A Novel Stick-Slip Nanopositioning Stage Integrated with a Flexure Hinge-Based Friction Force Adjusting Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
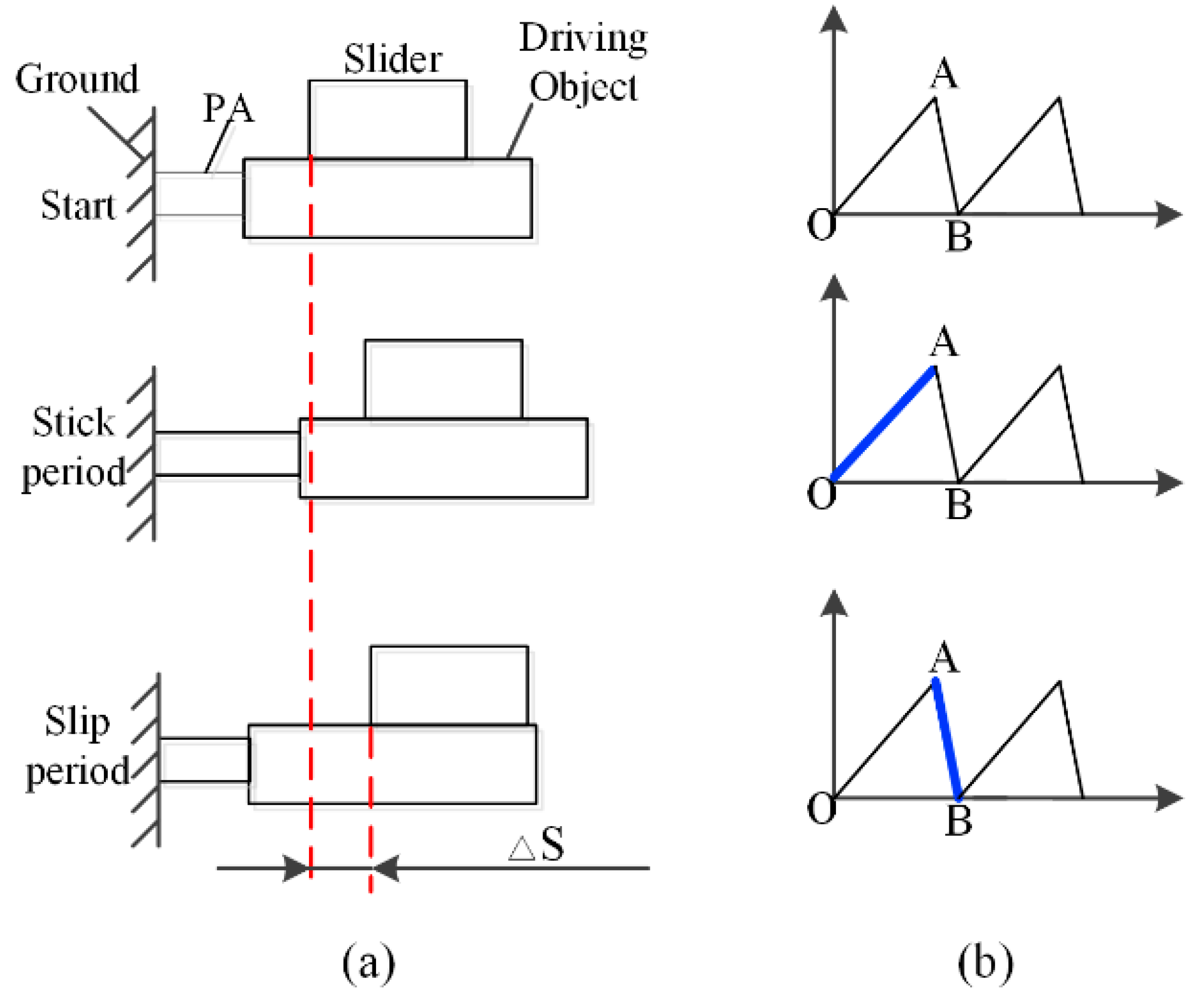
2. Design and Analysis
2.1. Design of the Piezoelectrically-Actuated Stick-Slip Nanopositioning Stage (PASSNS)
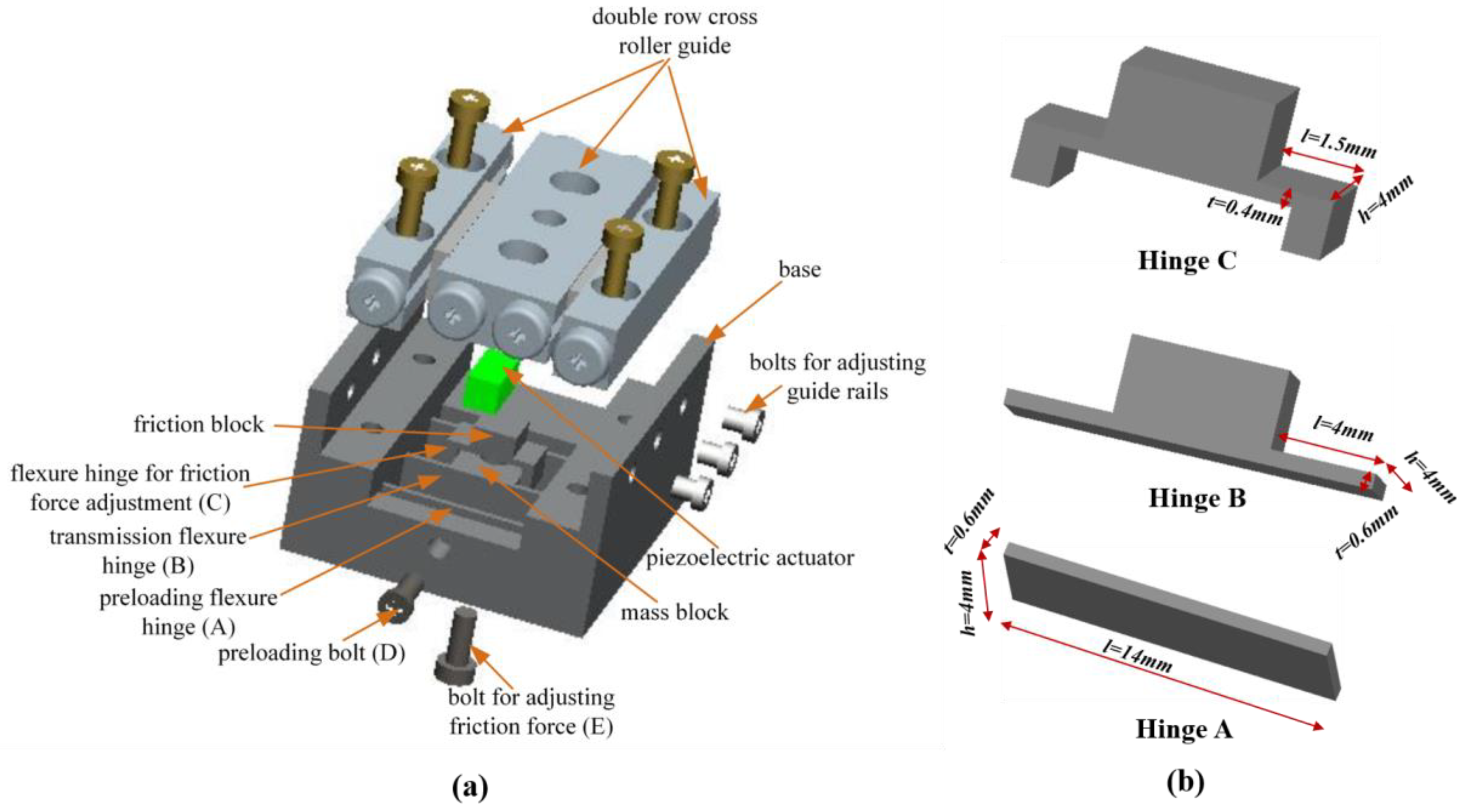
2.2. Design of Friction Force Adjustment Structure
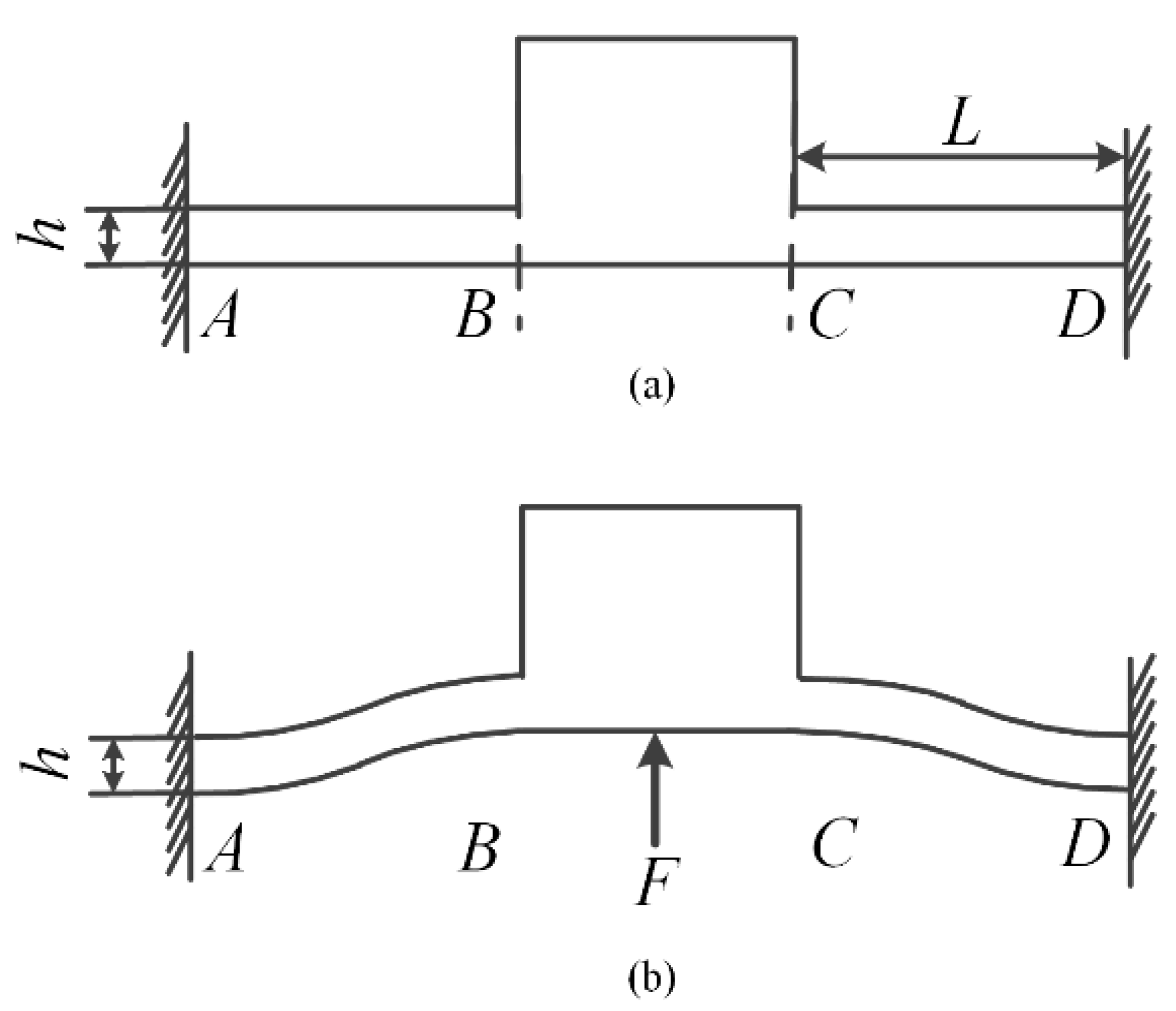
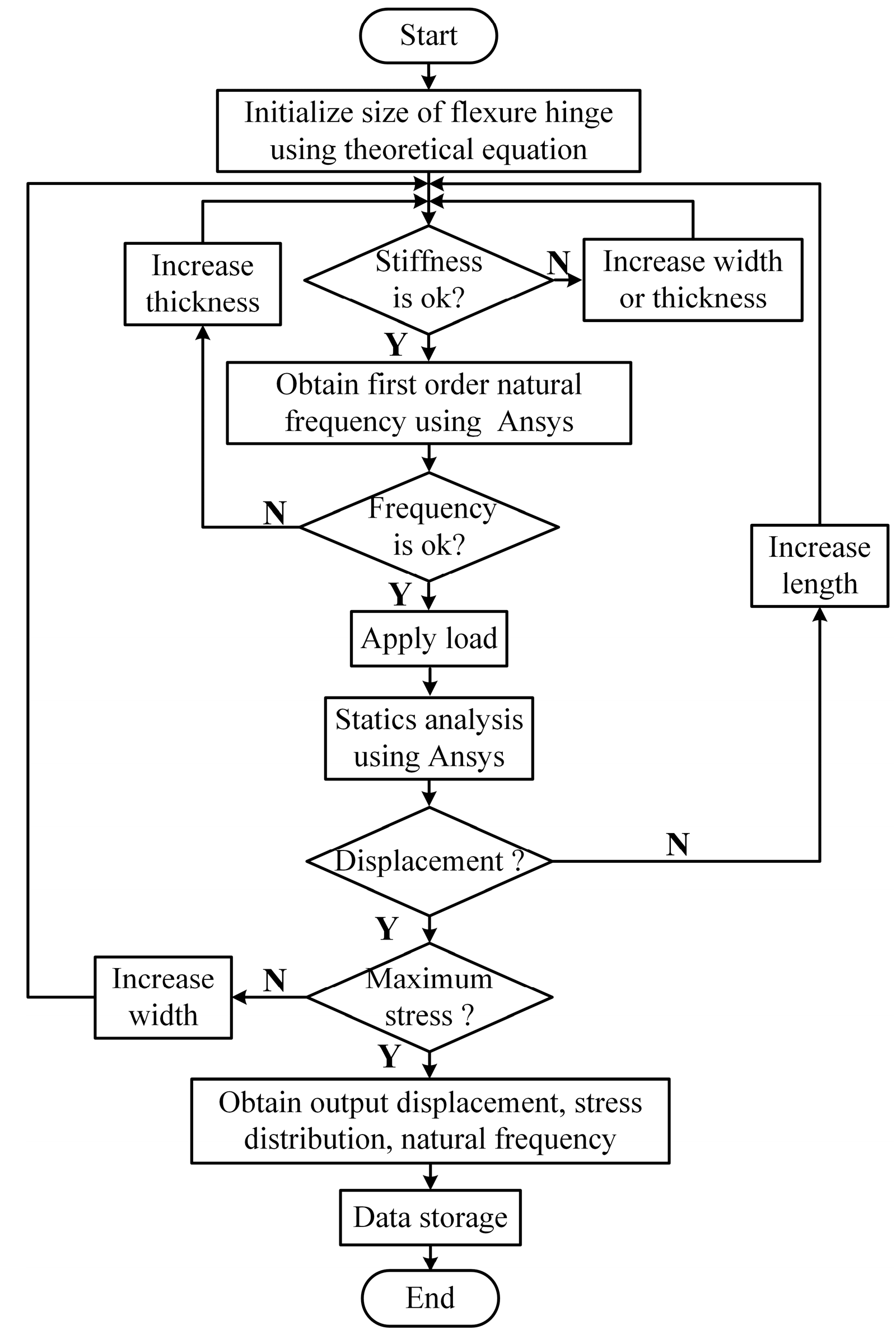
2.3. Determination of Flexure Hinge Size
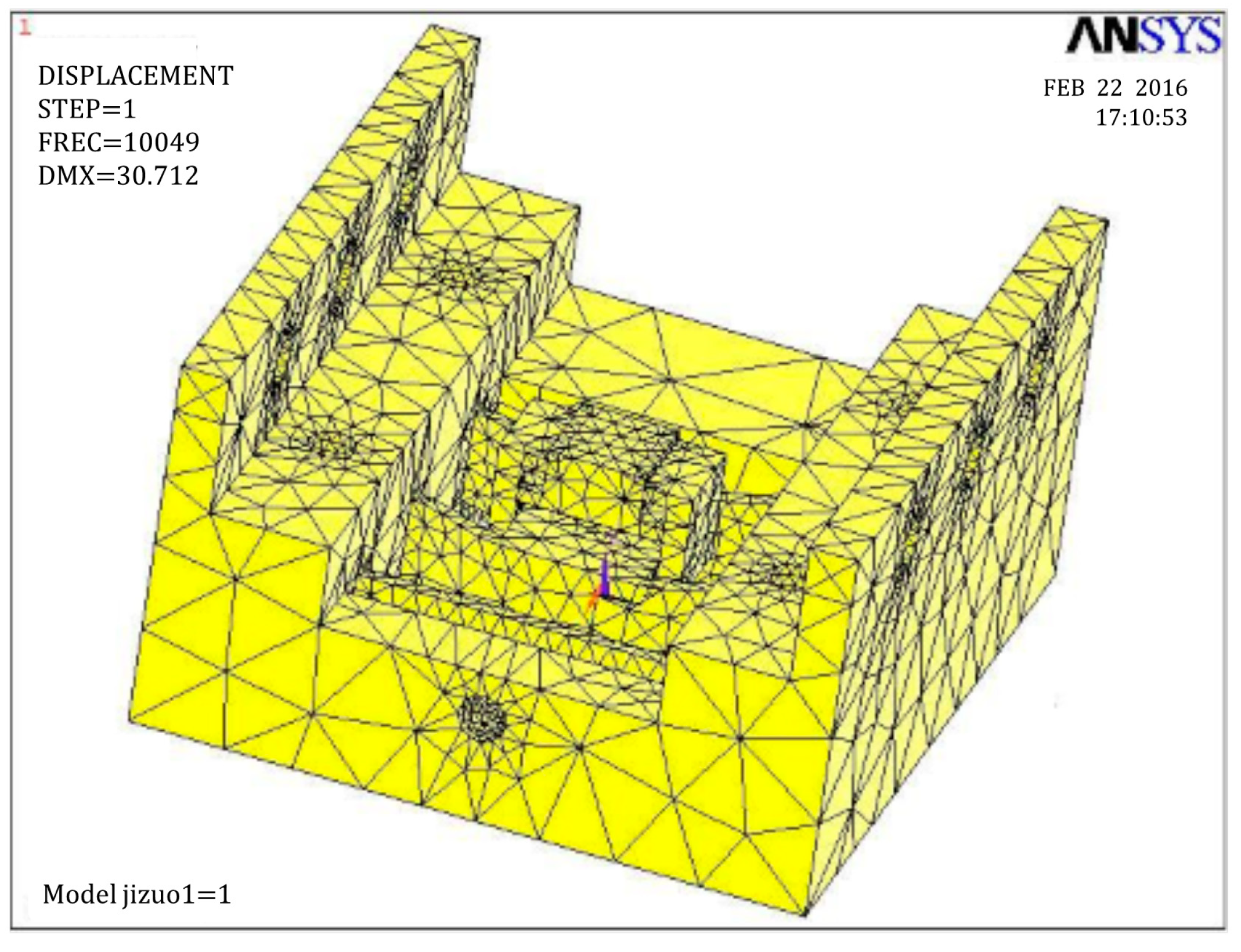
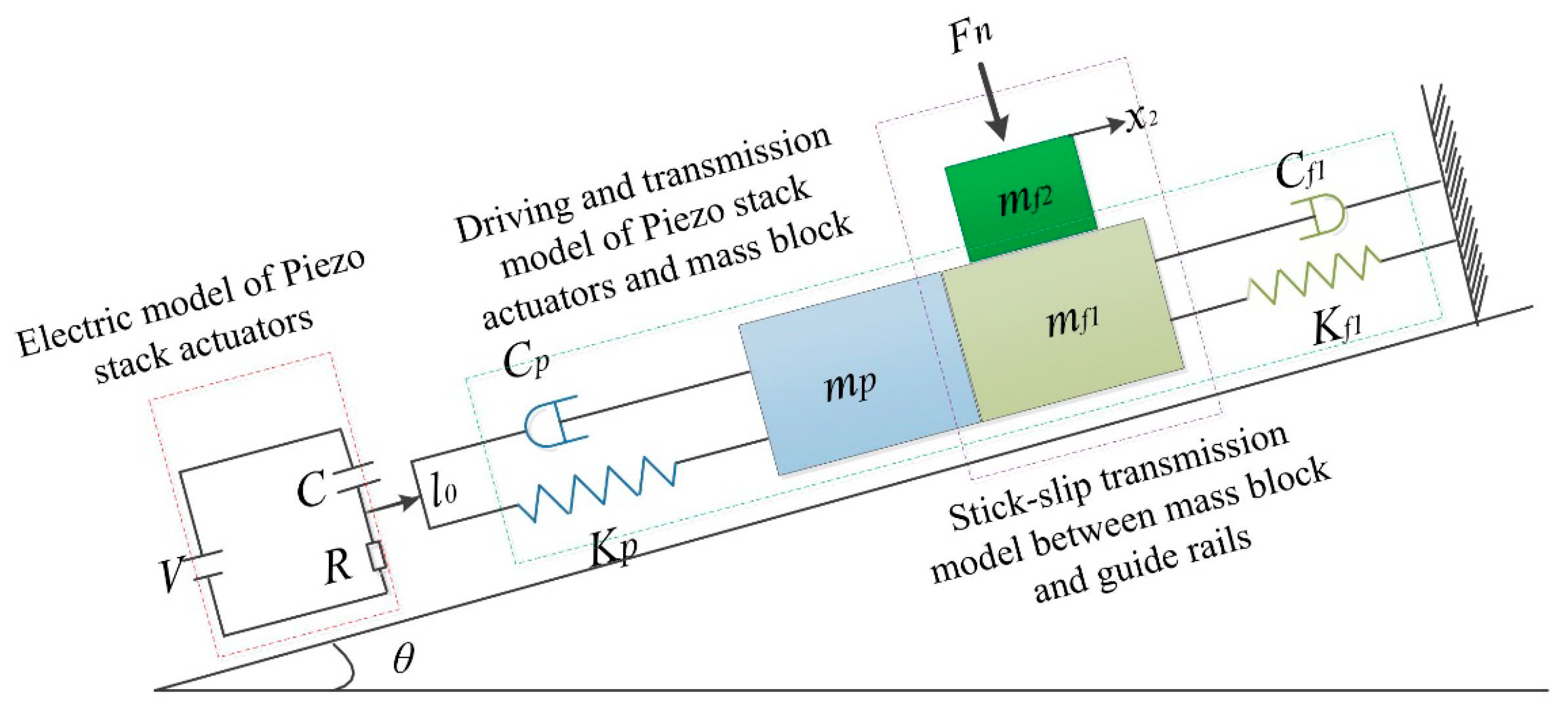
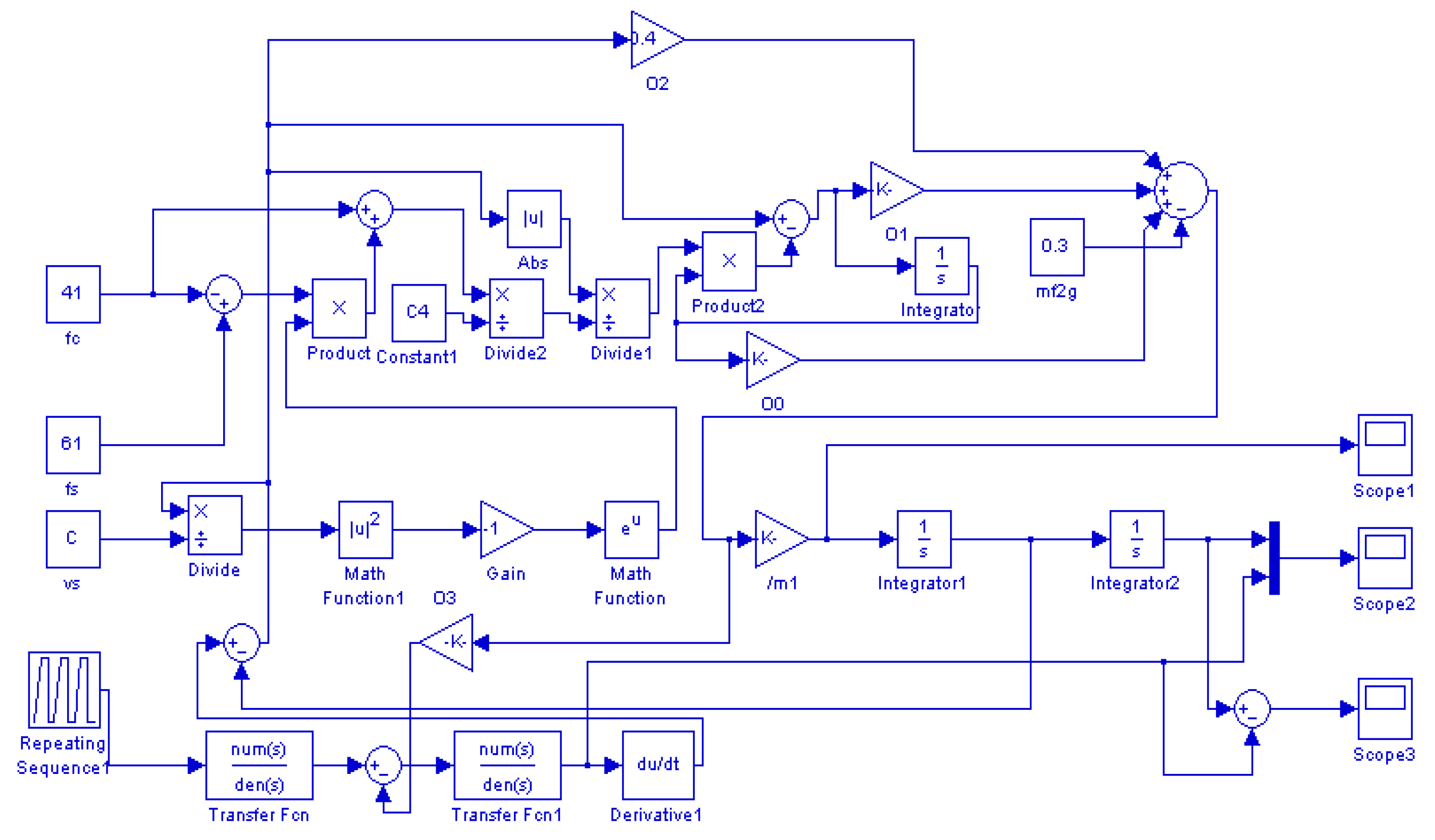
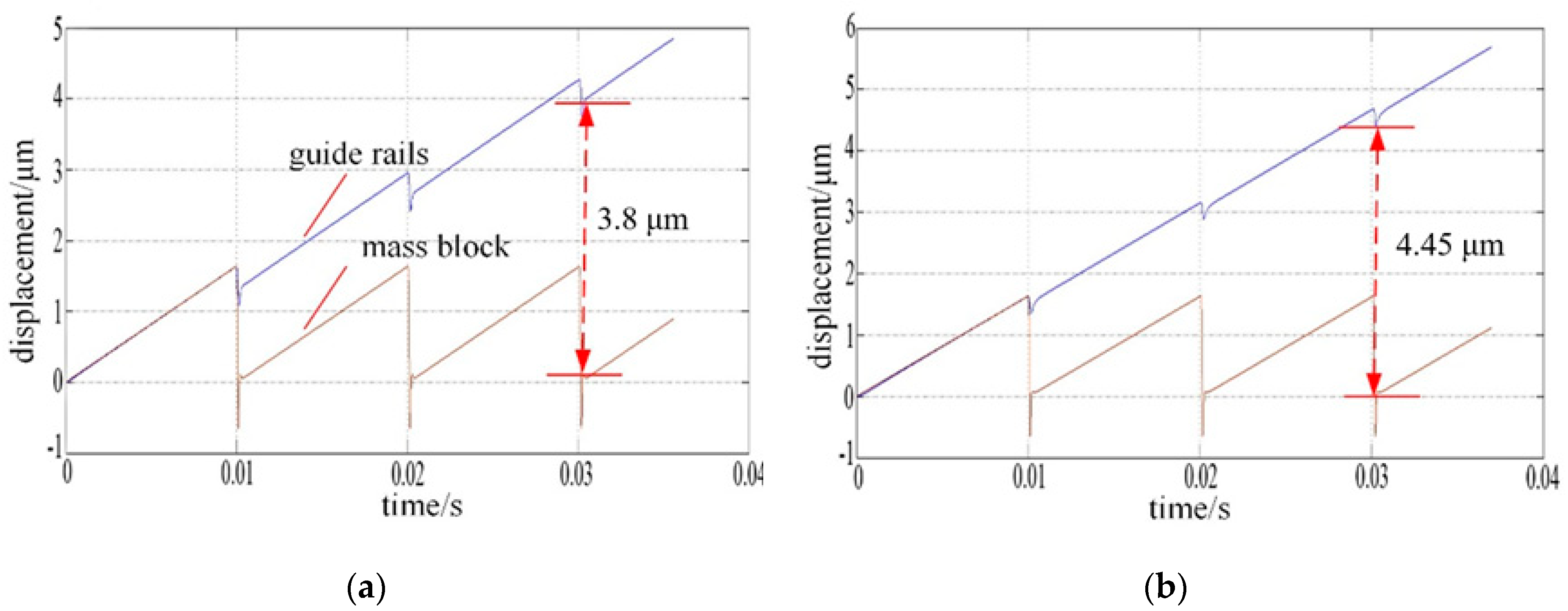
2.4. Analysis and Simulation of the PASSNS
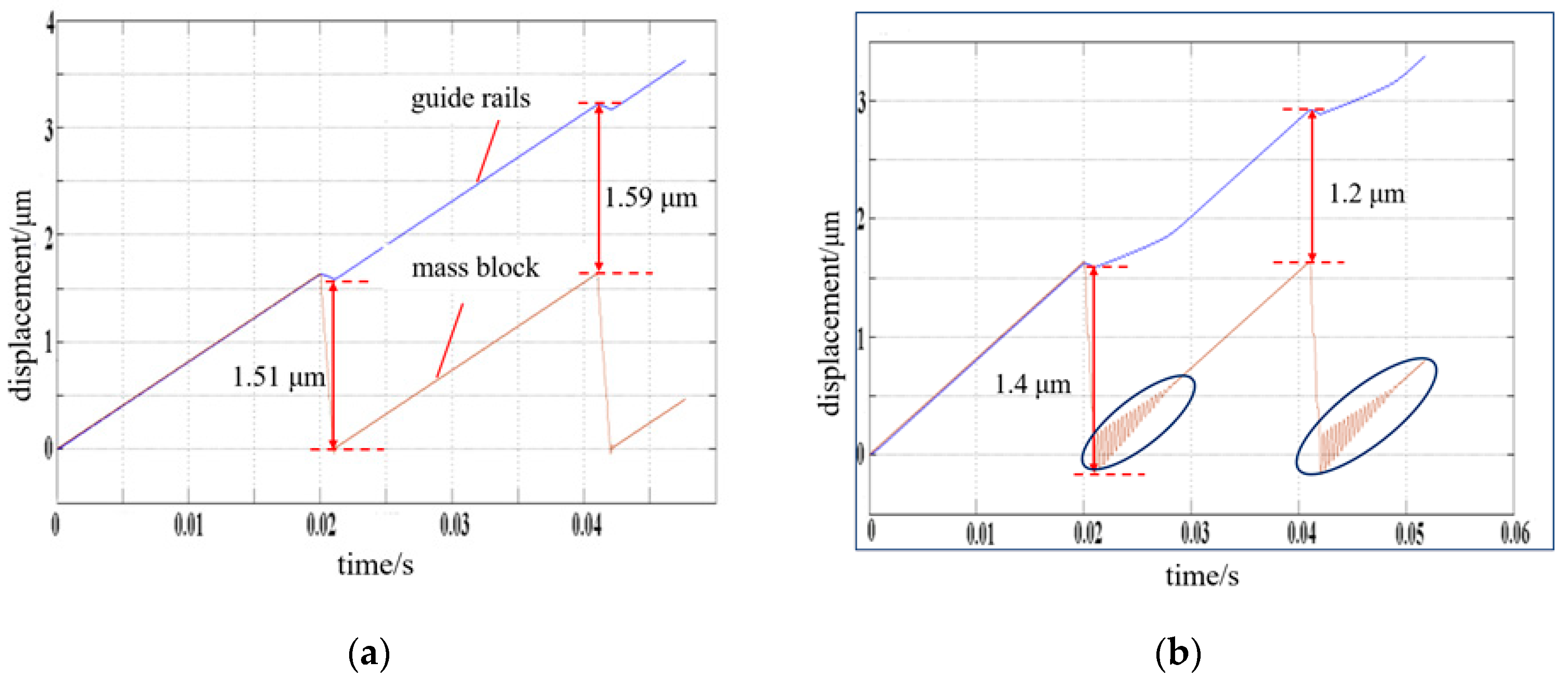
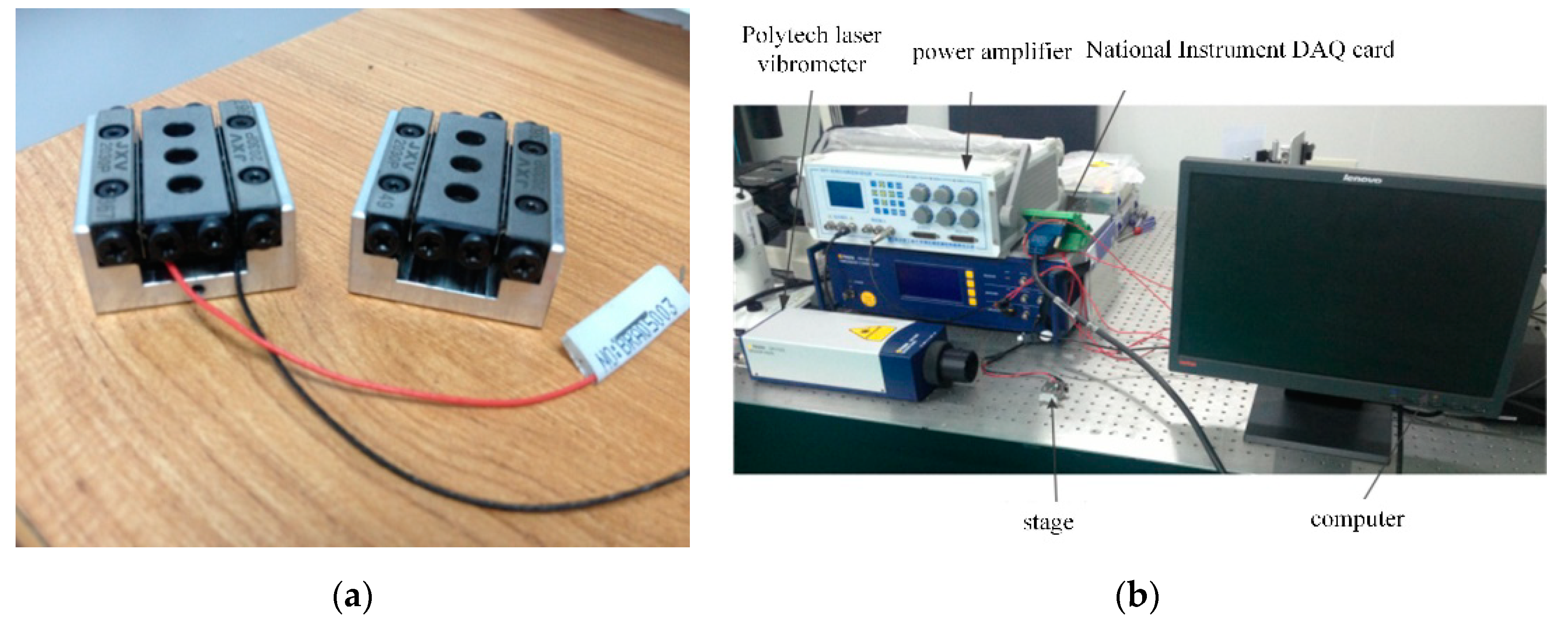
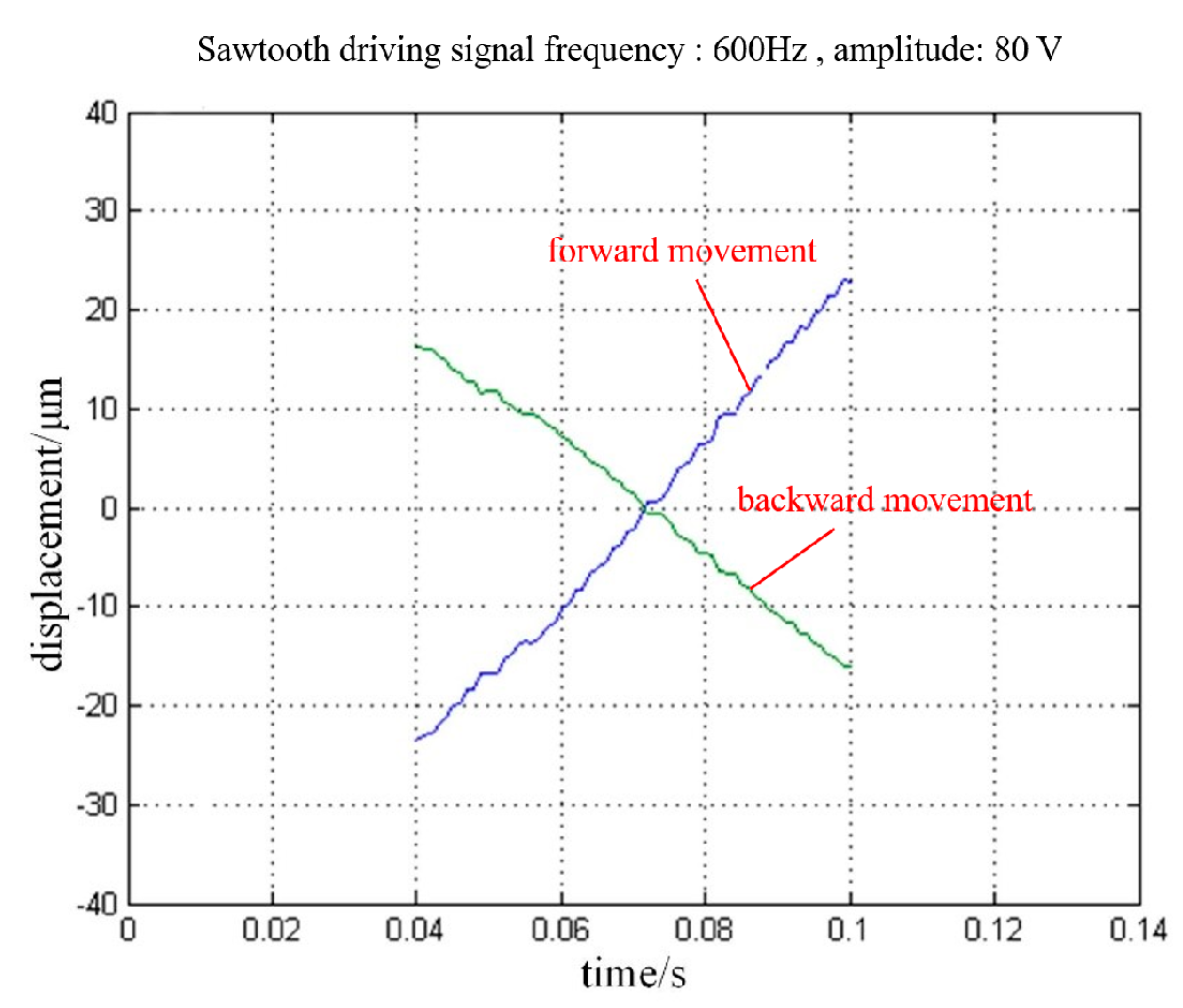
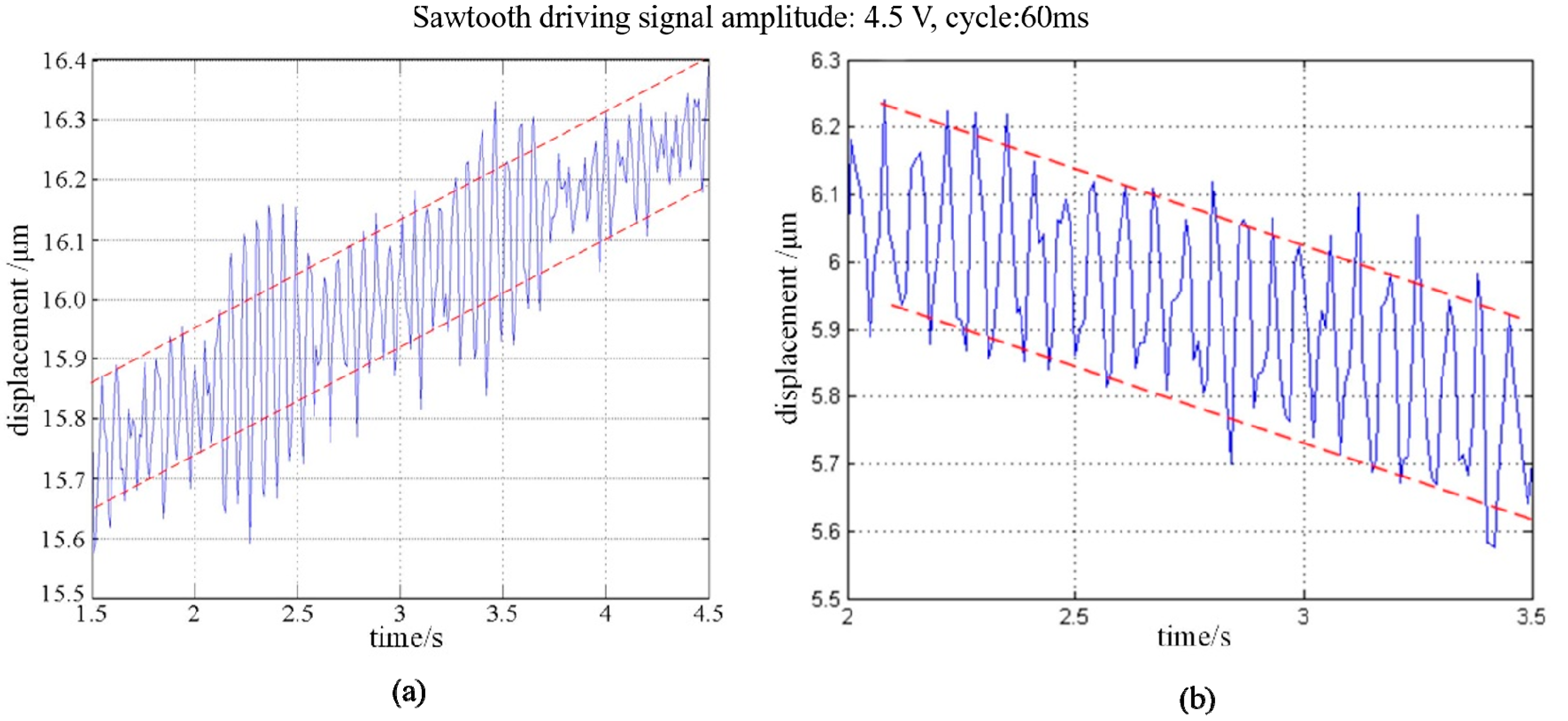
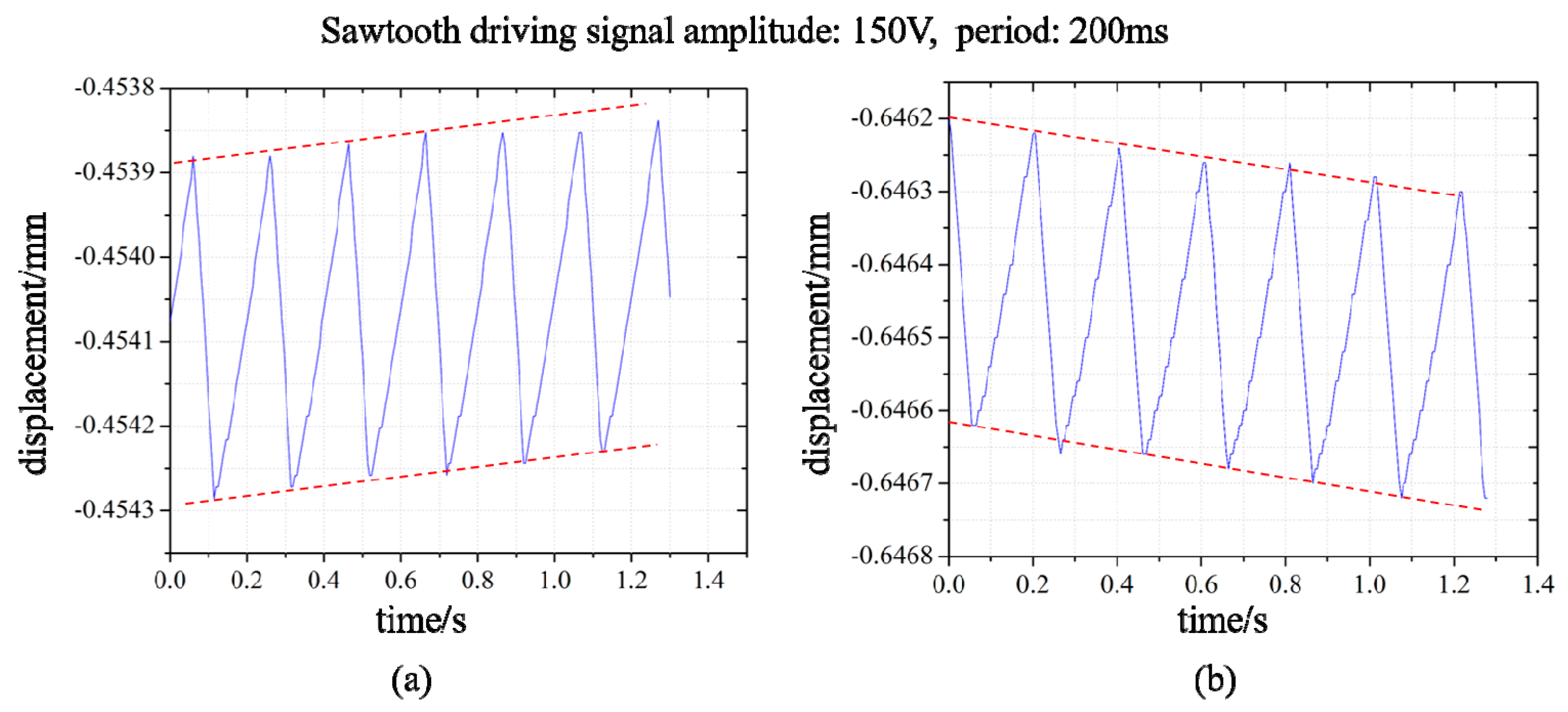
3. Experimental Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Canales-Benavides, A.; Zhuo, Y.; Amitrano, A.M.; Kim, M.; Hernandez-Aranda, R.I.; Carney, P.S.; Schnell, M. Accessible quantitative phase imaging in confocal microscopy with sinusoidal-phase synthetic optical holography. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, A55–A64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; Gong, Z.; Chen, B.K.; Cao, Z.; Yu, J.; Ru, C.; Tan, M.; Xie, S.; Sun, Y. A closed-loop controlled nanomanipulation system for probing nanostructures inside scanning electron microscopes. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y. Nanopositioning Technologies; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yacoot, A.; Klapetek, P.; Valtr, M.; Grolich, P.; Dongmo, H.; Lazzerini, G.M.; Bridges, A. Design and performance of a test rig for evaluation of nanopositioning stages. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Morita, T. Stepping piezoelectric actuators with large working stroke for nano-positioning systems: A review. Sens. Actuators A 2019, 292, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, Q. Survey on recent designs of compliant micro-/nano-positioning stages. Actuators 2018, 7, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. Experimental study on load characteristics of macro-micro dual-drive precision positioning mechanism. In Intelligent Robotics and Applications; Huang, Y., Wu, H., Liu, H., Yin, Z., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 464–471. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, L. Design of a control system for a macro-micro dual-drive high acceleration high precision positioning stage for IC packaging. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2009, 52, 1858–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X. Design of a piezo-driven inchworm flexure stage for precision positioning. Int. J. Appl. Electrom. 2016, 50, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Chu, X.; Yuan, S.; Zhong, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, S. Development of an ultrasonic linear motor with ultra-positioning capability and four driving feet. Ultrasonics 2016, 72, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhu, J.; Pang, M.; Ru, C. Long-stroke nanopositioning stage driven by piezoelectric motor. J. Sens. 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Jin, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L. Double closed-loop control of a trans-scale precision positioning stage based on the inertial stick–slip driving. Sens. Actuators A 2019, 297, 111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, J.; Salarieh, H.; Vossoughi, G. Study of a piezo-electric actuated vibratory micro-robot in stick-slip mode and investigating the design parameters. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 1927–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Xin, X.; Shen, X.; Yuan, X.; Yang, J.; Chu, Z.; Dong, S. A piezoelectric and electromagnetic dual mechanism multimodal linear actuator for generating macro-and nanomotion. Research 2019, 8232097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, B.; Hua, S.