Analyzing the Effect of Particle Shape on Deformation Mechanism during Cutting Simulation of SiC P/Al Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
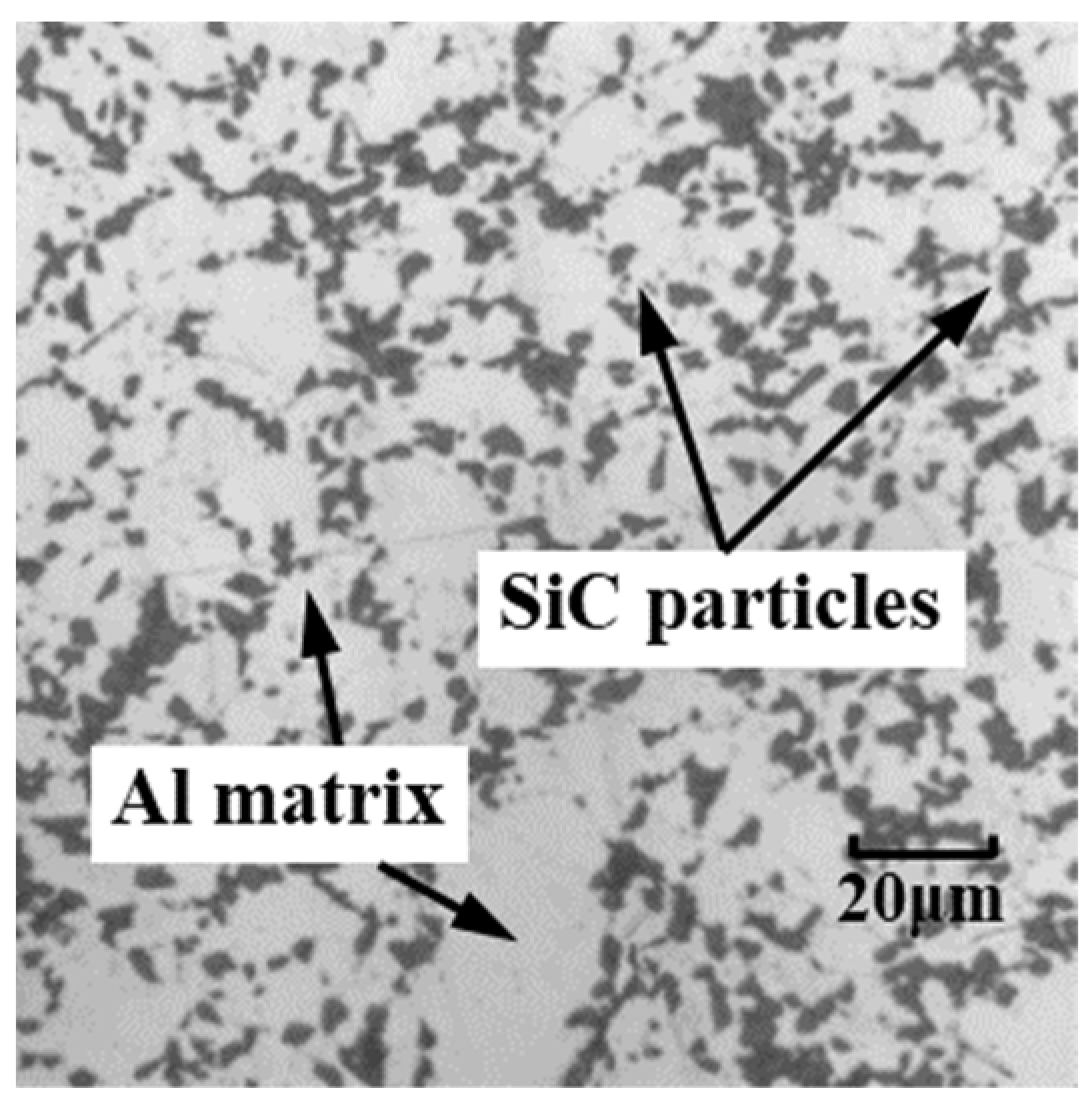
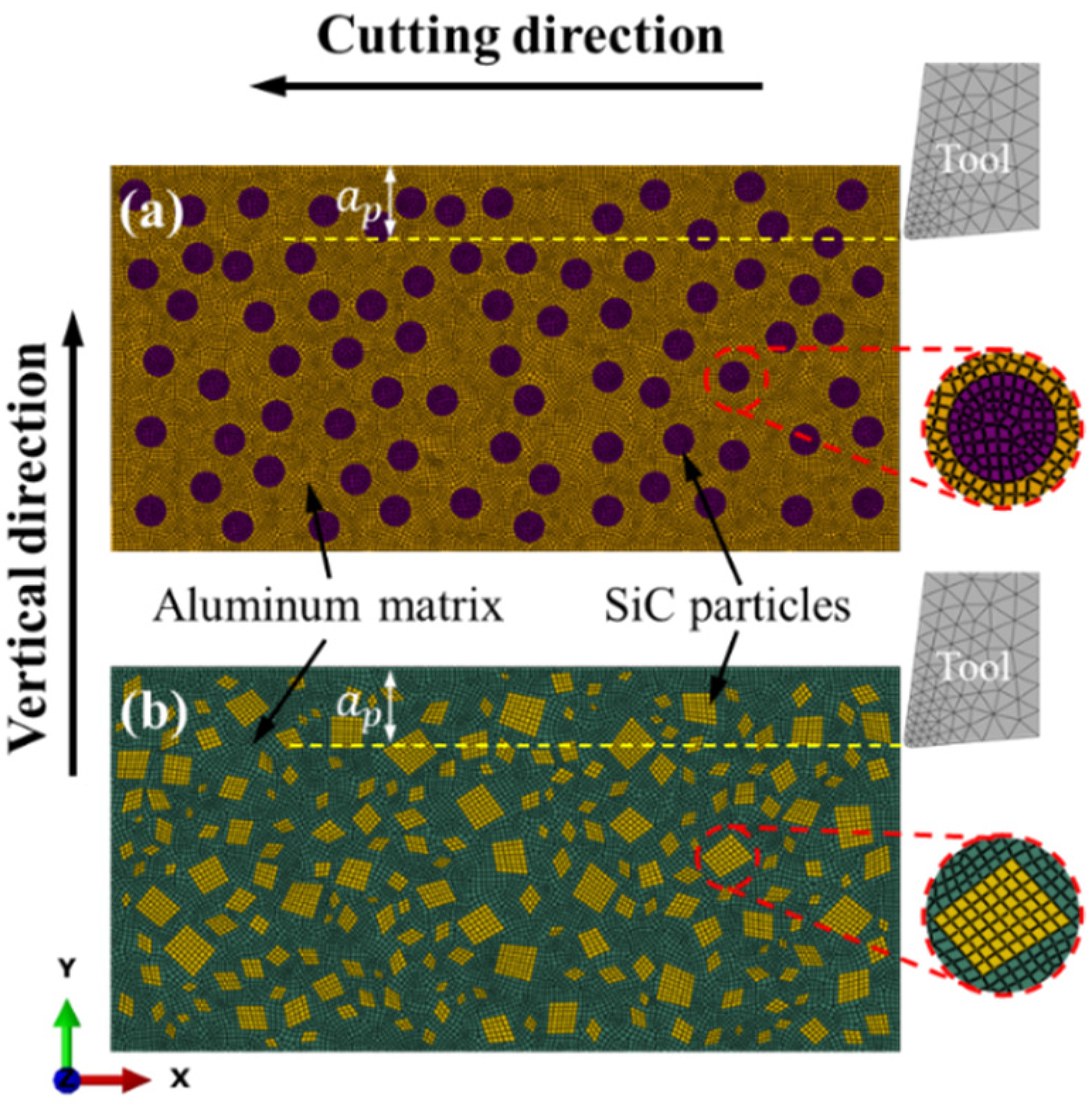
