Development of a Disposable Single-Nozzle Printhead for 3D Bioprinting of Continuous Multi-Material Constructs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
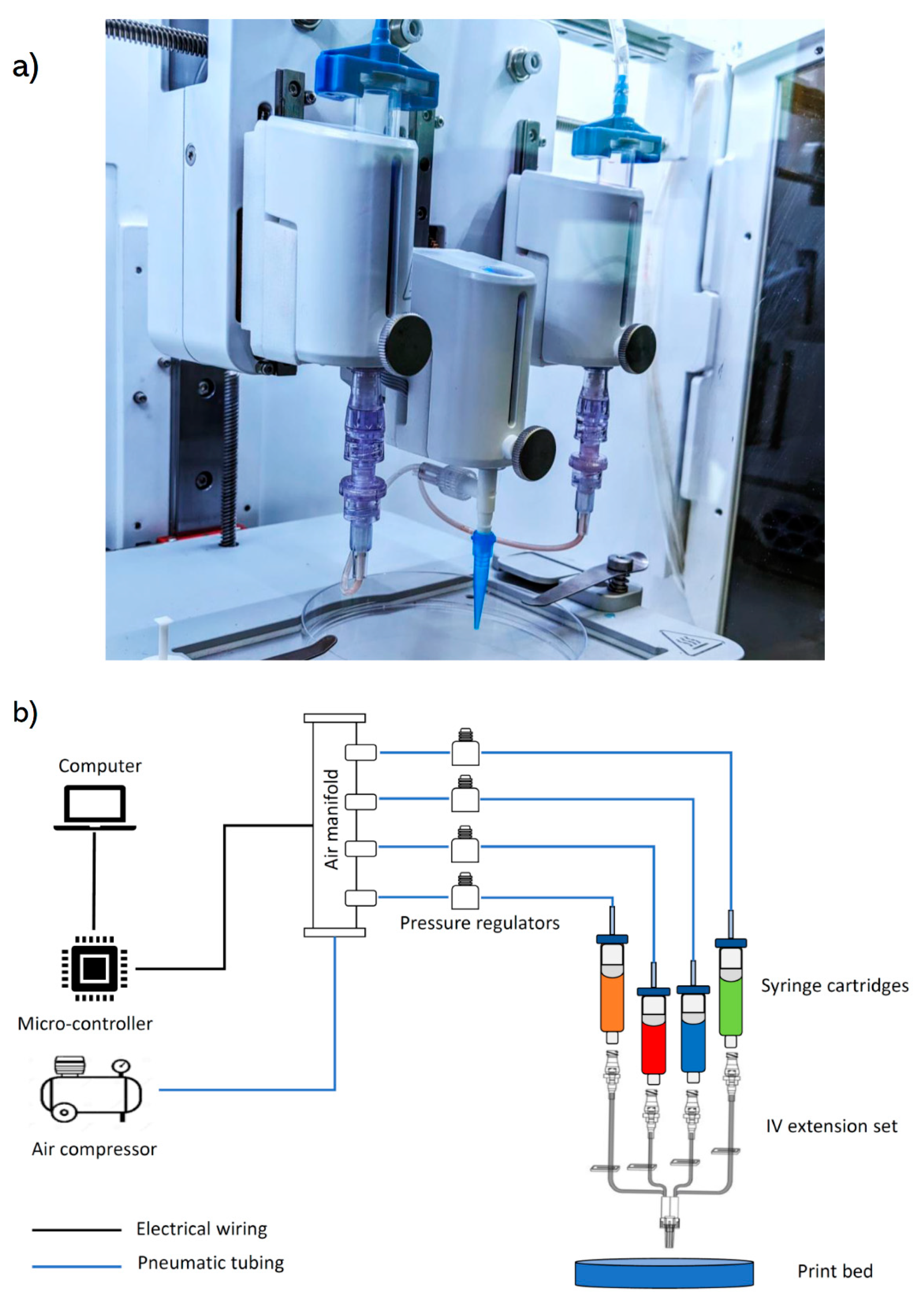
2.1. Printhead Set-up
2.2. Material Selection
2.3. Experimental Process
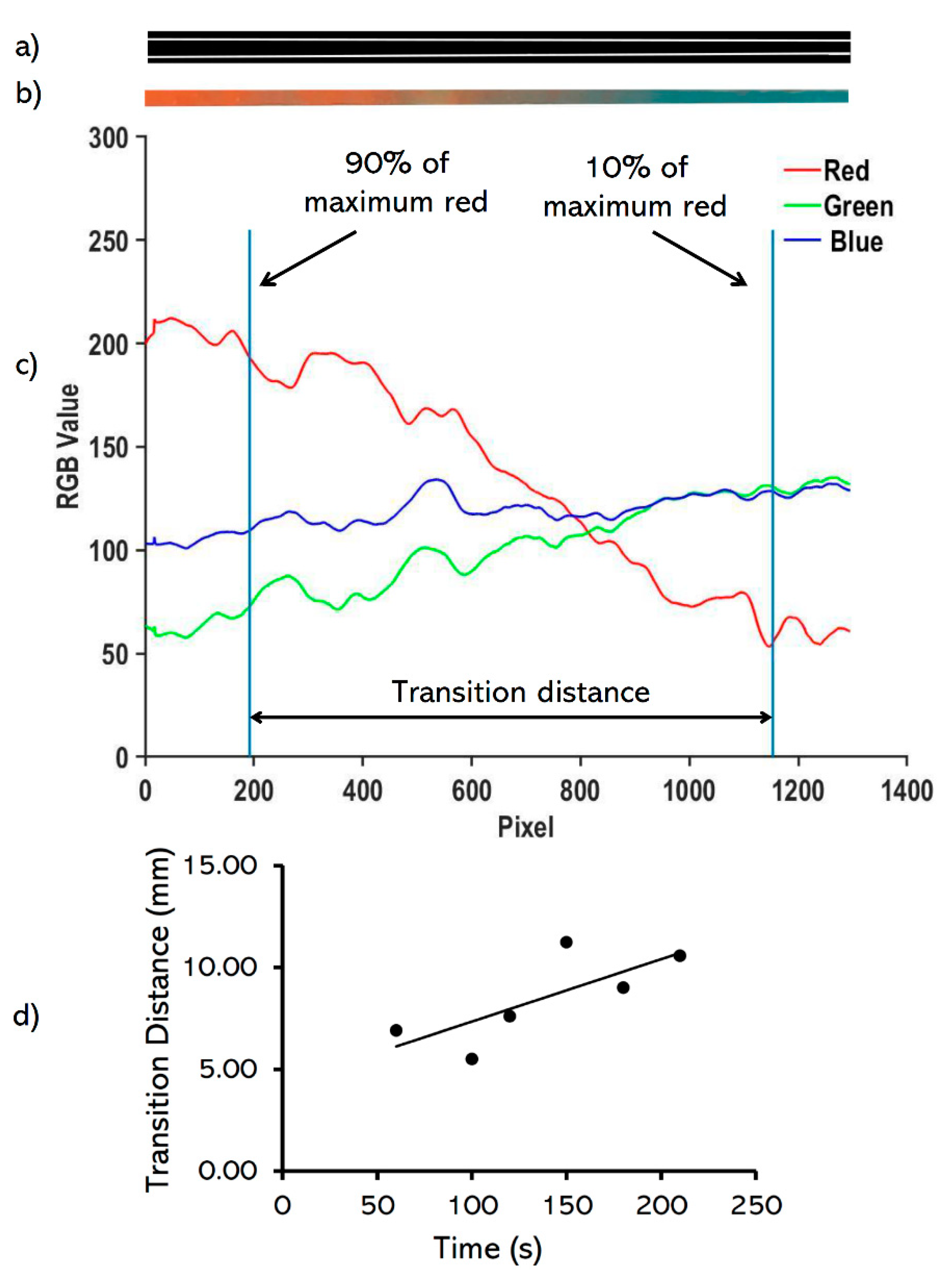
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Diffusion Rate Characterization
2.6. Hydrophobic Coating of the Printhead
3. Results and Discussion
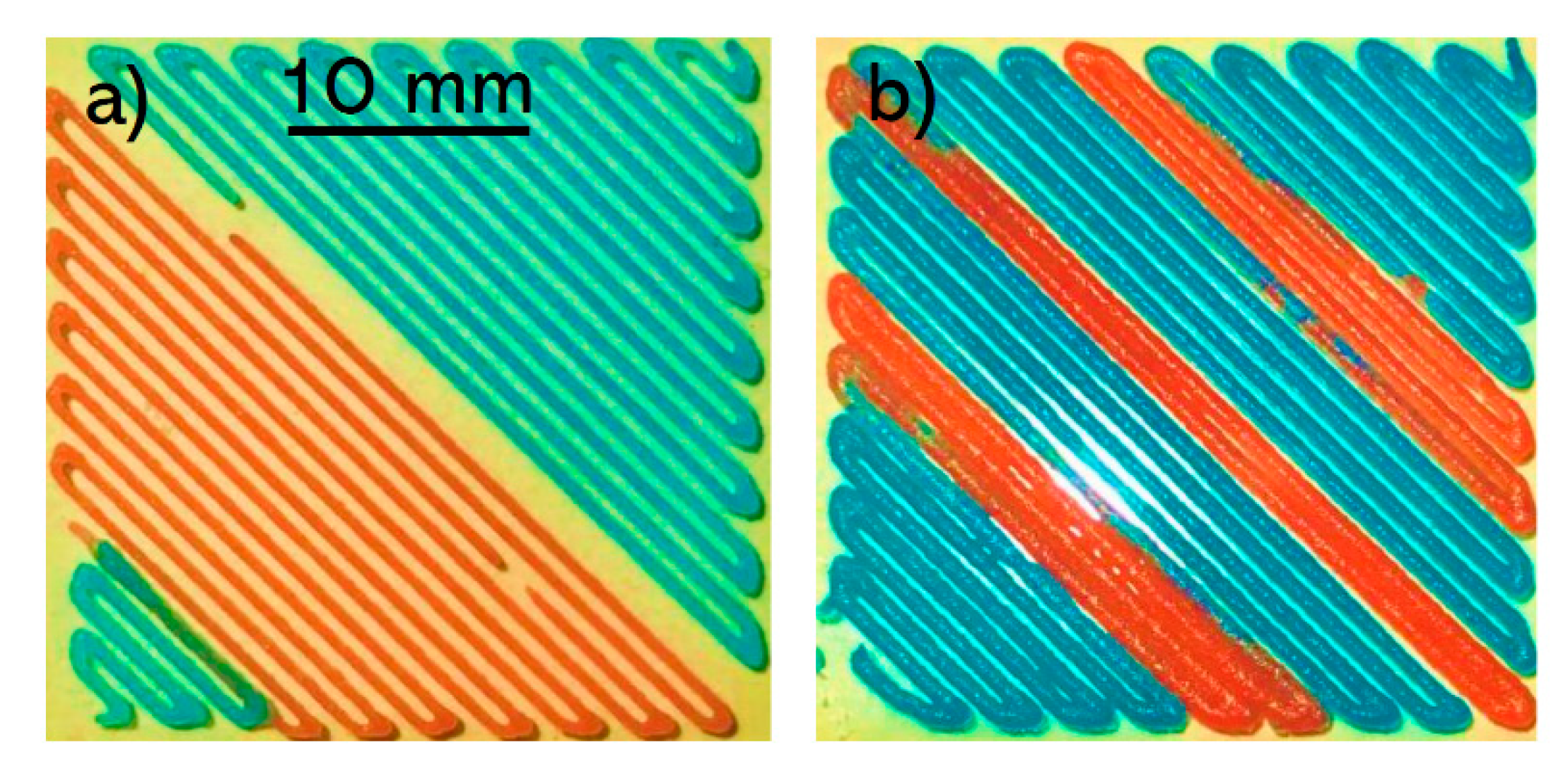
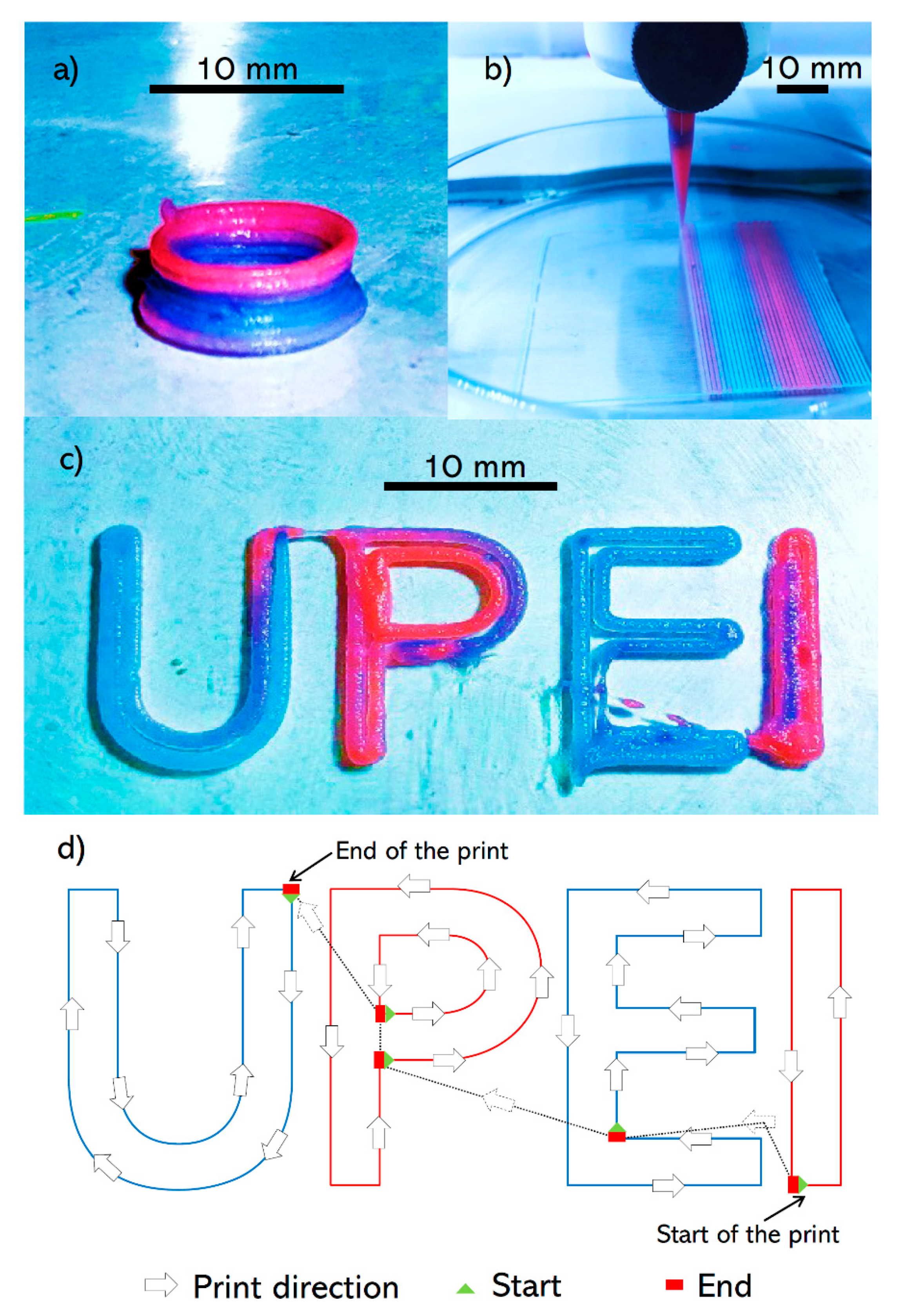
3.1. Printing Integrity
3.2. Printing Different Geometries
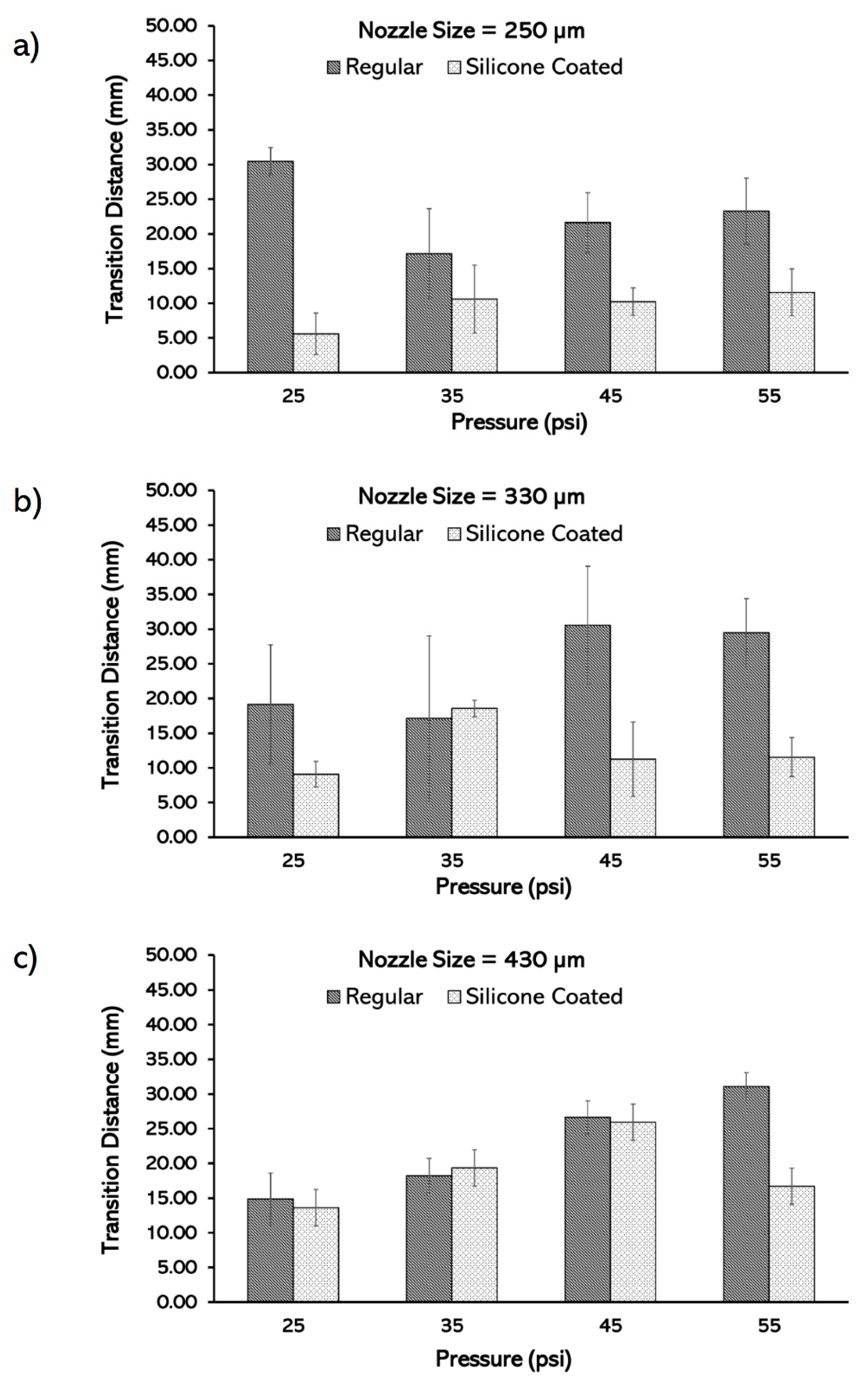
3.3. Characterizing the Transition Distance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, H.; Nowicki, M.; Fisher, J.P.; Zhang, L.G. 3D bioprinting for organ regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayavenkataraman, S.; Yan, W.C.; Lu, W.F.; Wang, C.H.; Fuh, J.Y.H. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs for regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 132, 296–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan-Yildiz, A.; el Assal, R.; Chen, P.; Guven, S.; Inci, F.; Demirci, U. Towards artificial tissue models: Past, present, and future of 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 014103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Lin, X.; Huang, P. 3D bioprinting of artificial tissues: Construction of biomimetic microstructures. