A 3D Printed Jet Mixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms
Abstract
1. Introduction
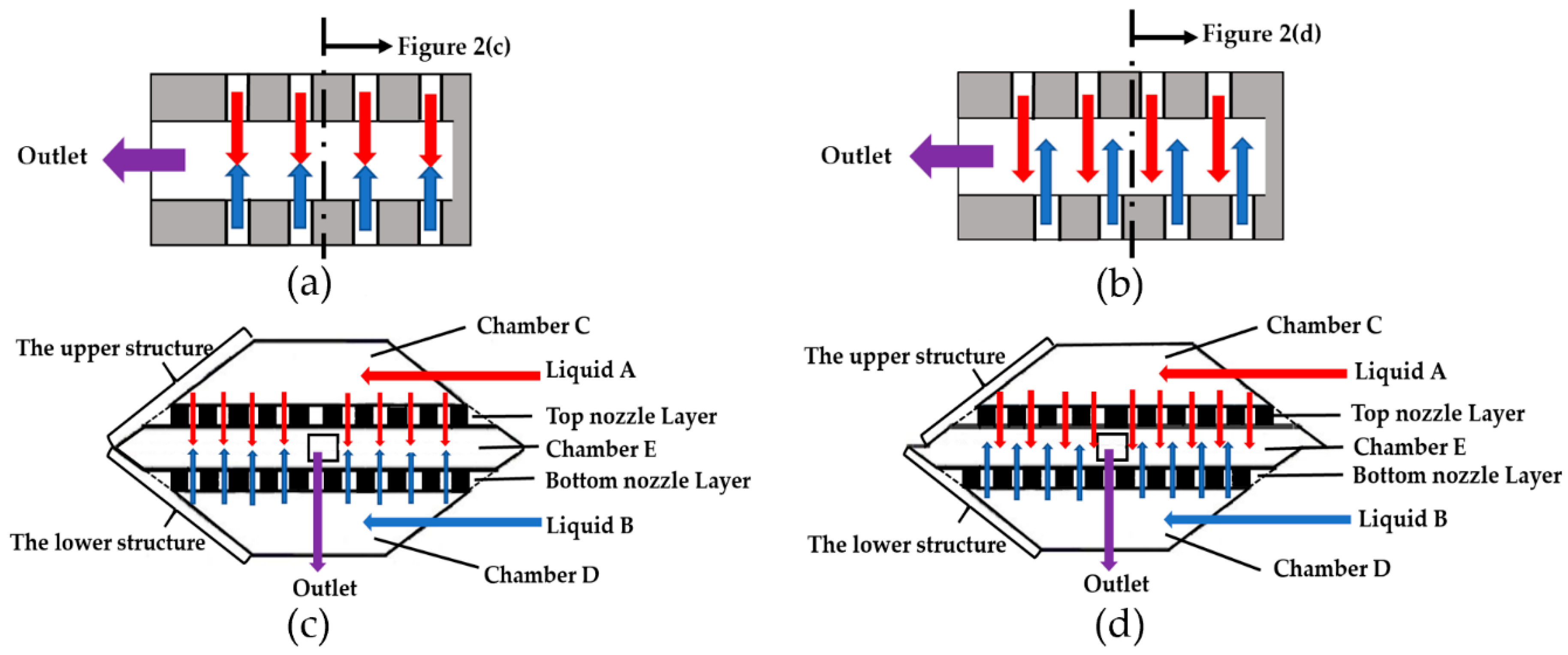
2. Principle and Design of the Jet Mixer
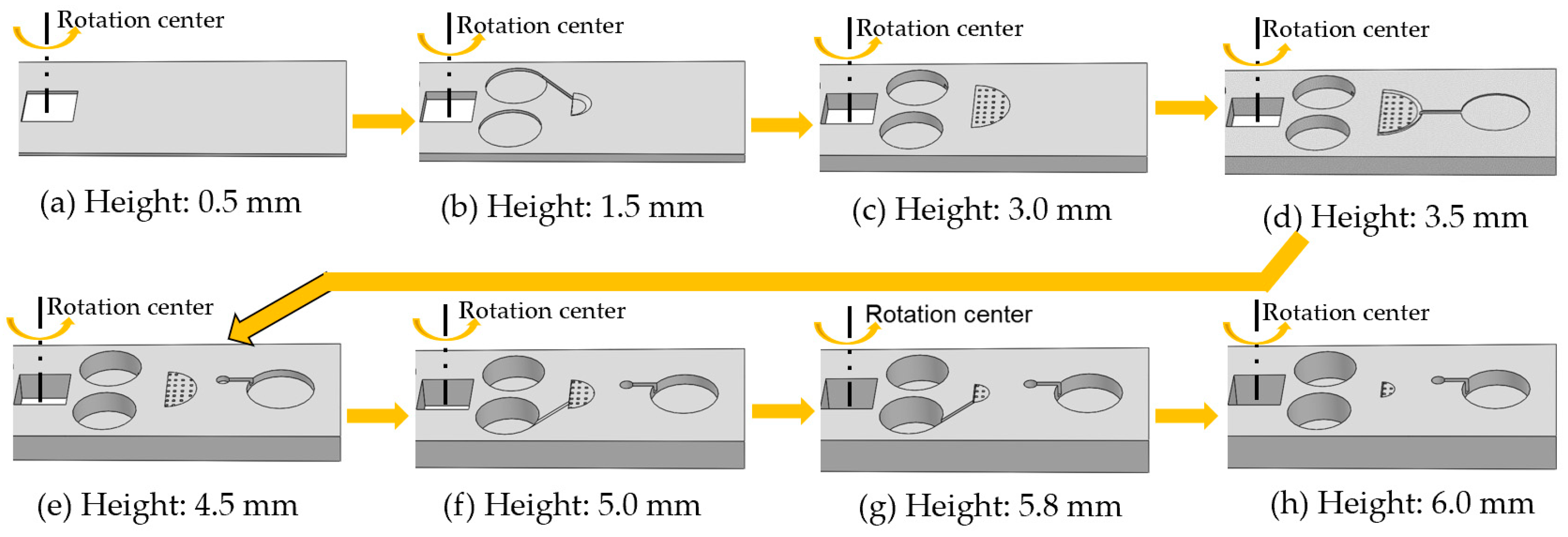
3. Fabrication of the Jet Mixer
4. Experimental Results and Discussions
4.1. The Experimental Setup
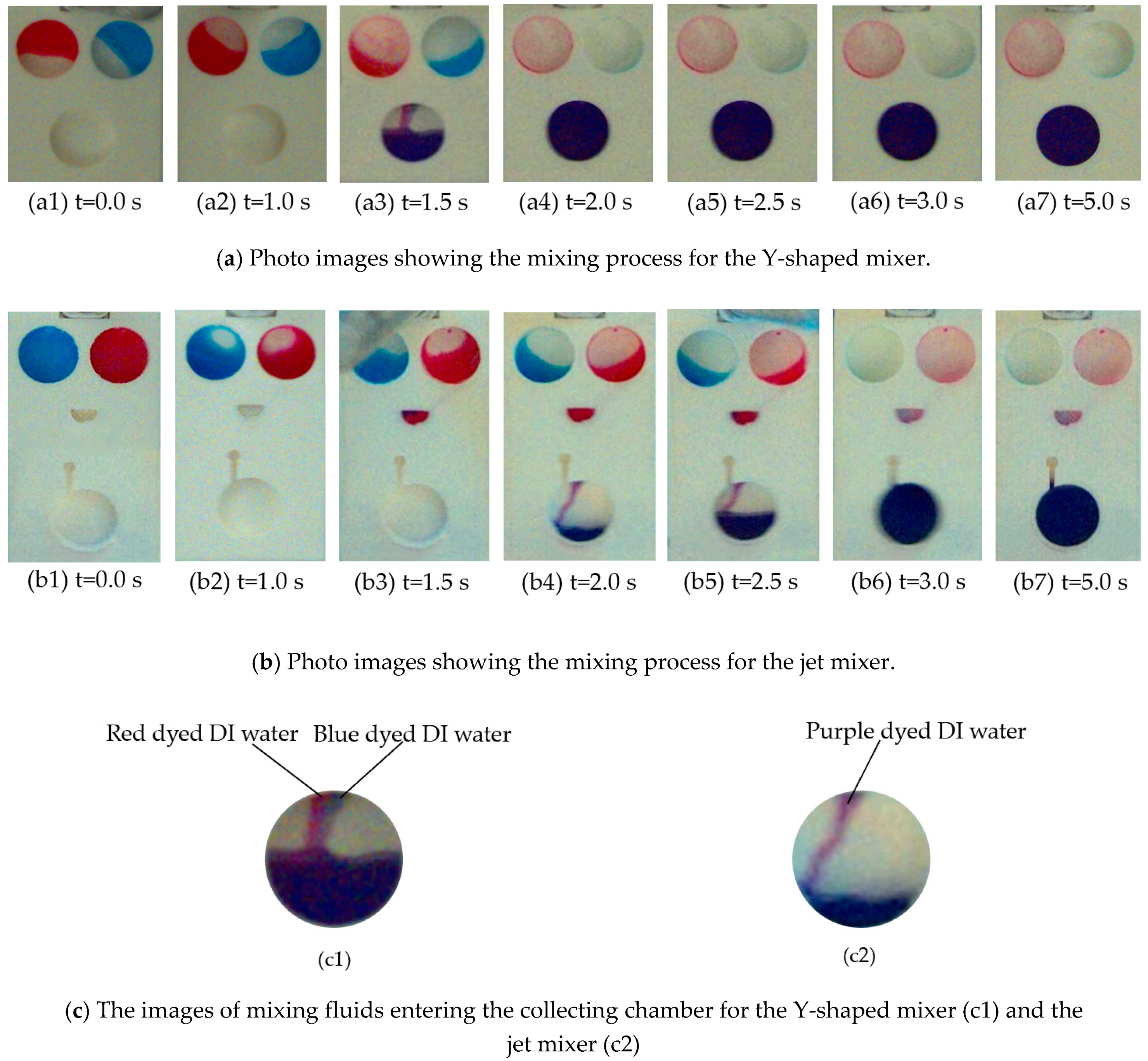
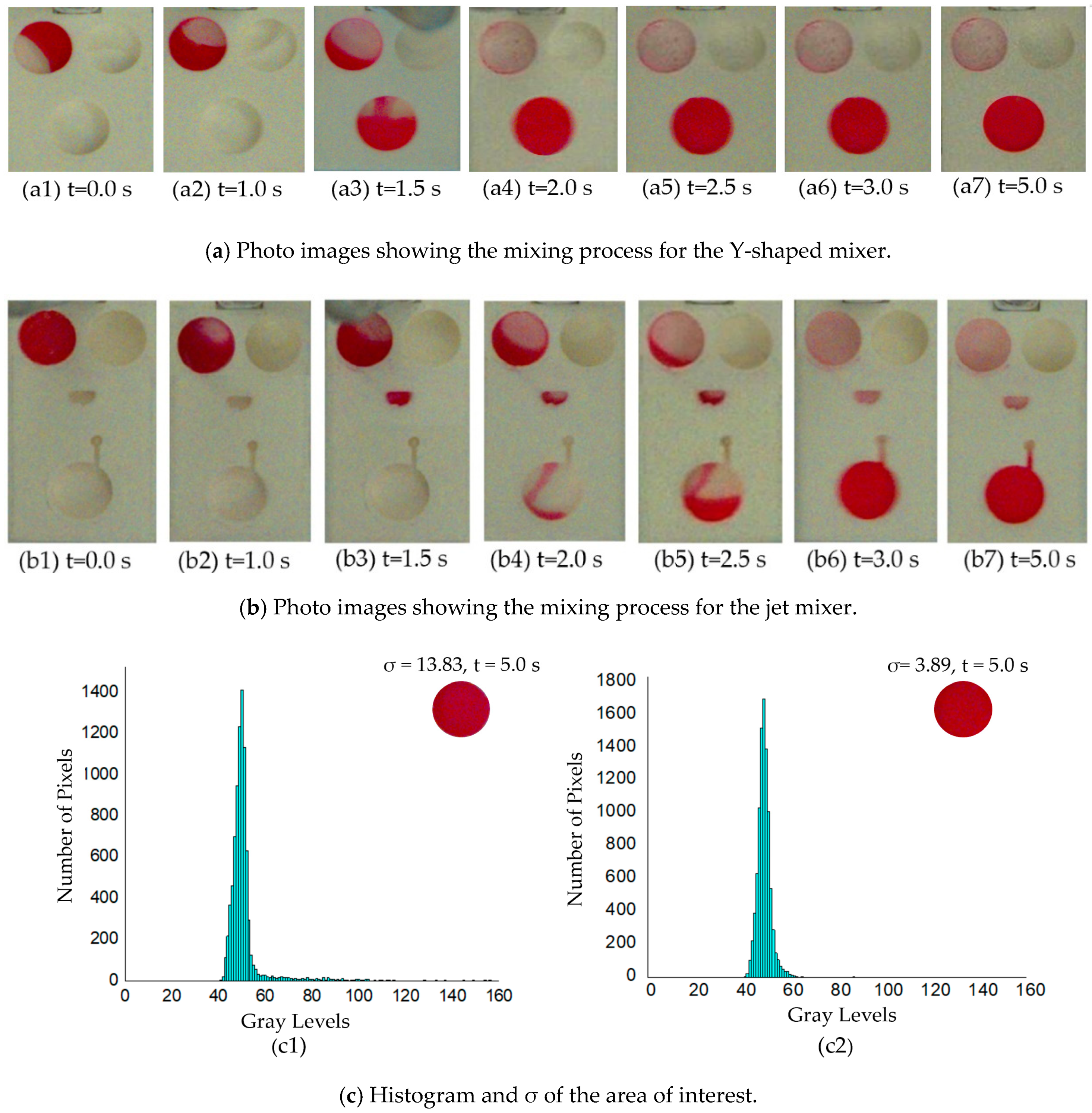
4.2. Mixing Efficiencies and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Tian, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, G. Centrifugal microfluidics for ultra-rapid fabrication of versatile hydrogel microcarriers. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 13, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaneuf, C.R.; Seamon, K.J.; Eckles, T.P.; Sinha, A.; Schoeniger, J.S.; Harmon, B.; Meagher, R.J.; Abhyankar, V.V.; Koh, C.Y. Ultrasensitive multi-species detection of CRISPR-Cas9 by a portable centrifugal microfluidic platform. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, X.; Qu, Y.; Xu, L.; Luo, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, W.; et al. Measurement of carcinoembryonic antigen in clinical serum samples using a centrifugal microfluidic device. Micromachines 2018, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, W. A 3D printed centrifugal microfluidic platform for spilled oil enrichment and detection based on solid phase extraction (SPE). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ould, A.; Moctar, E.; Aubry, N.; Batton, J. Electro-hydrodynamic micro-fluidic mixer. Lab Chip 2003, 3, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, S.H.; Russell, D.H. An experimental study of the solvent-dependent self-assembly/disassembly and conformer preferences of gramicidin A. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7826–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Kobayashi, I.M.; Nakajima, M.; Wu, D.; Nandagopal, S.; Lin, F. Microfluidics for food, agriculture and biosystems industries. Lab Chip. 2011, 11, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, W. A novel gravity valve and its application in a 3D printed centrifugal fluidic-system for solid phase extraction (SPE). In Microfluidics, BioMEMS, and Medical Microsystems XVIII; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, G.H.W.; Manz, A. Chip-based microsystems for genomic and proteomic analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2000, 19, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ali, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Jensen, K.F. Cells on chips. Nature 2006, 442, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, S.