2. Finite Element Modeling Procedure
2.1. Model Descriptions
2.2. Material Properties of Aluminum Matrix
2.3. Material Properties of SiC Particles
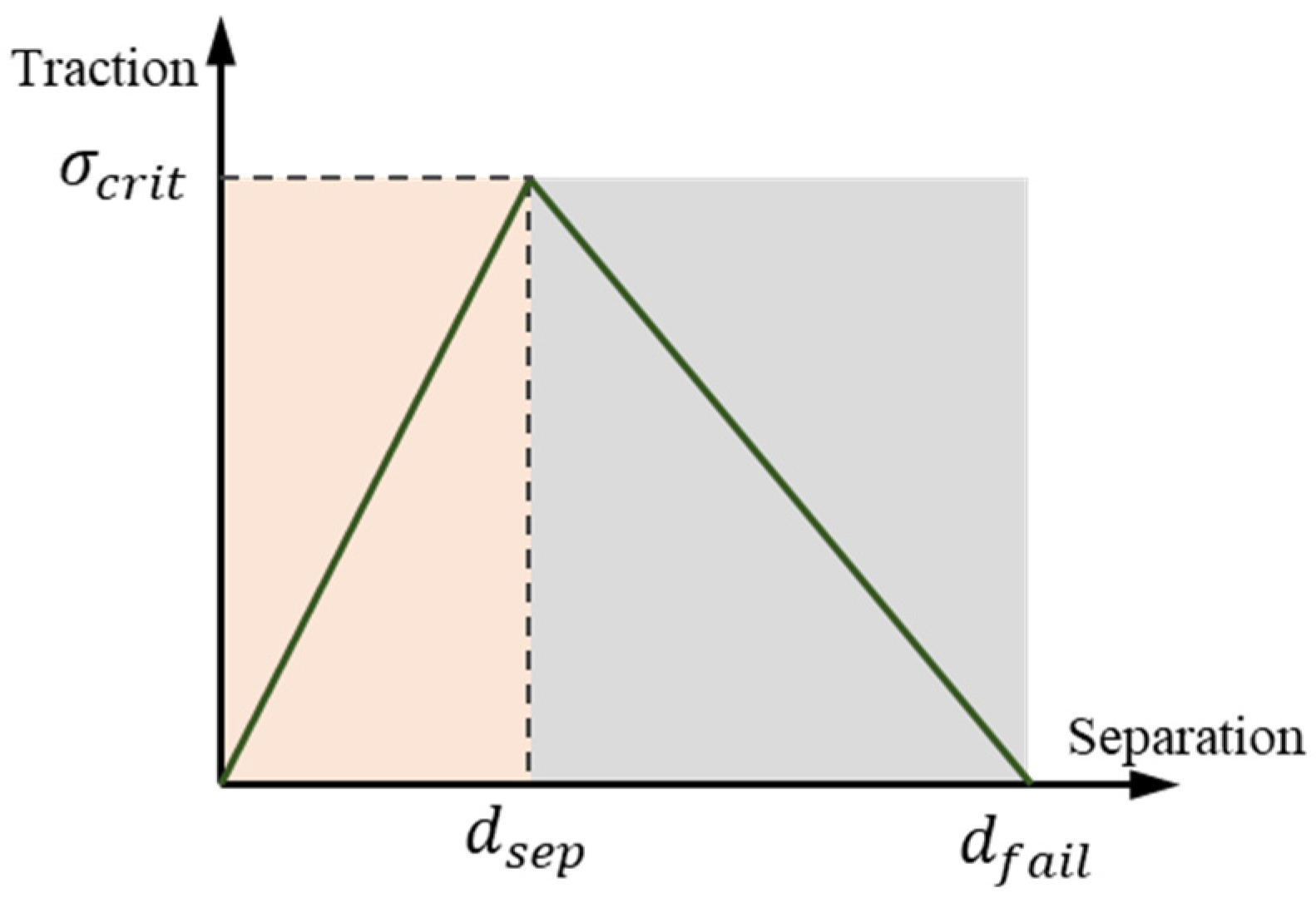
2.4. Properties of the Particle–Matrix Interface
2.5. Interaction