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrycky, C.; Wang, Z.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.H. 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Yue, K.; Aleman, J.; Moghaddam, K.M.; Bakht, S.M.; Yang, J.; Jia, W.; Erba, V.D.; Assawes, P.; Shin, S.R.; et al. 3D bioprinting for tissue and organ fabrication. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepowsky, E.; Muradoglu, M.; Tasoglu, S. Towards preserving post-printing cell viability and improving the resolution: Past, present, and future of 3D bioprinting theory. Bioprinting 2018, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiong, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Jin, L. Multinozzle low-temperature deposition system for construction of gradient tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 88, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesky, D.B.; Homan, K.A.; Skylar-scott, M.; Lewis, J.A. In vitro human tissues via multi-material 3-D bioprinting. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2018, 46, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, D.; Ahmadi, A.; Cheung, K.C. Improving piezoelectric cell printing accuracy and reliability through neutral buoyancy of suspensions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2932–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.F.D.; Blaeser, A.; Buellesbach, K.; Sen, K.S.; Xun, W.; Tillmann, W.; Fischer, H. Bioprinting organotypic hydrogels with improved mesenchymal stem cell remodeling and mineralization properties for bone tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, E.; Yu, H.; Ahmadi, A.; Cheung, K.C. Investigation of the hydrodynamic response of cells in drop on demand piezoelectric inkjet nozzles. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaeli, E. Tissue engineering of retina through high resolution 3-dimentional inkjet bioprinting. Int. Soc. Biofabrication 2019, 5, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kérourédan, O.; Bourget, J.M.; Rémy, M.; Crauste-Manciet, S.; Kalisky, J.; Catros, S.; Thébaud, N.B.; Devillard, R. Micropatterning of endothelial cells to create a capillary-like network with defined architecture by laser-assisted bioprinting. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Ng, W.L.; An, J.; Chua, C.K.; Tan, L.P. Layer-by-layer ultraviolet assisted extrusion-based (UAE) bioprinting of hydrogel constructs with high aspect ratio for soft tissue engineering applications. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Anand, S.; Naing, M.W. The arrival of commercial bioprinters—Towards 3D bioprinting revolution! Int. J. Bioprinting 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbolat, I.T.; Moncal, K.K.; Gudapati, H. Evaluation of bioprinter technologies. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 13, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, E.; Butler, H.; MacNevin, W.; Ahmed, M.; Ahmadi, A. Low-temperature solvent-based 3D printing of PLGA: A parametric printability study printability study. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodupe-Ortega, E.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Pernia-Espinoza, A.; Escobedo-Lucea, C. Accurate calibration in multi-material 3D bioprinting for tissue engineering. Materials 2018, 11, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesky, D.B.; Truby, R.L.; Gladman, A.S.; Busbee, T.A.; Homan, K.A.; Lewis, J.A. 3D bioprinting of vascularized, heterogeneous cell-laden tissue constructs. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3124–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serex, L.; Bertsch, A.; Renaud, P. Microfluidics: A new layer of control for extrusion-based 3D printing. Micromachines 2018, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, M.; Testa, S.; Mozetic, P.; Barbetta, A.; Fuoco, C.; Fornetti, E.; Tamiro, F.; Bernardini, S.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Święszkowski, W.; et al. Microfluidic-enhanced 3D bioprinting of aligned myoblast-laden hydrogels leads to functionally organized myofibers in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2017, 131, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Xie, M.; Nie, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, P.; Ramezani, H.; Fu, J.; Ouyang, H.; et al. Airflow-assisted 3D bioprinting of human heterogeneous microspheroidal organoids with microfluidic nozzle. Small 2018, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.M.; Yi, X.; Huang, Z.; Lv, P.; Duan, H. Multimaterial microfluidic 3D printing of textured composites with liquid inclusions. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, S.T.; Bsoul, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Walus, K. 3d Alginate constructs for tissue engineering printed using a coaxial flow focusing microfluidic device. In Proceedings of the 2013 Transducers Eurosensors XXVII 17th International Conference Solid-State Sensors, Actuators Microsystems, TRANSDUCERS EUROSENSORS 2013, Barcelona, Spain, 16–20 June 2013; pp. 1206–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, J.O.; Ober, T.J.; Valentine, A.D.; Lewis, J.A. Microfluidic printheads for multimaterial 3D printing of viscoelastic inks. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3279–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.S.; Heinrich, M.A.; De Ferrari, F.; Jang, H.L.; Bakht, S.M.; Alvarez, M.M.