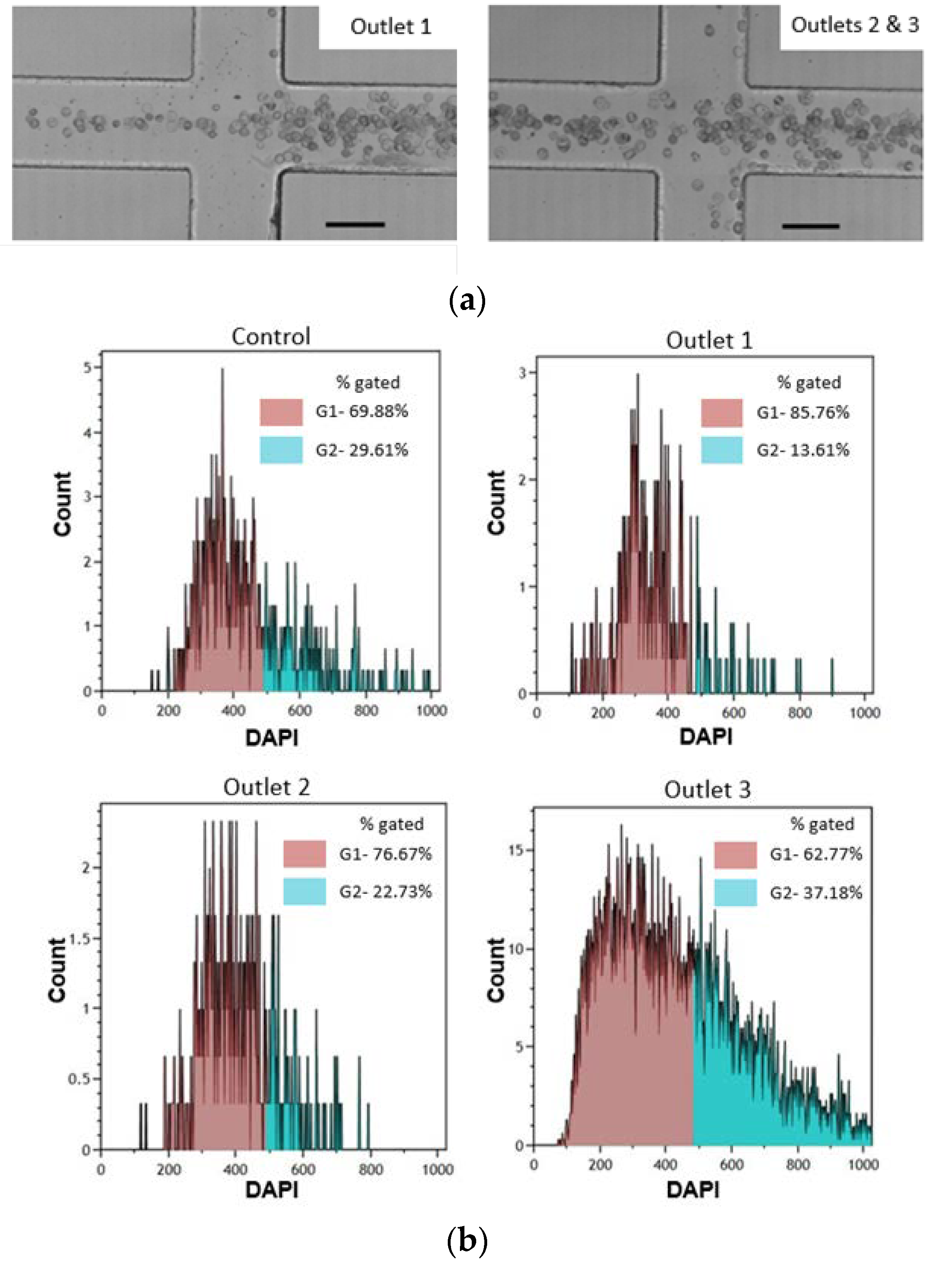
3.6. Application to Cell Cycle Synchronization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Shields, C.W., IV; Reyes, C.D.; López, G.P. Microfluidic cell sorting: A review of the advances in the separation of cells from debulking to rare cell isolation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1230–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.-T.; Hejazian, M.; Ooi, C.; Kashaninejad, N. Recent advances and future perspectives on microfluidic liquid handling. Micromachines 2017, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Mukherjee, P.; Gao, H.; Luan, Q.; Papautsky, I. Label-Free microfluidic sorting of microparticles. APL Bioeng. 2019, 3, 041504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.R. Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 2004, 304, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, J.; Jimenez, M.; Bridle, H. Deterministic lateral displacement for particle separation: A review. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4139–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, M.; Nakashima, M.; Seki, M. Pinched flow fractionation: Continuous size separation of particles utilizing a laminar flow profile in a pinched microchannel. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5465–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, A.A.S.; Hou, H.W.; Li, L.D.; Lim, C.T.; Han, J. Pinched flow coupled shear-modulated inertial microfluidics for high-throughput rare blood cell separation. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Seki, M. Hydrodynamic filtration for on-chip particle concentration and classification utilizing microfluidics. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamme, N. Continuous flow separations in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Zhou, J.; Liang, Y.; Huang, B.; Fang, Y.; Liang, X.; Ye, X. A flexible cell concentrator using inertial focusing. Biomed. Microdevices 2017, 19, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Guan, G.; Luan, K.B.; Lee, W.C.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Kant Chaudhuri, P.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lim, W.T.; Lee, S.C.; Chen, P.C.Y.; et al. Slanted spiral microfluidics for the ultra-fast, label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nivedita, N.; Papautsky, I. Continuous separation of blood cells in spiral microfluidic devices. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 054101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Carlo, D. Inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, H.; Lee, W.; Di Carlo, D. Inertial microfluidic physics. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, J.M.; Toner, M. Inertial focusing in microfluidics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 16, 371–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Yuan, D.; Alici, G.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Ebrahimi Warkiani, M.; Li, W. Fundamentals and applications of inertial microfluidics: A review. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 10–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Wu, L.; Tay, A.K.P.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Ultra-Fast, label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood using spiral microfluidics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojah, R.; Stoutamore, R.; Di Carlo, D. Size-Tunable microvortex capture of rare cells. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2542–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Willing, B.; Bjerketorp, J.; Jansson, J.K.; Hjort, K. Soft inertial microfluidics for high throughput separation of bacteria from human blood cells. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Kulasinghe, A.; Bogseth, A.; O’Byrne, K.; Punyadeera, C.; Papautsky, I. Isolation of circulating tumor cells in non-small-cell-lung-cancer patients using a multi-flow microfluidic channel. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, A.; Hou, H.W.; Mahan, A.E.; Han, J.; Alter, G. Multiplexed affinity-based separation of proteins and cells using inertial microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Shin, J.H.; Bae, C.Y.; Choi, S.; Park, J.-K. Label-Free cancer cell separation from human whole blood using inertial microfluidics at low shear stress. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6213–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zandi, M.; Ho, C.-C.; Kaval, N.; Papautsky, I. Single stream inertial focusing in a straight microchannel. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Papautsky, I. Single stream inertial focusing in low aspect-ratio triangular microchannels. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Wu, L.; Bhagat, A.A.; Li, Z.; Chen, P.C.Y.; Chao, S.; Ong, C.J.; Han, J. Spiral microchannel with rectangular and trapezoidal cross-sections for size based particle separation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhagat, A.A.S.; Kuntaegowdanahalli, S.S.; Papautsky, I. Continuous particle separation in spiral microchannels using dean flows and differential migration. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.-L.; Yan, Q.; Zhe, J.; Zhao, L. Single particle train ordering in microchannel based on inertial and vortex effects. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 065011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, U.; Jaber, S.; Trabzon, L. Super-Enhanced particle focusing in a novel microchannel geometry using inertial microfluidics. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, A.J.; Di Carlo, D. Continuous scalable blood filtration device using inertial microfluidics. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 107, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Papautsky, I. Size-Based microfluidic multimodal microparticle sorter. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Nebuloni, F.; Gao, H.; Zhou, J.; Papautsky, I. Rapid prototyping of soft lithography masters for microfluidic devices using dry film photoresist in a non-cleanroom setting. Micromachines 2019, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Papautsky, I. Fundamentals of inertial focusing in microchannels. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nivedita, N.; Garg, N.; Lee, A.P.; Papautsky, I. A high throughput microfluidic platform for size-selective enrichment of cell populations in tissue and blood samples. Analyst 2017, 142, 2558–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Wu, C.; Nam, S.; Di Carlo, D.; Lee, W. Inertial focusing in non-rectangular cross-section microchannels and manipulation of accessible focusing positions. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reece, A.E.; Oakey, J. Long-Range forces affecting equilibrium inertial focusing behavior in straight high aspect ratio microfluidic channels. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 043303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Papautsky, I. An integrated inertial microfluidic vortex sorter for tunable sorting and purification of cells. Technology 2016, 4, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Leong, S.; Lei, A.; Sohn, L.L. High-Throughput Microfluidic Device for Rare Cell Isolation. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng 2015, 9518, 95180E. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.C.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Huang, S.; Van Vliet, K.J.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. High-Throughput cell cycle synchronization using inertial forces in spiral microchannels. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.K.; Ho, A.; Dowdy, S.F. Biological methods for cell-cycle synchronization of mammalian cells. BioTechniques 2001, 30, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bogseth, A.; Zhou, J.; Papautsky, I. Evaluation of Performance and Tunability of a Co-Flow Inertial Microfluidic Device. Micromachines 2020, 11, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030287
Bogseth A, Zhou J, Papautsky I. Evaluation of Performance and Tunability of a Co-Flow Inertial Microfluidic Device. Micromachines. 2020; 11(3):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030287
Chicago/Turabian StyleBogseth, Amanda, Jian Zhou, and Ian Papautsky. 2020. "Evaluation of Performance and Tunability of a Co-Flow Inertial Microfluidic Device" Micromachines 11, no. 3: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030287
APA StyleBogseth, A., Zhou, J., & Papautsky, I. (2020). Evaluation of Performance and Tunability of a Co-Flow Inertial Microfluidic Device. Micromachines, 11(3), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030287