3. Experimental Conditions
4. Results and Discussion
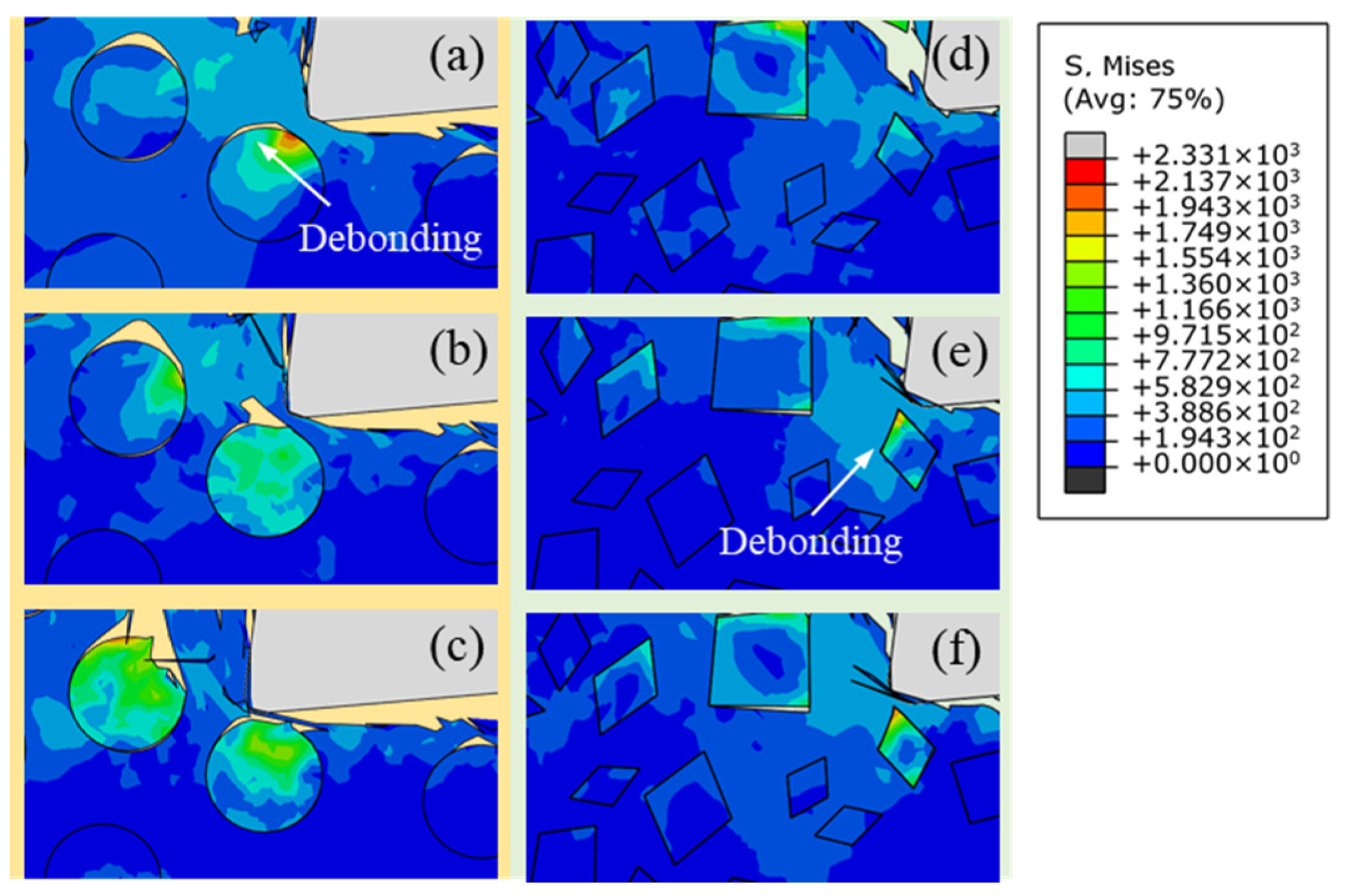
4.1. Particle Deformation Behavior
4.2. Cutting Force
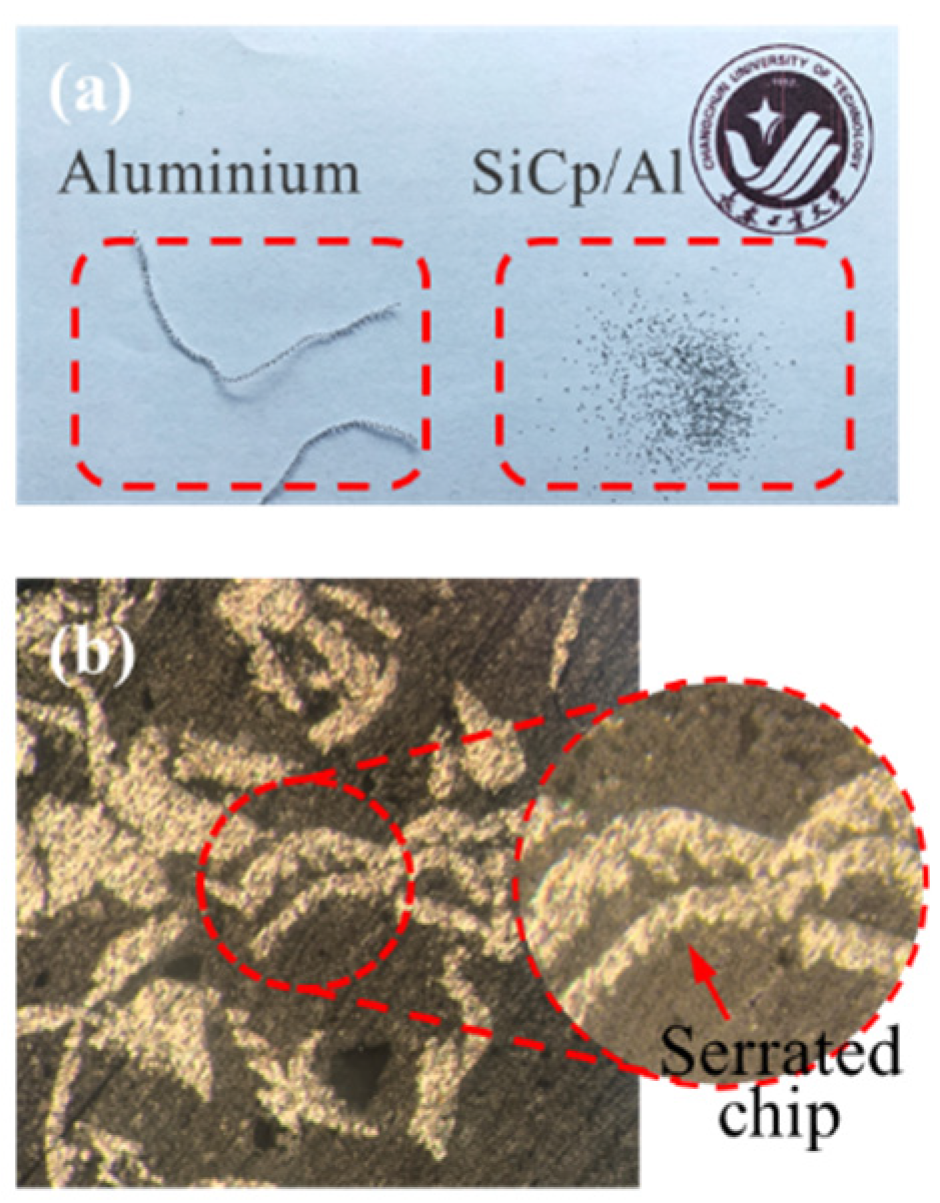
4.3. Chip Formation and Morphology
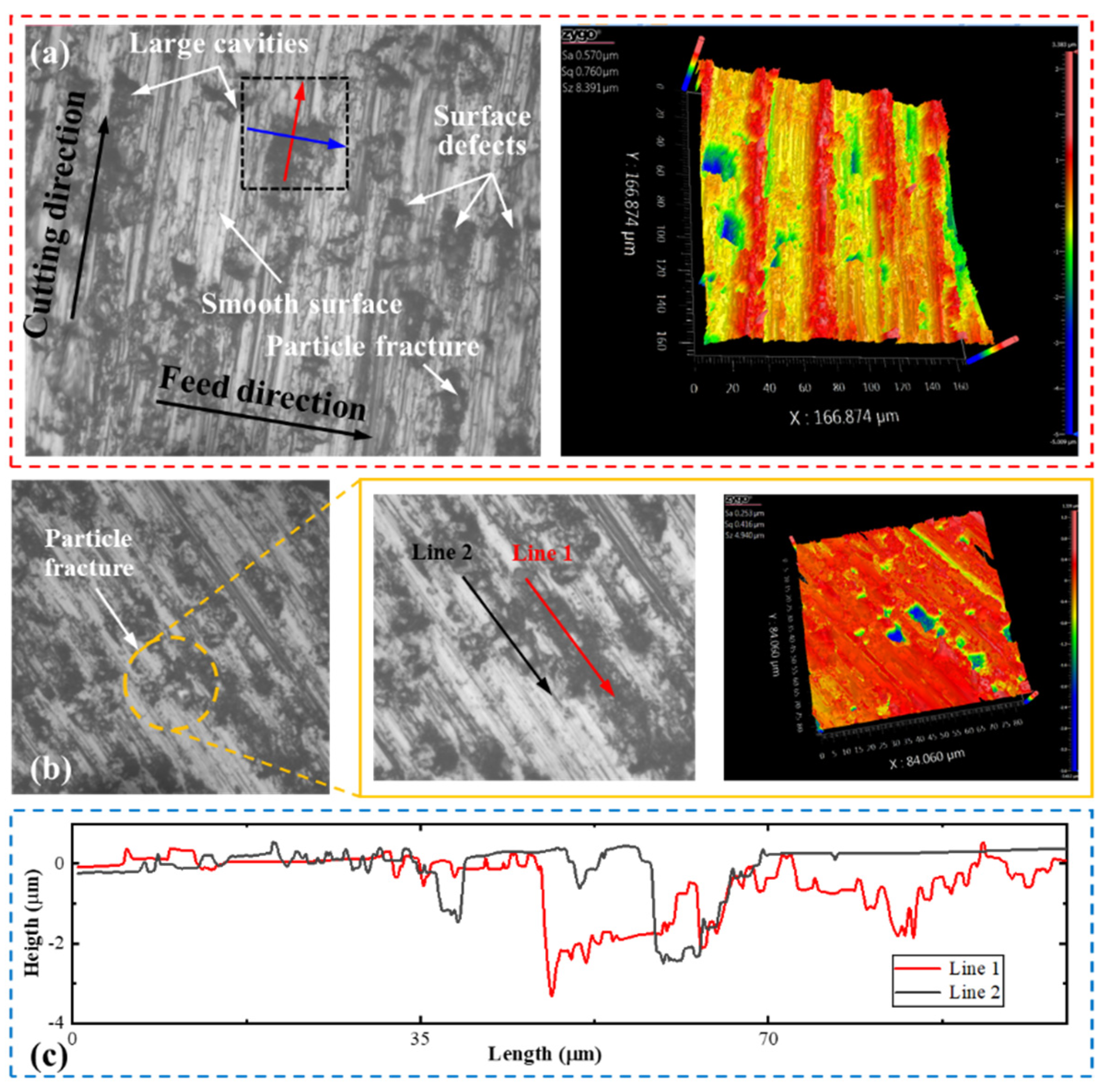
