Low-Cost Microbolometer Type Infrared Detectors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory and Development Trends
2.1. Basics of Microbolometer
2.2. Development Trends
3. Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)-Compatible Microbolometer Pixel
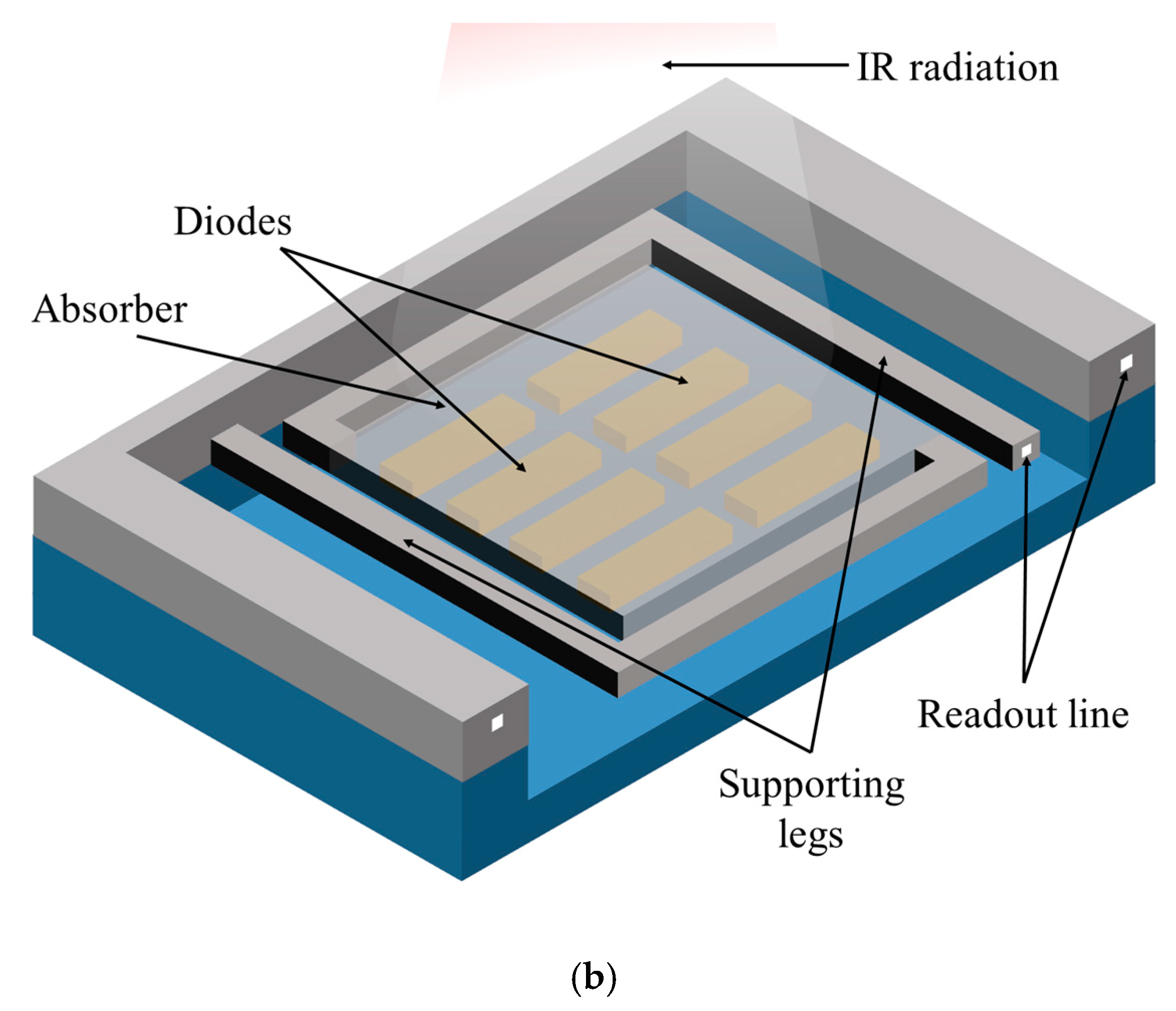
3.1. The Resistance Type Microbolometer Pixel
- The p+/n−well (2,3), gate oxide (4), and polysilicon (5) are fabricated on the substrate (1) via lithography, deposition, ion implantation, and annealing in order to form the transistor.
