Influence of Different Tool Electrode Materials on Electrochemical Discharge Machining Performances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanism of Electrochemical Discharge Machining (ECDM)
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Machine Tool
3.2. Materials and Properties
3.3. Measurements and Acquisitions
3.4. Machining Procedure and Condition
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Comparison of MRR, EWR, and OC by W80Cu20, Brass, TC4, and SS304 Electrodes
4.2. Surface Defects on Workpiece and Material Transfer on Electrodes
4.3. MRR, EWR, and OC Machining with W70Cu30, W80Cu20, and W90Cu10 Electrodes
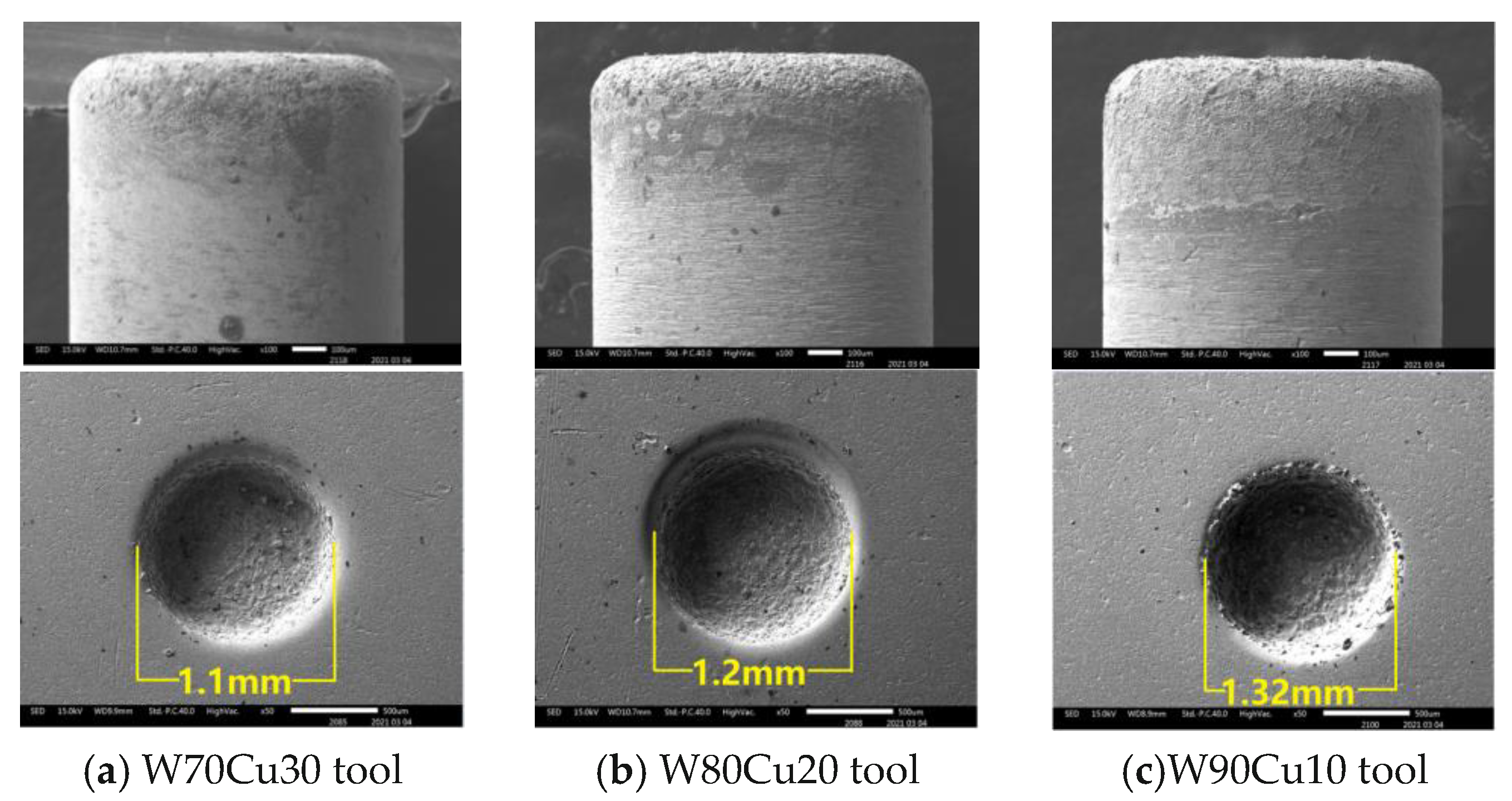
4.4. Surface Defects on Workpiece and Material Transfer on W90Cu10, W80Cu20, and W70Cu30 Electrodes
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- As a result of higher conductivity, the discharge channel forms quickly as the electrical conductivity increases, the discharge delay time decreases, and the discharge energy emitted to the workpiece at the same time increases, resulting in an increase in the MRR. Here, the highest MRR of about 70 μg/s is obtained when using the W70Cu30 electrode over using the other five electrodes;
- (2)
- All CuW electrodes exhibit the lowest EWR, followed by the brass, TC4, and SS304 electrodes. However, among all CuW electrodes, W70Cu30 has shown a lower EWR (8.1%) than the other two electrodes because this electrode has a very high thermal conductivity. Due to its high thermal conductivity, the heat produced during machining diffuses into the space, decomposing the electrolyte fluids’ oxygen at a very high temperature, with some accumulating around the electrode, preventing further electrode erosion;
- (3)
- All CuW electrodes represent the lowest side overcut, followed by the other three electrodes (brass, TC4, and SS304). Among all CuW, W70Cu30 exhibits the least overcut (0.05 mm). W70Cu30 has miniature craters with no cracks and a less rough surface. The unexpected oxygen deposition is the lowest for W70Cu30, followed by the other electrodes. Other material compositions to this electrode are in minimal percentages.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afzaal, A.; Tanjilul, M.; Rahman, M.; Kumar, A.S. Ultrafast drilling of Inconel 718 using hybrid EDM with different electrode materials. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 2281–2294. [Google Scholar]
- Ľuboslav, S.; Slavomíra, H. Optimization of material removal rate and tool wear rate of Cu electrode in die-sinking EDM of tool steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar]
- Rahul; Dileep, K.M.; Saurav, D.; Manjol, M. Effects of Tool Electrode on EDM Performance of Ti-6Al-4V. Silicon 2018, 10, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munmun, B.; Kalipada, M. Effect of different tool materials during EDM performance of titanium grade 6 alloy. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 21, 507–516. [Google Scholar]