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Tsukrov, D.I.; Yu, M.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Waltman, B.A.; Rothenberg, S.M.; Shah, A.M.; Smas, M.E.; Korir, G.K.; et al. Isolation of circulating tumor cells using a microvortex-generating herringbone-chip. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18392–18397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haswell, S.J.; Watts, P. Green chemistry: Synthesis in micro reactors. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lee, H.; Jetta, D.; Oh, K.W. Vacuum-driven power-free microfluidics utilizing the gas solubility or permeability of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3962–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.H.; Lin, L. Active microfluidic mixer and gas bubble filter driven by thermal bubble micropump. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2002, 97–98, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottausci, F.; Mezić, I.; Meinhart, C.D.; Cardonne, C. Mixing in the shear superposition micromixer: Three-dimensional analysis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 362, 1001–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Matsumoto, S.; Goto, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Maeda, R. Ultrasonic micromixer for microfluidic systems. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 93, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Goto, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Maeda, R. Active micromixer for microfluidic systems using lead-zirconate-titanate(PZT)-generated ultrasonic vibration. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaralioglu, G.G.; Wygant, I.O.; Marentis, T.C.; Khuri-Yakub, B.T. Ultrasonic mixing in microfluidic channels using integrated transducers. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3694–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.H.; Ryu, K.S.; Liu, C. A magnetic microstirrer and array for microfluidic mixing. J. Microelectromechanic. Syst. 2002, 11, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rida, A.; Gijs, M.A.M. Manipulation of self-assembled structures of magnetic beads for microfluidic mixing and assaying. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 6239–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, K.S.; Shaikh, K.; Goluch, E.; Fan, Z.; Liu, C. Micro magnetic stir-bar mixer integrated with parylene microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiele, I.; Huber, J.; Hillerich, B.; Kozlowski, F. Surface-micromachined electrostatic microrelay. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 66, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensing, G.A.; Pearce, T.M.; Graham, M.D.; Beebe, D.J. An externally driven magnetic microstirrer. Philosoph. Transact. Royal Soc. Lond. Series A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 362, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Fu, L.M.; Chien, Y.S. Microfluidic T-form mixer utilizing switching electroosmotic flow. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5265–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.C.; Lai, Y.W.; Ben, Y.; Chang, H.C. Microfluidic mixing by dc and ac nonlinear electrokinetic vortex flows. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, G.B.; Fu, L.M.; Lee, K.H.; Yang, R.J. Electrokinetically driven active micro-mixers utilizing zeta potential variation induced by field effect. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddiss, E.; Erickson, D.; Li, D. Heterogeneous surface charge enhanced micro-mixer for electrokinetic flows. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Microchannels and Minichannels, Rochester, NY, USA, 17–19 June 2004; Volume 76, pp. 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Nguyen, N.T.; Huang, X. Nonlinear diffusive mixing in microchannels: Theory and experiments. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.H.; Ward, M.C.L.; Wharton, C.W. Micro T-mixer as a rapid mixing micromixer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 100, 359–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bökenkamp, D.; Desai, A.; Yang, X.; Tai, Y.C.; Marzluff, E.M.; Mayo, S.L. Microfabricated silicon mixers for submillisecond quench-flow analysis. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobby, D.; Angeli, P.; Gavriilidis, A. Mixing characteristics of T-type microfluidic mixers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2001, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.B.; Vishwanath, A.; Brody, J.P.; Austin, R.H. Hydrodynamic focusing on a silicon chip: Mixing nanoliters in microseconds. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 3863–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löb, P.; Drese, K.S.; Hessel, V.; Hardt, S.; Hofmann, C.; Löwe, H.; Schenk, R.; Schönfeld, F.; Werner, B. Steering of liquid mixing speed in interdigital micro mixers—From very fast to deliberately slow mixing. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2004, 27, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardt, S.; Schönfeld, F. Laminar mixing in different interdigital micromixers: II. Numerical simulations. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfeld, F.; Hessel, V.; Hofmann, C. An optimised split-and-recombine micro-mixer with uniform “chaotic” mixing. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, C.P.; Wu, C.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Wu, C.Y. Design and simulation of the micromixer with chaotic advection in twisted microchannels. Lab Chip 2003, 3, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroock, A.D.; Dertinger, S.K.W.; Ajdari, A.; Mezić, I.; Stone, H.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 2002, 295, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H.; Stremler, M.A.; Sharp, K.V.; Olsen, M.G.; Santiago, J.G.; Adrian, R.J.; Aref, H.; Beebe, D.J. Passive mixing in a three-dimensional serpentine microchannel. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, A.; Heimgartner, S.; Cousseau, P.; Renaud, P. Static micromixers based on large-scale industrial mixer geometry. Lab Chip. 2001, 1, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holger, L.; Guan, H.; Wu, C.-J.; Tu, S.-T. Three-dimensional numerical study of flow structures of impinging jets in Y-typed micro-mixers. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2007, 8, 425–434. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Williams, J.D.; Wang, W. A rapid micro-mixer/reactor based on arrays of spatially impinging micro-jets. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengeaud, V.; Josserand, J.; Girault, H.H. Mixing processes in a zigzag microchannel: Finite element simulations and optical study. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4279–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.; Pamula, V.K.; Fair, R.B. Rapid droplet mixers for digital microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 2003, 3, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooch, J.W. Liquid injection molding. Encycl. Dict. Polym. 