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.C.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; et al. Rapid continuous multimaterial extrusion bioprinting. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadernezhad, A.; Khani, N.; Skvortsov, G.A.; Toprakhisar, B.; Bakirci, E.; Menceloglu, Y.; Unal, S.; Koc, B. Multifunctional 3D printing of heterogeneous hydrogel structures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zeng, S.; Zeng, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B. Properties of lotus seed starch–glycerin monostearin complexes formed by high pressure homogenization. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivhare, S.; Kuru, E. A study of the pore-blocking ability and formation damage characteristics of oil-based colloidal gas aphron drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 122, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mih, J.D.; Sharif, A.S.; Liu, F.; Marinkovic, A.; Symer, M.M.; Tschumperlin, D.J. A multiwell platform for studying stiffness-dependent cell biology. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, V.W.T.; Wardlaw, N.C. Effects of wettability and pore geometry on mobilization of oil and gas in physical models and application to water-alternating-gas (WAG) injections. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1991, 69, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaeser, A.; Campos, D.F.D.; Puster, U.; Richtering, W.; Stevens, M.M.; Fischer, H. Controlling shear stress in 3D bioprinting is a key factor to balance printing resolution and stem cell integrity. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cameron, T.; Naseri, E.; MacCallum, B.; Ahmadi, A. Development of a Disposable Single-Nozzle Printhead for 3D Bioprinting of Continuous Multi-Material Constructs. Micromachines 2020, 11, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050459
Cameron T, Naseri E, MacCallum B, Ahmadi A. Development of a Disposable Single-Nozzle Printhead for 3D Bioprinting of Continuous Multi-Material Constructs. Micromachines. 2020; 11(5):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050459
Chicago/Turabian StyleCameron, Tiffany, Emad Naseri, Ben MacCallum, and Ali Ahmadi. 2020. "Development of a Disposable Single-Nozzle Printhead for 3D Bioprinting of Continuous Multi-Material Constructs" Micromachines 11, no. 5: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050459
APA StyleCameron, T., Naseri, E., MacCallum, B., & Ahmadi, A. (2020). Development of a Disposable Single-Nozzle Printhead for 3D Bioprinting of Continuous Multi-Material Constructs. Micromachines, 11(5), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050459





