Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Microneedle-Based Delivery Approaches
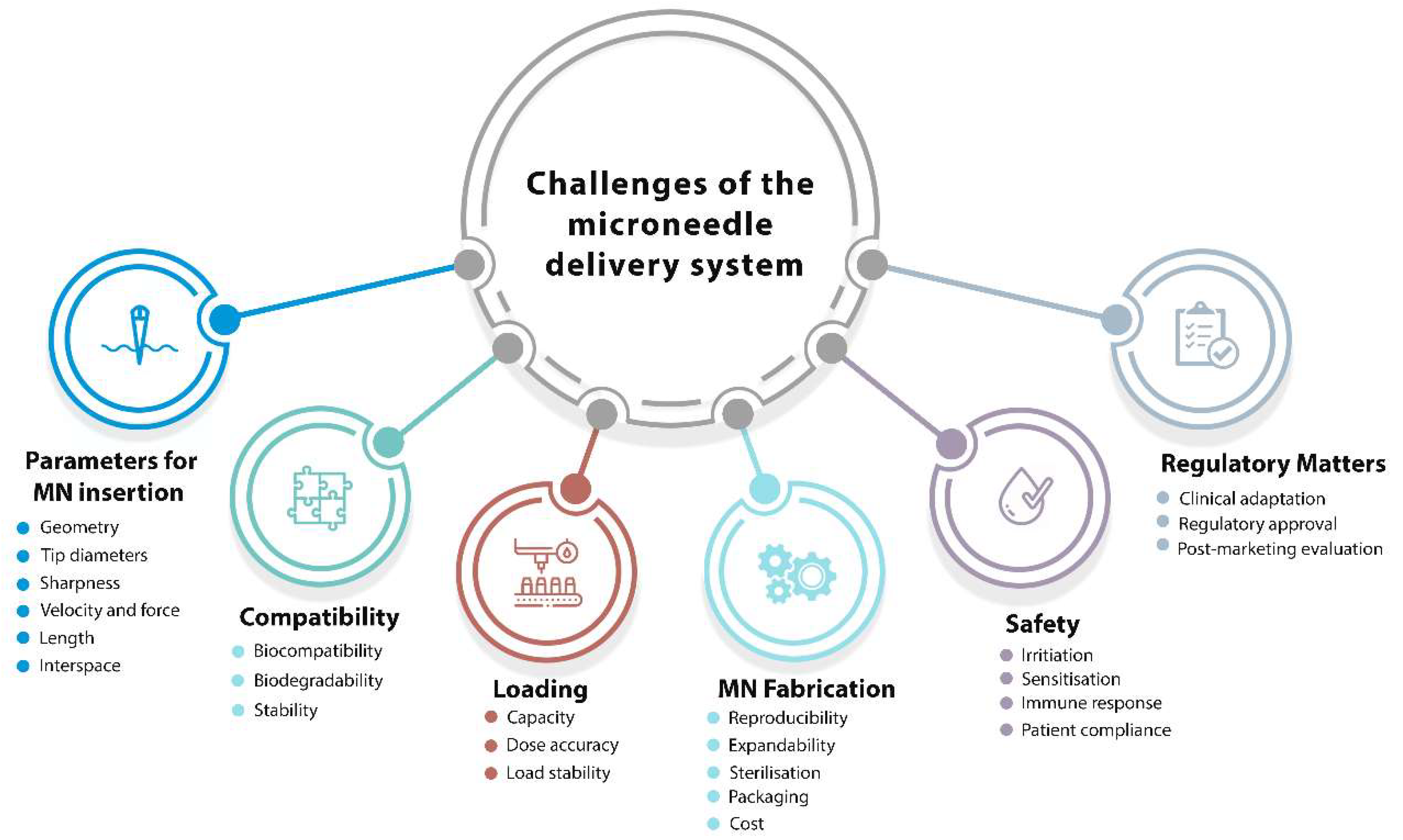
3. Challenges of the Microneedle Delivery System
3.1. Parameters Affecting MN Insertion
3.2. Biocompatibility, Biodegradability, and Stability
3.3. Loading Capacity and Dosage Accuracy
3.4. Skin Irritation and Recovery
3.5. Cost of Microneedle Fabrication
3.6. Sterilisation of the Microneedle Patches
3.7. Regulation of the Microneedle Patches
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ita, K. Transdermal Delivery of Drugs with Microneedles-Potential and Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alimardani, V.; Abolmaali, S.S.; Yousefi, G.; Rahiminezhad, Z.; Abedi, M.; Tamaddon, A.; Ahadian, S. Microneedle Arrays Combined with Nanomedicine Approaches for Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutics. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaume, S.E. The use of hydrofluoric acid in making glass microneedles. Science 1952, 116, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; McAllister, D.V.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated microneedles: A novel approach to transdermal drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcil, M.; Akman, G.; Klokkers, J.; Jeong, D.; Çelik, A. Efficacy of bioactive peptides loaded on hyaluronic acid microneedle patches: A monocentric clinical study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcil, M.; Akman, G.; Klokkers, J.; Jeong, D.; Çelik, A. Clinical efficacy of dissolvable microneedles armed with anti-melanogenic compounds to counter hyperpigmentation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, R.; Tohit, E.R.M.; Stanslas, J.; Mahmood, T.M.T. Recent advances and challenges in microneedle-mediated transdermal protein and peptide drug delivery. In Biomaterials and Bionanotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 495–525. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, S.; Ling, P.; Hashmi, G.; Reed, M.; Gaugler, R.; Trimmer, W. Genetic transformation of nematodes using arrays of micromechanical piercing structures. Biotechniques 1995, 19, 766–770. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, Y.K.; Choi, S.O.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Allen, M.G. Tapered conical polymer microneedles fabricated using an integrated lens technique for transdermal drug delivery. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2007, 54, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.P.; Murthy, N.; Prausnitz, M.R. Minimally invasive protein delivery with rapidly dissolving polymer microneedles. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.; Jung, H. Drawing lithography for microneedles: A review of fundamentals and biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7309–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.J.; Allender, C.J.; Brain, K.R.; Morrissey, A.; Birchall, J.C. Low temperature fabrication of biodegradable sugar glass microneedles for transdermal drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2012, 158, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.D.; Kim, M.; Yang, H.; Lee, K.; Jung, H. Droplet-born air blowing: Novel dissolving microneedle fabrication. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2013, 170, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchione, R.; Coppola, S.; Esposito, E.; Casale, C.; Vespini, V.; Grilli, S.; Ferraro, P.; Netti, P.A. Electro-drawn drug-loaded biodegradable polymer microneedles as a viable route to hypodermic injection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3515–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonificio, A.; Ghartey-Tagoe, E.; Gallorini, S.; Baudner, B.; Chen, G.; Singh, P.; O’Hagan, D.T.; Kommareddy, S. Fabrication of cell culture-derived influenza vaccine dissolvable microstructures and evaluation of immunogenicity in guinea pigs. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2930–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.C.; Ling, M.H.; Kusuma, S.J. Poly-γ-glutamic acid microneedles with a supporting structure design as a potential tool for transdermal delivery of insulin. Acta Biomater. 2015, 24, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; DiSanto, R.; Sun, W.; Ranson, D.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8260–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vrdoljak, A.; Allen, E.A.; Ferrara, F.; Temperton, N.J.; Crean, A.M.; Moore, A.C. Induction of broad immunity by thermostabilised vaccines incorporated in dissolvable microneedles using novel fabrication methods. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2016, 225, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Dave, K.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Microneedles in the clinic. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2017, 260, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pascual, C.; Lieu, C.; Oh, S.; Wang, J.; Zou, B.; Xie, J.; Li, Z.; Xie, J.; Yeomans, D.C.; et al. Analgesic Microneedle Patch for Neuropathic Pain Therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.C.; Lin, W.M.; Shu, J.C.; Tsai, S.W.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, M.T. Formulation of two-layer dissolving polymeric microneedle patches for insulin transdermal delivery in diabetic mice. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part. A 2017, 105, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, D.; Renaud, F.; Dewar, V.; Strodiot, L.; Wauters, F.; Janimak, J.; Shimada, T.; Nomura, T.; Kabata, K.; Kuruma, K.; et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen incorporated in dissolvable microneedle array patch is antigenic and thermostable. Biomaterials 2017, 145, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Hanne, N.J.; Cui, Z.; Qian, C.; Wang, C.; Xin, H.; Cole, J.H.; Gallippi, C.M.; et al. Thrombin-Responsive Transcutaneous Patch for Auto-Anticoagulant Regulation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandal, A.; Boopathy, A.V.; Lam, L.K.W.; Moynihan, K.D.; Welch, M.E.; Bennett, N.R.; Turvey, M.E.; Thai, N.; Van, J.H.; Love, J.C.; et al. Cell and fluid sampling microneedle patches for monitoring skin-resident immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.E.; Yin, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, S.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Duong, H.T.T.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.; et al. Enhanced Cancer Vaccination by In Situ Nanomicelle-Generating Dissolving Microneedles. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9702–9713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, P.; Yu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, Q.; Gu, Z. Ros-responsive microneedle patch for acne vulgaris treatment. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1800035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sulaiman, D.; Chang, J.Y.H.; Bennett, N.R.; Topouzi, H.; Higgins, C.A.; Irvine, D.J.; Ladame, S. Hydrogel-Coated Microneedle Arrays for Minimally Invasive Sampling and Sensing of Specific Circulating Nucleic Acids from Skin Interstitial Fluid. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9620–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economidou, S.N.; Pere, C.P.P.; Reid, A.; Uddin, M.J.; Windmill, J.F.C.; Lamprou, D.A.; Douroumis, D. 3D printed microneedle patches using stereolithography (SLA) for intradermal insulin delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 102, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Fakhraei Lahiji, S.; Jang, J.; Jang, M.; Jung, H. Micro-Pillar Integrated Dissolving Microneedles for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, H.; Liu, P.; Zhu, J.; Lan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Tao, J. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Dissolving Microneedle Patch Loaded with Methotrexate for Improved Treatment of Psoriasis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43588–43598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Danehy, R.; Cai, H.; Ao, Z.; Pu, M.; Nusawardhana, A.; Rowe-Magnus, D.; Guo, F. Microneedle Patch-Mediated Treatment of Bacterial Biofilms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14640–14646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Hegarty, C.; Casimero, C.; Davis, J. Electrochemically Controlled Dissolution of Nanocarbon-Cellulose Acetate Phthalate Microneedle Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 35540–35547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Bian, F.; Cai, L.; Zhao, Y. Encoded Microneedle Arrays for Detection of Skin Interstitial Fluid Biomarkers. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1902825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Morde, R.S.; Mariani, S.; La Mattina, A.A.; Vignali, E.; Yang, C.; Barillaro, G.; Lee, H. 4D printing of a bioinspired microneedle array with backward-facing barbs for enhanced tissue adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Wen, D.; Chan, A.; Gu, Z. Transdermal colorimetric patch for hyperglycemia sensing in diabetic mice. Biomaterials 2020, 237, 119782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ramirez, M.A.; Soto, F.; Wang, C.; Rueda, R.; Shukla, S.; Silva-Lopez, C.; Kupor, D.; McBride, D.A.; Pokorski, J.K.; Nourhani, A.; et al. Built-In Active Microneedle Patch with Enhanced Autonomous Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1905740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, T.; Pan, Q.; Ping, Y. Microneedle-assisted genome editing: A transdermal strategy of targeting NLRP3 by CRISPR-Cas9 for synergistic therapy of inflammatory skin disorders. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusama, S.; Sato, K.; Matsui, Y.; Kimura, N.; Abe, H.; Yoshida, S.; Nishizawa, M. Transdermal electroosmotic flow generated by a porous microneedle array patch. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Chew, S.W.T.; Zheng, M.; Lio, D.C.S.; Wiraja, C.; Mei, Y.; Ning, X.; Cui, M.; Than, A.; Shi, P.; et al. Cryomicroneedles for transdermal cell delivery. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.; Garland, M.J.; Migalska, K.; Majithiya, R.; McCrudden, C.M.; Kole, P.L.; Mahmood, T.M.; McCarthy, H.O.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.C.; Park, J.H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donnelly, R.F.; McCrudden, M.T.; Zaid Alkilani, A.; Larrañeta, E.; McAlister, E.; Courtenay, A.J.; Kearney, M.C.; Singh, T.R.; McCarthy, H.O.; Kett, V.L.; et al. Hydrogel-forming microneedles prepared from “super swelling” polymers combined with lyophilised wafers for transdermal drug delivery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zeng, M.; Shan, H.; Tong, C. Microneedle Patches as Drug and Vaccine Delivery Platform. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, B.K.; Kendall, M.A.F.; Williams, D.M.; Bett, A.J.; Dubey, S.; Gentzel, R.C.; Casimiro, D.; Forster, A.; Corbett, H.; Crichton, M.; et al. Immune response and reactogenicity of an unadjuvanted intradermally delivered human papillomavirus vaccine using a first generation Nanopatch™ in rhesus macaques: An exploratory, pre-clinical feasibility assessment. Vaccine: X 2019, 2, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.; Scoutaris, N.; Lamprou, D.; Mallinson, D.; Douroumis, D. Inkjet printing of insulin microneedles for transdermal delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daddona, P.E.; Matriano, J.A.; Mandema, J.; Maa, Y.F. Parathyroid hormone (1-34)-coated microneedle patch system: Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics for treatment of osteoporosis. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Luan, J.; Seth, A.; Liu, L.; You, M.; Gupta, P.; Rathi, P.; Wang, Y.; Cao, S.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Microneedle patch for the ultrasensitive quantification of protein biomarkers in interstitial fluid. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, D.V.; Wang, P.M.; Davis, S.P.; Park, J.H.; Canatella, P.J.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: Fabrication methods and transport studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13755–13760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, D.J.; Vines, J.B.; Park, H.; Lee, S.H. Microneedles: A versatile strategy for transdermal delivery of biological molecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, D.; Xuan, X.; He, H. Advances of Microneedles in Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, D.; Logan, K.A.; Sheng, Y.; Goa, J.; Farrell, S.; Dixon, D.; Callan, B.; McHale, A.P.; Callan, J.F. Rapid paper based colorimetric detection of glucose using a hollow microneedle device. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 547, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.M.; Tay, F.E.H.; Guo, D.G.; Xu, L.; Yap, K.L. A microfabricated electrode with hollow microneedles for ECG measurement. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 2009, 151, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, N.G.; Lai, L.; Tandon, S.; McCullough, M.P.; Kong, Y.; Kabbani, S.; Natrajan, M.S.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Immunologic mechanisms of seasonal influenza vaccination administered by microneedle patch from a randomized phase I trial. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ita, K. Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: Advances and challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraman, A.; Banga, A.K. Novel in situ forming hydrogel microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Moro-Oka, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Miyahara, Y.; Suganami, T.; Matsumoto, A. Smart Microneedle Fabricated with Silk Fibroin Combined Semi-interpenetrating Network Hydrogel for Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffarel-Salvador, E.; Brady, A.J.; Eltayib, E.; Meng, T.; Alonso-Vicente, A.; Gonzalez-Vazquez, P.; Torrisi, B.M.; Vicente-Perez, E.M.; Mooney, K.; Jones, D.S.; et al. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays Allow Detection of Drugs and Glucose In Vivo: Potential for Use in Diagnosis and Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eltayib, E.; Brady, A.J.; Caffarel-Salvador, E.; Gonzalez-Vazquez, P.; Zaid Alkilani, A.; McCarthy, H.O.; McElnay, J.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays: Potential for use in minimally-invasive lithium monitoring. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arb. Fur Pharm. Verfahr. E.V 2016, 102, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirbubalo, M.; Tucak, A.; Muhamedagic, K.; Hindija, L.; Rahić, O.; Hadžiabdić, J.; Cekic, A.; Begic-Hajdarevic, D.; Cohodar Husic, M.; Dervišević, A.; et al. 3D Printing-A “Touch-Button” Approach to Manufacture Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjar, A.; Huang, Y. Application of Micro-Scale 3D Printing in Pharmaceutics. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prausnitz, M.R. Engineering Microneedle Patches for Vaccination and Drug Delivery to Skin. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2017, 8, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizidou, E.Z.; Inoue, N.T.; Ashton-Barnett, J.; Barrow, D.A.; Allender, C.J. Evaluation of geometrical effects of microneedles on skin penetration by CT scan and finite element analysis. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arb. Fur Pharm. Verfahr. E.V 2016, 107, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q. Dissolving Microneedle Arrays with Optimized Needle Geometry for Transcutaneous Immunization. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 151, 105361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoudani, E.L.; Soltani, M. A new computational method of modeling and evaluation of dissolving microneedle for drug delivery applications: Extension to theoretical modeling of a novel design of microneedle (array in array) for efficient drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 150, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römgens, A.M.; Bader, D.L.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Baaijens, F.P.T.; Oomens, C.W.J. Monitoring the penetration process of single microneedles with varying tip diameters. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 40, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romani, N.; Thurnher, M.; Idoyaga, J.; Steinman, R.M.; Flacher, V. Targeting of antigens to skin dendritic cells: Possibilities to enhance vaccine efficacy. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makvandi, P.; Kirkby, M.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Shabani, M.; Yiu, C.K.Y.; Baghbantaraghdari, Z.; Jamaledin, R.; Carlotti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Mattoli, V.; et al. Engineering Microneedle Patches for Improved Penetration: Analysis, Skin Models and Factors Affecting Needle Insertion. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roxhed, N.; Gasser, T.C.; Griss, P.; Holzapfel, G.A.; Stemme, G. Penetration-enhanced ultrasharp microneedles and prediction on skin interaction for efficient transdermal drug delivery. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. A Jt. IEEE ASME Publ. Microstruct. Microactuators Microsens. Microsyst. 2007, 16, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, C. Structural characterization and in-vivo reliability evaluation of silicon microneedles. Biomed. Microdevices 2014, 16, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnik, D.; Možek, M.; Pečar, B.; Janež, A.; Urbančič, V.; Iliescu, C.; Vrtačnik, D. In Vivo Experimental Study of Noninvasive Insulin Microinjection through Hollow Si Microneedle Array. Micromachines 2018, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martanto, W.; Moore, J.S.; Couse, T.; Prausnitz, M.R. Mechanism of fluid infusion during microneedle insertion and retraction. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2006, 112, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. FDA Guidance. Use of International Standards. ISO 10993-1. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 1:Evaluation and Testing within a Risk Management Process; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2016.
