An Electric Field Microsensor with Mutual Shielding Electrodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sensor Design
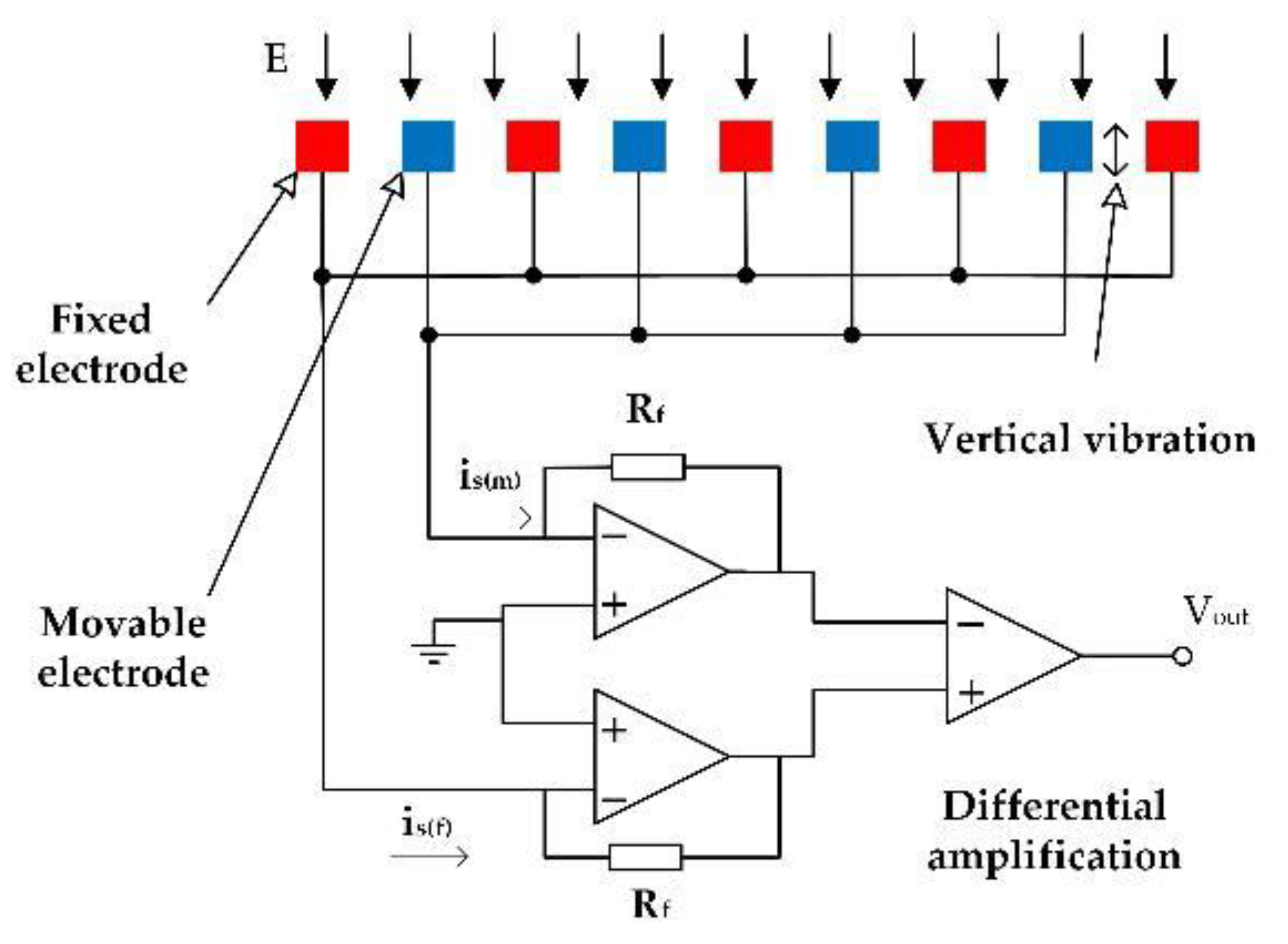
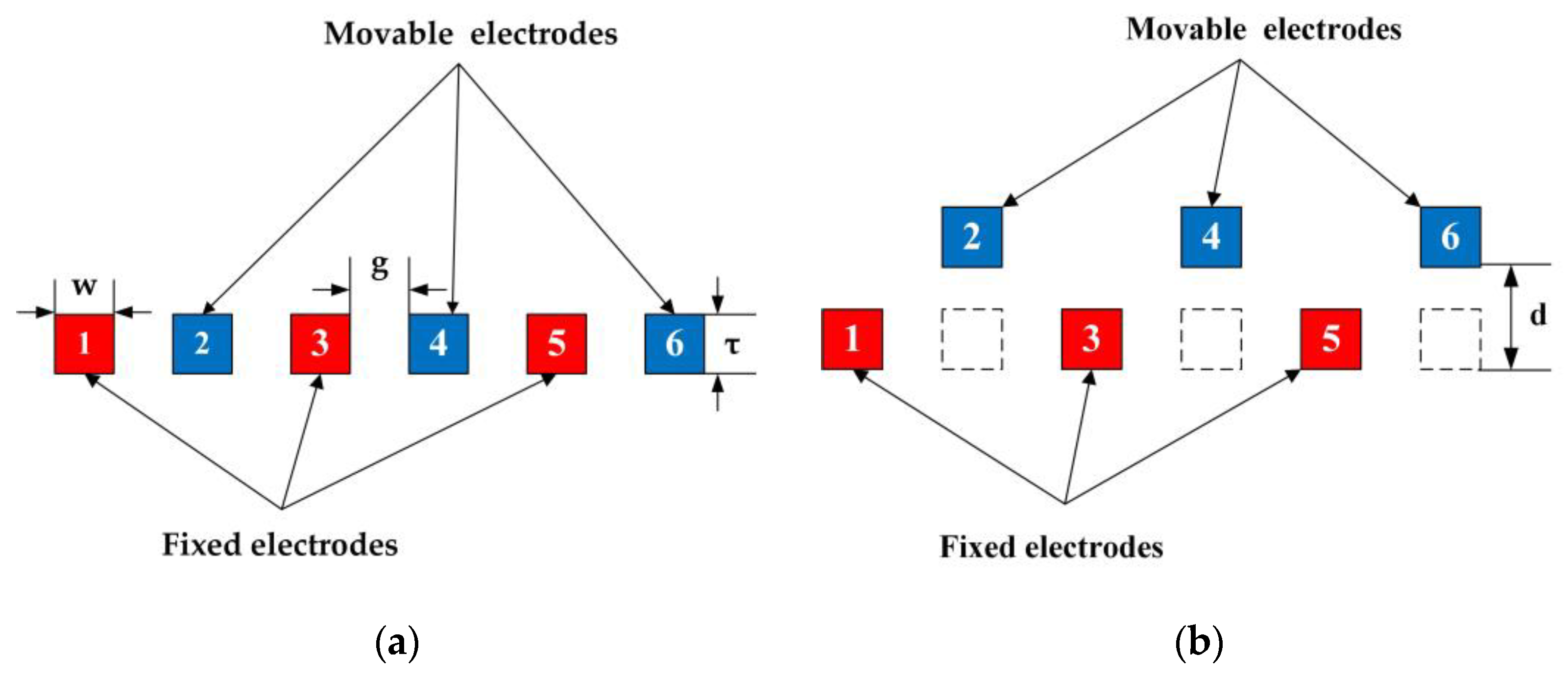
2.1. Structure Design
2.2. Working Principle
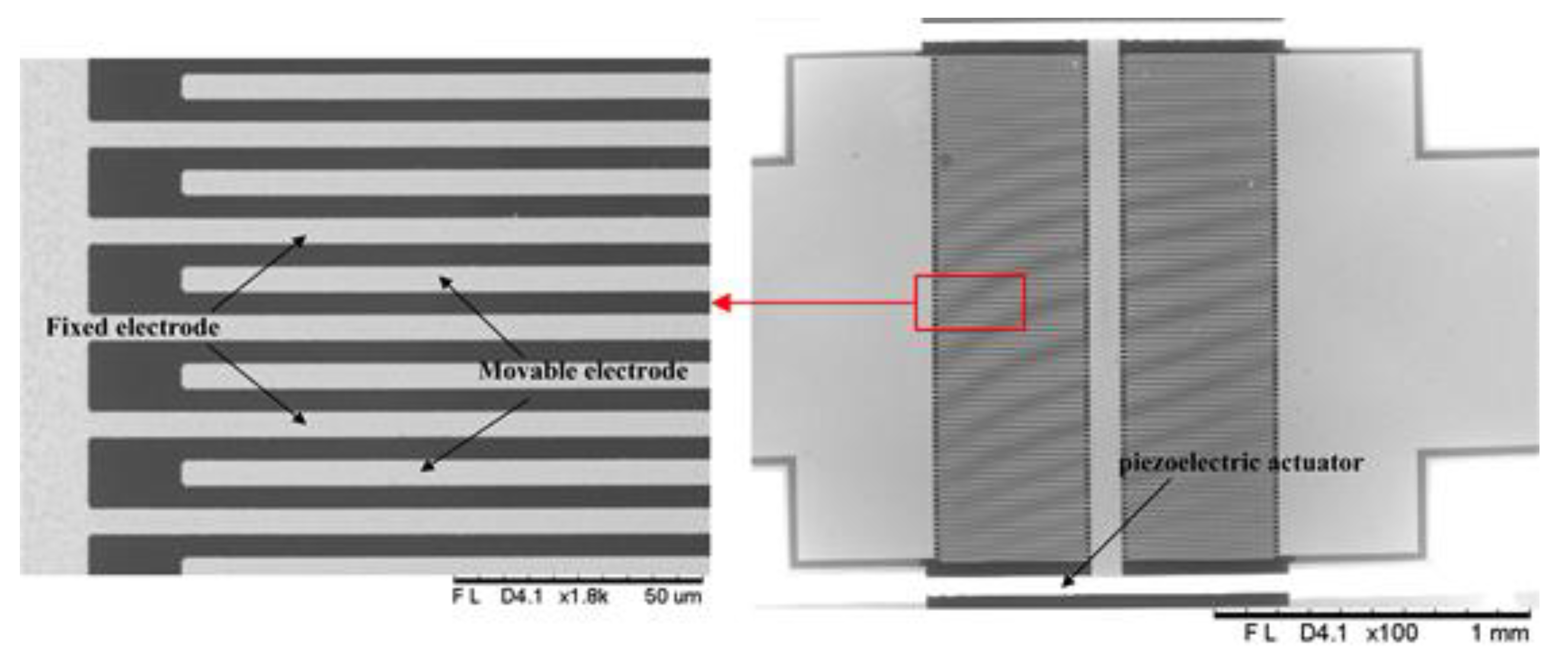
2.3. Electrode Design
3. Simulation
3.1. Simulation Model
3.2. Simulation Results
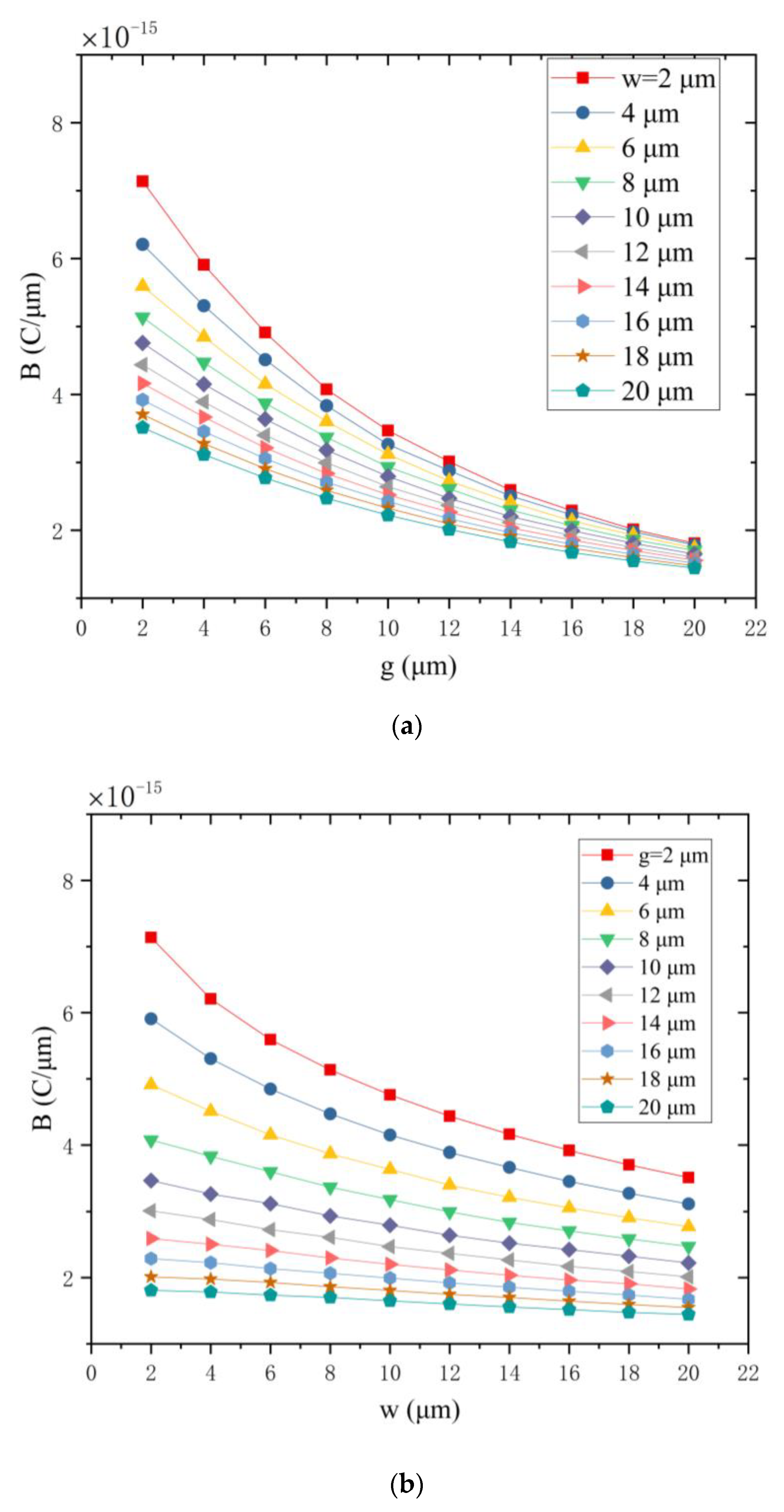
3.2.1. Electrode Width and Electrode Gap
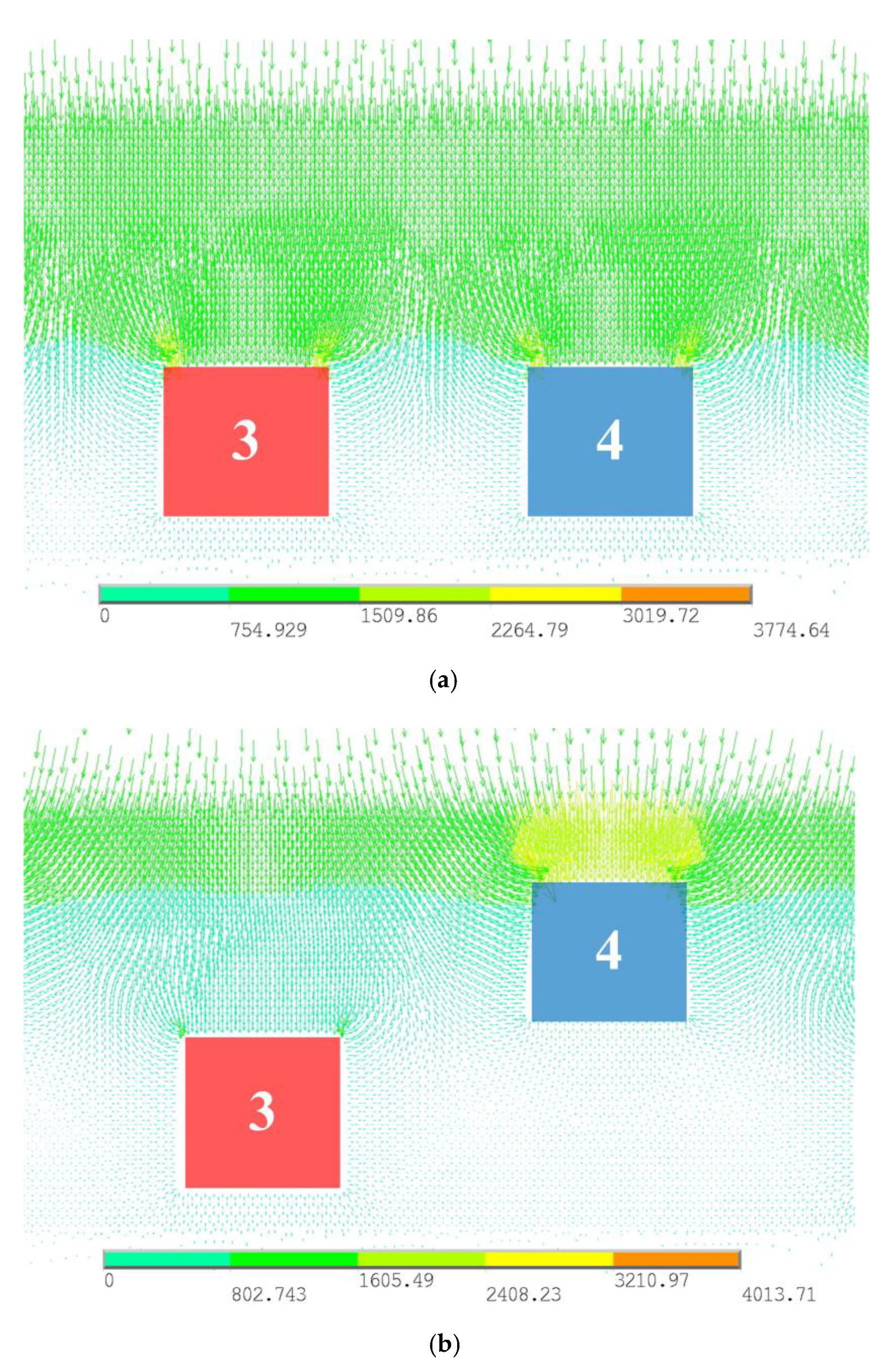
3.2.2. Electric Field Distribution
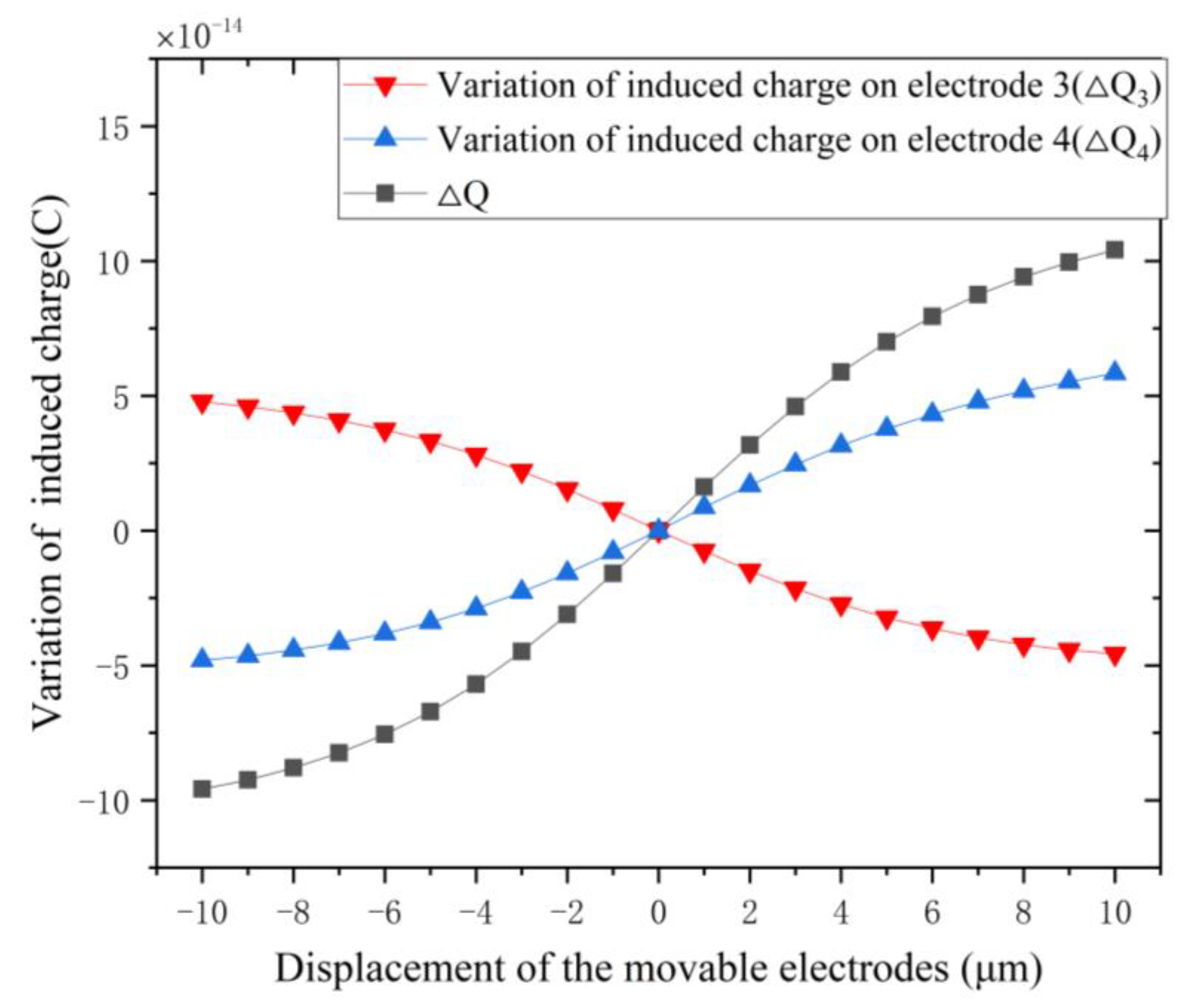
3.2.3. Variation of Induced Charge
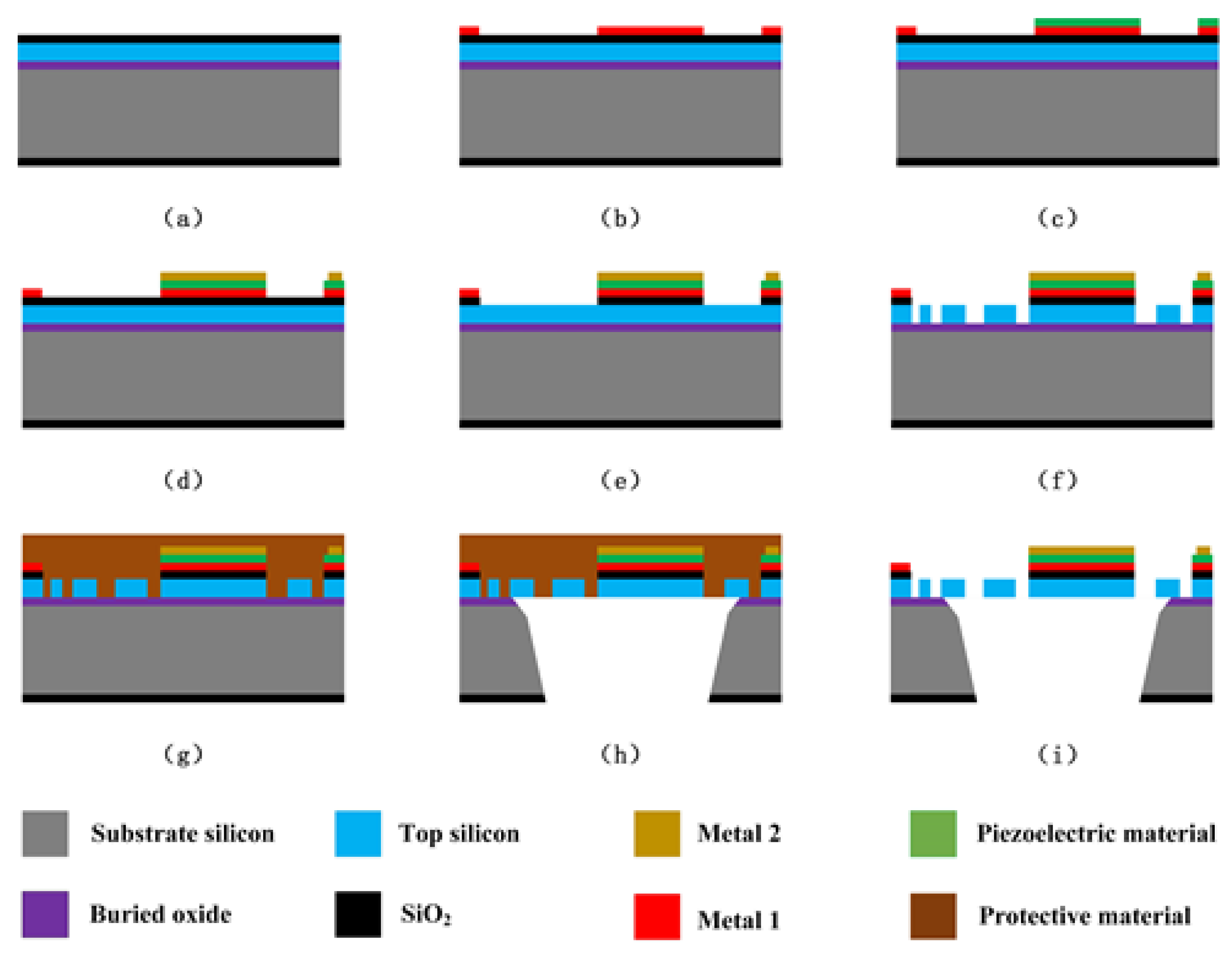
4. Fabrication
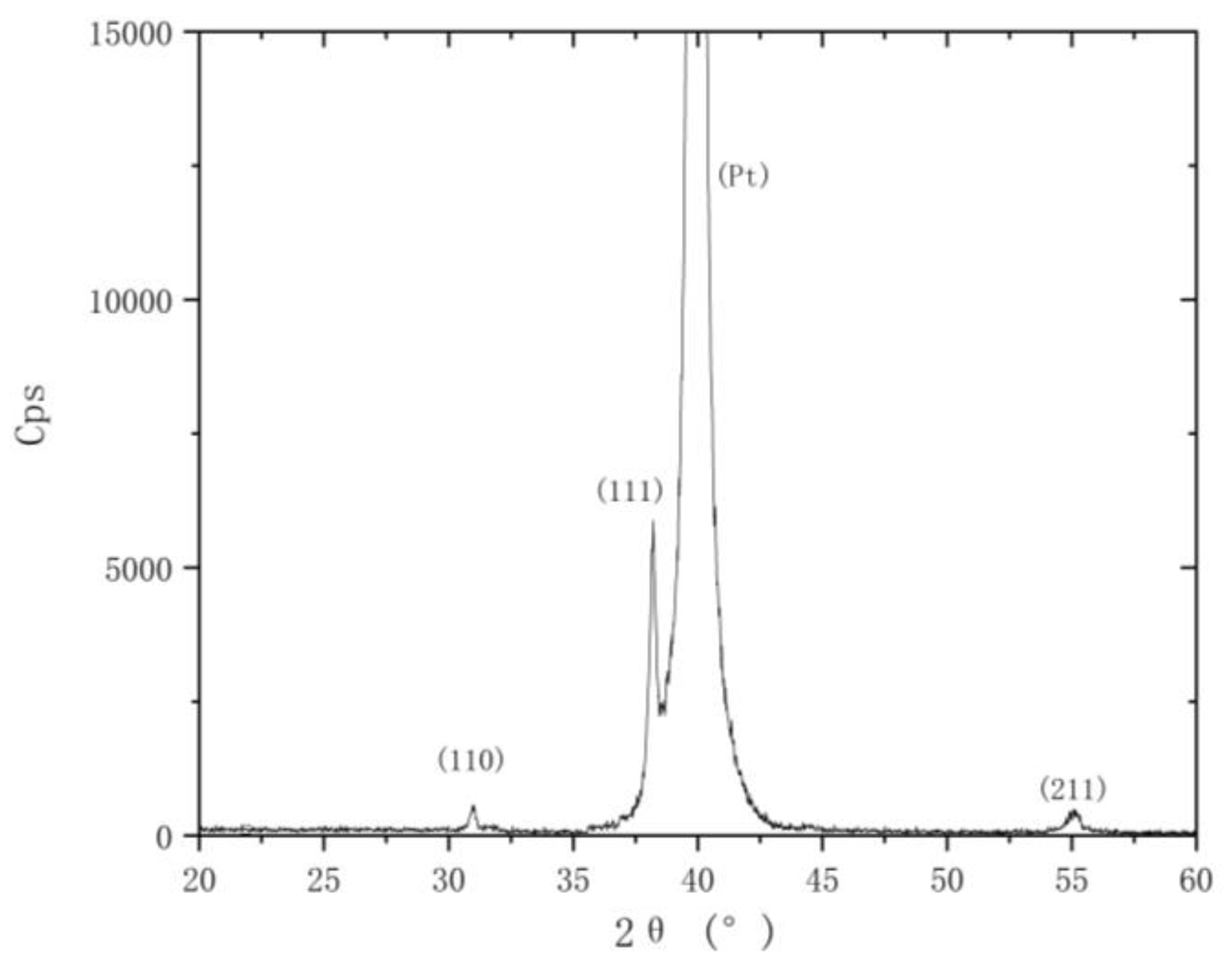
4.1. Preparation of Piezoelectric Material
4.2. Fabrication of Microsensor Chip
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, F.S.; Zhuang, H.C.; He, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.J.; Liu, Y.M.; Jiang, D.Z.; Qiu, X.G.; Chen, Z.Y. The principle of micro-rocket electric field instrument and its application. Chin. J. Geophys. 2000, 43, 616–620. [Google Scholar]
