Interaction Mechanism of Thermal and Mechanical Field in KDP Fly-Cutting Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
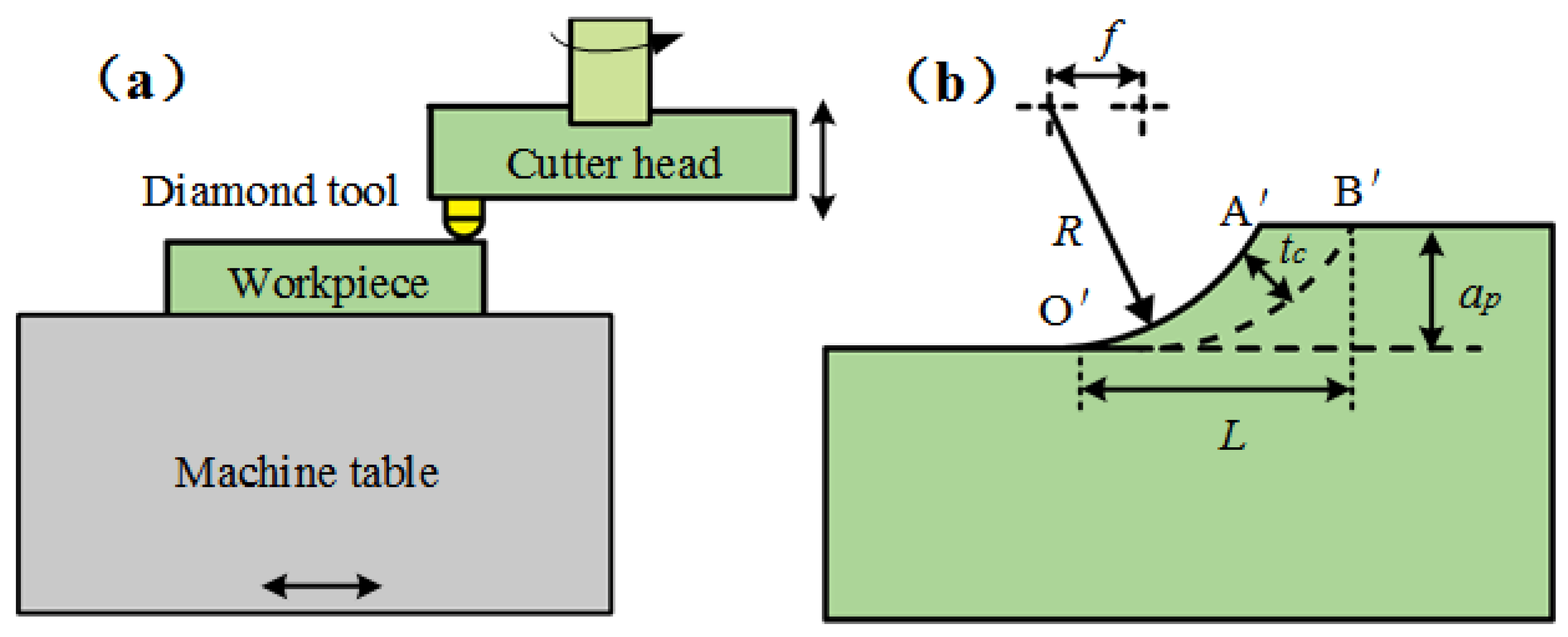
2. Simulation
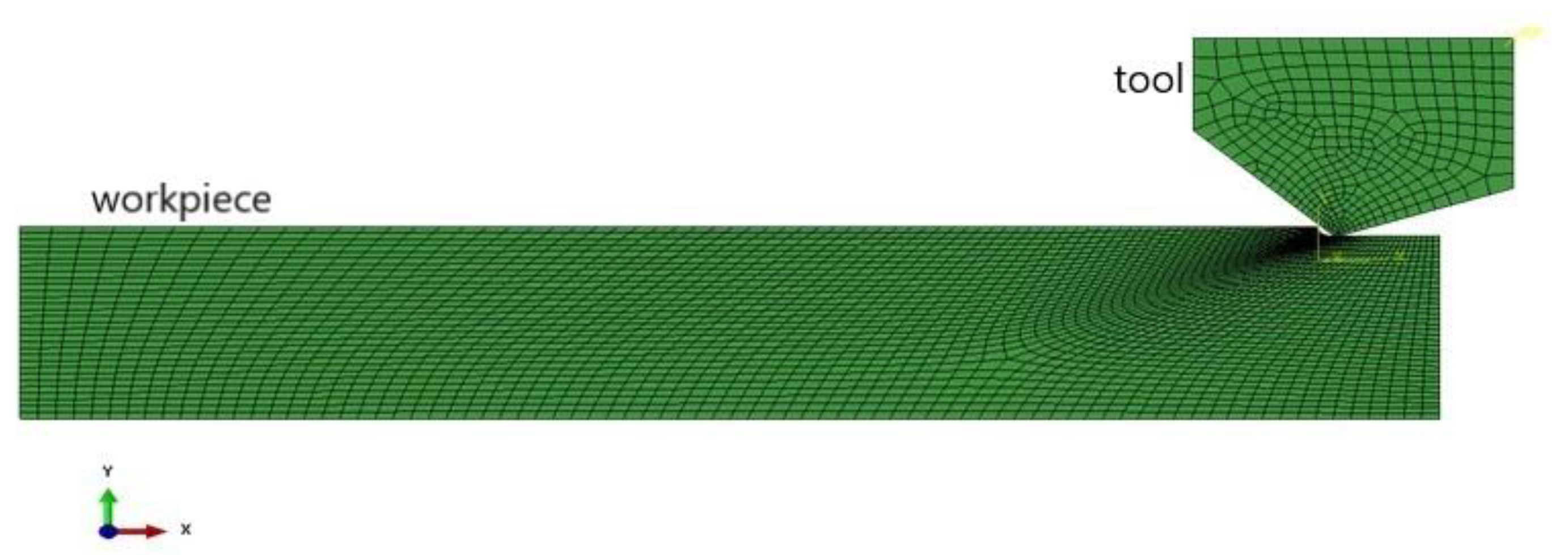
2.1. Simulation Modeling
2.2. Material Properties
2.2.1. Diamond
2.2.2. KDP Crystal
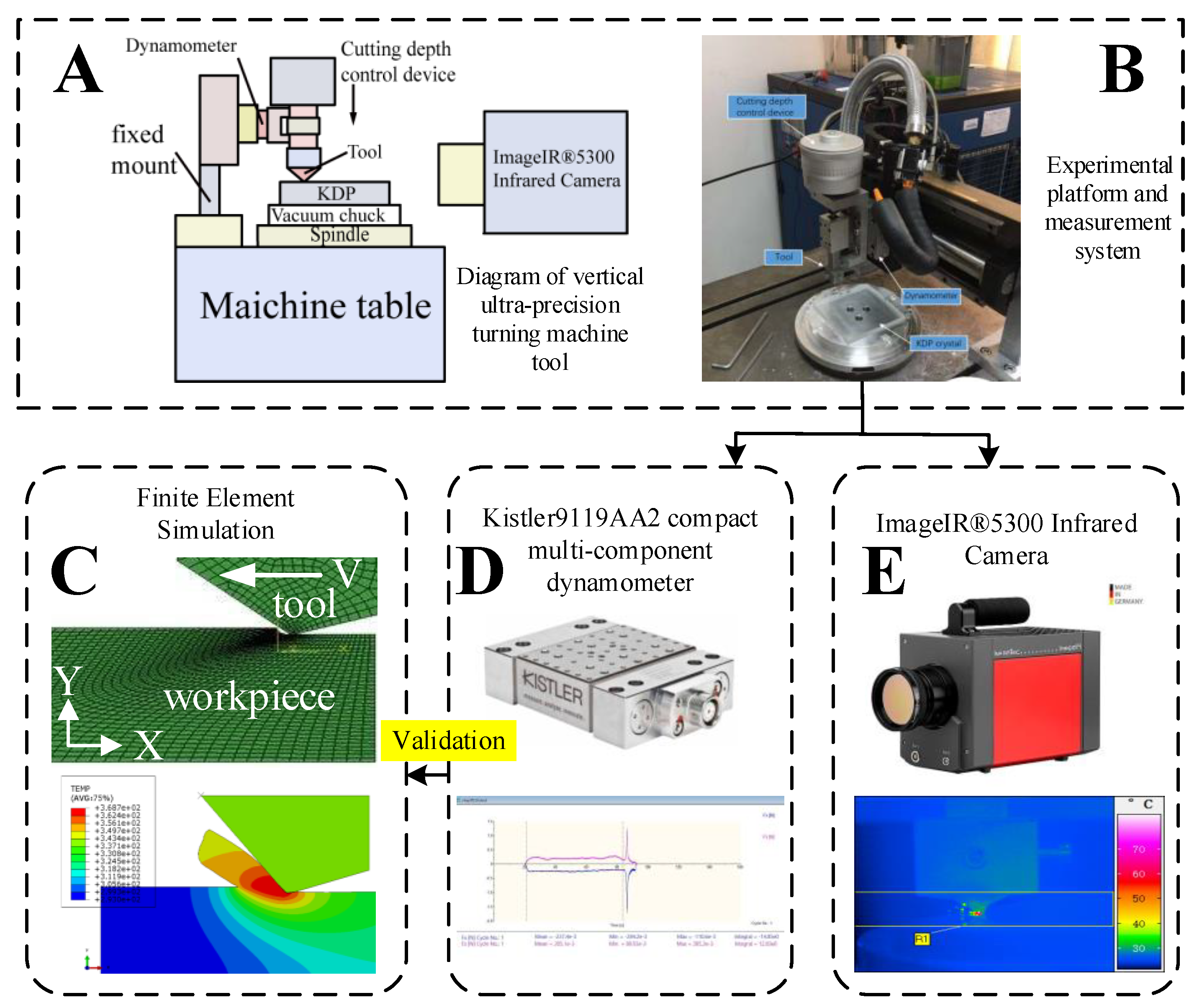
3. Experiment
3.1. Cutting Experiment
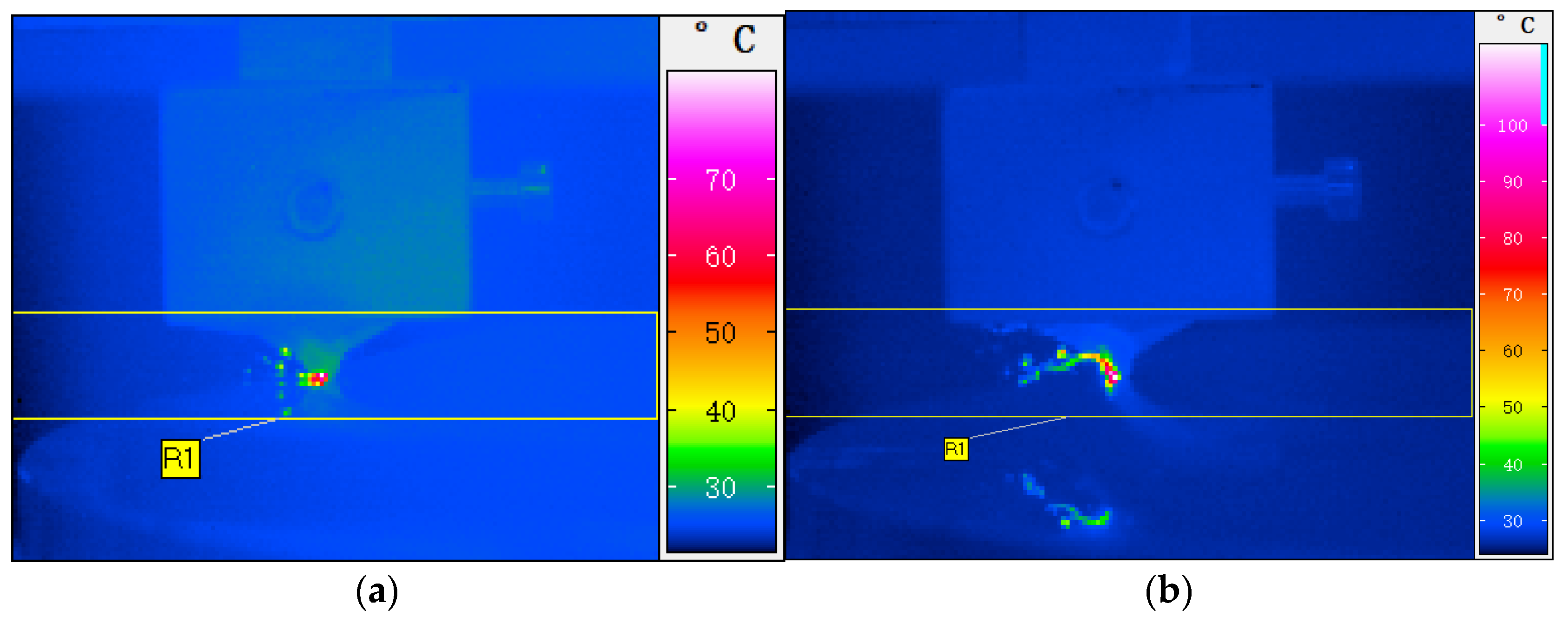
3.2. KDP Chip Morphology Observation Experiment
4. Results
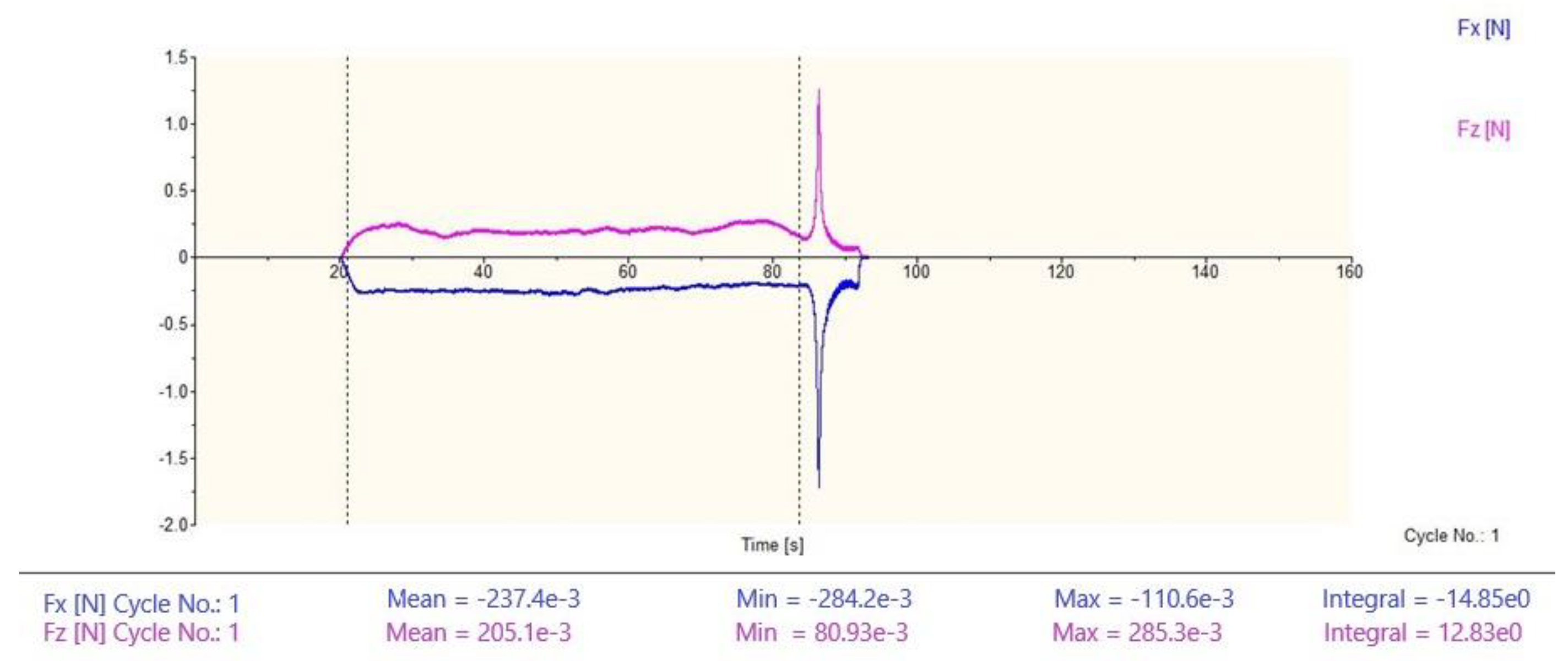
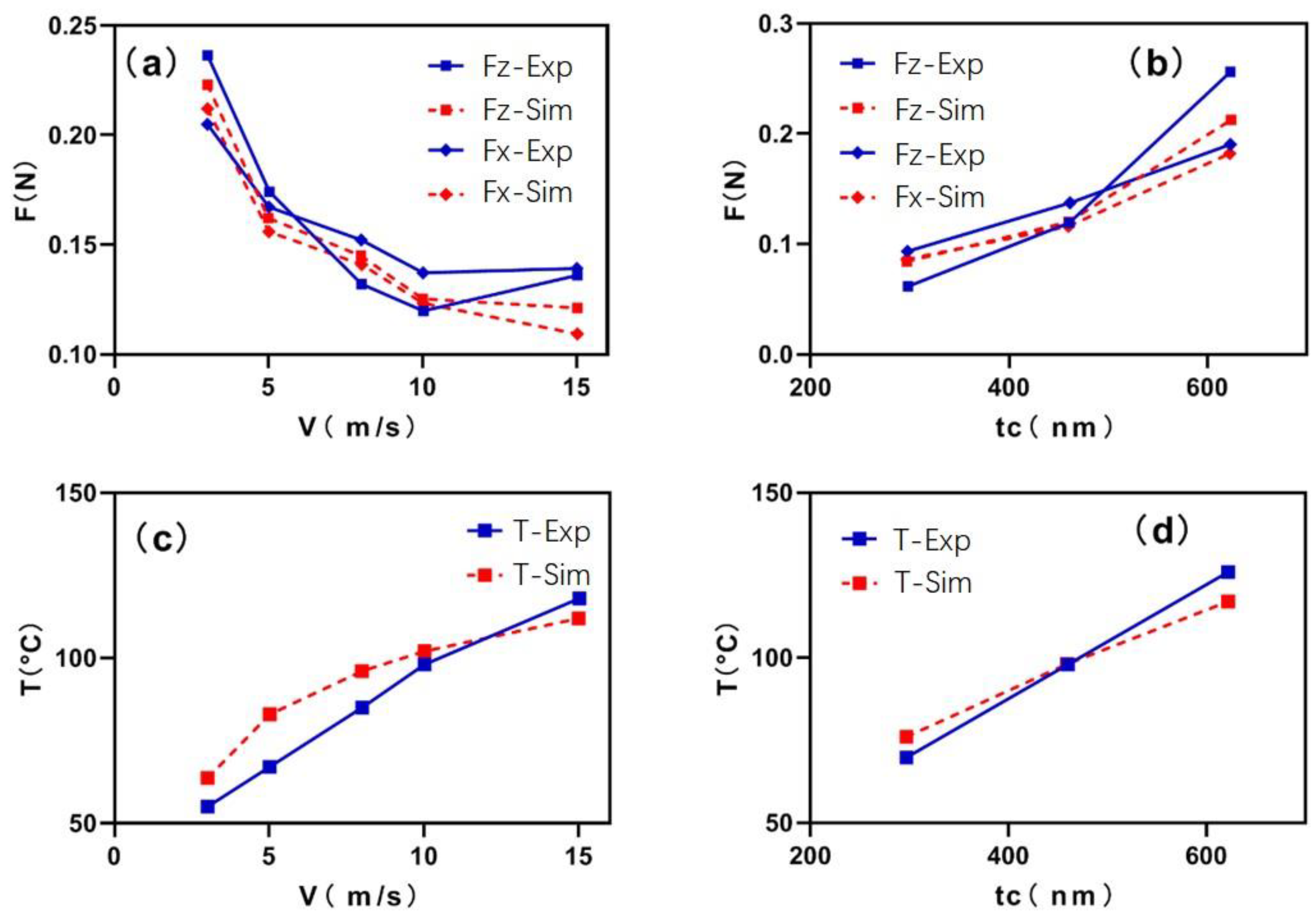
4.1. Results Comparison of Cutting Force
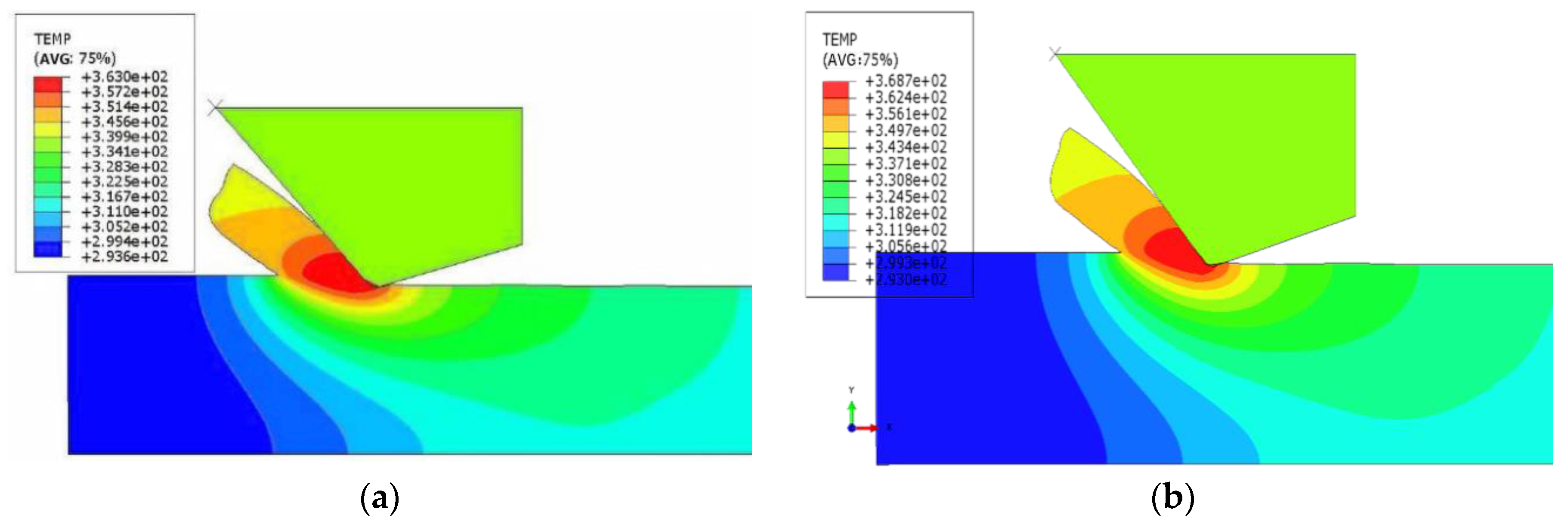
4.2. Results Comparison of Cutting Temperature
4.3. Influence of Cutting Speed
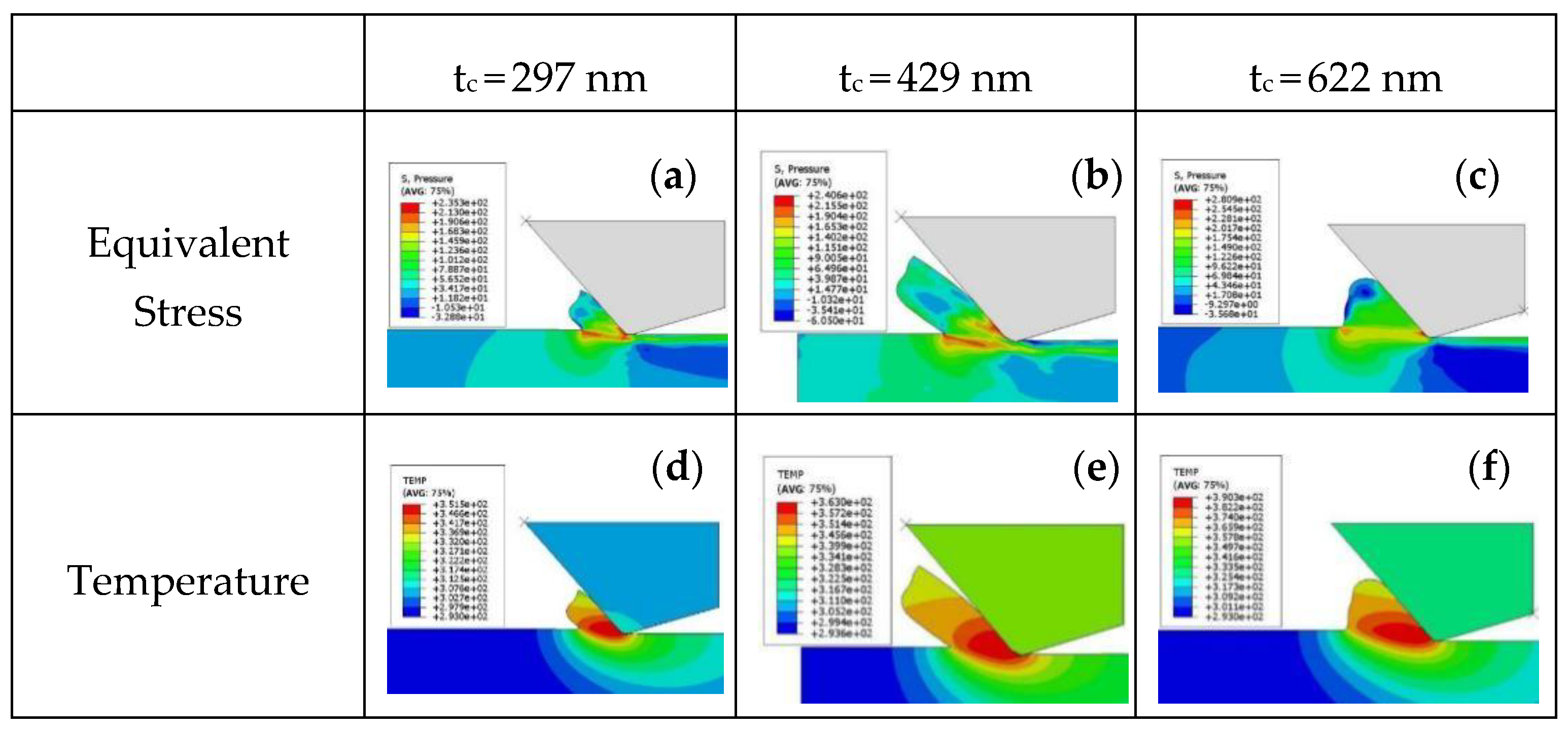
4.4. Influence of Unformed Chip Thickness
4.5. Chip Morphology
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- In this paper, the KDP crystal fly-cutting simulation model is established, the stress field, cutting force and cutting temperature are calculated, and the comparison experiment is carried out to verify the validity of the model. The maximum difference between the simulation temperature and the experimental results is less than 10 °C, which shows that the accuracy of the finite element simulation model can be accepted.