4.4. Surface Topography
5. Conclusions
- (1)
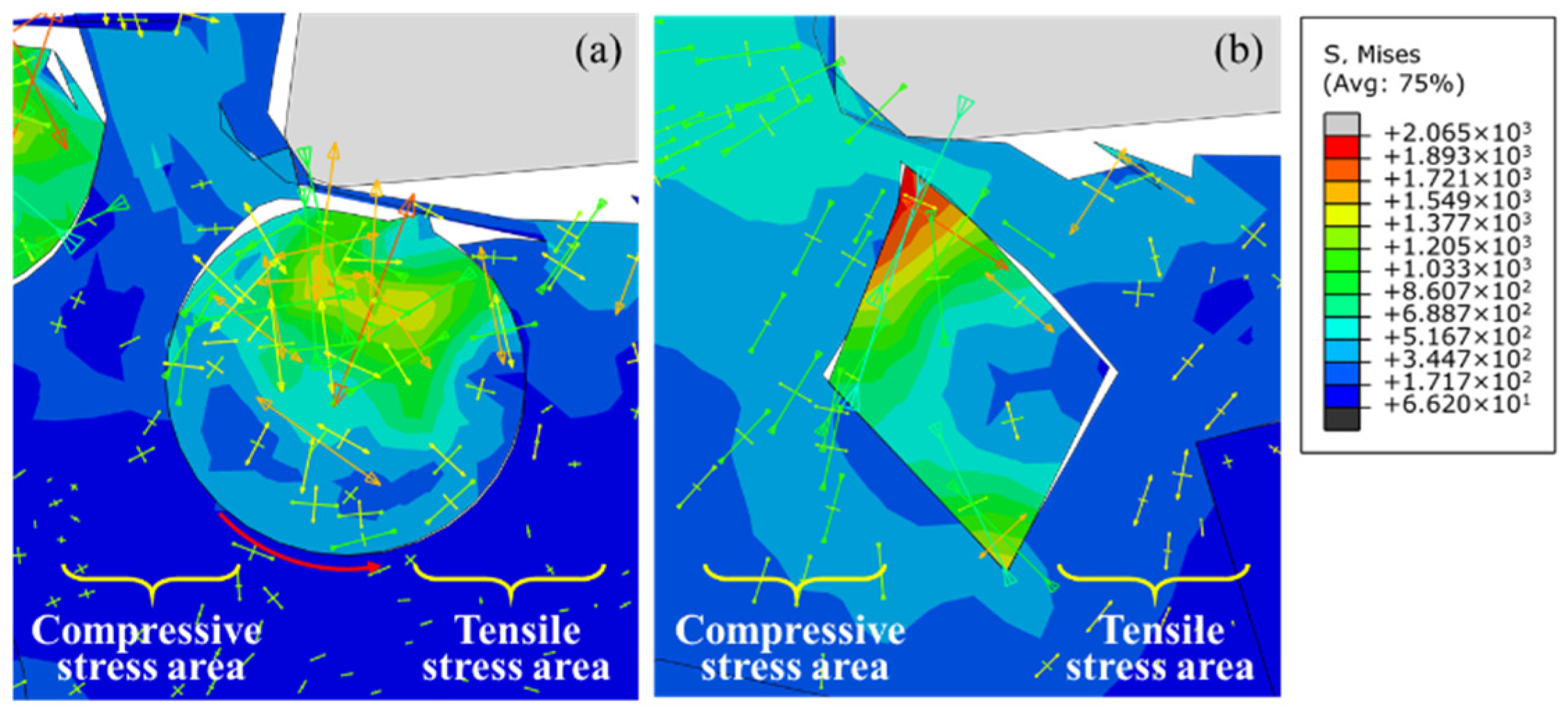
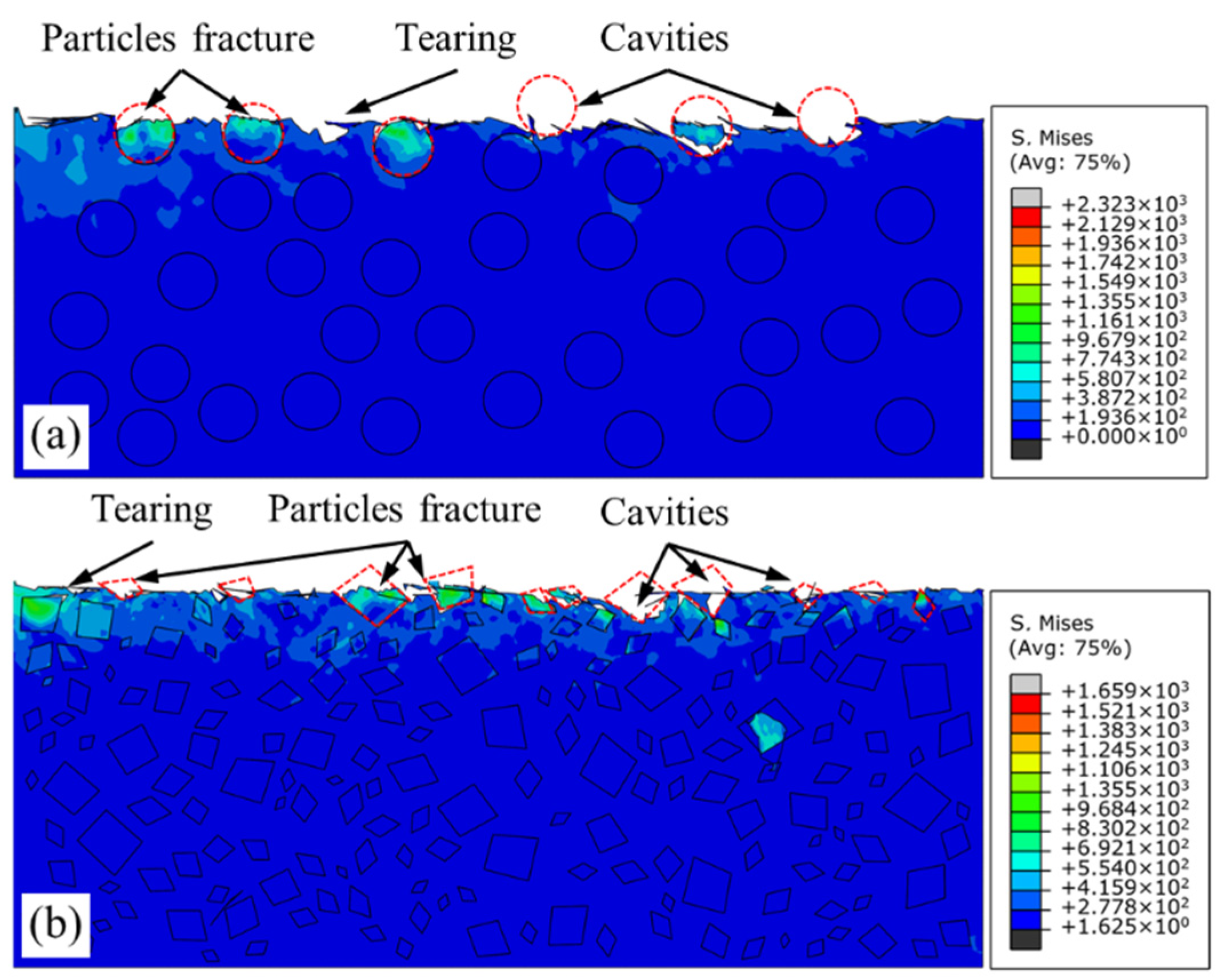
- Particle fracture is mainly determined by tool–particle interaction, and the metal matrix carries out the role of load transfer. Due to the existence of sharp corners, the stress concentration of irregular polygonal particles is not only affected by the extrusion of the rake face, but is also related to the interaction of the surrounding particles.