2011, 77, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, R.; Lammerink, T.S.J.; Elwenspoek, M.; Fluitman, J.H.J. Micro mixer with fast diffusion. IEEE Micro Electr. Mech. Syst. 1993, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadimisetty, K.; Spak, A.P.; Bhalerao, K.S.; Sharafeldin, M.; Mosa, I.M.; Lee, N.H.; Rusling, J.F. Automated 4-sample protein immunoassays using 3D-printed microfluidics. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4000–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadehgiashi, M.; Gevorkian, A.; Tebbe, M.; Seo, M.; Prince, E.; Kumacheva, E. 3D-printed microfluidic devices for materials science. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, S.M.; Rowe, W.; Christie, S.D.; Platt, M. 3D printed microfluidic device with integrated optical sensing for particle analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.K.; Nielsen, A.V.; Beauchamp, M.J.; Almughamsi, H.M.; Nielsen, J.B.; Sonker, M.; Gong, H.; Nordin, G.P.; Woolley, A.T. 3D printed microfluidic devices with immunoaffinity monoliths for extraction of preterm birth biomarkers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5405–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, M.; Benders, S.; Blümich, B.; Wessling, M. 3D MRI velocimetry of non-transparent 3D-printed staggered herringbone mixers. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, A.; Siller, I.G.; Urmann, K.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Bahnemann, J. 3D printed microfluidic mixers—A comparative study on mixing unit performances. Small 2019, 15, 1804326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereijgers, J.; Schalck, J.; Lölsberg, J.; Wessling, M.; Breugelmans, T. Indirect 3D printed electrode mixers. Chem. Electr. Chem. 2019, 6, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, K.C.; Ermagan, R.; Thompson, B.; Friedman, A.; Malmstadt, N. Modular, discrete micromixer elements fabricated by 3D printing. Micromachines 2017, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, A.; Boetker, J.; Wang, Y.; Jensen, H.; Rantanen, J.; Beck-Broichsitter, M. High-throughput fabrication of nanocomplexes using 3D-printed micromixers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.C.; Chabinyc, M.L.; Metallo, S.J.; Anderson, J.R.; Stroock, A.D.; Whitesides, G.M. Prototyping of microfluidic devices in poly (dimethylsiloxane) using solid-object printing. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symes, M.D.; Kitson, P.J.; Yan, J.; Richmond, C.J.; Cooper, G.J.; Bowman, R.W.; Vilbrandt, T.; Cronin, L. Integrated 3D-printed reactionware for chemical synthesis and analysis. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupal, B.S.; Garcia, E.A.; Ayranci, C.; Qureshi, A.J. 3D printed 3d-microfluidics: Recent developments and design challenges. J. Integr. Des. Proc. Sci. 2018, 1, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishbin, E.; Eghbal, M.; Fakhari, S.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Navidbakhsh, M. The effect of mo ment of inertia on the liquids in centrifugal microfluidics. Micromachines 2016, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Components | Dimensions in Jet-Mixer | Dimensions In Y-Shaped Mixer |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Loading Chamber A | 3.37 mm (R) × 5.00 mm (H) | 4.77 mm (R) × 2.50 mm (H) |
| Sample Loading Chamber B | 3.37 mm (R) × 5.00 mm (H) | 4.77 mm (R) × 2.50 mm (H) |
| Capillary Valve | 0.80 mm (W) × 0.50 mm (H) | 0.80 mm (W) × 0.50 mm (H) |
| Outlet | 0.80 mm (W) × 0.50 mm (H) | 0.80 mm (W) × 0.50 mm (H) |
| Collecting Chamber | 4.81 mm (R) × 2.75mm (H) | 5.05 mm (R) × 2.50 mm (H) |
| Test # | Standard Deviation of Jet-Mixer | Standard Deviation of Y-Shaped Mixer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.89 | 13.53 |
| 2 | 3.59 | 13.83 |
| 3 | 3.24 | 13.47 |
| 4 | 3.89 | 13.88 |
| 5 | 3.21 | 14.15 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, W. A 3D Printed Jet Mixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines 2020, 11, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070695
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Qiao Z, Wang W. A 3D Printed Jet Mixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines. 2020; 11(7):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070695
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yunxia, Yong Zhang, Zheng Qiao, and Wanjun Wang. 2020. "A 3D Printed Jet Mixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms" Micromachines 11, no. 7: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070695
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, Y., Qiao, Z., & Wang, W. (2020). A 3D Printed Jet Mixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines, 11(7), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070695