- Deposit SiO2 (6) as the isolation layer, then etch and deposit W (7) to form the contacts. Afterwards the metal interconnect layer Metal 1 (and the subsequent metal interconnection layers in the active region as well) is formed by depositing Al (8) as the connection of the read-out circuit.
- Deposit SiO2 (6) and then form the W (7) vias. The Al (8) in metal interconnect layer Metal 2 is deposited as the sacrificial layer in the sensor region.
- Deposit SiO2 (6), form the W (7) vias, and then deposit Al (8) for the interconnect layer Metal 3 to form the thermistor in the sensor region.
- Deposit SiO2/Si3N4 (6,9) to protect the device. Then dry etch the SiO2/Si3N4 over the pad area and expose the sacrificial layer.
- Use photoresist (10) to protect the pad area during the post-CMOS etching. Use the phosphoric acid solution to etch the sacrificial layer to form the cavity and expose the microbridge structure.
3.2. The Diode Type Microbolometer Pixel
3.3. Improvement in Absorber for Small Pixel Structure
4. Read-Out Integrated Circuit (ROIC)
4.1. Read-Out Circuit (ROC)
4.2. Analog-to-Digital Convertor (ADC)
5. Focal Plane Array (FPA)
6. Vacuum Packaging Technology
7. Limitation and Future Trends
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogalski, A. Infrared Detectors; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rogalski, A. HgCdTe infrared detector material: History, status and outlook. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 2267–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhan, R.K.; Dhar, V. Recent infrared detector technologies, applications, trends and development of HgCdTe based cooled infrared focal plane arrays and their characterization. Opto Electron. Rev. 2019, 27, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyniuk, P.; Rogalski, A. Quantum-dot infrared photodetectors: Status and outlook. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2008, 32, 89–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, A. Quantum well photoconductors in infrared detector technology. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 4355–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogalski, A. Infrared detectors: An overview. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2002, 43, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crastes, A.; Tissot, J.-L.; Guimond, Y.; Antonello, P.C.; Leleve, J.; Lenz, H.-J.; Potet, P.; Yon, J.-J. Low cost uncooled IRFPA and molded IR lenses for enhanced driver vision. Opt. Syst. Des. 2004, 5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregowski, P. Infrared detector arrays in the detection, automation and robotics-trends and development perspectives. Meas. Autom. Monit. 2018, 64, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, E.S. The infrared pioneers—III. Samuel Pierpont Langley. Infrared Phys. 1963, 3, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.M.; Beratan, H.R.; Owen, R.A.; Corbin, M.; McKenney, S. Uncooled thermal imaging at Texas Instruments. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s 1993 International Symposium on Optics, Imaging, and Instrumentation, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–16 July 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, R.; Han, C.; Kruse, P. Integrated uncooled infrared detector imaging arrays. In Proceedings of the Technical Digest IEEE Solid-State Sensor and Actuator Workshop, Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, 22–25 June 1992; pp. 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Tsukamoto, N.; Itoh, S.; Chiba, K.; Endoh, T.; Nakazato, A.; Okuyama, K.; Kumazawa, Y.; Hijikawa, M. Infrared focal plane array incorporating silicon IC process compatible bolometer. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1996, 43, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Ueno, M.; Endo, K.; Nakaki, Y.; Hata, H.; Sone, T.; Kimata, M. Low-cost 320 × 240 uncooled IRFPA using conventional silicon IC process. Opto Electron. Rev. 1999, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Ueno, M.; Nakaki, Y.; Endo, K.; Ohta, Y.; Nakanishi, J.; Kosasayama, Y.; Yagi, H.; Sone, T.; Kimata, M. Performance of 320 × 240 uncooled IRFPA with SOI diode detectors. In Proceedings of the SPIE International Symposium on Optical Science and Technology, San Diego, CA, USA, December 2000; Volume 4130, pp. 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, M.; Kosasayama, Y.; Sugino, T.; Nakaki, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Inoue, H.; Kama, K.; Seto, T.; Takeda, M.; Kimata, M. 640 × 480 pixel uncooled infrared FPA with SOI diode detectors. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense and Security, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 March–1 April 2005; Volume 5783, pp. 566–577. [Google Scholar]