- (2)
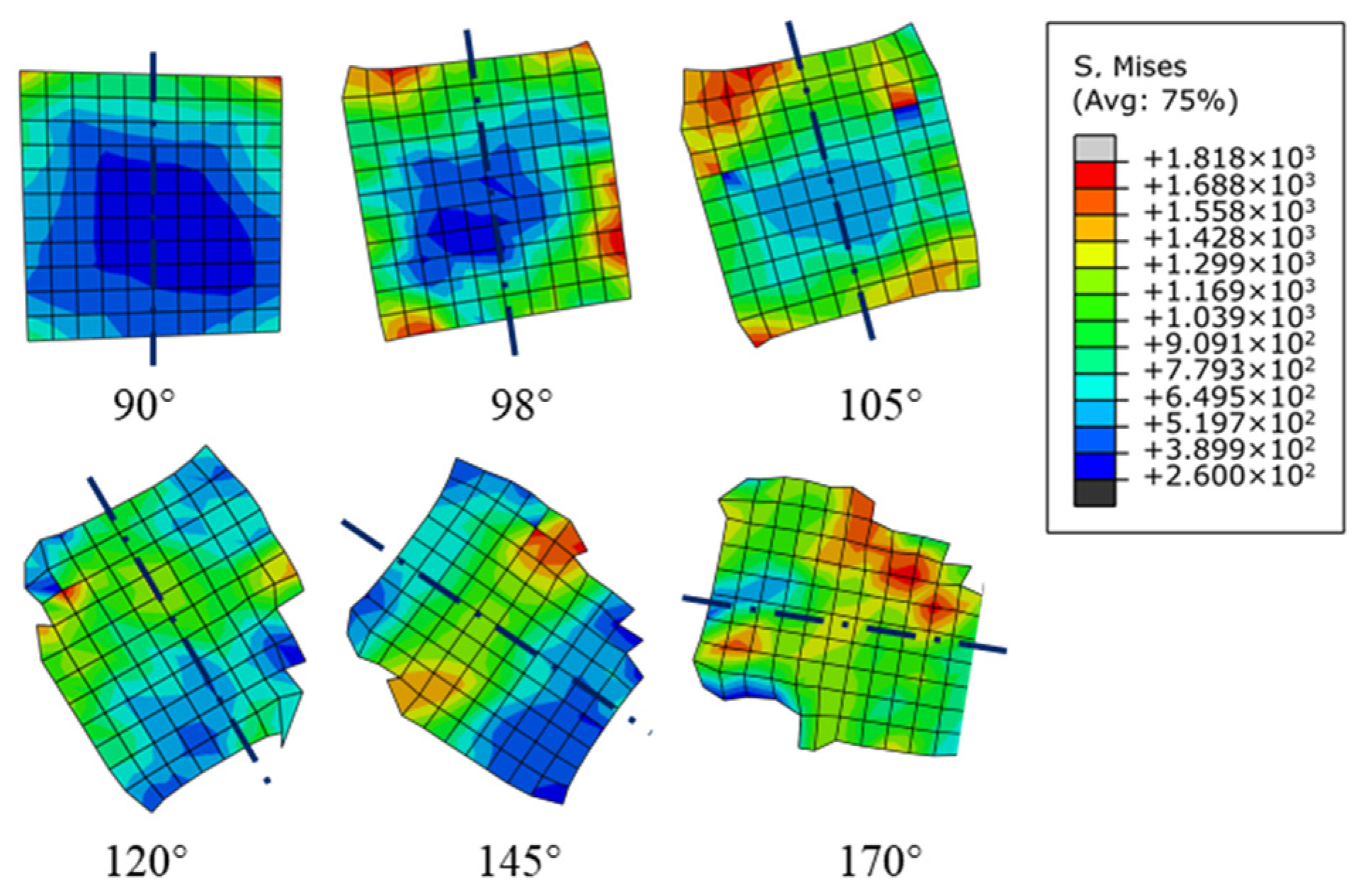
- The differences in tensile stress and compressive stress between the sides of the particles can explain the cause of the particle damage below cutting path. The particle–matrix interface of the irregular polygonal particle model is not able to uniformly transfer the unbalanced stress on both sides of particle under a trend of particle rotation, which leads to a centrosymmetric stress distribution in the particles. The difference in the speed of plastic deformation between both sides of the particles above the cutting path accounts for the particle rotation in the chips.
- (3)
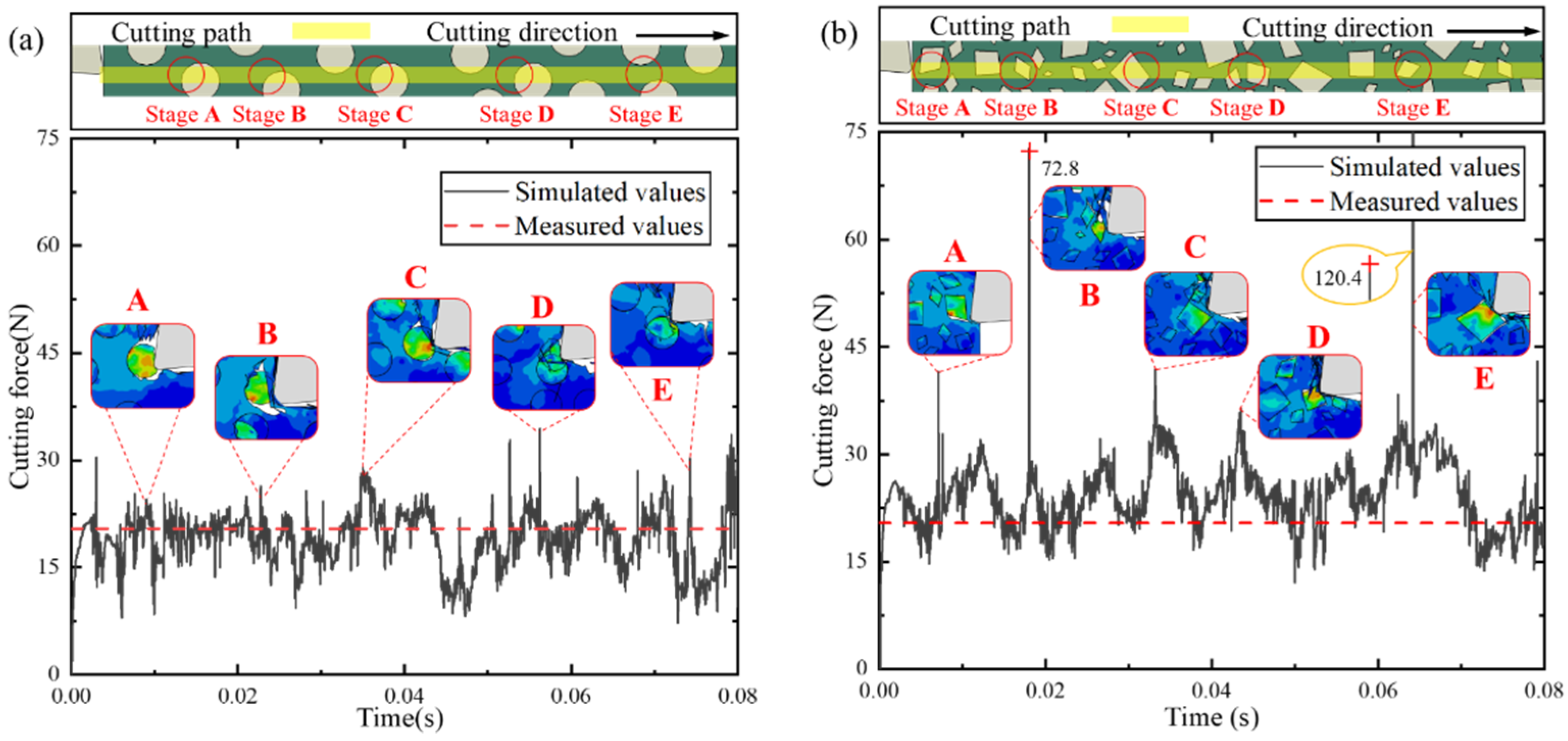
- The two models reinforced by circular and irregular polygonal particles were able to effectively predict variations in the cutting force, with large fluctuations and small fluctuations also appearing in the cutting force curve. Due to the dynamometer potentially not being able to capture all impacts caused by each of the SiC particles in the cutting test, the irregular polygonal particle model is more reasonable for reflecting changes in the cutting force in the actual cutting process of SiC p/Al composites than the circular particle model.