- Tant, P.; Bolsens, B.; Sels, T.; Van Dommelen, D.; Driesen, J.; Belmans, R. Design and application of a field mill as a high-voltage DC meter. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanya, J.; Bergas, J.; Hermoso, B. Electric field measurements at ground level as a basis of lightning hazard warning. J. Electrost. 2004, 60, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, A.; Mugnaini, M.; Vignoli, V.; Rocchi, S.; Perini, F.; Monari, J.; Schiaffino, M.; Fiocchi, F. Design, modeling, and test of a system for atmospheric electric field measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 2778–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, W.P.; Byerley, L.G. Electric field growth in thunderclouds. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 101, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizotto, R.; Mesquita, A.; Porto, R.W. Design and calibration of an atmospheric electric field sensor with wireless comunication. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Lightning Protection (XIII SIPDA), Balneario Camboriu, Brazil, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Michishita, K.; Ishii, M.; Hojo, J.I. Measurement of horizontal electric fields associated with distant cloud-to-ground strokes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 3861–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrard, C.A.; Gibson, J.R.; Jones, G.R.; Holt, L. Measurements of power system voltages using remote electric field monitoring. IEE Proc. Gener. Transm. Distrib. 1998, 145, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillancourt, G.H.; Carignan, S.; Jean, C. Experience with the detection of faulty composite insulators on high-voltage power lines by the electric field measurement method. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2002, 13, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthod, C.; Passard, M.; Bouillot, J.; Galez, C.; Farzaneh, M. High electric field measurement and ice detection using a safe probe near power installations. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2004, 113, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornfeldt, S.P. Dc-probes for electric field distribution measurements. Power Eng. Rev. IEEE 1991, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Muller, R.S. Micromechanical electrostatic voltmeter. In Proceedings of the 1991 International Conference on Solid-State Sensors and Actuators, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–27 June 1991; pp. 659–662. [Google Scholar]
- Horenstein, M.N.; Stone, P.R. A micro-aperture electrostatic field mill based on mems technology. J. Electrost. 