- Kimata, M.; Ueno, M.; Takeda, M.; Seto, T. SOI diode uncooled infrared focal plane arrays. In Proceedings of the SPIE Integrated Optoelectronic Devices, San Jose, CA, USA, 1 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, T.; Kama, K.; Kimata, M.; Takeda, M.; Hata, H.; Nakaki, Y.; Inoue, H.; Kosasayama, Y.; Ohta, Y.; Fukumoto, H. 160 × 120 Uncooled IRFPA for Small JR Camera. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE Conference on Sensors, Daegu, South Korea, 22–25 October 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Takamuro, D.; Maegawa, T.; Sugino, T.; Kosasayama, Y.; Ohnakado, T.; Hata, H.; Ueno, M.; Fukumoto, H.; Ishida, K.; Katayama, H. Development of new SOI diode structure for beyond 17 μm pixel pitch SOI diode uncooled IRFPAs. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 25–29 April 2011; Volume 8012. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, D.; Maegawa, T.; Ohta, Y.; Kosasayama, Y.; Ohnakado, T.; Hata, H.; Ueno, M.; Ohji, H.; Sato, R.; Katayama, H. Two-million-pixel SOI diode uncooled IRFPA with 15 µm pixel pitch. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 25–26 April 2012; Volume 8353. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, D.; Kosasayama, Y.; Takikawa, T.; Hata, H.; Takenaga, T.; Satake, T.; Yamashita, K.; Suzuki, D. Implementation of SOI diode uncooled IRFPA in TEC-less and shutter-less operation. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 April 2018; Volume 10624. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Ou, W.; Ming, A.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X. Design and analysis of a high fill-factor SOI diode uncooled infrared focal plane array. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 065004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Zhu, H.; Liu, M.; Wei, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Uncooled infrared detector based on silicon diode Wheatstone bridge. Microsyst. Technol. Micro Nanosyst. Inf. Storage Process. Syst. 2017, 23, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezcan, D.; Kocer, F.; Akin, T. An uncooled microbolometer infrared detector in any standard CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the International Conference On Solid-State Sensors&Actuators (TRANSDUCERS’99), Sendai, Japan, 7–10 June 1999; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Mastrangelo, C.H. A CMOS uncooled heat-balancing infrared imager. IEEE J. Solid State Circ. 2000, 35, 527–535. [Google Scholar]
- Tezcan, D.S.; Eminoglu, S.; Akar, O.S.; Akin, T. A low cost uncooled infrared microbolometer focal plane array using the CMOS n-well layer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Interlaken, Switzerland, 25–25 June 2001; pp. 566–569. [Google Scholar]
- Tezcan, D.S.; Eminoglu, S.; Akar, O.S.; Akin, T. Uncooled microbolometer infrared focal plane array in standard CMOS. In Proceedings of the SPIE Symposium on Integrated Optics, San Jose, CA, USA, 15 May 2001; Volume 4288, pp. 112–121. [Google Scholar]
- Eminoglu, S.; Tanrikulu, M.Y.; Tezcan, D.S.; Akin, T. Low-cost small-pixel uncooled infrared detector for large focal plane arrays using a standard CMOS process. In Proceedings of the the SPIE AeroSense 2002, Orlando, FL, USA, 1–5 April 2002; Volume 4721, pp. 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Eminoglu, S.; Tezcan, D.S.; Tanrikulu, M.Y.; Akin, T. Low-cost uncooled infrared detectors in CMOS process. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2003, 109, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansi, M.V.; Brookfield, M.; Porter, S.G.; Edwards, I.; Bold, B.; Shannon, J.; Lambkin, P.; Mathewson, A. AUTHENTIC: A very low-cost infrared detector and camera system. In Proceedings of the SPIE International Symposium on Optical Science and Technology, Seattle, WA, USA, 7–11 July 2002; Volume 4820, pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Tezcan, D.S.; Eminoglu, S.; Akin, T. A low-cost uncooled infrared microbolometer detector in standard CMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2003, 50, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socher, E.; Sinai, Y.; Nemirovsky, Y. A low-cost CMOS compatible serpentine-structured polysilicon-based microbolometer array. In Proceedings of the TRANSDUCERS’03, 12th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Digest of Technical Papers (Cat. No. 03TH8664), Boston, MA, USA, 8–12 June 2003; Volume 1, pp. 320–323. [Google Scholar]