- (4)
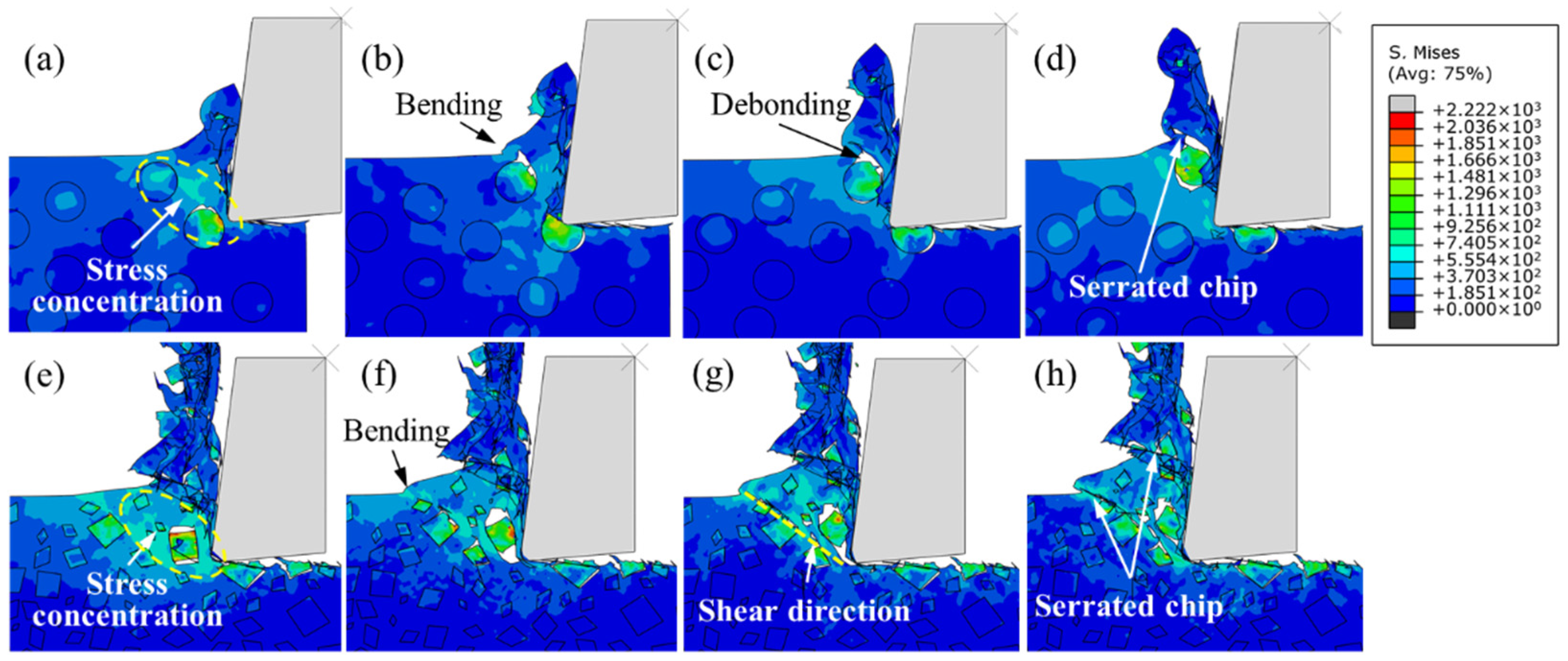
- The formation, propagation and convergence of microcracks have significant impacts on chip formation and morphology, particle fracture and debonding, and surface integrity. The interface stability is poor in the irregular polygonal particle model, which facilitates the formation of sharper serrated chips.
- (5)
- The machined surface of SiC/Al composites is mainly dominated by particle fracture, particle–matrix interface debonding, and interaction between tool and workpiece. Considering the actual microstructure of MMCs, the irregular polygonal particle model provides a more comprehensive prediction of subsurface damage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasan, M.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, Z. Micromanufacturing of composite materials: A review. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2019, 1, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Abdelhafeez, A.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Diaz, O.G.; Axinte, D. State-of-the-art of surface integrity in machining of metal matrix composites. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 143, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, K. Titanium–titanium boride composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6753–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, R.; Singh, T.P. Mechanisms in turning of metal matrix composites: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, M.; Park, J.; Park, M.; Kim, K.; Hong, S. Effect of aspect ratios of in situ formed TiB whiskers on the mechanical properties of TiBw/Ti–6Al–4V composites. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Shen, J.; Ye, X.; Jia, L.; Li, S.; Umeda, J.; Kondoh, K. Length effect of carbon nanotubes on the strengthening mechanisms in metal matrix composites. Acta Mater. 2017, 140, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, K.; Nataraj, M.; Duraisamy, P. Machinability analysis and application of response surface approach on CNC turning of LM6/SiCp composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2019, 34, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoba, C.; Ramanaiah, N.; Nageswara Rao, D. Effect of reinforcement on the cutting forces while machining metal matrix composites–An experimental approach. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2015, 18, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhan, Z.; Li, L.; He, N.; Shrestha, R. An experimental study on milling of high-volume fraction SiC P/Al composites with PCD tools of different grain size. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 79, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zherebtsov, S.; Ozerov, M.; Povolyaeva, E.; Sokolovsky, V.; Stepanov, N.; Moskovskikh, D.; Salishchev, G. Effect of hot rolling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a Ti-15Mo/TiB metal-matrix composite. Metals 2020, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozerov, M.; Klimova, M.; Stepanov, N.; Zherebtsov, S. Microstructure evolution of a Ti/TiB metal-matrix composite during high-temperature deformation. Mater. Phys. Mech. 2018, 38, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zherebtsov, S.; Ozerov, M.; Klimova, M.; Stepanov, N.; Vershinina, T.; Ivanisenko, Y.; Salishchev, G. Effect of high-pressure torsion on structure and properties of Ti-15Mo/TiB metal-matrix composite. Materials 2018, 11, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qayyum, F.; Guk, S.; Kawalla, R.; Prahl, U. On Attempting to Create a Virtual Laboratory for Application-Oriented Microstructural Optimization of Multi-Phase Materials. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, F.; Chaudhry, A.; Guk, S.; Schmidtchen, M.; Kawalla, R.; Prahl, U. Effect of 3D representative volume element (RVE) thickness on stress and strain partitioning in crystal plasticity simulations of multi-phase materials. Crystals 2020, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Jing, L.; Li, C.; Yu, Z.; Li, S.; Li, P.; Yue, W. Study on effects of tool nose radius on the formation mechanism of edge defects during milling SiC p/Al composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 114, 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kishawy, H.A. Influence of alumina particles on the mechanics of machining metal matrix composites. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A.; Zhang, L.C.; Arsecularatne, J.A. An FEM investigation into the behavior of metal matrix composites: Tool-particle interaction during orthogonal cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, S.T.; Wang, D.; Yu, X.L. Finite element and experimental studies of the cutting process of SiC p/Al composites with PCD tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 52, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.Y.; Yu, X.L. Finite element and experimental studies of the formation mechanism of edge defects during machining of SiC p/Al composites. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2014, 84, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cui, C.; Zhang, P.F.; Ma, Z.Y. Finite element and experimental analysis of machinability during machining of high-volume fraction SiC p/Al composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xie, L.; Wang, X. Simulation study on defect formation mechanism of the machined surface in milling of high volume fraction SiC p/Al composite. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 79, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandehariun, A.; Kishawy, H.A.; Umer, U.; Hussein, H.M. Analysis of tool-particle interactions during cutting process of metal matrix composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, U.; Ashfaq, M.; Qudeiri, J.A.; Hussein, H.M.A.; Danish, S.N.; Al-Ahmari, A.R. Modeling machining of particle-reinforced aluminum-based metal matrix composites using cohesive zone elements. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 78, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Huo, D.; Chen, W.; Wong, E.; Zheng, L.; Shyha, I. Finite element modelling on cutting mechanism of nano Mg/SiC metal matrix composites considering cutting edge radius. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 32, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, X.; Chen, W.; Huo, D.; Shyha, I.; Lin, C. Comparison of cutting mechanism when machining micro and nano-particles reinforced SiC/Al metal matrix composites. Compos. Struct. 2018, 203, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Sun, W.; Fu, C.; Zhang, F. Modeling and simulation of tool-chip interface friction in cutting Al/SiCp composites based on a three-phase friction model. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 142–143, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, R.A.; Li, J.; Yongxiang, W. Study of machining process of SiC p/Al particle reinforced metal matrix composite using finite element analysis and experimental verification. Materials 2020, 13, 5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L. A micromechanics analysis of the material removal mechanisms in the cutting of ceramic particle reinforced metal matrix composites. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2018, 22, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L. Microstructure-based modelling of fracture of particulate reinforced metal matrix composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 163, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L. Machining of particulate-reinforced metal matrix composites: An investigation into the chip formation and subsurface damage. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 274, 116315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, L. Microstructure-based three-dimensional characterization of chip formation and surface generation in the machining of particulate-reinforced metal matrix composites. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2020, 2, 045103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Chen, J.; Ming, W.; An, Q.; Chen, M. Experimental and FEM study of cutting mechanism and damage behavior of ceramic particles in orthogonal cutting SiC p/Al composites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 7183–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.R.; Cook, W.H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1983, 21, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, G.R.; Cook, W.H. Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1985, 21, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.C.; Prager, W. Soil mechanics and plastic analysis or limit design. Q. Appl. Math. 1952, 10, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Ouyang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Fan, G.; Su, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lavernia, E.J.; Schoenung, J.M.; Zhang, D. 3D Microstructure-based finite element modeling of deformation and fracture of SiC p/Al composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 123, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dandekar, C.R.; Shin, Y.C. Multiphase finite element modeling of machining unidirectional composites: Prediction of debonding and fiber damage. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 2008, 130, 051016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulk, J.W.; Allen, D.H.; Helms, K.L.E. Formulation of a three-dimensional cohesive zone model for application to a finite element algorithm. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2000, 183, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvergaard, V. Fibre debonding and breakage in a whisker-reinforced metal. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1995, 190, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandekar, C.R.; Shin, Y.C. Multi-step 3-D finite element modeling of subsurface damage in machining particulate reinforced metal matrix composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; He, N.; Li, L.; Zhan, Z.B.; Wu, Q.; Shi, Z.Y. Precision milling of high volume fraction SiC p/Al composites with monocrystalline diamond end mill. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 71, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Seah, W.K.H. Tool wear acceleration in relation to workpiece reinforcement percentage in cutting of metal matrix composites. Wear 2001, 247, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Cutting speed (mm/s) | 250 |
| Cutting depth (mm) | 0.025 |
| Feed rate (mm/rev) | 0.01 |
| Tool material | PCD |
| Rake angle (°) | 7 |
| Flank angle (°) | 5 |
| Particle size (μm) | 15 (5–20) |
| Volume fraction (%) | 25 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Density (ton/mm3) | 2820 × 10−12 |
| Young’s Modulus (MPa) | 70,600 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.35 |
| A (MPa) | 224 |
| B (MPa) | 426 |
| C | 0.003 |
| n | 0.2 |
| D1 | 0.13 |
| D2 | 0.13 |
| D3 | −1.5 |
| D4 | 0.011 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Density (ton/mm3) | 3200 × 10−12 |
| Young’s Modulus (MPa) | 408,000 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.35 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 2000 |
| Friction angle (°) | 13 |
| Expansion angle (°) | −5 |
| k | 0.92 |
| G (MPa) | 1000 |
| p | 2 |
| 0.2 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Fracture energy (J/m2) | 50 |
| Elastic moduli (MPa) | 180,600 |
| Shear moduli (MPa) | 76,600 |
| Interfacial strength (MPa) | 372 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Lin, J.; Lu, M.; Jing, X.; Jin, Y.; Song, D. Analyzing the Effect of Particle Shape on Deformation Mechanism during Cutting Simulation of SiC P/Al Composites. Micromachines 2021, 12, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080953
Zhou J, Lin J, Lu M, Jing X, Jin Y, Song D. Analyzing the Effect of Particle Shape on Deformation Mechanism during Cutting Simulation of SiC P/Al Composites. Micromachines. 2021; 12(8):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080953
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jiakang, Jieqiong Lin, Mingming Lu, Xian Jing, Yubo Jin, and Dunlan Song. 2021. "Analyzing the Effect of Particle Shape on Deformation Mechanism during Cutting Simulation of SiC P/Al Composites" Micromachines 12, no. 8: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080953
APA StyleZhou, J., Lin, J., Lu, M., Jing, X., Jin, Y., & Song, D. (2021). Analyzing the Effect of Particle Shape on Deformation Mechanism during Cutting Simulation of SiC P/Al Composites. Micromachines, 12(8), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080953