2001, 51–52 (Suppl. C), 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, P.S.; Scott, K.L.; Muller, R.S.; Howe, R.T.; Yasaitis, J.A. Electrostatic charge and field sensors based on micromechanical resonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncin, A.; Shafai, C.; Swatek, D.R. Electric field sensor using electrostatic force deflection of a micro-spring supported membrane. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2005, 123–124 (Suppl. C), 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Peng, C.; Tao, H.; Ye, C.; Bai, Q.; Chen, S.; Xia, S. Thermally driven micro-electrostatic fieldmeter. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2006, 132, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Chen, X.; Ye, C.; Tao, H.; Cui, G.; Bai, Q.; Chen, S.; Xia, S. Design and testing of a micromechanical resonant electrostatic field sensor. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denison, T.; Jinbo, K.; Shafran, J.; Judy, M.; Lundberg, K. A self-resonant mems-based electrostatic field sensor with 4v/m/hz sensitivity. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Solid State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 February 2006; pp. 1121–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Bahreyni, B.; Wijeweera, G.; Shafai, C.; Rajapakse, A. Analysis and design of a micromachined electric-field sensor. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshi, K.; Syoji, O.; Masaharu, T.; Ryutaro, M.; Toshihiro, I. Microelectromechanical systems-based electrostatic field sensor using pb(zr,ti)o 3 thin films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 7533. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T.; Oyama, S.; Okada, H.; Makimoto, N.; Tanaka, K.; Itoh, T.; Maeda, R. An electrostatic field sensor driven by self-excited vibration of sensor/actuator integrated piezoelectric micro cantilever. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 25th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Paris, France, 29 January–2 February 2012; pp. 527–530. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Peng, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Fang, D.; Xia, S. A high sensitivity soi electric-field sensor with novel comb-shaped microelectrodes. In Proceedings of the 2011 16th International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, Beijing, China, 5–9 June 2011; pp. 1034–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Ghionea, S.; Smith, G.; Pulskamp, J.; Bedair, S.; Meyer, C.; Hull, D. Mems electric-field sensor with lead zirconate titanate (pzt)-actuated electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE sensors, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Peng, C.; Fang, D.; Wen, X.; Xia, S. Design, fabrication and application of an SOI-based resonant electric field microsensor with coplanar comb-shaped electrodes. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 266–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shafai, C.; Rajapakse, A.; Park, B.Y. Micromachined electric field mill employing a vertical moving shutter. Procedia Eng. 2014, 87 (Suppl. C), 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, K.; Tong, J.; Wang, Y.; Fang, D.; Xia, S. Electric field microsensor based on the structure of piezoelectric interdigitated cantilever beams. J. Electron. (China) 2014, 31, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.R.; De Bruyker, D.P.; Limb, S.J.; Amendt, E.M.; Overland, D.A. Vacuum steered-electron electric-field sensor. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shafai, C.; Rajapakse, A.; Liyanage, J.S.H.; Neusitzer, T.D. Micromachined AC/DC electric field sensor with modulated sensitivity. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2016, 245, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, A.; Steiner, H.; Schalko, J.; Jachimowicz, A.; Kohl, F.; Stifter, M.; Beigelbeck, R.; Keplinger, F.; Hortschitz, W. Distortion-free measurement of electric field strength with a MEMS sensor. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Peng, C.; Ren, R.; Ling, B.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, H.; Xia, S. A high sensitivity electric field microsensor based on torsional resonance. Sensors 2018, 18, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, M.; Li, S.; Lei, Z. Study of (111)-oriented PZT thin films prepared by a modified sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laishram, R.; Thakur, O.P. Nanostructured PZT/PT multilayered thin films prepared by sol–gel process. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Structural Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| width of fixed and movable electrodes | 5 µm |
| gap between fixed and movable electrodes | 5 µm |
| thickness of fixed and movable electrodes | 5 µm |
| length of fixed and movable electrodes | 500 µm |
| width of piezoelectric actuators | 50 µm |
| thickness of piezoelectric actuators | 0.6 µm |
| length of piezoelectric actuators | 550 µm |
| number of piezoelectric actuators | 4 |
| number of fixed electrodes | 84 × 2 |
| number of movable electrodes | 84 × 2 |
| d (μm) | ΔQ (× 10−14(C)) | ΔQ3 (× 10−14(C)) |
|---|---|---|
| −10 | −9.59 | 4.78 |