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Qu, X. Dynamic performance of inchworm-type piezoelectric linear actuator. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2007, 15, 873–877. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Quan, Q.; Tian, X. Optimization and analysis of a u-shaped linear piezoelectric ultrasonic motor using longitudinal transducers. Sensors 2018, 18, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Fan, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Hong, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, D. Design and experimental research of a novel stick-slip type piezoelectric actuator. Micromachines 2017, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, R.; Okamoto, T.; Higuchi, T.; Hamamatsu, A. Development of smooth impact drive mechanism (SIDM)—Proposal of driving mechanism and basic performance. J. Jpn. Soc. Prec. Eng. 1999, 65, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Sueyoshi, H. Konica Minolta Technology Report; Konica Minolta Inc.: Tokyo, Japan, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, B.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L. A novel trans-scale precision positioning stage based on the stick-slip effect. Int. J. Intell. Mechatron. Robot. 2012, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrikanth, V.; Simha, K.; Bobji, M. Frictional force measurement during stick-slip motion of a piezoelectric walker. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT) IEEE, Seville, Spain, 17–19 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Hesselbach, J.; Kerle, H. Development of a two-degree-of-freedom piezoelectric rotary-linear actuator with high driving force and unlimited linear movement. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 035112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotondrabe, M.; Haddab, Y.; Lutz, P. Development, modeling, and control of a micro-/nanopositioning 2-dof stick–slip device. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2009, 14, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunstig, M.; Hemsel, T.; Sextro, W. Stick–slip and slip–slip operation of piezoelectric inertia drives. Part I: Ideal excitation. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 2013, 200, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Kaneko, J.; Azuma, T.; Ito, S.; Gao, W.; Lu, T.F. Design and construction of the motion mechanism of an XY micro-stage for precision positioning. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 201, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.smaract.com/linear-stages/product/slc-1720 (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Available online: https://www.attocube.com/en/products/nanopositioners/low-temperature-nanopositioners/anpx101reslt-linear-x-nanopositioner (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Chu, C.-L.; Fan, S.-H. A novel long-travel piezoelectric-driven linear nanopositioning stage. Precis. Eng. J. 2006, 30, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L. Movement modeling and testing of a novel trans-scale precision positioning stage based on the stick-slip effect. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 255, 484–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, D.; Konyo, M.; Nagano, H. Introducing whole finger effects in surface haptics: An extended stick-slip model incorporating finger stiffness. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2018, 11, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Zhu, J.; Gu, S.; Ru, C. Development of stick–slip nanopositioning stage capable of moving in vertical direction. Microsyst. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, B. A new methodology for developing flexure-hinged displacement amplifiers with micro-vibration suppression for a giant magnetostrictive micro drive system. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 263, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Sun, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z. The dynamics study of the stick-slip driving system based on LuGre dynamic friction model. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Beijing, China, 7–10 August 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 584–589. [Google Scholar]


| Researchers/Commercial Company | Main Characteristics of the Developed Stages | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimension & Weight | Travel Range | Resolution | Maximum Speed | Maximum Output Force | |
| Zhang et.al 2006 | - | - | 26 nm, 0.019° | 7.2 mm/s | 2.09 N |
| Rakotondrade et al. | 20 × 20 × 20 mm3 | 50 mm, 360° | 70 nm, 0.001° | 1.8 mm/s, 20°/s | 150 mN |
| Shimizu et al. | 24 × 24 × 5 mm3 | 2 mm | 10 nm | 5 mm/s | 60 mN |
| SmarAct GmbH (SLC-1720) | 22 × 17 × 8.5 mm3, 13 g | 12 mm | 1 nm (OL) 50 nm (CL) | >20 mm/s | 10 N |
| Attocube Inc. (ANPx101) | 24 × 24 × 11 mm3, 20 g | 5 mm | 200 nm | 3 mm/s | 1 N |
| Hinges | L (mm) | h (mm) | T (mm) | Theoretical Stiffness (N/μm) | FEA Simulation Stiffness (N/μm) | Maximum Stress (Mpa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 14 | 4 | 0.6 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| B | 4 | 4 | 0.6 | 3.888 | 3.777 | 36.2 |