- Pilligrin, J.C.; Asokan, P.; Jerald, J.; Kanagaraj, G. Effects of electrode materials on performance measures of electrical discharge micro-machining. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, G.; Maccarini, G.; Quarto, M.; Ravasio, C. Investigation on power discharge in micro-EDM stainless steel drilling using different electrodes. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 4341–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Mahapatra, S.S. Comparison of performance of different tool electrodes during electrical discharge machining. Int. J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2019, 26, 186–199. [Google Scholar]
- Anna, T.W.; Krzysztof, W. Multifilament carbon fibre tool electrodes in micro EDM-evaluation of process performance based on influence of input parameters. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 3737–3747. [Google Scholar]
- Renu, K.S.; Chinmaya, P.M. Sustainable Electrical Discharge Machining of Nimonic C263 Superalloy. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, G.; Manna, A.; Singh Sethi, A. Investigations on performance of ECDM process using different tool electrode while machining e-glass fibre reinforced polymer composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.H.; Dong, P.V.; Dung, H.T.; Thien, N.V.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Shirguppikar, S.; Tam, N.C.; Ly, N.T. Multi-object optimization of EDM by Taguchi-DEAR method using AlCrNi coated electrode. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 116, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekarappa, M.P.G.; Kumar, S.; Jagadish; Pimenov, D.Y.; Giasin, K. Experimental Analysis and Optimization of EDM Parameters on HcHcr Steel in Context with Different Electrodes and Dielectric Fluids Using Hybrid Taguchi-Based PCA-Utility and CRITIC-Utility Approaches. Metals 2021, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saodaen, R.; Janmanee, P.; Rodchanarowan, A. Characteristics of Ternary Metal (Cu-Ni-TiN) Electrodes Used in an Electrical Discharge Machining Process. Metals 2021, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Singh, S.; Pruncu, C.I.; Mishra, V.; Królczyk, G.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Pramanik, A. Surface Modifification of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy by Electrical Discharge Coating Process Using Partially Sintered Ti-Nb Electrode. Materials 2019, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Kong, L.; Qiu, M. Mechanism study of the combined process of electrical discharge machining ablation and electrochemical machining in aerosol dielectric. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 254, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julfekar, A.; Karan, P.; Pradeep, D. Effect of tool-electrode material in through-hole formation using ECDM process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2021, 36, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, M.; Allagui, A.; Ng, H.D.; Wuthrich, R. The Effect of Thermal Conductivity of the Tool Electrode in Spark-Assisted Chemical Engraving Gravity-Feed Micro-Drilling. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.K.; Cheng, C.P.; Mai, C.C.; Wang, A.C.; Hung, J.C.; Yan, B.H. Effect of Surface Roughness of Tool Electrode Materials in ECDM Performance. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Z.; Hang, Y.; Xing, J. Effect of solution conductivity on tool electrode wear in electrochemical discharge drilling of nickel-based alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Dvivedi, A.; Kumar, P. Developments on electrochemical discharge machining: A review of experimental investigations on tool electrode process parameters. Proceed. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 229, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dileep, K.M.; Rahul; Saurav, D.; Manoj, M.; Siba, S.M. Through hole making by electro-discharge machining on Inconel 625 super alloy using hollow copper tool electrode. Proceed. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process. Mech. Eng. 2019, 233, 348–370. [Google Scholar]














| Properties | TC4 | SS304 | Brass | W70Cu30 | W80Cu20 | W90Cu10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 4.43 | 8 | 8.73 | 13.80 | 15.15 | 16.75 |
| Melting point (°C) | 1660 | 1455 | 904 | 3420 | 3420 | 3420 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m K) | 7 | 16.2 | 159 | 200 | 180 | 170 |
| Specific heat capacity (J/kg K) | 553 | 500 | 920 | 232 | 190 | 155 |
| Tensile strength (Mpa) | 862 | 515 | 360 | 516 | 620 | 700 |
| Machining Parameters | Fixed Parameters |
|---|---|
| Pulse width, Ton (μs) | 12 |
| Pulse interval, Toff (μs) | 12 |
| Peak current, Ip(Amp.) | 14.17 |
| Open circuit voltage, VOC(V) | 85 |
| Electrolyte, NaNO3 (g/L) | 4 |
| Regulation per minute(RPM) | 300 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashedul, I.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, G.; Xi, T.; Ji, L. Influence of Different Tool Electrode Materials on Electrochemical Discharge Machining Performances. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12091077
Rashedul IM, Zhang Y, Zhou K, Wang G, Xi T, Ji L. Influence of Different Tool Electrode Materials on Electrochemical Discharge Machining Performances. Micromachines. 2021; 12(9):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12091077
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashedul, Islam Md., Yan Zhang, Kebing Zhou, Guoqian Wang, Tianpeng Xi, and Lei Ji. 2021. "Influence of Different Tool Electrode Materials on Electrochemical Discharge Machining Performances" Micromachines 12, no. 9: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12091077
APA StyleRashedul, I. M., Zhang, Y., Zhou, K., Wang, G., Xi, T., & Ji, L. (2021). Influence of Different Tool Electrode Materials on Electrochemical Discharge Machining Performances. Micromachines, 12(9), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12091077