- Zhu, D.D.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, B.L.; Hao, Y.Y.; Guo, X.D. Safety Assessment of Microneedle Technology for Transdermal Drug Delivery: A Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 2000033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.Y.; Ye, L.; Dong, K.; Compans, R.W.; Yang, C.; Prausnitz, M.R. Enhanced Stability of Inactivated Influenza Vaccine Encapsulated in Dissolving Microneedle Patches. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.J.; Kang, A.; Ahn, M.H.; Jun, H.; Baek, S.K.; Park, J.H.; Na, W.; Choi, S.O. Insertion-responsive microneedles for rapid intradermal delivery of canine influenza vaccine. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2018, 286, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Terry, R.N.; Tang, J.; Feng, M.R.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Rapidly separable microneedle patch for the sustained release of a contraceptive. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permana, A.D.; Nainu, F.; Moffatt, K.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Recent advances in combination of microneedles and nanomedicines for lymphatic targeted drug delivery. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 13, e1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sully, R.E.; Moore, C.J.; Garelick, H.; Loizidou, E.; Podoleanu, A.G.; Gubala, V. Nanomedicines and microneedles: A guide to their analysis and application. Anal. Methods Adv. Methods Appl. 2021, 13, 3326–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.B.; Goodson, J.L.; Chu, S.Y.; Rota, P.A.; Meltzer, M.I. Assessing the Potential Cost-Effectiveness of Microneedle Patches in Childhood Measles Vaccination Programs: The Case for Further Research and Development. Drugs RD 2016, 16, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.Y.; Bartsch, S.M.; Mvundura, M.; Jarrahian, C.; Zapf, K.M.; Marinan, K.; Wateska, A.R.; Snyder, B.; Swaminathan, S.; Jacoby, E.; et al. An economic model assessing the value of microneedle patch delivery of the seasonal influenza vaccine. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4727–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korkmaz, E.; Ozdoganlar, O.B. Dissolvable and Coated Microneedle Arrays: Design, Fabrication, Materials and Administration Methods. In Microneedling in Clinical Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Morrow, D.I.; Woolfson, A.D. Microneedle-Mediated Transdermal and Intradermal Drug Delivery; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Gadeela, P.R.; Thathireddy, P.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Microneedle-based drug delivery: Materials of construction. J. Chem. Sci. 2019, 131, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCrudden, M.T.; Alkilani, A.Z.; Courtenay, A.J.; McCrudden, C.M.; McCloskey, B.; Walker, C.; Alshraiedeh, N.; Lutton, R.E.; Gilmore, B.F.; Woolfson, A.D.; et al. Considerations in the sterile manufacture of polymeric microneedle arrays. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Ryu, H.R.; Roh, J.Y.; Park, J.H. Bleomycin-Coated Microneedles for Treatment of Warts. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Shayan, F.L.; Kim, S.; Huh, I.; Ma, Y.; Yang, H.; Kang, G.; Jung, H. Physicochemical study of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside loaded hyaluronic acid dissolving microneedles irradiated by electron beam and gamma ray. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González García, L.E.; MacGregor, M.N.; Visalakshan, R.M.; Ninan, N.; Cavallaro, A.A.; Trinidad, A.D.; Zhao, Y.; Hayball, A.J.D.; Vasilev, K. Self-sterilizing antibacterial silver-loaded microneedles. Chem. Commun. 2018, 55, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Mooney, K.; Caffarel-Salvador, E.; Torrisi, B.M.; Eltayib, E.; McElnay, J.C. Microneedle-mediated minimally invasive patient monitoring. Ther. Drug Monit. 2014, 36, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutton, R.E.; Moore, J.; Larrañeta, E.; Ligett, S.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle characterisation: The need for universal acceptance criteria and GMP specifications when moving towards commercialisation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avcil, M.; Çelik, A. Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111321
Avcil M, Çelik A. Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Micromachines. 2021; 12(11):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111321
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvcil, Muhammet, and Ayhan Çelik. 2021. "Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges" Micromachines 12, no. 11: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111321
APA StyleAvcil, M., & Çelik, A. (2021). Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Micromachines, 12(11), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111321