- The chip morphology of KDP crystal has been observed. Based on the finite element simulation results of the stress field and temperature field, the causes of chip morphology formation and surface cracks of the workpiece have been analyzed.
- When the max value of the unformed chip thickness is 429 nm, and cutting speed is 15 m/s, the measured chip temperature reaches approximately 110 °C, and at the time there is also a residual temperature of 30 °C~50 °C on the machined surface and a tensile stress of 7.792 MPa, possibly resulting in micro-cracks on the machined surface and sub-surface.
- In the case of semi-finishing and roughing, the chip temperature can reach 184 °C or higher, and it is quite possible for the KDP crystal to undergo a phase change reaction in the fly-cutting process, which makes the material easier to deform, and the chip is easier to perforate and melt, while higher residual temperatures can more easily damage the machined surface.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, D.; Jiang, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Zu, X. Effect of UV Laser Conditioning on the Structure of KDP Crystal. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2014, 2014, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Li, M.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Q. Influence of period and amplitude of microwaviness on KH[sub 2]PO[sub 4] crystal’s laser damage threshold. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 43109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, M.; Namba, Y. Optical Surface Generation of KDP Inorganic Nonlinear Optical Crystals by Ultraprecision Surface Grinding. J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng. 1999, 65, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menapace, J.A.; Ehrmann, P.R.; Bickel, R.C. Magnetorheological finishing (MRF) of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) crystals: Nonaqueous fluids development, optical finish, and laser damage performance at 1064 nm and 532 nm. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7504, 750414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, B. A hybrid method for crackless and high-efficiency ultraprecision chamfering of KDP crystal. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Modeling of dynamic characteristic of the aerostatic bearing spindle in an ultra-precision fly cutting machine. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturi, U.M.R.; Narala, S.K.R. Constitutive flow stress formulation, model validation and FE cutting simulation for AA7075-T6 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 605, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zou, L. Tool wear mechanism of diamond cutting of ferrous metals in frictional wear experiments. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2013, 21, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Gu, Y.; Cui, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, G. Investigation on high temperature behavior and thermal dehydration kinetics of KDP Crystal. J. Synth. Cryst. 2015, 44, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.-P. An analysis of cutting under different rake angles using the finite element method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 105, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.J.; Li, D.; Cheng, K.; Sun, T.; Liang, Y.C. Finite element optimization of diamond tool geometry and cutting-process parameters based on surface residual stresses. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 32, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Sun, T.; Li, D.; Cheng, K.; Liang, Y. FEM optimization of tool geometry based on the machined near surface’s residual stresses generate. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 180, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.J.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.C.; Sun, T.; An, C.H.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J. Finite element simulation of diamond tool geometries affecting the 3D surface topography in fly cutting of KDP crystals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 68, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; An, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Lei, X.; Zhang, J. Simulation research on the anisotropic cutting mechanism of KDP crystal using a new constitutive model. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2017, 21, 202–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Feng, K.; Wang, W.; Xu, Q.; Lei, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Study on thermal field in fly-cutting process of DKDP crystal. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 3013–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Liu, D.J.; Wang, S.L.; Zhang, N.; Mu, X.M.; Sun, Y. Mechanical Parameters Test and Analysis for KDP Crystal. J. Synth. Cryst. 2009, 38, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F. Assessing microstructure changes in potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals induced by mechanical stresses. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Xu, L.; Huang, P. Study on the cracking of a KDP seed crystal caused by temperature nonuniformity. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 3171–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, G.A. A review of experimental and theoretical techniques for assessing cutting temperatures. Ann. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1973, 22, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, D.; Ali, A. Tool Temperatures in Interrupted Metal Cutting. J. Eng. Ind. 1992, 114, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-C.; Tsao, C.-C.; Liang, P.-W. Determination of temperature distributions on the rake face of cutting tools using a remote method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 1997, 24, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Lambropoulos, J. Microhardness and Indentation Fracture of Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate (KDP). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Physical Quantity | Value |
|---|---|
| Elastic modulus (Gpa)) | 1114 |
| Poisson ratio | 0.07 |
| Linear expansion coefficient () | 1.18 |
| Specific heat capacity (J/(Kg °C)) | 507.9 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/(m °C)) | 2000 |
| Density () | 3520 |
| C11 | C12 | C13 | C33 | C44 | C66 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 71.6 GPa | −6.3 GPa | 14.9 GPa | 56.4 GPa | 12.5 GPa | 6.2 GPa |
| Parameters | Diamond | KDP Crystal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α[μm/(m°C)] | 2000 | αx | αy | αz |
| 16.1 | 16.1 | 29.0 | ||
| λ(10−6/°C) | 1.18 | λx | λy | λz |
| 2.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | ||
| C[J/(kg°C)] | 502 | |||
| k | 0.03 | 0.36 | ||
| Rake Angle | Flank Angle | Nose Radius | Edge Radius |
|---|---|---|---|
| −45° | 18° | 5 mm | 120 nm |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| cutting speed | 3 m/s, 5 m/s, 8 m/s, 10 m/s, 15 m/s |
| feed | 10 μm/rev |
| the max value of the unformed chip thickness (cutting depth) | 297 nm (2 μm), 429 nm (5 μm), 622 nm(10 μm) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, C.; Feng, K.; Wang, W.; Xu, Q.; Lei, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, X.; Li, H. Interaction Mechanism of Thermal and Mechanical Field in KDP Fly-Cutting Process. Micromachines 2021, 12, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080855
An C, Feng K, Wang W, Xu Q, Lei X, Zhang J, Yao X, Li H. Interaction Mechanism of Thermal and Mechanical Field in KDP Fly-Cutting Process. Micromachines. 2021; 12(8):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080855
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Chenhui, Ke Feng, Wei Wang, Qiao Xu, Xiangyang Lei, Jianfeng Zhang, Xuelian Yao, and Haibo Li. 2021. "Interaction Mechanism of Thermal and Mechanical Field in KDP Fly-Cutting Process" Micromachines 12, no. 8: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080855
APA StyleAn, C., Feng, K., Wang, W., Xu, Q., Lei, X., Zhang, J., Yao, X., & Li, H. (2021). Interaction Mechanism of Thermal and Mechanical Field in KDP Fly-Cutting Process. Micromachines, 12(8), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080855