| C | 1.5 | 4 | 0.4 | 10.771 | 10.652 | 351.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Pan, P.; Wang, Y.; Gu, S.; Zhai, R.; Pang, M.; Liu, X.; Ru, C. A Novel Stick-Slip Nanopositioning Stage Integrated with a Flexure Hinge-Based Friction Force Adjusting Structure. Micromachines 2020, 11, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11080765
Zhu J, Pan P, Wang Y, Gu S, Zhai R, Pang M, Liu X, Ru C. A Novel Stick-Slip Nanopositioning Stage Integrated with a Flexure Hinge-Based Friction Force Adjusting Structure. Micromachines. 2020; 11(8):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11080765
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Junhui, Peng Pan, Yong Wang, Sen Gu, Rongan Zhai, Ming Pang, Xinyu Liu, and Changhai Ru. 2020. "A Novel Stick-Slip Nanopositioning Stage Integrated with a Flexure Hinge-Based Friction Force Adjusting Structure" Micromachines 11, no. 8: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11080765
APA StyleZhu, J., Pan, P., Wang, Y., Gu, S., Zhai, R., Pang, M., Liu, X., & Ru, C. (2020). A Novel Stick-Slip Nanopositioning Stage Integrated with a Flexure Hinge-Based Friction Force Adjusting Structure. Micromachines, 11(8), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11080765