- CHEN, E.-Z.; Liang, P.-Z. Infrared microbolometer of lateral polysilicon p (+) p (-) n (+) junction based on standard CMOS processes. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2005, 3, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Eminoglu, S.; Tanrikulu, M.Y.; Akin, T. A low-cost 128 × 128 uncooled infrared detector array in CMOS process. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaki, H.; Honda, H.; Fujiwara, I.; Yagi, H.; Ishii, K.; Sasaki, K. A 160 × 120 pixel uncooled TEC-less infrared radiation focal plane array on a standard ceramic package. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 13 April 2009; Volume 7298. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, H.; Funaki, H.; Fujiwara, I.; Yagi, H.; Ishii, K.; Suzuki, K.; Sasaki, K.; Ogata, M.; Ueno, R.; Kwon, H. A 320 × 240 pixel uncooled TEC-less infrared radiation focal plane array with the reset noise canceling algorithm. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 April 2010; Volume 7660. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, R.; Honda, H.; Kwon, H.; Ishii, K.; Ogata, M.; Yagi, H.; Fujiwara, I.; Suzuki, K.; Sasaki, K.; Funaki, H. Uncooled Infrared Radiation Focal Plane Array with Low Noise Pixel Driving Circuit. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2010, 93, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujiwara, I.; Sasaki, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yagi, H.; Kwon, H.; Honda, H.; Ishii, K.; Ogata, M.; Atsuta, M.; Ueno, R. Scale down of pn junction diodes of an uncooled IR-FPA for improvement of the sensitivity and thermal time response by 0.13-µm CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 25–29 April 2011; Volume 8012. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, H.; Suzuki, K.; Ishii, K.; Yagi, H.; Honda, H.; Atsuta, M.; Fujiwara, I.; Sasaki, K.; Ogata, M.; Ueno, R. A SOI-based CMOS-MEMS IR image sensor with partially released reference pixels. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 025028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibing, W.; Dapeng, C.; Anjie, M.; Wen, O.; Zhanfeng, L. Integration of uncooled diode infrared focal plane array. Infrared Laser Eng. 2011, 40, 997–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Tepegoz, M.; Kucukkomurler, A.; Tankut, F.; Eminoglu, S.; Akin, T. A miniature low-cost LWIR camera with a 160 × 120 microbolometer FPA. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Baltimore, MD, USA, 6–8 May 2014; Volume 9070. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, N.; Tang, Z.; Yu, J.; Huang, Z. A low-cost infrared absorbing structure for an uncooled infrared detector in a standard CMOS process. J. Semicond. 2014, 35, 034014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Huang, Z.; Tang, Z. A double-sacrificial-layer uncooled infrared microbolometer in a standard CMOS process. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2015-2015 IEEE region 10 conference, Macao, China, 1–4 November 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, N.; Yu, J.; Tang, Z. An uncooled infrared microbolometer array for low-cost applications. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 1247–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Luo, M.; Si, W.; Yan, F.; Ji, X. Design of microbolometer by polycrystalline silicon in standard CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the China Semiconductor Technology International Conference, Shanghai, China, 18–19 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Akin, T. Low-cost LWIR-band CMOS infrared (CIR) microbolometers for high volume applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2020; pp. 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Tankut, F.; Cologlu, M.H.; Askar, H.; Ozturk, H.; Dumanli, H.K.; Oruc, F.; Tilkioglu, B.; Ugur, B.; Akar, O.S.; Tepegoz, M. An 80 × 80 microbolometer type thermal imaging sensor using the LWIR-band CMOS infrared (CIR) technology. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Anaheim, CA, USA, 9–13 April 2017; Volume 10177. [Google Scholar]
