Extreme Low-Resolution Activity Recognition Using a Super-Resolution-Oriented Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose an extreme low-resolution activity recognition approach aided by a super-resolution generative adversarial network.
- (2)
- A novel training strategy, called long-range temporal convolution, is used in the recognition module to learn action representations over a long temporal range.
- (3)
- Extensive experiments are conducted, which show that the performance of our approach outperforms several state-of-the-art methods by a large margin despite the fact that we use only RGB images as inputs to avoid the extraction of optical flow.
2. Related Work
2.1. General Activity Recognition
2.2. Low-Resolution Activity Recognition
2.3. Super-Resolution in Other Low-Resolution Recognition Field
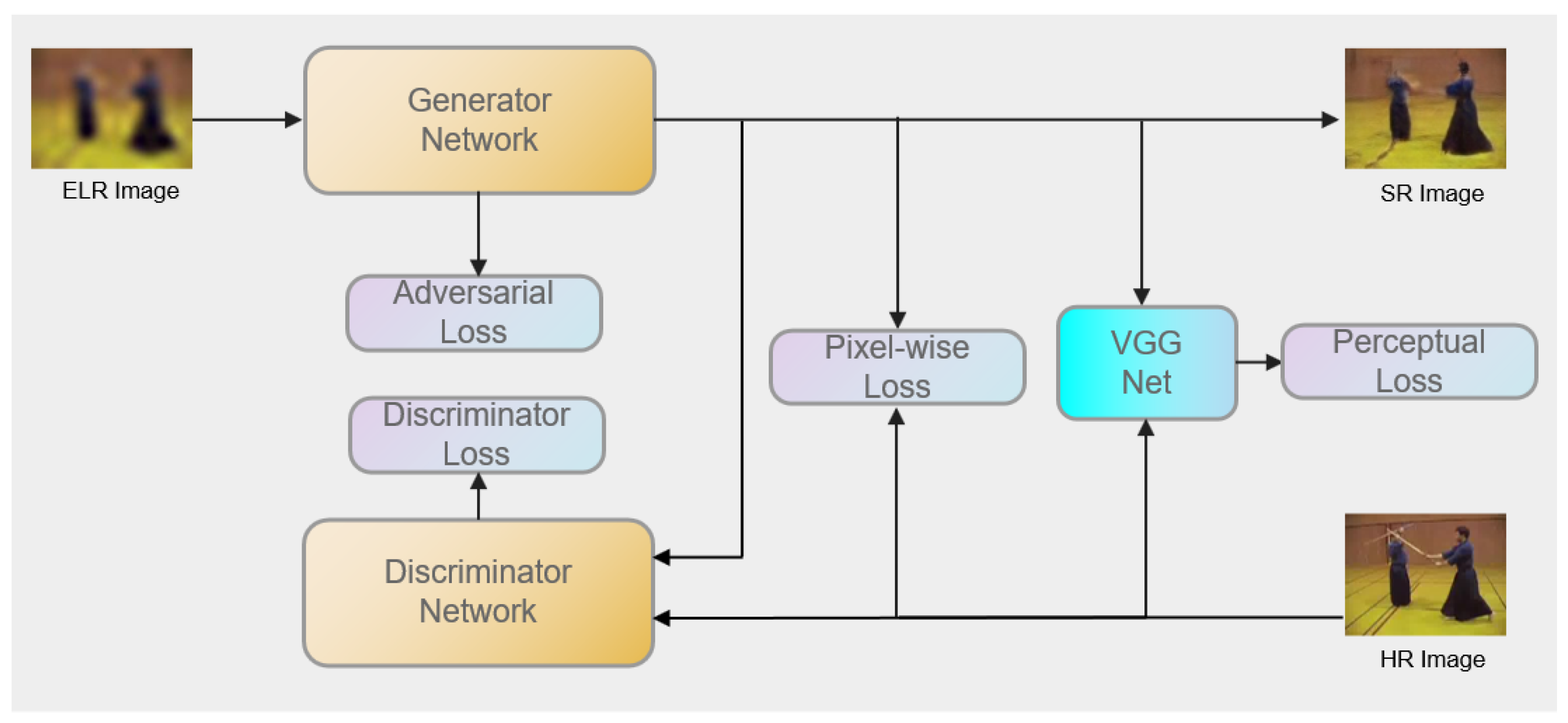
3. The Approach
3.1. Super-Resolution Module
3.1.1. Generative Adversarial Network
3.1.2. Network Architecture
3.1.3. The Loss Function for the Super-Resolution Module
3.2. Activity Recognition Module
3.3. Training Strategy
3.3.1. Data Augmentation
3.3.2. Long-Range Temporal Convolutions
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Implementation Details
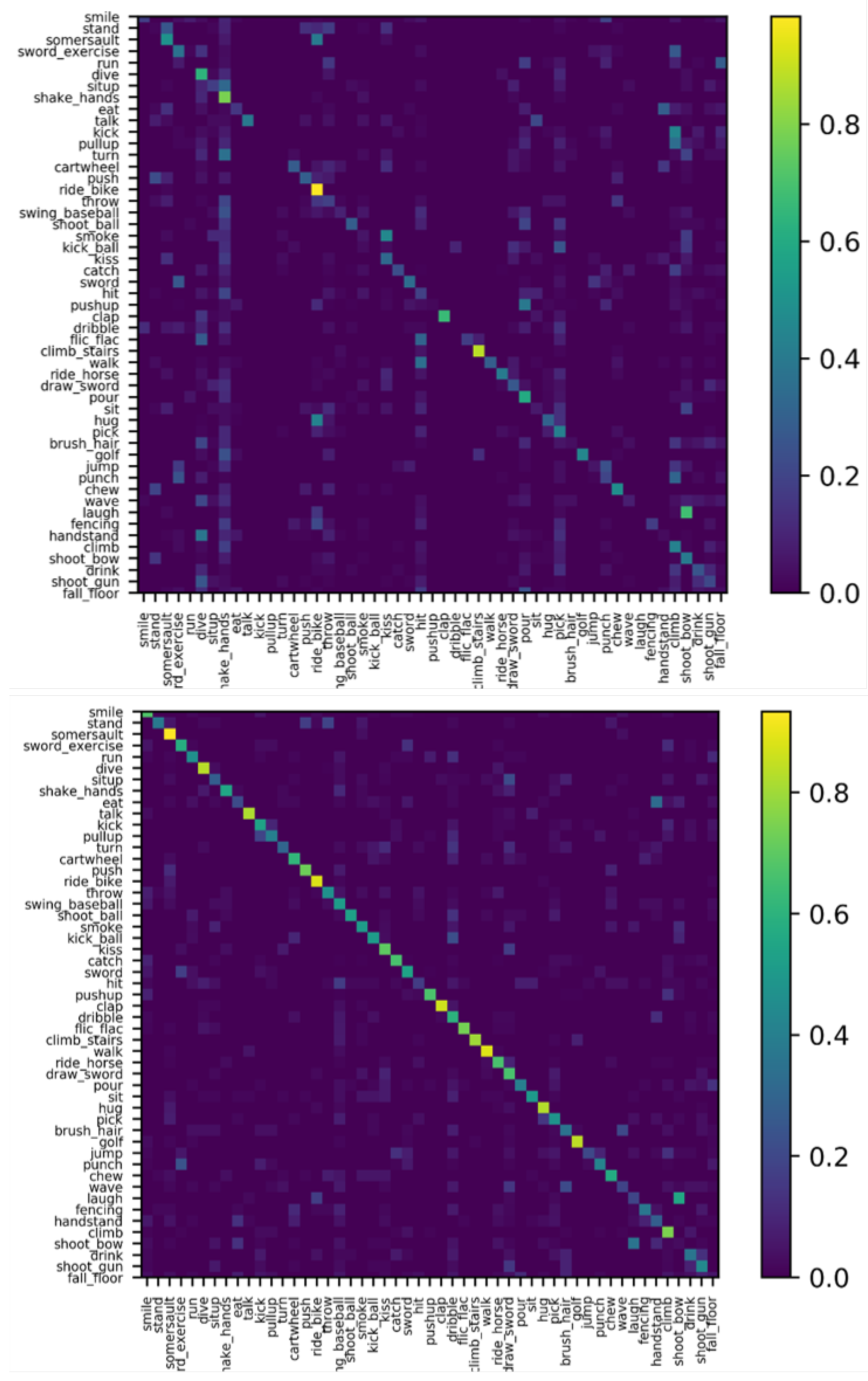
4.3. Ablation Studies
4.4. State-of-the-Art Comparison
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2199. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (CVPR), Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Konrad, J.; Ishwar, P. Semi-coupled two-stream fusion convnets for action recognition at extremely low resolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Santa Rose, CA, USA, 27–29 March 2017; pp. 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Sharghi, A.; Chen, X.; Crandall, D.J. Fully-coupled two-stream spatiotemporal networks for extremely low resolution action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 12–14 March 2018; pp. 1607–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Ryoo, M.; Kim, K.; Yang, H. Extreme low resolution activity recognition with multi-siamese embedding learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 7315–7322. [Google Scholar]
- Ataer-Cansizoglu, E.; Jones, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sullivan, A. Verification of very low-resolution faces using an identity-preserving deep face super-resolution network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.10974. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Ghanem, B. Sod-mtgan: Small object detection via multi-task generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 206–221. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, M.; Yang, F.; Bai, X.; Satoh, S. Cascaded SR-GAN for scale-adaptive low resolution person re-identification. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 3891–3897. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, U.; Rawat, Y.S.; Shah, M. Tinyvirat: Low-resolution video action recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 7387–7394. [Google Scholar]
