A Sub-1 Hz Resonance Frequency Resonator Enabled by Multi-Step Tuning for Micro-Seismometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design
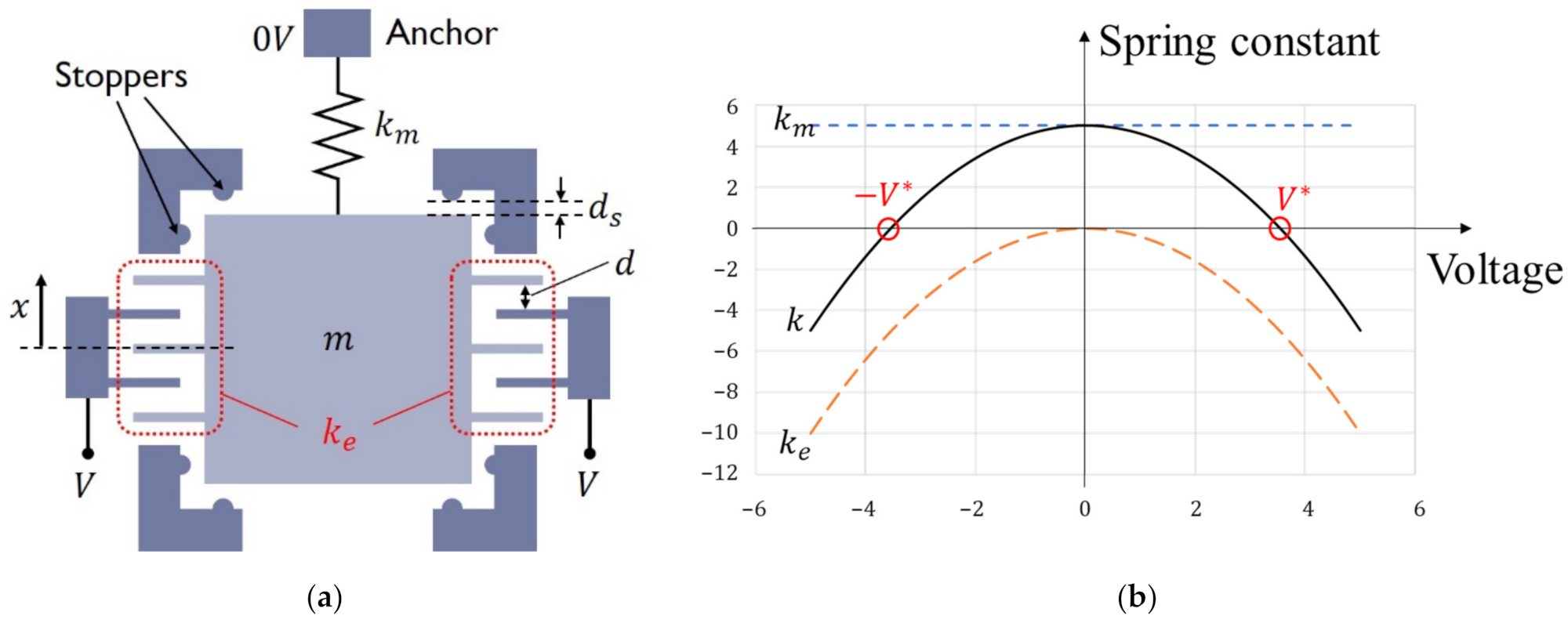
2.1. Electrically Tunable Spring
2.2. Multi-Step Electrical Tuning Method
2.3. Seismometer Structure
2.4. Fabrication
2.5. Demonstration of Multi-Step Tuning
2.6. Force-Balance System
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Y.; Jiao, R.; Yu, H. MEMS based geophones and seismometers. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 318, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havskov, J.; Alguaci, G. Instrumentation in Earthquake Seismology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Khan, I.; Choi, S.; Kwon, Y.-W. A Smart IoT Device for Detecting and Responding to Earthquakes. Electronics 2019, 8, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Middlemiss, R.; Samarelli, A.; Paul, D.; Hough, J.; Rowan, S.; Hammond, G.D. Measurement of the Earth tides with a MEMS gravimeter. Nature 2016, 531, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, S.; Liu, H.; Yan, S.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, C.; Tu, L. A high-sensitivity MEMS gravimeter with a large dynamic range. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pike, W.T.; Delahunty, A.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Dou, G.; Liu, H.; Calcutt, S.; Standley, I.M. A self-levelling nano-g silicon seismometer. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2014 IEEE, Valencia, Spain, 2–5 November 2014; pp. 1599–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Pike, W.T.; Standley, I.M.; Calcutt, S.B.; Mukherjee, A. A broad-band silicon microseismometer with 0.25 NG/rtHz performance. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Belfast, Ireland, 21–25 January 2018; pp. 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; Peng, D.; Liu, H.; Tu, L. A nano-g micromachined seismic sensor for levelling-free measurements. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 280, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, U.; Olsson, R.H.; Bogart, G.R.; Baker, M.S.; Carr, D.W.; Swiler, T.P.; Clews, P.J. In-plane MEMS-based nano-g accelerometer with sub-wavelength optical resonant sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 145–146, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Hwang, J.G.; Jahng, J.; Kim, Q.; Noh, H.; An, S.; Jhe, W. Electrical tuning of mechanical characteristics in qPlus sensor: Active Q and resonance frequency control. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 074503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, A.; Krust, A.; Lorenz, G.; Favorskiy, I.; Piirainen, T. Efficient nonlinear Simulink models of MEMS gyroscopes generated with a novel model order reduction method. In Proceedings of the 2015 Transducers—2015 18th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Anchorage, AK, USA, 21–25 June 2015; pp. 2184–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Wielandt, E.; Streckeisen, G. The leaf-spring seismometer: Design and performance. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1982, 72, 2349–2367. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Ikehashi, T. A Mode Localized Tilt Sensor with Ultra-Small Stiffness Spring. In Proceedings of the Microprocesses and Nanotechnology Conference (MNC), Osaka, Japan, 9–12 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- MEMS+®. Available online: https://www.coventor.com/products/coventormp/mems-plus/ (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Parent, A.; Krust, A.; Lorenz, G.; Favorskiy, I.; Piirainen, T. A novel model order reduction approach for generating efficient nonlinear Verilog-A models of mems gyroscopes. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (ISISS), Hapuna Beach, HI, USA, 23–26 March 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]











| Device | Proof Mass | Resonance Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Middlemiss, R. [4] | 13.64 mg | 2.3 Hz |
| Tang, S. [5] | 460 mg | 3.1 Hz |
| Pike, W. T. [6,7] | 400 mg | 6 Hz |
| Wu, W. [8] | 310 mg | 14 Hz |
| Krishnamoort, U. [9] | 33.6 mg | 36 Hz |
| This work | 24 mg | 0.39 Hz |
| Properties | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Si layer thickness | 500 | |
| Proof mass weight | 24 | mg |
| 1st electrical spring finger length | 1000 | |
| 1st electrical spring finger number | 2 × 50 | - |
| 2nd electrical spring finger length | 1000 | |
| 2nd electrical spring finger number | 2 × 6 | - |
| 3rd electrical spring finger length | 500 | |
| Position sensor finger length | 2 × 2 | - |
| Position sensor finger number | 1500 | |
| Actuator finger length | 2 × 2 × 2 | - |
| Actuator finger number | 1500 | |
| Minimum gap of electrodes | 2 × 2 × 13 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Maekoba, H.; Parent, A.; Ikehashi, T. A Sub-1 Hz Resonance Frequency Resonator Enabled by Multi-Step Tuning for Micro-Seismometer. Micromachines 2022, 13, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13010063
Wu J, Maekoba H, Parent A, Ikehashi T. A Sub-1 Hz Resonance Frequency Resonator Enabled by Multi-Step Tuning for Micro-Seismometer. Micromachines. 2022; 13(1):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13010063
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jun, Hideyuki Maekoba, Arnaud Parent, and Tamio Ikehashi. 2022. "A Sub-1 Hz Resonance Frequency Resonator Enabled by Multi-Step Tuning for Micro-Seismometer" Micromachines 13, no. 1: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13010063
APA StyleWu, J., Maekoba, H., Parent, A., & Ikehashi, T. (2022). A Sub-1 Hz Resonance Frequency Resonator Enabled by Multi-Step Tuning for Micro-Seismometer. Micromachines, 13(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13010063