- Foote, M.; Gaalema, S. Progress toward high-performance thermopile imaging arrays. In Proceedings of the SPIE Aerospace/Defense Sensing, Simulation, and Controls, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 April 2001; Volume 4369. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Xiong, B.; Wang, Y. Modeling of front-etched micromachined thermopile IR detector by CMOS technology. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2010, 19, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufelbuhl, A.; Schneeberger, N.; Munch, U.; Waelti, M.; Paul, O.; Brand, O.; Baltes, H.; Menolfi, C.; Huang, Q.; Doering, E. Uncooled low-cost thermal imager based on micromachined CMOS integrated sensor array. IEEE/ASME J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2001, 10, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xiong, B.; Wang, Y. Micromachined thermopile IR detector module with high performance. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2011, 23, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, A.J. Applications of pyroelectric materials in array-based detectors. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2011, 58, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger, V.; Shnider, M.; Sriram, S.; Dooley, D.; Stout, M. Thin Film Lithium Tantalate (TFLT) Pyroelectric Detectors. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–25 January 2012; Volume 8261. [Google Scholar]
- Suen, J.Y.; Fan, K.; Montoya, J.; Bingham, C.; Stenger, V.; Sriram, S.; Padilla, W.J. Multifunctional metamaterial pyroelectric infrared detectors. Optica 2017, 4, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, A.J. Pyroelectric sensor arrays for detection and thermal imaging. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 April–3 May2013; Volume 8704. [Google Scholar]
- Benford, D.; Allen, C.; Kutyrev, A.; Moseley, S.; Shafer, R.; Chervenak, J.; Grossman, E.; Irwin, K.; Martinis, J.; Reintsema, C. Superconducting transition edge sensor bolometer arrays for submillimeter astronomy. In Proceedings of the 11th Intl Symp. on Space Terahertz Tech., Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1–3 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.T.; Richards, P.L.; Nam, S.W.; Cabrera, B.; Irwin, K.D. A superconducting bolometer with strong electrothermal feedback. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 1801–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominic, J.B.; Johannes, G.S.; Gordon, J.S.; Lyman, P.; Moseley, J.S.H.; Kent, D.I.; James, A.C.; Christine, A.A. Design and fabrication of two-dimensional superconducting bolometer arrays. In Proceedings of the SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation, Glasgow, UK, 21–25 June 2004; Volume 5498. [Google Scholar]
- Zmuidzinas, J.; Richards, P.L. Superconducting detectors and mixers for millimeter and submillimeter astrophysics. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 1597–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimata, M. Uncooled infrared focal plane arrays. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 13, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, D.; Ray, M.; Wyles, J.; Hewitt, C.; Wyles, R.; Gordon, E.; Almada, K.; Sessler, T.; Baur, S.; van Lue, D.; et al. 640 × 512 17 µm microbolometer FPA and sensor development. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense and Security Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 10–12 April 2007; Volume 6542. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Han, C.-J.; Skidmore, G. Overview of DRS uncooled VOx infrared detector development. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 061017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.M.; Panjwani, D.; Ginn, J.; Warren, A.P.; Long, C.; Figuieredo, P.; Smith, C.; Nath, J.; Perlstein, J.; Walter, N. Dual band sensitivity enhancements of a VO x microbolometer array using a patterned gold black absorber. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissot, J.-L.; Rothan, F.; Vedel, C.; Vilain, M.; Yon, J.-J. LETI/LIR’s amorphous silicon uncooled microbolometer development. In Proceedings of the SPIE Aerospace/Defense Sensing and Controls, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 April 1998; Volume 3379. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Yue, R.; Liu, L. Fabrication and characterization of integrated uncooled infrared sensor arrays using a-Si thin-film transistors as active elements. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, J.-L.; Tinnes, S.; Durand, A.; Minassian, C.; Robert, P.; Vilain, M.; Yon, J.-J. High-performance uncooled amorphous silicon video graphics array and extended graphics array infrared focal plane arrays with 17-μm pixel pitch. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 061006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklaus, F.; Decharat, A.; Jansson, C.; Stemme, G. Performance model for uncooled infrared bolometer arrays and performance predictions of bolometers operating at atmospheric pressure. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2008, 51, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, P.W. Uncooled Thermal Imaging: Arrays, Systems, and Applications; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 51, p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, J.M. Thermal Imaging Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Yoon, J.; Yoon, E.; Ju, S.; Yong, Y.; Lee, W.; Kim, S. A high fill-factor IR bolometer using multi-level electrothermal structures. In Proceedings of the International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 December 1998; pp. 463–466. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, D.; Ray, M.; Wyles, R.; Asbrock, J.; Lum, N.; Wyles, J.; Hewitt, C.; Kennedy, A.; van Lue, D.; Anderson, J.; et al. High-sensitivity 25-micron microbolometer FPAs. In Proceedings of the SPIE AeroSense 2002, Orlando, FL, USA, 1–5 April 2002; Volume 4721. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, N. Study on the Microbolometer in a Standard CMOS Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Erturk, O.; Akin, T. Design and implementation of high fill-factor structures for low-cost CMOS microbolometers. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Belfast, UK, 21–25 June 2018; pp. 692–695. [Google Scholar]
- Tanrikulu, M.Y. Three-level microbolometer structures: Design and absorption optimization. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 083102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger, N.; Paul, O.; Baltes, H. Spectral infrared absorption of CMOS thin film stacks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 21 June 1999; pp. 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M. Research on Microbolometers Based on Standard Integrated Circuit Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, M.; Kaneda, O.; Ishikawa, T.; Yamada, K.; Yamada, A.; Kimata, M.; Nunoshita, M. Monolithic uncooled infrared image sensor with 160 by 120 pixels. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s 1995 International Symposium on Optical Science, Engineering, and Instrumentation, San Diego, CA, USA, 5 October 1995; Volume 2552. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, A.; Suzuki, M.; Asahi, R.; Tabata, O.; Sugiyama, S. Infrared linear image sensor using a poly-Si pn junction diode array. Infrared Phys. 1992, 33, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, E.H.; Reay, R.J.; Storment, C.; Kovacs, G.T.A. Micromachined thermally isolated circuits. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1997, 58, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, A.; Martyniuk, P.; Kopytko, M. Challenges of small-pixel infrared detectors: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 046501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, S. Controlling thermal emission of phonon by magnetic metasurfaces. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Qu, C.; Almasri, M.; Kinzel, E. Design and analysis of frequency-selective surface enabled microbolometers. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–21 April 2016; Volume 9819. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Zhang, C.; Ren, F.; Yang, Q.; Lin, X.; Yan, F.; Ji, X. Metasurface-coupled microbolometers in CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the Applied Computational Electromagnetic Society Symposium, Beijing, China, 29 July−1 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, A.; Koppula, A.; Alkorjia, O.; Liu, T.; Kinzel, E.; Almasri, M. Metasurface integrated microbolometers. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Research and Applications of Photonics in Defense Conference (RAPID), Miramar Beach, FL, USA, 19–21 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, C.; Ajmera, S.; Brady, J.; Fagan, T.; McCardel, W.; Morgan, D.; Schimert, T.; Syllaios, A.J.; Taylor, M. Small Pixel a-Si/a-SiGe Bolometer Focal Plane Array Technology at L-3 Communications. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 April 2010; Volume 7660. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Tsukamoto, N.; Itoh, S.; Chiba, K.; Endoh, T.; Nakazato, A.; Okuyama, K.; Kumazawa, Y.; Hijikawa, M. Influence of bias-heating on a titanium bolometer infrared sensor. In Proceedings of the SPIE AeroSense’97, Orlando, FL, USA, 13 August 1997; Volume 3061, pp. 198–209. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, Y.; Woo, D.H.; Lee, H.C. TEC-less ROIC with self-bias equalization for microbolometer FPA. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Eminoglu, S.; Gulden, M.A.; Bayhan, N.; Incedere, O.S.; Soyer, S.T.; Ustundag, C.M.; Isikhan, M.; Kocak, S.; Turan, O.; Yalcin, C.; et al. MT3825BA: A 384×288-25µm ROIC for Uncooled Microbolometer FPAs. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5–9 May 2014; Volume 9070. [Google Scholar]
- Tissot, J.-L.; Chatard, J.-P.; Fieque, B.; Legras, O. High-Performance and Low-Thermal Time Constant Amorphous Silicon-Based 320 × 240 Uncooled Microbolometer IRFPA. In Proceedings of the SPIE Photonics Asia, Beijing, China, 8 November 2004; Volume 5640. [Google Scholar]
- Tissot, J.L.; Trouilleau, C.; Fieque, B.; Crastes, A.; Legras, O. Uncooled microbolometer detector: Recent developments at ULIS. Opto Electron. Rev. 2006, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Moezzi, M. A mismatch compensated readout IC for an uncooled microbolometer infrared FPA. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2020, 123, 153263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lv, Q. A versatile CMOS readout integrated circuit for microbolometric infrared focal plane arrays. Optik 2013, 124, 4639–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchagaspanian, M.; Villard, P.; Dupont, B.; Chammings, G.; Martin, J.; Pistre, C.; Lattard, D.; Chantre, C.; Arnaud, A.; Yon, J. Design of ADC in 25 µm pixels pitch dedicated for IRFPA image processing at LETI. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense and Security Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 10–12 April 2007; Volume 6542. [Google Scholar]
- Weiler, D.; Hochschulz, F.; Würfel, D.; Lerch, R.; Geruschke, T.; Wall, S.; Heß, J.; Wang, Q.; Vogt, H. Uncooled digital IRFPA-family with 17 μm pixel-pitch based on amorphous silicon with massively parallel Sigma-Delta-ADC readout. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5 May 2014; Volume 9070. [Google Scholar]
- Weiler, D.; Russ, M.; Würfel, D.; Lerch, R.; Yang, P.; Bauer, J.; Vogt, H. A digital 25 µm pixel-pitch uncooled amorphous silicon TEC-Less VGA IRFPA with massive parallel sigma-delta-ADC readout. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 April 2010; Volume 7660. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, P.; Dupont, B.; Pochic, D. Design trade-offs in ADC architectures dedicated to uncooled infrared focal plane arrays. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense and Security Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–21 March 2008; Volume 6940. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, B.; Robert, P.; Dupret, A.; Villard, P.; Pochic, D. Model based on-chip 13bits ADC design dedicated to uncooled infrared focal plane arrays. In Proceedings of the SPIE Optics/Photonics in Security and Defence, Florence, Italy, 17–18 September 2007; Volume 6737. [Google Scholar]
- Shafique, A.; Ceylan, Ö.; Yazici, M.; Kaynak, M.; Gurbuz, Y. A low-power CMOS readout IC with on-chip column-parallel SAR ADCs for microbolometer applications. In Proceedings of the SPIE. Defense + Security, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 April 2018; Volume 10624. [Google Scholar]