- Laptev, I. On space-time interest points. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2005, 64, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, R.; Ravichandran, A.; Hager, G.; Vidal, R. Histograms of oriented optical flow and binet-cauchy kernels on nonlinear dynamical systems for the recognition of human actions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami beach, FL, USA, 20–21 June 2009; pp. 1932–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Klaser, A.; Marszałek, M.; Schmid, C. A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3D-gradients. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Leeds, UK, 3–9 September 2008; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Scovanner, P.; Ali, S.; Shah, M. A 3-dimensional sift descriptor and its application to action recognition. In Proceedings of the ACM international conference on Multimedia, Augsburg, Germany, 24–29 September 2007; pp. 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Schmid, C. Action recognition with improved trajectories. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Sydney, Australia, 3–6 December 2013; pp. 3551–3558. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Karpathy, A.; Toderici, G.; Shetty, S.; Leung, T.; Sukthankar, R.; Fei-Fei, L. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 1725–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Van Gool, L. Temporal segment networks for action recognition in videos. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 2740–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soomro, K.; Zamir, A.R.; Shah, M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.0402. [Google Scholar]
- Kuehne, H.; Jhuang, H.; Garrote, E.; Poggio, T.; Serre, T. HMDB: A large video database for human motion recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Bercelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2556–2563. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6299–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L.; Ray, J.; LeCun, Y.; Paluri, M. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6450–6459. [Google Scholar]
- Ryoo, M.; Rothrock, B.; Fleming, C.; Yang, H.J. Privacy-preserving human activity recognition from extreme low resolution. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; pp. 4255–4262. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4681–4690. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Qiao, Y.; Change Loy, C. ESRGAN: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Shao, Z.; Ran, M.; Zhou, J.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous denoising and super-resolution of optical coherence tomography images based on generative adversarial network. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 12289–12307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haris, M.; Shakhnarovich, G.; Ukita, N. Deep back-projection networks for super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 1664–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur-Martineau, A. The relativistic discriminator: A key element missing from standard GAN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.00734. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, K.; Kataoka, H.; Satoh, Y. Can spatiotemporal 3D CNNs retrace the history of 2D CNNs and imagenet? In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 6546–6555. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, G.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwashita, Y.; Takamine, A.; Kurazume, R.; Ryoo, M.S. First-person animal activity recognition from egocentric videos. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 4310–4315. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Polyak, B.T.; Juditsky, A.B. Acceleration of stochastic approximation by averaging. SIAM J. Control. Optim. 1992, 30, 838–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, L.; Guo, C.; Gu, H.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. Pseudo low rank video representation. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 85, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Part | Output Size | F | N |
|---|---|---|---|
| conv1 | 8 × 56 × 56 | 64 | conv 7 × 7 × 7, 64 |
| conv2_x | 8 × 56 × 56 | 128 | 8 |
| conv3_x | 4 × 28 × 28 | 256 | 24 |
| conv4_x | 2 × 14 × 14 | 512 | 36 |
| conv5_x | 1 × 7 × 7 | 1024 | 3 |
| Super-Resolution | Long-Range | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Module | Temporal Convolutions | HMDB51 | UCf101 |
| × | × | 45.8% | 65.3% |
| √ | × | 46.6% | 66.2% |
| × | √ | 53.3% | 69.6% |
| √ | √ | 54.6% | 71.1% |
| Super-Resolution | Long-Range Temporal | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|
| Module | Convoluton Module | TinyVIRAT |
| × | × | 73.89% |
| √ | × | 74.11% |
| × | √ | 79.02% |
| √ | √ | 79.77% |
| Methods | Modalities | Input Frames | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| pLRN + Tennet [35] | RGB | - | 21.7% |
| ISR [23] | RGB | - | 28.68% |
| Semi-Coupled [3] | RGB + Optical flow | 64 | 29.2% |
| Multi-Siamese [5] | RGB + Optical flow | 64 | 37.7% |
| DVSR [9] | RGB | 16 | 41.63% |
| Fully-Coupled [4] | RGB + Optical flow | 64 | 44.96% |
| Ours | RGB | 16 | 46.4% |
| Ours | RGB | 64 | 54.4% |
| Method | Input Size | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Bicubic I3D | 14 × 14 | 14.1% |
| DVSR | 14 × 14 | 68.2% |
| Prog.DVSR | 14 × 14 | 70.6% |
| Ours | 12 × 16 | 66.2% |
| Ours + LRTC. | 12 × 16 | 71.1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, M.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z. Extreme Low-Resolution Activity Recognition Using a Super-Resolution-Oriented Generative Adversarial Network. Micromachines 2021, 12, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060670
Hou M, Liu S, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Feng Z. Extreme Low-Resolution Activity Recognition Using a Super-Resolution-Oriented Generative Adversarial Network. Micromachines. 2021; 12(6):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060670
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Mingzheng, Song Liu, Jiliu Zhou, Yi Zhang, and Ziliang Feng. 2021. "Extreme Low-Resolution Activity Recognition Using a Super-Resolution-Oriented Generative Adversarial Network" Micromachines 12, no. 6: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060670
APA StyleHou, M., Liu, S., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y., & Feng, Z. (2021). Extreme Low-Resolution Activity Recognition Using a Super-Resolution-Oriented Generative Adversarial Network. Micromachines, 12(6), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060670