| −8 | −8.8 | 4.37 |
| −6 | −7.56 | 3.74 |
| −4 | −5.7 | 2.81 |
| −2 | −3.11 | 1.53 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 3.17 | −1.49 |
| 4 | 5.88 | −2.73 |
| 6 | 7.94 | −3.63 |
| 8 | 9.41 | −4.23 |
| 10 | 10.41 | −4.57 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, H.; Xia, S.; Chu, Z.; Ling, B.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. An Electric Field Microsensor with Mutual Shielding Electrodes. Micromachines 2021, 12, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040360
Lei H, Xia S, Chu Z, Ling B, Peng C, Zhang Z, Liu J, Zhang W. An Electric Field Microsensor with Mutual Shielding Electrodes. Micromachines. 2021; 12(4):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040360
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Hucheng, Shanhong Xia, Zhaozhi Chu, Biyun Ling, Chunrong Peng, Zhouwei Zhang, Jun Liu, and Wei Zhang. 2021. "An Electric Field Microsensor with Mutual Shielding Electrodes" Micromachines 12, no. 4: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040360
APA StyleLei, H., Xia, S., Chu, Z., Ling, B., Peng, C., Zhang, Z., Liu, J., & Zhang, W. (2021). An Electric Field Microsensor with Mutual Shielding Electrodes. Micromachines, 12(4), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040360