- Scribner, D.A.; Kruer, M.R.; Killiany, J.M. Infrared focal plane array technology. Proc. IEEE 1991, 79, 66–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compact LWIR-Thermal Camera Core: Boson. Available online: www.flir.com (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Kimata, M.; Tokuda, T.; Tsuchinaga, A.; Matsumura, T.; Abe, H.; Tokashiki, N. Vacuum packaging technology for uncooled infrared sensor. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2010, 5, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Han, C.J.; Skidmore, G.; Cook, G.; Kubala, K.; Bates, R.; Temple, D.; Lannon, J.; Hilton, A.; Glukh, K.; et al. Low-cost uncooled VOx infrared camera development. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 April–3 May 2013; Volume 8704. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, J.; Schimert, T.; Ratcliff, D.; Gooch, R.; Ritchey, B.; McCardel, P.; Rachels, K.; Ropson, S.; Wand, M.; Weinstein, M.; et al. Advances in amorphous silicon uncooled IR systems. In Proceedings of the SPIE AeroSense’99, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 April 1999; Volume 3698. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, A.; Masini, P.; Lamb, M.; Hamers, J.; Kocian, T.; Gordon, E.; Parrish, W.; Williams, R.; LeBeau, T. Advanced uncooled sensor product development. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Baltimore, MD, USA, 20–24 April 2015; Volume 9451. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, G.; Rabaud, W.; Yon, J.-J.; Carle, L.; Goudon, V.; Vialle, C.; Becker, S.; Hamelin, A.; Arnaud, A. Current progress on pixel level packaging for uncooled IRFPA. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 25–26 April 2012; Volume 8353. [Google Scholar]
- Yon, J.; Dumont, G.; Goudon, V.; Becker, S.; Arnaud, A.; Cortial, S.; Tisse, C. Latest improvements in microbolometer thin film packaging: Paving the way for low-cost consumer applications. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5–9 May 2014; Volume 9084. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, G.; Arnaud, A.; Imperinetti, P.; Mottin, E.; Simoens, F.; Vialle, C.; Rabaud, W.; Grand, G.; Baclet, N. Innovative on-chip packaging applied to uncooled IRFPA. In Proceedings of the SPIE Photonics Asia 2007, Beijing, China, 11–15 November 2007; Volume 6835. [Google Scholar]










| Material | Resistivity (10−4 Ω∙cm, at 300 K) | TCR (%/K) |
|---|---|---|
| undoped polysilicon | 199 | −0.085 |
| n−polysilicon | 62.2 | −0.016 |
| Al | 0.03 | 0.38 |
| Ti | 1.2 | 0.25 |
| Reference | Analog Output Swing (V) | Power Dissipation (mW) | Integration Capacitance (pF) | Linearity | Supply Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| METU [87] | 2.5 | 85 | 1–32 (programmable) | 3.3 | |
| ULIS [88] | 2.8 | 150 | ≈1% | 5 | |
| ULIS [89] | 2.8 | 150 | <1% | 5 | |
| AUT [90] | 351 | 3.3 | |||
| WPU [91] | 2.7 | 29.8 | 10 | 5 |
| Effective Number of Bits | Signal-to-Noise Ratio | Differential Nonlinearity | Integral Nonlinearity | Total Harmonic Distortion | Power Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.9 | 79 dB | 0.76 | 4.9 | −72 dB | 95 mW |
| Reference | Material | Array Size | Pixel Size | ROIC Type | Frame Rate 1 | NETD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitsubishi [20] | Diode | 320 × 240 | 17 μm | CTIA | 60 Hz | 50 mK |
| MikroSens [45] | CMOS-compatible resistance | 120 × 160 | 35 μm | CTIA | 11 Hz | 117 mK |
| Toshiba [37] | Diode | 320 × 240 | 22 μm | GMI | 25 ms | 200 mK |
| Raytheon [60] | VOx | 640 × 512 | 20 μm | 30 Hz | <50 mK | |
| DRS [61] | VOx | 1024 × 768 | 17 μm | DI | 30 Hz | <50 mK |
| FLIR [99] | VOx | 640 × 512 | 12 μm | 60 Hz | <40 mK | |
| L-3 Communications [85] | a-Si/a-SiGe | 1024 × 768 | 17 μm | DI | 10 ms | 35 mK |
| ULIS [65] | a-Si | 1024 × 768 | 17 μm | CTIA | 30 Hz | 46 mK |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, H.; Luo, M.; Han, P.; Ji, X. Low-Cost Microbolometer Type Infrared Detectors. Micromachines 2020, 11, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11090800
Yu L, Guo Y, Zhu H, Luo M, Han P, Ji X. Low-Cost Microbolometer Type Infrared Detectors. Micromachines. 2020; 11(9):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11090800
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Le, Yaozu Guo, Haoyu Zhu, Mingcheng Luo, Ping Han, and Xiaoli Ji. 2020. "Low-Cost Microbolometer Type Infrared Detectors" Micromachines 11, no. 9: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11090800
APA StyleYu, L., Guo, Y., Zhu, H., Luo, M., Han, P., & Ji, X. (2020). Low-Cost Microbolometer Type Infrared Detectors. Micromachines, 11(9), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11090800





